|
|
|
- Clemence Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Mechanical Engineering ME METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT LAB LABORATORY MANUAL Name Register No. Branch Year & Semester : : : : 1
2 CONTENTS S.NO. DATE EXPERIMENT NAME PAGE NO. 1 Calibration of outside micrometer SIGNATURE 2 Calibration of vernier height gauge 3 Mechanical Comparator 4 Calibration of vernier caliper 5 Angle of taper rod using sine bar 6 Angle of taper rod using sine center 7 Angle of V-block optical bevel protector 8 Measurement of spur gear tooth dimensions 9 Vibration Set up 10 Displacement using strain gauge 11 Measurement of screw thread using profile projector 12 Vibration set up 13 Measurement of straightness and flatness using auto collimators 14 Force measurement 15 Temperature measurement 16 Tool maker microscope 3
3 Ex No: Date : CALIBRATION OF OUTSIDE MICROMETER Aim: To calibrate the outside micrometer using slip gauge Instruments Required: 1. Micrometer stand 2. outside Micrometer 3. Slip gauge Specifications: 1. Outside micrometer Description: Range =0-25mm Graduations=0.01mm Outside Micrometer It is used for checking the thickness of the square Rectangular and circular round balls. It is consists of various parts such as anvil spindle frame thimble ratchet. Procedure: 1. The micrometer is checked for zero error. 2. The given slip gauge is held between the faces of the anvil and spindle. 3. The spindle is moved by rotating the thimble until the anvil and spindle touches the surface of the component. 4. Fine adjustment is made by ratchet. The main scale reading and thimble scale reading are noted. 5. Two are more reading are taken at different places of the component. 6. The readings are tabulated and calculated. 4
4 Tabulation: Least count=0.01mm TR = MSR+ (TSC x L.C) Range = 0-25mm S.NO MICROMETER READINGS MSR TSV TSR TR SLIP GAUGE READINGS ERROR Model Calculation: Main scale reading = mm Thimble scale coincides = Total reading = MSR+ (VSCXLC) Error= Measured value True value 5
5 Results: Thus the outside micrometer using slip gauge was calibrated. 6
6 Ex No: CALIBRATION OF VERNIER HEIGHT GAUGE USING SLIP GAUGE Date : Aim: To calculate the Vernier height gauge using slip gauges Instruments Required 1. Vernier height gauge 2. Slip gauge Formula Used: TR = MSR+ (VSCXLC) Where, TR-Total Reading MSR-Main Scale Reading VSC-Vernier Scale Coincide LC-Least Count Description: Vernier height gauge consists of a special base block and other attachment.the whole assembly is made such a way to measure height of parts to be measured. A removable clamp is attached b/w measuring jaws and Vernier both the upper and lower end of measuring jaws and Vernier are parallel to the base of Vernier height gauge. A scribing attachment is fitted to mark scribe line on the parts where is required sometimes measuring jaws of Vernier caliper are replaced by a dial gauge according to the type of measurement. Procedure: Vernier height gauge is cleaned with a cloth. The clamping screws are loosened. The given component is fixed in both the two jaws. The component should be perfectly holded. The height is measured with the external jaws. The height of the component is measured by adjusting the movable jaws. 7
7 The procedure is repeated for all the components. At least three readings should be taken and then average will give the accurate measurement. Tabulation: Least count = 0.02 mm S.NO VERNIER HEIGHT GAUGE READING MSR VSC VSR TR SLIP GAUGE READINGS ERROR Model Calculation: Main scale reading = mm Vernier scale coincides = Total reading = MSR+ (VSCXLC) Error = Measured value True value 8
8 Result: Thus the Vernier height gauge was calculated using slip gauge. 9
9 Ex No: Date : CALIBRATION OF DIAL GAUGE Aim: To calibrate the dial gauge by using dial tester Instruments Required: 1. Dial gauge 2. Dial tester Description: Dial test indicator are used for checking surface of parallelism of rods and bars. They are also used for measurement of linear dimensions of jobs which regulate easy readability of moderate precision. It has two pointers which are actuate by rock and pinion arrangement which acts as spindle. The spindle is made to come in contact in work piece. The linear displacement is calculated. Procedure: 1. The slip gauges are built up to the given weight of the component. 2. Dial gauge with stand is placed on the surface plate. 3. The built up gauge is placed under the plunger. 4. The indicator is set to zero. 5. The built up gauge is removed. 6. The given machined component is placed under the plunger. 7. The variation in the height of the component is noted from the reading of the dial. 10
10 Tabulation: Least Count: Dial gauge = 0.01mm S.NO SLIP GAUGE READING UNKNOWN READING ERROR 11
11 Result: Thus the dial gauge is calibrated using dial tester 12
12 Ex No: Date : CALIBRATION OF VERNIER CALIPER Aim: To calibrate the Vernier caliper by using slip gauge Instruments Required: 1. Vernier Caliper 2. Slip gauge Description: Vernier Caliper: Vernier caliper has two sides namely main scale and vernier scale which moves along the main scale vernier are used to measure both internal and external dimension. Procedure: 1. Vernier caliper is cleaned with a cloth. 2. The clamping screws are loosened. 3. The given component is fixed in both the two jaws. 4. The component should be perfectly holded. 5. The thickness is measured with the external jaws. 6. The length of the component is measured by adjusting the movable jaws. 7. The procedure is repeated for all the components. At least three readings should be taken and then average will give the accurate measurement 13
13 Tabulation: Least count=0.02mm S.NO VERNIER READING SLIP GAUGE MSR TR READINGS VSR ERROR Model Calculation: Main scale reading = mm Vernier scale coincides = Total reading = MSR + (VSCXLC) 14
14 Result: Thus the vernier caliper has calibrated using slip gauge 15
15 Ex No: Date : ANGLE OF TAPER BLOCK BY SINE BAR Aim: To measure the angle of the given taper block by using sine bar. Instruments Required: 1. Sine bar 2. Slip gauge 3. Taper block Formula: Sin Ø = h / L Where, H - Height of the slip gauge L - Distance between the centers Ø - Inclined angle of the specimen Description: A Sine bar consist of an accurately ground bar since on which two accurately ground cylinder of the same diameter are mounted at an exact distance apart. The axis of the Cylinder on the plane that is parallel to the upper or working surface of the sine bar.the axis of the cylinder are parallel to each other. The upper surface has high degree of feathers. The principal used in the measurement angle is that the sine of the given angle is the ratio of the opposite side of the angle to the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle. Procedure: 1. The given component is placed on the surface plate. 2. One roller of sine bar is placed on surface plate and bottom surface of sine bar is seated on the taper surface of the component. 3. The combination of slip gauges is inserted between the second roller of sine bar and the surface plate. 16
16 4. The angle of the component is then calculated by the formula given above. Tabulation: LENGTH OF THE BAR CENTER (L) h1 h2 h1- h2 ANGLE OF INCLINATION OF SINE BAR Model Calculation: For measuring the angle of the given taper block by using the Sine bar Sin Ф = h1-h2/ L Ф =sin -1 (h1-h2 /L) 17
17 Result: Thus the angle of the given taper block is measured by using the Sine bar Taper angle of the given block by using sine bar = 18
18 Ex No: Date : ANGLE OF TAPER ROD BY SINE CENTER Aim: To measure the angle of the given taper block by using sine center and slip gauge. Instruments Required: 1. Sine center 2. Slip gauge 3. Dial gauge Description: It is a sine center with block holding center which can be adjusted and reading clamped in any position. A one center connection with slip gauge consists of case fuel device for pressure measurement of conical between the centers. There are made from high carbon chromium corrosive resistant steel hardened cylinders of equal diameter are attached at ends then to each other and also parallel to equal distance from the super surface of the sine center. The distance between the center of two cylinder of the given sine center exactly 100mm. Procedure: Where, 1. To check and measure the angle the sine center is plane over the surface plate. 2. The two center are clamped tightly place slip gauge below are one end to other along the work rod and zero readings. 3. It is not added to few slip gauges in steps till the dial gauge move along the work for the center and entire length of the taper readings is zero. 4. The angle is given by Sin Ф = h1-h2 / L Ф =Height of the slip gauge 19
