Noble Group of Institutions, Junagadh. Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
|
|
|
- Christian Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering ( ) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat Q.2 Explain different types energy. Q.3 State and explain zeroth and first law of thermodynamics. Q.4 Classify thermodynamic system and give example of each. Q.5 Define pressure and explain Absolute pressure, Gauge pressure and Atmospheric pressure. Q.7 State the similarities and difference between heat and work. Q.8 In compressor, the work done on the air is 150 kj. The heat rejected to the surroundings is 60 kj/kg. find the change in internal energy. Q.9 Give various statement of second law of thermodynamics. Q.10 Explain process, path, and cycle. TUTORIAL 2 ENERGY Q.1 Which are the common solid fuels? Explain in brief about each of them. Q.2 List the various liquid fuels. State its merits and demerits Q.3 Enlist the various gaseous fuels and explain in brief about each of them. Q.4 State the advantages and disadvantages of gaseous fuel over solid and liquid fuels. Q.5 Write short note on 1. CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) 2. LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas). 3. Bio-fuel 4. Wind energy 5. Solar energy Q.6 Write a short note on nuclear energy and their utilization. TUTORIAL 3 PROPERTIES OF GASES Q.1 Derive characteristic equation of a perfect gas. Q.2 Define specific heat and derive the Mayer s equation. Q.3 Explain the adiabatic process with derivation.
2 Q.4 What is the difference between flow and non-flow process? Q.5 Explain isothermal process with derivation. Q.6 Explain polytropic process with derivation. Q.7 1 kg of air at 9 bar pressure and 80 C temperature undergoes air non flow work polytropic process. The law of expansion is (PV)¹ ¹ = C. The pressure falls to 1.4 bar during process. Calculate 1) Final temperature 2) Work done 3) Change in internal energy 4) Heat exchange. Take R=287 J/kg K and ϒ=1.4 for air. Q.8 A steal cylinder contains oxygen at a pressure of 25 bar and temperature of 27 C. After using some quantity of the gas the pressure was found to be 5 bar and temperature 20 C. 700 liters of oxygen was originally put in the cylinder at NTP. Density of O₂ at NTP = 1.43 gms/liter. Calculate the mass of O₂ used. Q kg of ideal gas heating a volume of 0.08 m³ is expanded at constant pressure of 6 bar in a cylinder until its volume becomes 0.12 m³. The gas is then expanded isentropically until its volume becomes 0.30 m³. Calculate 1) the temperature and the pressure at the end of each process 2) Work done. Take Cp = KJ/kg K and Cv = 0.36 KJ/kg K. Q.10 1 kg of air at a pressure of 1 bar and temperature of 27 C is compressed to a pressure of 10 bar isothermally and adiabatically. Calculate 1) Work done 2) Heat transfer 3) Change in internal energy in both the cases. Take Cp = KJ/kg K, Cv = KJ/kg K. TUTORIAL 4 PROPERTIES OF STEAM Q.1 Define : 1. Sensible heat 2. Latent heat 3. Dryness fraction 4. Enthalpy of liquid and evaporation 5. Dry steam 6. Wet steam 7. Superheated steam 8. Degree of superheat 9. Heat of superheat Q.2 Explain the construction and working of following calorimeter Separating 3. Throttling 4. Combined separating and throttling Q.3 A sample of wet steam at a pressure of 25 bar has dryness fraction 0.8. Determine its enthalpy and internal energy [Ans: 2433 kj/kg, 2275 kj/kg ] Q.4 What amount of heat would be required to produce 5 kg of steam at a pressure of5bar and temperature of 250 C from water at 30 C. Cps=2.1kJ/kgK.[Ans:14140 kj] Q.5 Calculate the enthalpy per kg of steam at 10 bar pressure and a temperature of C. Find also the change in enthalpy if this steam is expanded to 1.4 bar and dryness fraction of 0.8.Cps=2.29 kj/kgk. [Ans: 3051 kj/kg, 808 kj/kg]
