INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
|
|
|
- Cornelia Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INSTITUTE OF ERONUTIL ENGINEERING (utonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad MEHNIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BNK ourse Name : THERML ENGINEERING-I ourse ode : lass : II B. Tech II Semester Branch : Mechanical Engineering Year : ourse Faculty : Mr. S V Durga Prasad, ssociate Professor Mr. nudeep Kumar, ssistant Professor OBJETIVES To meet the challenge of ensuring excellence in engineering education, the issue of quality needs to be addressed, debated and taken forward in a systematic manner. ccreditation is the principal means of quality assurance in higher education. The major emphasis of accreditation process is to measure the outcomes of the program that is being accredited. In line with this, Faculty of Institute of eronautical Engineering, Hyderabad has taken a lead in incorporating philosophy of outcome based education in the process of problem solving and career development. So, all students of the institute should understand the depth and approach of course to be taught through this question bank, which will enhance learner s learning process. GROUP - (SHORT NSWER QUESTIONS) S. No Question UNIT I 1 What is valve timing diagram why the inlet valve is opened before TD and closed after BD? 1 P a g e Blooms ourse concept 2 What is combustion efficiency and combustion back duration? nalyse 3 What is fluid friction in an engine? define B 4 What are the products formed during combustion process Understand 5 What is an internal combustion engine? concept 6 What is scavenging? define B 7 What is meant by compression ratio? 8 Define firing order Remembering 9 What do you mean by SF define 10 Define mean effective pressure. define 11 List the advantages of valve timing diagram? concept 12 What is stoichiometry? nalyse 13 Stoichiometric air-fuel ratio means? define B 14 What are the fuel injection systems? Understand 15 Differentiate cooling system and lubrication system. concept 16 Give the required properties of good fuel? define B 17 What is combustion stoichiometry? 18 What is indicator diagram? Remembering 19 What is the difference between indicator diagram and valve timing define
2 diagram? 20 Differentiate valve and port? define UNIT-II OMBUSTION IN SI ND I ENGINES 1 What is the normal combustion and abnormal combustion in SI engine? Understand 2 What is called flame front and flame velocity? Understand B 3 What is knocking in both SI and I engines? nalyze 4 What decides severity of knocking in both SI and I Engines? nalyze 5 What is pre ignition and optimum ignition timing? 6 What is ignition delay period? 7 Define suction induced swirl and combustion induced swirl? nalyze B 8 What is mixture strength? How it influences the combustion? 9 What are anti knock agents? Main difference between working of anti knock agent in SI and I ENGINES? nalyse G 10 What is a combustion chamber? What are the different combustion zones in combustion chamber? concept G 11 What are the types of ignition systems? Understand 12 Give the two methods of cooling systems? Understand B 13 List the properties of lubricants? nalyze 14 Factors affecting normal combustion in SI system? nalyze 15 What are the properties of liquid fuels? 16 What are the tests for identifying pre-ignition? 17 Differentiate auto ignition and detonation? nalyze B 18 What are the effects of detonation? 19 How to control detonation? nalyse G 20 Draw the pressure - crank angle diagram of petrol engine? concept G 21 What is turbulance? Squish and Tumble? Understand UNIT-III TESTING ND PERFORMNE 1 Define brake power nalyze D 2 Define mechanical efficiency nalyze F 3 List the devices used to measure the cylinder pressure. discuss E 4 What is an indicated power Define G 5 What are the various losses of I Engine? nalyze F 6 How do you determine heat losses explain with sankey diagram? reate D 7 Define clearance ratio. nalyze B 8 What is the function of air compressor? 9 Define Isothermal work done discuss E 10 What is volumetric efficiency in case of compressor? Define E 11 What is the use of heat balance sheet of an engine? nalyze D 12 What is specific fuel consumption? nalyze F 13 Define volumetric efficiency? discuss E 14 What is the purpose of engine testing? Define G 15 What are the performance parameters for testing engines? nalyze F 16 For what purpose rope brake dynamometer used? Draw the diagram? reate D 17 What is the Morse test importance? nalyze B 18 What is the clearance in the compressor? What are the advantages of clearance? 19 What is the efficiency of compressor? discuss E 20 Draw the PV-diagram for two stage compressors? What is the advantage? Define E UNIT-IV OMPRESSORS 1 What is volumetric efficiency in case of compressor? Understand 2 Define slip factor Understand B 3 Define pressure coefficient. nalyze 4 What is the difference between reciprocating and rotary compressors? nalyze 2 P a g e
3 5 What is stalling? 6 Draw p-v and T-S diagram of a MULTI stage reciprocating compressors? 7 What is the function of an intercooler in compressors? nalyze B 8 What are rotary compressors? 9 What is the difference between positive displacement and non positive displacement compressors? nalyse F 10 What do you mean by hoking? concept F 11 What is the difference between rotary compressor and reciprocating compressor? Understand 12 Draw the diagram of Roots blower compressor? Understand B 13 Draw the diagram of Vane blower compressor? nalyze 14 What is the working principle of centrifugal compressor? nalyze 15 What is the importance of velocity triangle in centrifugal compressor? 16 What is the mechanical efficiency of compressor? 17 State five uses of compressors? nalyze B 18 On what factors compressors are to be selected? 19 What is power input factor in compressor? nalyse F 20 lassify the types of compressors concept F UNIT-V REFRIGERTION 1 Define refrigeration Understand 2 Define (i) actual OP (ii) Theoretical OP (iii) Relative OP Understand 3 What is the difference between wet compression and dry compression? Understand 4 Write short notes on p-h chart. Understand 5 What is unit of refrigeration Define B 6 What is the function of capillary tube in vapour compression refrigeration system. D 7 What are the different components of vapour compression system pply E 8 what is the effect of subcooling nalyze F 9 Effect of superheating nalyze F 10 What is the function of Expansion valve? pply F 11 What are the elements of refrigeration system? Understand 12 Write the important applications of refrigeration? Understand 13 List the various refrigeration systems? Understand 14 What is the standard rating of a Refrigeration machine Understand 15 Enumerate important refrigeration applications? Define B 16 What is the wet compression? D 17 What is dry compression? pply E 18 What is relative OP? nalyze F 19 What is relative OP? nalyze F 20 List the principles of commonly used refrigerants? pply F 3 P a g e