19 h = Height between the cylinder L = Length of the sine bar Tabulation: S.NO DISTANCE BETWEEN ROLLERS r SLIP GAUGES h1 mm h2 mm h mm HALF ANGLE Model Calculation: For measuring the angle of the given taper rod by using the Sine center Sin Ф = h/ L, Ф =sin -1 (h /L) 20
20 Result: Thus the angle of the given taper rod is measured by using the Sine center. Taper angle of the given rod by using sine angle= 21
21 Ex No: Date : ANGLE OF V-BLOCK BY VERNIER BEVEL PROTRACTOR Aim: To measure the angle of V-block component by using vernier bevel protractor. Instruments Required: 1. Vernier bevel protector 2. V-block Description: Protector is an instrument used to measure and layout the angles with an optical level protector. It is possible to read to an extent of Z. The blades present in the protractor slides in its clamps. The unusual available blade lengths are 150mm and 300mm. inside the body protector there is a glass side. The stock and the body are attached to each other such that the body are attached to each other such that the outlet edges of the stock its tangential to the outside diameter of the body The blades are clamped to the inner rotating member of the body. The inner rotating member of the body carries a small eye piece. It is possible to view the circle graduation against a fixed index circle. Procedure: 1. For measuring the angle of V blocks the number of whole degree on the main scale up to vernier center zero mark is noted in the vernier optical bevel protector. 2. The mark in the main scale is found and this is added to the number of whole degree to obtain the reading provision is made to adjust the focus of the optical magnifying systems. 3. It is being adjusted in order to make accommodation of normal variation in eye sight 22
22 Tabulation: Least Count = 5 S.No. MSR VSC VSR TR V Block angle Error Result: Thus the angle of the given taper block is measured by using the optical protector. (i) Angle of V-blocks = (ii) Angle of V-blocks = 23
23 Ex No: Date : MEASUREMENT OF SPUR GEAR TOOTH DIMENSIONS Aim: To measure gear parameter by using gear tooth vernier. Instruments Required: 1. Gear tooth Vernier 2. Gear specimen. Formula Used: 1. Depth, d = (Nm/2) (1+2/Z-COS(90/Z) 2. Width, w =Nm x sin (90/Z) 3. Outer diameter of gear, D =(Z+2)m 4. Module, m =D/(N+2) Where, w = Chordal width of tooth in mm d = Chordal addendum of gear in mm M = Module of gear in mm N = NO. Of teeth D = outside Dia in gear in mm Procedure: 1. Find the zero error in the horizontal scale and vertical scale of the given gear toot vernier. 2. Find outer diameter of the given gear by using vernier caliper. 3. Count the no of tooth on the given gear. 4. Calculate the depth of pitch circle from the top circle. 5. Calculate the module (m) of the gear. 6. Similarly calculate the theoretical width by substituting and no of gear tooth in the formula. 7. The vertical gear tooth vernier is made of point to calculate the depth value. 8. Now the gear tooth, i.e. kept in between in the two jaws of the gear tooth vernier. 9. Observe the main scale reading and vernier scale coincidence of the horizontal scale. 10. Repeat the observation of different position of the same tooth and calculate the average. 24
24 Tabulation: Least count: Horizontal Scale = 0.02 mm Vertical Scale = 0.02 mm Measurement of Addendum and Chordal Width S.No. MSR Chordal addendum (d) VSC VSR TR MSR Chordal width (w) VSC VSR TR S.No. Chordal addendum (d) Chordal width (w) Actual value Theoretical value Actual value Theoretical value 25
25 Result: Thus the chordal thickness and addendum of gear are measured using gear tooth Vernier. 26
26 Ex No: Date : MEASUEMENT OF SCREW THREAD USING PROFILE PROJECTOR Aim: To determine the major and minor diameter, pitch and flank angle of a screw tread using profile projector. Instruments Required: Profile projector Screw thread Description: Profile Projector: Profile projections are highly sophisticated and versatile designed as per international standards. This comprehensive range covers all conceivable application its ideal for the rapid inspection and measurement (linear and angular) of small to medium size components such as watch parts, tools, rubber components, miniature electronic assemblies and so on. It s best quality high resolution optics provides accurate, bright, clear and sharp images. The special front and back surface mirror are highly polished and lobbied distortion and reproduction. Three element condenser system and high intensity halogen lamps provides brilliant images even in day light condition commitment to quality insure that offer the highest level of precision, quality, reliability and performance. Two types profile projectors are, Vertical floor model, ideal for the rapid inspection Horizontal floor model, ideal for the tracing for projected images Procedure: Measurement of Major Diameter: The given material thread is placed horizontal plan plate of material profile projector and transmitted light is switched on the vertical measurement 27
27 known is located fill of thread is on screen the difference of reading is major diameter Measurement: The wire is made to coincide with and touch the line on one side of thread and micrometer reading are noted the cross wire is coinciding to touch level on other side. The crosswire is to coincide on to root of one side of thread. The horizontal Knob is adjusted to coincide on next root on same side. The cross wire is made to coincide the root of v-groove of thread and the angle of project is noted. The other side of V-groove is made to coincide with wires of adjusting the projector. The difference is reading is twice the flank angle. Tabulation: MAJOR DIAMETER S.NO Micrometer reading I (R1) Micrometer reading II (R2) MSR VSR VR TR MSR VSR VR TR Difference R1 R2 28
28 MAJOR DIAMETER S.NO Micrometer reading I (R1) Micrometer reading II (R2) MSR VSR VR TR MSR VSR VR TR Difference R1 R2 PITCH S.NO Micrometer reading I (R1) Micrometer reading II (R2) MSR VSR VR TR MSR VSR VR TR Difference R1 R2 To Measure Flank Angle S.NO Angle of the left side Angle of the right side Induced angle 29
29 RESULT Thus using the profile projector the depth pitch and flank angle major and minor diameter or given screw thread are measured. Major diameter of given thread - Pitch of given thread - Minor diameter of given thread - Flank angle of given thread - 30
30 Ex No: Date : MEASUREMENT OF DISPLACEMENT USING LVDT Aim: To measure the displacement in terms of microns or mm using LVDT system Description: The instruments is equipped with internal calibration setting which enables the operator to calibrate only LVDT with the instrument provided the output of the transducer for rated display is accurately known with the suitable extension units the channels occupies can be increased and multipoint can be made faster response a compared to the moving coil meter Specification: (i) (ii) LVDT displacement transducer Voltage: 1-30 v Frequency: 2 KHz Sensitivity: (0.2-1)mv/v10 micron Operating temperature:5-55ºc Linearity elevation: 1%max Displacement meter: Transducer LVDT Range: 1999 micron/1.99 m Frequency: 2 KHz Frequency display: 3.5 digits LED display Working temperature: 10-45ºC Power requirement: 230V, 50 Hz, 1Ф Procedure: Null Balance: LVDT transducer consists of primary coil and secondary coil round on a cyclic bobbin. When the soft iron wire is put exactly in the middle and primary windings is exited equal voltage are induced in secondary windings. The differential voltage is proportional to the displacement of wire form centre. This 31
31 voltage is complicated phase directed and fed to the display. The null circuit is used to reduce the finite output to minimum. Now the core is slightly moved so that further reduction in value is got. By alternatively adjusting the core position and null ball potentiometer. A minimum possible null voltage will be loss than 1mv rms Zero Adjustment After adjusting the null through zero control potentiometer on the barrel is adjusted so that display range zero. Cal Adjustment After carrying but the above two adjustment a known displacement is given to the shaft of transducer and by operating CAL potentiometer for display is set to read the given displacement for the adjustment it is necessary to use LVDT calibration figure. The shaft iron core is to be used with LVDT is to be served to shaft and the calibration. The shaft can be of any non material such as a cyclic shaft or non magnetic material stainless steel. Tabulation: S.NO MICROMETER READING LVDT READING ERROR=LVDT READING- MICROMETER READING Result: Thus the displacement was determined by using LVDT and graph was plotted. 32