3 TUTORIAL-5 HEAT ENGINES Q.1 Explain the Carnot cycle with P-V diagram and derive the expression for the efficiency for it. Q.2 Explain the working of Rankine cycle with P-V diagram and derive the expression for the efficiency for it. Q.3 Derive the equation for the air standard efficiency of Otto cycle. Q.4 Derive the equation for the air standard efficiency of Diesel cycle. Q.5 In an Otto cycle the compression ratio is 8.The temperatures at the beginning of compression and at the end of heat supply are 310 K and 1600 K respectively. Assume γ = 1.4 and Cv = kj/kg K. Find : 1.Heat Supplied 2. Efficiency of the cycle.[ans:636 kj/kg, %] Q.6 The compression ratio of an oil engine working on Diesel Cycle is 15.Cut off takes place at 12 % of the working stroke. The air is drawn into cylinder at 100 kpa and 270C. Assume Cp=1.006 kj/kg K and Cv =0.717 kj/kg K. Calculate: 1. Temperature at the end of compression 2. Pressure at the end of compression 3. Air standard efficiency of the cycle. [Ans: 893 K, kpa, %] TUTORIAL-6 STEAM BOILERS Q.1 Differentiate between fire tube and water tube boilers. Q.2 Define and list out various mountings and accessories. Q.3 Explain with neat sketch the construction and working of different boilers that you have studied. Q.4 Explain with neat sketch the construction and working of different boiler mountings that you have studied. Q.5 Explain with neat sketch the construction and working of different boiler accessories that you have studied. TUTORIAL-7 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE Q.1 Define following: 1)Carburetor 2)Fuel injector 3)Clearance volume 4)Stroke volume(swept volume) 5)Compression ratio 6)Specific fuel consumption 7)Volumetric efficiency 8)Bore 9)Stroke 10)Pistonspeed. Q.2 Explain the working of 4 stroke Petrol and Diesel engine with P-V diagram. Q.3 Explain the working of 2 stroke Petrol and Diesel engine. Q.4 Compare 2 stroke and 4 stroke I.C.engine.
4 Q.5 Compare C.I.(Compression Ignition) and S.I.(Spark Ignition) engine. Q.6 State advantages and disadvantages of two stroke engine over four stroke engine. Q.7 The following data refer to a single cylinder four stroke petrol engine. Cylinder diameter = 25 cm, stroke of the piston = 40 cm, engine speed = 1400rpm, indicated mean effective pressure = 4 bar, fuel consumption = 20 liters/hr, calorific value of the fuel = KJ/kg K, specific gravity of the fuel = 0.8. Determine the indicated termefficiency. Q.8 The four cylinder two stroke cycle petrol engine develop 30 KW at 2500 rpm. The indicated mean effective pressure of each is 800 KPa and ηm = 80%. Calculate the diameter and stroke of each of the cylinder if L/D = 1.5. also calculate the brake specific fuel consumption of the engine if break thermal efficiency is 28%. The calorific value of petrol is KJ/kg K. Q.9 The following data refer to a single cylinder four stroke petrol engine. Cylinder diameter = 30 cm Stroke of the piston = 40 cm Engine speed = 1400 rpm Indicated mean effective pressure = 5 bar Fuel consumption = kg/hr C.V. of the fuel = KJ/kg K Specific gravity of the fuel = 0.8 Determine the indicated thermal efficiency? Q.10 The following results refer to a test on I.C. engine. Indicated power = 42 KW Frictional power = 7 KW Engine speed = 1800 rpm Specific fuel consumption per B.P. = 0.30 kg/kw hr Calorific value of fuel used = KJ/kg K Calculate 1) ηm 2) ηbt 3) ηit. Q.11 During a test on a single cylinder four stroke engine having compression ratio of 6. Following data is recorded, Bore = 10 cm, Stroke = 12.5 cm, Indicated mean effective pressure = 2.6 bar, Dead load on dynamometer = 60 N, Spring balance reading = 90 N, Effective radius of flywheel = 40 cm, Fuel consumption = 1 kg/hr, Calorific value of fuel = KJ/kg K, Speed = 2000 rpm. Determine I.P., B.P., ηm, ηbt, ηit, ηair, ηra. Q.12 Four cylinder two stroke petrol engine with stroke to bore ratio 1.2 develops 32 KW B.P. at 2500 rpm the indicated mean effective pressure in each cylinder is 9 bar & ηm 86%. Determine bore & stroke of each cylinder and ηbt & ηit. If fuel consumption mf = 9 kg/hr, C.V. = KJ/kg K.
