SUBSYNCHRONOUS VIBRATION PROBLEM AND SOLUTION IN MULTISTAGE CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR by Paul E. Allaire. Carroll G. (Chet) Stroh. Ronald D.
|
|
|
- Ann Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUBSYNCHRONOUS VBRATON PROBLEM AND SOLUTON N MULTSTAGE CENTRFUGAL COMPRESSOR by Paul E. Allaire Professor Mehanial and Aerospae Engineering Department University of Virginia Charlottesville, Virginia Carroll G. (Chet) Stroh Mehanial Consultant Engineering Servies Division E.. dupont de Nemours and Company, norporated Neark, Delaare Ronald D. Flak Professor John A. Kour Jr. and Lloyd E. Barrett Assoiate Professor Mehanial and Aerospae Engineering Department University of Virginia Charlottesville, Virginia Paul E. Allaire is Professor of Mehanial Engineering at the University of Virginia. He reeived his B.E. and M.E. degrees from Yale, in Mehanial Engineering. After to years in the Peae Corps, teahing at the Teleommuniations nstitute in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, he earned his Ph. D. in Mehanial Engineering at Northestern University. He is the founder of the Rotating Mahinery and Controls (ROMAC) ndustrial Researh Program at the University, hih no has over 5 orporate members. n addition to riting one textbook on finite elements and editing three books, Dr. Allaire has presented over 8papers at tehnial onferenes and injournals. lloyd E. Barrett is an Assoiate Professor of Mehanial Engineering at the University of Virginia. He reeived an M. S. degree in 1975 and a Ph. D. degree in 1978, both from the University of Virginia. He has orked in the areas of turbomahine vibration and lubriation for 16 years. Speial areas of interest inlude bearing design and optimiation to redue rotor vibrations and the effets of strutures and foundations on turbomahinery vibration. He has ritten over 4 papers in these areas and has been a onsultant to industry on a ide variety of turbomahine vibration problems. 65 Dr. Barrett is urrently the Diretor of the Rotating Mahinery and Controls ndustrial Researh Program at the University of Virginia. R. D. Flak reeived his B.S.M. E., M.S.M.E. and Ph.D. degrees from Purdue University, in 197, 1973, and 1975, respetively. He as an Analytial Design Engineer for Pratt & Whitney Airraft for to years, and is urrently a Professor of Mehanial and Aerospae Engineering at the University of Virginia. Dr. Flak peiforms researh in experimental fluid film bearings and internal turbomahinery flos and is ative in several professional soieties, inluding ASME, ASLE, and ASEE. John A. Kour, Jr., is a Researh Engineer at the Amoo Corportation Researh Center in Naperville, llinois. n this apaity, he onduts applied researh in the areas of mahinery vibration analysis, rotor bearing system dynamis and omputational fluids. He also ats as a onsultant to the refineries, hemial plants and prodution failities of the Amoo subsidiaries, both domesti and foreign. 1 Mr. Kour has B. S.M.E. andm.s.m.e. degrees from the University of Virginia and an MBA from Tulane
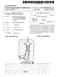
2 66 PROCEEDNGS OF THE SXTEENTH TURBOMACHNERY SYMPOSUM University. He is urrently finishing requirements for a Ph.D., from the University of Virginia. The dissertation researh involves a finite element analysis of three dimensinal visous fluid flo in bounded regions. He has o-authored papers on hydrostati bearing analysis, oil seal/rotor interations, and numerial methods for aurately evaluating dynami oefftients for hydrodynami bearings. He is a member of ASME. Carroll G. (Chet) Stroh is a Consultant ith E.. du Pont de Nemours and Company, norporated. He is assigned to the Mehanial Engineering Consultants of the Engineering Servie Division. His onsulting servie involves turbomahinery and reiproating ompressor analysis, repair, and speifation. He has 13 years ith Du Pont, during hih he spent five years in a regional engineering offie at Beaumont, Texas, onsulting on turbomahinery problems for Du Pont plants along the Gulf Coast, three years in turbomahinery rotordynamis researh at the Experimental Station in Wilmington, Delaare, and five years at his present position in Neark, Delaare. Prior to joining Du Pont, Mr. Stroh orked four years for the Westinghouse rge Steam Turbine Division in Lester, Pennsylvania, here he as involved ith the design of rotors and blades. He earned a B.S. degree, M.S. degree, and did three years of post graduate ork in Mehanial Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania. He also has a B.A. degree in Mathamatis from Lebanon Valley Colege. He is a member of Tau Beta Pi. ABSTRACT The investigation of a subsynhronous vibration problem enountered in a six stage entrifugal ompressor is disussed. At a running speed of approximately 9 rpm, a subsynhronous vibration (at 42 rpm) of nearly to times the synhronous vibration level as enountered. A systemati program as undertaken to identify the problem and orret it. A detailed analysis of the floating ring annular oil seals, balane piston labyrinth seals and impeller aerodynami ross oupling as onduted. The oil seals ere identified as the primary ause of the subsynhronous vibration due to lok up, and a modified seal design inorporating irumferential grooves as developed. This radially redued the seal ross oupled stiffness. Further, a modified bearing design as investigated to inrease the rotor logarithmi derement. Changes ere implemented in the ompressor ith the result of no subsynhronous vibrations for the operating onditions of the ompressor thus far. NTRODUCTON High speed multistage ompressors are often subjet to unanted vibrations. Partiularly undesirable are subsynhronous vibrations, hih may inrease suddenly, or over a long period of time. Often the subsynhronous vibration is larger than the synhronous omponent and may limit mahine safe running speeds. n addition, ompressors have failed as a result of subsynhronous vibrations. t is best to remove these vibrations, if possible. Often the ause of the subsynhronous vibration is not ell understood at the onset of the problem [1]. Several possible auses have been identified in reent years: 1) fixed pad bearings, 2) annular oil seals, 3) balane piston labyrinth seals, and 4) impeller aerodynami effets. n many ases, to or more of these are present. A systemati rotordynamis analysis as undertaken to identify and orret the problem in a partiular ompressor. The ompressor (Figure 1) as a six stage entrifugal ompressor ith an average shaft diameter of approximately 6.25 in, bearing span of 67.8 in, rotor eight of 16 lb, and design speed of 96 rpm. The ompressor rotor and the key omponents are illustrated in Figure 2. Figure 1. Geometry of Six-Stage Centrifugal Compressor. SHAFT??? ll ' '. g, ltm m l) ::a :: ;J;J ::tl ll ) : l) R/liiiiiiRllllli\Ff E A B O A M E T E R D=159mm (S.251n) ;: : ANNULAR OL SEAL ANNULAR OL SE AL TLTNG PAD TLTNG PAD A SEARNG SPAN --- SEARNG 1 =1.77m (67.61n) NG Figure 2. Shaft Parameters and Geometry for Six-Stage Compressor. The rotor as supported on five-pad tilting pad bearings ith load-on-pad orientation. The bearing learane as 3. mils (radial) and the bearings had a preload of.5. The length to diameter ratio as.45. The bearing stiffness and damping oeffiients at 9 rpm [2] are given in Table 1. t is ell knon that tilting pad bearings ill not ause subsynhronous vibrations by themselves but may or may not have the damping required to suppress other auses of instability [3]. Table 1. Tiliting Pad Bearing Properties at 9 RMP. Kxx (lb/in) K yy (lb/in) Cxx (lb-se/in) 979 yy (lb-se/in) 1134 e/ch.235 Load (lb) 89 At a running speed of approximately 9 rpm, a large subsynronous vibration (at 42 rpm) of nearly to times the synhronous vibration level as enountered [ 4]. The vibration pattern is shon in Figure 3 at a ontinuous running speed of 921 rpm. The subsynhronous vibration persisted at modest levels hen operating belo 92 rpm, but ould suddenly spike hen operating at or above this speed, requiring im-
3 SUBSYNCHRONOUS VBRATON PROBLEM AND SOLUTON N MULTSTAGE CENTRFUGAL COMPRESSOR 67 mediate operational hanges. Servie as limited to belo 92 rpm for fear of larger vibration spikes at higher speeds. Figure 4 that the rotor is running above the first ritial speed but just belo the seond, third and fourth. There as some orry that softening the bearings to improve mahine stability might loer the seond or third ritial speed too near the operating speed of 96 rpm. The measured rotor response at one of the bearings for probe horiontal and probe vertial is shon in Figure 5. The predited vertial ritial speed of 34 rpm (from Figure 4) is about nine perent belo the measured values of 37 and 38 rpm. 3 a: " e "' <t if 2 1 Subsynhronous Vibration At 42 RPM Synhronous Vibration At 921 RPM Figure 3. Vibration Pattern at 921 RPM. With the plant running, it as not onsidered eonomially feasible to shut the ompressor don for investigation of possible fixes. Thus a rotordynamis analysis as performed to determine the problem and its solution. The ompressor shaft and impellers, bearings, floating annular oil seals, balane piston labyrinth seals, and impeller aerodynamis ere inluded in the omputer model. A logarithmi derement as evaluated for possible mehanisms ausing the subsynhronous vibration, on a relative basis. On this basis, the oil seals ere identified as the primary ause. The seals ere modified to redue exitation, and the bearings ere also modified to inrease the rotor damping properties. After installation, the ompressor had no subsynhronous vibration up to the operating pressures attained so far.-these levels are not quite up to the peak pressures possible ith this ompressor. UNDAMPED CRTCAL SPEEDS The rotor as modelled using standard transfer matrix methods. Undamped ritial speeds ere obtained and are shon in Figure 4. Four ritial speeds are shon on the figure. The horiontal and vertial tilting pad bearing stiffnesses are shon on the rital speed map as ell. t an be seen from "' ;: X E e- a. rt)..j <( () j::: a: () a. ::;; <( :::> N N2 --N3 - - N = -- 1 L- lll _u -- LLUUU.1 1 STFFNESS (lbf/in x t o6) Figure 4. Undamped Critial Speed Map. ::>, :J?" 2 a.. ". <t g. 1 E 1 > SPEED x 13 (RPM) Figure 5. Measured First Critial Speed. OL SEAL ANALYSS A summary of the oil seal analysis by Allaire, Kour, and Stroh [4] follos. The oil seal in this ompressor has a seal ring around the shaft, as shon in Figure 6. The seal ring minimies the leakage of the proess gas into the atmosphere. HGH PRESSURE SHAFT (a) Seal Ring Geometry SURE f STATONARY COMPONENT RNG l.r1 A<T J E3 s t r 11 t t tjlld SSURE (b) Pressure Fores Ating On Seal Ring Figure 6. Seal Ring Geometry and Pressure Fores. LOW PRESSURE The ring is a nonrotating omponent normally designed to float (move radially) ith the shaft to prevent unbalaned fores in the seal ring annulus. To seal, suh seal rings must have a ontat fae (Figure 6b), hih inhibits this floating motion. High pressure, also sho\vn in Figure 6b, reates a normal fore ating on the ontat fae. This is related to the frition fore
