MECHANICAL ENGINEERING IC ENGINES, REFRIGERATION
|
|
|
- Abigayle Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ES ID: 0 ESE- 09 (Prelims) - Offline est Series est 5 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING IC ENGINES, REFRIGERAION and AIR CONDIIONING + POWER PLAN ENGINEERING SOLUIONS 0. Ans: (c) otal heat loss area = Heat loss from cylinder surface + Heat loss from cylinder head + Heat loss through piston = DL D D Ans: (c) When SHF = (sensible cooling) c i e e c BPF c i 0 e c = 0 e = c Room dew point temperature will be equal to the coil dew point temperature. 0. Ans: (c) 0. Ans: (a) Pulse jet engine can be idealised to follow Lenoir cycle. it consists of constant olume Disadantages of gas turbine power plant in utility system are : heat addition, reersible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejection. Low cycle efficiency, due to large exhaust loss, large compressor work and inefficiencies. Large compressor work input, since power required to drie the compressor is considerably higher. Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata
2 : : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions Large exhaust loss, since exhaust gas temperature is quite high. Machine inefficiencies, since with decreases in compressor efficiency take work input to compressor increases and with decreases in turbine efficiency work output from turbine decreases. Gas turbine plants respond quickly to load changes. 05. Ans: (d) he ultimate analysis gies the chemical elements that comprise coal substance together with ash and moisture. It is used to determine percentage of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur, nitrogen, moisture and ash on mass basis. Some types of coal during and after release of olatile matter become soft and pasty and form agglomerate. hese are called caking coal. Swelling index is a property used to determine the extent of caking of coal. 06. Ans: (a) E = 7C = 80 K G = 87C = 60 K O = 7C = 0 K COP E G G O O E Ans: (c) Due to shortcomings of distribution and limited intermixing of fuel CI engine are operated at high air fuel ratios than stoichiometric requirements. -methyl naphthalene is a hydrocarbon with poor ignition quality. It is assigned zero centene number. 08. Ans: (c) For a constant elocity of flow, if the duct diameter is increased he flow through duct will increase he friction pressure drop in the duct will decrease 09. Ans: (b) In CI engine detonation occurs at the beginning of combustion. 0. Ans: (c) Reheating and intercooling decreases turbine efficiency. Regeneration improes thermal efficiency of gas turbine by increasing mean temperature of heat addition. Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
3 : : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series. Ans: (a) Crank case dilution and eaporation loss are effected by tail end olatility. Engine warm up is effected by mid range olatility.. Ans: (b) Increase in injection adance increases delay period, because pressure and temperature are lower when injection begins. Increase in jacket water temperature increases compressed air temperature and hence delay period is reduced.. Ans: (d) COP of heat pump = W net 0 W net H H kw L Q W From first law of thermodynamics Q L + W net = Q H Q L kw H net. Ans: (c) Air has 79 % Nitrogen by olume, Nitrogen does not participate in chemical reaction. 5. Ans: (b) COP 6. Ans: (b) Re frigerating eff W net.5 N.75 kw W = (h h ) = kj/kg = 00 kj/kg Pump work = kj/kg W net = 00 = 000 kj/kg Specific steam consumption 7. Ans: (d).5 N COP (as R =.5 kw) 600 = kg / kw hr 000 =.6 kg/kw-hr Degree of saturation () = s s Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
4 work capacity capacity : : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions 8. Ans: (b) Due to reheating of steam in steam turbine power plant Efficiency improes marginally Specific work output increases Blade erosion reduces 9. Ans: (b) Regeneratie feed water heating increases the mean temperature of heat addition. Hence, cycle efficiency increases. 0. Ans: (b) Economiser heats the feed water to the saturated temperature corresponding to the boiler pressure. 00 P = 9.76 P P =.97 kpa P Relatie humidity () = P.97 = = %. Ans: (a) Approach of cooling tower is difference between cold water outlet temperature and wet bulb temperature.. Ans: (b) c =0C i =0C e =5C s. Ans: (b) W c max p max min = 5 00 = 5 0 = 5 kj/kg Contact factor BPF Ans: (a) Specific humidity () = m m a 0.6 P P P t 5. Ans: (c) P 0 00 P.88 P P (r p ) opt (r p) max r p Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
5 : 5 : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series If pressure ratio increases, the work capacity of Brayton cycle first increases, becomes maximum and then decreases. Work capacity is zero when r p is unity ; becomes maximum when (r p ) opt = r p max min max max min, and again becomes zero when as shown in the figure below. At maximum pressure ratio the efficiency of Brayton cycle becomes equal to Carnot efficiency and work output become zero. 6. Ans: (d) hermostatic expansion ale maintains a constant degree of super heat. 7. Ans: (a) he air fuel ratio in gas turbine is kept ery high. It aries from 60 / to 0 /. Because of high air fuel ratio used, gases entering HP turbine contain high percentage of oxygen and therefore if reheating is performed, the additional fuel can be burnt in the HP turbine. Reheating in gas turbine increases turbine work. Intercooling and reheating in gas turbine decreases thermal efficiency. 8. Ans: (b) Risers installed all around the furnace walls act as cooling tubes or a water wall and carry away heat from furnace at the same rate at which heat is released in it by the burning of fuel. If circulation is inadequate the rate at which heat is carried away will be less than heat released. he difference will be stored in riser tubes leading to their oerheating and rupturing. Riser located in the corners of furnace are relatiely cooler. So these will hae more circulation ratio than other riser tubes. Circulation ratio = = flow of saturated waterin downcomer flow of steam released from drum m = m g 9. Ans: (c) m g m m g Use of condenser increases the work output and efficiency of steam power plant. Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
