Q1. Figure 1 shows how atmospheric pressure varies with altitude.
|
|
|
- Tobias Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRESSURE IN A FLUID Q1. Figure 1 shows how atmospheric pressure varies with altitude. Figure 1 (a) Explain why atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude. (3) (b) When flying, the pressure inside the cabin of an aircraft is kept at 70 kpa. The aircraft window has an area of 810 cm 2. Use data from Figure 1 to calculate the resultant force acting on an aircraft window when the aircraft is flying at an altitude of 12 km. Give your answer to two significant figures
2 Resultant force = N (5) (c) Figure 2 shows the cross-section of one type of aircraft window. Figure 2 Explain why the window has been designed to have this shape. (Total 10 marks) Q2. The figure below is a simplified diagram of a hydraulic brake system. (a) Which is the correct statement about the pressure at X and the pressure at Y? Tick ( ) one box. The pressure at X is greater than at Y The pressure at X is the same as at Y
3 Pressure = N/mm 2 The pressure at X is less than at Y (b) Piston B is larger than piston A. How will this affect the size of the force on piston B? Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. smaller than the same as larger than The force on piston B will be the force on piston A. (c) (i) A force of 24 N acts on piston A. The cross-sectional area of piston A is 8 mm 2. Calculate the pressure in N/mm 2 at position X. (ii) The unit N/mm 2 is not often used to measure pressure. Which unit is usually used to measure pressure? Tick ( ) one box. newton pascal watt (d) The liquid used in the hydraulic brake system freezes at 30 C. Suggest one effect a temperature below 30 C would have on the brake system. (Total 6 marks)
4 Q3. The diagram shows a water butt used to collect rainwater. A tap allows water to be collected from the water butt in a watering can. (a) If the tap was placed higher up on the water butt, what difference would it make to the rate of flow of water from the tap? Explain your answer. (b) A hosepipe is now attached to the tap. The hosepipe takes water to where it is needed. A gardener did an investigation to see how the rate of flow of water through a hosepipe, from a water butt, varies with the length of the hosepipe. His results are shown in below table. Length of hosepipe in metres Water collected in 10 seconds in cm
5 (i) What conclusions can you make based on the results in the table above? (ii) Suggest further readings that should be taken to improve the investigation. Give reasons for your answers. (4) (c) In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. You are provided with a water butt and lengths of hosepipe of different diameter. Describe how you would investigate how the rate of flow of water through a hosepipe varies with the diameter of the hosepipe. In your description you should include: any additional equipment that you would use any measurements you would make using the equipmentz any variables that need to be controlled and how this would be achieved.
6 (6) (Total 14 marks) Q4. Before a new bus can be used on the roads, it must pass a stability test. Figure 1 shows how the bus is tested. (a) (i) The bus will topple over if the ramp is tilted at too great an angle. Explain why. (ii) The bus is tested to angles of tilt far greater than it would experience in normal use. Suggest two reasons why. 1.
7 2. (b) Figure 2 shows the hydraulic machine that is used to make the ramp tilt. The pressure applied to the hydraulic liquid at the master piston is the same as the pressure applied by the hydraulic liquid to the slave piston. (i) State the property of the liquid that keeps the pressure at both pistons the same. (ii) A 360 N force acts on the master piston. Use information from Figure 2 to calculate the force applied by the hydraulic liquid to the slave piston. Force = N (3) (Total 8 marks) Q5. Levers and hydraulic systems can act as force multipliers. (a) Figure 1 shows a girl trying to lift a large rock using a long rod as a lever.