32 Ex No: Date : MEASUREMENT OF VIBRATION PARAMETERS USING VIBRATION SET UP Aim: To study the various parameters involved in the vibrations of a given system. To plot the characteristic curves of the given specimen Instruments Required: 1, Vibration exciter 2, Vibration pick-up 3, Vibration analyzer 4, Power amplifier 5, Oscillator Description: The mechanical vibration, if not within limits may cause damage to the materials, structures associated with it. Vibration exciter is an electrodynamic device. It consists of a powerful magnet placed centrally surrounding which is suspended the exciter coil. This assembly is enclosed by a high permeability magnetic circuit. When an electrical current is passed through the exciter coil, a magnetic field is created around the coil resulting in the upward or downward movement of the suspended coil depending upon the direction of the current flow in the coil. Thus controlling the frequency of the coil current, the frequency of vibration is controlled. Power amplifier is the control unit for the exciter. Piezo electric crystals produce an emf when they are deformed. This output emf may be measured to know the value of applied force and hence the pressure. 33
33 A piezo electric material is one in which an electric potential appears across certain surfaces of a crystal of the dimensions of the crystal are charged by the application of a mechanical force. The effect is reversible. Common piezo electric materials include quartz, Rochelle salt, lithium sulphate etc., Caution: Do not remove the fuse cap while power chord is connected to 230V AC mains Procedure: 1. Connect power amplifier output to vibration exciter. 2. Place the vibration pick up on vibration exciter spindle. 3. Connect vibration pick up cable to vibration analyzer sensor socket. 4. Select the range by two way switch. 5. Note down the displacement, velocity and acceleration from vibration analyzer. 6. Similarly noted above parameters in frequency range of Hz. S.No Frequency (Hz) Displacement Velocity (cm/sec) Acceleration (m/sec 2 )
34 Result: Various parameters of vibration such as displacement, velocity and acceleration are studied and the following characteristic curves were plotted. 1. Displacement Vs Frequency = 2. Velocity Vs Frequency = 3. Acceleration Vs Frequency = 35
35 Ex No: Date : MEASUREMENT OF STRAIGHTNESS AND FLATNESS USING TWO AXIS AUTO COLLIMATOR Aim: To measure the straightness and Flatness given specimen using two axis auto collimator. Instruments required: Procedure: Collimator unit, Base, plain reflector, optical Scanner Formulae: 1. Testing square with auto collimator. 2. Level auto collimator unit on a stand a table. 3. Straighten the light. 4. Observe measuring graphical through the eye below. 5. The smallest discussion of linear scale is measured. 6. Bring plain reflector in front of the auto collimator to get reflector. 7. Depending upon the verification in surface. 8. Using micrometer provided for eye piece we can measure the frequency up in lose. Deviation = Sin θ (A-B) Parallel to the Axis: Where angle θ in rad & Distance A-B in mm S.No. Distance from ref A- B ( mm) MSR (Min) Micrometer (Sec) Result - θ degree Deviations 1 36
36 Perpendicular to the Axis: Sl.no Distance from ref A- B ( mm) MSR (Min) Micrometer (Sec) Result - θ Degree Deviations
37 Result: Thus the straightness and Flatness are determined using autocollimator. Graph: Deviation Vs Distance from reference 38
38 Ex No: Date : FORCE MEASUREMENT Aim: To measure the force using load cell. Instruments Required: 1. Proving Ring 2. Load cell 3. Force indicator 4. Screw jack 5. Dial gauge. 6. Capacity of proving Ring =2.5 KN. Description: Force is one of the major derived parameter having fundamental dimension of mass length and time. It is a vector quantity which, when applied result in a change of momentum in a body. Basically mechanical force is created due to variation of started potential energy. This is different types of load cell like column type, shear type, s-type, and compression type. In this setup, s-type load cell is provided. Procedure: 1. Ensure that proving ring along with load all is perfectly in vertical position. 2. Check and ensure that the axis of screw jacks perfectly aligned with load cell. 3. Ensure that load cell with socket is connected to the rear side of the load indicator. 4. Apply a small load without any slip in the system. 5. Note down the reading of dial gauge of force indicator. 39
39 Sl.no Actual load applied (kg) Deflection (div) 1 division = 0.002mm Result: Thus the force measurement has been measured using load cell. Graph: Deflection Vs Applied load 40
40 Ex No: Date : TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT Aim: To measure the temperature using copper constantan thermo couple. Instruments Required: 1. Thermo couple 2. Temperature measuring setup. 3. Ice cubes. Procedure: 1. Connect the thermocouple supplied at the input terminal if copper constantan Thermocouple is used. Copper wire must be connected to the terminal and constantan wire to ve terminal. 2. Immerse the junction of thermocouple in ice and adjust the meter reading at 0 C using potentiometer. 3. Immerse the junction of thermocouple in boiling at 98 C by using Potentiometer marked max. 4. Repeat the procedure for 2 to 3 times. Sl.No Actual temperature C Indicated temperature C 41
41 Result: Thus the temperature is measured using thermocouple. Graph: Indicated Temperature Vs Actual Temperature 42
42 Ex No: Date : MEASUREMENT OF DIMENSION OF GIVEN SPECIMEN USING TOOL MAKER S MICROSCOPE Aim: To measure various dimension of a given specimen using Tool maker s microscope. Instruments Required: Procedure: Tool maker s microscope, Specimen, Eyepiece. 1. To find the Major and Minor diameter: One end of screw thread in made to coincide with cross wire & fixed. Reading is taken. The different between readings given linear measurement. 2. Measurement of pitch: The contour is get so that the same it an screen. The reading of micrometer is noted. The reading of are subtracted & different is noted. 3. Measurement of thread angle: The screw is rotated till linear cross wire coincides with flank of thread profile. The angle of screw rotation and than the same line coincides with flank thread. 43
43 Result: The various parameters of the given specimen are measured. 44
Gear Measurement. Lecture (7) Mechanical Measurements
 18 3. Gear profile checking 2. Involute measuring machine In this method the gear is held on a mandrel and circular disc of same diameter as the base circle of gear for the measurement is fixed on the
18 3. Gear profile checking 2. Involute measuring machine In this method the gear is held on a mandrel and circular disc of same diameter as the base circle of gear for the measurement is fixed on the
Small Tool Instruments and Data Management
 Small Tool Instruments and Data Management Dial Gauge Stands Pages 268 272 Comparator Stands Pages 273 274 Joint Magnetic Stands Concentricity testers Pages 275 280 Angulometers, steel squares Pages 281
Small Tool Instruments and Data Management Dial Gauge Stands Pages 268 272 Comparator Stands Pages 273 274 Joint Magnetic Stands Concentricity testers Pages 275 280 Angulometers, steel squares Pages 281
Measuring. Affordable. Effective. Instruments
 Measuring Effective Affordable Instruments 2 Electronic Calipers 00534002 00534003 00534020 n Stainless steel frame n Thumb wheel for rapid setting n Direct Metric/Inch conversion n Accuracy to 0,02 mm
Measuring Effective Affordable Instruments 2 Electronic Calipers 00534002 00534003 00534020 n Stainless steel frame n Thumb wheel for rapid setting n Direct Metric/Inch conversion n Accuracy to 0,02 mm
1 135 teeth to rack
 1. A spur gear with 46 teeth, 2.5 module has to be cut on a column and knee type horizontal milling machine with a rotary disc type form gear milling cutter. The 2.5 module cutter no. 3 is used on a blank
1. A spur gear with 46 teeth, 2.5 module has to be cut on a column and knee type horizontal milling machine with a rotary disc type form gear milling cutter. The 2.5 module cutter no. 3 is used on a blank
Alcalab Private Limited, 3rd Floor, Ashiana Trade Centre, Adityapur, Jamshedpur, Jharkhand. Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 11 I. DIMENSIONS 1. SLIP 0.5 mm to 25 mm 0.25 μm Using Slip Gauge (K-Grade) & > 25 mm to 50 mm 0.34 μm Double Probe Comparator > 50 mm to 75 mm 0.46 μm > 75 mm to 100 mm 0.58
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 11 I. DIMENSIONS 1. SLIP 0.5 mm to 25 mm 0.25 μm Using Slip Gauge (K-Grade) & > 25 mm to 50 mm 0.34 μm Double Probe Comparator > 50 mm to 75 mm 0.46 μm > 75 mm to 100 mm 0.58
Lecture (7) on. Gear Measurement. By Dr. Emad M. Saad. Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering. Fayoum University.