6 : 6 : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions 0. Ans: (c) he following are the reasons for the pressure drop :. Friction, due to fluid elocity, resulting in frictional pressure drop.. Acceleration, due to the flashing off the liquid refrigerant into apour, resulting in momentum pressure drop.. Ans: (c) Benson boiler is a drumless once through boiler. his boiler can operate at super critical pressure.. Ans: (d) Proximate analysis indicate behaiour of coal when it is heated. It is used to determine percentage of fixed carbon, ash, olatile matter and moisture.. Ans: (c) Function of high steam and low water safety ale is two fold :. It blows out if the steam pressure is higher than the working pressure.. It blows out steam when water leel in the boiler is low.. Ans: (b) During cooling and dehumidification process, relatie humidity may increases, decreases or remain constant. Chemical dehumidification process 5. Ans: (c) (DP) < (DP) Bomb calorimeter is used to determine higher calorific alue of fuels by olume. Orsat apparatus is used to determine products of only dry constituents of combustion by olume. 6. Ans: (b) DB (DP) (DP) (DP) (DP) DB Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
7 : 7 : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series During adiabatic saturation process : DP Process is cooling and humidification WB = constant Enthalpy = constant 7. Ans: (c) 9 t = sec 6N 6 00 = sec sprayed into the steam mixes directly with cold water and gets condensed. Jet condenser, spray condenser and barometric condenser are direct contact type condenser.. Ans: (a) Absorption system is not a reersible refrigerating machine. Because of the mixing process of refrigerant and absorbent, a degree of irreersibility is inoled. 8. Ans: (a) Compressed gas enters the tube tangentially not normally. 9. Ans: (d) he component which is used to recoer heat of exhaust gases before boiler furnace is air preheater. 0. Ans: (b) In shell tube surface condenser for conenience of cleaning and maintenance cooling water flows through tubes and steam condenses outside the tube. Spray condenser is a direct contact type condenser in which cooling water is. Ans: (c) Efficiency of Otto cycle is gien by r where r is compression ratio Adiabatic index, for Helium is.67, Air is. and CO is.. otto (Helium) > otto (Air) > otto (Carbon dioxide). Ans: (b) For maximum power the fuel-air mixture should be 0% rich.. Ans: (a) he third fluid remains mainly in the eaporator thus reducing the partial pressure of the refrigerant to enable it to eaporate at low pressure and hence low temperature. Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
8 : 8 : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
9 : 9 : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series 5. Ans: (b) For maximum work output in two stage expansion turbine with perfect reheating, the intermediate pressure is 6. Ans: (a) p p p. he octane number in a single cylinder CFR diesel engine, the engine speed and jacket water temperature are 900 rpm and 00C respectiely. 7. Ans: (c) From the energy balance : M W = Q + S 8. Ans: (a) As engine speed increases in terms of crank angle hence ignition delay increases. Because of retarding due to increased heat loss ignition delay increases. Due to ignition adance, as pressure and temperature are low ignition delay increases. Due to engine size increases, ignition delay decreases in terms of crank angle. i d s 50. Ans: (a) If the inlet pressure is low temperature at the end of compression is low, temperature at the end of heat supply is low, low peak pressure and temperatures, reduce knocking. Hence, statement is wrong. 5. Ans: (b) Vapour pressure Effectie temperature is the temperature saturated air (00 % RH) at which the subject would experience the same feeling of comfort as experienced in the actual unsaturated enironment. Vapour pressure corresponding to effectie temperature is more than that of actual comfort condition. 00 % RH 50 % RH 9. Ans: (b) he delay period decreases with cetane number of the fuel because it reduces the self ignition temperature of the fuel. E 5C where, E = effectie temperature emperature Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