4 68 PROCEEDNGS OF THE SXTEENTH TURBOMACHNERY SYMPOSUM ating along the ontat fae by the oeffiient of frition times the normal fore. f the frition fore is large enough, the ring ill not move radially. The oil film beteen the shaft and loked-up seal ring then ats as a fixed plain journal bearing. A plain journal bearing produes ross oupled stiffness terms, Ky, and K, y, hih an ause rotor instability [3]. Ordinarily, the axial pressure drop aross the seal suppresses any possible avitation in the oil film for the seal. t may be onsidered as a nonavitating plain journal bearing hih further inreases the destabling effets. To papers by Kirk, et al. [5, 6], disuss the properties of loked-up oil seal rings. These orks are extended by Kirk's 1986 paper [7] hih inludes plots of seal ring stiffness and damping oeffiients vs eentriity for short seals. The ross oupled stiffness oeffient of the seal ring an gro by over a fator of ten in magnitude, ith inreasing lokup eentriity. Kirk also shos some results for ompressor modifiations to the oil seals, but does not give details of the modifiations. Several other authors disuss oil seal effets on ompressors. Doyle [8] and Wahel [9] presented papers at orkshops. A paper by Emerik [1] desribes a seal lokup problem aused by ear of a taper on one of the seal omponents. A redesigned seal removed the subsynhronous vibration problem from the multistage ompressor. n that ase, the seal ring as redesigned to be better balaned, thus reduing the frition fores tending to lok the ring against the stationary seal omponent. A different effet of seal ring lokup as reported by Cerinske, Nelson, and Salamone [11]. n this ase, synhronous vibrations ere the problem. A rotordynami analysis indiated that seal ring lokup may have arried most or all of the shaft load. Beause the seals are loser together than the bearings, a signifiant shift in ritial speeds an be enountered. Elimination of radial looseness under the bearings ensured that the bearings arried the load and suessful running as reported. Allaire, et al. [ 4], presented a quasi-stati method for estimating the lokup eentriity of the seal ring. The steps are: At ero shaft speed, the shaft rests in the bottom of the bearings and the oil seal ring rests on the shaft. The geometry for the ompressor seal is illustrated in Figure 7. /" / y -.,; Searing -- Pod Cirle... ',,/ ' \ \ y i = - 3. mils y r = mils prevent further motion of the seal ring (lokup). The geometry for this seal is presented in Figure 8. f the ring loks, up it stays at the same postion in spae y Searing -----, Pod Cirle ' \ -2.i9 mils Seal Ring X nner Radius Figure 8. Bearing and Seal Ring Clearane Cirle Plots at Lokup Speed (611 RPM). f the seal ring is loked up, ontinuing inreases in shaft speed provide bearing fores hih lift the shaft upard. This produes an oil seal ring eentriity of the shaft ithin the oil seal ring (Figure 9). Generally, inreasing the eentriity auses higher oil seal ring ross oupled stiffness oeffiients. y Bearing , ; Pad Cirle ' ' \ -.85 mils.lrt-:...-: mils Seal Ring nner Radius (Position At Lok-up 611 RPM Shon) X Figure 9. Bearing and Seal Ring Clearane Cirle Plots at nstability Threshold Speed (9, RPM). Figure 7. Bearing and Seal Ring Clearane Cirle Plots at Zero Speed. As the shaft speed inreases, the oil film fore lifts the seal ring so that the fore must exatly equal the ring eight (if dynami fores are small). The radial frition fore on the ring ontat fae inreases ith speed as pressure builds. The point of interest is hether the frition fore beomes large enough to Dynami fores due to unbalane are alays present on shafts and generally inrease ith speed. f the dynami fores are large enough, a loked-up seal ring may break free and move ith the shaft. This possibility must be explored to determine if the oil seal ring ill stay loked-up. These steps an be investigated for a given seal design. A lokup speed equation as developed in [ 4] as N lok = Nd ( f.l s;: A ) 'll 1 (1)
5 SUBSYNCHRONOUS VBRATON PROBLEM AND SOLUTON N MULTSTAGE CENTRFUGAL COMPRESSOR 69 The exat lokup speed is not very important. What is important is the likelihood of seal ring lokup belo runing speed. f it is likely to lok up ell belo running speed, then a stability analysis inluding the seal ross oupled effet, should be ompleted. f lokup is unlikely due to good seal ring balaning, then there ill be no ross oupled stiffness terms and the seal is not going to ause subsynhronous vibration. The reported seal ring analysis [4] indiated that the seal ring ould be loked up at 611 rpm, hih as far belo the shaft running speed. Numerial values for the seal stiffness and damping oeffiients at 98 rpm are given in Table 2. The method used to alulate the seal dynami oeffiients is a finite element approah [12] hih inludes the effets of an axial pressure drop and turbulene. The axial pressure drop effets produe prinipal stiffness terms hih may be important in the rotordynamis analysis. Table 2. Summary of Seal Properties at 9,8 RPM ith Attitude Angle -135" and Eentriity.5 Seal Design Existing To Groove (1A) Three Groove (1B) To Groove Large Clearane (1C) Load Flo Rate (lbf) (gavmin) Kxx Stiffness (lbfi'in) Damping (lbf-sedin) K,y Kyx Kyy, C,y Cy, Cyy The ross oupled stiffness values are 19,3 lb/in. The alulated value of the oil leakage through the seal, 13.5 gal/min, as rather lose to the average measured leakage, approximately 12 gal/min. This as one indiation that a good model of the oil film as used. Some information an be gained by omparing stiffness and damping numbers for the bearings and seals. n nearly all ompressors, the bearings and oil seals are in lose proximity. Prinipal stiffness terms of the original bearings, K,. and K yy are on the order of 1,, lb/in. The orresponding prinipal stiffness terms of the seals are only about 1, lb/in, so the bearing stiffnesses dominate. Conversely, the tilting pad bearings have no ross oupling stiffness terms, K y x and Kx, so here the oil seal terms dominate. The ross oupled stiffuess terms ause subsynhronous vibration, so the seals are very important. Also, the bearing prinipal damping terms, C,. and C yy, are muh larger than the oil seal terms so the bearing damping terms dominate. This led to modifying the bearings to improve overall system damping properties after the seals ere improved. CAUSE OF NSTABLTY nitially, the ause of the subsynhronous vibration as unlear. Suspeted omponents ere the oil seals, the balane piston labyrinth seals, and aerodynami ross oupling at the ompressor impellers. A systemati rotordynamis stability analysis as arried out to determine the ause. The objetive as to evaluate the sensitivity of the ompressor to eah possible ause. This involved alulating the logarithmi derement of the least stable eigenvalue for a series of analyses. The largest destabiliing hange ould indiate the primary ause. First, a baseline run as made ith the free-free shaft. The log derement of., as it should be, is given in Table 3. The hirl speed of the least stable mode as 37 rpm. Next, the tilting pad bearings ere added and the log derement improved to.19. The balane piston labyrinth seal ross oupling stiffness as alulated as 19,8 lb/in [13]. t as added to the model and the log derement dropped to.14. Removing the balane piston and adding the loked up oil seal dynami oeffiients gave a log derement of.9. Thus, the oil seal redued the stability by.1, hile the balane piston only redued it by.5. Table 3. Sensitivity of Current Design to Different Destabiliing Mehanisms at 9 RPM. Shaft Only (.5X 1 6 lb/in Supports) Shaft, Bearings Shaft, Bearings, Balane Piston (19.8 Klb/in) Shaft, Bearings, Seals Shaft, Bearings, Seals, Balane Piston Shaft, Bearings, Seals, Balane Piston, Aerodynami Cross Coupling at Wheels (1 Klb/in) Logarithmi Derement Whirl Speed 8 (pm) The analysis as ontinued to inlude shaft, bearings, oil seals and balane piston. The log derement as.6, or very lose to ero. One should reall that the onset of the subsynhronous vibration, shon in Figure 3, must our at a log derement value of ero. Finally, aerodynami ross oupling as added at the ompressor impellers. At the time the analysis as done, industrial experiene indiated that a value of about 2, lb/in per heel of ross oupling ould be representative. n this ase, a value of 2, lb/in as hosen for eah of the four entral impellers and 1, lb/in taken for the end impellers. The resulting log derement as -.6 for a derease of.66 over the previous ase. Again, this hange as less than the oil seals. t as judged that the oil seal as the major ause of the subsynhronous vibration. The alulated hirl speed, indiated in Table 3, as 378 rpm. This ompares fairly ell ith the observed ritial speed of 42 rpm. The alulated hirl speed is lo by 1 perent. Currently, there are several methods for better evaluation of the ompressor labyrinth seal effets, hih seem to be primarily responsible for impeller aerodynami ross oupling. That partiular possible ause of instability did not turn out to be the major ause for this problem so no further efforts ere made to better model them. One partiularly enouraging feature of the analysis as that the stability analysis yielded a logarithmi derement very lose to ero hen all possible auses ere inluded. This implies that the theoretial model reated for this problem as a very aurate one. Component modelling for the shaft, bearings, oil seals and balane piston as obtained from the basi equations of engineering, rather than empirial field data. A fe years ago, the omputer modelling and solution of subsynhronous vibration problems in ompressors as muh more empirial in nature.