4 ESSY TYPE QUESTIONS S. No Question Blooms Taxonomy Level 4 P a g e ourse Outcom e UNIT I 1 Give classification of I Engines. lassify 2 Distinguish between SI engines and I engines? nalyze 3 Sketch and explain the valve timing diagram of a four stroke Otto cycle engine? 4 In what respect two stroke engines differs from 4-stroke engine Discuss? nalyze B 5 Explain fuel injection system of an SI engine? Explain B 6 What are the different lubrication systems available for I engines? 7 Discuss the importance of cooling system for an I engines. Describe different cooling systems? Discuss 8 List out the properties of fuel for (i) SI engine (ii) I engine. lassify 9 Explain lubrication system for I engines? Explain B 10 Explain cooling system for I engines? Discuss 11 what is scavenging? explain with sketches? lassify 12 List the factors causes detonation and explain in detail? 13 Explain Magneto ignition system with a neat diagram? 14 Explain coil ignition system with a neat diagram? nalyze 15 What is Octane number? What is the role of Octane number in the performance of engine? For higher performance of engine which rated Explain B fuels are to be selected? 16 Explain Battery ignition system with a neat diagram? Explain B 17 Name two general classes of combustion engines and state how do they basically differ in principle? nalyze B 18 What are the two basic types of internal combustion engines? What are the fundamental differences between the two? nalyze B 19 Discuss the relative advantages and disadvantages of I engines and external combustion engines? nalyze B 20 What is the function of a governor? Enumerate the types of governors? Sketch the porter governor with a neat sketch? Explain B UNIT II 1 State and explain different combustion stages in SI engine? 2 State and explain different combustion stages in I engine? Describe 3 Explain knocking, properties and its effects in I engine? Define G 4 Explain different types of combustion chambers in SI and I engines? F 5 Explain the need for air motion and types? Factors influencing knocking in SI and I engine? 6 What are the requirements of fuel for a diesel engine? B 7 Differentiate between normal combustion and abnormal combustion phenomena incase of SI Engine. nalyze D 8 What is the importance of variables like flame speed flame front in case of delay period. 9 Explain knocking additives. Explain B 10 Discuss air flow movements in I engines Discuss c 11 Explain the Splash lubrication system with the diagram? 12 Explain the carburetor working principle with diagram? Describe 13 What are the types of fuel injection systems? Explain any one with a neat sketch? Define G 14 How to tell a two stroke cycle engine from a 4 stroke cycle engine? F 15 Explain the Pressure feed system with a diagram? B
5 S. No Question Blooms Taxonomy Level ourse Outcom e 16 In what respect four-stroke diesel cycle(compression Ignition) engine differs from four stroke cycle spark ignition engine? 17 What do you mean by Pre-ignition? How can it be detected? 18 Explain the difference between Pre-ignition, auto-ignition and detonation? 19 What is meant by ignition delay? Explain the steps in SI engines ignition delay? 20 Why do we feel the necessity of cooling an I engine? Explain briefly the following methods of cooling I engines: ir-cooling and Liquid - cooling? UNIT - III 1 Explain the Morse test to fins the frictional power. explain 2 What is wilaan s line.how do you measure frictional power using this. analyse G 3 Discuss different types of dynamometers. discuss D 4 Write short notes on Exhaust gas analysis pply E 5 Derive volumetric efficiency of air compressor Discuss b 6 lassify compressors lassify 7 Explain Isothermal work done Explain 8 Derive equation for workdone of reciprocating air compressor with T-S Derive and p-v diagrams 9 Explain about intercooling Explain 10 Explain multistage compression Explain 11 What is the significance of heat balance sheet? Discuss the procedure to draw heat balance sheet for I engine? explain 12 Define the following terms: Indicated Power, Brake power, Friction analyse Power, Mechanical efficiency, Mean effectiveness. G 13 Explain the working principle of reciprocating compressor with a neat sketch. discuss D 14 Explain the work required for Multi-stage compressor? pply E 15 What is the condition for maximum efficiency in multistage compression? Discuss b 16 Explain the working principle of rope brake dynamometer? Explain 17 Describe how the IP of a multi-cylinder engine is measured? Explain 18 Describe the procedure using for balancing heat? What is Sankey Explain diagram? 19 Explain the phenomenon of knocking in SI engines? What are the different factors influencing the knocking? Explain 20 Enumerate the applications of compressed air? How are air compressors classified? analyze G UNIT IV 1 State how the air compressors are classified? Understand B 2 Explain the working of roots blower? 3 Explain the working of vane blower and also draw the actual p -v diagram of a compressor? 4 What is rotary compressor how are they classified? pply D 5 Draw the velocity diagram of an axial flow compressor? F 6 What do you mean by multistage compression? nd state its pply advantages? 7 Draw velocity diagrams of centrifugal compressors? F 8 ompare between reciprocating and rotary compressors? ompare B 9 ompare between axial flow and centrifugal compressors? ompare B 10 Discuss of working centrifugal compressors? Discuss D 11 Discus the merits and demerits of rotary compressor over reciprocating compressor? Understand B 12 List the various types of rotary compressors. Explain with a neat sketch B 5 P a g e
