Energy Conversions Questions CfE
|
|
|
- Alexander Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the kinetic energy of the mass just before it hits the ground? ii) Calculate the speed of the mass just before it hits the ground. 2) A student records the time that it takes to run up a flight of stairs in school. The following information was recorded during the run by a fellow student. Mass of student (kg) 60 Height of stairs (m) 15 Time to climb stairs (s) 12 a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by the student at the top of the stairs. b) Calculate the power developed by the student.
2 3) A climber of mass 65kg is attached by a rope to point A on a rock face. She climbs up to point B in 20s, where B is 3.2m vertically above point A. a) i) Calculate the average speed of the climber between A and B. ii) Calculate the weight of the climber. iii) Calculate the gain in gravitational potential energy of the climber. b) She then loses her footing and free falls from point B. After passing point A she is held safely by the rope. i) Calculate her speed as she passes point A. ii) How would her actual speed when passing point A compare with the speed Calculated in b) i)? Explain your answer. 4) The first car crash testing involved a car rolling down a slope with a wall at the bottom. In one test a car of mass 779kg starts from rest at the top of a slope with a height of 7.2m. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the car at the top of the slope. b) i) State the kinetic energy of the car at the bottom of the slope. ii) Calculate the speed of the car at the bottom of the slope just before hitting the wall, assuming there is no force of friction on the slope.
3 5) Builders repair the roof of a local community centre. They use scaffolding and a motorised pulley system to lift a pallet of tiles to roof level. a) Calculate the weight of the pallet and tiles, which have a total mass of 230kg. b) State the minimum force required to lift the tiles. c) Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by the tiles if they are lifted up to a height of 6m. d) When they are unloaded on to the scaffolding at a height of 6m, one tile falls. If a tile has a mass of 1.98kg and falls from rest: i) Calculate the speed of the tile just before it hits the ground. ii) Explain why the actual speed of the tile just before hitting the ground is less than that calculated in d) i). 6) In a garage, a mechanic lifts an engine from a car using a pulley system. a) The mechanic pulls 4.5m of chain with a constant force of 300N. Calculate the work done by the mechanic. b) The engine has a mass of 146kg and is raised 0.80m. Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by the engine.
4 7) A family have a wind turbine electrical energy generator installed on their roof. The table below gives information about the wind turbine. a) In 2014 the wind turbine generated electrical energy for 2000 hours. Calculate the electrical energy generated in kilowatt-hours during b) An electricity supplier charges 15p per kilowatt-hour. Calculate the cost of buying the same quantity of electrical energy as generated by the wind turbine in c) The wind turbine costs 2100 to install. It is used to generate electrical energy for 20years. Each year it generates the same amount of energy as it did in Calculate how much money the householder will save if the turbine is used to generate electrical energy over this time.
5 8) A traffic information sign is located in a remote area. The sign is supplied with energy by both a panel of a solar cells and a wind generator. They are both connected to a rechargeable battery. a) One square metre of solar cells can generate up to 80 watts. The panel of solar cells has an area of 0.4m 2. i) State the energy change that takes place in the solar cells. ii) Calculate the maximum power produced by the panel of solar cells. b) The following table shows the power produced by the wind generator at different wind speeds. i) Suggest the power produced when the wind speed is 6ms -1. ii) At a wind speed of 10ms -1 the voltage produced by the wind generator is 16 volts. Calculate the current produced by the wind generator. c) Explain why a rechargeable battery is also required to supply energy to the traffic information sign.
6 9) Increasing the electrical energy generated from renewable sources is important for the future of the country. a) At present, fossil fuels are the main source of energy. State one problem with this source of energy. b) The bar chart shows the main energy sources used in Scotland. Use the names of the energy sources in the bar chart to compete the table. c) From the bar graph above, how many hydroelectric power stations would be required to produce the same power output as a nuclear power station? (approx.!!!) d) If a bar graph of the same energy sources was drawn 10 years later, comment on what you think would happen to the power readings for: i) Coal ii) Wind?