8 Figure 1 The girl is pushing down on the rod but is just unable to lift the rock. Which of the following changes would allow her to lift the rock? Tick ( ) two boxes. Change Tick ( ) Move the pivot away from the rock Make the rod longer Push the rod upwards Push down on the rod with a greater force (b) Liquids are used in hydraulic systems because they are virtually incompressible. Explain how the spacing of particles in a liquid cause it to be virtually incompressible. (c) Figure 2 shows a man using a car jack to lift his car. Figure 2
9 lisafx/istock/thinkstock Figure 3 shows a simple diagram of a car jack. Figure 3 (i) The man pushes down with an effort force. This results in a much larger force acting upwards on the car. Use information from Figure 3 to explain how. (4)
10 (ii) Which of the following statements about the forces in Figure 3 is correct? Tick ( ) one box. Tick ( ) The force acting on the car moves a greater distance than the effort force. The force acting on the car moves less distance than the effort force. The force acting on the car moves the same distance as the effort force. (Total 9 marks) Q6. Musicians sometimes perform on a moving platform. The figure below shows the parts of the lifting machine used to move the platform up and down. (a) What name is given to a system that uses liquids to transmit forces? Draw a ring around the correct answer. electromagnetic hydraulic ionising (b) To move the platform upwards, the liquid must cause a force of 1800 N to act on the piston. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 200 cm 2. Calculate the pressure in the liquid, in N / cm 2, when the platform moves.
11 Pressure = N / cm 2 (c) A new development is to use oil from plants as the liquid in the machine. Growing plants and extracting the oil requires less energy than producing the liquid usually used in the machine. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. an environmental Using the oil from the plants gives an ethical a social advantage over the liquid usually used. (Total 4 marks) Q7. Musicians sometimes perform on a moving platform. Figure 1 shows the parts of the lifting machine used to move the platform up and down. Figure 1 (a) What type of system uses a liquid to transmit a force? (b) The pump creates a pressure in the liquid of 8.75 x 10 4 Pa to move the platform
12 upwards. Calculate the force that the liquid applies to the piston. Force = N (c) The liquid usually used in the machine is made by processing oil from underground wells. A new development is to use plant oil as the liquid. Extracting plant oil requires less energy than extracting oil from underground wells. Suggest an environmental advantage of using plant oil. (d) Musicians often use loudspeakers. Figure 2 shows how a loudspeaker is constructed. Figure 2 The loudspeaker cone vibrates when an alternating current flows through the coil. Explain why.
13 (4) (Total 8 marks) Q8. Some students fill an empty plastic bottle with water. The weight of the water in the bottle is 24 N and the cross-sectional area of the bottom of the bottle is m 2. (a) Calculate the pressure of the water on the bottom of the bottle and give the unit. Pressure = (3) (b) The students made four holes in the bottle along a vertical line. They put the bottle in a sink. They used water from a tap to keep the bottle filled to the top. The students measured and recorded the vertical heights of the holes above the
14 sink. They also measured the horizontal distances the water landed away from the bottle. A pair of measurements for one of the holes is shown in the diagram. The complete data from the experiment is shown in the table. Hole Vertical height in cm Horizontal distance in cm J K L M 6 40 (i) Which hole is shown in the diagram? Draw a ring around the correct answer. J K L (ii) On the diagram, draw the path of the water coming out of hole M. Use the information in the table to help you. (c) Suggest one problem that might arise from trying to collect data from a fifth hole with a vertical height of 1 cm above the sink. (Total 7 marks) Q9. Mountain bike riders use brakes to slow down.
15 Ljupco Smokovski/Shutterstock Some mountain bikes use liquid-filled pipes to transmit the force from the rider s hand on the brake lever to the brake pads. These brakes are called hydraulic brakes. (a) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. (i) Liquids can be used to transmit the forces in a brake system,
16 Pressure = N/mm 2 are incompressible. because liquids can flow. take the shape of the container. (ii) against force F only. The pressure in the liquid is transmitted downwards only. in all directions. (b) When the rider s hand pulls on the brake lever, the force F applied to the liquid by the master piston is 80 N. The cross-sectional area of this piston is 50 mm 2. Calculate the pressure, in N/mm 2, exerted on the liquid by the master piston. (c) The unit N/mm 2 is not the usual unit of pressure. Which unit is usually used when calculating pressure? Draw a ring around the correct answer. N Nm 2 Pa (d) The rider applies a larger force to the brake lever. How would this increase in force affect the pressure in the liquid? (Total 6 marks) Q10. Mountain bike riders use brakes to slow down.