6 S. No Question Blooms Taxonomy Level ourse Outcom e the working of a vane blower. 13 Explain the working of an axial flow compressor with a neat sketch? 14 How does the working of centrifugal compressor differ from the axial flow compressor? 15 Give the analysis of centrifugal compressor with the help of velocity diagrams? 16 State the conditions which lower the volumetric efficiency? 17 Explain with a neat sketch actual pv diagram for a single-stage compressor? 18 What is the effect of atmospheric conditions on the output of a compressor? 19 Draw the velocity diagrams of an axial-flow compressor? Explain the various parameters? 20 Explain with a neat sketch the actual pv diagram for a two stage compressor? UNIT V 1 Describe a simple vapour compression cycle giving clearly its flow diagram pply analyse ompare analyse Explain Define 2 Show the vapour compression cycle on T-S diagram when the vapour is dry saturated,super heated, and is wet after compression Define 3 What are the factors that effect the performance of a vapour compression system and explain. oncept B 4 What are desired properties of refrigerants oncept B 5 Explain with neat sketch the working of a vapour absorption system. apply D 6 ompare between vapour compression and vapour absorption systems compare E 7 Explain air refrigeration system Explain 8 Explain reversed carnot cycle on T-S diagram, Explain 9 What are the different components of vapour compression system and explain with neat sketch Describe B 10 lassify refrigerants. classify 11 Draw the basic refrigeration cycle with all components and explain each component in detail? Define 12 Derive the OP of a Refrigeration cycle? Define 13 What is mechanical refrigeration and explain various types with diagrams? oncept B 14 Define the following? (i)refrigeration (ii)refrigerating system (iii)refrigerated system. Define 15 State elements of refrigeration systems and explain? Explain 16 Differentiate clearly between open cycle and closed air refrigeration systems? 17 Define the following? (i) ctual OP (ii) theoretical OP (iii) relative OP. oncept B 18 What are the main characteristic features of an air refrigeration systems. oncept B 19 State merits and demerits of Vapor compression system and air refrigeration systems? compare E 20 State the functions of the following parts of a simple vapor compression system: (i) compressor (ii) condenser (iii) Expansion Valve (iv) Evaporator Explain D F G B G NLYTIL QUESTIONS S. No Question Blooms ourse 6 P a g e
7 S. No Question Blooms ourse UNIT-III TESTING ND PERFORMNE 1 The data recorded during the trial of a two stroke diesel engine are as follows: Engine speed =1500rpm Load on brakes =110kg brake arm pply d =900mmDetermine the following: (a) Brake torque, (b) Power available at the brakes of the engine. 2 During testing a two stroke, diesel engine with rope brake dynamometer, d the following were recorded: Engine speed=700rpm Diameter of brake drum=600mm Diameter of rope =50mm Dead load on the brake drum=35kg Spring balance reading =4.5kg Find the power available at the brakes, in KW. 3 During the trial on a single cylinder, four stroke, diesel engine the f following are noted: Load on hydraulic dynamometer=950n Dynamometer constant =7500 Fuel used per hour = 10.5kg/hr alorific values of fuel =50000kJ/Kg Engine speed = 400rpmalculate brake thermal efficiency of the engine 4 n Otto cycle four stroke gas engine has a cylinder 25cm in diameter and the stroke of the piston is 40cm. It operates under the following conditions: Speed =200rpm misfires per minute =10 Mean effective f pressure=6.2kg/cm2 Mechanical efficiency =80% Determine (a) IHP, (b) BHP and (c) Friction horse power 5 alculate the volumetric efficiency of a petrol engine of 6cm bore and 9cm stroke if each cylinder sucks kg of charge during suction stroke. ssume R as solve 6 four cylinder engine running at 1200rpm developed 25.3BHP. The average torque when one cylinder was cut out was 10.5kg_m. Determine the indicated thermal efficiency, if the calorific value of the fuel used is 10000kcal/kg, and the engine uses 0.25kg of petrol per BHP hour. evaluate a 7 In the Morse test with a four cylinder four stroke petrol engine, the following data were obtained for a particular setting and speed. BHP with all cylinders working =32.0 BHP with No 1 cylinder cut off=21.6 b BHP with No 2 cylinder cut off=22.3 pply BHP with No 3 cylinder cut off=22.5 BHP with No 4 cylinder cut off=23.0 Estimate the IHP of the engine and its mechanical efficiency 8 During the trial of a single cylinder, four stroke oil engine, the following observations were recorded: Bore and Stroke =300mm x 450mm Engine speed=220rpm Duration of trial =60minutesFuel consumption =7.0kgalorific valve of fuel=45000kj/kg rea of indicator diagram =320mm 2 Length of indicator diagram=60mmspring index=1.1bar/mm Net load on brakes =130kgBrake drum diameter =1650kgTotal weight of jacket cooling water =500kgTemperature rise of jacket cooling DETERMINE B water=400 Temperature of exhaust gases=300 air onsumption=300kgssume specific heat of exhaust gases= kj/kg K, specific heat of water =4.185kJ/kg k and room temperature =25 0 Determine the following a Power available at brakes. b. Indicated power developed, c. Mechanical efficiency, d. Thermal efficiency, e. Heat balance sheet 9 The following readings are observed during the trial of a single cylinder, four stroke diesel engine. Fuel used per hour=11kg;mass analysis of fuel is carbon 85%, oxygen 14%, non-combustibles 1%;calorific value of fuel is 50000kJ/kg. The volumetric analysis of the exhaust gases is carbon dioxide 8.5%, oxygen 10%, nitrogen 81.5%. Temperature of exhaust gases is 400c. Specific heat of Exhaust gases is 1.05kJ/kg. EVLUTE B 7 P a g e