7 10) A thermal power station has an efficiency of 40%. A combined heat and power station is more efficient; it uses heat to produce hot water for homes as well as generating electrical energy. The energy output for each power station is shown in the diagram below. a) i) Calculate the % of waste heat for the thermal power station. ii) Calculate the total % useful energy output of the combined heat and power station. b) A combined heat and power station saves energy in the power industry. i) Describe one method of saving energy in the home. ii) Describe one method of saving energy in the transport.
8 11) A hydroelectric power station uses water stored in a dam to generate electrical energy. The power station generates electrical energy at 16kV. The electrical energy is then transmitted across the country at 275kV using the National Grid. a) State the energy transformation: i) in the water pipes; ii) at the generator. b) Why is the electrical energy transmitted at a very high voltage across the National Grid? 12) An underwater generator is designed to produce electrical energy from water currents in the sea.
9 The output power of the generator depends on the speed of the water currents as shown in Graph 1. The speed of the water current is recorded at different times of the day shown in Graph 2. a) i) State the output power of the generator at 09:00. ii) State one disadvantage of using this type of generator. b) The voltage produced by the generator is stepped-up by a transformer. At one point in the day the electrical current at the input of the transformer is 900A and the voltage is 2kV. i) Calculate the input power to the transformer at this time. ii) Calculate the output power from the transformer at this time if it is 95% efficient.
10 13) A wind generator is used to charge a 12V battery. The charging current depends on the wind speed. The graph shows the charging current at different wind speeds. a) During one charge of the battery, the wind speed is constant at 15ms -1. During this time of charge of 4500C is transferred to the battery. Calculate the time taken to transfer this charge to the battery. b) At another wind speed the generator has an output power of 120W and is 30% efficient. Calculate the input power to the generator. c) A bicycle has a small generator called a dynamo. The dynamo contains a magnet that spins near a coil of wire. When the magnet spins, a voltage is induced in the coil. State two factors that affect the size of the induced voltage.
11 14) A farm in a remote location has a wind turbine to generate electrical energy. a) In one year the wind turbine produces 18,250 kilowatt-hours of energy. Calculate the number of kilowatt-hours produced per day. b) On average the wind turbine operates for 8 hours per day. Calculate the average power of the wind turbine. c) i) The wind turbine uses an ac generator. A diagram of the ac generator is shown. Label the diagram using the following words: Rotor, Stator Coil and Iron Core. ii) Explain how the ac generator works. iii) State two changes that can be made to the generator to increase the power output.
12 15) Electrical energy can be generated from different energy sources. a) Examples of energy sources are: Gas, Wind, Oil, Solar, Wave, Hydro and Coal. These energy sources can be classified as renewable or non-renewable. Complete the table below to show which of these examples are renewable and which are non-renewable. b) A coal-fired power station burns coal in order to generate electrical energy. A simplified diagram of a coal-fired power station is shown. State the energy transformation that takes place in the: i) Boiler ii) Turbine iii) Generator.
Calculate the current in the kettle element. (3)
 1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater.
 Q1.(a) A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater. (i) Before starting the experiment, the student drew Graph A. Graph A shows how the student expected
Q1.(a) A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater. (i) Before starting the experiment, the student drew Graph A. Graph A shows how the student expected
Intermediate 2 Momentum & Energy Past Paper questions
 Intermediate 2 Momentum & Energy Past Paper questions 2000-2010 2000 Q23. A chairlift at a ski resort carries skiers through a vertical distance of 400 m. (a) One of the skiers has a mass of 90.0 kg.
Intermediate 2 Momentum & Energy Past Paper questions 2000-2010 2000 Q23. A chairlift at a ski resort carries skiers through a vertical distance of 400 m. (a) One of the skiers has a mass of 90.0 kg.
Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. N S
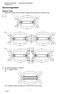 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8. Name:
 Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8 Name: Exploration 1 Rapidly turn the handles clockwise on all three generators at the end of the table, watching the System Voltage panel: 1. Draw the needle when the
Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8 Name: Exploration 1 Rapidly turn the handles clockwise on all three generators at the end of the table, watching the System Voltage panel: 1. Draw the needle when the
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy.
 Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Energy and Electricity
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race.
 Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
(2) The graph below shows how the power output of a wind turbine changes over one day.
 Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources... 2.. (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity.
Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources... 2.. (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity.
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
time in seconds Amy leaves diving board
 1 Amy dives from the high diving board at a swimming pool. Look at the graph of her motion. speed in m / s 15 10 Amy enters water P Q 5 0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 time in seconds Amy leaves diving board (a)
1 Amy dives from the high diving board at a swimming pool. Look at the graph of her motion. speed in m / s 15 10 Amy enters water P Q 5 0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 time in seconds Amy leaves diving board (a)
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy. Lesson 1-
 Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy Lesson 1- Most atoms have equal numbers of protons, which are positively charged, and electrons, which are negatively charged. These atoms have no charge; they
Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy Lesson 1- Most atoms have equal numbers of protons, which are positively charged, and electrons, which are negatively charged. These atoms have no charge; they
National 4 Physics - Electricity and Energy Summary Notes
 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS. Unit 1 Electricity and Energy. Revision Notes
 Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Generating Electricity
 Generating Electricity The dynamo effect An electric current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil of wire in a circuit. The direction of the current is reversed when the magnet is moved out of
Generating Electricity The dynamo effect An electric current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil of wire in a circuit. The direction of the current is reversed when the magnet is moved out of
kwh. 6 February
 14 10 The Robinson family have an electricity meter. The diagram shows their meter on two different dates. 28182 kwh 6 January 2 9 030 kwh 6 February (a) Use the meters to find the number of kilowatt hours
14 10 The Robinson family have an electricity meter. The diagram shows their meter on two different dates. 28182 kwh 6 January 2 9 030 kwh 6 February (a) Use the meters to find the number of kilowatt hours
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity
 Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Solutions
 Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Solutions 2015 Question 12 (d) [Ordinary Level] A solenoid (long coil of wire) is connected to a battery as shown. (i) Copy the diagram into your
Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Solutions 2015 Question 12 (d) [Ordinary Level] A solenoid (long coil of wire) is connected to a battery as shown. (i) Copy the diagram into your
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy
 Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
The graph shows how far the car travelled and how long it took. (i) Between which points was the car travelling fastest? Tick ( ) your answer.
 Q1. This question is about a car travelling through a town. (a) The graph shows how far the car travelled and how long it took. (i) Between which points was the car travelling fastest? Tick ( ) your answer.
Q1. This question is about a car travelling through a town. (a) The graph shows how far the car travelled and how long it took. (i) Between which points was the car travelling fastest? Tick ( ) your answer.
Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in.
 Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in. (a) Choose from the following words to complete the sentences below. distance energy force speed time You
Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in. (a) Choose from the following words to complete the sentences below. distance energy force speed time You
GraspIT AQA GCSE Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Questions
 A. Permanent and Induced Magnetism, Magnetic Forces and Fields 1. The following question is about magnets. a. Iron is a magnetic material. Name two other magnetic elements. (2) b. Describe the effect a
A. Permanent and Induced Magnetism, Magnetic Forces and Fields 1. The following question is about magnets. a. Iron is a magnetic material. Name two other magnetic elements. (2) b. Describe the effect a
National 4/5. Dynamics and Space
 North Berwick High School National 4/5 Department of Physics Dynamics and Space Section 1 Mechanics Problem Booklet KINEMATICS PROBLEMS Speed, distance and time 1. A runner completes a 200 m race in 25
North Berwick High School National 4/5 Department of Physics Dynamics and Space Section 1 Mechanics Problem Booklet KINEMATICS PROBLEMS Speed, distance and time 1. A runner completes a 200 m race in 25
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance.
 Q1. (a) A driver may have to make an emergency stop. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance. Give three different factors which affect the thinking distance or the braking distance. In
Q1. (a) A driver may have to make an emergency stop. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance. Give three different factors which affect the thinking distance or the braking distance. In
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
What is Electricity? Lesson one
 What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
Physical Science Lecture Notes Chapter 13
 Physical Science Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Section 13-1 Electricity, Magnetism & Motion A. Electrical & mechanical energy 1. Magnetic forces repel when alike and attract when opposite 2. Electric current
Physical Science Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Section 13-1 Electricity, Magnetism & Motion A. Electrical & mechanical energy 1. Magnetic forces repel when alike and attract when opposite 2. Electric current
Activity 3: Electricity
 Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Thinking distance in metres. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. One of the values of stopping distance is incorrect.
