Technology Exploration_II
|
|
|
- Gavin Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011
2 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion of this module, students should be able to: Define energy. Differentiate between the different forms of energy. Draw energy transfer diagrams. Give examples of electrical machines. Define the purpose of motors and generators. State the function of a capacitor. State the purpose of a Power Distribution Network. Conduct practical tasks to demonstrate the application of motors, generators, and capacitors. Module Contents No Topic Page 7.1 Introduction to Energy Electrical Energy Practical Tasks Worksheet 18 2 Module 1: Electrical Machines
3 1.1 Introduction to Energy What is energy? Energy does things for us. It makes televisions and laptops work. It moves cars along the road and boats on the water. It helps our bodies grow and makes us do things. Energy is the ability to do work. What are the different forms of energy? Energy can have several forms, but they all fall into two main typespotential or kinetic. Potential energy is the energy stored in an object/body due to its position. Examples of potential energy are, water in a lake in the mountains, or an object held at a certain height as shown in figure 1.1. Gravity gives potential energy to an object. Figure 1.1:Potential energy example Kinetic energy is the energy which a body has due to its motion. A boy running, flowing water and wind are good examples of kinetic energy. Electricity is also kinetic energy because it involves the movement of electrons. Figure 1.2:Kinetic energy example Module 7: Electrical Machines 3
4 Transfer of Energy Energy can be changed or transferred from one form to another. An example is the roller coaster illustrated in figure 1.3. When it is on its way up, it is using kinetic energy since the energy is in motion. When it reaches the top it has potential (or stored) energy. When it goes down the hill it is using kinetic energy again. Figure 1.3: Roller coaster The example of a cycle rider (shown in figure 1.4) riding to the top of the hill, and then downwards demonstrates how the energy is transferred from one form to another during his ride. Figure 1.4: Cycle rider 4 Module 1: Electrical Machines
5 Other Forms of Energy Examples of other forms of energy are light energy, heat (or thermal) energy, chemical energy, electrical energy and so on. This module will focus on electrical energy, and the electrical machines. Figure 1.5: Energy forms Some energy changes (transformations) are useful, while others are not. Figure 1.6: Energy transformation For example, a windmill collects kinetic energy from the wind and converts it into useful mechanical and electrical energy. The Chinese used windmills to water their farms as illustrated in figure 1.7. This kind of energy is called Renewable Energy. This will be covered in details in Module 7: Electrical Machines 5
6 Module 2. Figure 1.7: Windmill Class Activity 1: Energy transfer tables and diagrams are an excellent way of displaying the energy transfers taking place in a process. Complete the energy transfer table given below: Energy Converter Energy in Energy out Other Energy out Windmill Wind Mechanical Electrical 6 Module 1: Electrical Machines
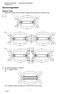
7 1.2 Electrical Energy Electrical energy is what is stored in a battery, and can be used to power a cell phone or start a car. Electrical energy is delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, typically moving through a wire. Generating Electrical Energy Electrical machine is a device that converts either mechanical energy to electrical energy or vice versa. Motors and generators are examples of electrical machines. Figure 1.8: DC Motor Figure 1.9: DC Motor connected to a battery If a motor is connected to a battery as shown in figure 7.9, the motor will turn. Here it converts electrical energy to kinetic (Mechanical) energy. A motor can also be used to generate electricity, and when a motor functions in this way, it is called a generator or a dynamo. Electricity is generated when the axle of the motor is turned. Module 7: Electrical Machines 7
8 Storing Electrical Energy A capacitor is a device that could be used to store electrical energy. Unlike the battery, it does not use chemicals to store the electricity. It is made from two metal plates with a thin layer of insulator in between them. When the capacitor is charged (filled), the positive (+) charge goes on one plate, and an equal negative (-) charge goes on the other plate. When the capacitor is discharged (empty), both plates will have no charge. Figure 1.10: Capacitor 8 Module 1: Electrical Machines
9 1.3 Practical Tasks Task 1: 1. Connect the Lego motor to a battery and watch the motor run. In this case, the motor converts energy to energy. 2. Attach a large pulley wheel to the motor axle. A grey connector peg makes a good handle. Add two green tiles to show that the motor is being used as a generator of electricity. Figure 1.11: Generator 3. Turn the handle and feel how it turns a. Was it easy or hard to turn the handle? b. When you turn the handle, what sort of energy do you put in? Module 7: Electrical Machines 9
10 4. Connect a lamp at one end of a connecting wire and attach the other end to the motor/generator. Turn the handle to light the lamp. Feel how it turns. Figure 1.12: Lamp connected to the generator a. Was it easier of harder to turn the handle than before? b. Is the motor used as a generator in this activity? 5. Write down the energy transfer taking place in a generator: From to 6. Explain why it is harder to turn the handle when the lamp is connected? 7. Write down the useful energy transfer in a lamp. From to 01 Module 1: Electrical Machines
11 8. Complete the energy transfer diagram for the lamp. Figure 1.13: Lamp connected to the generator 9. Which form of energy do we get from the lamp that we do not use? Module 7: Electrical Machines 00
