Technology of Machine Tools
|
|
|
- Maximilian Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PowerPoint to accompany Technology of Machine Tools 6 th Edition Krar Gill Smid Gear Cutting Unit 70 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
2 70-2 Objectives Select the proper cutter for any gear to be cut Calculate gear-tooth dimensions for inch gears Calculate gear-tooth dimensions for metric gears Set up and cut a spur gear
3 70-3 Gear Cutting Usually cut to repair or replace gear broken or lost or no longer carried in inventory Industry mass-produces gears on special machines designed for this purpose Gear-shaping machines Gear-hobbing machines
4 70-4 Involute Gear Cutters Sharpened on face Ensures exact duplication of shape of teeth Regardless of how far back face of tooth has been ground Available in many sizes Range from 1 to 48 diametral pitch (DP) Special cutters for teeth smaller than 48 DP
5 70-5 Comparative Gear-Tooth Sizes: 4 to 16 DP Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
6 70-6 Gear Cutting Cutter must be chosen to suit both DP and number of teeth (N) Tooth space for small pinion cannot be same shape as tooth space for large mating gear Teeth on smaller gears must be more curved to prevent binding of meshing gear teeth Sets of gear cutters Made in series of slightly different shapes to permit cutting of any desired number of teeth with assurance that teeth will mesh with another gear(same DP)
7 70-7 Cutters Generally made in sets of eight Numbered from 1 to 8 (also in half sizes) Gradual change in shape (sides) #1 cutter with straight to #8 with curved sides Number of teeth #1 will cut teeth in gear 135 teeth to a rack #8 will cut only 12 and 13 teeth Cutter number permits a more accurate meshing of teeth (for gears to mesh must have same DP)
8 70-8 Involute Gear Cutters Cutter Number Range teeth to a rack to 134 teeth 2 55 to 134 teeth to 54 teeth 3 35 to 54 teeth to 34 teeth 4 26 to 34 teeth to 25 teeth Cutter Number Range 5 21 to 25 teeth and 20 teeth 6 17 to 20 teeth and 16 teeth 7 14 to 16 teeth teeth 8 12 and 13 teeth
9 70-9 Example: Selecting a Cutter A 10-DP gear and a pinion in mesh have 100 teeth and 24 teeth, respectively. What cutters should be used to cut these gears? Cutter Selection Since the gears are in mesh, both must be cut with a 10-DP cutter. A #2 cutter should be used to cut the teeth on the gear, since it will cut from 55 to 134 teeth. A #5 cutter should be used to cut the pinion, since it will cut from 21 to 25 teeth.
10 70-10 Procedure For Machining a Spur Gear Example: A 52-tooth gear with an 8 DP is required 1. Calculate all necessary gear data (See previous table) N a. Outside diameter = = = = in. DP b. Whole depth of tooth = = =.2697 in. DP 8 Cutter number = 3 (35 to 54 teeth) Continue
11 70-11 d. Indexing (using Cincinnati standard plate) 40 = N = = x 3 3 = 30 holes on 39 hole circle 2. Turn gear blank to proper outside diameter (6.750 in.) 3. Press gear blank firmly onto mandrel 4. Mount index head and footstock, and check the alignment of the index centers 5. Set dividing head so index pin fits into hole on 39-hole circle and sector arms set for 30 holes
12 Mount mandrel (and workpiece), with large end toward indexing head, between index centers 7. Move table close to column to keep setup as rigid as possible 8. Mount an 8 DP#3 cutter on milling machine arbor over approximate center of the gear Be sure to have cutter rotating in direction of indexing head
13 9. Center gear blank with cutter by either of the following methods: Place square against outside diameter of gear With pair of inside calipers or rule, check distance between square and side of cutter Adjust table until distances from both sides of gear blank to sides of cutter are the same More accurate method of centralizing cutter is to use gage blocks instead of inside calipers 10. LOCK THE CROSS-SLIDE 11. Start milling cutter and run work under cutter 70-13
14 Raise table until cutter just touches work 13. Set graduated feed collar on the vertical feed to zero 14. Move work clear of cutter by means of the longitudinal feed handle Raise table to 2/3 depth of tooth (.180 in.) Lock knee clamp 15. Slightly notch all gear teeth on end of work to check for correct indexing
15 Rough-out first tooth and set automatic feed trip dog after cutter is clear of work 17. Return table to starting position Clear end of work with cutter 18. Cut remaining teeth and return table to starting position 19. Loosen knee clamp, raise table to full depth of.270 in., and lock knee clamp 20. Finish-cut all teeth
16 70-16 Metric Gears Countries using metric system usually use module system of gearing Module (M) of a gear equal pitch diameter (PD) divided by number of teeth (N) M is actual dimension M = PD N Table 70.2 in text gives necessary rules and formulas for metric spur gears
17 70-17 Metric Module Gear Cutters Most common available in modules ranging from 0.5 to 10 mm Available in set of eight cutters numbered from #1 to #8 Range of each cutter reverse of DP cutter Table on next slide shows cutters available and rang of each cutter in set
18 70-18 Milling Cutter Numbers Module Size (mm) Cutter No. For Cutting to 13 teeth to 16 teeth to 20 teeth to 25 teeth to 34 teeth to 54 teeth to 134 teeth teeth to rack Metric Module Gear Cutters
19 70-19 Metric Example: A spur gear has a PD of 60 mm and 20 teeth. Calculate: 1. Module 2. Circular pitch 3. Addendum 4. Outside diameter 5. Dedendum 6. Whole depth 7. Cutter number
20 70-20 Solution: PD M= = = N 20 3mm 2. CP= M x π = 3 x = mm 3. A = M= 3 mm 4. OD= (N+ 2) x M= 22 x 3= 66 mm 5. D= M x 1.166= 3 x 1.166= mm 6. WD= M x 2.166= 3 x 2.166= mm 7. Cutter number (see previous table) = 3
21 70-21 Another Metric Example: Two identical gears in mesh have a CCD of 120 mm. Each gear has 24 teeth. Calculate: 1. Pitch diameter 2. Module 3. Outside diameter 4. Whole depth 5. Circular pitch 6. Chordal thickness
22 70-22 Solution: 2 x CD 2 x PD= = = = PD M= = = 5 N mm 3. OD= (N+ 2) x M= 26 x 5= 130 mm 4. WD= M x = 5 x 2.166= 10.83mm 5. CP= M x π = 5 x = mm M x π 5 x CT= = = 7.85 mm 2 2
23 70-23 Gear-Tooth Measurement Measure with gear tooth vernier caliper Set to corrected addendum May also be checked by measuring over wires or pins of a specific diameter placed in two diametrically opposite tooth spaces of the gear Tables in most handbooks give measurement over wires having given number of teeth and specific pressure angle
24 70-24 Gear-Tooth Measurement Accurate measurement of inch gears need diametral pitch and number of teeth of gear For metric gears, the module must be known Wire or pin size to use determined by 1. For external inch spur gears, wire or pin size equal to divided by DP of gear 2. For internal inch spur gears, wire size equal to 1.44 divided by DP of gear 3. Metric module gears measured using wire size equal to multiplied by module of gear
25 70-25 Example (Inch): Determine wire size and measurement over the wires for a 10-DP external gear having 28 teeth and a 14.50º pressure angle Wire size= =.1728 in. 10 In handbook tables, size over wires for gear having 28 teeth and 14.50º pressure angle should be in. divided by DP = = in.