6 7 PROCEEDNGS OF THE SXTEENTH TURBOMACHNERY SYMPOSUM OL SEAL MODFCATONS To possible objetives ould be onsidered in modifying the seals. They ere: Redue seal ross oupling hile maintaining present leakage rate. Ensure that the seal ring moves ith the seal. nitially, it as deided to investigate the first option. Design options ith irumferential grooves ut in the seal are shon in Figure 1 (a) and (b). A pressure j balaning arangement for the three groove seal is also given in Figure 1 (). L L = Land Length t L G = Groove Length DG = Groove Depth log derement at 98 rpm as alulated as.12 (stable). This value, given the inauraies of omputer modelling, as good, but judged not to be as large as desired. The seond objetive of ensuring that the seal ring moves ith the seal as not pursued, beause the first modifiation appeared to be suffiient to remove the subsynhronous vibration. Also, the first modifiation introdued the least number of seal hanges. From a leakage point of vie, the seal performed ell, so there as no desire for major hanges. BEARNG MODFCATONS The tilting pad bearings used in this ompressor ere modified to further improve stability. To parameters ere hosen for modifiation: the bearing preload, m, and learane b. These are related to the bearing ground in pad learane of CP by the equation (2) (a) To Groove Design =t> Qj (b) Three Groove Design Note that all values of learane in this paper are radial rather than diametral values. The original bearings had a pad learane of CP 6 mils = and a preload of m =.5. First, the pad learane as held onstant and the preload varied. The original seal dynami oeffiients at 9 rpm ere employed here. The results are depited in Figure 11. A derease in the bearing preload gives a signifiant inrease in the system log derement. Seond, the bearing learane as held onstant and the preload varied. This produed an even larger improvement in stability, as seen in Figure 11. () Balane Ring Fae Design Figure 1. Geometry for Cirumferential Groove and Balaning Seal Modifiations. Cutting irumferential grooves in the seal land region redues the ross oupled stiffness. Generally, the ross oupled stiffness is proportional to the length, ubed. ntroduing to grooves, as indiated in Figure 1 (a), redues the length by a fator of 3, but triples the number of lands, so the net redution in ross oupled stiffness is a fator of 9. n a similar fashion, the three groove design of Figure lob yields a redution fator of 16. The alulated values of loked up seal ring stiffness and damping are given in Table 1. A larger learane ase also redued the ross oupled stiffness but the oil leakage rate nearly doubled. This as onsidered unaeptable. Modifying the seals to improve the pressure balaning, and thus redue the frition fore ating on the seal ontat fae, as also onsidered. This ould not affet the ross oupled stiffness diretly, but ould ensure that the seal ring ould not lok up at a large eentriity. The dynami fores ating on the seal ring ould move it toard the entered position. Thus, the very large ross oupled stiffness hih ours at high eentriity ould be avoided. This design feature as not adopted due to ear onsiderations. The three groove seal design as adopted for the seal modifiations. With all of the other omponents kept the same, the 1-.4 :::!! a:.2 Cl...J. ' f Cb=.3 ln. L/=.45. a=.5 '\. 5 pad-load on pad '\ original seals, 9rpm " " C p =.6 in,l/=.45, a=.5 5 pad-load on pad original seals, 9rpm Baseline, Cb=.3 in P =.6 in, m =.5, a=.5 5 pad-load on pad, original seals ::::-. 9rpm -.2L- J _J _J BEARNG PRELOAD Figure 11. Log Derement vs Bearing Preload for Original Seals for Constant Values of Cb and C P at 9 RPM. This type of study as repeated for the rotor ith the three groove seal design and at 98 rpm. Figure 12 depits the results. Again, holding the bearing learane onstant and varying the preload produed the largest inrease in log derement. Also, the balane piston as removed for one set of runs, to determine hether the redution of ross oupled stiffness ould greatly inrease the log derement. As seen in Figure 12, the improvement is marginal. Finally, the optimum bearing design as hosen to have a preload fator of.1 and the bearing learane varied. The results, inluding the three groove seals and a running speed of 98 rpm, are presented in Figure 13. The bearing design modifiation as fixed at a bearing learane of 3.5 mils (radial) and a preload fator of.1. The final stiffness and damping oeffiients at 98 rpm are given in Table 4. Note, the pre-
7 SUBSYNCHRONOUS VBRATON PROBLEM AND SOLUTON N MULTSTAGE CENTRFUGAL COMPRESSOR ,... :::;: a:.2 (!)..J. -.2 ' ' ' " " " ', Cb =.3 in, LD =.45, a =.5, 5 pad-load on pad, 3 groove seal, 98rpm.4 C p =.6 in, L/=.45, Q =.5, 5 pad-load on pad, 3 groove seal, 96rpm, ' (No Balane piston, C b =.3 n, LD=.45, a =o.s, 5 pad-load on pad, 3 groove seal, 98rpm BEARNG PRELOAD Figure 12. Log Derement vs Bearing Preload for Three-Groove Seals for Constant Values of Cb and C P at 98 RPM. Table 4. Dynami Coeffiients for Modified Bearing at 98 RPM.,... :::;:.4 a:.2 (!)..J 2 Kxx = 21614lb/in K yy = lb/in Cxx = 789 lb-se/in C YY = 1184 lb-se/in 3 Groove Seals Reommended m=.1, a =.5, Bearing Cb=3.5 mils, 5 pad-load on pad, L/ =.45 Bearing: m =.1, a=.5, 5 pad-load on pad, L/=.45, 98rpm 4 6 b (mils) Figure 13. Log Derement vs Radial Bearing Seals for m. 1 at 98 RPM. third mode is at 9193 rpm, hih is in the operating speed range. Hoever, it too has large predited motion in the bearing loations, and thus ill be damped out. t is not a matter for onern. The next mode is at 13,15 rpm, ell above the running speed range ::l: () <(...J a. en. N ::::i <( ::l: a: STATON NUMBER Figure 14. Mode Shapes for First Four Damped Eigenvalues. UNBALANCE RESPONSE N MODFED ROTOR Unbalane response has not been a problem ith this ompressor. Again, hoever, it as desired to verify that no ne problems ere introdued ith the design modifiations. Unbalane response alulations ere arried out for the modified rotor. The first unbalane ase as hosen to simulate a typial unbalane in the rotor enter. This ould exite both the first mode at 3563 and the third mode at 9193 rpm. To.5 o-in unbalanes ere plaed in the enter impellers, and to similar unbalanes ere plaed in the to outer impellers at 18 degrees out of phase ith the first to. The response vs speed at several loations is given in Figure 15. There is a first ritial speed peak at the midspan, ith another very broad peak at the bearings at the third ritial speed. t is easily seen that there are no strong vibration peaks in the running speed range of 9, to 1, rpm. dieted log derement is no about.5, as ompared to the value of.12, ith just the modified seals. This is a major improvement. CRTCAL SPEEDS AND MODE SHAPES N MODFED ROTOR t is important \\oith any rotordynamis redesign that the hanges introdued to remove one problem do not introdue other problems. One should reall from the ritial speed map in Figure 4 that the ompressor operated at just belo the seond and third ritial speeds. There as some onern that reduing the bearing stiffness, as done by the above bearing modifiation, ould possibly drop one of these ritial speeds into the operating speed range. This as investigated by looking at the mode shapes for the modified rotor. The alulated damped mode shapes for the modified rotor running at 98 rpm are shon in Figure 14. All ere overdamped. The first mode is at 3563 rpm and is a standard first shaft bending mode. The seond mode is at 5465 rpm and represents a onial mode, ith large predited amplitudes at the bearings. Bearing damping ill damp this mode out. The i X UJ :::>,... :J a. ::l: <( 1. LNE S T ATON NUMBER DESCRPTON UNBALANCE STA TON NUMBER Tilt pad brg Mid-disk Tilt pad brg NFORMATON AMOUNT (o-ln) o. PHASE (degree) o.o FREQUENCY (RPM x 1) Figure 15. Unbalane Response for Compressor- nterior Distributed Unbalane (Case 1).
8 72 PROCEEDNGS OF THE SXTEENTH TURBOMACHNERY SYMPOSUM Another unbalane ase as hosen to exite the seond mode at 5465 rpm and the fourth mode at 13,159 rpm. To unbalanes of.5 o-in ere plaed 18 degrees out of phase at the to impellers nearest the bearings. The unbalane response is shon in Figure 16. There is no peak near 5465 rpm indiating that the seond mode is very ell damped. There is a large peak at 13, rpm, ell above running speed. The rotor modifiations do not appear to have reated any vibration problems, due to turbulene. LNE STATON DESCRPTON Till pad brg 24. Mid-disk 39 Tilt pad brg in Figure 17 (a). t started at 46 rpm, then dropped to 18 rpm, and finally disappeared. This ourred over a period of hours. The vibration spetrum after the lo frequeny as gone is shon in Figure 17 (b). Kirk observed a similar vibrational behavior on a ompressor test stand. He attributes the lo frequeny vibrations to an unstable motion of the seal ring [14]. The lo frequeny did not reappear. Perhaps the ause as a rubbing omponent hih ore in during startup. The ompressor as finally run up to 9621 rpm and the vibration spetra reorded (Figure 18). There as no subsynhronous vibration present. The objetive of the redesign as to remove the subyshronous vibration so it has been suessful to date ui e 9621 rpm STATON AMOUNT (o-ln) PHASE (degree) :::> 1-.J D. ::E < Figure 16. Unbalane Response for Out of Phase Unbalane Distribution (Case 2). VBRATONS AFTER NSTALLATON OF MODFCATONS During plant dontime, the modifiations to the oil seals and bearings ere made and installed. The plant as restarted and vibration data ere reorded. The initial startup data taken at 86 rpm are shon in Figure 17. There as a synhronous vibration omponent at 86 rpm as expeted, plus a very lo frequeny omponent, as indiated ui E Very Lo Frequeny 861 Orpm 1 :;)... ::; Q. ::::; 12, < -.. U) e: :;) 1. FREQUENCY (rpm) a) nitial Vibration Spetrum 861rpm...J Q..AJ ::::; 3 12, < FREQUENCY (rpm) b) Vibration Spetrum After a Fe Hours Figure 17. Vibration Spetrum just after Startup Folloing Modified Seals and Bearings at 86 RPM. FREQUENCY (rpm) 12, Figure 18. Final Spetrum Folloing Modifiation of Seals and Bearings. NOMENCLATURE A b p m n Nd N lok pd J..l.s Unbalaned Seal Ring Area Bearing Clearane Pad Clearane Bearing Preload Pressure Poer La Shaft Speed at Design Lok Up Speed for Seal Ring Seal Pressure Drop at Design Coeffiient of Stati Frition REFERENCES 1. Stroh, C. G., "Rotordynami Stability-A Simplified Approah," Proeedings of 14th Turbomahinery Symposium, Turbomahinery Laboratories, Department of Mehanial Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, pp. 3-1 (1985) Niholas, J. C., Gunter, E. J., and Allaire, P. E., "Stiffness and Damping Coeffiients for the Five-Pad Tilting Pad Bearing," Transations of the Amerian Soiety of Lubriation Engineers," 22 (2), pp (April 1979). Allaire, P. E., and Flak, R. D., "Design ofjournal bearings for Rotating Mahinery," Proeedings of loth Turbomahinery Symposium, Turbomahinery Laboratories, Department of Mehanial Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, pp (1981). Allaire, P. E., Kour, J. A., and Stroh, C. G., "Oil Seal Effets and Subsynhronous Vibrations in High Speed Compressors," Presented at nstability in Rotating Mahin-
9 SUBSYNCHRONOUS VBRATON PROBLEM AND SOLUTON N MULTSTAGE CENTRFUGAL COMPRESSOR 73 ery Sysposium, Bently Nevada, Carson City, Nevada, June 1985, NASA CP 249 (1986). 5. Kirk, R. G., and Miller, W. H., "The nfluene of High Pressure Oil Seals on Turbo-Rotor Stability," ASLE Transations, 22 (1), pp Ganuary 1979). 6. Kirk, R. G., and Niholas, J. C., "Analysis of High Pressure Oil Seals for Optimum Turboompressor Dynami Performane," Vibrations in Rotating Mahinery Seond nternational Conferene, nstitution of Mehanial Engineers, Cambridge, pp (September 198). 7. Kirk, R. G., "Oil Seal Dynamis: Considerations for Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors," Proeedings of 15th Turbomahinery Symposium, Turbomahinery Laboratory, Department of Mehanial Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, pp (1986). 8. Doyle, H. E., "Field Experienes With Rotor Dynami nstability in High-Performane Turbomahinery," Rotordynami nstability Problems in High-Performane Turbomahinery Conferene, Texas A&M University, pp (198). 9. Wahel, J. C., "Rotordynami nstability Field Problems," Rotordynami nstability Problems in High-Performane Turbomahinery Conferene, Texas A&M University, pp (1982). 1. Emerik, M. F., "Vibration and Destabiliing Effets of Floating Ring Seals in Compressors," Proeedings of Rotordynami nstability Problems in High-Performane Turbomahinery Conferene, Texas A&M University, pp (198). ll. Cerinske, T. J., Nelson, W. E., and Salamone, D. J., "Effets of High Pressure Oil Seals on the Rotordynami Response of a Centrifugal Compressor," Proeedings of 15th Turbomahinery Symposium, Turbomahinery Laboratory, Department of Mehanial Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, pp (1986). 12. Shmaus, R. H., "Stati and Dynami Properties of Finite Length Turbulent Annular Flo Seals," M. S. Thesis, University of Virginia (1981). 13. latsubo, T. Motooka, N., and Kaai, R. "Flo ndued Fore of Labyrinth Seal," Proeeding ofrotordynami nstability Problems in High Performane Turbomahinery Conferene, Texas A&M University, pp (1982). 14. Kirk, G. R., and Simpson, M., "Full Load Shop Testing of 18, HP Gas Turbine Centrifugal Compressor for Off shore Platform Servie: Evaluation of Rotordynamis Performane," Proeedings of an nstability in Rotating Mahinery Symposium, sponsored by Bently Rotordynamis Researh Corporation, (1985), NASA CP 249 (1986).