17 Some mountain bikes have hydraulic brakes. Ljupco Smokovski/Shutterstock (a) What property of a liquid enables a hydraulic brake system to work? (b) When the rider s hand pulls on the brake lever, the master piston applies a pressure
18 of pascals to the liquid. Using information from the diagram, calculate the force F exerted on the liquid by the master piston. Force F = N (c) The pressure in the liquid applies a force to move each slave piston. How does the size of this force compare to the force F applied by the master piston? Give a reason for your answer. (Total 5 marks)
19
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
Unit P.3, P3.2. Using physics to make things work. 1. (a) Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the centre of mass?
 Using physics to make things work 1. Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the centre of mass? The drawing shows a thin sheet of plastic. The sheet is 250 mm wide. Two holes, each with a
Using physics to make things work 1. Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the centre of mass? The drawing shows a thin sheet of plastic. The sheet is 250 mm wide. Two holes, each with a
Mechanical Systems. Section 1.0 Machines are tools that help humans do work. 1.1 Simple Machines- Meeting Human Needs Water Systems
 Unit 4 Mechanical Systems Section 1.0 Machines are tools that help humans do work. Define: machine- 1.1 Simple Machines- Meeting Human Needs Water Systems Then: Now: The earliest devices were devices.
Unit 4 Mechanical Systems Section 1.0 Machines are tools that help humans do work. Define: machine- 1.1 Simple Machines- Meeting Human Needs Water Systems Then: Now: The earliest devices were devices.
How valves function in hydraulic systems *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m31728 1 How valves function in hydraulic systems * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 2 TECHNOLOGY
OpenStax-CNX module: m31728 1 How valves function in hydraulic systems * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 2 TECHNOLOGY
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... PRESSURE INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1. The diagram below shows a container filled with a liquid. www.kcpe-kcse.com
NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... PRESSURE INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1. The diagram below shows a container filled with a liquid. www.kcpe-kcse.com
vehicle 6.0 kn elephant elephant Fig. 4.1
 1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows a top view of a tourist vehicle in a game park and two elephants pushing against the vehicle. The two forces indicated are at right angles to each other. vehicle elephant 4.0 kn 6.0
1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows a top view of a tourist vehicle in a game park and two elephants pushing against the vehicle. The two forces indicated are at right angles to each other. vehicle elephant 4.0 kn 6.0
d / cm t 2 / s 2 Fig. 3.1
 7 5 A student has been asked to determine the linear acceleration of a toy car as it moves down a slope. He sets up the apparatus as shown in Fig. 3.1. d Fig. 3.1 The time t to move from rest through a
7 5 A student has been asked to determine the linear acceleration of a toy car as it moves down a slope. He sets up the apparatus as shown in Fig. 3.1. d Fig. 3.1 The time t to move from rest through a
A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater.
 Q1.(a) A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater. (i) Before starting the experiment, the student drew Graph A. Graph A shows how the student expected
Q1.(a) A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater. (i) Before starting the experiment, the student drew Graph A. Graph A shows how the student expected
A B C length 1. Look at the results that they collect for four cars passing the school. Time taken to travel length 1. in seconds
 1 This question is about speed. (a) Pupils at a school measure the time cars take to travel two 100 m lengths. Look at the diagram. A B C length 1 length 2 100 m 100 m Look at the results that they collect
1 This question is about speed. (a) Pupils at a school measure the time cars take to travel two 100 m lengths. Look at the diagram. A B C length 1 length 2 100 m 100 m Look at the results that they collect
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race.
 Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Unit 1: Energy and Motion
 5 5 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 5: Work and Machines 5.1: Work 5.2: Using Machines 5.3: Simple Machines 5.1 Work What is work? To many people, the word work means something they
5 5 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 5: Work and Machines 5.1: Work 5.2: Using Machines 5.3: Simple Machines 5.1 Work What is work? To many people, the word work means something they
The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance.