 1 Lecture (7) on Gear Measurement Fayoum University By Dr. Emad M. Saad Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Dept. 2015-2016
1 Lecture (7) on Gear Measurement Fayoum University By Dr. Emad M. Saad Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Dept. 2015-2016
EXPERIMENT CALIBRATION OF 1PHASE ENERGY METER
 EXPERIMENT CALIBRATION OF PHASE ENERGY METER THEORY:- Energy Meters are integrating instruments used to measure the quantity of electrical energy supplied to a circuit in a given time. Single phase energy
EXPERIMENT CALIBRATION OF PHASE ENERGY METER THEORY:- Energy Meters are integrating instruments used to measure the quantity of electrical energy supplied to a circuit in a given time. Single phase energy
EMaSM. Principles Of Sensors & transducers
 EMaSM Principles Of Sensors & transducers Introduction: At the heart of measurement of common physical parameters such as force and pressure are sensors and transducers. These devices respond to the parameters
EMaSM Principles Of Sensors & transducers Introduction: At the heart of measurement of common physical parameters such as force and pressure are sensors and transducers. These devices respond to the parameters
TYPICAL EXPERIMENTS Centers of gravity. Force triangle. Force polygon and Bow s Notation. Non- concurrent forces.
 MM 500-001 BASIC PANEL The panel is made from a perforated stainless steel sheet mounted on two supports with adjustable footings. The panel can be tilted, put in portrait or landscape position. Accessories
MM 500-001 BASIC PANEL The panel is made from a perforated stainless steel sheet mounted on two supports with adjustable footings. The panel can be tilted, put in portrait or landscape position. Accessories
To study the constructional features of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter and energymeter.
 Experiment o. 1 AME OF THE EXPERIMET To study the constructional features of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter and energymeter. OBJECTIVE 1. To be conversant with the constructional detail and working of common
Experiment o. 1 AME OF THE EXPERIMET To study the constructional features of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter and energymeter. OBJECTIVE 1. To be conversant with the constructional detail and working of common
Small Tool Instruments and Data Management
 Small Tool Instruments and Data Management Digital Micrometers Pages 28 34 Analogue Micrometers Pages 35 42 Special Version Micrometers Pages 43 63 External screw type micrometers accessories Pages 65
Small Tool Instruments and Data Management Digital Micrometers Pages 28 34 Analogue Micrometers Pages 35 42 Special Version Micrometers Pages 43 63 External screw type micrometers accessories Pages 65
Cal-Tech Calibration Services Pvt. Ltd., Flat No.8, Avadhut Heights, Anand Nagar, Sinhgad Road, Pune, Maharashtra
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 5 I. DIMENSION 1. CALIPER $ L.C. :-10 µm 0 to 300 mm 12.0 µm Using Caliper Checker; Gauge 0 to 1000 mm 12.0 µm Block Set L.C. :-20 µm 0 to 600 mm 16.0 µm 0 to 1000 mm 20.0 µm
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 5 I. DIMENSION 1. CALIPER $ L.C. :-10 µm 0 to 300 mm 12.0 µm Using Caliper Checker; Gauge 0 to 1000 mm 12.0 µm Block Set L.C. :-20 µm 0 to 600 mm 16.0 µm 0 to 1000 mm 20.0 µm
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere. Lecture 25 Introduction of Gears
 Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 25 Introduction of Gears I welcome you for the series of lecture on gear measurement and at module
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 25 Introduction of Gears I welcome you for the series of lecture on gear measurement and at module
Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations
 Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations Page 1 of 8 EQUIPMENT Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations 2 Rotary Motion Sensors CI-6538 1 Mechanical Oscillator/Driver ME-8750 1 Chaos Accessory CI-6689A 1 Large Rod
Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations Page 1 of 8 EQUIPMENT Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations 2 Rotary Motion Sensors CI-6538 1 Mechanical Oscillator/Driver ME-8750 1 Chaos Accessory CI-6689A 1 Large Rod
Caliber Gauges & Instruments Laboratory, S. No. 14/1, Dattadigamber Soc. B, Warje Jakat Naka, Pune, Maharashtra
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 10 I. DIMENSION (Basic Measuring, Gauge etc.) 1. PLAIN PLUG / WIDTH/ DEPTH/ Upto 100 mm 1.9 µm Using Electronic FLUSH PIN GAUGE DIAMETER /WIDTH / DEPTH $ 100 mm to 300 mm 3.8
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 10 I. DIMENSION (Basic Measuring, Gauge etc.) 1. PLAIN PLUG / WIDTH/ DEPTH/ Upto 100 mm 1.9 µm Using Electronic FLUSH PIN GAUGE DIAMETER /WIDTH / DEPTH $ 100 mm to 300 mm 3.8
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
Experimental Question 1: Levitation of Conductors in an Oscillating Magnetic Field
 Experimental Question 1: Levitation of Conductors in an Oscillating Magnetic Field In an oscillating magnetic field of sufficient strength, levitation of a metal conductor becomes possible. The levitation
Experimental Question 1: Levitation of Conductors in an Oscillating Magnetic Field In an oscillating magnetic field of sufficient strength, levitation of a metal conductor becomes possible. The levitation
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Faraday s Law and Dynamo. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Faraday s Law and Dynamo Your name Lab section 1. What do you investigate in this lab? 2. In a dynamo, the coil is wound with N=100 turns of wire and has an area A=0.0001 m 2. The
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Faraday s Law and Dynamo Your name Lab section 1. What do you investigate in this lab? 2. In a dynamo, the coil is wound with N=100 turns of wire and has an area A=0.0001 m 2. The
Basic Instruments Introduction Classification of instruments Operating principles Essential features of measuring
 Basic Instruments www.worldwebsites8.blogspot.com Introduction Classification of instruments Operating principles Essential features of measuring instruments PMMC Instruments Moving Iron instruments Introduction
Basic Instruments www.worldwebsites8.blogspot.com Introduction Classification of instruments Operating principles Essential features of measuring instruments PMMC Instruments Moving Iron instruments Introduction
Page : 1 of 16. FIELD OF TESTING : Calibration and Measurement CALIBRATION & MEASUREMENT CAPABILITY EXPRESSED AS AN UNCERTAINITY *
 Metrix Precision Pte Ltd Certificate No. : LA-2014-0581-C No. 23 Tagore Lane #02-03/04 Tagore 23 Warehouse Issue No. : 2 Singapore 787601 Date : 29 July 2016 FIELD OF TESTING : Calibration and Measurement
Metrix Precision Pte Ltd Certificate No. : LA-2014-0581-C No. 23 Tagore Lane #02-03/04 Tagore 23 Warehouse Issue No. : 2 Singapore 787601 Date : 29 July 2016 FIELD OF TESTING : Calibration and Measurement
Theory of Machines II EngM323 Laboratory User's manual Version I
 Theory of Machines II EngM323 Laboratory User's manual Version I Table of Contents Experiment /Test No.(1)... 2 Experiment /Test No.(2)... 6 Experiment /Test No.(3)... 12 EngM323 Theory of Machines II
Theory of Machines II EngM323 Laboratory User's manual Version I Table of Contents Experiment /Test No.(1)... 2 Experiment /Test No.(2)... 6 Experiment /Test No.(3)... 12 EngM323 Theory of Machines II
Linear Shaft Motors in Parallel Applications
 Linear Shaft Motors in Parallel Applications Nippon Pulse s Linear Shaft Motor (LSM) has been successfully used in parallel motor applications. Parallel applications are ones in which there are two or
Linear Shaft Motors in Parallel Applications Nippon Pulse s Linear Shaft Motor (LSM) has been successfully used in parallel motor applications. Parallel applications are ones in which there are two or
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
Lecture 3.3. Velocity, motion, force and pressure sensors
 1. Tachogenerator Lecture 3.3 Velocity, motion, force and pressure sensors Figure 2.4.1 Principle of working of Techogenerator[1] Tachogenerator works on the principle of variable reluctance. It consists
1. Tachogenerator Lecture 3.3 Velocity, motion, force and pressure sensors Figure 2.4.1 Principle of working of Techogenerator[1] Tachogenerator works on the principle of variable reluctance. It consists
Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date Certificate Number C-0752 Valid Until Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6 I DIMENSION 1. Caliper $ (Vernier/Dial/Digital) LC : 0.01mm 0 to 600 mm 0 to 1000 mm 12.2 µm 13.3 µm Using Caliper Checker, Slip Gauge Block & 2. Depth Caliper $ (Vernier/Dial/Digital)
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6 I DIMENSION 1. Caliper $ (Vernier/Dial/Digital) LC : 0.01mm 0 to 600 mm 0 to 1000 mm 12.2 µm 13.3 µm Using Caliper Checker, Slip Gauge Block & 2. Depth Caliper $ (Vernier/Dial/Digital)
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train
 Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
S-SERIES DISPLACEMENT TRANSDUCERS
 user manual S-SERIES DISPLACEMENT TRANSDUCERS Index Section Title Page 1.0 Introduction.................. 3 2.0 Installation................... 4 2.1 Mounting the Transducer........ 4 2.2 Cores.......................