Gear Engineering Data. Spur Gear Gear Formulas Drive Selection Horsepower and Torque Tables
 Engineering Gear Engineering Data Spur Gear Gear Formulas Drive Selection Horsepower and Torque Tables G-79 Gear Selection Stock Spur Gear Drive Selection When designing a stock gear drive using the horsepower
Engineering Gear Engineering Data Spur Gear Gear Formulas Drive Selection Horsepower and Torque Tables G-79 Gear Selection Stock Spur Gear Drive Selection When designing a stock gear drive using the horsepower
1 135 teeth to rack
 1. A spur gear with 46 teeth, 2.5 module has to be cut on a column and knee type horizontal milling machine with a rotary disc type form gear milling cutter. The 2.5 module cutter no. 3 is used on a blank
1. A spur gear with 46 teeth, 2.5 module has to be cut on a column and knee type horizontal milling machine with a rotary disc type form gear milling cutter. The 2.5 module cutter no. 3 is used on a blank
Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle
 Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle Addendum: The radial distance between the top land and the pitch circle. Addendum Circle: The circle defining the outer
Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle Addendum: The radial distance between the top land and the pitch circle. Addendum Circle: The circle defining the outer
Bibliography. [1] Buckingham, Earle: "Analytical Mechanics of Gears", McGraw-Hill, New York, 1949, and republished by Dover, New York, 1963.
![Bibliography. [1] Buckingham, Earle: Analytical Mechanics of Gears, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1949, and republished by Dover, New York, 1963. Bibliography. [1] Buckingham, Earle: Analytical Mechanics of Gears, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1949, and republished by Dover, New York, 1963.](/thumbs/87/96820687.jpg) Bibliography The first five references listed are books on gearing. Some of them deal not only with the geometry, but also with many other aspects of gearing. However, the books are included in this bibliography
Bibliography The first five references listed are books on gearing. Some of them deal not only with the geometry, but also with many other aspects of gearing. However, the books are included in this bibliography
Program Internal Gear Set Profile Shift Coefficients With Zero Backlash Introduction
 Program 60-107 Internal Gear Set Profile Shift Coefficients With Zero Backlash Introduction The purpose of this model is to provide data for a gear set when the tooth thickness and/or the center distance
Program 60-107 Internal Gear Set Profile Shift Coefficients With Zero Backlash Introduction The purpose of this model is to provide data for a gear set when the tooth thickness and/or the center distance
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere. Lecture 25 Introduction of Gears
 Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 25 Introduction of Gears I welcome you for the series of lecture on gear measurement and at module
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 25 Introduction of Gears I welcome you for the series of lecture on gear measurement and at module
GEAR CONTENTS POWER TRANSMISSION GEAR TYPES OF GEARS NOMENCLATURE APPLICATIONS OF GEARS VELOCITY RATIO GEAR TRAINS EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS
 GEAR CONTENTS POWER TRANSMISSION GEAR TYPES OF GEARS NOMENCLATURE APPLICATIONS OF GEARS VELOCITY RATIO GEAR TRAINS EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS GEAR.. Power transmission is the movement of energy from
GEAR CONTENTS POWER TRANSMISSION GEAR TYPES OF GEARS NOMENCLATURE APPLICATIONS OF GEARS VELOCITY RATIO GEAR TRAINS EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS GEAR.. Power transmission is the movement of energy from
SECTION 4 SPUR GEAR CALCULATIONS
 Function of α, or invα, is known as involute function. Involute function is very important in gear design. Involute function values can be obtained from appropriate tables. With the 3.1 Contact Ratio center
Function of α, or invα, is known as involute function. Involute function is very important in gear design. Involute function values can be obtained from appropriate tables. With the 3.1 Contact Ratio center
Session #3 Gears: Force Transmission & Gear Trains. Dan Frey
 Session #3 Gears: Force Transmission & Gear Trains Dan Frey Today s Agenda Pass out second reading packet Pass out loaner laptops Introduce project teams Gears Force Transmission Gear Trains Survey HW
Session #3 Gears: Force Transmission & Gear Trains Dan Frey Today s Agenda Pass out second reading packet Pass out loaner laptops Introduce project teams Gears Force Transmission Gear Trains Survey HW
12/6/2013 9:09 PM. Chapter 13. Gears General. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING
 SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING For intersecting shafts, bevel gears offer a good means of transmitting motion and power. Most transmissions occur at right angles, Figure 8-1, but the shaft angle can be any value.
SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING For intersecting shafts, bevel gears offer a good means of transmitting motion and power. Most transmissions occur at right angles, Figure 8-1, but the shaft angle can be any value.