 Q1.An investigation was carried out to show how thinking distance, braking distance and stopping distance are affected by the speed of a car. The results are shown in the table. Speed in metres per second
Q1.An investigation was carried out to show how thinking distance, braking distance and stopping distance are affected by the speed of a car. The results are shown in the table. Speed in metres per second
3 Electricity from Magnetism
 CHAPTER 2 3 Electricity from Magnetism SECTION Electromagnetism BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can a magnetic field make an electric current?
CHAPTER 2 3 Electricity from Magnetism SECTION Electromagnetism BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can a magnetic field make an electric current?
Stay Safe Around Electricity Teacher s Guide
 Stay Safe Around Electricity Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Stay Safe Around Electricity activity booklet can be used as a follow-up to an electric utility presentation or as a stand-alone piece to teach
Stay Safe Around Electricity Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Stay Safe Around Electricity activity booklet can be used as a follow-up to an electric utility presentation or as a stand-alone piece to teach
The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch bulb.
 Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Technology Exploration_II
 Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion
Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion
(a) A 36 volt battery powers the electric motor. The battery is made using individual 1.2 volt cells.
 Q1.The picture shows an electric bicycle. The bicycle is usually powered using a combination of the rider pedalling and an electric motor. (a) A 36 volt battery powers the electric motor. The battery is
Q1.The picture shows an electric bicycle. The bicycle is usually powered using a combination of the rider pedalling and an electric motor. (a) A 36 volt battery powers the electric motor. The battery is
ST.MARY S CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI
 ST.MARY S CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI YR. 9 / YR. 10 PHYSICS REVISION WORKSHEET 1. (a) In 2009 the sprinter Usain Bolt ran the 100m sprint in a time of 9.58s. Calculate his average speed during this race.
ST.MARY S CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI YR. 9 / YR. 10 PHYSICS REVISION WORKSHEET 1. (a) In 2009 the sprinter Usain Bolt ran the 100m sprint in a time of 9.58s. Calculate his average speed during this race.
Period 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and Generators
 Name Section Period 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and Generators Activity 16.1: How Are Electric Motors and Generators Related? a) Generators. 1) Attach a hand-cranked generator to a small motor and turn the
Name Section Period 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and Generators Activity 16.1: How Are Electric Motors and Generators Related? a) Generators. 1) Attach a hand-cranked generator to a small motor and turn the
Electricity All Around Us
 ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST ANSWER KEY Section 1: or False 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed close to water are a safety hazard. 3.
ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST ANSWER KEY Section 1: or False 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed close to water are a safety hazard. 3.
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
SCIENCE 8. Unit 4 Booklet. Machines and Mechanical Systems
 SCIENCE 8 Unit 4 Booklet Machines and Mechanical Systems TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT Levers Have Class BLM 4-2 Goal Identify items as Class 1, Class 2, or Class 3 levers. Introduction There are three classes
SCIENCE 8 Unit 4 Booklet Machines and Mechanical Systems TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT Levers Have Class BLM 4-2 Goal Identify items as Class 1, Class 2, or Class 3 levers. Introduction There are three classes
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME
 ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
Magnets and magnetism
 Chapter 2 Electromagnetism Section 1 Magnets and magnetism Vocabulary: magnet magnetic pole magnetic force Properties of Magnets Magnetic Poles on a magnet, the magnetic poles are the locations where the
Chapter 2 Electromagnetism Section 1 Magnets and magnetism Vocabulary: magnet magnetic pole magnetic force Properties of Magnets Magnetic Poles on a magnet, the magnetic poles are the locations where the
[2] [2]
![[2] [2] [2] [2]](/thumbs/88/114953460.jpg) High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 A jet aircraft is taking off from an international airport. Its mass, including passengers and fuel is 150,000 kg. Its take-off speed is 100 ms -1. The maximum thrust
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 A jet aircraft is taking off from an international airport. Its mass, including passengers and fuel is 150,000 kg. Its take-off speed is 100 ms -1. The maximum thrust
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... ELECTROMAGNETISM 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1 1. Fran has a balancing game.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... ELECTROMAGNETISM 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1 1. Fran has a balancing game.