5 Q.13 A two cylinder four stroke petrol engine has 100 mm bore and 140 mm stroke. It runs at 900 rpm. It consumed 2.1 KJ/hr of petrol having a colorific value of KJ/kg K. The indicated mean effective pressure in both cylinders is 7.5 bar. Calculate ηit & ηra. It clearance volume 15% of stroke volume. TUTORIAL-8 PUMPS Q.1 Define and give the detailed classification of pump. Q.2 Explain the working of a single acting and double acting reciprocating pump. Q.3 Classify centrifugal pumps and explain the working of each. Q.4 Why priming is required in centrifugal pump? Q.5 Explain the working of following rotary pumps 1. Gear pump 2. Screw pump 3. Vane pump TUTORIAL-9 AIR COMPRESSOR Q.1 Classify the air compressor and state the applications of compressed air. Q.2 Prove that the volumetric efficiency of air compressor is given by, ηv = 1-c((p2/p1) 1/n -1) Q.3 Prove that the work done per kg of air in a compressor is given by, W = RT1 n/n-1 ((Rp) n-1/n -1) Q.4 Classify the rotary air compressor and explain the working of each. Q.5 Air is to be Compressed in a single stage reciprocating compressor from bar and 15 C to 7 bar. Calculate the power required for a free air delivery of0.3 m 3 / min when the compression process is. 1. Adiabatic 2. Isothermal 3. Polytropic (n = 1.25) What will be the delivery temperature in each case? Neglect clearance. [ANS:1.3 kw, 500 K, 0.98 kw, 288 K, 1.2 kw, 424 K ] Q.6 Air is to be compressed through a pressure ratio of 10 from a pressure of 1 bar in a single stage air compressor. Free air delivery is 3 m 3 /min. Swept volume = 14 litre. n =1.3. Neglect clearance volume. Calculate : 1. Power required in kw 2. Rotational speed of the compressor Q.7 Differentiate reciprocating air compressor and rotary air compressor. [ANS: 15.2 kw, 214 rpm ]
6 TUTORIAL-10 REFRIGERATION AND AIR-CONDITIONING Q.1 Define: 1. Refrigeration 2. Refrigerating effect 3. One ton of refrigeration 4. C.O.P Q.2 Define and classify the refrigerants. Q.3 With neat sketch explain the working of simple vapour compression refrigeration system using p-h and T-S diagram. Q.4 With neat sketch explain the working of vapour absorption refrigeration system. Q.5 Write short note on the following 1. Domestic Refrigerator 2. Window A/C 3. Split A/C TUTORIAL-11 COUPLINGS, CLUTCHES AND BRAKES Q.1 What is coupling? Classify and explain each with neat sketch. Q.2 What is clutch? Classify and explain each with neat sketch. Q.3 What is brake? Classify and explain each with neat sketch. Q.4 Differentiate the clutch and brake. TUTORIAL-12 TRANSMISSION OF MOTION AND POWER Q.1 Classify and explain various types of belt drive with neat sketch. Q.2 Explain with neat sketch the chain drive. Q.3 Classify and explain various types of gear drive with neat sketch. Q.4 Compare belt drive, chain drive and gear drive. TUTORIAL-13 ENGINEERING MATERIALS Q.1 Enlist different properties of engineering materials and explain it wherever possible. Q.2 Classify the metals and explain in detail about each (both ferrous and non ferrous) Q.3 Explain the following non metals 1. Ceramic 2. Glass 3. Concrete 4. Plastic 5. Timber
GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) SUBJECT: ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Assignment Ch 1
 1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) QUESTION BANK UNIT I I.C ENGINES
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles
 Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
MEB THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I PART-A
 MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
GOVERNMENT ENGINEERING COLLEGE, GODHRA
 Practical No. - 1 To understand construction and working of various types of Steam boilers. 1) What is the function of Steam boiler? And what are factors should be considered while selecting a boiler?
