(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
|
|
|
- Heather Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines. Air is used, as the working fluid and the efficiency calculated to these engines are known as air standard efficiencies. ASSUMPTIONS The assumptions made are, (i) Air is the working fluid, assumed to be a perfect gas. (ii) Effect of calorific values of fuels is neglected by using hot and cold body contacts with the engine cylinder head for addition and rejection of heat respectively. (iii) Frictionless. (iv)no heat is either gained or lost during the cycle except during the contact of hot body and cold body with the cylinder head. IMPORTANT TERMINOLOGIES USED IN AIR STANDARD CYCLES (i) Bore It is diameter of the cylinder measured internally and is denoted by D. (ii) Stroke Stroke is defined as the displacement of the piston from its Top Dead Centre to the Bottom Dead Centre and is denoted by L (iii) Clearance volume It is the minimum volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Top Dead Centre (T.D.C) and is denoted by V c (iv) Swept or stroke volume It is the volume of a cylinder when the piston is moving from T.D.C to B.D.C and is denoted by (v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V. (vi) Compression ratio It is defined as the ratio of cylinder volume to the clearance volume and is denoted by γ. (vii) Air standard efficiency It is defined as the ratio of work done by the engine to the heat supplied. It is also known as ideal efficiency of the cycle. It is denoted by η
2 (viii) Mean effective pressure It is defined as the average pressure required for developing same power as that of the same engine operating under different pressures under same operating conditions. It can be calculated from P-V diagram. It is also defined as the ratio of work output to the stroke volume. OTTO CYCLE / CONSTANT VOLUME CYCLE Otto cycle was invented by German scientist Nichloas Otto in In this cycle he proposed constant volume heat addition and rejection instead of isothermal heat addition and rejection used in Carnot cycle. All petrol, Spark ignition (S.I.) and gas engines are working under this cycle. Figure 1.2 P-v and T-s diagram of Otto Cycle 1-2 Adiabatic / Isentropic compression 2-3 Heat addition at constant volume 3-4 Adiabatic / Isentropic Expansion 4-1 Heat rejection at constant volume Isentropic compression process 1-2 Air is compressed isentropically from state 1 to state 2. During this process pressure, temperature of air increases and volume decreases. Constant volume heat addition process 2-3 Heat is added at constant volume from state 2 to state 3. During this process temperature, pressure increases and volume remains constant.
3 Isentropic expansion process 3-4 Air is expanded isentropically from state 3 to state 4. During the process pressure, temperature decreases and volume increases. Constant volume heat rejection process 4 1 Heat is rejected from the air at constant volume from state 4 to state 1. During the process pressure, temperature decreases and volume remains constant. In this cycle combustion takes place fully at constant volume process, so this cycle is also called as constant volume cycle.
4 From the above equation, air standard efficiency of Otto cycle increases with increase in compression ratio and vice-versa. Compression ratio is maintained 7 10 for better performance in engines operating under this cycle. If it increases more than 10 knocking will take place due to this life of the cylinder is reduced. Expression for mean effective pressure Mean effective pressure is the average pressure in Newton s per unit area which acts on the piston throughout the cycle. It is given by the breadth of rectangle whose length is equal to the swept volume. Work done = force x distance moved = pressure x area x length = P x A x L = pressure x Volume
5 DIESEL CYCLE / CONSTANT PRESSURE CYCLE Diesel cycle was invented by Rudolph Diesel in All Diesel, Compression Ignition (C.I.) engines are working under this cycle.