Exampro GCSE Physics. P2 Forces and their effects Self Study Questions Higher tier. Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 117. Marks: 117.
 Exampro GCSE Physics P2 Forces and their effects Self Study Questions Higher tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 117 Marks: 117 Comments: Page 1 of 32 Q1. (a) The stopping distance of a vehicle is made
Exampro GCSE Physics P2 Forces and their effects Self Study Questions Higher tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 117 Marks: 117 Comments: Page 1 of 32 Q1. (a) The stopping distance of a vehicle is made
KS3 Revision. 8J Magnets and Electromagnets
 KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
BSA Electricity Merit Badge. Electricity Merit Badge AC Alternating Current
 Electricity Merit Badge AC Alternating Current AC=Alternating Current Output Output Spinning Wire Coil When a coil of wire passes through a magnetic field it produces an Alternating Current AC=Alternating
Electricity Merit Badge AC Alternating Current AC=Alternating Current Output Output Spinning Wire Coil When a coil of wire passes through a magnetic field it produces an Alternating Current AC=Alternating
P5 STOPPING DISTANCES
 P5 STOPPING DISTANCES Practice Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 84 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 28 The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and
P5 STOPPING DISTANCES Practice Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 84 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 28 The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and
Understanding Electricity and Electrical Safety Teacher s Guide
 Understanding Electricity and Electrical Safety Teacher s Guide Note to Instructor: The activities and experiments in this booklet build on each other to develop a student s understanding of electricity
Understanding Electricity and Electrical Safety Teacher s Guide Note to Instructor: The activities and experiments in this booklet build on each other to develop a student s understanding of electricity
Thinking distance in metres. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. One of the values of stopping distance is incorrect.
 Q1.An investigation was carried out to show how thinking distance, braking distance and stopping distance are affected by the speed of a car. The results are shown in the table. Speed in metres per second
Q1.An investigation was carried out to show how thinking distance, braking distance and stopping distance are affected by the speed of a car. The results are shown in the table. Speed in metres per second
MS.RAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3
 MSRAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3 1- In Fig 91, A and B are two conductors on insulating stands Both A and B were initially uncharged X Y A B Fig 91 (a) Conductor A is given the positive charge shown
MSRAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3 1- In Fig 91, A and B are two conductors on insulating stands Both A and B were initially uncharged X Y A B Fig 91 (a) Conductor A is given the positive charge shown
The drag lift pulls the skier from the bottom to the top of a ski slope.
 ACCELERATION Q1. Figure 1 shows a skier using a drag lift. The drag lift pulls the skier from the bottom to the top of a ski slope. The arrows, A, B, C and D represent the forces acting on the skier and
ACCELERATION Q1. Figure 1 shows a skier using a drag lift. The drag lift pulls the skier from the bottom to the top of a ski slope. The arrows, A, B, C and D represent the forces acting on the skier and
Eastside Invitational Jan 28, 2017 Wind Power Div C - Part 2
 Eastside Invitational Jan 28, 2017 Wind Power Div C - Part 2 Team Information Team Name and number: Name of Students: and Instructions Wind Power is a combination of hands on activities and written test
Eastside Invitational Jan 28, 2017 Wind Power Div C - Part 2 Team Information Team Name and number: Name of Students: and Instructions Wind Power is a combination of hands on activities and written test
TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical Generation System Sample Lab Experiment Procedure
 TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical Generation System Sample Lab Experiment Procedure Lab Session #1: System Overview and Operation Purpose: To gain an understanding of the TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical
TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical Generation System Sample Lab Experiment Procedure Lab Session #1: System Overview and Operation Purpose: To gain an understanding of the TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical
(3) When the brake pedal of the car is pushed, brake pads press against very hard steel discs.