Catalog Q Conversion For those wishing to ease themselves into working with metric gears
 1.3.4 Conversion For those wishing to ease themselves into working with metric gears by looking at them in terms of familiar inch gearing relationships and mathematics, Table 1-5 is offered as a means
1.3.4 Conversion For those wishing to ease themselves into working with metric gears by looking at them in terms of familiar inch gearing relationships and mathematics, Table 1-5 is offered as a means
Gear Measurement. Lecture (7) Mechanical Measurements
 18 3. Gear profile checking 2. Involute measuring machine In this method the gear is held on a mandrel and circular disc of same diameter as the base circle of gear for the measurement is fixed on the
18 3. Gear profile checking 2. Involute measuring machine In this method the gear is held on a mandrel and circular disc of same diameter as the base circle of gear for the measurement is fixed on the
1/2/2015 2:04 PM. Chapter 13. Gears General. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
1.8 Rack shift of the gear
 1.8 Rack shift of the gear Undercut When Number of teeth is belo minimum as shon in Fig. 3, part of dedendum is no longer an Involute curve but ill look like a shape scooped out by cutter tool. Refer to
1.8 Rack shift of the gear Undercut When Number of teeth is belo minimum as shon in Fig. 3, part of dedendum is no longer an Involute curve but ill look like a shape scooped out by cutter tool. Refer to
Chapter 8 Kinematics of Gears
 Chapter 8 Kinematics of Gears Gears! Gears are most often used in transmissions to convert an electric motor s high speed and low torque to a shaft s requirements for low speed high torque: Speed is easy
Chapter 8 Kinematics of Gears Gears! Gears are most often used in transmissions to convert an electric motor s high speed and low torque to a shaft s requirements for low speed high torque: Speed is easy
11. GEAR TRANSMISSIONS
 11. GEAR TRANSMISSIONS 11.1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS Gears are one of the most important elements used in machinery. There are few mechanical devices that do not have the need to transmit power and motion
11. GEAR TRANSMISSIONS 11.1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS Gears are one of the most important elements used in machinery. There are few mechanical devices that do not have the need to transmit power and motion
Chain Drives. Pitch. Basic Types -There are six major types of power-
 1 2 Power transmission chains have two things in common; side bars or link plates, and pin and bushing joints. The chain articulates at each joint to operate around a toothed sprocket. The pitch of the
1 2 Power transmission chains have two things in common; side bars or link plates, and pin and bushing joints. The chain articulates at each joint to operate around a toothed sprocket. The pitch of the
Lecture (7) on. Gear Measurement. By Dr. Emad M. Saad. Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering. Fayoum University.
 1 Lecture (7) on Gear Measurement Fayoum University By Dr. Emad M. Saad Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Dept. 2015-2016
1 Lecture (7) on Gear Measurement Fayoum University By Dr. Emad M. Saad Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Dept. 2015-2016
The Geometry of Involute Gears
 The Geometry of Involute Gears J.R. Colbourne The Geometry of Involute Gears With 217 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo J.R. Colbourne Department of Mechanical
The Geometry of Involute Gears J.R. Colbourne The Geometry of Involute Gears With 217 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo J.R. Colbourne Department of Mechanical
Finite element analysis of profile modified spur gear
 Finite element analysis of profile modified spur gear Sagar Gaur Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, YashluvVirwani Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Rudresh
Finite element analysis of profile modified spur gear Sagar Gaur Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, YashluvVirwani Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Rudresh
CH#13 Gears-General. Drive and Driven Gears 3/13/2018
 CH#13 Gears-General A toothed wheel that engages another toothed mechanism in order to change the speed or direction of transmitted motion The gear set transmits rotary motion and force. Gears are used
CH#13 Gears-General A toothed wheel that engages another toothed mechanism in order to change the speed or direction of transmitted motion The gear set transmits rotary motion and force. Gears are used
INVOLUTE SPIRAL FACE COUPLINGS AND GEARS: DESIGN APPROACH AND MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE
 УДК 621.9.015 Dr. Alexander L. Kapelevich, Stephen D. Korosec 38 INVOLUTE SPIRAL FACE COUPLINGS AND GEARS: DESIGN APPROACH AND MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE This paper presents spiral face gears with an involute
УДК 621.9.015 Dr. Alexander L. Kapelevich, Stephen D. Korosec 38 INVOLUTE SPIRAL FACE COUPLINGS AND GEARS: DESIGN APPROACH AND MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE This paper presents spiral face gears with an involute
Introduction to Gear Design
 Introduction to Gear Design Course No: M03-016 Credit: 3 PDH Robert P. Tata, P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Introduction to Gear Design Course No: M03-016 Credit: 3 PDH Robert P. Tata, P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Martin Sprocket & Gear, Inc.
 GEAR MANUAL Published by Martin Sprocket & Gear, Inc. Dave Walton, Technical Advisor TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.....................................1 Work.......................................2 Power......................................2
GEAR MANUAL Published by Martin Sprocket & Gear, Inc. Dave Walton, Technical Advisor TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.....................................1 Work.......................................2 Power......................................2
Sheet 1 Variable loading
 Sheet 1 Variable loading 1. Estimate S e for the following materials: a. AISI 1020 CD steel. b. AISI 1080 HR steel. c. 2024 T3 aluminum. d. AISI 4340 steel heat-treated to a tensile strength of 1700 MPa.
Sheet 1 Variable loading 1. Estimate S e for the following materials: a. AISI 1020 CD steel. b. AISI 1080 HR steel. c. 2024 T3 aluminum. d. AISI 4340 steel heat-treated to a tensile strength of 1700 MPa.
Engineering Information
 Engineering nformation Gear Nomenclature ADDENDUM (a) is the height by which a tooth projects beyond the pitch circle or pitch line. BASE DAMETER (D b ) is the diameter of the base cylinder from which
Engineering nformation Gear Nomenclature ADDENDUM (a) is the height by which a tooth projects beyond the pitch circle or pitch line. BASE DAMETER (D b ) is the diameter of the base cylinder from which
GEAR GENERATION GEAR FORMING. Vipin K. Sharma
 GEAR GENERATION GEAR FORMING 1 GEAR MANUFACTURING Manufacturing of gears needs several processing operations in sequential stages depending upon the material and type of the gears and quality desired.
GEAR GENERATION GEAR FORMING 1 GEAR MANUFACTURING Manufacturing of gears needs several processing operations in sequential stages depending upon the material and type of the gears and quality desired.