12 1.3.2 Task 2: Connect a generator to drive a motor 1. Connect a motor to a generator with a wire. Put a large pulley wheel on each. Add a connector peg to act as a handle on the generator. Add two green tiles to indicate that it is a generator. Figure 7.14: Motor connected to the generator 2. Turn the generator handle. Watch what happens to the pulley wheel on the motor. What is your observation regarding the other motor? 3. Use a force-meter to measure the force needed to turn the generator handle. What force was needed (in Newtons)? Figure 7.15: Measuring force with a force-meter 02 Module 1: Electrical Machines
13 4. Draw an energy transfer diagram for the motor. 5. Draw an energy transfer diagram for the generator. Module 7: Electrical Machines 03
14 1.3.3 Task 3: Storing Electrical Energy In this task, you will see how a capacitor could be used to store electrical energy. 1. As a first step, check that the capacitor is discharged or empty. This can be done by connecting the capacitor to the motor as shown in figure The motor will not turn if the capacitor has discharged. 2. Put a large pulley wheel on the axle of the motor and add a grey connector peg to make a handle. Add two green tiles to indicate that it is a generator. 3. Now, connect the capacitor to the generator. Take care to connect it as shown on page 18 of the building booklet. Figure 1.16: Capacitor connected to the motor 4. Turn the handle clockwise a few times then let go. What happens to the pulley? 5. When it is discharged (motor stops turning) try turning it 20 turns. What was different? 6. Next try turning the handle until the red light shows that the capacitor is fully charged. What was different? 04 Module 1: Electrical Machines
15 1.3.4 Task 4: Power Distribution Network This activity will let you build an electricity grid system. 1. Attach a handle and green tiles to the generator, then connect a motor to the generator. Turn the generator. Note what happens to the motor and how hard it is to turn the generator handle. Figure 1.17: Motor connected to the generator 2. Now connect a lamp and another motor. Figure 1.18: Lamp connected to the motor and generator Keep turning at the same speed and feel how hard it will turn. When you add more load what happens to: a. The torque (turning force) needed by the generator? b. The motors and lamps? c. What happens to the motors when you stop generating Module 7: Electrical Machines 05
16 electricity? 3. Add a second generator to your system. Figure 1.17:A second generator connected to the system What happens to: a. The torque needed by the first generator when the second generator was added? b. The motors and lamps? 4. Having a real power station on standby, ready to take over when demand is high, is very expensive. A storage capacitor could be added to smooth out demand. Connect a generator, capacitor and motor. Check the connections. 06 Module 1: Electrical Machines
17 Turn the handle to generate electricity to charge the capacitor and turn the motor. What did you notice about the torque (turning force) as the capacitor charged up? 5. Add a lamp, or second motor. Figure 1.18:Generator, lamp, motor and capacitor connected What happens when you start turning the generator? Module 7: Electrical Machines 07
18 1.4 Worksheet 1. What are the two main types of energy? 2. Classify the following examples as potential and kinetic energy: Flowing water A ball held at a certain height A stretched rubber band A boy running 3. A lamp is connected to the generator as shown in the figure below. The lamp turns on when the handle of the generator is turned. Draw the energy transfer diagram for the lamp. 08 Module 1: Electrical Machines
19 4. Complete the energy transfer table given below: Energy Converter Energy in Energy out Other Energy out Windmill Car engine Electric lamp Module 7: Electrical Machines 09
Technology Exploration-I Curriculum Development Unit
 Technology Exploration-I Modu le 4: Pulleys and Gears PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 4: Pulleys and Gears Module Objectives After the completion
Technology Exploration-I Modu le 4: Pulleys and Gears PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 4: Pulleys and Gears Module Objectives After the completion
Energy Conversions Questions CfE
 Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
THE UNITED GEAR FORCE STEM ACTIVITY. By Linda Morales-Burton Tech Ed. teacher at Christiansburg Middle School
 THE UNITED GEAR FORCE STEM ACTIVITY By Linda Morales-Burton Tech Ed. teacher at Christiansburg Middle School State Competencies: Identify the six simple machines and examples of each Investigate energy
THE UNITED GEAR FORCE STEM ACTIVITY By Linda Morales-Burton Tech Ed. teacher at Christiansburg Middle School State Competencies: Identify the six simple machines and examples of each Investigate energy
Module 3: Wheel & Axle
 Technology Exploration-I Module 3: Wheel & Axle PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 3: Wheel & Axle Module Objectives After the completion of
Technology Exploration-I Module 3: Wheel & Axle PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 3: Wheel & Axle Module Objectives After the completion of
ELECTRICAL BATTERIES FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY
 ELECTRICAL BATTERIES FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY Abstract The lead acid battery is the most used in industry. It s advantageous to use because of its low cost. Modern renewable energy systems need batteries to
ELECTRICAL BATTERIES FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY Abstract The lead acid battery is the most used in industry. It s advantageous to use because of its low cost. Modern renewable energy systems need batteries to
Draft copy. Friction and motion. Friction: pros and cons
 As you have learned, moving objects often slow down because there is a force acting on them. The force is acting in the opposite direction to the way the objects are moving. This force is called friction.
As you have learned, moving objects often slow down because there is a force acting on them. The force is acting in the opposite direction to the way the objects are moving. This force is called friction.