 Q1. A car travels along a level road at 20 metres per second. (a) Calculate the distance travelled by the car in 4 seconds. (Show your working.) (b) When the brake pedal of the car is pushed, brake pads
Q1. A car travels along a level road at 20 metres per second. (a) Calculate the distance travelled by the car in 4 seconds. (Show your working.) (b) When the brake pedal of the car is pushed, brake pads
Magnetism Ch Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance
 Magnetism Ch 21 22.1 Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance 1 Magnets attract & repel other magnets. The attraction between the north pole of a magnet and the south pole of another magnet is based
Magnetism Ch 21 22.1 Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance 1 Magnets attract & repel other magnets. The attraction between the north pole of a magnet and the south pole of another magnet is based
Driver Driven. InputSpeed. Gears
 Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED?
 ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
A B C length 1. Look at the results that they collect for four cars passing the school. Time taken to travel length 1. in seconds
 1 This question is about speed. (a) Pupils at a school measure the time cars take to travel two 100 m lengths. Look at the diagram. A B C length 1 length 2 100 m 100 m Look at the results that they collect
1 This question is about speed. (a) Pupils at a school measure the time cars take to travel two 100 m lengths. Look at the diagram. A B C length 1 length 2 100 m 100 m Look at the results that they collect
Incandescent Lightbulb. Electricity passes through a tungsten (W) filament, which in turn glows white hot (4500F).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Incandescent Lightbulb Electricity passes through a tungsten (W) filament, which in turn glows white hot (4500F). Very inefficient: 90% of the electrical energy is lost
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Incandescent Lightbulb Electricity passes through a tungsten (W) filament, which in turn glows white hot (4500F). Very inefficient: 90% of the electrical energy is lost
Electrical Theory. Generator Theory. PJM State & Member Training Dept. PJM /22/2018
 Electrical Theory Generator Theory PJM State & Member Training Dept. PJM 2018 Objectives The student will be able to: Describe the process of electromagnetic induction Identify the major components of
Electrical Theory Generator Theory PJM State & Member Training Dept. PJM 2018 Objectives The student will be able to: Describe the process of electromagnetic induction Identify the major components of
Motional emf. as long as the velocity, field, and length are mutually perpendicular.
 Motional emf Motional emf is the voltage induced across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. If a metal rod of length L moves at velocity v through a magnetic field B, the motional emf is: ε =
Motional emf Motional emf is the voltage induced across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. If a metal rod of length L moves at velocity v through a magnetic field B, the motional emf is: ε =
Ch. 3 Magnetism and Electromagnetism
 Ch. 3 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet a. are only perpendicular
Ch. 3 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet a. are only perpendicular
Electrical Connections
 Electrical Connections TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment
Electrical Connections TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment
Chapter 14 Learning Objectives-Study this for TEST. Chapter 14 Work and Power. Chapter 14 Learning Objectives-Study this for TEST
 Chapter 14 Work and Power GOAL: Students will be able to compare and contrast work and power qualitatively and quantitatively. Standard: SC.912.P.10.3 Students will: Level Scale 4 design and conduct experiments
Chapter 14 Work and Power GOAL: Students will be able to compare and contrast work and power qualitatively and quantitatively. Standard: SC.912.P.10.3 Students will: Level Scale 4 design and conduct experiments
Just what is an alternator?
 Just what is an alternator? An alternator is the device used to produce the electricity the car needs to run and to keep the battery charged. The battery is the heart of your electrical system. But you
Just what is an alternator? An alternator is the device used to produce the electricity the car needs to run and to keep the battery charged. The battery is the heart of your electrical system. But you
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications
 UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
1. Which device creates a current based on the principle of electromagnetic induction?
 Assignment 2 Electromagnetism Name: 1. Which device creates a current based on the principle of electromagnetic induction? A) galvanometer B) generator C) motor D) solenoid 2. The bar magnet below enters
Assignment 2 Electromagnetism Name: 1. Which device creates a current based on the principle of electromagnetic induction? A) galvanometer B) generator C) motor D) solenoid 2. The bar magnet below enters
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
Overview of hydro electric dams and how they work Provide background on basic principles of hydropower and its history. Explain features that all
 Overview of hydro electric dams and how they work Provide background on basic principles of hydropower and its history. Explain features that all hydro power dams have and compare the design of Revelstoke
Overview of hydro electric dams and how they work Provide background on basic principles of hydropower and its history. Explain features that all hydro power dams have and compare the design of Revelstoke
electric cars reduce the CO2 emissions of our society?