Part VII: Gear Systems: Analysis
 Part VII: Gear Systems: Analysis This section will review standard gear systems and will provide the basic tools to perform analysis on these systems. The areas covered in this section are: 1) Gears 101:
Part VII: Gear Systems: Analysis This section will review standard gear systems and will provide the basic tools to perform analysis on these systems. The areas covered in this section are: 1) Gears 101:
INCREASE IN FATIGUE LIFE OF SPUR GEAR BY INTRODUCING CIRCULAR STRESS RELIEVING FEATURE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET), ISSN 0976 6340(Print), ISSN 0976 6359(Online), Volume TECHNOLOGY 6, Issue 5,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET), ISSN 0976 6340(Print), ISSN 0976 6359(Online), Volume TECHNOLOGY 6, Issue 5,
Index SECTION L PLASTICS
 Index SECTION L PLASTICS PRODUCT PAGE SECTION I NON-METALLIC SPROCKETS.... L-2 L-30 SPROCKETS - STOCK NO. 25 ¼" PITCH...L-5 NO. 35 3 8" PITCH...L-6 NO. 40 ½" PITCH...L-7 NO. 50 5 8" PITCH...L-8 NO. 60
Index SECTION L PLASTICS PRODUCT PAGE SECTION I NON-METALLIC SPROCKETS.... L-2 L-30 SPROCKETS - STOCK NO. 25 ¼" PITCH...L-5 NO. 35 3 8" PITCH...L-6 NO. 40 ½" PITCH...L-7 NO. 50 5 8" PITCH...L-8 NO. 60
Tooth thickness Dedendum. Addendum. Centre distance Nominal
 FORMULAS SPUR GEARS TO FIND:- PCD ØD MODULE No. of TEETH CP ADDENDUM DEDENDUM MODULE No. of TEETH x MOD (mm) (No. of TEETH + ) x MOD (mm) 5.4 MODULE CP π (mm) PCD MODULE (mm) MODULE x π (mm) MODULE (mm)
FORMULAS SPUR GEARS TO FIND:- PCD ØD MODULE No. of TEETH CP ADDENDUM DEDENDUM MODULE No. of TEETH x MOD (mm) (No. of TEETH + ) x MOD (mm) 5.4 MODULE CP π (mm) PCD MODULE (mm) MODULE x π (mm) MODULE (mm)
Simple Gears and Transmission
 Simple Gears and Transmission Simple Gears and Transmission page: of 4 How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be?
Simple Gears and Transmission Simple Gears and Transmission page: of 4 How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be?
T25 T25 T25 T27 T27 T28 T28 T28 T28 T29 T29 T29 T31 T37 T37 T38 T T T48
 1.0 INTRODUCTION 2.0 BASIC GEOMETRY OF SPUR GEARS 2.1 Basic Spur Gear Geometry 2.2 The Law of Gearing 2.3 The Involute Curve 2.4 Pitch Circles 2.5 Pitch 2.5.1 Circular Pitch 2.5.2 Diametral Pitch 2.5.3
1.0 INTRODUCTION 2.0 BASIC GEOMETRY OF SPUR GEARS 2.1 Basic Spur Gear Geometry 2.2 The Law of Gearing 2.3 The Involute Curve 2.4 Pitch Circles 2.5 Pitch 2.5.1 Circular Pitch 2.5.2 Diametral Pitch 2.5.3
Simple Gears and Transmission
 Simple Gears and Transmission Contents How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be? Initial Problem Statement 2 Narrative
Simple Gears and Transmission Contents How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be? Initial Problem Statement 2 Narrative
Siddhant Dange 1, Saket Sant 2, Anish Sali 3, Parthan Pethodam 4, Mr. Sandeep Belgamwar 5
 International Journal of Latest Research in Engineering and Technology (IJLRET) ISSN: 2454-5031 ǁ Volume 2 Issue 4ǁ April 2016 ǁ PP 41-45 Design and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox for Industrial Concrete
International Journal of Latest Research in Engineering and Technology (IJLRET) ISSN: 2454-5031 ǁ Volume 2 Issue 4ǁ April 2016 ǁ PP 41-45 Design and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox for Industrial Concrete
2. a) What is pantograph? What are its uses? b) Prove that the peaucellier mechanism generates a straight-line motion. (5M+10M)
 Code No: R22032 R10 SET - 1 1. a) Define the following terms? i) Link ii) Kinematic pair iii) Degrees of freedom b) What are the inversions of double slider crank chain? Describe any two with neat sketches.
Code No: R22032 R10 SET - 1 1. a) Define the following terms? i) Link ii) Kinematic pair iii) Degrees of freedom b) What are the inversions of double slider crank chain? Describe any two with neat sketches.
Basic Fundamentals of Gear Drives
 Basic Fundamentals of Gear Drives Course No: M06-031 Credit: 6 PDH A. Bhatia Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Basic Fundamentals of Gear Drives Course No: M06-031 Credit: 6 PDH A. Bhatia Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
A Study on Noncircular Gears with Non-Uniform Teeth
 A Study on Noncircular Gears with Non-Uniform Teeth Kazushi Kumagai* 1 and Tetsuya Oizumi* *1 Department of Infomation System, Sendai National College of Technology 4-16-1 Ayashi-Chuo, Aoba-ku, Sendai
A Study on Noncircular Gears with Non-Uniform Teeth Kazushi Kumagai* 1 and Tetsuya Oizumi* *1 Department of Infomation System, Sendai National College of Technology 4-16-1 Ayashi-Chuo, Aoba-ku, Sendai
Set your Mobile Phones to Silent Respect your colleagues no private conversations Be on time
 Set your Mobile Phones to Silent Respect your colleagues no private conversations Be on time E. Francalanza 1 Thread Applications Thread Manufacturing Thread Design Thread Gaging Thread Measurement CMMs
Set your Mobile Phones to Silent Respect your colleagues no private conversations Be on time E. Francalanza 1 Thread Applications Thread Manufacturing Thread Design Thread Gaging Thread Measurement CMMs
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
Bevel Gears. Fig.(1) Bevel gears
 Bevel Gears Bevel gears are cut on conical blanks to be used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts. The simplest bevel gear type is the straighttooth bevel gear or straight bevel gear as can be
Bevel Gears Bevel gears are cut on conical blanks to be used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts. The simplest bevel gear type is the straighttooth bevel gear or straight bevel gear as can be
Marine Engineering Exam Resource Review of Couplings
 1. What are rigid couplings used for? Used to join drive shafts together. True alignment and rigidity are required. Example Drive shafts and production lines, bridge cranes, solid shaft that needs to be
1. What are rigid couplings used for? Used to join drive shafts together. True alignment and rigidity are required. Example Drive shafts and production lines, bridge cranes, solid shaft that needs to be
Introduction. Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines. Involute profile. 7. Gears
 Introduction The kinematic function of gears is to transfer rotational motion from one shaft to another Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines 7. Gears Since these shafts may be parallel, perpendicular, or
Introduction The kinematic function of gears is to transfer rotational motion from one shaft to another Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines 7. Gears Since these shafts may be parallel, perpendicular, or
BEARING GUIDE. Bearing Guide Created by REV Robotics 2016, Licensed Under CC BY-SA 1
 fg BEARING GUIDE This guide is intended as a reference on how to build with the new REV Robotics 15mm Building System using bearings and brackets to achieve basic motion. Bearing Guide Created by REV Robotics
fg BEARING GUIDE This guide is intended as a reference on how to build with the new REV Robotics 15mm Building System using bearings and brackets to achieve basic motion. Bearing Guide Created by REV Robotics
(POWER TRANSMISSION Methods)
 UNIT-5 (POWER TRANSMISSION Methods) It is a method by which you can transfer cyclic motion from one place to another or one pulley to another pulley. The ways by which we can transfer cyclic motion are:-
UNIT-5 (POWER TRANSMISSION Methods) It is a method by which you can transfer cyclic motion from one place to another or one pulley to another pulley. The ways by which we can transfer cyclic motion are:-
1. (a) Discuss various types of Kinematic links with examples. (b) Explain different types of constrained motions with examples.