Practical No. - 1 To understand construction and working of various types of Steam boilers. 1) What is the function of Steam boiler? And what are factors should be considered while selecting a boiler?
2. Discuss the effects of the following operating variables on detonation
 Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]
![(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16] (a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]](/thumbs/79/80273804.jpg) Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Scheme G Sample Question Paper Course Name : Diploma in Automobile Engineering Course Code : AE
 Sample Question Paper Semester : Fourth Marks : 100 Time: 03 Hours Q1.A. Attempt any SIX a. State different types of ideal gas processes 12 Marks b. Define dryness fraction and degree of superheat. c.
Sample Question Paper Semester : Fourth Marks : 100 Time: 03 Hours Q1.A. Attempt any SIX a. State different types of ideal gas processes 12 Marks b. Define dryness fraction and degree of superheat. c.
2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Assignment-1 Introduction
 Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Scheme - G. Sample Test Paper-I. Course Name : Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Code : ME Semester : Fifth Subject Title : Power Engineering
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Question Bank. UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks)
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C OBJECTIVE:
 ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME Thermal Engineering Question Bank
 ME2301 - Thermal Engineering Question Bank UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycles, Calculation of mean effective pressure, and air standard efficiency -Actual and theoretical PV diagram
ME2301 - Thermal Engineering Question Bank UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycles, Calculation of mean effective pressure, and air standard efficiency -Actual and theoretical PV diagram
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
'' ''' '' ''' Code No: R R16 SET - 1
 Code No: R161232 R16 SET - 1 1. a) List the Primary requirements of a Steam Boiler. (2M) b) What are the distinguishing features between a Casting and a Pattern? (2M) c) Define (i) Brake Power; (ii) Indicated
Code No: R161232 R16 SET - 1 1. a) List the Primary requirements of a Steam Boiler. (2M) b) What are the distinguishing features between a Casting and a Pattern? (2M) c) Define (i) Brake Power; (ii) Indicated
Lab Manual Elements of Mechanical Engineering ( )
 Lab Manual Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Darshan Institute of Engineering and Technology, Rajkot. Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology Certificate This is to certify that Mr./Ms.
Lab Manual Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Darshan Institute of Engineering and Technology, Rajkot. Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology Certificate This is to certify that Mr./Ms.
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME THERMAL ENGINEERING. Part-A (2 Marks)
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? 2. What is meant by air standard cycle? 3.. Name
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? 2. What is meant by air standard cycle? 3.. Name
Government of Karnataka Department of Technical Education Board of Technical Examinations, Bangalore
 CIE- 25 Marks Government of Karnataka Department of Technical Education Board of Technical Examinations, Bangalore Prerequisites: Knowledge of basic mathematics and Applied Science Course Objectives: 1.
CIE- 25 Marks Government of Karnataka Department of Technical Education Board of Technical Examinations, Bangalore Prerequisites: Knowledge of basic mathematics and Applied Science Course Objectives: 1.