 FORCES AND BRAKING Q1. The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed.
FORCES AND BRAKING Q1. The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed.
9L Pressure and Moments ILU
 9L Pressure and Moments ILU Level 3 4 5 6 7 no of qus 1 1 1 1 17 Level 3 1 Five people take it in turns to sit on a see-saw The table gives the weight of each person person weight, in N Jack 510 Ellie
9L Pressure and Moments ILU Level 3 4 5 6 7 no of qus 1 1 1 1 17 Level 3 1 Five people take it in turns to sit on a see-saw The table gives the weight of each person person weight, in N Jack 510 Ellie
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance.
 Q1. (a) A driver may have to make an emergency stop. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance. Give three different factors which affect the thinking distance or the braking distance. In
Q1. (a) A driver may have to make an emergency stop. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance. Give three different factors which affect the thinking distance or the braking distance. In
AQA GCSE Physics. 55 minutes. 55 marks. Q1 to Q4 to be worked through with tutor. Q5 to Q7 to be worked through independently.
 AQA GCSE Physics Magnetism & Electromagnetism 4.7.. - 4.7.2.: Magnets & Electromagnets Name: Class: Date: Time: 55 minutes Marks: 55 marks Comments: Q to Q4 to be worked through with tutor. Q5 to Q7 to
AQA GCSE Physics Magnetism & Electromagnetism 4.7.. - 4.7.2.: Magnets & Electromagnets Name: Class: Date: Time: 55 minutes Marks: 55 marks Comments: Q to Q4 to be worked through with tutor. Q5 to Q7 to
Hovercraft
 1 Hovercraft 2017-2018 Names: Score: / 44 Show all equations and work. Point values are shown in parentheses at the end of the question. Assume g=9.8 m/s/s for all calculations. Include units in your answer.
1 Hovercraft 2017-2018 Names: Score: / 44 Show all equations and work. Point values are shown in parentheses at the end of the question. Assume g=9.8 m/s/s for all calculations. Include units in your answer.
James wore a blindfold and ear defenders. He rested his head on a wooden stick pushed into the ground so that he could feel vibrations.
 Level 7 Physics Questions 1. Three pupils took part in an investigation into the speed of sound. All three pupils stood 1020 m from an explosion. Sylvia wore a blindfold. Paul wore ear defenders. James
Level 7 Physics Questions 1. Three pupils took part in an investigation into the speed of sound. All three pupils stood 1020 m from an explosion. Sylvia wore a blindfold. Paul wore ear defenders. James
Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack
 Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack Name: Class: Date: Time: 63 minutes Marks: 63 marks Comments: Page of 49 The graphs in List A show how the velocities of three vehicles change with time. The statements
Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack Name: Class: Date: Time: 63 minutes Marks: 63 marks Comments: Page of 49 The graphs in List A show how the velocities of three vehicles change with time. The statements
P5 STOPPING DISTANCES
 P5 STOPPING DISTANCES Practice Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 84 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 28 The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and
P5 STOPPING DISTANCES Practice Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 84 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 28 The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism
 7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
MECHANICAL SYSTEMS - Reference Page
 ANSWER KEY Student Class MECHANICAL SYSTEMS - Reference Page Refer to the following Formulas that you may need to use throughout this exam Science I n Action 8 Mechanical Systems UNIT Test Numerical Response
ANSWER KEY Student Class MECHANICAL SYSTEMS - Reference Page Refer to the following Formulas that you may need to use throughout this exam Science I n Action 8 Mechanical Systems UNIT Test Numerical Response
Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in.
 Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in. (a) Choose from the following words to complete the sentences below. distance energy force speed time You
Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in. (a) Choose from the following words to complete the sentences below. distance energy force speed time You
National 4/5. Dynamics and Space
 North Berwick High School National 4/5 Department of Physics Dynamics and Space Section 1 Mechanics Problem Booklet KINEMATICS PROBLEMS Speed, distance and time 1. A runner completes a 200 m race in 25
North Berwick High School National 4/5 Department of Physics Dynamics and Space Section 1 Mechanics Problem Booklet KINEMATICS PROBLEMS Speed, distance and time 1. A runner completes a 200 m race in 25
Page 2. The go-kart always had the same mass and used the same motor.