10 : 0 : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions 5. Ans: (d) Fuel is injected on to the hot piston. Slow rate of pressure rise takes place resulting in less noise. Cold starting is difficult as the piston is cold. 5. Ans: (a) EGR displaces some incoming air and also heats the air, lowering its density. he olumetric efficiency is thus reduced by EGR. 57. Ans: (b) COP of the Bell-Coleman cycle = when r p COP where, r p = pressure ratio c r p = ratio of specific heats c 58. Ans: (a) Knocking tendency in SI engine is reduced by decreasing the compression ratio. p 5. Ans: (c) Due to the expansion of the refrigerant, temperature of the refrigerant decreases in the capillary tube. For cooling process : Joule-homson coefficient () > Ans: (a) he main objectie of supercharging is to obtain more power by burning the large amount of fuel or to reduce the weight and the size of the engine for a gien power output. 56. Ans: (d) A method usually employed for starting the engine from the cold is to shut off most of the main air supply to the main jets and thus produce rich mixture necessary for cold starting. 59. Ans: (c) Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad Actual gas refrigeration cycle : Actual cycle Ideal cycle Pressure, P > P P > P entry to compressor exit from compressor entry to turbine exit from turbine S
11 : : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series 60. Ans: (b) Volumetric efficiency of four stroke engine is higher than two stroke engine due to greater time of induction. In two stroke engine cycle is completed in two stroke of piston cylinder in one reolution of crankshaft. hus, more uniform turning moment than four stroke engine. 6. Ans: (b) For better starting 0% of the fuel should eaporate at low temperatures. In winter, as atmospheric temperature are low, olatility cure should be lower. 6. Ans: (c) Constant specific olume line WB line 6. Ans: (a) hermal efficiency of combined cycle plant is higher than indiidual cycles. hus, higher conersion efficiency from fuel to electricity can be achieed. 6. Ans: (b) In SI engines supercharging increases the tendency to detonate and pre-ignite whereas in CI engines supercharging tend to preent knocking. 65. Ans: (b) When the body temperature is less than the air temperature. Heat will not be transfer from the body by conection, conduction and radiation. he heat will be transferred by eaporatie cooling. 66. Ans: (d) As the number of cylinders increases, the dwell angle decreases as the firings are more for eery two reolutions. DB For constant specific olume line, specific humidity changes. (i.e., moisture content changes). Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
12 : : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
13 : : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series 67. Ans: (a) Joule -homson coefficient for an ideal gas () = 0 d dp h 0 d = 0 If we use throttling ale, there will not be change in the temperature. 68. Ans: (a) Net work is practically unity W W W p W W P Pump work is ery small compared to turbine work because pump compresses the saturated liquid which has small specific olume. 69. Ans: (a) Fuel leel in the compensating well decreases with the increase in air flow rate. For compensating jet or double jet engine, the compensating jet supplies leaner mixture and the main jet makes richer mixture and both together maintain constant air fuel ratio at all speeds. 70. Ans: (b) V-C cycle : x x S New peak temperaure of the cycle 7. Ans: (b) Octane rating of gasoline is based on isooctane and normal-heptane. etraethyl lead is added to gasoline to increase octane number. 7. Ans: (a) In diesel engine, cut off ratio depends on load. Hence, unlike Otto cycle the air standard efficiency of diesel cycle depends on load and increase as the load is increased. 7. Ans: (d) x < x S Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
14 Per cent of full load efficiency Specific fuel consumption kg/kwh consumption h Where x = quality of the mixture. As condenser temperature decrease, refrigerating effect increases and power input decreases. Because of this COP will increases. 7. Ans: (b) % 75% 00% Regeneration effectieness 00% 75% 5% 50% 5% No generation Pressure ratio, r p (a) Fig. (a) shows, ariation of specific fuel consumption with pressure ratio with different degree of regeneration. It is clear that there is a optimum pressure ratio for each degree of regeneration. semi-closed cycle Open cycle with regenerator intercooler & reheater Simple open cycle Per cent Load (b) Closed cycle with regenerator intercooler & reheater : : Mechanical Engg._ est 5 _ Solutions Fig. (b) shows the ariation of percentage of fuel load efficiency with part load. It is clear that for semi-closed cycle the part load efficiency is the best. 75. Ans: (b) At high engine speed acuum at the throat is high and we get too rich mixtures. In multicylinder engines, the mixture passing through the intake many fold generally contains a certain amount of petrol in the droplet form. hese droplets hae greater inertia then gaseous mixture and, hence, wheneer the direction of flow is changed abruptly, the droplets tend to continue in their original direction of moement. As a result, there is a ariation in the A/F ratio between cylinders, the outer cylinders getting richer mixture than the inner cylinders, the outer cylinders getting richer mixture than the inner cylinders. Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
15 : 5 : ESE - 09 (Prelims) Offline est Series Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Lucknow Patna Bengaluru Chennai Vijayawada Vizag irupati Kukatpally Kolkata Ahmedabad
Scheme - G. Sample Test Paper-I. Course Name : Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Code : ME Semester : Fifth Subject Title : Power Engineering
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]
![(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16] (a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]](/thumbs/79/80273804.jpg) Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C OBJECTIVE:
 ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Question Bank. UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks)
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
MEB THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I PART-A
 MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) QUESTION BANK UNIT I I.C ENGINES
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
ACTUAL CYCLE. Actual engine cycle
 1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles
 Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
In this lecture... Gas power cycles
 7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
Chapter 4 ANALYTICAL WORK: COMBUSTION MODELING
 a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
Gas Power Cycles. Tarawneh
 Gas Power Cycles Dr.Mohammad Tarawneh ) Carnot cycle 2) Otto cycle ) Diesel cycle - Today 4) Dual Cycle 5) Stirling cycle 6) Ericsson cycles 7) Brayton cycle Carnot Cycle Reversible isothermal expansion
Gas Power Cycles Dr.Mohammad Tarawneh ) Carnot cycle 2) Otto cycle ) Diesel cycle - Today 4) Dual Cycle 5) Stirling cycle 6) Ericsson cycles 7) Brayton cycle Carnot Cycle Reversible isothermal expansion
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) SUBJECT: ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Assignment Ch 1
 1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
Lecture 5. Abnormal Combustion
 Lecture 5 Abnormal Combustion Abnormal Combustion The Abnormal Combustion:- When the combustion gets deviated from the normal behavior resulting loss of performance or damage to the engine. It is happened
Lecture 5 Abnormal Combustion Abnormal Combustion The Abnormal Combustion:- When the combustion gets deviated from the normal behavior resulting loss of performance or damage to the engine. It is happened
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME THERMAL ENGINEERING. Part-A (2 Marks)
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? 2. What is meant by air standard cycle? 3.. Name
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? 2. What is meant by air standard cycle? 3.. Name
ME Thermal Engineering Question Bank
 ME2301 - Thermal Engineering Question Bank UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycles, Calculation of mean effective pressure, and air standard efficiency -Actual and theoretical PV diagram
ME2301 - Thermal Engineering Question Bank UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycles, Calculation of mean effective pressure, and air standard efficiency -Actual and theoretical PV diagram
Heat engine. Heat engine
 Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
2. Discuss the effects of the following operating variables on detonation
 Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Noble Group of Institutions, Junagadh. Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: 2017-18 Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat
Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: 2017-18 Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition
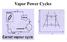 Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
L34: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Introduction to Gas Cycles Definitions
 Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Lecture 14:Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions
 Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
Introduction Outline of Some Descriptive Systems
 Introduction Outline of Some Descriptive Systems 1 1.1. Steam power plant : Layout components of a modern steam power plant. 1.2. Nuclear power plant. 1.3. Internal combustion engines : Heat engines development
Introduction Outline of Some Descriptive Systems 1 1.1. Steam power plant : Layout components of a modern steam power plant. 1.2. Nuclear power plant. 1.3. Internal combustion engines : Heat engines development
UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES
 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES Air Standard Cycles - Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycle with intercooling, reheating and regeneration- Calculation of airstandard efficiency and mean effective
THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES Air Standard Cycles - Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycle with intercooling, reheating and regeneration- Calculation of airstandard efficiency and mean effective
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat
 Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
Assignment-1 Introduction
 Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF
 PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1036 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDES : KS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1036 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDES : KS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE
BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FS81504 BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FS81504 BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL
Internal Combustion Engines
 Air and Fuel Induction Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss the following: A/F mixture preparation in gasoline engines using carburetion. Air Charging technologies: Superchargers Turbochargers
Air and Fuel Induction Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss the following: A/F mixture preparation in gasoline engines using carburetion. Air Charging technologies: Superchargers Turbochargers
Engine Cycles. T Alrayyes
 Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines.
 Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines. 4.2 Construction and working of gas turbines i) Open cycle ii) Closed cycle gas Turbines, P.V. and
Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines. 4.2 Construction and working of gas turbines i) Open cycle ii) Closed cycle gas Turbines, P.V. and
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
2) Rich mixture: A mixture which contains less air than the stoichiometric requirement is called a rich mixture (ex. A/F ratio: 12:1, 10:1 etc.
 Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System
 Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE
 INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE Engine: An engine is motor which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Fuel/petrol engine: A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is
INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE Engine: An engine is motor which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Fuel/petrol engine: A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is
Heat Transfer in Engines. Internal Combustion Engines
 Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
IC ENGINES. Differences between SI and CI engines: Petrol is fuel, which has a high self ignition temperature
 IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
η th W = Q Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle.
 Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Focus on Training Section: Unit 2
 All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES
 CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
Combustion. T Alrayyes
 Combustion T Alrayyes Fluid motion with combustion chamber Turbulence Swirl SQUISH AND TUMBLE Combustion in SI Engines Introduction The combustion in SI engines inside the engine can be divided into three
Combustion T Alrayyes Fluid motion with combustion chamber Turbulence Swirl SQUISH AND TUMBLE Combustion in SI Engines Introduction The combustion in SI engines inside the engine can be divided into three
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
Principles of Engine Operation. Information
 Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes
 8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines Reading Problems 8-3 8-7 8-35, 8-45, 8-52 Definitions 1. spark ignition: a mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a spark plug applications requiring power to about 225 kw (300
Internal Combustion Engines Reading Problems 8-3 8-7 8-35, 8-45, 8-52 Definitions 1. spark ignition: a mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a spark plug applications requiring power to about 225 kw (300
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 11 Internal Combustion
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 11 Internal Combustion
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics I. C. Engine Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi
Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics I. C. Engine Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi
Thermodynamic Cycles. Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares
 Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine 1. A 9-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle, radial SI engine operates at 900rpm. Calculate: (1) How often ignition occurs, in degrees of engine rev. (2) How many power strokes per rev.
Internal Combustion Engine 1. A 9-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle, radial SI engine operates at 900rpm. Calculate: (1) How often ignition occurs, in degrees of engine rev. (2) How many power strokes per rev.
Automobiles. Introductory Question. 6 Questions about Automobiles. Observations about Automobiles. Question 1. Heat Engines
 Automobiles 1 Automobiles 2 Introductory Question Automobiles A car burns gasoline to obtain energy but allows some heat to escape into the air. Could a mechanically perfect car avoid releasing heat altogether?
Automobiles 1 Automobiles 2 Introductory Question Automobiles A car burns gasoline to obtain energy but allows some heat to escape into the air. Could a mechanically perfect car avoid releasing heat altogether?
Module7:Advanced Combustion Systems and Alternative Powerplants Lecture 32:Stratified Charge Engines
 ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 9:Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd.
 Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd. The Lecture Contains: HC from Lubricating Oil Film Combustion Chamber Deposits HC Mixture Quality and In-Cylinder Liquid Fuel HC from Misfired Combustion
Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd. The Lecture Contains: HC from Lubricating Oil Film Combustion Chamber Deposits HC Mixture Quality and In-Cylinder Liquid Fuel HC from Misfired Combustion
Combustion engines. Combustion
 Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION IN SI ENGINES B. PAVAN VISWANADH P. ASHOK KUMAR. Mobile No : Mobile No:
 GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION IN SI ENGINES SUBMIT TED BY B. PAVAN VISWANADH P. ASHOK KUMAR Y06ME011, III/IV B. Tech Y06ME003, III/IV B. Tech Pavan.visu@gmail.com ashok.me003@gmail.com Mobile No :9291323516
GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION IN SI ENGINES SUBMIT TED BY B. PAVAN VISWANADH P. ASHOK KUMAR Y06ME011, III/IV B. Tech Y06ME003, III/IV B. Tech Pavan.visu@gmail.com ashok.me003@gmail.com Mobile No :9291323516
Approved by AICTE, Government of India & affiliated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1. Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) Term-End Examination June 2016
 No. of Printed Pages : 5 I BIME-010 I B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) 00 1 Ems, Term-End Examination June 2016 BIME-010 : THERMAL ENGINEERING Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Attempt
No. of Printed Pages : 5 I BIME-010 I B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) 00 1 Ems, Term-End Examination June 2016 BIME-010 : THERMAL ENGINEERING Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Attempt
REVIEW STUDY ON EXHAUST OF A DIESEL ENGINE THERMAL STORAGE
 REVIEW STUDY ON EXHAUST OF A DIESEL ENGINE THERMAL STORAGE Prateek Jain 1, Sushil Yadav 2, Durgesh Singh 3 1,2 B.Tech. Scholar, 3 Assistant Professor, Vedant College of Engineering and Technology, Bundi,
REVIEW STUDY ON EXHAUST OF A DIESEL ENGINE THERMAL STORAGE Prateek Jain 1, Sushil Yadav 2, Durgesh Singh 3 1,2 B.Tech. Scholar, 3 Assistant Professor, Vedant College of Engineering and Technology, Bundi,
USO4CICV01/US04CICH02:
 Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 Serial : 0 PT_ME_A+B_IC Engine_6098 CLASS TEST Delhi Noida Bhoal Hyderabad Jaiur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-56 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING I.C. Engine
Serial : 0 PT_ME_A+B_IC Engine_6098 CLASS TEST Delhi Noida Bhoal Hyderabad Jaiur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: 0-56 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING I.C. Engine
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Attempt any three. One Mark each. Following are the applications of compressed air ( any four)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
AT AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK
 AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
Fuels, Combustion and Environmental Considerations in Industrial Gas Turbines - Introduction and Overview
 Brian M Igoe & Michael J Welch Fuels, Combustion and Environmental Considerations in Industrial Gas Turbines - Introduction and Overview Restricted Siemens AG 20XX All rights reserved. siemens.com/answers
Brian M Igoe & Michael J Welch Fuels, Combustion and Environmental Considerations in Industrial Gas Turbines - Introduction and Overview Restricted Siemens AG 20XX All rights reserved. siemens.com/answers
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 3: Introduction to Pollutant Formation POLLUTANT FORMATION
 Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Week 10. Gas Power Cycles. ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1
 Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Question: Automobiles. Observations About Automobiles. Heat Engines. Heat Pumps. Question:
 Automobiles 1 Automobiles 2 Question: Automobiles A car burns gasoline to obtain energy but allows some heat to escape into the air. Could a mechanically perfect car avoid releasing heat altogether? Automobiles
Automobiles 1 Automobiles 2 Question: Automobiles A car burns gasoline to obtain energy but allows some heat to escape into the air. Could a mechanically perfect car avoid releasing heat altogether? Automobiles
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems
 Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy : Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy : Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal Combustion Engines
 State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal Combustion Engines July 1997 State of New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Air Quality Permitting Program State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal
State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal Combustion Engines July 1997 State of New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Air Quality Permitting Program State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal
Gas Power System. By Ertanto Vetra
 Gas Power System 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Otto Cycles Diesel Cycles Gas Turbine Cycles Gas Turbine Based Combined Cycles Gas Turbines for Aircrafts Turbojets
Gas Power System 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Otto Cycles Diesel Cycles Gas Turbine Cycles Gas Turbine Based Combined Cycles Gas Turbines for Aircrafts Turbojets
SUPERCHARGER AND TURBOCHARGER
 SUPERCHARGER AND TURBOCHARGER 1 Turbocharger and supercharger 2 To increase the output of any engine more fuel can be burned and make bigger explosion in every cycle. i. One way to add power is to build
SUPERCHARGER AND TURBOCHARGER 1 Turbocharger and supercharger 2 To increase the output of any engine more fuel can be burned and make bigger explosion in every cycle. i. One way to add power is to build
Combustion Systems What we might have learned
 Combustion Systems What we might have learned IMechE ADSC, 6 December 2012 Chris Whelan Contents Engines Big & Small Carnot, Otto & Diesel Thermodynamic Cycles Combustion Process & Systems Diesel & Otto
Combustion Systems What we might have learned IMechE ADSC, 6 December 2012 Chris Whelan Contents Engines Big & Small Carnot, Otto & Diesel Thermodynamic Cycles Combustion Process & Systems Diesel & Otto
LECTURE NOTES INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION
 LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Power Cycles. Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion
 Gas Power Cycles Power Cycles Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion Otto cycle, spark ignition Diesel cycle, compression ignition Sterling & Ericsson cycles Brayton cycles Jet-propulsion cycle Ideal Cycles,
Gas Power Cycles Power Cycles Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion Otto cycle, spark ignition Diesel cycle, compression ignition Sterling & Ericsson cycles Brayton cycles Jet-propulsion cycle Ideal Cycles,
Aero Engines. Review Oil & Fuel
 Aero Engines 9.02 Oil & Fuel References: FTGU pages 57-61 Review 1. What are the 4 strokes in a complete cycle? 2. Name 3 types of combustion engine. 3. List a few advantages and/or disadvantages to each
Aero Engines 9.02 Oil & Fuel References: FTGU pages 57-61 Review 1. What are the 4 strokes in a complete cycle? 2. Name 3 types of combustion engine. 3. List a few advantages and/or disadvantages to each
Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry. 1 Introduction Preface Model-Building Simulation... 5 References...
 Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL
 Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
UNIT 2 RCET, BHILAI. [Prof. Santosh Bopche & Prof. S. A. K. Jilani] 1
![UNIT 2 RCET, BHILAI. [Prof. Santosh Bopche & Prof. S. A. K. Jilani] 1 UNIT 2 RCET, BHILAI. [Prof. Santosh Bopche & Prof. S. A. K. Jilani] 1](/thumbs/82/84884218.jpg) UNIT 2 Fuels Basic requirement of I.C. Engine fuels, requirement of an ideal gasoline, structure of petroleum, effect of fuel structure on combustion, volatility of liquid fuels, effect of volatility on
UNIT 2 Fuels Basic requirement of I.C. Engine fuels, requirement of an ideal gasoline, structure of petroleum, effect of fuel structure on combustion, volatility of liquid fuels, effect of volatility on
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Modifications on a Small Two Wheeler Two Stroke SI Engine for Reducing Fuel Consumption and Exhaust Emissions
 RIO 5 - World Climate & Energy Event, 15-17 February 5, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Modifications on a Small Two Wheeler Two Stroke SI Engine for Reducing Fuel Consumption and Exhaust Emissions Kunam Anji Reddy,
RIO 5 - World Climate & Energy Event, 15-17 February 5, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Modifications on a Small Two Wheeler Two Stroke SI Engine for Reducing Fuel Consumption and Exhaust Emissions Kunam Anji Reddy,
Scheme G Sample Question Paper Course Name : Diploma in Automobile Engineering Course Code : AE
 Sample Question Paper Semester : Fourth Marks : 100 Time: 03 Hours Q1.A. Attempt any SIX a. State different types of ideal gas processes 12 Marks b. Define dryness fraction and degree of superheat. c.
Sample Question Paper Semester : Fourth Marks : 100 Time: 03 Hours Q1.A. Attempt any SIX a. State different types of ideal gas processes 12 Marks b. Define dryness fraction and degree of superheat. c.
Figure 1: The spray of a direct-injecting four-stroke diesel engine
 MIXTURE FORMATION AND COMBUSTION IN CI AND SI ENGINES 7.0 Mixture Formation in Diesel Engines Diesel engines can be operated both in the two-stroke and four-stroke process. Diesel engines that run at high
MIXTURE FORMATION AND COMBUSTION IN CI AND SI ENGINES 7.0 Mixture Formation in Diesel Engines Diesel engines can be operated both in the two-stroke and four-stroke process. Diesel engines that run at high
AE 1005 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES COMBUSTION IN SI ENGINES
 AE 1005 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES COMBUSTION IN SI ENGINES Syllabus Combustion in premixed and diffusion flames - Combustion process in IC engines. Stages of combustion - Flame propagation - Flame velocity and
AE 1005 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES COMBUSTION IN SI ENGINES Syllabus Combustion in premixed and diffusion flames - Combustion process in IC engines. Stages of combustion - Flame propagation - Flame velocity and
Basic Requirements. ICE Fuel Metering. Mixture Quality Requirements. Requirements for Metering & Mixing
 Basic Requirements ICE Fuel Metering Dr. M. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Basic Requirements ICE Fuel Metering Dr. M. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