B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) Term-End Examination June 2016
 No. of Printed Pages : 5 I BIME-010 I B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) 00 1 Ems, Term-End Examination June 2016 BIME-010 : THERMAL ENGINEERING Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Attempt
No. of Printed Pages : 5 I BIME-010 I B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) 00 1 Ems, Term-End Examination June 2016 BIME-010 : THERMAL ENGINEERING Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Attempt
05 Marks (c) Sketch and explain Lancashire Boiler.
 Model question paper No.1 1. Answer any FIVE full questions choosing at least two questions from part A & two questions from part B 2. Use of steam tables is permitted 1. (a) Discuss briefly the different
Model question paper No.1 1. Answer any FIVE full questions choosing at least two questions from part A & two questions from part B 2. Use of steam tables is permitted 1. (a) Discuss briefly the different
Elements of Mechanical Engineering (EME) QUESTIONS
 QUESTIONS 1) In First angle projection method (a) Plan comes above elevation (b) Plan comes below elevation (c) Plan comes besides elevation (d) Plan is on the left hand side. (2) Where LHSV in third angle
QUESTIONS 1) In First angle projection method (a) Plan comes above elevation (b) Plan comes below elevation (c) Plan comes besides elevation (d) Plan is on the left hand side. (2) Where LHSV in third angle
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition
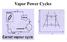 Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
AT AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK
 AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FS81504 BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FS81504 BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES
 CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics I. C. Engine Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi
Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics I. C. Engine Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL
 Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
USO4CICV01/US04CICH02:
 Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
EME MCQ QUESTION BANK
 EME MCQ QUESTION BANK 1. Work is considered positive when a) Work is done on the system b) work is done by the system c) both a and b d) none of the above 2. A source of energy is known as renewable source
EME MCQ QUESTION BANK 1. Work is considered positive when a) Work is done on the system b) work is done by the system c) both a and b d) none of the above 2. A source of energy is known as renewable source
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System
 Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
Combustion engines. Combustion
 Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Page 2. (a) (i) Show that during the change AB the gas undergoes an isothermal change.
 Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat
 Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
L34: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Introduction to Gas Cycles Definitions
 Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT, GMIT, BHAVNAGAR. QUESTION BANK
 , GMIT, BHAVNAGAR. QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE:21100 SUBJECT: ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Sr. INTRODUCTION 1. What is Prime mover? How are they classified? + 2. State and explain Zero th law of Thermodynamics.
, GMIT, BHAVNAGAR. QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE:21100 SUBJECT: ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Sr. INTRODUCTION 1. What is Prime mover? How are they classified? + 2. State and explain Zero th law of Thermodynamics.
B. Tech Degree II Semester Examination in Polymer Science and
 BT PSRT 9 14 PTF 123 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PART - A (Answer any FIVE questions) 9) (5 x 5 = 25) What are the general classification of engineering materials? Give three examples for each group. What are
BT PSRT 9 14 PTF 123 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PART - A (Answer any FIVE questions) 9) (5 x 5 = 25) What are the general classification of engineering materials? Give three examples for each group. What are
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF ERONUTIL ENGINEERING (utonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MEHNIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BNK ourse Name : THERML ENGINEERING-I ourse ode : 40313 lass : II B. Tech II Semester Branch : Mechanical
INSTITUTE OF ERONUTIL ENGINEERING (utonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MEHNIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BNK ourse Name : THERML ENGINEERING-I ourse ode : 40313 lass : II B. Tech II Semester Branch : Mechanical
Thermodynamic Cycles. Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares
 Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
AT 2303 AUTOMOTIVE POLLUTION AND CONTROL Automobile Engineering Question Bank
 AT 2303 AUTOMOTIVE POLLUTION AND CONTROL Automobile Engineering Question Bank UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. What are the design considerations of a vehicle?(jun 2013) 2..Classify the various types of vehicles.
AT 2303 AUTOMOTIVE POLLUTION AND CONTROL Automobile Engineering Question Bank UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. What are the design considerations of a vehicle?(jun 2013) 2..Classify the various types of vehicles.
I.C ENGINES. CLASSIFICATION I.C Engines are classified according to:
 I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
2.61 Internal Combustion Engine Final Examination. Open book. Note that Problems 1 &2 carry 20 points each; Problems 3 &4 carry 10 points each.