 Q1.(a) Some students have designed and built an electric-powered go-kart. After testing, the students decided to make changes to the design of their go-kart. The go-kart always had the same mass and used
Q1.(a) Some students have designed and built an electric-powered go-kart. After testing, the students decided to make changes to the design of their go-kart. The go-kart always had the same mass and used
SCIENCE 8. Unit 4 Booklet. Machines and Mechanical Systems
 SCIENCE 8 Unit 4 Booklet Machines and Mechanical Systems TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT Levers Have Class BLM 4-2 Goal Identify items as Class 1, Class 2, or Class 3 levers. Introduction There are three classes
SCIENCE 8 Unit 4 Booklet Machines and Mechanical Systems TOPIC 1 REINFORCEMENT Levers Have Class BLM 4-2 Goal Identify items as Class 1, Class 2, or Class 3 levers. Introduction There are three classes
Fig There is a current in each wire in a downward direction (into the page).
 1 (a) Two straight, vertical wires X and Y pass through holes in a horizontal card. Fig. 8.1 shows the card viewed from above. card wire in hole X Y wire in hole Fig. 8.1 There is a current in each wire
1 (a) Two straight, vertical wires X and Y pass through holes in a horizontal card. Fig. 8.1 shows the card viewed from above. card wire in hole X Y wire in hole Fig. 8.1 There is a current in each wire
units edition imperial PSI & lbs/in2 Name
 L R E W O P D I FLU Name Set: imperial units edition PSI & lbs/in2 This lab will provide you an understanding of: Hydraulic Systems Pneumatic Systems Cylinders Pascal s Law Liquids & Gases Pressure Kinetic
L R E W O P D I FLU Name Set: imperial units edition PSI & lbs/in2 This lab will provide you an understanding of: Hydraulic Systems Pneumatic Systems Cylinders Pascal s Law Liquids & Gases Pressure Kinetic
A-level PHYSICS A PHYA5/2C. Unit 5C Applied Physics. Section B. Tuesday 28 June 2016
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature A-level PHYSICS A Unit 5C Applied Physics Section B Tuesday 28 June 2016 Materials For this
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature A-level PHYSICS A Unit 5C Applied Physics Section B Tuesday 28 June 2016 Materials For this
Boss, clamp 4 x 60cm threads drawn together with sticky tape
 Do-it-yourself loudspeaker (Electromagnetism practical) AF 9/3/2017 Winchester College Physics Department. Scope A loudspeaker is essentially a suspended cone which is oscillated in such a way that the
Do-it-yourself loudspeaker (Electromagnetism practical) AF 9/3/2017 Winchester College Physics Department. Scope A loudspeaker is essentially a suspended cone which is oscillated in such a way that the
The table below gives information about milk bottles. Raw materials Sand, limestone, salt Crude oil. Bottle material Soda-lime glass HD poly(ethene)
 Q1.Plastic and glass can be used to make milk bottles. The figure below shows the percentage of milk bottles made from glass between 1975 and 2010. (a) Plot the points and draw a line on the figure above
Q1.Plastic and glass can be used to make milk bottles. The figure below shows the percentage of milk bottles made from glass between 1975 and 2010. (a) Plot the points and draw a line on the figure above
Thinking distance in metres. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. One of the values of stopping distance is incorrect.
 Q1.An investigation was carried out to show how thinking distance, braking distance and stopping distance are affected by the speed of a car. The results are shown in the table. Speed in metres per second
Q1.An investigation was carried out to show how thinking distance, braking distance and stopping distance are affected by the speed of a car. The results are shown in the table. Speed in metres per second
The graph shows how far the car travelled and how long it took. (i) Between which points was the car travelling fastest? Tick ( ) your answer.