user manual S-SERIES DISPLACEMENT TRANSDUCERS Index Section Title Page 1.0 Introduction.................. 3 2.0 Installation................... 4 2.1 Mounting the Transducer........ 4 2.2 Cores.......................
Q-Tech Engineering Services, S-134, C/o, Precision Engineering Works, MIDC, Bhosari, Pune, Maharashtra
 Last Amended on 24.05.2015 Page 1 of 5 I. DIMENSION 1. EXTERNAL MICROMETER $ L.C. 1 µm Φ >100 mm to 300 mm 1.4 µm 3.0 µm Using Slip Gauge Blocks Gr '0' / Long Slip Gauges, by Comparison 2. DEPTH MICROMETER
Last Amended on 24.05.2015 Page 1 of 5 I. DIMENSION 1. EXTERNAL MICROMETER $ L.C. 1 µm Φ >100 mm to 300 mm 1.4 µm 3.0 µm Using Slip Gauge Blocks Gr '0' / Long Slip Gauges, by Comparison 2. DEPTH MICROMETER
Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date Certificate Number C-0393 Valid Until Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6 I. DIMENSION 1. Vernier Caliper (Digital/ Dial/ Scale) $ L.C.: 0.01 mm 0 to 150 mm 7.7 µm Using Caliper Checker 0 to 200 mm 8.1 µm 0 to 300 mm 9.3 µm 0 to 600 mm 13.9 µm 2.
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6 I. DIMENSION 1. Vernier Caliper (Digital/ Dial/ Scale) $ L.C.: 0.01 mm 0 to 150 mm 7.7 µm Using Caliper Checker 0 to 200 mm 8.1 µm 0 to 300 mm 9.3 µm 0 to 600 mm 13.9 µm 2.
SHOCK ABSORBER/DAMPER TESTING MACHINE
 SHOCK ABSORBER/DAMPER TESTING MACHINE Dampening force of a shock absorber is directly proportional to velocity and this parameter needs to be precisely controlled. A small variation of 1mm in a stroke
SHOCK ABSORBER/DAMPER TESTING MACHINE Dampening force of a shock absorber is directly proportional to velocity and this parameter needs to be precisely controlled. A small variation of 1mm in a stroke
Price List. Calibration Fee
 3/4-5 Moo 3, Klong 5, Klong Luang, Pathumthani, 110, Thailand Tel. +66 577 5100 (Please contact : Customer Service Section Ext. 3101, 310) Fax. +66 577 3659 E-mail : cs@nimt.or.th Website : http://www.nimt.or.th
3/4-5 Moo 3, Klong 5, Klong Luang, Pathumthani, 110, Thailand Tel. +66 577 5100 (Please contact : Customer Service Section Ext. 3101, 310) Fax. +66 577 3659 E-mail : cs@nimt.or.th Website : http://www.nimt.or.th
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
Introduction. // Points of contact Standard pressure angel is pressure angle available on request
 Introduction The use of specially adapted thread grinding machines gives our rack a highly accurate helicoidal tooth profile which provides two distinct advantages - very good pitch accuracy and sufficient
Introduction The use of specially adapted thread grinding machines gives our rack a highly accurate helicoidal tooth profile which provides two distinct advantages - very good pitch accuracy and sufficient
SHAFT ALIGNMENT FORWARD
 Service Application Manual SAM Chapter 630-76 Section 24 SHAFT ALIGNMENT FORWARD One of the basic problems of any installation is aligning couplings or shafts. Therefore, this section will endeavor to
Service Application Manual SAM Chapter 630-76 Section 24 SHAFT ALIGNMENT FORWARD One of the basic problems of any installation is aligning couplings or shafts. Therefore, this section will endeavor to
UNIT-5 MEASUREMENT OF SPEDD, ACCLERATION AND VIBRATION
 UNIT-5 MEASUREMENT OF SPEDD, ACCLERATION AND VIBRATION Introduction: Speed is a rate variable defined as the time-rate of motion. Common forms and units of speed measurement include: linear speed expressed
UNIT-5 MEASUREMENT OF SPEDD, ACCLERATION AND VIBRATION Introduction: Speed is a rate variable defined as the time-rate of motion. Common forms and units of speed measurement include: linear speed expressed
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS LABORATROY MANUAL
 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS LABORATROY MANUAL K CHAITANYA Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering A. NARESH KUMAR Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electrical
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS LABORATROY MANUAL K CHAITANYA Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering A. NARESH KUMAR Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electrical
(POWER TRANSMISSION Methods)
 UNIT-5 (POWER TRANSMISSION Methods) It is a method by which you can transfer cyclic motion from one place to another or one pulley to another pulley. The ways by which we can transfer cyclic motion are:-
UNIT-5 (POWER TRANSMISSION Methods) It is a method by which you can transfer cyclic motion from one place to another or one pulley to another pulley. The ways by which we can transfer cyclic motion are:-
Accurate Measurements, Plot No.103, D Block, Meethapur Ext., Badarpur, New Delhi. Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date
 Last Amended on 11.11.2014 Page 1 of 6 I. DIMENSION 1. Dial/ Digital Vernier Caliper $ L.C.: 0.01mm Φ 0 to 200 mm 7.5 µm Using Slip Gauge Set & L.C.: 0.01mm Φ 0 to 300 mm 12.17 µm Using Slip Gauges & Caliper
Last Amended on 11.11.2014 Page 1 of 6 I. DIMENSION 1. Dial/ Digital Vernier Caliper $ L.C.: 0.01mm Φ 0 to 200 mm 7.5 µm Using Slip Gauge Set & L.C.: 0.01mm Φ 0 to 300 mm 12.17 µm Using Slip Gauges & Caliper
Ball Bearing Positioners miniature and standard
 all earing Positioners miniature and standard Parker Daedal precision linear stages provide controlled, precise pointto-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
all earing Positioners miniature and standard Parker Daedal precision linear stages provide controlled, precise pointto-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
A.A. Calibration Pvt. Ltd., 13-C/18, Vasundhara Haat, Vasundhara, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh. Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date
 Last Amended on 02.09.2014 Page 1 of 10 I. DIMENSION 1. VERNIER CALIPER $ L.C. 0.01mm 0 to 300 mm 0 to 600 mm 0 to 1000 mm 8 µm 14 µm 16 µm, Slip Gauge Accessories, Gauge Block L.C. 0.02 mm 0 to 1500 mm
Last Amended on 02.09.2014 Page 1 of 10 I. DIMENSION 1. VERNIER CALIPER $ L.C. 0.01mm 0 to 300 mm 0 to 600 mm 0 to 1000 mm 8 µm 14 µm 16 µm, Slip Gauge Accessories, Gauge Block L.C. 0.02 mm 0 to 1500 mm
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 6 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 06.01 Electromagnetic induction When the magnetic flux linked with a coil or conductor changes, an emf is developed in it. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
6 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 06.01 Electromagnetic induction When the magnetic flux linked with a coil or conductor changes, an emf is developed in it. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
200 m IP67. Partner for specialist retailers. Precision Offers. In Germany at home in demand worldwide. valid until
 3 1 4. 9 4 5 20.- L E st! A S s la n O tock w hile s 200 m m IP67 Partner for specialist retailers Precision Offers In Germany at home in demand worldwide valid until 31.08.2016 1 CALIPERS Pocket vernier
3 1 4. 9 4 5 20.- L E st! A S s la n O tock w hile s 200 m m IP67 Partner for specialist retailers Precision Offers In Germany at home in demand worldwide valid until 31.08.2016 1 CALIPERS Pocket vernier
INDEX. PAGE Adjustment mechanism for radial position of block on rotating
 INDEX Adjustment mechanism for radial position of block on rotating arm 520 Amplifying mechanism for precision measuring instruments--491 Angular movement, crank and link mechanisms for increasing 251,
INDEX Adjustment mechanism for radial position of block on rotating arm 520 Amplifying mechanism for precision measuring instruments--491 Angular movement, crank and link mechanisms for increasing 251,
Displacement Sensor. Model 8739, 8740, 8741
 w Technical Product Information Displacement Sensor 1. Introduction... 2 2. Preparations for use... 2 2.1 Unpacking... 2 2.2 Grounding and potential connection... 2 2.3 Storage... 2 3. Principle of operation...