 2.61 Internal Combustion Engine Final Examination Open book. Note that Problems 1 &2 carry 20 points each; Problems 3 &4 carry 10 points each. Problem 1 (20 points) Ethanol has been introduced as the bio-fuel
2.61 Internal Combustion Engine Final Examination Open book. Note that Problems 1 &2 carry 20 points each; Problems 3 &4 carry 10 points each. Problem 1 (20 points) Ethanol has been introduced as the bio-fuel
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine 1. A 9-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle, radial SI engine operates at 900rpm. Calculate: (1) How often ignition occurs, in degrees of engine rev. (2) How many power strokes per rev.
Internal Combustion Engine 1. A 9-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle, radial SI engine operates at 900rpm. Calculate: (1) How often ignition occurs, in degrees of engine rev. (2) How many power strokes per rev.
STEAM-ENGINE AND PROFESSOR OF MECHANISM AND APPLIED MECHANICS IN THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE. CAMBRIDGE: AT THE UNIVERSITY PRESS.
 THE STEAM-ENGINE AND OTHEE HEAT-ENGINES BY J. A. EWING, M.A., B.Sc, F.E.S., M.INST.C.E., PROFESSOR OF MECHANISM AND APPLIED MECHANICS IN THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE. CAMBRIDGE: AT THE UNIVERSITY PRESS.
THE STEAM-ENGINE AND OTHEE HEAT-ENGINES BY J. A. EWING, M.A., B.Sc, F.E.S., M.INST.C.E., PROFESSOR OF MECHANISM AND APPLIED MECHANICS IN THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE. CAMBRIDGE: AT THE UNIVERSITY PRESS.
η th W = Q Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle.
 Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines.
 Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines. 4.2 Construction and working of gas turbines i) Open cycle ii) Closed cycle gas Turbines, P.V. and
Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines. 4.2 Construction and working of gas turbines i) Open cycle ii) Closed cycle gas Turbines, P.V. and
Heat engine. Heat engine
 Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) Summer 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: 1/18
 Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: /8 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer
Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: /8 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
Internal Combustion Engine. Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST
 Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Attempt any three. One Mark each. Following are the applications of compressed air ( any four)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES
 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES Air Standard Cycles - Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycle with intercooling, reheating and regeneration- Calculation of airstandard efficiency and mean effective
THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT 1 GAS POWER CYCLES Air Standard Cycles - Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycle with intercooling, reheating and regeneration- Calculation of airstandard efficiency and mean effective
SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1. ) AIM : Study
SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1. ) AIM : Study
Gas Power Cycles. Tarawneh
 Gas Power Cycles Dr.Mohammad Tarawneh ) Carnot cycle 2) Otto cycle ) Diesel cycle - Today 4) Dual Cycle 5) Stirling cycle 6) Ericsson cycles 7) Brayton cycle Carnot Cycle Reversible isothermal expansion
Gas Power Cycles Dr.Mohammad Tarawneh ) Carnot cycle 2) Otto cycle ) Diesel cycle - Today 4) Dual Cycle 5) Stirling cycle 6) Ericsson cycles 7) Brayton cycle Carnot Cycle Reversible isothermal expansion
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 ME110. Aircraft and Automotive Systems
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 ME110 Aircraft and Automotive Systems Time allowed: TWO hours Answer TWO questions from THREE in Section A and TWO questions
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 ME110 Aircraft and Automotive Systems Time allowed: TWO hours Answer TWO questions from THREE in Section A and TWO questions
Model Question Papers
 QUESTION CARRIES 2 MARKS Model Question Papers 1. Define engine. Give their classification? 6 th Semester I.C. ENGINE [ME-604] UNIT -1 2. Define the performance parameters of IC engine ie indicated power,
QUESTION CARRIES 2 MARKS Model Question Papers 1. Define engine. Give their classification? 6 th Semester I.C. ENGINE [ME-604] UNIT -1 2. Define the performance parameters of IC engine ie indicated power,
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines
 Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Department of Mechanical Engineering UBMC701 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES. Part A (Two Marks Questions)
 Department of Mechanical Engineering UBMC701 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK UNIT- I VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES 1. Define Automobile. Give the typical specifications of an automobile 2. Name the