8 S. No Question Blooms ourse Partial pressure of steam in the exhaust gases is 0.030bar.mbient temperature is 20 0 c.alculate the percentage of heat carried away by the exhaust gases. 10 large four-stroke cycle diesel engine runs at 2000rpm. The engine has a displacement of 25litres and a brake mean effective pressure of 0.6MN/m 2 b pply It consumes 0.018kg/s of fuel (calorific value=42000kj/kg).determine the brake power and brake thermal efficiency. UNIT-IV OMPRESSORS 1 n air compressor takes in air at 1 bar and 20 0 and compresses it according to law pv 1.2 = constant.it is then delivered to a receiver at a constant pressure of 10 bar. R=0.287 KJ/Kg K. Determine : (i) Temperature at the end of compression (ii) Work done and heat transferred during compression per kg of air. pply d 2 single stage, double-acting compressor has a free air delivery (FD) of 14 m3/min. measured at bar and 150. The pressure and temperature in the cylinder during induction are 0.95 bar 320. The d delivery pressure is 7 bar and index of compression and expansion, n=1.3.the clearance volume is 5 % of the swept volume. alculate (i) Indicated power required (ii) Volumetric efficiency. 3 ir at 103 K Pa and 27 0 is drawn in LP cylinder of a two stage air compressor and is isentropic ally compressed to 700 KPa. The air is then cooled at constant pressure to 37 0 in an intercooler and is then again compressed isentropic ally to 4 MPa in the H.P cylinder, and is then f delivered at this pressure Determine the power required to run the compressor if it has to deliver 30 m 3 of air per hour measured at inlet conditions. 4 roots blower compresses 0.08 m 3 of air from 1.0 bar to 1.5 bar per revolution.alculate the compressor efficiency. f 5 centrifugal compressor delivers 16.5 kg/s of air with a total head pressure ratio of 4 :1.The speed of the compressor is 1500 r.p.m. Inlet total head temperature is 20 0, slip factor 0.9 Power input factor 1.04 solve and 80 % isentropic efficiency. alculate: Overall diameter of the impeller ii. Power input 6 multi stage axial flow compressor delivers 20 kg/sec of air. The inlet stagnation condition is 1 bar and The power consumed by the evaluate compressor is 4350 kw.alculate (i) The delivery pressure (ii)number of stages (iii) Overall isentropic efficiency of the compressor 7 n axial flow compressor with an overall isentropic efficiency of 85 % draws air at 20 0 and compresses it in the pressure ratio 4:1.The mean blade speed and flow velocity are constant throughout the compressor. ssuming 50 % reaction blading and taking blade velocity as 180 m/sec. and work input factor as 0.82.calculate (i)flow velocity (ii) Number of stages. pply b 8 ir at 1bar and 27 is taken into single stage single acting reciprocating air compressor with law of pv 1.1 = to find a final pressure of 7bar and compressor takes 1m 3 /min. alculate indicated power and isothermal efficiency. lso calculate the cylinder dimensions and power of the motor required to drive compressor. Speed of the compressor is 5rps, stroke to bore ratio 1.5:1; mechanical efficiency is 85%; Transmission efficiency is 90%. f 9 centrifugal compressor receives air at the rate of 1400m 3 /min at 100kPa and 35 0 and delivers at 350kPa. It has an isentropic efficiency of 82%. Mechanical losses amounts 2.5% of the shaft power. Determine power required and exit air temperature. solve 10 n axial flow compressor stage consisting of a rotating and stationary blade row receives air at 100KN/m 2 and The axial velocity of air solve 8 P a g e
9 S. No Question Blooms ourse is 200m/s. Inlet and exit blade angles of rotor row are 50 0 and22 0 respectively. ssuming degree of reaction to be 50%.alculate the power required if the air compressed is 1.2Kg/s. UNIT-V REFRIGERTION 1 n air refrigeration system operates between 1 MPa and 100 K Pa is required to produce a cooling effect of 2000 KJ/min. Temperature of the air leaving the cold chamber is -5 0 and at leaving the cooler is Neglect losses and clearance in the compressor and expander determine (i) Mass of air circulated per min (ii) ompressor work,expander work,cycle work(iii) OP and power in KW required 28 tonnes of ice from and at 0 0 is produced per day in an ammonia 2 refrigerator. The temperature range in the compressor is from 25 0 to The vapour is dry and saturated at the end of compression and an expansion valve is used. ssuming a co efficient of performance of 62 % of the theoretical, calculate the power required to drive the compressor. take latent heat of ice is 335 KJ/kg. 3 refrigerator operating on stand vapour compression cycle has a coefficient performance of 6.5 and is driven by a 50 KW compressor. The enthalpies of saturated liquid and saturated vapour refrigerant at the operating condensing temperatures of 35 0 are KJ/Kg and KJ/Kg. The standard refrigerant vapour leaving evaporator has B an enthalpy of kj/kg. Find the refrigeration temperature at compressor discharge. The p of refrigerant vapour may be taken to be kj/kg In a simple vapour compression cycle the piston displacement volume for compressor is 1.5 liters per stroke and its volumetric efficiency is 80 %.The speed of compressor is 1600 rpm. Find the power rating of compressor and refrigerating effect. 5 Ice is formed at 0 from water at 20. The temperature of the brine is 8. Find out the kg of ice formed per kwh. ssume that the refrigeration cycle used is perfect reversed arnot cycle. Take latent heat of ice as 335 kj/kg. B 6 refrigerating machine of 6 tonnes capacity working on Bell-oleman cycle has an upper limit of pressure of 5.2 bar. The pressure and temperature at the start of the compression are 1.0 bar and 16 respectively. The compressed air cooled at constant pressure to a temperature of 41 enters the expansion cylinder. ssuming both expansion and compression processes to be adiabatic with γ= 1.4, calculate (i)o-efficient of performance. (ii)quantity of air in circulation per minute. (iii)piston displacement of compressor and expander. (iv)bore of compressor and expansion cylinders. The unit runs at 240 r.p.m. and is double-acting. Stroke length = 200 mm. (v)power required to drive the unit For air take γ= 1.4 and cp= kj/kg K. B 7 simple vapour compression plant produces 5 tonnes of refrigeration. The enthalpy values at inlet to compressor, at exit from the compressor, and at exit from thecondenser are , and kj/kg respectively. Estimate : (i)the refrigerant flow rate, (ii)the.o.p., (iii)the power required to drive the compressor, and (iv)the rate of heat rejection to the condenser. 8 9 P a g e Pressure, bar Temperature, Enthalpy, kj/kg Entropy, kj/kg K
10 S. No Question Blooms ourse Liquid Vapour Liquid Vapour vapour compression heat pump is driven by a power cycle having a thermal efficiency of 25%. For the heat pump, refrigerant-12 is compressed from saturated vaporat 2.0 bar to the condenser pressure of 12 bar. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 80%.Saturated liquid enters the expansion valve at 12 bar. For the power cycle 80% of the heatrejected by it is transferred to the heated space which has a total heating requirement of 500 kj/min.determine the power input to the heat pump compressor. The following data for refrigerant-12may be used : 9 refrigeration machine is required to produce i.e., at 0 from water at 20. The machine has a condenser temperature of 298 K while the evaporator temperature is268 K. The relative efficiency of the machine is 50% and 6 kg of Freon-12 refrigerant is circulatedthrough the system per minute. The refrigerant enters the compressor with a dryness fraction of0.6. Specific heat of water is kj/kg K and the latent heat of ice is 335 kj/kg. alculate theamount of ice produced on 24 hours. 10 arnot refrigerator requires 1.3 kw per tonne of refrigeration to maintain a region at low temperature of 38. Determine : (i).o.p. of arnot refrigerator (ii) Higher temperature of the cycle (iii) The heat delivered and.o.p. when this device is used as heat pump. pply b HOD, MEHNIL ENGINEERING 10 P a g e