10 74 PROCEEDNGS OF THE SXTEENTH TURBOMACHNERY SYMPOSUM
due to self-excitations
 SOLUTO OF SUBSYCHROOUS VBRATO PROBLMS RADAL FLOW HGHSPD TURBS by Heilm D. Sandstede ngineering Manager Klaus Reishl Mehanis ngineer Martin L. Leonhard Mehanis Manager Atlas Copo Applied Compressor Tehnique
SOLUTO OF SUBSYCHROOUS VBRATO PROBLMS RADAL FLOW HGHSPD TURBS by Heilm D. Sandstede ngineering Manager Klaus Reishl Mehanis ngineer Martin L. Leonhard Mehanis Manager Atlas Copo Applied Compressor Tehnique
Simulations on cross-ties for vibration control of long span cablestayed
 ibe 00 Nottingham University Press Proeedings of the International Conferene on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Simulations on ross-ties for vibration ontrol of long span
ibe 00 Nottingham University Press Proeedings of the International Conferene on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Simulations on ross-ties for vibration ontrol of long span
An Investigation into Dynamics and Stability of a Powertrain with Half-Toroidal Type CVT
 004-4-886 An Investigation into Dynamis and Stability of a Powertrain with Half-Toroidal Type CVT Zhang N, Dutta-Roy T Mehatronis and Intelligent Systems Group, University of Tehnology, Sydney, Australia
004-4-886 An Investigation into Dynamis and Stability of a Powertrain with Half-Toroidal Type CVT Zhang N, Dutta-Roy T Mehatronis and Intelligent Systems Group, University of Tehnology, Sydney, Australia
Corps of Engineers Low-Volume Road Design
 90 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1128 Corps of Engineers Lo-Volume Road Design JOHN C. POTTER, RAYMOND S. ROLLINGS, AND WALTER R. BARKER The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' pavement design proedures are
90 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1128 Corps of Engineers Lo-Volume Road Design JOHN C. POTTER, RAYMOND S. ROLLINGS, AND WALTER R. BARKER The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' pavement design proedures are
Safety Considerations for Truck Climbing Lanes on Rural Highways
 74 TRANSP()RTATl()N RF.SF.ARl.H RECORD 133 Safety Considerations for Truk Climbing Lanes on Rural Highways ANDREW D. ST. JOHN AND DOUGLAS w. HARWOOD Data on the speed profiles of truks on sustained upgrades
74 TRANSP()RTATl()N RF.SF.ARl.H RECORD 133 Safety Considerations for Truk Climbing Lanes on Rural Highways ANDREW D. ST. JOHN AND DOUGLAS w. HARWOOD Data on the speed profiles of truks on sustained upgrades
2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Spring 2008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 2.615 Internal Combustion
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Spring 2008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 2.615 Internal Combustion
A Low-Cost Efficient Hardware-in-the-Loop Testbed for Distributed Generation Penetration Analysis
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 11 (017) 69-78 doi: 10.1765/194-8975/017.04.007 D DVID PUBLISHING Low-Cost Effiient Hardware-in-the-Loop Testbed for Distributed Generation Penetration nalysis Kourosh
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 11 (017) 69-78 doi: 10.1765/194-8975/017.04.007 D DVID PUBLISHING Low-Cost Effiient Hardware-in-the-Loop Testbed for Distributed Generation Penetration nalysis Kourosh
Analysis & Optimization of Torsional Vibrations in a Four-Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Crankshaft
 International Journal of Engineering and ehnial Researh (IJER) ISSN: 2-0869, Volume-3, Issue-4, April 205 Analysis & Optimization of orsional Vibrations in a Four-Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Crankshaft
International Journal of Engineering and ehnial Researh (IJER) ISSN: 2-0869, Volume-3, Issue-4, April 205 Analysis & Optimization of orsional Vibrations in a Four-Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Crankshaft
INVESTIGATIONS ON POSSIBLE CHARACTERISTICS OF FW SUPERHIGH SEATING CAPACITY AIRPLANE
 ICAS 2000 CONGRESS INVESTIGATIONS ON POSSIBLE CHARACTERISTICS OF A.L. Bolsunovsky, N.P. Buzoverya, B.I. Gurevih, V.E. Denisov, L.M. Shkadov, A.Yu. Udzhukhu Central Aerohydrodynami Institute, Russia Abstrat
ICAS 2000 CONGRESS INVESTIGATIONS ON POSSIBLE CHARACTERISTICS OF A.L. Bolsunovsky, N.P. Buzoverya, B.I. Gurevih, V.E. Denisov, L.M. Shkadov, A.Yu. Udzhukhu Central Aerohydrodynami Institute, Russia Abstrat
Notes 11. High Pressure Floating Ring Oil Seals
 Notes 11. High Pressure Floating Ring Oil Seals Outer seal P a Outer seal land Oil supply (P S +P) Shaft Inner seal land Anti-rotation pin Seal loading spring Inner seal Process Gas (P S ) Fig. 1 Typical
Notes 11. High Pressure Floating Ring Oil Seals Outer seal P a Outer seal land Oil supply (P S +P) Shaft Inner seal land Anti-rotation pin Seal loading spring Inner seal Process Gas (P S ) Fig. 1 Typical
Proposal for Standard U.S. Headlamp Beam Pattern for Evaluation of Retroreflection
 TRASPORTATO RESEARCH RECORD 1456 91 Proposal for Standard U.S. Headlamp Beam Pattern for Evaluation of Retrorefletion THEODORE J. SZCZECH AD SUSA T. CHRYSLER Confusion arises among researhers and designers
TRASPORTATO RESEARCH RECORD 1456 91 Proposal for Standard U.S. Headlamp Beam Pattern for Evaluation of Retrorefletion THEODORE J. SZCZECH AD SUSA T. CHRYSLER Confusion arises among researhers and designers
Interpretation of Accelerated Test Method ASTM P214 Test Results
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1458 129 Interpretation of Aelerated Test Method.. ASTM P214 Test Results DANIEL P. JOHNSTON In South Dakota during the lt deade, alkali-silia reativity (ASR) h hanged from
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1458 129 Interpretation of Aelerated Test Method.. ASTM P214 Test Results DANIEL P. JOHNSTON In South Dakota during the lt deade, alkali-silia reativity (ASR) h hanged from
Emission Measurement and Testing of Multi Cylinder C.I. Engine Operated by Intercooled Turbocharger
 IJSRD - International Journal for Sientifi Researh & Development Vol., Issue, ISSN (online): - Emission Measurement and Testing of Multi Cylinder C.I. Engine Operated by ooled Turboharger Akshay Karande
IJSRD - International Journal for Sientifi Researh & Development Vol., Issue, ISSN (online): - Emission Measurement and Testing of Multi Cylinder C.I. Engine Operated by ooled Turboharger Akshay Karande
Airborne Noise Flanking of Shipboard Vibration Isolation Systems
 Airborne Noise Flanking of Shipboard Vibration Isolation Systems Ray Fisher, Leo Boroditsky, Ron Dempsey, Nathan Jones and Mike Bahtiarian Noise Control Engineering, In., Billeria, Massahusetts Theoretial
Airborne Noise Flanking of Shipboard Vibration Isolation Systems Ray Fisher, Leo Boroditsky, Ron Dempsey, Nathan Jones and Mike Bahtiarian Noise Control Engineering, In., Billeria, Massahusetts Theoretial
ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS
 Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
GEH-230W StPersetles GEH-230V INSTRUCTIONS. f:. l I ' INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS DRY AND COMPOUND-FILLED TYPES. GENERAL. E,LECTRIC
 i. ' r f:. l I ' I. : I INSTRUCTIONS INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS DRY AND COMPOUND-FILLED TYPES. GENERAL. E,LECTRIC GEH-230W StPersetles GEH-230V 2 TECHNICAL DATA This book presents GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS whih
i. ' r f:. l I ' I. : I INSTRUCTIONS INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS DRY AND COMPOUND-FILLED TYPES. GENERAL. E,LECTRIC GEH-230W StPersetles GEH-230V 2 TECHNICAL DATA This book presents GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS whih
POWERING THE WAY Rental Power Planner
 POWERING THE WAY Rental Power Planner PLANNING FOR TEMPORARY POWER: A Critial Management Duty As a faility manager, you know better than anyone that eletrial power is the lifeblood of business. Without
POWERING THE WAY Rental Power Planner PLANNING FOR TEMPORARY POWER: A Critial Management Duty As a faility manager, you know better than anyone that eletrial power is the lifeblood of business. Without
Effect of Aggregate Gradation on Measured Asphalt Content
 TRANSPORTATON RESEARCH RECORD 1417 21 Effet of Aggregate Gradation on Measured Asphalt Content PRTHV S. l
TRANSPORTATON RESEARCH RECORD 1417 21 Effet of Aggregate Gradation on Measured Asphalt Content PRTHV S. l
A Study on the Measuring System of the Variation of the Aiming Baseline in the Aiming Sights
 Preision Instrument and Mehanology July 0, Vol. Iss., PP. -7 A Study on the Measuring System of the Variation of the Aiming Baseline in the Aiming Sights Yundong Zhu *, Jinsong Wang College of Opto-Eletroni
Preision Instrument and Mehanology July 0, Vol. Iss., PP. -7 A Study on the Measuring System of the Variation of the Aiming Baseline in the Aiming Sights Yundong Zhu *, Jinsong Wang College of Opto-Eletroni
Deburring and fettling systems for robots and CNC machine tools
 Partner for the professionals Pneumati spindles Pneumati built-in motors For automati proessing b Deburring b Milling b Sanding b Brushing b Drilling b Polishing Deburring and fettling systems for robots
Partner for the professionals Pneumati spindles Pneumati built-in motors For automati proessing b Deburring b Milling b Sanding b Brushing b Drilling b Polishing Deburring and fettling systems for robots
Chapter - 4. Variable Displacement Axial-Piston Pump - Design and Analysis