Department of Mechanical Engineering UBMC701 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK UNIT- I VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES 1. Define Automobile. Give the typical specifications of an automobile 2. Name the
1. (a) If a large power generating station is operating with steam at 16,000 kpa and 500 and exhausting to a condenser at, 37.6 mm mercury absolute;
 Sample Questions REVISED SECOND CLASS PARTS B1, B2, AND B3 (NOTE: these questions are intended as representations of the style of questions that may appear on examinations, they are not intended as study
Sample Questions REVISED SECOND CLASS PARTS B1, B2, AND B3 (NOTE: these questions are intended as representations of the style of questions that may appear on examinations, they are not intended as study
LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E)
 LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. Name of the Experiment 1. To study the constructional details & working principles of two-stroke petrol/ four-stroke
LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. Name of the Experiment 1. To study the constructional details & working principles of two-stroke petrol/ four-stroke
AME 436. Energy and Propulsion. Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters
 AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 ME110. Aircraft and Automotive Systems
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 014/015 ME110 Aircraft and Automotive Systems Time allowed: ONE hour THIRTY minutes Answer TWO questions from THREE Items permitted:
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 014/015 ME110 Aircraft and Automotive Systems Time allowed: ONE hour THIRTY minutes Answer TWO questions from THREE Items permitted:
SINGLE CYLINDER FOUR STROKE PETROL ENGINE TEST RIG WITH EDDY CURRENT DYNAMOMETER
 SINGLE CYLINDER FOUR STROKE PETROL ENGINE TEST RIG WITH EDDY CURRENT DYNAMOMETER AIM: Conducting a performance test on the engine. DESCRIPTION The Eddy current Dynamometer is coupled to the Engine and
SINGLE CYLINDER FOUR STROKE PETROL ENGINE TEST RIG WITH EDDY CURRENT DYNAMOMETER AIM: Conducting a performance test on the engine. DESCRIPTION The Eddy current Dynamometer is coupled to the Engine and
density ratio of 1.5.
 Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes
 8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
Theory of Machines. CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms
 CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms 1. Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. 2. Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one. 3. Define (1) Mechanism (2) Inversion
CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms 1. Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. 2. Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one. 3. Define (1) Mechanism (2) Inversion
Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Air-standard cycles Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje CH. 2 ۱ Cold-air-standard assumptions: When the working fluid is considered to be air with constant specific heats at room temperature (25 C). Air-standard
Air-standard cycles Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje CH. 2 ۱ Cold-air-standard assumptions: When the working fluid is considered to be air with constant specific heats at room temperature (25 C). Air-standard
Chapter 1 Internal Combustion Engines
 Chapter 1 Internal Combustion Engines 1.1 Performance Parameters Engine performance parameters can be measured by two means; the indicator equipment or the dynamometer. The indicator system consists of
Chapter 1 Internal Combustion Engines 1.1 Performance Parameters Engine performance parameters can be measured by two means; the indicator equipment or the dynamometer. The indicator system consists of
Power Cycles. Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion
 Gas Power Cycles Power Cycles Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion Otto cycle, spark ignition Diesel cycle, compression ignition Sterling & Ericsson cycles Brayton cycles Jet-propulsion cycle Ideal Cycles,
Gas Power Cycles Power Cycles Ideal Cycles, Internal Combustion Otto cycle, spark ignition Diesel cycle, compression ignition Sterling & Ericsson cycles Brayton cycles Jet-propulsion cycle Ideal Cycles,
Approved by AICTE, Government of India & affiliated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Lecture 11 HYDRAULIC MOTORS [CONTINUED]
![Lecture 11 HYDRAULIC MOTORS [CONTINUED] Lecture 11 HYDRAULIC MOTORS [CONTINUED]](/thumbs/71/66190666.jpg) Lecture 11 HYDRULIC MOORS [CONINUED] 1.12Performance of Hydraulic Motors he performance of hydraulic motors depends upon many factors such as precision of their parts, tolerances between the mating parts,
Lecture 11 HYDRULIC MOORS [CONINUED] 1.12Performance of Hydraulic Motors he performance of hydraulic motors depends upon many factors such as precision of their parts, tolerances between the mating parts,