 Q1. This question is about a car travelling through a town. (a) The graph shows how far the car travelled and how long it took. (i) Between which points was the car travelling fastest? Tick ( ) your answer.
Q1. This question is about a car travelling through a town. (a) The graph shows how far the car travelled and how long it took. (i) Between which points was the car travelling fastest? Tick ( ) your answer.
(a) A 36 volt battery powers the electric motor. The battery is made using individual 1.2 volt cells.
 Q1.The picture shows an electric bicycle. The bicycle is usually powered using a combination of the rider pedalling and an electric motor. (a) A 36 volt battery powers the electric motor. The battery is
Q1.The picture shows an electric bicycle. The bicycle is usually powered using a combination of the rider pedalling and an electric motor. (a) A 36 volt battery powers the electric motor. The battery is
Moments. It doesn t fall because of the presence of a counter balance weight on the right-hand side. The boom is therefore balanced.
 Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
Figure 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement?
 Q1.A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the
Q1.A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken by the train. Figure 1 has been drawn to scale. Figure 1 (a) The distance the train travels between A and B is not the same as the
Unit P.2, P2.3. Currents in electric circuits E ½. F Fuel gauge indicator. Fuel tank. Ammeter. Float. Battery. Sliding contact. Pivot 12V.
 Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
1. What are some everyday examples (that are NOT listed above) in which you use torque to complete a task?
 ID: NAME: DATE: CLASS: Chapter 11: Torque Notes POGIL #1 REMEMBER: Throughout this paper, you will see some symbols. The stop sign means STOP and check with a teacher before continuing. The key means THIS
ID: NAME: DATE: CLASS: Chapter 11: Torque Notes POGIL #1 REMEMBER: Throughout this paper, you will see some symbols. The stop sign means STOP and check with a teacher before continuing. The key means THIS
Fluid Power Lab. What s inside? This lab will provide you with experiences in and an understanding of: Cylinders. Friction
 Revision 4.2 luid Power Lab Name: Set: Date: Version: English Measurement System (inches & pounds). metric version also available. What s inside? This lab will provide you with experiences in and an understanding
Revision 4.2 luid Power Lab Name: Set: Date: Version: English Measurement System (inches & pounds). metric version also available. What s inside? This lab will provide you with experiences in and an understanding
Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period
 Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period Basic Brake System Matching 1. Metal tubing and rubber hose that transmit pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. 2. Mechanical system for applying
Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period Basic Brake System Matching 1. Metal tubing and rubber hose that transmit pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. 2. Mechanical system for applying
CDI Revision Notes Term 1 ( ) Grade 12 Advanced Unit 2 Mechanical Systems
 CDI Revision Notes Term 1 (2017 2018) Grade 12 Advanced Unit 2 Mechanical Systems STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Student must attempt all questions. For this examination, you must have: (a) An ink pen blue. (b)
CDI Revision Notes Term 1 (2017 2018) Grade 12 Advanced Unit 2 Mechanical Systems STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Student must attempt all questions. For this examination, you must have: (a) An ink pen blue. (b)
Work done and Moment. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift.
 Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
The drag lift pulls the skier from the bottom to the top of a ski slope.