6 Figure 1.3 P-v and T-s diagram of Diesel Cycle 1-2 Adiabatic / Isentropic compression 2-3 Constant pressure heat addition 3-4 Adiabatic / Isentropic expansion 4-1 Constant volume heat rejection Isentropic Compression Process 1-2 Air is compressed isentropically from state 1 to state 2. During this process pressure, temperature of air increases and volume decreases. Heat addition Process 2-3 Heat is added at constant pressure from state 2 to state 3. During this process temperature, volume increases and pressure remains constant. Expansion Process 3-4 Air is expanded isentropically from state 3 to state 4. During the process pressure, temperature decreases and volume increases. Heat rejection process 4 1 Heat is rejected from the air at constant volume from state 4 to state 1. During the process pressure, temperature decreases and volume remains constant. In this cycle combustion takes place fully at constant pressure process, so this cycle is also called as constant pressure cycle. Expression for air standard efficiency
7
8 Expression for Mean Effective Pressure DUAL CYCLE / LIMITED PRESSURE CYCLE Figure 1.4 P-v and T-s diagram of Dual Cycle
9 1-2 Isentropic Compression 2-3 Constant Volume Heat addition 3-4 Constant Pressure Heating 4-5 Isentropic Expansion 5-1 Constant Volume Cooling Isentropic Compression Process 1-2 Air is compressed isentropically from state 1 to state 2. During this process pressure, temperature of air increases and volume decreases. Heat addition Process 2-3 Heat is added at constant volume from state 2 to state 3. During this process temperature, pressure increases and volume remains constant. Heat addition Process 3-4 Heat is added at constant pressure from state 3 to state 4. During this process temperature, volume increases and pressure remains constant. Expansion Process 4-5 Air is expanded isentropically from state 4 to state 5. During the process pressure, temperature decreases and volume increases. Heat rejection process 5-1 Heat is rejected from the air at constant volume from state 5 to state 1. During the process pressure, temperature decreases and volume remains constant. In this cycle combustion takes place partially at constant volume and partially at constant pressure, so this cycle is called as Dual cycle. Expression for air standard efficiency
10 Pressure ratio (rp): It is the ratio of the final pressure to the initial pressure during constant volume combustion. Expression for mean effective pressure
11 COMPARISON OF OTTO, DIESEL AND DUAL CYCLES The important variable factors which are used as the basis for comparison of the cycles are compression ratio, peak pressure, heat addition, heat rejection and the network. In order to compare the performance of the Otto, Diesel and Dual combustion cycles, some of the variable factors must be fixed. In this section, a comparison of these three cycles is made for the same compression ratio, same heat addition, constant maximum pressure and temperature, same heat rejection and network output. This analysis will show which cycle is more efficient for a given set of operating conditions. Case 1: Same Compression Ratio and Heat Addition The Otto cycle , the Diesel cycle 1-2-3'-4'-1 and the Dual cycle are shown in p-v and T-s diagram in Fig (a) and (b) respectively for the same compression ratio and heat input. From the T-s diagram, it can be seen that Area = Area 5-2-3'-6 = Area 5-2-2"- 3"-6" as this area represents the heat input which is the same for all cycles. All the cycles start from the same initial state point 1 and the air is compressed from state 1 to 2 as the compression ratio is same. It is seen from the T-s diagram for the same heat input, the heat rejection in Otto cycle (area ) is minimum and heat rejection in Diesel cycle (5-1-4'-6') is maximum. Consequently, Otto cycle has the highest work output and efficiency. Diesel cycle has the least efficiency and Dual cycle having the efficiency between the two. One more observation can be made i.e., Otto cycle allows the working medium to expand more whereas Diesel cycle is least in this respect. The reason is heat is added before expansion in the case of Otto cycle and the last portion of heat supplied to the fluid has a relatively short expansion in case of the Diesel cycle. Case 2: Same Compression Ratio and Heat Rejection
12 Efficiency of Otto cycle is given by [Figs (a) and (b)], Where, Qs is the heat supplied in the Otto cycle and is equal to the area under the curve 2-3 on the T-s diagram [Fig (b)]. The efficiency of the Diesel cycle is given by, Where Q s is heat supplied in the Diesel cycle and is equal to the area under the curve 2-3' on the T-s diagram [Fig (b)]. From the T-s diagram in Fig.4.7.2, it is clear that Qs > Q s i.e., heat supplied in the Otto cycle is more than that of the Diesel cycle. Hence, it is evident that, the efficiency of the Otto cycle is greater than the efficiency of the Diesel cycle for agiven compression ratio and heat rejection. THEORETICAL AND ACTUAL CYCLES FOUR STROKE PETROL ENGINE