Template for the Storyboard stage
 Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
Week 10. Gas Power Cycles. ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1
 Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
In this lecture... Gas power cycles
 7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY
 1 B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
1 B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
AME 436. Energy and Propulsion. Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters
 AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A
 KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
Evaluation Of Parameters Affecting The Performance Of Spark-Ignition Engine BY Bello Lawal And Dr. Isa Garba
 Evaluation Of Parameters Affecting The Performance Of Spark-Ignition Engine BY Bello Lawal And Dr. Isa Garba ABSTRACT This paper focused on the performance of a spark-ignition (engine, which is affected
Evaluation Of Parameters Affecting The Performance Of Spark-Ignition Engine BY Bello Lawal And Dr. Isa Garba ABSTRACT This paper focused on the performance of a spark-ignition (engine, which is affected
TUTORIAL QUESTIONS FOR COURSE TEP 4195
 TUTORIL QUESTIONS FOR COURSE TEP 4195 Data: Hydraulic Oil Density 870 kg/m 3 bsolute viscosity 0.03 Ns/m 2 Spool valve discharge coefficient 0.62. 1) hydrostatic transmission has a variable displacement
TUTORIL QUESTIONS FOR COURSE TEP 4195 Data: Hydraulic Oil Density 870 kg/m 3 bsolute viscosity 0.03 Ns/m 2 Spool valve discharge coefficient 0.62. 1) hydrostatic transmission has a variable displacement
ICAL ENG LAB MANUAL. Dharmapuri Regulation : 2013 Branch : B.E. - Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester: II Year / IV Semester VVIT
 Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : 2013 Branch : B.E. - Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester: II Year / IV Semester ME6412 -THERMAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY - I ICAL ENG 1 GENERAL INSTRUCTION All
Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : 2013 Branch : B.E. - Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester: II Year / IV Semester ME6412 -THERMAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY - I ICAL ENG 1 GENERAL INSTRUCTION All
PART B - UNIT I - VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI 635854. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6602 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS PART A - UNIT I - VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES 1.
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI 635854. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6602 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS PART A - UNIT I - VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES 1.
Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes:
 Classification of thermodynamics cycles Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes: Gas and vapor cycles - Gas cycle: the working
Classification of thermodynamics cycles Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes: Gas and vapor cycles - Gas cycle: the working
Natural gas engine E 0836 LE 202 Technical data
 Page 1 Principle: No of cylinders : Supercharging: Mixture cooling: Engine cooling : Lubrication : Spark plugs: Starter motor: 4-stroke Otto gas engine 6 in line Exhaust turbocharger with water-cooled
Page 1 Principle: No of cylinders : Supercharging: Mixture cooling: Engine cooling : Lubrication : Spark plugs: Starter motor: 4-stroke Otto gas engine 6 in line Exhaust turbocharger with water-cooled
The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle)
 The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle) The Otto cycle is a set of processes used by spark ignition internal combustion engines (2-stroke or 4-stroke cycles). These engines a) ingest a mixture of fuel
The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle) The Otto cycle is a set of processes used by spark ignition internal combustion engines (2-stroke or 4-stroke cycles). These engines a) ingest a mixture of fuel
IC ENGINES. Differences between SI and CI engines: Petrol is fuel, which has a high self ignition temperature
 IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
Engine Cycles. T Alrayyes
 Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
WINTER -14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: 1/22
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER - EXAMINATION Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER - EXAMINATION Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
Natural Gas Engine E 0836 E 302 Technical Data
 Page 1 Principle: 4-stroke Otto gas engine No of cylinders : 6 in line Engine cooling : Without engine water pump, coolant to be circulated by external water pump with temperature control. Lubrication
Page 1 Principle: 4-stroke Otto gas engine No of cylinders : 6 in line Engine cooling : Without engine water pump, coolant to be circulated by external water pump with temperature control. Lubrication