 Can electric cars reduce the energy consumption and the CO2 emissions of our society? A school project at Bundesrealgymnasium 16 Schuhmeierplatz 7 1160 Vienna Austria by Albert Jaros Contents information
Can electric cars reduce the energy consumption and the CO2 emissions of our society? A school project at Bundesrealgymnasium 16 Schuhmeierplatz 7 1160 Vienna Austria by Albert Jaros Contents information
The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance.
 FORCES AND BRAKING Q1. The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed.
FORCES AND BRAKING Q1. The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed.
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5
 Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack
 Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack Name: Class: Date: Time: 63 minutes Marks: 63 marks Comments: Page of 49 The graphs in List A show how the velocities of three vehicles change with time. The statements
Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack Name: Class: Date: Time: 63 minutes Marks: 63 marks Comments: Page of 49 The graphs in List A show how the velocities of three vehicles change with time. The statements
TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical Generation System Sample Lab Experiment Procedure
 TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical Generation System Sample Lab Experiment Procedure Lab Session #1: System Overview and Operation Purpose: To gain an understanding of the TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical
TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical Generation System Sample Lab Experiment Procedure Lab Session #1: System Overview and Operation Purpose: To gain an understanding of the TurboGen TM Gas Turbine Electrical
Figure 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement?
 Q1.A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the
Q1.A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the
Distributed Energy Storage & More. P.K. Sen, Professor Colorado School of Mines
 Distributed Energy Storage & More, Professor Colorado School of Mines psen@mines.edu 1 Energy and Electricity 2 1970 1972 1974 1976 1978 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004
Distributed Energy Storage & More, Professor Colorado School of Mines psen@mines.edu 1 Energy and Electricity 2 1970 1972 1974 1976 1978 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004
James wore a blindfold and ear defenders. He rested his head on a wooden stick pushed into the ground so that he could feel vibrations.
 Level 7 Physics Questions 1. Three pupils took part in an investigation into the speed of sound. All three pupils stood 1020 m from an explosion. Sylvia wore a blindfold. Paul wore ear defenders. James
Level 7 Physics Questions 1. Three pupils took part in an investigation into the speed of sound. All three pupils stood 1020 m from an explosion. Sylvia wore a blindfold. Paul wore ear defenders. James
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction
 Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8019038925* PHYSICS 0625/03 Paper 3 Extended October/November 2007 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8019038925* PHYSICS 0625/03 Paper 3 Extended October/November 2007 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Physics - Chapters Task List
 Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
7/29/2014. Wisconsin Public Utility Institute ENERGY UTILITY BASICS. Wisconsin Public Utility Institute
 ENERGY UTILITY BASICS Systems within the Electric Utility Business Generation Transmission Distribution - Consumption RTOs and Markets Ken Copp July 31, 2014 SOURCE Generating Plant Distribution System
ENERGY UTILITY BASICS Systems within the Electric Utility Business Generation Transmission Distribution - Consumption RTOs and Markets Ken Copp July 31, 2014 SOURCE Generating Plant Distribution System
Physics Professor Ani Aprahamian. Science Literacy. Chapter 3: Energy
 Physics 10062 Professor Ani Aprahamian Science Literacy Chapter 3: Energy What can we do about it? Renewable Energy Resources? Solar Wind Hydropower Waves Geothermal If we have such inexhaustible solar
Physics 10062 Professor Ani Aprahamian Science Literacy Chapter 3: Energy What can we do about it? Renewable Energy Resources? Solar Wind Hydropower Waves Geothermal If we have such inexhaustible solar
Page 2. The go-kart always had the same mass and used the same motor.