4.2 Friction. Some causes of friction
 4.2 Friction Friction is a force that resists motion. Friction is found everywhere in our world. You feel the effects of when you swim, ride in a car, walk, and even when you sit in a chair. Friction can
4.2 Friction Friction is a force that resists motion. Friction is found everywhere in our world. You feel the effects of when you swim, ride in a car, walk, and even when you sit in a chair. Friction can
LEGO Parts Guide. Naming and Building with LEGO parts. Version 1.3 4/12/10
 LEGO Parts Guide Naming and Building with LEGO parts Version 1.3 4/12/10 Table of Contents Connectors... 4 Friction Pegs... 4 Frictionless Pegs... 5 Ball Joints / Tie Rods... 6 Bushings... 7 Angle Connectors...
LEGO Parts Guide Naming and Building with LEGO parts Version 1.3 4/12/10 Table of Contents Connectors... 4 Friction Pegs... 4 Frictionless Pegs... 5 Ball Joints / Tie Rods... 6 Bushings... 7 Angle Connectors...
STATION #1: Can you make the energy flow? 2) Put the correct objects into the correct sequences to make the energy flow.
 STATION #1: Can you make the energy flow? 1) Go to: http://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/energy/media/games/web/energyflows.swf 2) Put the correct objects into the correct sequences to make the energy flow.
STATION #1: Can you make the energy flow? 1) Go to: http://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/energy/media/games/web/energyflows.swf 2) Put the correct objects into the correct sequences to make the energy flow.
Amtek Basic Electronics 1
 Page 1 Page 2 Contents Worksheet 1 - Conductors and insulators 3 Worksheet 2 - Circuits 5 Worksheet 3 - Electric current 7 Worksheet 4 - Electromagnetism 9 Worksheet 5 - Electrolysis 11 Worksheet 6 - Switches
Page 1 Page 2 Contents Worksheet 1 - Conductors and insulators 3 Worksheet 2 - Circuits 5 Worksheet 3 - Electric current 7 Worksheet 4 - Electromagnetism 9 Worksheet 5 - Electrolysis 11 Worksheet 6 - Switches
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and. the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Circuits with Friends What is a circuit, and what
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Circuits with Friends What is a circuit, and what
reflect energy: the ability to do work
 reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8. Name:
 Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8 Name: Exploration 1 Rapidly turn the handles clockwise on all three generators at the end of the table, watching the System Voltage panel: 1. Draw the needle when the
Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8 Name: Exploration 1 Rapidly turn the handles clockwise on all three generators at the end of the table, watching the System Voltage panel: 1. Draw the needle when the
Mechanical Systems. Section 1.0 Machines are tools that help humans do work. 1.1 Simple Machines- Meeting Human Needs Water Systems
 Unit 4 Mechanical Systems Section 1.0 Machines are tools that help humans do work. Define: machine- 1.1 Simple Machines- Meeting Human Needs Water Systems Then: Now: The earliest devices were devices.
Unit 4 Mechanical Systems Section 1.0 Machines are tools that help humans do work. Define: machine- 1.1 Simple Machines- Meeting Human Needs Water Systems Then: Now: The earliest devices were devices.
Objectives: I can convert units using conversion factors in the same system. I can convert units using conversion factors between systems.
 Unit 1: Relationships between Quantities and Reasoning with Equations Lesson 1- Converting Units Objectives: I can convert units using conversion factors in the same system. I can convert units using conversion
Unit 1: Relationships between Quantities and Reasoning with Equations Lesson 1- Converting Units Objectives: I can convert units using conversion factors in the same system. I can convert units using conversion
What is Electricity? Lesson one
 What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
MECHANISMS. AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX
 MECHANISMS AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION 2 LEVER 3 PULLEYS 4 BELT AND PULLEY SYSTEM 5 GEARS 6 GEARS WITH CHAIN 7 WORM GEAR 8 RACK AND PINION 9 SCREW AND NUT 10 CAM 11 ECCENTRIC
MECHANISMS AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION 2 LEVER 3 PULLEYS 4 BELT AND PULLEY SYSTEM 5 GEARS 6 GEARS WITH CHAIN 7 WORM GEAR 8 RACK AND PINION 9 SCREW AND NUT 10 CAM 11 ECCENTRIC
Friction and Momentum
 Lesson Three Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to: understand friction as a force that opposes motion, and use this to explain why falling objects reach a terminal velocity know that the
Lesson Three Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to: understand friction as a force that opposes motion, and use this to explain why falling objects reach a terminal velocity know that the
Chapter 14 Learning Objectives-Study this for TEST. Chapter 14 Work and Power. Chapter 14 Learning Objectives-Study this for TEST
 Chapter 14 Work and Power GOAL: Students will be able to compare and contrast work and power qualitatively and quantitatively. Standard: SC.912.P.10.3 Students will: Level Scale 4 design and conduct experiments
Chapter 14 Work and Power GOAL: Students will be able to compare and contrast work and power qualitatively and quantitatively. Standard: SC.912.P.10.3 Students will: Level Scale 4 design and conduct experiments
Genecon Teaching notes
 How to use Genecon V3 / DUE...2 Precautions...3 Teaching ideas and activities. 1. Using a Genecon as an alternative power supply...4 Using a data logger and Voltage sensor...5 2. Demonstrating the efficiency
How to use Genecon V3 / DUE...2 Precautions...3 Teaching ideas and activities. 1. Using a Genecon as an alternative power supply...4 Using a data logger and Voltage sensor...5 2. Demonstrating the efficiency
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME
 ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
Construction Set: Smart Grid System
 Construction Set: Smart Grid System Curriculum for Grades 3-5 Student Edition Center for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Illinois State University 2017 www.smartgridforschools.org Look around your
Construction Set: Smart Grid System Curriculum for Grades 3-5 Student Edition Center for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Illinois State University 2017 www.smartgridforschools.org Look around your
Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current
 Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current Activity 11.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what
Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current Activity 11.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what
AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552
 AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552 Mechanical devices Unit 2 Energy, materials, systems and devices 8 Objectives Be able to recognise and identify a range of movements Understand the functions of mechanical
AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552 Mechanical devices Unit 2 Energy, materials, systems and devices 8 Objectives Be able to recognise and identify a range of movements Understand the functions of mechanical
A) Draw the levers in your notes and use the drawings to record your results.