 Code No: RR310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3
Code No: RR310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3
Design of Helical Gear and Analysis on Gear Tooth
 Design of Helical Gear and Analysis on Gear Tooth Indrale Ratnadeep Ramesh Rao M.Tech Student ABSTRACT Gears are mainly used to transmit the power in mechanical power transmission systems. These gears
Design of Helical Gear and Analysis on Gear Tooth Indrale Ratnadeep Ramesh Rao M.Tech Student ABSTRACT Gears are mainly used to transmit the power in mechanical power transmission systems. These gears
MECHANICAL DRIVES 1 SPUR GEAR DRIVES LEARNING ACTIVITY PACKET BB502-XD06AEN
 MECHANICAL DRIVES 1 LEARNING ACTIVITY PACKET SPUR GEAR DRIVES BB502-XD06AEN LEARNING ACTIVITY PACKET 6 SPUR GEAR DRIVES INTRODUCTION This LAP will begin the study of the third type of adjacent shaft-to-shaft
MECHANICAL DRIVES 1 LEARNING ACTIVITY PACKET SPUR GEAR DRIVES BB502-XD06AEN LEARNING ACTIVITY PACKET 6 SPUR GEAR DRIVES INTRODUCTION This LAP will begin the study of the third type of adjacent shaft-to-shaft
KISSsoft 03/2013 Tutorial 15
 KISSsoft 03/2013 Tutorial 15 Bevel gears KISSsoft AG Rosengartenstrasse 4 8608 Bubikon Switzerland Tel: +41 55 254 20 50 Fax: +41 55 254 20 51 info@kisssoft.ag www.kisssoft.ag Contents 1 Starting KISSsoft...
KISSsoft 03/2013 Tutorial 15 Bevel gears KISSsoft AG Rosengartenstrasse 4 8608 Bubikon Switzerland Tel: +41 55 254 20 50 Fax: +41 55 254 20 51 info@kisssoft.ag www.kisssoft.ag Contents 1 Starting KISSsoft...
LAPPING OR GRINDING? WHICH TECHNOLOGY IS THE RIGHT CHOICE IN THE AGE OF INDUSTRY 4.0?
 LAPPING OR GRINDING? WHICH TECHNOLOGY IS THE RIGHT CHOICE IN THE AGE OF INDUSTRY 4.0? Bevel gear transmissions for the automotive industry are subject to extremely stringent requirements. They must be
LAPPING OR GRINDING? WHICH TECHNOLOGY IS THE RIGHT CHOICE IN THE AGE OF INDUSTRY 4.0? Bevel gear transmissions for the automotive industry are subject to extremely stringent requirements. They must be
KISSsoft 03/2017 Tutorial 15
 KISSsoft 03/2017 Tutorial 15 Bevel gears KISSsoft AG Rosengartenstrasse 4 8608 Bubikon Switzerland Tel: +41 55 254 20 50 Fax: +41 55 254 20 51 info@kisssoft.ag www.kisssoft.ag Contents 1 Starting KISSsoft...
KISSsoft 03/2017 Tutorial 15 Bevel gears KISSsoft AG Rosengartenstrasse 4 8608 Bubikon Switzerland Tel: +41 55 254 20 50 Fax: +41 55 254 20 51 info@kisssoft.ag www.kisssoft.ag Contents 1 Starting KISSsoft...
Horological Wheel Cutting -
 Horological Wheel Cutting - (Jerry Kieffer s) Modern Means & Methods Authored By: David M. Morrow, CC21 Twenty First Century Certified Clockmaker American Watchmakers-Clockmakers Institute 1 Table of Contents/Index
Horological Wheel Cutting - (Jerry Kieffer s) Modern Means & Methods Authored By: David M. Morrow, CC21 Twenty First Century Certified Clockmaker American Watchmakers-Clockmakers Institute 1 Table of Contents/Index
Design & Manufacturing of an Effective Steering System for a Formula Student Car
 Design & Manufacturing of an Effective Steering System for a Formula Student Car Nikhil N. Gitay 1, Siddharth A. Joshi 2, Ajit A. Dumbre 3, Devesh C. Juvekar 4 1,2,3,4 Student, Department of Mechanical
Design & Manufacturing of an Effective Steering System for a Formula Student Car Nikhil N. Gitay 1, Siddharth A. Joshi 2, Ajit A. Dumbre 3, Devesh C. Juvekar 4 1,2,3,4 Student, Department of Mechanical
SHAFT ALIGNMENT FORWARD
 Service Application Manual SAM Chapter 630-76 Section 24 SHAFT ALIGNMENT FORWARD One of the basic problems of any installation is aligning couplings or shafts. Therefore, this section will endeavor to
Service Application Manual SAM Chapter 630-76 Section 24 SHAFT ALIGNMENT FORWARD One of the basic problems of any installation is aligning couplings or shafts. Therefore, this section will endeavor to
A comparison of the gear calculation process according to Swedish and American textbooks for higher education
 World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education Vol.6, No.1, 2007 2007 UICEE A comparison of the gear calculation process according to Swedish and American textbooks for higher education Samir
World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education Vol.6, No.1, 2007 2007 UICEE A comparison of the gear calculation process according to Swedish and American textbooks for higher education Samir
ANALYSIS OF STRESSES AND DEFLECTIONS IN SPUR GEAR
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 461 473 Article ID: IJMET_08_04_050 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=4
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 461 473 Article ID: IJMET_08_04_050 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=4
Tel
 30 20 10 60 0 60 H B g ed e A H1 A1 VSC-5A SUIT FOR BS-0 OR HV-6, VUT-6, VU-150 VSC-6A SUIT FOR BS-1 OR HV-8, 10, VUT-6, VU-200 VSC-7A, 8A SUIT FOR BS-2 OR HV-10, 12, 14, VUT-10, 12 VSC-10A SUIT FOR HV-14,
30 20 10 60 0 60 H B g ed e A H1 A1 VSC-5A SUIT FOR BS-0 OR HV-6, VUT-6, VU-150 VSC-6A SUIT FOR BS-1 OR HV-8, 10, VUT-6, VU-200 VSC-7A, 8A SUIT FOR BS-2 OR HV-10, 12, 14, VUT-10, 12 VSC-10A SUIT FOR HV-14,
Bevel Gears n A Textbook of Machine Design
 080 n A Textbook of Machine Design C H A P T E R 30 Bevel Gears. Introduction.. Classification of Bevel Gears. 3. Terms used in Bevel Gears. 4. Determination of Pitch Angle for Bevel Gears. 5. Proportions
080 n A Textbook of Machine Design C H A P T E R 30 Bevel Gears. Introduction.. Classification of Bevel Gears. 3. Terms used in Bevel Gears. 4. Determination of Pitch Angle for Bevel Gears. 5. Proportions
Instantaneous Centre Method
 Instantaneous Centre Method The combined motion of rotation and translation of the link AB may be assumed to be a motion of pure rotation about some centre I, known as the instantaneous centre of rotation.