2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
2. Discuss the effects of the following operating variables on detonation
 Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) QUESTION BANK UNIT I I.C ENGINES
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR UNIT I I.C ENGINES 1 (a) Explain any six types of classification of Internal Combustion engines. (6M) (b) With a neat sketch explain any three
(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]
![(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16] (a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]](/thumbs/79/80273804.jpg) Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Noble Group of Institutions, Junagadh. Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: 2017-18 Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat
Semester:1 st Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Faculty: Mr. Ishan Bhatt Year: 2017-18 Class: Comp. & IT Ele TUTORIAL 1 INTRODUCTION Q.1 Define: Force, Work, Pressure, Energy, Heat
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Question Bank. UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks)
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING Year/Sem: III/VI 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? UNIT-I THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES
MEB THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I PART-A
 MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
MEB 420 - THERMAL ENGINEERING - I QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Each question carries 1 mark. PART-A 1. Define temperature. 2. Define intensive property 3. Explain the term absolute zero of temperature 4. State
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C OBJECTIVE:
 ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME Thermal Engineering Question Bank
 ME2301 - Thermal Engineering Question Bank UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycles, Calculation of mean effective pressure, and air standard efficiency -Actual and theoretical PV diagram
ME2301 - Thermal Engineering Question Bank UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton cycles, Calculation of mean effective pressure, and air standard efficiency -Actual and theoretical PV diagram
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6404 THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I - GAS POWER CYCLES 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? Thermodynamic cycle is defined
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles
 Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
AT AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK
 AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
Assignment-1 Introduction
 Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) Term-End Examination June 2016
 No. of Printed Pages : 5 I BIME-010 I B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) 00 1 Ems, Term-End Examination June 2016 BIME-010 : THERMAL ENGINEERING Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Attempt
No. of Printed Pages : 5 I BIME-010 I B.Tech. - VIEP - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (BTMEVI) 00 1 Ems, Term-End Examination June 2016 BIME-010 : THERMAL ENGINEERING Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Attempt
GOVERNMENT ENGINEERING COLLEGE, GODHRA
 Practical No. - 1 To understand construction and working of various types of Steam boilers. 1) What is the function of Steam boiler? And what are factors should be considered while selecting a boiler?
Practical No. - 1 To understand construction and working of various types of Steam boilers. 1) What is the function of Steam boiler? And what are factors should be considered while selecting a boiler?
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME THERMAL ENGINEERING. Part-A (2 Marks)
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? 2. What is meant by air standard cycle? 3.. Name
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Question Bank ME1351 - THERMAL ENGINEERING UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is a thermodynamic cycle? 2. What is meant by air standard cycle? 3.. Name
Scheme - G. Sample Test Paper-I. Course Name : Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Code : ME Semester : Fifth Subject Title : Power Engineering
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17529 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) SUBJECT: ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Assignment Ch 1
 1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
1. 3. GYANMANJARI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (GMIT) Assignment Ch 1 A steel ball having mass of 10 kg and a specific heat of 460 J/kg K is heated from 50 o C to 200 o C. Determine the heat required. In a
05 Marks (c) Sketch and explain Lancashire Boiler.
 Model question paper No.1 1. Answer any FIVE full questions choosing at least two questions from part A & two questions from part B 2. Use of steam tables is permitted 1. (a) Discuss briefly the different
Model question paper No.1 1. Answer any FIVE full questions choosing at least two questions from part A & two questions from part B 2. Use of steam tables is permitted 1. (a) Discuss briefly the different
Scheme G Sample Question Paper Course Name : Diploma in Automobile Engineering Course Code : AE
 Sample Question Paper Semester : Fourth Marks : 100 Time: 03 Hours Q1.A. Attempt any SIX a. State different types of ideal gas processes 12 Marks b. Define dryness fraction and degree of superheat. c.
Sample Question Paper Semester : Fourth Marks : 100 Time: 03 Hours Q1.A. Attempt any SIX a. State different types of ideal gas processes 12 Marks b. Define dryness fraction and degree of superheat. c.