w Technical Product Information Displacement Sensor 1. Introduction... 2 2. Preparations for use... 2 2.1 Unpacking... 2 2.2 Grounding and potential connection... 2 2.3 Storage... 2 3. Principle of operation...
Standard Scales SERIES 182 Made of Low-Expansion Glass. Working Standard Scales SERIES 182 E-32
 Standard Scales SERIES 182 Made of Low-Expansion Glass High-precision glass scales manufactured under Mitutoyo s leading-edge Linear Scale production technology. High accuracy is guaranteed to be used
Standard Scales SERIES 182 Made of Low-Expansion Glass High-precision glass scales manufactured under Mitutoyo s leading-edge Linear Scale production technology. High accuracy is guaranteed to be used
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 Schedule of ccreditation United Kingdom ccreditation Service ccredited to Division of Cromwell Tools Ltd Services Block 65 Chartwell Drive Wigston Leicester LE18 2FS Contact: Mr T still Tel: +44 (0)116-2572396
Schedule of ccreditation United Kingdom ccreditation Service ccredited to Division of Cromwell Tools Ltd Services Block 65 Chartwell Drive Wigston Leicester LE18 2FS Contact: Mr T still Tel: +44 (0)116-2572396
Ball Bearing Positioners miniature and standard
 all earing Positioners miniature and standard Parker Daedal precision linear stages provide controlled, precise pointto-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
all earing Positioners miniature and standard Parker Daedal precision linear stages provide controlled, precise pointto-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute, Mahatma Gandhi Avenue, Durgapur, West Bengal
 Last Amended on 23.09.2014 Page 1 of 9 I. DIMENSION 1. GAUGE BLOCKS $ 0.5 mm to 25 mm 25 mm to 50 mm 50 mm to 75 mm 75 mm to 100 mm 2. LENGTH BAR $ Upto 300 mm 300 mm to 600 mm 300 mm to 1000 mm 0.11µm
Last Amended on 23.09.2014 Page 1 of 9 I. DIMENSION 1. GAUGE BLOCKS $ 0.5 mm to 25 mm 25 mm to 50 mm 50 mm to 75 mm 75 mm to 100 mm 2. LENGTH BAR $ Upto 300 mm 300 mm to 600 mm 300 mm to 1000 mm 0.11µm
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 Schedule of ccreditation United Kingdom ccreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK ccredited to Laboratory locations: Unit 9 G B Quality ssurance (Consultants)
Schedule of ccreditation United Kingdom ccreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK ccredited to Laboratory locations: Unit 9 G B Quality ssurance (Consultants)
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Code No: R05310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Multimar. Universal Gage 844 T for external and internal dimensions
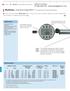 - 10-4 Multimar. Universal Gage 844 T for external and internal dimensions The Universal Gage Multimar 844 T. Easy to use and versatile; ideal for all your measuring requirements in dimensional metrology.
- 10-4 Multimar. Universal Gage 844 T for external and internal dimensions The Universal Gage Multimar 844 T. Easy to use and versatile; ideal for all your measuring requirements in dimensional metrology.
1. This question is about electrical energy and associated phenomena.
 1. This question is about electrical energy and associated phenomena. Electromagnetism The current in the circuit is switched on. electromagnet State Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction and use
1. This question is about electrical energy and associated phenomena. Electromagnetism The current in the circuit is switched on. electromagnet State Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction and use
Chapter 3. Transmission Components
 Chapter 3. Transmission Components The difference between machine design and structure design An important design problem in a mechanical system is how to transmit and convert power to achieve required
Chapter 3. Transmission Components The difference between machine design and structure design An important design problem in a mechanical system is how to transmit and convert power to achieve required
Dial and Electronic. Indicators Gauges
 Dial and Electronic Indicators Gauges 37 AGD Group 2 2900 Electronic Indicators Innovative, Full Featured & Tough 2900 Electronic Indicators are available in a choice of configurations to meet a range
Dial and Electronic Indicators Gauges 37 AGD Group 2 2900 Electronic Indicators Innovative, Full Featured & Tough 2900 Electronic Indicators are available in a choice of configurations to meet a range
ENSC387: Introduction to Electromechanical Sensors and Actuators LAB 5: DC MOTORS WARNING:
 ENSC387: Introduction to Electromechanical Sensors and Actuators LAB 5: DC MOTORS WARNING: Please be extremely cautious to precisely follow the procedures described in this manual. It is very easy to break
ENSC387: Introduction to Electromechanical Sensors and Actuators LAB 5: DC MOTORS WARNING: Please be extremely cautious to precisely follow the procedures described in this manual. It is very easy to break
STI LVDT Displacement Sensors
 STI LVDT Displacement Sensors The LVDT Still the most reliable and widely used displacement transducer available today. The best performance to cost ratio of any of its rival products in today s market.
STI LVDT Displacement Sensors The LVDT Still the most reliable and widely used displacement transducer available today. The best performance to cost ratio of any of its rival products in today s market.
Ball Bearing Positioners miniature and standard
 all earing Positioners miniature and standard Parker Daedal precision linear stages provide controlled, precise pointto-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
all earing Positioners miniature and standard Parker Daedal precision linear stages provide controlled, precise pointto-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
Measurements Lab (620451):
 Measurements Lab (620451): To introduce the practical side of actuators and sensors, also helping to understand how that device can be used. 1. INTRODUCTION FOR MEASURMENT 2. NOISE MEASUREMENT 3. PIEZO-ELECTRIC
Measurements Lab (620451): To introduce the practical side of actuators and sensors, also helping to understand how that device can be used. 1. INTRODUCTION FOR MEASURMENT 2. NOISE MEASUREMENT 3. PIEZO-ELECTRIC
Technology of Machine Tools
 PowerPoint to accompany Technology of Machine Tools 6 th Edition Krar Gill Smid Gear Cutting Unit 70 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 70-2 Objectives
PowerPoint to accompany Technology of Machine Tools 6 th Edition Krar Gill Smid Gear Cutting Unit 70 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 70-2 Objectives
Accurate Labs, 311, 312 Govinda Complex, GIDC Char Rasta, Vapi, Valsad, Gujarat. Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 9 I. DIMENSION 1. CALIPER $ Vernier L.C. 0.01mm 7.5 µm 9.0 µm Using Caliper Checker & Slip Gauges L.C. 0.05mm 29.5 µm 30.0 µm Dial / Electronic L.C. 0.02mm 12.5 µm 13.5 µm 2.