 Simple Machines Station One 1 st Class Levers This station should have 2 levers set up. One where the fulcrum is @.5m and one where it is @.65m. Don t change them in any way! You should also have Newton
Simple Machines Station One 1 st Class Levers This station should have 2 levers set up. One where the fulcrum is @.5m and one where it is @.65m. Don t change them in any way! You should also have Newton
Lesson Plan 11 Electric Experiments
 Lesson Plan 11 Electric Experiments Brief description Students experiment with aluminium foil, batteries and cheap, readily availably low voltage light bulbs* to construct a simple conductivity tester.
Lesson Plan 11 Electric Experiments Brief description Students experiment with aluminium foil, batteries and cheap, readily availably low voltage light bulbs* to construct a simple conductivity tester.
Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 19 November 2012
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2012 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 19 November 2012 Reading time: 9.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2012 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 19 November 2012 Reading time: 9.00
The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch bulb.
 Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Harnessing Human Energy
 Harnessing Human Energy Article Compilation 2018 by The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
Harnessing Human Energy Article Compilation 2018 by The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
Physical Sciences (Energy and Matter) Objective: To determine what household items are good conductors of electricity. The purpose of this
 Objective: To determine what household items are good conductors of electricity. The purpose of this investigation is to demonstrate an understanding of simple closed circuits as well as evaluate the electrical
Objective: To determine what household items are good conductors of electricity. The purpose of this investigation is to demonstrate an understanding of simple closed circuits as well as evaluate the electrical
Design and build a kinetic sculpture with your gears and pulleys tinker set.
 Design and build a kinetic sculpture with your gears and pulleys tinker set. Kinetic Energy is energy in motion. With your gears and pulleys, you can harness this energy to power animated sculptures and
Design and build a kinetic sculpture with your gears and pulleys tinker set. Kinetic Energy is energy in motion. With your gears and pulleys, you can harness this energy to power animated sculptures and
Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 20 November 2017
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Two Cell Battery. 6. Masking tape 7. Wire cutters 8. Vinegar 9. Salt 10. Lemon Juice DC ammeter
 Your Activity Build a two-cell Wet battery Materials 1. 2 150 ml beakers 2. 2 pieces aluminum foil (8 X 12 inch) 3. 2 small paper cups, cut ¾ from bottom 4. 3 31.5 inch of non-insulated copper wire gauge
Your Activity Build a two-cell Wet battery Materials 1. 2 150 ml beakers 2. 2 pieces aluminum foil (8 X 12 inch) 3. 2 small paper cups, cut ¾ from bottom 4. 3 31.5 inch of non-insulated copper wire gauge
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
Regents Physics Summer Assignment. Physics: Balloon Car Lab
 Regents Physics Summer Assignment Name: Physics: Balloon Car Lab A rocket is simply a chamber filled with pressurized gas. A small opening called a nozzle allows the air to escape, causing thrust that
Regents Physics Summer Assignment Name: Physics: Balloon Car Lab A rocket is simply a chamber filled with pressurized gas. A small opening called a nozzle allows the air to escape, causing thrust that
Unit 1: Energy and Motion
 5 5 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 5: Work and Machines 5.1: Work 5.2: Using Machines 5.3: Simple Machines 5.1 Work What is work? To many people, the word work means something they
5 5 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 5: Work and Machines 5.1: Work 5.2: Using Machines 5.3: Simple Machines 5.1 Work What is work? To many people, the word work means something they
Unit 5. Guided Work Sheet Sci 701 NAME: 1) Define the following key terms. Acceleration. DC motor. Direct current (DC) Force.