 Chapter - 4. Variale Displaement Axial-Piston Pump - Design and Analysis 4.1 Overview In a pressure-ompensated design of a variale displaement axial piston pump as shown in Fig. 4.1, the inlination of
Chapter - 4. Variale Displaement Axial-Piston Pump - Design and Analysis 4.1 Overview In a pressure-ompensated design of a variale displaement axial piston pump as shown in Fig. 4.1, the inlination of
Symbol indicating an action that must not be done. Symbol indicating an action that should be done. Symbol indicating related or useful information
 Installation Manual Using the Produt Safely Safety Instrutions This guide explains how to suspend the EV-100/EV-105 from a eiling or install it on a wall using the supplied Diret Mount. Make sure you read
Installation Manual Using the Produt Safely Safety Instrutions This guide explains how to suspend the EV-100/EV-105 from a eiling or install it on a wall using the supplied Diret Mount. Make sure you read
WIM and dynamic loading on pavements
 IM and dynami loading on pavements M. HUHTALA, LiTeh, Head of Road Researh, J. PIHLAJAMAKI, MS(ng), Researh Sientist, and P. HALONN, BS(ng), Researh ngineer, Tehnial Researh Centre of Finland (VTT), Road
IM and dynami loading on pavements M. HUHTALA, LiTeh, Head of Road Researh, J. PIHLAJAMAKI, MS(ng), Researh Sientist, and P. HALONN, BS(ng), Researh ngineer, Tehnial Researh Centre of Finland (VTT), Road
AAE 451 UAV PROPOSAL SYSTEMS DEFINITION REVIEW DOCUMENTATION TEAM 4
 AAE 451 UAV PROPOSAL SYSTEMS DEFINITION REVIEW DOCUMENTATION TEAM 4 Kevin Kwan Dan Pothala Mohammed Abdul Rahim Niole Risley Sara Tassan John Thornton Sean Wook Alvin Yip April 5, 2007 Page 1 of 72 Table
AAE 451 UAV PROPOSAL SYSTEMS DEFINITION REVIEW DOCUMENTATION TEAM 4 Kevin Kwan Dan Pothala Mohammed Abdul Rahim Niole Risley Sara Tassan John Thornton Sean Wook Alvin Yip April 5, 2007 Page 1 of 72 Table
CHAPTER 1. Introduction and Literature Review
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction and Literature Review 1.1 Introduction The Active Magnetic Bearing (AMB) is a device that uses electromagnetic forces to support a rotor without mechanical contact. The AMB offers
CHAPTER 1 Introduction and Literature Review 1.1 Introduction The Active Magnetic Bearing (AMB) is a device that uses electromagnetic forces to support a rotor without mechanical contact. The AMB offers
HYDRODYNAMIC JOURNAL BEARINGS - TYPES, CHARACTERISTICS AND APPL/CATIONS
 ROTATNG MACHNERY TECHNOLOGY, NC. PRECSON BEARNGS AND SEALS TURBOMACHNERY REPAR ROTORDYNAMC ANALYSES HYDRODYNAMC JOURNAL BEARNGS - TYPES, CHARACTERSTCS AND APPL/CATONS John C. Nicholas, Ph.D. July 1996
ROTATNG MACHNERY TECHNOLOGY, NC. PRECSON BEARNGS AND SEALS TURBOMACHNERY REPAR ROTORDYNAMC ANALYSES HYDRODYNAMC JOURNAL BEARNGS - TYPES, CHARACTERSTCS AND APPL/CATONS John C. Nicholas, Ph.D. July 1996
Z SLIDERS. Introducing a low profile actuator installing a circulating type linear guide!
 Z SLIDERS Introduing a low profile atuator installing a irulating type linear guide! Developed mainly for movement in the Z axis diretion, as refleted in the Z Slider name. The thin, lightweight, and ompat
Z SLIDERS Introduing a low profile atuator installing a irulating type linear guide! Developed mainly for movement in the Z axis diretion, as refleted in the Z Slider name. The thin, lightweight, and ompat
Examination of a PHEV Bidirectional Charger System for V2G Reactive Power Compensation
 Examination of a PHEV Bidiretional Charger System for VG Reative Power Compensation Mithat C. Kisaikoglu 1, Burak Ozpinei, and Leon M. Tolbert 1, 1 Dept. of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene The
Examination of a PHEV Bidiretional Charger System for VG Reative Power Compensation Mithat C. Kisaikoglu 1, Burak Ozpinei, and Leon M. Tolbert 1, 1 Dept. of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene The
SAF MODUL t AIR SUSPENSION SYSTEM WITH DISC AND DRUM BRAKE 17.5, 19.5 AND 22.5
 SAF MODUL 7 14-t AIR SUSPENSION SYSTEM WITH DISC AND DRUM BRAKE 17.5, 19.5 AND 22.5 THE MODUL FAMILY One of the speial advantages of the SAF MODUL system is its versatility Individual solutions for eonomial
SAF MODUL 7 14-t AIR SUSPENSION SYSTEM WITH DISC AND DRUM BRAKE 17.5, 19.5 AND 22.5 THE MODUL FAMILY One of the speial advantages of the SAF MODUL system is its versatility Individual solutions for eonomial
USER INSTRUCTIONS. Valtek VL-ES Actuators. Installation Operation Maintenance. Experience In Motion FCD VLENIM /06
 USER INSTRUCTIONS Valtek VL-ES Atuators FCD VLENIM0114-00 09/06 Installation Operation Maintenane Experiene In Motion Contents 1 General Information 3 1.1 Using 3 1.2 Appliability 3 1.3 Terms Conerning
USER INSTRUCTIONS Valtek VL-ES Atuators FCD VLENIM0114-00 09/06 Installation Operation Maintenane Experiene In Motion Contents 1 General Information 3 1.1 Using 3 1.2 Appliability 3 1.3 Terms Conerning
ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, September 2005
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 APPLICATION OF ROTOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR EVALUATION OF SYNCHRONOUS SPEED INSTABILITY AND AMPLITUDE HYSTERESIS
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 APPLICATION OF ROTOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR EVALUATION OF SYNCHRONOUS SPEED INSTABILITY AND AMPLITUDE HYSTERESIS
Nickel Cadmium Battery
 Nikel Cadmium Battery Introdution Ò STLONG Batteries are manufatured in basi range to math speifi operating ondition and providing different performane harateristi. Our Batteries will ombine maximum performane
Nikel Cadmium Battery Introdution Ò STLONG Batteries are manufatured in basi range to math speifi operating ondition and providing different performane harateristi. Our Batteries will ombine maximum performane
SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS
 Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2013 Prague, February 5 6, 2013 CzechNC 1. I SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS Jiří Šimek Abstract: Turbochargers for combustion engines are
Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2013 Prague, February 5 6, 2013 CzechNC 1. I SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS Jiří Šimek Abstract: Turbochargers for combustion engines are
A Motor Designer Looks at Positive Temperature Coefficient Resistors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1974 A Motor Designer Looks at Positive Temperature Coefficient Resistors W. R. Hoffmeyer
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1974 A Motor Designer Looks at Positive Temperature Coefficient Resistors W. R. Hoffmeyer
Rotor Dynamics as a Tool for Solving Vibration Problems Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Company
 Rotor Dynamics as a Tool for Solving Vibration Problems Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Company Introduction This paper continues the series begun in 2001 for the Vibration Institute
Rotor Dynamics as a Tool for Solving Vibration Problems Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Company Introduction This paper continues the series begun in 2001 for the Vibration Institute
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A TURBOCHARGER IN FLOATING BUSHING BEARINGS
 Dyrobes Rotoynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A TURBOCHARGER IN FLOATING BUSHING BEARINGS Edgar J. Gunter RODYN VIBRATION ANALYSIS,
Dyrobes Rotoynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A TURBOCHARGER IN FLOATING BUSHING BEARINGS Edgar J. Gunter RODYN VIBRATION ANALYSIS,
CONTENTS. 5 BALANCING OF MACHINERY Scope Introduction Balancing Machines Balancing Procedures
 CONTENTS 1 OVERVIEW.....................................................................1-1 1.1 Introduction.................................................................1-1 1.2 Organization.................................................................1-1
CONTENTS 1 OVERVIEW.....................................................................1-1 1.1 Introduction.................................................................1-1 1.2 Organization.................................................................1-1
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 ME340. Power Train Engineering
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 ME340 Power Train Engineering Time allowed: TWO hours Answer: Any FOUR questions only Items permitted: This is a losed-book
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 ME340 Power Train Engineering Time allowed: TWO hours Answer: Any FOUR questions only Items permitted: This is a losed-book
The Nature and Causes of the 1982 Traffic Accident Casualty Reductions in British Columbia
 Transportation Researh Reord 147 1 The Nature and Causes of the 1982 Traffi Aident Casualty Redutions in British Columbia PETER J. COOPER ABSTRACT The extent of the 1982 traffi aident asualty redution
Transportation Researh Reord 147 1 The Nature and Causes of the 1982 Traffi Aident Casualty Redutions in British Columbia PETER J. COOPER ABSTRACT The extent of the 1982 traffi aident asualty redution
Crash Testing with a Massive Moving Barrier as an Accident Reconstruction Tool
 SAE TECHNICAL PAPER SERIES 000-01-0604 Crash Testing with a assive oving Barrier as an Aident Reonstrution Tool Ronald L. Woolley, Alan F. Asay and Dagmar Buzeman Jewkes Woolley Engineering Researh Corp.