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 9 I. DIMENSION 1. CALIPER $ Vernier L.C. 0.01mm 7.5 µm 9.0 µm Using Caliper Checker & Slip Gauges L.C. 0.05mm 29.5 µm 30.0 µm Dial / Electronic L.C. 0.02mm 12.5 µm 13.5 µm 2.
Crossed Roller Bearing Positioners
 rossed Roller earing Positioners Parker Daedal precision crossed roller stages provide controlled, precise point-to-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
rossed Roller earing Positioners Parker Daedal precision crossed roller stages provide controlled, precise point-to-point positioning along a linear axis. Stages are comprised of two basic components:
LIST OF PRACTICAL FOR IX-X GRADES
 LIST OF PRACTICAL FOR IX-X GRADES Standard experiments 1 To measure the area of cross section by measuring diameter of a solid cylinder with vernier callipers. 2 To measure the volume of a solid cylinder
LIST OF PRACTICAL FOR IX-X GRADES Standard experiments 1 To measure the area of cross section by measuring diameter of a solid cylinder with vernier callipers. 2 To measure the volume of a solid cylinder
Moments. It doesn t fall because of the presence of a counter balance weight on the right-hand side. The boom is therefore balanced.
 Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE
 ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE II PRACTICAL JOURNAL DATA 1 EXPERIMENT NO. 1 AIM: TO FIND VOLTAGE RATIO OF A GIVEN TRANSFORMER. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: OBSERVATION TABLE: Sr.No. 1 2 3 4 Primary Voltage (V 1 ) Secondary
ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE II PRACTICAL JOURNAL DATA 1 EXPERIMENT NO. 1 AIM: TO FIND VOLTAGE RATIO OF A GIVEN TRANSFORMER. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: OBSERVATION TABLE: Sr.No. 1 2 3 4 Primary Voltage (V 1 ) Secondary
Lectures on mechanics
 Lectures on mechanics (lesson #3) francesco.becchi@telerobot.it LESSONS TIME TABLE (pls. take note) 28/11 h9/12- mech components 1 (3h) 4/12 h9/12 mech components 2 (3h) 11/12 h9/12 mech technologies (3h)
Lectures on mechanics (lesson #3) francesco.becchi@telerobot.it LESSONS TIME TABLE (pls. take note) 28/11 h9/12- mech components 1 (3h) 4/12 h9/12 mech components 2 (3h) 11/12 h9/12 mech technologies (3h)
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY
 135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
Instantaneous Centre Method
 Instantaneous Centre Method The combined motion of rotation and translation of the link AB may be assumed to be a motion of pure rotation about some centre I, known as the instantaneous centre of rotation.
Instantaneous Centre Method The combined motion of rotation and translation of the link AB may be assumed to be a motion of pure rotation about some centre I, known as the instantaneous centre of rotation.
Rev /07/2015 CATALOGUE - CALIBRATION SERVICES 1
 Rev. 02 07/07/2015 CATALOGUE - CALIBRATION SERVICES 1 OVER 100 ITEMS We are proud to present to you our new catalogue for 2015. In the following pages we present more than 100 instrument types, which we
Rev. 02 07/07/2015 CATALOGUE - CALIBRATION SERVICES 1 OVER 100 ITEMS We are proud to present to you our new catalogue for 2015. In the following pages we present more than 100 instrument types, which we
INDEX. 414 Agitator reversing mechanism which varies point of reversal. 250 Alternate and intermittent drive for two shafts
 INDEX Agitating device for pin hopper.----------------------------------------- 414 Agitator reversing mechanism which varies point of reversal. 250 Alternate and intermittent drive for two shafts.-----.----------.--..--
INDEX Agitating device for pin hopper.----------------------------------------- 414 Agitator reversing mechanism which varies point of reversal. 250 Alternate and intermittent drive for two shafts.-----.----------.--..--
APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat, sand paper, connecting wires.
 ACTIVITIES ACTIVITY 1 AIM To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat, sand paper,
ACTIVITIES ACTIVITY 1 AIM To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat, sand paper,
Chapter seven. Gears. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter seven Gears Laith Batarseh Gears are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts
Chapter seven Gears Laith Batarseh Gears are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts
Metrology Laboratory, CMTI, Central Manufacturing Technology Institute, Tumkur Road, Bangalore, Karnataka Accreditation Standard ISO/IEC 17025: 2005
 aboratory Metrology aboratory, CMTI, Central Manufacturing Technology ast Amended on 22.09.2016 Page 1 of 15 I. DIMENSION (Basic Measuring, Gauge etc.,) 1. ANGE GAUGE BOCKS $ 0 to 90 2.8 arc sec Using
aboratory Metrology aboratory, CMTI, Central Manufacturing Technology ast Amended on 22.09.2016 Page 1 of 15 I. DIMENSION (Basic Measuring, Gauge etc.,) 1. ANGE GAUGE BOCKS $ 0 to 90 2.8 arc sec Using
Thermal Analysis of Helical and Spiral Gear Train
 International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Thermal Analysis of Helical and Spiral Gear Train Dr. D V Ghewade a, S S Nagarale b & A N Pandav c a Principal, Department of Mechanical, GENESIS, Top-Kolhapur,
International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Thermal Analysis of Helical and Spiral Gear Train Dr. D V Ghewade a, S S Nagarale b & A N Pandav c a Principal, Department of Mechanical, GENESIS, Top-Kolhapur,
ME6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT- I (Basics of Mechanism)
 ME6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT- I (Basics of Mechanism) 1) Define resistant body. 2) Define Link or Element 3) Differentiate Machine and Structure 4) Define Kinematic Pair. 5) Define Kinematic Chain.
ME6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT- I (Basics of Mechanism) 1) Define resistant body. 2) Define Link or Element 3) Differentiate Machine and Structure 4) Define Kinematic Pair. 5) Define Kinematic Chain.
Tension and Compression Load Cell Model 8435
 Technical Product Information w Tension and Compression Load Cell 1. Introduction... 2 2. Preparing for use... 2 2.1 Unpacking... 2 2.2 Using the instrument for the first time... 2 2.3 Grounding and potential
Technical Product Information w Tension and Compression Load Cell 1. Introduction... 2 2. Preparing for use... 2 2.1 Unpacking... 2 2.2 Using the instrument for the first time... 2 2.3 Grounding and potential
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction
 Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
Metal forming machines: a new market for laser interferometers O. Beltrami STANIMUC Ente Federate UNI, via A. Vespucci 8, Tbrmo,
 Metal forming machines: a new market for laser interferometers O. Beltrami STANIMUC Ente Federate UNI, via A. Vespucci 8, Tbrmo, Abstract Laser interferometers have traditionally been a synonymous of very
Metal forming machines: a new market for laser interferometers O. Beltrami STANIMUC Ente Federate UNI, via A. Vespucci 8, Tbrmo, Abstract Laser interferometers have traditionally been a synonymous of very
Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors Jack Sauls Trane Follow this and additional
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors Jack Sauls Trane Follow this and additional
DYNAMICS LABORATORY. AIM: To apply the knowledge gained in kinematics and dynamics of machines to real system.
 DYNAMICS LABORATORY AIM: To apply the knowledge gained in kinematics and dynamics of machines to real system. OBJECTIVES: To supplement the principles learnt in kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery. To
DYNAMICS LABORATORY AIM: To apply the knowledge gained in kinematics and dynamics of machines to real system. OBJECTIVES: To supplement the principles learnt in kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery. To
CERTIFICATE OF ACCREDITATION
 CERTIFICATE OF ACCREDITATION ANSI-ASQ National Accreditation Board 500 Montgomery Street, Suite 625, Alexandria, VA 22314, 877-344-3044 This is to certify that SP Metrology System Thailand Co., LTD 88/115
CERTIFICATE OF ACCREDITATION ANSI-ASQ National Accreditation Board 500 Montgomery Street, Suite 625, Alexandria, VA 22314, 877-344-3044 This is to certify that SP Metrology System Thailand Co., LTD 88/115
Electromagnetic Induction
 Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper Level ubject Exam oard Unit Topic ooklet O Level Physics ambridge International Examinations Electricity and Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper
Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper Level ubject Exam oard Unit Topic ooklet O Level Physics ambridge International Examinations Electricity and Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper
Calitron Calibration Laboratory, U1: 207, Kohinoor Arcade, Tilak Chowk, Nigdi, Pune, Maharashtra
 Last Amended on 12.09.2014 Page 1 of 7 I. MASS 1. Weights $ (Conventional Mass) 1 mg 0.015 mg Using Weights of 2 mg 0.015 mg accuracy Class F1 and 5 mg 0.015 mg 10 mg 0.015 mg 20 mg 0.020 mg 50 mg 0.020
Last Amended on 12.09.2014 Page 1 of 7 I. MASS 1. Weights $ (Conventional Mass) 1 mg 0.015 mg Using Weights of 2 mg 0.015 mg accuracy Class F1 and 5 mg 0.015 mg 10 mg 0.015 mg 20 mg 0.020 mg 50 mg 0.020
user leaflet ANALOGUE BLOCK GAUGE
 user leaflet ANALOGUE BLOCK GAUGE 1.0 Index Section Title Page 1.0 Index....................... 2 2.0 Safety Summary............... 3 3.0 Introduction.................. 4 4.0 Components of the Block Gauge...
user leaflet ANALOGUE BLOCK GAUGE 1.0 Index Section Title Page 1.0 Index....................... 2 2.0 Safety Summary............... 3 3.0 Introduction.................. 4 4.0 Components of the Block Gauge...
Bistable Rotary Solenoid
 Bistable Rotary Solenoid The bistable rotary solenoid changes state with the application of a momentary pulse of electricity, and then remains in the changed state without power applied until a further
Bistable Rotary Solenoid The bistable rotary solenoid changes state with the application of a momentary pulse of electricity, and then remains in the changed state without power applied until a further
Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle
 Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle Addendum: The radial distance between the top land and the pitch circle. Addendum Circle: The circle defining the outer
Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle Addendum: The radial distance between the top land and the pitch circle. Addendum Circle: The circle defining the outer
Discipline Mechanical Calibration Issue Date Certificate Number C-0751 Valid Until Last Amended on
 Last Amended on 10.03.2016 Page 1 of 5 I. DIMENSION 1. Vernier caliper $ 0 to 300 mm/0.01 mm ± 12.0 µm Using Caliper Checker 0 to 300 mm/0.02 mm ± 16.1 µm Using Caliper Checker 0 to 600 mm/0.01 mm ± 14.0
Last Amended on 10.03.2016 Page 1 of 5 I. DIMENSION 1. Vernier caliper $ 0 to 300 mm/0.01 mm ± 12.0 µm Using Caliper Checker 0 to 300 mm/0.02 mm ± 16.1 µm Using Caliper Checker 0 to 600 mm/0.01 mm ± 14.0
ni.com Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series
 Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series Load, Pressure, and Torque Measurements Key Takeaways Bridge-based measurement fundamentals Load, pressure, torque fundamentals Transducer Electronic Data Sheet (TEDS)
Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series Load, Pressure, and Torque Measurements Key Takeaways Bridge-based measurement fundamentals Load, pressure, torque fundamentals Transducer Electronic Data Sheet (TEDS)
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology LABORATORY Department of Electrical And Electronics Engg. Electro-mechanical Energy Conversion II
 REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE: 1 Electro-mechanical Energy Conversion II 1. To perform no load and blocked rotor tests on a three phase squirrel cage induction motor and determine equivalent circuit. 2.
REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE: 1 Electro-mechanical Energy Conversion II 1. To perform no load and blocked rotor tests on a three phase squirrel cage induction motor and determine equivalent circuit. 2.
Pre-lab Questions: Please review chapters 19 and 20 of your textbook
 Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING
 SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING For intersecting shafts, bevel gears offer a good means of transmitting motion and power. Most transmissions occur at right angles, Figure 8-1, but the shaft angle can be any value.
SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING For intersecting shafts, bevel gears offer a good means of transmitting motion and power. Most transmissions occur at right angles, Figure 8-1, but the shaft angle can be any value.
Exercise 4-1. Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Rotameters. How do rotameter tubes work?
 Exercise 4-1 Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the basics of differential pressure flowmeters via the use of a Venturi tube and learn how to safely connect (and disconnect) a differential pressure flowmeter
Exercise 4-1 Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the basics of differential pressure flowmeters via the use of a Venturi tube and learn how to safely connect (and disconnect) a differential pressure flowmeter
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #6: Magnetic Fields
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #6: Magnetic Fields Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, March 5/7/8/9, 2018 Background Magnetic fields
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #6: Magnetic Fields Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, March 5/7/8/9, 2018 Background Magnetic fields
LIGHTWEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SHALLOW DIAMETER GAGES
 SERIES 77 For use at machine or inspection area for checking inside and outside diameters, shallow bores, counter bores, pitch diameters of gears, and many other dimensions. LIGHTWEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SHALLOW
SERIES 77 For use at machine or inspection area for checking inside and outside diameters, shallow bores, counter bores, pitch diameters of gears, and many other dimensions. LIGHTWEIGHT ADJUSTABLE SHALLOW
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
Institute for Design of Electrical Measuring Instruments, Swatantryaveer Tatya Tope Marg, Chunabhatti, Sion, Mumbai, Maharashtra
 Last Amended on 02.09.2014 Page 1 of 10 I. DIMENSION 1 Calipers $ Up to 600 mm 10.4 µm Using Caliper Checker by Up to 1000 mm 13.2 µm Using Long Slip Gauge by 2 Height Gauges $ Up to 600 mm 12.8 µm Using
Last Amended on 02.09.2014 Page 1 of 10 I. DIMENSION 1 Calipers $ Up to 600 mm 10.4 µm Using Caliper Checker by Up to 1000 mm 13.2 µm Using Long Slip Gauge by 2 Height Gauges $ Up to 600 mm 12.8 µm Using
Chapter 5. Design of Control Mechanism of Variable Suspension System. 5.1: Introduction: Objective of the Mechanism:
 123 Chapter 5 Design of Control Mechanism of Variable Suspension System 5.1: Introduction: Objective of the Mechanism: In this section, Design, control and working of the control mechanism for varying
123 Chapter 5 Design of Control Mechanism of Variable Suspension System 5.1: Introduction: Objective of the Mechanism: In this section, Design, control and working of the control mechanism for varying
R10 Set No: 1 ''' ' '' '' '' Code No: R31033
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
MECHATRONICS LAB MANUAL
 MECHATRONICS LAB MANUAL T.E.(Mechanical) Sem-VI Department of Mechanical Engineering SIESGST, Nerul, Navi Mumbai LIST OF EXPERIMENTS Expt. No. Title Page No. 1. Study of basic principles of sensing and
MECHATRONICS LAB MANUAL T.E.(Mechanical) Sem-VI Department of Mechanical Engineering SIESGST, Nerul, Navi Mumbai LIST OF EXPERIMENTS Expt. No. Title Page No. 1. Study of basic principles of sensing and
Faraday's Law of Induction
 Purpose Theory Faraday's Law of Induction a. To investigate the emf induced in a coil that is swinging through a magnetic field; b. To investigate the energy conversion from mechanical energy to electrical
Purpose Theory Faraday's Law of Induction a. To investigate the emf induced in a coil that is swinging through a magnetic field; b. To investigate the energy conversion from mechanical energy to electrical
EXPERIMENT 13 QUALITATIVE STUDY OF INDUCED EMF
 220 13-1 I. THEORY EXPERIMENT 13 QUALITATIVE STUDY OF INDUCED EMF Along the extended central axis of a bar magnet, the magnetic field vector B r, on the side nearer the North pole, points away from this
220 13-1 I. THEORY EXPERIMENT 13 QUALITATIVE STUDY OF INDUCED EMF Along the extended central axis of a bar magnet, the magnetic field vector B r, on the side nearer the North pole, points away from this