'' ''' '' ''' Code No: R R16 SET - 1
 Code No: R161232 R16 SET - 1 1. a) List the Primary requirements of a Steam Boiler. (2M) b) What are the distinguishing features between a Casting and a Pattern? (2M) c) Define (i) Brake Power; (ii) Indicated
Code No: R161232 R16 SET - 1 1. a) List the Primary requirements of a Steam Boiler. (2M) b) What are the distinguishing features between a Casting and a Pattern? (2M) c) Define (i) Brake Power; (ii) Indicated
BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FS81504 BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FS81504 BASIC CIVIL & MECHANICAL
Model Question Papers
 QUESTION CARRIES 2 MARKS Model Question Papers 1. Define engine. Give their classification? 6 th Semester I.C. ENGINE [ME-604] UNIT -1 2. Define the performance parameters of IC engine ie indicated power,
QUESTION CARRIES 2 MARKS Model Question Papers 1. Define engine. Give their classification? 6 th Semester I.C. ENGINE [ME-604] UNIT -1 2. Define the performance parameters of IC engine ie indicated power,
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics I. C. Engine Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi
Problems of Practices Of Basic and Applied Thermodynamics I. C. Engine Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
AT 2303 AUTOMOTIVE POLLUTION AND CONTROL Automobile Engineering Question Bank
 AT 2303 AUTOMOTIVE POLLUTION AND CONTROL Automobile Engineering Question Bank UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. What are the design considerations of a vehicle?(jun 2013) 2..Classify the various types of vehicles.
AT 2303 AUTOMOTIVE POLLUTION AND CONTROL Automobile Engineering Question Bank UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. What are the design considerations of a vehicle?(jun 2013) 2..Classify the various types of vehicles.
L34: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Introduction to Gas Cycles Definitions
 Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
1. (a) If a large power generating station is operating with steam at 16,000 kpa and 500 and exhausting to a condenser at, 37.6 mm mercury absolute;
 Sample Questions REVISED SECOND CLASS PARTS B1, B2, AND B3 (NOTE: these questions are intended as representations of the style of questions that may appear on examinations, they are not intended as study
Sample Questions REVISED SECOND CLASS PARTS B1, B2, AND B3 (NOTE: these questions are intended as representations of the style of questions that may appear on examinations, they are not intended as study
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES
 CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
Combustion engines. Combustion
 Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
Principles of Engine Operation. Information
 Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System
 Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
Class Notes on Thermal Energy Conversion System For the students of Civil & Rural 3 rd semester Ramesh Khanal Assistant Professorr Nepal Engineering College Bhaktapur, Nepal 2015 Course Structure MEC 209.3:
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL
 Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
Internal Combustion Engines TUTORIAL College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Class 3 rd Year Class Subject Lecturer Internal Combustion Engines Dr. Raoof M. Radhi
Lab Manual Elements of Mechanical Engineering ( )
 Lab Manual Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Darshan Institute of Engineering and Technology, Rajkot. Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology Certificate This is to certify that Mr./Ms.
Lab Manual Elements of Mechanical Engineering (2110006) Darshan Institute of Engineering and Technology, Rajkot. Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology Certificate This is to certify that Mr./Ms.
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines.
 Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines. 4.2 Construction and working of gas turbines i) Open cycle ii) Closed cycle gas Turbines, P.V. and
Content : 4.1 Brayton cycle-p.v. diagram and thermal efficiency. 4Marks Classification of gas turbines. 4.2 Construction and working of gas turbines i) Open cycle ii) Closed cycle gas Turbines, P.V. and
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat
 Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat Different sources of power, such as solar energy (from sun), kinetic energy from atmospheric winds and potential energy from tides. The most important source of
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWER 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Ans: Thermal engineering is the science that deals with the
USO4CICV01/US04CICH02:
 Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Kul Internal Combustion Engine Technology. Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5
 Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
2.61 Internal Combustion Engine Final Examination. Open book. Note that Problems 1 &2 carry 20 points each; Problems 3 &4 carry 10 points each.
 2.61 Internal Combustion Engine Final Examination Open book. Note that Problems 1 &2 carry 20 points each; Problems 3 &4 carry 10 points each. Problem 1 (20 points) Ethanol has been introduced as the bio-fuel
2.61 Internal Combustion Engine Final Examination Open book. Note that Problems 1 &2 carry 20 points each; Problems 3 &4 carry 10 points each. Problem 1 (20 points) Ethanol has been introduced as the bio-fuel
Elements of Mechanical Engineering (EME) QUESTIONS
 QUESTIONS 1) In First angle projection method (a) Plan comes above elevation (b) Plan comes below elevation (c) Plan comes besides elevation (d) Plan is on the left hand side. (2) Where LHSV in third angle
QUESTIONS 1) In First angle projection method (a) Plan comes above elevation (b) Plan comes below elevation (c) Plan comes besides elevation (d) Plan is on the left hand side. (2) Where LHSV in third angle
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition
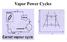 Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines
 Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine 1. A 9-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle, radial SI engine operates at 900rpm. Calculate: (1) How often ignition occurs, in degrees of engine rev. (2) How many power strokes per rev.
Internal Combustion Engine 1. A 9-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle, radial SI engine operates at 900rpm. Calculate: (1) How often ignition occurs, in degrees of engine rev. (2) How many power strokes per rev.
Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes
 8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E)
 LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. Name of the Experiment 1. To study the constructional details & working principles of two-stroke petrol/ four-stroke
LABORATORY MANUAL I. C. ENGINES & GAS TURBINES (ME-317-E) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. Name of the Experiment 1. To study the constructional details & working principles of two-stroke petrol/ four-stroke
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) Summer 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: 1/18
 Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: /8 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer
Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: /8 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer
Lecture 11 HYDRAULIC MOTORS [CONTINUED]
![Lecture 11 HYDRAULIC MOTORS [CONTINUED] Lecture 11 HYDRAULIC MOTORS [CONTINUED]](/thumbs/71/66190666.jpg) Lecture 11 HYDRULIC MOORS [CONINUED] 1.12Performance of Hydraulic Motors he performance of hydraulic motors depends upon many factors such as precision of their parts, tolerances between the mating parts,
Lecture 11 HYDRULIC MOORS [CONINUED] 1.12Performance of Hydraulic Motors he performance of hydraulic motors depends upon many factors such as precision of their parts, tolerances between the mating parts,
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Lecture 14:Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions
 Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1. ) AIM : Study
SHRI SHANKARACHARYA INSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1. ) AIM : Study
density ratio of 1.5.
 Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
4. With a neat sketch explain in detail about the different types of fuel injection system used in SI engines. (May 2016)
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
IC ENGINES. Differences between SI and CI engines: Petrol is fuel, which has a high self ignition temperature
 IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
Heat Transfer in Engines. Internal Combustion Engines
 Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Department of Mechanical Engineering UBMC701 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES. Part A (Two Marks Questions)
 Department of Mechanical Engineering UBMC701 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK UNIT- I VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES 1. Define Automobile. Give the typical specifications of an automobile 2. Name the
Department of Mechanical Engineering UBMC701 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK UNIT- I VEHICLE STRUCTURE AND ENGINES 1. Define Automobile. Give the typical specifications of an automobile 2. Name the
Attempt any three. One Mark each. Following are the applications of compressed air ( any four)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
Approved by AICTE, Government of India & affiliated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
Al-Balqa Applied University
 تا سست عام 997 Specialization Common Course Number 202073 Course Title Internal Combustion Engines Credit Hours 3 Theoretical Hours 3 Practical Hours 0 صفحة () من (0) تا سست عام 997 Brief Course Description:
تا سست عام 997 Specialization Common Course Number 202073 Course Title Internal Combustion Engines Credit Hours 3 Theoretical Hours 3 Practical Hours 0 صفحة () من (0) تا سست عام 997 Brief Course Description:
UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES
 UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES The Otto Cycle The Otto cycle, which was first proposed by a Frenchman, Beau de Rochas in 1862, was first used on an engine built by a German, Nicholas A. Otto, in 1876. The cycle
UNIT I GAS POWER CYCLES The Otto Cycle The Otto cycle, which was first proposed by a Frenchman, Beau de Rochas in 1862, was first used on an engine built by a German, Nicholas A. Otto, in 1876. The cycle
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer
Subject Code: 708 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer
EME MCQ QUESTION BANK
 EME MCQ QUESTION BANK 1. Work is considered positive when a) Work is done on the system b) work is done by the system c) both a and b d) none of the above 2. A source of energy is known as renewable source
EME MCQ QUESTION BANK 1. Work is considered positive when a) Work is done on the system b) work is done by the system c) both a and b d) none of the above 2. A source of energy is known as renewable source
TUTORIAL QUESTIONS FOR COURSE TEP 4195
 TUTORIL QUESTIONS FOR COURSE TEP 4195 Data: Hydraulic Oil Density 870 kg/m 3 bsolute viscosity 0.03 Ns/m 2 Spool valve discharge coefficient 0.62. 1) hydrostatic transmission has a variable displacement
TUTORIL QUESTIONS FOR COURSE TEP 4195 Data: Hydraulic Oil Density 870 kg/m 3 bsolute viscosity 0.03 Ns/m 2 Spool valve discharge coefficient 0.62. 1) hydrostatic transmission has a variable displacement
Week 10. Gas Power Cycles. ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1
 Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
In this lecture... Gas power cycles
 7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
7 Lect-7 Gas power cycles In this lecture... he Carnot cycle and its significance Air-standard assumptions An oeriew of reciprocating engines Otto cycle: the ideal cycle for sparkignition engines Diesel
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines Reading Problems 8-3 8-7 8-35, 8-45, 8-52 Definitions 1. spark ignition: a mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a spark plug applications requiring power to about 225 kw (300
Internal Combustion Engines Reading Problems 8-3 8-7 8-35, 8-45, 8-52 Definitions 1. spark ignition: a mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a spark plug applications requiring power to about 225 kw (300
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 ME110. Aircraft and Automotive Systems
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 ME110 Aircraft and Automotive Systems Time allowed: TWO hours Answer TWO questions from THREE in Section A and TWO questions
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 ME110 Aircraft and Automotive Systems Time allowed: TWO hours Answer TWO questions from THREE in Section A and TWO questions
Internal Combustion Engine. Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST
 Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines
 Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Figure 1: The spray of a direct-injecting four-stroke diesel engine
 MIXTURE FORMATION AND COMBUSTION IN CI AND SI ENGINES 7.0 Mixture Formation in Diesel Engines Diesel engines can be operated both in the two-stroke and four-stroke process. Diesel engines that run at high
MIXTURE FORMATION AND COMBUSTION IN CI AND SI ENGINES 7.0 Mixture Formation in Diesel Engines Diesel engines can be operated both in the two-stroke and four-stroke process. Diesel engines that run at high
LECTURE NOTES INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION
 LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
OPERATIONS SEAFARER CERTIFICATION GUIDANCE NOTE SA MARITIME QUALIFICATIONS CODE. Deck: Ship s Power Plants
 Page 1 of 8 Compiled by Approved by Chief Examiner Syllabus Committee: 26 February 2013 OPERATIONS SEAFARER CERTIFICATION GUIDANCE NOTE SA MARITIME QUALIFICATIONS CODE Deck: Page 2 of 8 KNOWLEDGE, UNDERSTANDING
Page 1 of 8 Compiled by Approved by Chief Examiner Syllabus Committee: 26 February 2013 OPERATIONS SEAFARER CERTIFICATION GUIDANCE NOTE SA MARITIME QUALIFICATIONS CODE Deck: Page 2 of 8 KNOWLEDGE, UNDERSTANDING
Engine Cycles. T Alrayyes
 Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Government of Karnataka Department of Technical Education Board of Technical Examinations, Bangalore
 CIE- 25 Marks Government of Karnataka Department of Technical Education Board of Technical Examinations, Bangalore Prerequisites: Knowledge of basic mathematics and Applied Science Course Objectives: 1.