SAE TECHNICAL PAPER SERIES 000-01-0604 Crash Testing with a assive oving Barrier as an Aident Reonstrution Tool Ronald L. Woolley, Alan F. Asay and Dagmar Buzeman Jewkes Woolley Engineering Researh Corp.
Three-phase Induction Motors. Empowering the Future
 Three-phase Indution s Eming the Future Catalog 0-20 Combining Over Years of Ex In the Manufature of Produts Toshiba Mitsubishi-Eletri Industrial Systems Corporation (TMEIC) stands proud as a key player
Three-phase Indution s Eming the Future Catalog 0-20 Combining Over Years of Ex In the Manufature of Produts Toshiba Mitsubishi-Eletri Industrial Systems Corporation (TMEIC) stands proud as a key player
DETERMINING THE ROOT CAUSES OF SUBSYNCHRONOUS INSTABILITY PROBLEMS IN TWO CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
 DETERMINING THE ROOT CAUSES OF SUBSYNCHRONOUS INSTABILITY PROBLEMS IN TWO CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS by Ed Wilcox CVO Rotating Equipment Team Lead Lyondell/Equistar Channelview, Texas and David P. O Brien
DETERMINING THE ROOT CAUSES OF SUBSYNCHRONOUS INSTABILITY PROBLEMS IN TWO CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS by Ed Wilcox CVO Rotating Equipment Team Lead Lyondell/Equistar Channelview, Texas and David P. O Brien
ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY
 ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. P.O. BOX 157 Dickinson, TX 77539 MLeader@RotorBearingDynamics.COM Abstract: This paper continues
ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. P.O. BOX 157 Dickinson, TX 77539 MLeader@RotorBearingDynamics.COM Abstract: This paper continues
RX 50 Technical Data.
 @ RX 50 Tehnial Data. Eletri Forklift Truks RX 5010 RX 5013 RX 5015 RX 5016 2 RX 50 ELECTRIC FORKLIFT TRUCKS. In aordane with VDI guidelines 2198, this speifiation applies to the standard model only. Alternative
@ RX 50 Tehnial Data. Eletri Forklift Truks RX 5010 RX 5013 RX 5015 RX 5016 2 RX 50 ELECTRIC FORKLIFT TRUCKS. In aordane with VDI guidelines 2198, this speifiation applies to the standard model only. Alternative
A VIRTUAL-CAM BASED CONTROL METHODOLOGY FOR FREE-PISTON ENGINES CHAO YONG. Dissertation. Submitted to the Faculty of the
 A VIRTUAL-CAM BASED CONTROL METHODOLOGY FOR FREE-PISTON ENGINES By CHAO YONG Dissertation Submitted to the Faulty of the Graduate Shool of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfilment of the requirements
A VIRTUAL-CAM BASED CONTROL METHODOLOGY FOR FREE-PISTON ENGINES By CHAO YONG Dissertation Submitted to the Faulty of the Graduate Shool of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfilment of the requirements
Measurement of Tractive Force in the Creep Region and Maximum Adhesion Control of High Speed Railway Systems
 Measurement of Trative Fore in the Creep Region and Maximum Adhesion Control of High Speed Railway Systems Atsuo Kawamura (Yokohama National University, Japan) Meifen Cao (Corporation for Advaned Transport
Measurement of Trative Fore in the Creep Region and Maximum Adhesion Control of High Speed Railway Systems Atsuo Kawamura (Yokohama National University, Japan) Meifen Cao (Corporation for Advaned Transport
Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps Abstract By Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. Kelly J. Conner
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps Abstract By Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. Kelly J. Conner
Trolley Bus and Motor Coach Operational Cost Comparisons Utilizing Section 15 Data
 52 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1165 Trolley Bus and Motor Coah Operational Cost Comparisons Utilizing Setion 15 Data D. DUNOYE AND W. DIEWALD An examination of the osts of operating and maintaining
52 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1165 Trolley Bus and Motor Coah Operational Cost Comparisons Utilizing Setion 15 Data D. DUNOYE AND W. DIEWALD An examination of the osts of operating and maintaining
Design Friction Factors of Different Countries Versus Actual Pavement Friction Inventories
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 126 135 Design Frition Fators of Different Countries Versus Atual Pavement Frition Inventories RUEDIGER LAMM, ELIAS M. CHOUEIRI, PREM B. GOYAL, AND THEODOR MAILAENDER A fundamental
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 126 135 Design Frition Fators of Different Countries Versus Atual Pavement Frition Inventories RUEDIGER LAMM, ELIAS M. CHOUEIRI, PREM B. GOYAL, AND THEODOR MAILAENDER A fundamental
Structural and Rotordynamic Force Coefficients of a Shimmed Bump Foil Bearing: an Assessment of a Simple Engineering Practice
 Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada Paper GT2015-43734 Structural and Rotordynamic Force Coefficients of a Shimmed Bump
Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada Paper GT2015-43734 Structural and Rotordynamic Force Coefficients of a Shimmed Bump
Contact Stress Analysis of Composite Spur Gear using Photo-Stress Method and Finite Element Analysis
 International Researh Journal of Engineering and Tehnology (IRJET) e-issn: 395-0056 Volume: 03 Issue: 07 July-06 www.irjet.net p-issn: 395-007 Contat Stress Analysis of Composite Spur Gear using Photo-Stress
International Researh Journal of Engineering and Tehnology (IRJET) e-issn: 395-0056 Volume: 03 Issue: 07 July-06 www.irjet.net p-issn: 395-007 Contat Stress Analysis of Composite Spur Gear using Photo-Stress
Ride Quality and Drivability of a Typical Passenger Car subject to Engine/Driveline and Road Non-uniformities Excitations
 Ride Quality and Drivability of a Typial Passenger Car subjet to Engine/Driveline and Road Non-uniformities Exitations Examensarbete utfört i Fordonssystem vid Tenisa högsolan i Linöping av Neda Nimehr
Ride Quality and Drivability of a Typial Passenger Car subjet to Engine/Driveline and Road Non-uniformities Exitations Examensarbete utfört i Fordonssystem vid Tenisa högsolan i Linöping av Neda Nimehr
VQE: 2-way flanged valve, PN 16
 Ambient onditions 1) Operating temperature 2) -10...150 C Produt data sheet 56.117 VQE: 2-way flanged valve, PN 16 How energy effiieny is improved Effiient use in ontinuous ontrol systems Features Continuous
Ambient onditions 1) Operating temperature 2) -10...150 C Produt data sheet 56.117 VQE: 2-way flanged valve, PN 16 How energy effiieny is improved Effiient use in ontinuous ontrol systems Features Continuous
Failure of a Test Rig Operating with Pressurized Gas Bearings: a Lesson on Humility
 Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada GT2015-42556 Failure of a Test Rig Operating with Pressurized Gas Bearings: a Lesson
Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada GT2015-42556 Failure of a Test Rig Operating with Pressurized Gas Bearings: a Lesson
FROM OIL TO MAGNETIC FIELDS: ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VIBRATION CONTROL
 ata mehania et automatia, vol. no. (8) FROM OIL TO MAGNETIC FIELDS: ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VIBRATION CONTROL Gianarlo Genta *, Andrea Festini *, Xavier Delepine * * Department of Mehanis, Politenio di Torino,
ata mehania et automatia, vol. no. (8) FROM OIL TO MAGNETIC FIELDS: ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VIBRATION CONTROL Gianarlo Genta *, Andrea Festini *, Xavier Delepine * * Department of Mehanis, Politenio di Torino,
Characteristics TeSys contactors 0 Model d
 Charateristis TeSys ontators 0 Model d Contator type LC1 D09 D18 D25 D38 D40 D50 D95 D115 and D150 DT20 and DT25 DT32 and DT40 Environment Rated insulation voltage (Ui) Conforming to IEC 60947-4-1, V 690
Charateristis TeSys ontators 0 Model d Contator type LC1 D09 D18 D25 D38 D40 D50 D95 D115 and D150 DT20 and DT25 DT32 and DT40 Environment Rated insulation voltage (Ui) Conforming to IEC 60947-4-1, V 690
Sofia F. Franco* Nova School of Business and Economics Universidade Nova de Lisboa & UECE. May 25th, Abstract
 Downtown Parking Supply, Work-Trip Mode hoie and Urban Spatial Struture Sofia F. Frano* ova Shool of Business and Eonomis Universidade ova de Lisboa & UEE May 25th, 2015 Abstrat This paper examines the
Downtown Parking Supply, Work-Trip Mode hoie and Urban Spatial Struture Sofia F. Frano* ova Shool of Business and Eonomis Universidade ova de Lisboa & UEE May 25th, 2015 Abstrat This paper examines the
T E C H N I C A L P A P E R
 Wheeler Industries, Inc. An ISO9002 Certified Supplier 7261 Investment Drive N. Charleston, SC 29418 Tel: 843-552-1251 Fax: 843-552-4790 Website: www.wheeler-ind.com T E C H N I C A L P A P E R Design
Wheeler Industries, Inc. An ISO9002 Certified Supplier 7261 Investment Drive N. Charleston, SC 29418 Tel: 843-552-1251 Fax: 843-552-4790 Website: www.wheeler-ind.com T E C H N I C A L P A P E R Design
ELIMINATING A RUB-INDUCED STARTUP VIBRATION PROBLEM IN AN ETHYLENE DRIVE STEAM TURBINE
 ELIMINATING A RUB-INDUCED STARTUP VIBRATION PROBLEM IN AN ETHYLENE DRIVE STEAM TURBINE by John C. Nicholas President and Chief Engineer Rotating Machinery Technology, Inc. Wellsville, New York Stephen
ELIMINATING A RUB-INDUCED STARTUP VIBRATION PROBLEM IN AN ETHYLENE DRIVE STEAM TURBINE by John C. Nicholas President and Chief Engineer Rotating Machinery Technology, Inc. Wellsville, New York Stephen
DATA SHEET LC-D CONTACTORS
 Issued November 2009 DATA SHEET LC-D CONTACTORS Based on Shneider MKTED205103EN Catalogue Charateristis 5 d Contator type LC1 D09 D18 D25 D38 D40 D50 D95 D115 and D150 DT20 and DT25 DT32 and DT40 Environment