Instantaneous Centre Method The combined motion of rotation and translation of the link AB may be assumed to be a motion of pure rotation about some centre I, known as the instantaneous centre of rotation.
Graphical representation of a gear
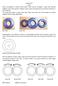 Homework 4 Gears Gears are designed to transmit rotary motion. Often they are arranged in a gear train (meshed together). Gear trains provide a change in speed, torque (turning force) and direction (clockwise
Homework 4 Gears Gears are designed to transmit rotary motion. Often they are arranged in a gear train (meshed together). Gear trains provide a change in speed, torque (turning force) and direction (clockwise
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
Bevel and hypoid gear geometry
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 23509 Second edition 2016-11-15 Bevel and hypoid gear geometry Géométrie des engrenages coniques et hypoïdes Reference number ISO 2016 Provläsningsexemplar
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 23509 Second edition 2016-11-15 Bevel and hypoid gear geometry Géométrie des engrenages coniques et hypoïdes Reference number ISO 2016 Provläsningsexemplar
What are the functions of gears? What is gear?
 8//0 hapter seven Laith atarseh are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts - Maintain
8//0 hapter seven Laith atarseh are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts - Maintain
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Bevel and hypoid gear geometry. Géométrie des engrenages coniques et hypoïdes. First edition
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 23509 First edition 2006-09-01 Bevel and hypoid gear geometry Géométrie des engrenages coniques et hypoïdes Reference number ISO 2006 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview PDF disclaimer
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 23509 First edition 2006-09-01 Bevel and hypoid gear geometry Géométrie des engrenages coniques et hypoïdes Reference number ISO 2006 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview PDF disclaimer
Program Center Distance Change
 Introduction Program 60-146--Center Distance Change When the coefficient of thermal expansion of the material used for gears is different from the coefficient for the mountg or housg material, it is necessary
Introduction Program 60-146--Center Distance Change When the coefficient of thermal expansion of the material used for gears is different from the coefficient for the mountg or housg material, it is necessary
Mechanism Feasibility Design Task
 Mechanism Feasibility Design Task Dr. James Gopsill 1 Contents 1. Last Week 2. Types of Gear 3. Gear Definitions 4. Gear Forces 5. Multi-Stage Gearbox Example 6. Gearbox Design Report Section 7. This Weeks
Mechanism Feasibility Design Task Dr. James Gopsill 1 Contents 1. Last Week 2. Types of Gear 3. Gear Definitions 4. Gear Forces 5. Multi-Stage Gearbox Example 6. Gearbox Design Report Section 7. This Weeks
Power transmission. Components used to transmit power: gears, belt, clutch and brakes. Gear (Stresses) act on the tooth Lewis formula and AGMA
 1 Power transmission Components used to transmit power: gears, belt, clutch and brakes. Failure Types Gear (Stresses) Bending: resulted from bending stress. t act on the tooth Lewis formula and AGMA Pitting:
1 Power transmission Components used to transmit power: gears, belt, clutch and brakes. Failure Types Gear (Stresses) Bending: resulted from bending stress. t act on the tooth Lewis formula and AGMA Pitting:
TECHNOLOGY MECHANISMS
 TECHNOLOGY MECHANISMS 3º ESO IES CHAN DO MONTE URTAZA 1 WHAT IS A MECHANISM? Mechanism are devices that have been designed to make jobs easier. They all have certain things in common: They involve some
TECHNOLOGY MECHANISMS 3º ESO IES CHAN DO MONTE URTAZA 1 WHAT IS A MECHANISM? Mechanism are devices that have been designed to make jobs easier. They all have certain things in common: They involve some
Chapter seven. Gears. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter seven Gears Laith Batarseh Gears are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts
Chapter seven Gears Laith Batarseh Gears are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts
CHAPTER 6 GEARS CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 6 GEARS CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to do the following: Compare the types of gears and their advantages. Did you ever take a clock apart to
CHAPTER 6 GEARS CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to do the following: Compare the types of gears and their advantages. Did you ever take a clock apart to
Chapter 1 Gear Design
 Chapter 1 Gear Design GTU Paper Analysis Sr. No. Questions Nov 16 May 17 Nov 17 May 18 Theory 1. Explain the following terms used in helical gears: (a) Helix angle; (b) Normal pitch; (c) Axial pitch; (d)
Chapter 1 Gear Design GTU Paper Analysis Sr. No. Questions Nov 16 May 17 Nov 17 May 18 Theory 1. Explain the following terms used in helical gears: (a) Helix angle; (b) Normal pitch; (c) Axial pitch; (d)
STRAIGHT SPUR GEARS and RACKS
 STRAIGHT SPUR GEARS and RACKS SPUR GEARS WITH LATERAL HUB page 4 SPUR GEARS WITHOUT HUB 7 RACKS 9 SPUR GEARS AND RACKS SPUR GEARS AND RACKS SPUR GEARS WITHOUT HUB SPUR GEARS WITH LATERAL HUB RACKS STRAIGHT
STRAIGHT SPUR GEARS and RACKS SPUR GEARS WITH LATERAL HUB page 4 SPUR GEARS WITHOUT HUB 7 RACKS 9 SPUR GEARS AND RACKS SPUR GEARS AND RACKS SPUR GEARS WITHOUT HUB SPUR GEARS WITH LATERAL HUB RACKS STRAIGHT
Effect of Geometry Factor I & J Factor Multipliers in the performance of Helical Gears
 Effect of Geometry Factor I & J Factor Multipliers in the performance of Helical Gears 1 Amit D. Modi, 2 Manan B. Raval, 1 Lecturer, 2 Lecturer, 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, 2 Department of
Effect of Geometry Factor I & J Factor Multipliers in the performance of Helical Gears 1 Amit D. Modi, 2 Manan B. Raval, 1 Lecturer, 2 Lecturer, 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, 2 Department of