 Unit 5 Guided Work Sheet Sci 701 NAME: 1) Define the following key terms. Acceleration DC motor Direct current (DC) Force Power Shaft Speed Torque Work Wrench flat 1. Determine free wheel speed and stall
Unit 5 Guided Work Sheet Sci 701 NAME: 1) Define the following key terms. Acceleration DC motor Direct current (DC) Force Power Shaft Speed Torque Work Wrench flat 1. Determine free wheel speed and stall
 1 (a) (i) State what is meant by the direction of an electric field....[1] Fig. 9.1 shows a pair of oppositely-charged horizontal metal plates with the top plate positive. Fig. 9.1 The electric field between
1 (a) (i) State what is meant by the direction of an electric field....[1] Fig. 9.1 shows a pair of oppositely-charged horizontal metal plates with the top plate positive. Fig. 9.1 The electric field between
ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions
 CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current
 Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current Physical Science Georgia Performance Standards: SPS10a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction. SPS10b. Explain
Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current Physical Science Georgia Performance Standards: SPS10a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction. SPS10b. Explain
SNC1D PHYSICS 4/6/2013. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P ) Electrical Resistance. Electrical Resistance
 SNC1D PHYSICS THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P.441-443) Electrical Resistance Have you ever noticed that when you recharge your cellphone, MP3 player, or laptop computer, the
SNC1D PHYSICS THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P.441-443) Electrical Resistance Have you ever noticed that when you recharge your cellphone, MP3 player, or laptop computer, the
Unit Standard Demonstrate knowledge of the safe operation of a motorcycle
 Unit standard: 24555v2 Level: 2 Credits: 3 Assessment version: 3 Unit Standard 24555 Demonstrate knowledge of the safe operation of a motorcycle Applied Assessment Task Learner to complete Learner Name
Unit standard: 24555v2 Level: 2 Credits: 3 Assessment version: 3 Unit Standard 24555 Demonstrate knowledge of the safe operation of a motorcycle Applied Assessment Task Learner to complete Learner Name
PHYSICS KINETIC AND GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGIES WORKSHEET
 Kinetic Energy Basics 1. What is the kinetic energy of a 80 kg football player running at 8 m/s? 2. What is the kinetic energy of a 0.01 kg dart that is thrown at 20 m/s? 3. What is the kinetic energy
Kinetic Energy Basics 1. What is the kinetic energy of a 80 kg football player running at 8 m/s? 2. What is the kinetic energy of a 0.01 kg dart that is thrown at 20 m/s? 3. What is the kinetic energy
Engaging Inquiry-Based Activities Grades 3-6
 ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUITS Engaging Inquiry-Based Activities Grades 3-6 Janette Smith 2016 Janette Smith 2016 1 What s Inside Activity 1: Light it Up!: Students investigate different ways to light a light
ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUITS Engaging Inquiry-Based Activities Grades 3-6 Janette Smith 2016 Janette Smith 2016 1 What s Inside Activity 1: Light it Up!: Students investigate different ways to light a light
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
Draw a Circuit! Fun with graphite. by Kyle Seyler.
 Draw a Circuit! Fun with graphite by Kyle Seyler http://cei.washington.edu 1 Overview Students explore the conductive properties of graphite and graphene as they create simple circuits. Next Generation
Draw a Circuit! Fun with graphite by Kyle Seyler http://cei.washington.edu 1 Overview Students explore the conductive properties of graphite and graphene as they create simple circuits. Next Generation
Newton Scooters TEACHER NOTES. Forces Chapter Project. Materials and Preparation. Chapter Project Overview. Keep Students on Track Section 2
 TEACHER NOTES Lab zonetm Newton Scooters The following steps will walk you through the. Use the hints as you guide your students through planning, construction, testing, improvements, and presentations.
TEACHER NOTES Lab zonetm Newton Scooters The following steps will walk you through the. Use the hints as you guide your students through planning, construction, testing, improvements, and presentations.
What is electricity?
 Electrical Safety Part 1 What is electricity? Note to Teachers: Behind the Lesson: Why is it important to understand the basics of electricity before learning about electrical safety? The world around
Electrical Safety Part 1 What is electricity? Note to Teachers: Behind the Lesson: Why is it important to understand the basics of electricity before learning about electrical safety? The world around
ROBOTICS BUILDING BLOCKS
 ROBOTICS BUILDING BLOCKS 2 CURRICULUM MAP Page Title...Section Estimated Time (minutes) Robotics Building Blocks 0 2 Imaginations Coming Alive 5...Robots - Changing the World 5...Amazing Feat 5...Activity
ROBOTICS BUILDING BLOCKS 2 CURRICULUM MAP Page Title...Section Estimated Time (minutes) Robotics Building Blocks 0 2 Imaginations Coming Alive 5...Robots - Changing the World 5...Amazing Feat 5...Activity
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy
 Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
SHOCK DYNAMOMETER: WHERE THE GRAPHS COME FROM
 SHOCK DYNAMOMETER: WHERE THE GRAPHS COME FROM Dampers are the hot race car component of the 90s. The two racing topics that were hot in the 80s, suspension geometry and data acquisition, have been absorbed
SHOCK DYNAMOMETER: WHERE THE GRAPHS COME FROM Dampers are the hot race car component of the 90s. The two racing topics that were hot in the 80s, suspension geometry and data acquisition, have been absorbed
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707
 FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 DC I Lesson Objectives: 1. What is Electricity? 2. Discover the Electron 3. Learn about Conductors and Insulators 4. Learn about Voltage and Current 5. Learn the difference