Issued November 2009 DATA SHEET LC-D CONTACTORS Based on Shneider MKTED205103EN Catalogue Charateristis 5 d Contator type LC1 D09 D18 D25 D38 D40 D50 D95 D115 and D150 DT20 and DT25 DT32 and DT40 Environment
BIODIESEL INFLUENCE ON DIESEL ENGINE EMISSION
 4 Mehanial Testing and Diagnosis ISSN 2247 9635, 211 (I), Volume 1, 4-47 BIODIESEL INFLUENCE ON DIESEL ENGINE EMISSION Breda KEGL, Stanislav PEHAN University of Maribor, Maribor, Slovenia, b, 2 Maribor,
4 Mehanial Testing and Diagnosis ISSN 2247 9635, 211 (I), Volume 1, 4-47 BIODIESEL INFLUENCE ON DIESEL ENGINE EMISSION Breda KEGL, Stanislav PEHAN University of Maribor, Maribor, Slovenia, b, 2 Maribor,
VQD: 2-way flanged valve, PN 6
 Ambient onditions 1) Operating temperature 2) -10...150 C Produt data sheet 56.112 VQD: 2-way flanged valve, PN 6 How energy effiieny is improved Effiient use in ontinuous ontrol systems Features Continuous
Ambient onditions 1) Operating temperature 2) -10...150 C Produt data sheet 56.112 VQD: 2-way flanged valve, PN 6 How energy effiieny is improved Effiient use in ontinuous ontrol systems Features Continuous
IJTC STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AUTOMOTIVE TURBOCHARGER. Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software http://dyrobes.com Proceedings of IJTC26 STLE/ASME international Joint Tribology Conference October 22-25, 26, San Antonio, TX, USA STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AUTOMOTIVE
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software http://dyrobes.com Proceedings of IJTC26 STLE/ASME international Joint Tribology Conference October 22-25, 26, San Antonio, TX, USA STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AUTOMOTIVE
Thyristor Based HVDC with Forced Commutation
 1 Thyristor Based HVDC with Fored Commutation D. Jovi, Member IEEE Abstrat This paper presents a novel onverter onfiguration, based solely on onventional thyristors and aimed for the use with High Voltage
1 Thyristor Based HVDC with Fored Commutation D. Jovi, Member IEEE Abstrat This paper presents a novel onverter onfiguration, based solely on onventional thyristors and aimed for the use with High Voltage
EFFECT OF LUBRICANT SUPPLY PRESSURE ON SFD PERFORMANCE: ENDS SEALED WITH O-RINGS & PISTON RINGS
 May 2017 Year V EFFECT OF LUBRICANT SUPPLY PRESSURE ON SFD PERFORMANCE: ENDS SEALED WITH O-RINGS & PISTON RINGS TRC-SFD-01-17 Bonjin Koo Leping Yu Graduate Research Assistants Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs
May 2017 Year V EFFECT OF LUBRICANT SUPPLY PRESSURE ON SFD PERFORMANCE: ENDS SEALED WITH O-RINGS & PISTON RINGS TRC-SFD-01-17 Bonjin Koo Leping Yu Graduate Research Assistants Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs
Estimation of Wear Depth on Normal Contact Ratio Spur Gear
 Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 24 (S1): 38-42, 2016 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2016 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2016.24.S1.9 Estimation of Wear Depth on Normal Contact Ratio Spur Gear
Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 24 (S1): 38-42, 2016 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2016 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2016.24.S1.9 Estimation of Wear Depth on Normal Contact Ratio Spur Gear
Case History: Field Balancing of a Bowed Steam Turbine Rotor. My Background
 Rotating Machinery Consultants Helping You Provide Maintenance That Matters Case History: Field Balancing of a Bowed Steam Turbine Rotor Vibration Institute Regional Training Conference Peek n Peak Resort,
Rotating Machinery Consultants Helping You Provide Maintenance That Matters Case History: Field Balancing of a Bowed Steam Turbine Rotor Vibration Institute Regional Training Conference Peek n Peak Resort,
VEHICLE COLLISION FORCE IN OFFSET BARRIER AND CAR TO CAR OFFSET TESTS
 VEHICLE COLLISION FORCE IN OFFSET BARRIER AND CAR TO CAR OFFSET TESTS Hirotoshi lshikawa(1l, Kennerly H Digges(2l, Jason B Ennis(2l (1) Japan Automobile Researh Institute (2) National Crash Analysis Center,
VEHICLE COLLISION FORCE IN OFFSET BARRIER AND CAR TO CAR OFFSET TESTS Hirotoshi lshikawa(1l, Kennerly H Digges(2l, Jason B Ennis(2l (1) Japan Automobile Researh Institute (2) National Crash Analysis Center,
PCU CORE FIRE PROTECTION ELECTRICAL DETAIL
 PU ORE PROTETION ELETRIAL DETAIL ELETRIIAN: 1) WIRE MAIN ONTROL PANEL PER INLUDED SHEMATI 04/14/2014 Rev. 14 ELETRIAL ONTRATOR REQUIREMENT ITEM ONNETION IN PANEL ONNETION ON VOLTAGE AMPERAGE OMMENTS PU
PU ORE PROTETION ELETRIAL DETAIL ELETRIIAN: 1) WIRE MAIN ONTROL PANEL PER INLUDED SHEMATI 04/14/2014 Rev. 14 ELETRIAL ONTRATOR REQUIREMENT ITEM ONNETION IN PANEL ONNETION ON VOLTAGE AMPERAGE OMMENTS PU
EFFECT OFSHIMMING ON THE ROTORDYNAMIC FORCE COEFFICIENTS OF A BUMP TYPE FOIL BEARING TRC-B&C
 TRC Project 32513/1519F3 EFFECT OFSHIMMING ON THE ROTORDYNAMIC FORCE COEFFICIENTS OF A BUMP TYPE FOIL BEARING TRC-B&C-01-2014 A Shimmed Bump Foil Bearing: Measurements of Drag Torque, Lift Off Speed, and
TRC Project 32513/1519F3 EFFECT OFSHIMMING ON THE ROTORDYNAMIC FORCE COEFFICIENTS OF A BUMP TYPE FOIL BEARING TRC-B&C-01-2014 A Shimmed Bump Foil Bearing: Measurements of Drag Torque, Lift Off Speed, and
CASE STUDY ON RESOLVING OIL WHIRL ISSUES ON GAS COMPRESSOR
 CASE STUDY ON RESOLVING OIL WHIRL ISSUES ON GAS COMPRESSOR John J. Yu, Ph.D. Nicolas Péton Sergey Drygin, Ph.D. GE Oil & Gas 1 / Abstract This case is a site vibration issue on a Gas compressor module.
CASE STUDY ON RESOLVING OIL WHIRL ISSUES ON GAS COMPRESSOR John J. Yu, Ph.D. Nicolas Péton Sergey Drygin, Ph.D. GE Oil & Gas 1 / Abstract This case is a site vibration issue on a Gas compressor module.
Ultimate bearing capacity of existing heavy haul railway concrete simple double-t girder strengthened by anchoring assisted steel beams
 International Conferene on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 03) Ultimate bearing apait of existing heav haul railwa onrete simple double-t girder strengthened b anhoring
International Conferene on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 03) Ultimate bearing apait of existing heav haul railwa onrete simple double-t girder strengthened b anhoring
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION. Brussels, 13 May /13 ADD 7 ENER 177 ENV 386 DELACT 19 COVER NOTE
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 13 May 2013 9443/13 ADD 7 COVER NOTE from: ENER 177 ENV 386 DELACT 19 Seretary-General of the European Commission, signed by Mr Jordi AYET PUIGARNAU, Diretor date
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 13 May 2013 9443/13 ADD 7 COVER NOTE from: ENER 177 ENV 386 DELACT 19 Seretary-General of the European Commission, signed by Mr Jordi AYET PUIGARNAU, Diretor date
Gearbox Radiated Noise
 Influence of Gear Design on Gearbox Radiated Noise Fred B. Osald Dennis P. Tonsend Mark J. Valco Robert H. Spencer Raymond J. Drago & Joseph W. Lenski Jr. Introduction A major source of helicopter cabin
Influence of Gear Design on Gearbox Radiated Noise Fred B. Osald Dennis P. Tonsend Mark J. Valco Robert H. Spencer Raymond J. Drago & Joseph W. Lenski Jr. Introduction A major source of helicopter cabin
US-CE -C Property ot the
 TA7 W34m no. CERC-96-5 '. 2 J US Army Corps of Engineers Waterways Experiment Station US-CE -C Property ot the UnUed States Governmont Misellaneous Paper CERC-96-5 June 1996 ndex and Bulk Parameters for
TA7 W34m no. CERC-96-5 '. 2 J US Army Corps of Engineers Waterways Experiment Station US-CE -C Property ot the UnUed States Governmont Misellaneous Paper CERC-96-5 June 1996 ndex and Bulk Parameters for
EVALUATION OF ROTORDYNAMIC CRITERIA FOR MULTISTAGE PUMP SHAFTS
 EVALUATION OF ROTORDYNAMIC CRITERIA FOR MULTISTAGE PUMP SHAFTS by Wolfram Lienau Manager, Analysis and Mechanics Sulzer Pumps Ltd. Winterthur, Switzerland and Nicolas Lagas Engineer in Mechanics Sulzer
EVALUATION OF ROTORDYNAMIC CRITERIA FOR MULTISTAGE PUMP SHAFTS by Wolfram Lienau Manager, Analysis and Mechanics Sulzer Pumps Ltd. Winterthur, Switzerland and Nicolas Lagas Engineer in Mechanics Sulzer
Cement by Heat of Neutralization
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1295 17 D~termining Cement Content of Soil Cement by Heat of Neutralization RonERT SA vuzzo A heat of neutralization test method (a modified by the Bureau of Relamation)
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1295 17 D~termining Cement Content of Soil Cement by Heat of Neutralization RonERT SA vuzzo A heat of neutralization test method (a modified by the Bureau of Relamation)
Emergency Medical Service Rescue Time in Fatal Road Accidents
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1270 89 Emergeny Medial Servie Resue Time in Fatal Road Aidents HAROLD BRODSKY Ambulane resue times in fatal road aidents in the United States have improved little over the
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1270 89 Emergeny Medial Servie Resue Time in Fatal Road Aidents HAROLD BRODSKY Ambulane resue times in fatal road aidents in the United States have improved little over the
Simulation study on performance and emissions of a Small Direct Injection Diesel Engine fueled by Dimethyl Ether
 Simulation study on performane and emissions of a Small Diret Injetion Engine fueled by Dimethyl Ether Nguyen Lan Huong, *, Kanit Wattanavihien, Luong ong Nho and Pham Huu Tuyen 3 Mehanial Engineering
Simulation study on performane and emissions of a Small Diret Injetion Engine fueled by Dimethyl Ether Nguyen Lan Huong, *, Kanit Wattanavihien, Luong ong Nho and Pham Huu Tuyen 3 Mehanial Engineering