13 Fig (a) and (b) shows the actual p-v diagram and theoretical p-v diagram of four stroke Petrol engine. The line 5-1 represents the suction stroke in which the charge enters into the cylinder. The suction of mixture is possible only if the pressure inside the cylinder is below atmospheric pressure. That s the reason line 5-1 lies below the atmospheric pressure line. The burnt gases can be pushed out only if the pressure of the exhaust gas is above atmospheric pressure. This is represented by the line 1-5. The area in between the process 5-1 and 1-5 in the indicator diagram gives pumping loss of the engine. The compression stroke is shown by the line 1-2 which shows that the inlet valve closes (IVC) a little beyond 1. At the end of this stroke, there is an increase in pressure inside the engine cylinder. Before the end of compression stroke, the charge is ignited (IGN) with the help of spark plug. Thus, the pressure and temperature of the cylinder increase. But the volume remains constant as shown by line 2-3. Expansion is shown by the line 3-4. The exhaust valve opens (EVO) little before 4. The burnt gases are exhausted to atmosphere. It has been found practically, that the actual pressure rise in such an engine is only half of the theoretical value. The corners are rounded off because both inlet and exhaust valves do not open and close suddenly. THEORETICAL AND ACTUAL CYCLES FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE Fig (a) and (b) shows the actual p-v diagram and theoretical p-v diagram of four stroke Diesel engine. The line 5-1 represents the suction stroke in which the air enters into the cylinder. The suction of mixture is possible only if the pressure inside the cylinder is below atmospheric pressure. That s the reason line 5-1 lies below the atmospheric pressure line. The burnt gases can be pushed out only if the pressure of the exhaust gas is above atmospheric pressure. This is represented by the line 1-5. The air is compressed adiabatically in the cylinder during 1-2 process which takes place after inlet valve closed. Before the end of compression stroke, fuel is injected through the fuel injector (FVO). The fuel is ignited due to the temperature of highly compressed air inside the cylinder. The combustion takes place at constant pressure as shown in line 2-3. Actually, combustion at constant pressure is not possible as the fuel will not burn completely as it is introduced into the cylinder. Then the charge is expanded adiabatically is shown by the line 3-4. The exhaust valve opens (EVO) little before 4. The burnt gases are exhausted to atmosphere.
14 Theoretically, the compression and expansion are followed adiabatically. But in actual cycle it is not so. Because of heat and pressure losses are involved. THEORETICAL AND ACTUAL CYCLES FOR TWO STROKE PETROL ENGINE Fig (a) and (b) shows the actual p-v diagram and theoretical p-v diagram of two strokepetrol engine. The suction stroke is carried out from transfer ports open (TPO) and transfer port close (TPC). During half of the suction stroke, exhaust port is also opened. Now, the volume of air fuel mixture is entered into the cylinder. This happens as the piston moves from TDC to BDC. During second half of the suction stroke (i.e. BDC to TPC), the air and fuel mixture is compressed and burnt gases pushed out. A little beyond TPC, the exhaust port closes (EPC) at 1. These processes are represented in theoretical cycle as and Now, the air fuel mixture is compressed isentropically in the cylinder. This is shown by line 1-2. A little before the end of compression, the charge is ignited (IGN) with the help of spark plug as shown in the above diagram. Combustion of air fuel mixture increases the pressure and temperature of the products of combustion. During this process, volume remains constant. This represented by the line 2-3. The expansion process is shown by line 3-4. The end of the expansion stroke, exhaust port opens (EPO) at 4 and burnt gases are pushed out to the atmosphere. During this, the pressure falls suddenly to the atmospheric pressure. As the piston is moving towards BDC, the volume of burnt gases increases from 4 to 5. At 5, transfer port opens (TPO) and the suction starts. THEORETICAL AND ACTUAL CYCLES FOR TWO STROKE DIESEL ENGINE Fig (a) and (b) shows the actual p-v diagram and theoretical p-v diagram of two stroke Diesel engine
15 The suction stroke is carried out from transfer ports open (TPO) and transfer port close (TPC). During half of the suction stroke, exhaust port is also opened. Now, the volume of air is entered into the cylinder. This happens as the piston moves from TDC to BDC. During second half of the suction stroke (i.e. BDC to TPC), the air is compressed and burnt gases pushed out. A little beyond TPC, the exhaust port closes (EPC) at 1. These processes are represented in theoretical cycle as and Now, the air is compressed isentropically in the cylinder. This is shown by line 1-2. A little before the end of compression, the fuel is admitted into the cylinder by means of fuel injector (INJ).Combustion of fuel increases the pressure and temperature of the products of combustion. During this process, pressure remains constant. This represented by the line 2-3. The expansion process is shown by line 3-4. The end of the expansion stroke, exhaust port opens (EPO) at 4 and burnt gases are pushed out to the atmosphere. During this, the pressure falls suddenly to the atmospheric pressure. As the piston is moving towards BDC, the volume of burnt gases increases from 4 to 5. At 5, transfer port opens (TPO) and the suction starts. APPLICATION OF IC ENGINES Internal combustion engines are most commonly used for mobile propulsion in vehicles and portable machinery. In mobile equipment, internal combustion is advantageous since it can provide high power-to-weight ratios together with excellent fuel energy density. Generally using fossil fuel (mainly petroleum), these engines have appeared in transport in almost all vehicles (automobiles, trucks, motorcycles, boats, and in a wide variety of aircraft and locomotives). Where very high power-to-weight ratios are required, internal combustion engines appear in the form of gas turbines. These applications include jet aircraft, helicopters, large ships and electric generators.