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 DC I Lesson Objectives: 1. What is Electricity? 2. Discover the Electron 3. Learn about Conductors and Insulators 4. Learn about Voltage and Current 5. Learn the difference
Electricity. Grade: 1 st grade Category: Physical Science NGSS: ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems
 Electricity Grade: 1 st grade Category: Physical Science NGSS: ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems Description: In this lesson, the students will learn that some objects need electricity
Electricity Grade: 1 st grade Category: Physical Science NGSS: ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems Description: In this lesson, the students will learn that some objects need electricity
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
Circuits. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-9ewbpqddg
 Circuits https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-9ewbpqddg L.O: To differentiate between complete and incomplete circuits. Components of an Electrical Circuit battery (cell) bulb holder crocodile clip bulb What
Circuits https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-9ewbpqddg L.O: To differentiate between complete and incomplete circuits. Components of an Electrical Circuit battery (cell) bulb holder crocodile clip bulb What
LETTER TO PARENTS SCIENCE NEWS. Dear Parents,
 LETTER TO PARENTS Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Parents, SCIENCE NEWS Our class is beginning a new science unit using the FOSS Magnetism and Electricity Module. We
LETTER TO PARENTS Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Parents, SCIENCE NEWS Our class is beginning a new science unit using the FOSS Magnetism and Electricity Module. We
units edition imperial PSI & lbs/in2 Name
 L R E W O P D I FLU Name Set: imperial units edition PSI & lbs/in2 This lab will provide you an understanding of: Hydraulic Systems Pneumatic Systems Cylinders Pascal s Law Liquids & Gases Pressure Kinetic
L R E W O P D I FLU Name Set: imperial units edition PSI & lbs/in2 This lab will provide you an understanding of: Hydraulic Systems Pneumatic Systems Cylinders Pascal s Law Liquids & Gases Pressure Kinetic
Question 2: Around the bar magnet draw its magnetic fields. Answer:
 Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Table Of Contents. Motor Selection Guide Installation Instructions Operators 20-32
 Table Of Contents Motor Selection Guide 2-12 - Shades, Shutters and Doors - Retractable Awnings Installation Instructions 13-1 - Operator Adaptors - Operator Limit Adjustment - Wiring Considerations -
Table Of Contents Motor Selection Guide 2-12 - Shades, Shutters and Doors - Retractable Awnings Installation Instructions 13-1 - Operator Adaptors - Operator Limit Adjustment - Wiring Considerations -
1.69 Electric Conductors and Insulators
 1.69 Electric Conductors and Insulators Relate electric current to matter. Define electric conductor, and give examples of conductors. Describe electric insulators, and identify materials that are insulators.
1.69 Electric Conductors and Insulators Relate electric current to matter. Define electric conductor, and give examples of conductors. Describe electric insulators, and identify materials that are insulators.
THE FOURTH STATE. Gaining a universal insight into the diagnosis of automotive ignition systems. By: Bernie Thompson
 THE FOURTH STATE Gaining a universal insight into the diagnosis of automotive ignition systems By: Bernie Thompson Did you know that the forth state of matter powers the spark ignition internal combustion
THE FOURTH STATE Gaining a universal insight into the diagnosis of automotive ignition systems By: Bernie Thompson Did you know that the forth state of matter powers the spark ignition internal combustion
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707
 FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 6 Volt Lantern Battery Spring terminals (also available in screw terminals) Alligator Clips Best method to attach wires to the spring terminals on a lantern battery.
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 6 Volt Lantern Battery Spring terminals (also available in screw terminals) Alligator Clips Best method to attach wires to the spring terminals on a lantern battery.
What Are Gears? What Do They Do?
 What Are Gears? What Do They Do? Pre-Lesson Quiz 1. What is a gear? 2. List as many examples as you can of gears or objects that use gears. 2 Pre-Lesson Quiz Answers 1. What is a gear? A gear is a wheel
What Are Gears? What Do They Do? Pre-Lesson Quiz 1. What is a gear? 2. List as many examples as you can of gears or objects that use gears. 2 Pre-Lesson Quiz Answers 1. What is a gear? A gear is a wheel
Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. N S
 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
LEGO Education WeDo 2.0 Toolbox
 LEGO Education WeDo 2.0 Toolbox WeDo 2.0 Table of Contents Program with WeDo 2.0 3-21 Build with WeDo 2.0 22-36 Program with WeDo 2.0 Programming is an important part of twenty-first century learning,
LEGO Education WeDo 2.0 Toolbox WeDo 2.0 Table of Contents Program with WeDo 2.0 3-21 Build with WeDo 2.0 22-36 Program with WeDo 2.0 Programming is an important part of twenty-first century learning,
Work done and Moment. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift.
 Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
U-Score U-Score AAC Rank AAC Rank Vocabulary Vocabulary
 go 1 927 you 2 7600 i 3 4443 more 4 2160 help 5 659 it 6 9386 want 7 586 in 8 19004 that 9 10184 like 10 1810 what 11 2560 make 12 1264 is 13 10257 on 14 6674 out 15 2350 do 16 2102 here 17 655 eat 18
go 1 927 you 2 7600 i 3 4443 more 4 2160 help 5 659 it 6 9386 want 7 586 in 8 19004 that 9 10184 like 10 1810 what 11 2560 make 12 1264 is 13 10257 on 14 6674 out 15 2350 do 16 2102 here 17 655 eat 18
HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED?
 ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes)
 Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Electronic Circuits. How to Make a Paper Circuit
 Electronic Circuits How to Make a Paper Circuit What is a Circuit? A circuit is a closed loop through which charges can continually move. Charges run from positive to negative. In this activity, a circuit
Electronic Circuits How to Make a Paper Circuit What is a Circuit? A circuit is a closed loop through which charges can continually move. Charges run from positive to negative. In this activity, a circuit
Calculate the current in the kettle element. (3)
 1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
Sensors for hybrid power generation system
 Sensors for hybrid power generation system Michael Gouzman, Ph.D. 1 Objectives and scope New calls for sensor technologies Sensors for incorporated local generation and battery storage Sensors for renewable
Sensors for hybrid power generation system Michael Gouzman, Ph.D. 1 Objectives and scope New calls for sensor technologies Sensors for incorporated local generation and battery storage Sensors for renewable
Rubber Band Car. Tommy Stewart Corey Marineau John Martinez
 Tommy Stewart Corey Marineau John Martinez Rubber Band Car PURPOSE: Create a rubber band propelled car that will travel three meters. Then create a regression line using the data that represents how the
Tommy Stewart Corey Marineau John Martinez Rubber Band Car PURPOSE: Create a rubber band propelled car that will travel three meters. Then create a regression line using the data that represents how the
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
Teaching Aids and Materials: This week the students will: Standards addressed and expectations of Students for the week:
 Teacher: Subject Area: Room No: William Schraer STEM - Intro to Engineering Design 513 Lesson Week: Meeting Time Period: Day: February 2 February 6 1..5..7.. Wednesday 4 th Teaching Aids and Materials:
Teacher: Subject Area: Room No: William Schraer STEM - Intro to Engineering Design 513 Lesson Week: Meeting Time Period: Day: February 2 February 6 1..5..7.. Wednesday 4 th Teaching Aids and Materials:
Disco 3 Clock Spring / Rotary Coupler replacement
 Disco 3 Clock Spring / Rotary Coupler replacement I recently had to change my Clock spring and thought some folks may find it helpful to see what it entailed. I did lots of reading around but couldn t
Disco 3 Clock Spring / Rotary Coupler replacement I recently had to change my Clock spring and thought some folks may find it helpful to see what it entailed. I did lots of reading around but couldn t
WINDUP TORCH KIT TEACHING RESOURCES. Version 1.1 LIGHT UP YOUR DAY WITH THIS
 TEACHING RESOURCES SCHEMES OF WORK DEVELOPING A SPECIFICATION COMPONENT FACTSHEETS HOW TO SOLDER GUIDE LIGHT UP YOUR DAY WITH THIS WINDUP TORCH KIT Version 1.1 Index of Sheets TEACHING RESOURCES Index
TEACHING RESOURCES SCHEMES OF WORK DEVELOPING A SPECIFICATION COMPONENT FACTSHEETS HOW TO SOLDER GUIDE LIGHT UP YOUR DAY WITH THIS WINDUP TORCH KIT Version 1.1 Index of Sheets TEACHING RESOURCES Index
Roehrig Engineering, Inc.
 Roehrig Engineering, Inc. Home Contact Us Roehrig News New Products Products Software Downloads Technical Info Forums What Is a Shock Dynamometer? by Paul Haney, Sept. 9, 2004 Racers are beginning to realize
Roehrig Engineering, Inc. Home Contact Us Roehrig News New Products Products Software Downloads Technical Info Forums What Is a Shock Dynamometer? by Paul Haney, Sept. 9, 2004 Racers are beginning to realize
SCIENCE 8. Unit 4 Booklet. Machines and Mechanical Systems
 SCIENCE 8 Unit 4 Booklet Machines and Mechanical Systems TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT Levers Have Class BLM 4-2 Goal Identify items as Class 1, Class 2, or Class 3 levers. Introduction There are three classes
SCIENCE 8 Unit 4 Booklet Machines and Mechanical Systems TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT Levers Have Class BLM 4-2 Goal Identify items as Class 1, Class 2, or Class 3 levers. Introduction There are three classes
Q1. Figure 1 shows how atmospheric pressure varies with altitude.
 PRESSURE IN A FLUID Q1. Figure 1 shows how atmospheric pressure varies with altitude. Figure 1 (a) Explain why atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude. (3) (b) When flying, the pressure
PRESSURE IN A FLUID Q1. Figure 1 shows how atmospheric pressure varies with altitude. Figure 1 (a) Explain why atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude. (3) (b) When flying, the pressure
Planning Advisory Notice
 Capstan hoists, often referred to as catheads, make back-breaking work faster, easier and more productive. They are used for many applications in multiple industries including telecommunications, electric
Capstan hoists, often referred to as catheads, make back-breaking work faster, easier and more productive. They are used for many applications in multiple industries including telecommunications, electric
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 1 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 1 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism. If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0.
 SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism GALVAOMETERS If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0. otice how the current runs in the opposite directions on opposite
SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism GALVAOMETERS If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0. otice how the current runs in the opposite directions on opposite
A. 1. In first case, friction acts along the right. In second case, friction acts along the left.
 Chapter 12 Friction Topicwise Assignment Force of Friction A. 1. In first case, friction acts along the right. In second case, friction acts along the left. 2. Friction opposes the motion of one surface
Chapter 12 Friction Topicwise Assignment Force of Friction A. 1. In first case, friction acts along the right. In second case, friction acts along the left. 2. Friction opposes the motion of one surface
IT'S MAGNETIC (1 Hour)
 IT'S MAGNETIC (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will create a simple electromagnet using a nail, a battery, and copper wire. They will
IT'S MAGNETIC (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will create a simple electromagnet using a nail, a battery, and copper wire. They will
Rear Wheel Removal (by BassCliff)
 Rear Wheel Removal (by BassCliff) Hello to my GS riding friends! After picking up a nail in my rear tire (while on the freeway at 75mph!) I thought I would take a few pictures to help illustrate the rear
Rear Wheel Removal (by BassCliff) Hello to my GS riding friends! After picking up a nail in my rear tire (while on the freeway at 75mph!) I thought I would take a few pictures to help illustrate the rear
Electricity. Electric Charge. Before You Read. Read to Learn. Positive and Negative Charges. Picture This. section.
 chapter 6 Electricity 1 section Electric Charge What You ll Learn how electric charges exert forces about conductors and insulators how things become electrically charged Before You Read Think about some
chapter 6 Electricity 1 section Electric Charge What You ll Learn how electric charges exert forces about conductors and insulators how things become electrically charged Before You Read Think about some
Matching Speed to the Road Surface You can't steer or brake a vehicle unless you have traction. Traction is friction between the tires and the road.
 Matching Speed to the Road Surface You can't steer or brake a vehicle unless you have traction. Traction is friction between the tires and the road. There are some road conditions that reduce traction
Matching Speed to the Road Surface You can't steer or brake a vehicle unless you have traction. Traction is friction between the tires and the road. There are some road conditions that reduce traction
Jake can skate on ice.
 Jake can skate on ice. He loves to skate really fast! He will go to the lake to skate. The ice must be thick for him to skate. Today, the ice is firm. It is safe to skate. Take care, Jake! 5 1 1 19 28
Jake can skate on ice. He loves to skate really fast! He will go to the lake to skate. The ice must be thick for him to skate. Today, the ice is firm. It is safe to skate. Take care, Jake! 5 1 1 19 28
13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ
 13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ In Activity 13.2, you observed that when the two lamps were connected in series, the brightness of the lamps was less than when the lamps were connected in
13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ In Activity 13.2, you observed that when the two lamps were connected in series, the brightness of the lamps was less than when the lamps were connected in
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race.
 Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Driver Driven. InputSpeed. Gears
 Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
MiSTE STEM Camp Solar Lesson July, 2016 Standard(s) Learning targets Assessment Essential vocabulary. Informal - Discussion and participation
 MiSTE STEM Camp Solar Lesson July, 2016 Standard(s) Learning targets Assessment Essential vocabulary Science SEPS.1 - I can clarify problems to determine criteria for possible solutions. Science SEPS.8
MiSTE STEM Camp Solar Lesson July, 2016 Standard(s) Learning targets Assessment Essential vocabulary Science SEPS.1 - I can clarify problems to determine criteria for possible solutions. Science SEPS.8
Research and Development Objectives
 CO2 Dragster Design Research and Development Objectives Research in CO2 auto design involves the study of a few sciences related to the motion of your dragster. Aerodynamics- the study of how solid objects
CO2 Dragster Design Research and Development Objectives Research in CO2 auto design involves the study of a few sciences related to the motion of your dragster. Aerodynamics- the study of how solid objects
Is it Magnetic? 1. Fill in each table. List things ATTRACTED by a magnet on the LEFT and things NOT ATTRACTED on the RIGHT.
 Is it Magnetic? 1. Fill in each table. List things ATTRACTED by a magnet on the LEFT and things NOT ATTRACTED on the RIGHT. MAGNETIC NON-MAGNETIC # Object Made from check # Object Made from check --- ------------
Is it Magnetic? 1. Fill in each table. List things ATTRACTED by a magnet on the LEFT and things NOT ATTRACTED on the RIGHT. MAGNETIC NON-MAGNETIC # Object Made from check # Object Made from check --- ------------
The Starter motor. Student booklet
 The Starter motor Student booklet The Starter motor - INDEX - 2006-04-07-13:20 The Starter motor The starter motor is an electrical motor and the electric motor is all about magnets and magnetism: A motor
The Starter motor Student booklet The Starter motor - INDEX - 2006-04-07-13:20 The Starter motor The starter motor is an electrical motor and the electric motor is all about magnets and magnetism: A motor
Pressure Distribution. Western Canada Onsite Wastewater Management Association
 Pressure Distribution EFFLUENT DISTRIBUTION Get even distribution Space the doses Layout the distribution system Make choices for: piping, orifices, volumes Use worksheets for calculations Dose or flush
Pressure Distribution EFFLUENT DISTRIBUTION Get even distribution Space the doses Layout the distribution system Make choices for: piping, orifices, volumes Use worksheets for calculations Dose or flush
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE Electrical Circuits VINSE/VSVS Rural
 VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs/ Electrical Circuits 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Series and Parallel Circuits (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs/ Electrical Circuits 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Series and Parallel Circuits (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity
 Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