ON THE DETERMINATION OF BEARING SUPPORT PEDESTAL STIFFNESS USING SHAKER TESTING
 ON THE DETERMINATION OF BEARING SUPPORT PEDESTAL STIFFNESS USING SHAKER TESTING R. Subbiah Siemens Energy, Inc., 4400 Alafaya trail, Orlando FL 32817 USA Abstract An approach that enables rotor dynamists
ON THE DETERMINATION OF BEARING SUPPORT PEDESTAL STIFFNESS USING SHAKER TESTING R. Subbiah Siemens Energy, Inc., 4400 Alafaya trail, Orlando FL 32817 USA Abstract An approach that enables rotor dynamists
A SOLUTION TO YEARS OF HIGH VIBRATION PROBLEMS IN THREE REINJECTION COMPRESSOR TRAINS RUNNING AT 33 MPa DISCHARGE PRESSURE. Jong Kim, PhD/Presenter
 A SOLUTION TO YEARS OF HIGH VIBRATION PROBLEMS IN THREE REINJECTION COMPRESSOR TRAINS RUNNING AT 33 MPa DISCHARGE PRESSURE Jong Kim, PhD/Presenter Authors Jong Kim, PhD Senior Principal Engineer, Waukesha
A SOLUTION TO YEARS OF HIGH VIBRATION PROBLEMS IN THREE REINJECTION COMPRESSOR TRAINS RUNNING AT 33 MPa DISCHARGE PRESSURE Jong Kim, PhD/Presenter Authors Jong Kim, PhD Senior Principal Engineer, Waukesha
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012
 US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
TH-DEX PRODUCT INFORMATION. Direct fixing concrete screw, for use in cracked and non cracked concrete. TECHNICAL GUIDE Direct fixing anchor
 MECHAICAL ACHORS TH Diret fixing onrete srew, for use in raked and non raked onrete Assessed ETA Option 1. Steel with Silver Ruspert oating. PRODUCT IFORMATIO DESCRIPTIO Metalli srew, with thread for fixing
MECHAICAL ACHORS TH Diret fixing onrete srew, for use in raked and non raked onrete Assessed ETA Option 1. Steel with Silver Ruspert oating. PRODUCT IFORMATIO DESCRIPTIO Metalli srew, with thread for fixing
An Area/Delay Efficient Dual-Modular Flip-Flop with Higher SEU/SET Immunity
 340 PAPER Speial Setion on Ciruits and Design Tehniques for Advaned Large Sale Integration An Area/Delay Effiient Dual-Modular Flip-Flop with Higher SEU/SET Immunity Jun FURUTA a), Nonmember, Kazutoshi
340 PAPER Speial Setion on Ciruits and Design Tehniques for Advaned Large Sale Integration An Area/Delay Effiient Dual-Modular Flip-Flop with Higher SEU/SET Immunity Jun FURUTA a), Nonmember, Kazutoshi
IDENTIFICATION OF ABNORMAL ROTOR DYNAMIC STIFFNESS USING MEASURED VIBRATION INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL MODELING
 Proceedings of PWR2009 ASME Power July 21-23, 2009, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Power2009-81019 IDENTIFICATION OF ABNORMAL ROTOR DYNAMIC STIFFNESS USING MEASURED VIBRATION INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL MODELING
Proceedings of PWR2009 ASME Power July 21-23, 2009, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Power2009-81019 IDENTIFICATION OF ABNORMAL ROTOR DYNAMIC STIFFNESS USING MEASURED VIBRATION INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL MODELING
Diaphragm Seals NEW! For Pressure Products For Pressure Products
 NEW! For Produts For Produts Diaphragm Seals Produt Overview Introdution Diaphragm Seals (or Chemial Seals) use a flexible barrier, or diaphragm, to isolate a pressure sensor (swith or transduer) from
NEW! For Produts For Produts Diaphragm Seals Produt Overview Introdution Diaphragm Seals (or Chemial Seals) use a flexible barrier, or diaphragm, to isolate a pressure sensor (swith or transduer) from
No ALLOCATION OF RAILWAY ROLLING STOCK FOR PASSENGER TRAINS. By Erwin Abbink, Bianca van den Berg, Leo Kroon and Marc Salomon.
 No. 2002-43 ALLOCATION OF RAILWAY ROLLING STOCK FOR PASSENGER TRAINS By Erwin Abbink, Biana van den Berg, Leo Kroon and Mar Salomon April 2002 ISSN 0924-7815 Alloation of Railway Rolling Stok for Passenger
No. 2002-43 ALLOCATION OF RAILWAY ROLLING STOCK FOR PASSENGER TRAINS By Erwin Abbink, Biana van den Berg, Leo Kroon and Mar Salomon April 2002 ISSN 0924-7815 Alloation of Railway Rolling Stok for Passenger
Hydronic Accessories H YDRONIC C OMPONENTS & S YSTEMS. Taco Catalog # Supersedes: Dated: 02/1/01
 Hydroni essories ESP Zone Valve he ao ESP is the most intelligent zone valve in the world. he unique patented tehnology in the ESP utilizes a miroiruit based logi to ontrol a gear driven, apaitor powered
Hydroni essories ESP Zone Valve he ao ESP is the most intelligent zone valve in the world. he unique patented tehnology in the ESP utilizes a miroiruit based logi to ontrol a gear driven, apaitor powered
Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery
 The 6 th International Supercritical CO 2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery Richard Shultz Chief Engineer Waukesha
The 6 th International Supercritical CO 2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery Richard Shultz Chief Engineer Waukesha
Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics
 D23 Externally Pressurized MD.qxd 9/1/22 11:17 AM Page 499 499 Chapter 23 Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics IN PREVIOUS SECTIONS OF THIS BOOK, we have discussed machinery diagnostics
D23 Externally Pressurized MD.qxd 9/1/22 11:17 AM Page 499 499 Chapter 23 Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics IN PREVIOUS SECTIONS OF THIS BOOK, we have discussed machinery diagnostics
Associated controllers Controller selection
 Assoiated ontrollers Controller seletion 053058 053058 By ombining a remote-operated sourehangeover system with an integrated BA or UA automati ontroller, it is possible to automatially ontrol soure transfer
Assoiated ontrollers Controller seletion 053058 053058 By ombining a remote-operated sourehangeover system with an integrated BA or UA automati ontroller, it is possible to automatially ontrol soure transfer
ARM Annual Report
 ARM Coal experiened a hallenging year, with the weak priing environment ompounded by operational issues and a marked redution in demand and pries in the seond half. ARM Annual Report 2009 49 ARM Coal Divisional
ARM Coal experiened a hallenging year, with the weak priing environment ompounded by operational issues and a marked redution in demand and pries in the seond half. ARM Annual Report 2009 49 ARM Coal Divisional
LESSON Transmission of Power Introduction
 LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
Conceptual Design and Analysis of a Small and Low-cost Launch Vehicle
 Coneptual Design and Analysis of a Small and Low-ost Launh Vehile AE8900 MS Speial Problems Report Spae Systems Design Lab (SSDL) Shool of Aerospae Engineering Georgia Institute of Tehnology Atlanta, GA
Coneptual Design and Analysis of a Small and Low-ost Launh Vehile AE8900 MS Speial Problems Report Spae Systems Design Lab (SSDL) Shool of Aerospae Engineering Georgia Institute of Tehnology Atlanta, GA
Improving the Film Cooling of a Rotor Blade Platform
 Improving the Film Cooling of a Rotor Blade Platform Giovanna Barigozzi, Antonio Perdihizzi, Roberto Abram To ite this version: Giovanna Barigozzi, Antonio Perdihizzi, Roberto Abram. Improving the Film
Improving the Film Cooling of a Rotor Blade Platform Giovanna Barigozzi, Antonio Perdihizzi, Roberto Abram To ite this version: Giovanna Barigozzi, Antonio Perdihizzi, Roberto Abram. Improving the Film
Gallery of Charts Created by XLRotor
 Gallery of Charts Created by XLRotor What follows are samples of the charts created automatically by XLRotor. The formats for each chart are copied from templates in a file named XLRGRPH.XLS located in
Gallery of Charts Created by XLRotor What follows are samples of the charts created automatically by XLRotor. The formats for each chart are copied from templates in a file named XLRGRPH.XLS located in
Vibration and Stability of 3000-hp, Titanium Chemical Process Blower
 International Journal of Rotating Machinery, 9(2): 197 217, 2003 Copyright c 2003 Taylor & Francis 1023-621X/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/10236210390147407 Vibration and Stability of 3000-hp, Titanium Chemical
International Journal of Rotating Machinery, 9(2): 197 217, 2003 Copyright c 2003 Taylor & Francis 1023-621X/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/10236210390147407 Vibration and Stability of 3000-hp, Titanium Chemical
VEGETABLE CUTTING MACHINE OPERATION MANUAL TT-F60 / TT-F65 TT-F60 TT-F65
 VEGETABLE UTTING MAHINE OPERATION MANUAL TT-F60 / TT-F65 TT-F60 TT-F65 1. GENERAL PROFILE 1.1. DESRIPTION THE MULTI-PURPOSE VEGETABLE UTTER MAHINE AN SLIE, SHRED, GRATE, HIP AND DIE VARIOUS FOODSTUFFS
VEGETABLE UTTING MAHINE OPERATION MANUAL TT-F60 / TT-F65 TT-F60 TT-F65 1. GENERAL PROFILE 1.1. DESRIPTION THE MULTI-PURPOSE VEGETABLE UTTER MAHINE AN SLIE, SHRED, GRATE, HIP AND DIE VARIOUS FOODSTUFFS
Use of ASTM Type-C Fly Ash and
 44 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1478 Use of ASTM Type-C Fly Ash and Limestone in Sand-Gravel Conrete MOHAMED NAGIB ABOU-ZEID, JOHN R WOJAKOWSKI, AND STEPHEN A. CROSS Serious damage in onrete strutures
44 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1478 Use of ASTM Type-C Fly Ash and Limestone in Sand-Gravel Conrete MOHAMED NAGIB ABOU-ZEID, JOHN R WOJAKOWSKI, AND STEPHEN A. CROSS Serious damage in onrete strutures
Case Study - Fluidic Instability
 Case Study - Fluidic Instability Date : October 6, 2014 Fluidic Instability - Its Detection, Causes and Rectification Fluidic instability is one such malfunction in rotary machines which is uncommon and
Case Study - Fluidic Instability Date : October 6, 2014 Fluidic Instability - Its Detection, Causes and Rectification Fluidic instability is one such malfunction in rotary machines which is uncommon and