Competitive VEX Robot Designer
 Competitive VEX Robot Designer Skill Set 2: Builder I Terminal Objective 2.2: construct a boom crane Performance Objective: Given provided VEX components, construct a boom crane that extends a minimum
Competitive VEX Robot Designer Skill Set 2: Builder I Terminal Objective 2.2: construct a boom crane Performance Objective: Given provided VEX components, construct a boom crane that extends a minimum
Unit IV GEARS. Gallery
 Gallery Components of a typical, four stroke cycle, DOHC piston engine. (E) Exhaust camshaft, (I) Intake camshaft, (S) Spark plug, (V) Valves, (P) Piston, (R) Connecting rod, (C) Crankshaft, (W) Water
Gallery Components of a typical, four stroke cycle, DOHC piston engine. (E) Exhaust camshaft, (I) Intake camshaft, (S) Spark plug, (V) Valves, (P) Piston, (R) Connecting rod, (C) Crankshaft, (W) Water
10,000 Series. Highlights C-6
 Highlights Features higher flows Benefits demanding mobile and industrial applications from Applications Description This is the biggest disc valve motor of our line with up to 45 GPM and 24,000 in-lb
Highlights Features higher flows Benefits demanding mobile and industrial applications from Applications Description This is the biggest disc valve motor of our line with up to 45 GPM and 24,000 in-lb
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A
 KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
1.6 Features of common gears
 1.6 Features of common gears Chapter 1.2 covered briefly on types of gear. The main gear features are explained here. Helical gear Helical gear has characteristics of transferability of larger load, less
1.6 Features of common gears Chapter 1.2 covered briefly on types of gear. The main gear features are explained here. Helical gear Helical gear has characteristics of transferability of larger load, less
DUDLEY'S" HANDBOOK OF PRACTICAL GEAR DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE. Stephen P. Radzevich
 Second Edition DUDLEY'S" HANDBOOK OF PRACTICAL GEAR DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE Stephen P. Radzevich LßP) CRC Press VV J Taylors Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor
Second Edition DUDLEY'S" HANDBOOK OF PRACTICAL GEAR DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE Stephen P. Radzevich LßP) CRC Press VV J Taylors Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor
CHAPTER 5 PREVENTION OF TOOTH DAMAGE IN HELICAL GEAR BY PROFILE MODIFICATION
 90 CHAPTER 5 PREVENTION OF TOOTH DAMAGE IN HELICAL GEAR BY PROFILE MODIFICATION 5.1 INTRODUCTION In any gear drive the absolute and the relative transmission error variations normally increases with an
90 CHAPTER 5 PREVENTION OF TOOTH DAMAGE IN HELICAL GEAR BY PROFILE MODIFICATION 5.1 INTRODUCTION In any gear drive the absolute and the relative transmission error variations normally increases with an
EXAMPLES GEARS. page 1
 (EXAMPLES GEARS) EXAMPLES GEARS Example 1: Shilds p. 76 A 20 full depth spur pinion is to trans mit 1.25 kw at 850 rpm. The pinion has 18 teeth. Determine the Lewis bending stress if the module is 2 and
(EXAMPLES GEARS) EXAMPLES GEARS Example 1: Shilds p. 76 A 20 full depth spur pinion is to trans mit 1.25 kw at 850 rpm. The pinion has 18 teeth. Determine the Lewis bending stress if the module is 2 and
Effortless Water Lifting Bucket Elevator Biswa Bihari Rath 1, Nabnit Panigrahi 2
 Effortless Water Lifting Bucket Elevator Biswa Bihari Rath 1, Nabnit Panigrahi 2 1 Assistant Professor, Gandhi Institute For Technology, Bhubaneswar, Odisha India 2 Dean Research, Gandhi Institute For
Effortless Water Lifting Bucket Elevator Biswa Bihari Rath 1, Nabnit Panigrahi 2 1 Assistant Professor, Gandhi Institute For Technology, Bhubaneswar, Odisha India 2 Dean Research, Gandhi Institute For
STUDY OF MANUAL GEAR TRANSMISSION
 STUDY OF MANUAL GEAR TRANSMISSION Pranav P Kulkarni 1, Kalpesh Chaudhari 2, Prashant Patil 3, Dattatray Gite 4 1Pranav P Kulkarni, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, SVIT, Nashik, Maharashtra, India 2Prashant
STUDY OF MANUAL GEAR TRANSMISSION Pranav P Kulkarni 1, Kalpesh Chaudhari 2, Prashant Patil 3, Dattatray Gite 4 1Pranav P Kulkarni, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, SVIT, Nashik, Maharashtra, India 2Prashant
HAKO Overheadmodels - Section 7 Mechanical engineering, pneumatics, hyraulics
 Order no. 216 Caliper gauge - design of a caliper gauge - four different vernier scales can be read (1/10mm, 1/20mm extended and 1/50mm) - all values can be clearly read Order no. 218 Micrometer - full
Order no. 216 Caliper gauge - design of a caliper gauge - four different vernier scales can be read (1/10mm, 1/20mm extended and 1/50mm) - all values can be clearly read Order no. 218 Micrometer - full
Different types of gears. Spur gears. Idler gears. Worm gears. Bevel gears. Belts & Pulleys
 GEARS Robot Gears By using different gear diameters, you can exchange between rotational (or translation) velocity and torque. by looking at the motor datasheet you can determine the output velocity and
GEARS Robot Gears By using different gear diameters, you can exchange between rotational (or translation) velocity and torque. by looking at the motor datasheet you can determine the output velocity and
Chapter 3. Transmission Components
 Chapter 3. Transmission Components The difference between machine design and structure design An important design problem in a mechanical system is how to transmit and convert power to achieve required
Chapter 3. Transmission Components The difference between machine design and structure design An important design problem in a mechanical system is how to transmit and convert power to achieve required
The Basics of Gear Theory, Part 2
 The Basics of Gear Theory, Part 2 Hermann J. Stadtfeld Bevel Gears: By the Book Introduction (Chapter 1, Part 2) The first part of this publication series covered the general basics of involute gearing