CIE- 25 Marks Government of Karnataka Department of Technical Education Board of Technical Examinations, Bangalore Prerequisites: Knowledge of basic mathematics and Applied Science Course Objectives: 1.
Heat engine. Heat engine
 Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
Heat engine Device that transforms heat into work. It requires two energy reservoirs at different temperatures An energy reservoir is a part of the environment so large wrt the system that its temperature
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into
 ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
ME2301 THERMAL ENGINEERING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermo dynamics into analysis of cyclic processes To apply the thermodynamic
Knowledge of diagnosis and rectification of light vehicle engine faults
 Unit 157 Knowledge of diagnosis and rectification of light vehicle engine faults UAN: F/601/3733 Level: No Level Credit value: 6 GLH: 45 Relationship to NOS: This unit is linked to LV07 Diagnose and Rectify
Unit 157 Knowledge of diagnosis and rectification of light vehicle engine faults UAN: F/601/3733 Level: No Level Credit value: 6 GLH: 45 Relationship to NOS: This unit is linked to LV07 Diagnose and Rectify
Thermodynamics II MIDTERM MECH 351/2 Fall 06 CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 Thermodynamics II MIDTERM MEH 35/ Fall 06 ONORDIA UNIVERSITY FAULTY OF ENGINEERING AND OMPUTER SIENE DEPARTMENT OF MEHANIAL ENGINEERING Student s Name: I.D.: I. [50 points] A steam power plant operates
Thermodynamics II MIDTERM MEH 35/ Fall 06 ONORDIA UNIVERSITY FAULTY OF ENGINEERING AND OMPUTER SIENE DEPARTMENT OF MEHANIAL ENGINEERING Student s Name: I.D.: I. [50 points] A steam power plant operates
Knowledge of Diagnosis and Rectification of Light Vehicle Engine Faults
 Unit 157 Knowledge of Diagnosis and Rectification of Light Vehicle Engine Faults UAN: F/601/3733 Level: Level 3 Credit value: 6 GLH: 45 Relationship to NOS: This unit is linked to LV07 Diagnose and Rectify
Unit 157 Knowledge of Diagnosis and Rectification of Light Vehicle Engine Faults UAN: F/601/3733 Level: Level 3 Credit value: 6 GLH: 45 Relationship to NOS: This unit is linked to LV07 Diagnose and Rectify
B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY
 1 B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
1 B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
Automobiles. Introductory Question. 6 Questions about Automobiles. Observations about Automobiles. Question 1. Heat Engines
 Automobiles 1 Automobiles 2 Introductory Question Automobiles A car burns gasoline to obtain energy but allows some heat to escape into the air. Could a mechanically perfect car avoid releasing heat altogether?
Automobiles 1 Automobiles 2 Introductory Question Automobiles A car burns gasoline to obtain energy but allows some heat to escape into the air. Could a mechanically perfect car avoid releasing heat altogether?
CHAPTER 2 : ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE VEHICLE AND ENGINE AND INFORMATION CONCERNING THE CONDUCT OF TESTS
 CHAPTER 2 : ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE VEHICLE AND ENGINE AND INFORMATION CONCERNING THE CONDUCT OF TESTS 1.0 Description of the Vehicle - 1.1 Trade name or mark of the vehicle - 1.2 Vehicle type
CHAPTER 2 : ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE VEHICLE AND ENGINE AND INFORMATION CONCERNING THE CONDUCT OF TESTS 1.0 Description of the Vehicle - 1.1 Trade name or mark of the vehicle - 1.2 Vehicle type
A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE
 A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE Prakash Kumar Sen 1, Lalit Kumar 2, Shailendra Kumar Bohidar 3 1 Student of M.Tech. Manufacturing Management, BITS Pilani (India) 2 Student of Mechanical
A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE Prakash Kumar Sen 1, Lalit Kumar 2, Shailendra Kumar Bohidar 3 1 Student of M.Tech. Manufacturing Management, BITS Pilani (India) 2 Student of Mechanical
Page 2. (a) (i) Show that during the change AB the gas undergoes an isothermal change.
 Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
Simulation of Performance Parameters of Spark Ignition Engine for Various Ignition Timings
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277-4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved. Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Simulation of Performance
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277-4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved. Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Simulation of Performance
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY MAMALLAPURAM, CHENNAI
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY MAMALLAPURAM, CHENNAI -603104 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VII SEMESTER EE6501-Power system Analysis
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY MAMALLAPURAM, CHENNAI -603104 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VII SEMESTER EE6501-Power system Analysis
Thermodynamic Cycles. Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares
 Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
Thermodynamic Cycles Alicia Ma. Esponda Cascajares Power Cycles Cycles which convert a heat input into a mechanical work output. Power cycles can be divided according to the type of heat engine they seek
B. Tech Degree II Semester Examination in Polymer Science and
 BT PSRT 9 14 PTF 123 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PART - A (Answer any FIVE questions) 9) (5 x 5 = 25) What are the general classification of engineering materials? Give three examples for each group. What are
BT PSRT 9 14 PTF 123 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PART - A (Answer any FIVE questions) 9) (5 x 5 = 25) What are the general classification of engineering materials? Give three examples for each group. What are