 Q1.(a) Some students have designed and built an electric-powered go-kart. After testing, the students decided to make changes to the design of their go-kart. The go-kart always had the same mass and used
Q1.(a) Some students have designed and built an electric-powered go-kart. After testing, the students decided to make changes to the design of their go-kart. The go-kart always had the same mass and used
Technology Exploration-I Curriculum Development Unit
 Technology Exploration-I Modu le 4: Pulleys and Gears PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 4: Pulleys and Gears Module Objectives After the completion
Technology Exploration-I Modu le 4: Pulleys and Gears PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 4: Pulleys and Gears Module Objectives After the completion
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Construction Set: Smart Grid System
 Construction Set: Smart Grid System Curriculum for Grades 3-5 Student Edition Center for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Illinois State University 2017 www.smartgridforschools.org Look around your
Construction Set: Smart Grid System Curriculum for Grades 3-5 Student Edition Center for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Illinois State University 2017 www.smartgridforschools.org Look around your
10% SIGNPOSTING THE FUTURE INCREASE. Implications of evolving technology for the pricing of New Zealand s distribution services
 SIGNPOSTING THE FUTURE Implications of evolving technology for the pricing of New Zealand s distribution services An exciting range of technologies are starting to transform the way consumers use electricity.
SIGNPOSTING THE FUTURE Implications of evolving technology for the pricing of New Zealand s distribution services An exciting range of technologies are starting to transform the way consumers use electricity.
Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism
 Name: Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism 1. An electron, travelling with a constant velocity, enters a region of uniform magnetic field. Which of the following is not a possible pathway? 2. A bar magnet
Name: Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism 1. An electron, travelling with a constant velocity, enters a region of uniform magnetic field. Which of the following is not a possible pathway? 2. A bar magnet
Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 20 November 2017
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Human Energy Generation and Electrical Signal Measurement
 Human Energy Generation and Electrical Signal Measurement Energy Generation and Usage Earth s Energy Balance Yearly energy resources (TWh) Solar energy absorbed by atmosphere, oceans, Earth[1] 751,296,000.0
Human Energy Generation and Electrical Signal Measurement Energy Generation and Usage Earth s Energy Balance Yearly energy resources (TWh) Solar energy absorbed by atmosphere, oceans, Earth[1] 751,296,000.0
Energy & Sustainability. Lecture 8: Electric Power Generation And Distribution February 5, 2009
 Energy & Sustainability Lecture 8: Electric Power Generation And Distribution February 5, 2009 Illumination Example Input stage Power Station Distribution system Your meter Useful energy! Electric Power
Energy & Sustainability Lecture 8: Electric Power Generation And Distribution February 5, 2009 Illumination Example Input stage Power Station Distribution system Your meter Useful energy! Electric Power
Paper Reference(s) Edexcel GCSE Science (5009) Physics (5045) P1a Topics 9 and 10 Foundation and Higher Tier
 Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 59 545 Edexcel GSE Science (59) Physics (545) P1a Topics 9 and 1 Foundation and Higher Tier Friday 21 November 28 Morning Time: 2 minutes Materials required
Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 59 545 Edexcel GSE Science (59) Physics (545) P1a Topics 9 and 1 Foundation and Higher Tier Friday 21 November 28 Morning Time: 2 minutes Materials required
Why choose Electronic Engineering?
 Outline Why choose Electronic Engineering? Professor Peter Kennedy Professor of Microelectronic Engineering University College Dublin What is Engineering? What is Electrical and Electronic Engineering?
Outline Why choose Electronic Engineering? Professor Peter Kennedy Professor of Microelectronic Engineering University College Dublin What is Engineering? What is Electrical and Electronic Engineering?
Unit 32 Three-Phase Alternators
 Unit 32 Three-Phase Alternators Objectives: Discuss the operation of a three-phase alternator. Explain the effect of rotation speed on frequency. Explain the effect of field excitation on output voltage.
Unit 32 Three-Phase Alternators Objectives: Discuss the operation of a three-phase alternator. Explain the effect of rotation speed on frequency. Explain the effect of field excitation on output voltage.
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes)
 Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM
 CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1: MAGNETIC EFFECT OF A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR Electromagnets 1. Conductor is a material that can flow.. current 2. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between.and
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1: MAGNETIC EFFECT OF A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR Electromagnets 1. Conductor is a material that can flow.. current 2. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between.and