The Basics of Gear Theory, Part 2 Hermann J. Stadtfeld Bevel Gears: By the Book Introduction (Chapter 1, Part 2) The first part of this publication series covered the general basics of involute gearing
6000 Series Highlights
 Highlights Features 9 displacements available Presents a multitude of options that make this motor very smart and flexible to apply Benefits Very tough motor for demanding applications Can be used in a
Highlights Features 9 displacements available Presents a multitude of options that make this motor very smart and flexible to apply Benefits Very tough motor for demanding applications Can be used in a
ANALYSIS OF SURFACE CONTACT STRESS FOR A SPUR GEAR OF MATERIAL STEEL 15NI2CR1MO28
 ANALYSIS OF SURFACE CONTACT STRESS FOR A SPUR GEAR OF MATERIAL STEEL 15NI2CR1MO28 D. S. Balaji, S. Prabhakaran and J. Harish Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chennai, India E-Mail: balajimailer@gmail.com
ANALYSIS OF SURFACE CONTACT STRESS FOR A SPUR GEAR OF MATERIAL STEEL 15NI2CR1MO28 D. S. Balaji, S. Prabhakaran and J. Harish Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chennai, India E-Mail: balajimailer@gmail.com
Chapter 6 CALIPERS HOW TO CHOOSE AND USE THEM TM 9-243
 HOW TO CHOOSE AND USE THEM Chapter 6 CALIPERS The Types and Uses section provides you with a list of types of calipers. These pages should help you select the right calipers for the job. The Reading Calipers
HOW TO CHOOSE AND USE THEM Chapter 6 CALIPERS The Types and Uses section provides you with a list of types of calipers. These pages should help you select the right calipers for the job. The Reading Calipers
Swivelling Mechanism Design and Manufacturing
 Swivelling Mechanism Design and Manufacturing 1.Dr.A.Pandhare, 2.Aakash Dorwat, 3.Atul Shirode, (2,3) B.E. Students (1) HOD Mechanical Department, SKNCOE, Atul Shirode- email- atulshirode21@gmail.com/
Swivelling Mechanism Design and Manufacturing 1.Dr.A.Pandhare, 2.Aakash Dorwat, 3.Atul Shirode, (2,3) B.E. Students (1) HOD Mechanical Department, SKNCOE, Atul Shirode- email- atulshirode21@gmail.com/
MANUFACTURING OF GEAR BOXES
 Profile No.: 29 NIC Code: 29301 MANUFACTURING OF GEAR BOXES 1. INTRODUCTION: Gears play a prominent role in mechanical power transmission. A gear or cogwheel is a rotating machine part having cut teeth,
Profile No.: 29 NIC Code: 29301 MANUFACTURING OF GEAR BOXES 1. INTRODUCTION: Gears play a prominent role in mechanical power transmission. A gear or cogwheel is a rotating machine part having cut teeth,
Robotic Systems ECE 401RB Fall 2006
 The following notes are from: Robotic Systems ECE 401RB Fall 2006 Lecture 8: Actuators Part 2 Chapter 19, G. McComb, and M. Predko, Robot Builder's Bonanza, Third Edition, Mc- Graw Hill, 2006. I. Gears
The following notes are from: Robotic Systems ECE 401RB Fall 2006 Lecture 8: Actuators Part 2 Chapter 19, G. McComb, and M. Predko, Robot Builder's Bonanza, Third Edition, Mc- Graw Hill, 2006. I. Gears
we will learn how to conduct force and torque analysis on gears in order to calculate bearing
 8.1 Introduction to Gears Gears are used to transmit motion and torque from one shaft to another. In this section we will discuss the kinematics of gears; that is, the motion relationships between gears.
8.1 Introduction to Gears Gears are used to transmit motion and torque from one shaft to another. In this section we will discuss the kinematics of gears; that is, the motion relationships between gears.
TECHNICAL PAPER. New Opportunities with Molded Gears. by: R.E. Kleiss, A.L. Kapelevich and N.J. Kleiss Jr., Kleiss Gears, Inc.
 01FTM9 New Opportunities with Molded Gears by: R.E. Kleiss, A.L. Kapelevich and N.J. Kleiss Jr., Kleiss Gears, Inc. American Gear Manufacturers Association TECHNICAL PAPER New Opportunities with Molded
01FTM9 New Opportunities with Molded Gears by: R.E. Kleiss, A.L. Kapelevich and N.J. Kleiss Jr., Kleiss Gears, Inc. American Gear Manufacturers Association TECHNICAL PAPER New Opportunities with Molded
All levers are one of three types, usually called classes. The class of a lever depends on the relative position of the load, effort and fulcrum:
 Página 66 de 232 Mechanisms A mechanism is simply a device which takes an input motion and force, and outputs a different motion and force. The point of a mechanism is to make the job easier to do. The
Página 66 de 232 Mechanisms A mechanism is simply a device which takes an input motion and force, and outputs a different motion and force. The point of a mechanism is to make the job easier to do. The
11/23/2013. Chapter 13. Gear Trains. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhiba, PE
 Chapter 13 Gear Trains 1 2 13.2. Types of Gear Trains 1. Simple gear train 2. Compound gear train 3. Reverted gear train 4. Epicyclic gear train: axes of shafts on which the gears are mounted may move
Chapter 13 Gear Trains 1 2 13.2. Types of Gear Trains 1. Simple gear train 2. Compound gear train 3. Reverted gear train 4. Epicyclic gear train: axes of shafts on which the gears are mounted may move
Boston Gear ORC Series
 Boston Gear ORC Series Trig-O-Matic Overload Release Clutches Installation and Maintenance Instructions Doc. No. ORC Series Model S www.bostongear.com ORC SERIES TRIG-O-MATIC OVERLOAD RELEASE CLUTCHES
Boston Gear ORC Series Trig-O-Matic Overload Release Clutches Installation and Maintenance Instructions Doc. No. ORC Series Model S www.bostongear.com ORC SERIES TRIG-O-MATIC OVERLOAD RELEASE CLUTCHES
HAFCO METALMASTER HM-48. Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO. (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm. Product Brochure
 Product Brochure M126D HAFCO METALMASTER HM-48 Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Page 1 of 6 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification -
Product Brochure M126D HAFCO METALMASTER HM-48 Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Page 1 of 6 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification -