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES
 CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle)
 The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle) The Otto cycle is a set of processes used by spark ignition internal combustion engines (2-stroke or 4-stroke cycles). These engines a) ingest a mixture of fuel
The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle) The Otto cycle is a set of processes used by spark ignition internal combustion engines (2-stroke or 4-stroke cycles). These engines a) ingest a mixture of fuel
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Combustion engines. Combustion
 Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Air-standard cycles Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje CH. 2 ۱ Cold-air-standard assumptions: When the working fluid is considered to be air with constant specific heats at room temperature (25 C). Air-standard
Air-standard cycles Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje CH. 2 ۱ Cold-air-standard assumptions: When the working fluid is considered to be air with constant specific heats at room temperature (25 C). Air-standard
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines Reading Problems 8-3 8-7 8-35, 8-45, 8-52 Definitions 1. spark ignition: a mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a spark plug applications requiring power to about 225 kw (300
Internal Combustion Engines Reading Problems 8-3 8-7 8-35, 8-45, 8-52 Definitions 1. spark ignition: a mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a spark plug applications requiring power to about 225 kw (300
L34: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Introduction to Gas Cycles Definitions
 Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
I.C ENGINES. CLASSIFICATION I.C Engines are classified according to:
 I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat
 Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
Engine Cycles. T Alrayyes
 Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles
 Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
In this lecture... Gas power cycles
 7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
Internal Combustion Engine. Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST
 Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Week 10. Gas Power Cycles. ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1
 Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
ACTUAL CYCLE. Actual engine cycle
 1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
Gas Power System. By Ertanto Vetra
 Gas Power System 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Otto Cycles Diesel Cycles Gas Turbine Cycles Gas Turbine Based Combined Cycles Gas Turbines for Aircrafts Turbojets
Gas Power System 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Otto Cycles Diesel Cycles Gas Turbine Cycles Gas Turbine Based Combined Cycles Gas Turbines for Aircrafts Turbojets
(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]
![(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16] (a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]](/thumbs/79/80273804.jpg) Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes
 8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System
 Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition
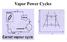 Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
Gas Power Cycles. Tarawneh
 Gas Power Cycles Dr.Mohammad Tarawneh ) Carnot cycle 2) Otto cycle ) Diesel cycle - Today 4) Dual Cycle 5) Stirling cycle 6) Ericsson cycles 7) Brayton cycle Carnot Cycle Reversible isothermal expansion
Gas Power Cycles Dr.Mohammad Tarawneh ) Carnot cycle 2) Otto cycle ) Diesel cycle - Today 4) Dual Cycle 5) Stirling cycle 6) Ericsson cycles 7) Brayton cycle Carnot Cycle Reversible isothermal expansion
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Power Cycles. Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion
 Gas Power Cycles Power Cycles Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion Otto cycle, spark ignition Diesel cycle, compression ignition Sterling & Ericsson cycles Brayton cycles Jet-propulsion cycle Ideal Cycles,
Gas Power Cycles Power Cycles Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion Otto cycle, spark ignition Diesel cycle, compression ignition Sterling & Ericsson cycles Brayton cycles Jet-propulsion cycle Ideal Cycles,
USO4CICV01/US04CICH02:
 Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES
 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES Air Standard Cycles - Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycle with intercooling, reheating and regeneration- Calculation of airstandard efficiency and mean effective
THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES Air Standard Cycles - Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycle with intercooling, reheating and regeneration- Calculation of airstandard efficiency and mean effective
η th W = Q Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle.
 Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
OBJECTIVE: GENERAL ASPECTS ABOUT ENGINES MECHANISM:
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1. Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
Thermodynamic Cycles. Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares
 Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes:
 Classification of thermodynamics cycles Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes: Gas and vapor cycles - Gas cycle: the working
Classification of thermodynamics cycles Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes: Gas and vapor cycles - Gas cycle: the working
Assignment-1 Introduction
 Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT:- To study about two stroke and four stroke petrol engines. APPARATUS REQUIRED:- Sl.no Name of the apparatus Specification Quant
 EXPERIMENT ON TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE PETROL ENGINES Prepared By Prof. (Dr.) M. K. Roul Professor and Principal, Gandhi Institute for Technological Advancement (GITA), Bhubaneswar 752054 June 2014 1
EXPERIMENT ON TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE PETROL ENGINES Prepared By Prof. (Dr.) M. K. Roul Professor and Principal, Gandhi Institute for Technological Advancement (GITA), Bhubaneswar 752054 June 2014 1
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
2. Discuss the effects of the following operating variables on detonation
 Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
MEB THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I PART-A
 MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
Approved by AICTE, Government of India & affiliated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) SUBJECT: ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Assignment Ch 1
 1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
The Four Stroke Cycle
 1 Induction As the piston travels down the cylinder it draws filtered air at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature through an air filter and inlet valves into the cylinder. 2 Compression When the
1 Induction As the piston travels down the cylinder it draws filtered air at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature through an air filter and inlet valves into the cylinder. 2 Compression When the
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Heat engine. Heat engine
 Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
Principles of Engine Operation. Information
 Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Page 2. (a) (i) Show that during the change AB the gas undergoes an isothermal change.
 Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE
 INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE Engine: An engine is motor which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Fuel/petrol engine: A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is
INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE Engine: An engine is motor which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Fuel/petrol engine: A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is
Noble Group of Institutions, Junagadh. Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: 2017-18 Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat
Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: 2017-18 Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat
New Polytechnic, Kolhapur
 01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 16 marks Content 1.1 Introduction 4 Marks Definition of I C engine. Engine nomenclature. 1.2 The working principle of Engine 6 Marks Four-Stroke
01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 16 marks Content 1.1 Introduction 4 Marks Definition of I C engine. Engine nomenclature. 1.2 The working principle of Engine 6 Marks Four-Stroke
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE
 A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE Prakash Kumar Sen 1, Lalit Kumar 2, Shailendra Kumar Bohidar 3 1 Student of M.Tech. Manufacturing Management, BITS Pilani (India) 2 Student of Mechanical
A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE Prakash Kumar Sen 1, Lalit Kumar 2, Shailendra Kumar Bohidar 3 1 Student of M.Tech. Manufacturing Management, BITS Pilani (India) 2 Student of Mechanical
Combustion Systems What we might have learned
 Combustion Systems What we might have learned IMechE ADSC, 6 December 2012 Chris Whelan Contents Engines Big & Small Carnot, Otto & Diesel Thermodynamic Cycles Combustion Process & Systems Diesel & Otto
Combustion Systems What we might have learned IMechE ADSC, 6 December 2012 Chris Whelan Contents Engines Big & Small Carnot, Otto & Diesel Thermodynamic Cycles Combustion Process & Systems Diesel & Otto
Template for the Storyboard stage
 Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
Scheme - G. Sample Test Paper-I. Course Name : Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Code : ME Semester : Fifth Subject Title : Power Engineering
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1. ) AIM : Study
SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1. ) AIM : Study
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C OBJECTIVE:
 ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
Kul Internal Combustion Engine Technology. Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5
 Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
GAS POWER CYCLES. Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering i Hashemite University 2 Objectives Evaluate the performance of gas power cycles for which h the working fluid remains a
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering i Hashemite University 2 Objectives Evaluate the performance of gas power cycles for which h the working fluid remains a
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Question Bank. UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks)
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle
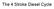 The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) QUESTION BANK UNIT I I.C ENGINES
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
density ratio of 1.5.
 Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Chapter 9. Two important areas of application for thermodynamics GAS POWER CYCLES. Objectives
 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Two important areas of application for thermodynamics are power generation and refrigeration. Both are usually accomplished by systems that operate on a thermodynamic cycle.
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Two important areas of application for thermodynamics are power generation and refrigeration. Both are usually accomplished by systems that operate on a thermodynamic cycle.
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
Introduction to Fuel-Air Injection Engine. (A discrete structured IC engine) KansLab
 Introduction to Fuel-Air Injection Engine (A discrete structured IC engine) KansLab 1 Fig. 1: A Fuel-Air Injection (FAI) Engine is: 1) A two-stroke engine with fuel and air injections. 2) A hybrid engine
Introduction to Fuel-Air Injection Engine (A discrete structured IC engine) KansLab 1 Fig. 1: A Fuel-Air Injection (FAI) Engine is: 1) A two-stroke engine with fuel and air injections. 2) A hybrid engine
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
IC ENGINES. Differences between SI and CI engines: Petrol is fuel, which has a high self ignition temperature
 IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines
 Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
A REVIEW ON STIRLING ENGINES
 A REVIEW ON STIRLING ENGINES Neeraj Joshi UG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sandip Foundation s Sandip Institute of Technology and Research Centre,Mahiravani, Nashik Savitribai Phule Pune
A REVIEW ON STIRLING ENGINES Neeraj Joshi UG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sandip Foundation s Sandip Institute of Technology and Research Centre,Mahiravani, Nashik Savitribai Phule Pune
LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E)
 LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. Name of the Experiment 1. To study the constructional details & working principles of two-stroke petrol/ four-stroke
LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. Name of the Experiment 1. To study the constructional details & working principles of two-stroke petrol/ four-stroke
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL
 Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES
 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
Simulation of Performance Parameters of Spark Ignition Engine for Various Ignition Timings
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277-4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved. Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Simulation of Performance
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277-4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved. Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Simulation of Performance
Name Date. True-False. Multiple Choice
 Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
AT AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK
 AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
Design and Fabrication of Simple Turbo Alternator
 Design and Fabrication of Simple Turbo Alternator S.Arunkumar, A.Sridhar, S.Praveen vaitheeswaran, S.Sasikumar, Sefin Jose Department of mechanical engineering, Nandha College of technology, Erode. Abstract
Design and Fabrication of Simple Turbo Alternator S.Arunkumar, A.Sridhar, S.Praveen vaitheeswaran, S.Sasikumar, Sefin Jose Department of mechanical engineering, Nandha College of technology, Erode. Abstract
California State University, Bakersfield. Signals and Systems. Kristin Koehler. California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 6 July 23 rd, 2013
 Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 6 July 23 rd, 2013 1 Outline Review (2 and 4 stroke engines) Diesel Engines 2 stroke 4 stroke Benefits of diesel Uses of diesel engines
Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 6 July 23 rd, 2013 1 Outline Review (2 and 4 stroke engines) Diesel Engines 2 stroke 4 stroke Benefits of diesel Uses of diesel engines
Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below.
 Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below. 4 BASIC OPERATIONS The Induction Stroke On the induction stroke, the inlet valve opens and the piston, moving down, creates
Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below. 4 BASIC OPERATIONS The Induction Stroke On the induction stroke, the inlet valve opens and the piston, moving down, creates
Development of Low-Exergy-Loss, High-Efficiency Chemical Engines
 Development of Low-Exergy-Loss, High-Efficiency Chemical Engines Investigators C. F., Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering; Kwee-Yan Teh, Shannon L. Miller, Graduate Researchers Introduction The
Development of Low-Exergy-Loss, High-Efficiency Chemical Engines Investigators C. F., Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering; Kwee-Yan Teh, Shannon L. Miller, Graduate Researchers Introduction The
Internal Combustion Engines
 Introduction Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will learn about: Definition of internal combustion Development of the internal combustion engine Different engine classifications We will also draw
Introduction Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will learn about: Definition of internal combustion Development of the internal combustion engine Different engine classifications We will also draw
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 11 Internal Combustion
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 11 Internal Combustion
THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL
 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 1. I.C ENGINES PERFORMANCE TEST (4-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE 2. I.C ENGINES HEAT BALANCE 3. ECONAMICAL SPPED TEST (4-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE) 4. PERFORMANCE TEST
THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 1. I.C ENGINES PERFORMANCE TEST (4-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE 2. I.C ENGINES HEAT BALANCE 3. ECONAMICAL SPPED TEST (4-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE) 4. PERFORMANCE TEST
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines
 Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines Aravind. I. Garagad. Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College of Engineering and Technology, Dharwad, Karnataka, India. ABSTRACT Large reductions
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines Aravind. I. Garagad. Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College of Engineering and Technology, Dharwad, Karnataka, India. ABSTRACT Large reductions
THERMAL ENGINEERING. SHIBIN MOHAMED Asst. Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Al Ameen Engineering College.
 THERMAL ENGINEERING SHIBIN MOHAMED Asst. Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Al Ameen Engineering College Al- Ameen Engg. College 1 Steam Engine: Definition A steam engine is a heat engine that converts
THERMAL ENGINEERING SHIBIN MOHAMED Asst. Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Al Ameen Engineering College Al- Ameen Engg. College 1 Steam Engine: Definition A steam engine is a heat engine that converts
Analytical Determination of the Performance Parameters of CompressedAir vehicle
 Analytical Determination of the Performance Parameters of CompressedAir vehicle Abhijith.R abhijith.rajan@acetvm.com Sivaprakash.SC shivaprakash.sc@acetvm.com Akhil.BS akhil.bs@acetvm.com Arun.S Assistant
Analytical Determination of the Performance Parameters of CompressedAir vehicle Abhijith.R abhijith.rajan@acetvm.com Sivaprakash.SC shivaprakash.sc@acetvm.com Akhil.BS akhil.bs@acetvm.com Arun.S Assistant
Introduction Outline of Some Descriptive Systems
 Introduction Outline of Some Descriptive Systems 1 1.1. Steam power plant : Layout components of a modern steam power plant. 1.2. Nuclear power plant. 1.3. Internal combustion engines : Heat engines development
Introduction Outline of Some Descriptive Systems 1 1.1. Steam power plant : Layout components of a modern steam power plant. 1.2. Nuclear power plant. 1.3. Internal combustion engines : Heat engines development
Focus on Training Section: Unit 2
 All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
2) Rich mixture: A mixture which contains less air than the stoichiometric requirement is called a rich mixture (ex. A/F ratio: 12:1, 10:1 etc.
 Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4.
 THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? WE KNOW ABOUT:- WHICH WE KNOW AS:- LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4. EXHAUST SQUEEZE BANG BLOW Inlet valve
THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? WE KNOW ABOUT:- WHICH WE KNOW AS:- LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4. EXHAUST SQUEEZE BANG BLOW Inlet valve
Introduction. Internal Combustion Engines
 Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines A heat engine that converts chemical energy in a fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy first converted into thermal energy (Combustion)
Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines A heat engine that converts chemical energy in a fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy first converted into thermal energy (Combustion)