 ACCELERATION Q1. Figure 1 shows a skier using a drag lift. The drag lift pulls the skier from the bottom to the top of a ski slope. The arrows, A, B, C and D represent the forces acting on the skier and
ACCELERATION Q1. Figure 1 shows a skier using a drag lift. The drag lift pulls the skier from the bottom to the top of a ski slope. The arrows, A, B, C and D represent the forces acting on the skier and
Engineering Diploma Resource Guide ST280 ETP Hydraulics (Engineering)
 Engineering Diploma Resource Guide ST80 ETP Hydraulics (Engineering) Introduction Hydraulic systems are a fundamental aspect of engineering. Utilised across a variety of sectors including aviation, construction,
Engineering Diploma Resource Guide ST80 ETP Hydraulics (Engineering) Introduction Hydraulic systems are a fundamental aspect of engineering. Utilised across a variety of sectors including aviation, construction,
Friction and Momentum
 Lesson Three Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to: understand friction as a force that opposes motion, and use this to explain why falling objects reach a terminal velocity know that the
Lesson Three Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to: understand friction as a force that opposes motion, and use this to explain why falling objects reach a terminal velocity know that the
10. FORCES AND SIMPLE MACHINES
 10. FORCES AND SIMPLE MACHINES 10.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter is about forces and simple machines. Whenever you push, or pull or turn anything you use force. Look at the illustrations below. (i) An elephant
10. FORCES AND SIMPLE MACHINES 10.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter is about forces and simple machines. Whenever you push, or pull or turn anything you use force. Look at the illustrations below. (i) An elephant
Mechanisms and Structures. Mechanical Systems. Levers. Basic Forces
 Mechanisms and Structures Mechanical Systems Levers Basic Forces Pupil Name Teacher Class Page 1 MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Our every day lives are made much easier by a variety of mechanical systems that help
Mechanisms and Structures Mechanical Systems Levers Basic Forces Pupil Name Teacher Class Page 1 MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Our every day lives are made much easier by a variety of mechanical systems that help
Driver Driven. InputSpeed. Gears
 Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
(3) When the brake pedal of the car is pushed, brake pads press against very hard steel discs.
 Q1. A car travels along a level road at 20 metres per second. (a) Calculate the distance travelled by the car in 4 seconds. (Show your working.) (b) When the brake pedal of the car is pushed, brake pads
Q1. A car travels along a level road at 20 metres per second. (a) Calculate the distance travelled by the car in 4 seconds. (Show your working.) (b) When the brake pedal of the car is pushed, brake pads
STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Friday 12 November 2010
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2010 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Friday 12 November 2010 Reading time: 11.45
Victorian Certificate of Education 2010 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Friday 12 November 2010 Reading time: 11.45
(Source: How Brakes Work! Mark Lam University of British Columbia
 (Source: http://www.sub5zero.com/sites/default/files/uploads/2010/05/audi-r8-gt-01_0.jpg) How Brakes Work! Mark Lam University of British Columbia (Source: http://www.math.nyu.edu/~crorres/archimedes/lever/lever.jpg)
(Source: http://www.sub5zero.com/sites/default/files/uploads/2010/05/audi-r8-gt-01_0.jpg) How Brakes Work! Mark Lam University of British Columbia (Source: http://www.math.nyu.edu/~crorres/archimedes/lever/lever.jpg)
Technology Exploration-I Curriculum Development Unit
 Technology Exploration-I Modu le 4: Pulleys and Gears PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 4: Pulleys and Gears Module Objectives After the completion
Technology Exploration-I Modu le 4: Pulleys and Gears PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 4: Pulleys and Gears Module Objectives After the completion
Name: Date: Class: 6. Which of these activities would require the least effort?
 Fry 1. An inclined plane is an example of : a. A simple machine b. A complex machine c. An effort machine d. A time-saving machine 2. on what amusement6iir ride mighl you inclined plane? a. lnclined Plane
Fry 1. An inclined plane is an example of : a. A simple machine b. A complex machine c. An effort machine d. A time-saving machine 2. on what amusement6iir ride mighl you inclined plane? a. lnclined Plane
Electricity to Light
 Powerful Classroom Assessment for STC/MS Energy, Machines, and Motion Unit to be given after Lesson 4 Electricity to Light Grade 8 Inquiry Scenario Published by the Team of the Washington Office of the
Powerful Classroom Assessment for STC/MS Energy, Machines, and Motion Unit to be given after Lesson 4 Electricity to Light Grade 8 Inquiry Scenario Published by the Team of the Washington Office of the
VCE Systems Engineering
 VCE Systems Engineering Mechanical formula and Electrotechnology formula and worked examples - speed (m/s) or (ms distance (m) metre time (s) second ) metre per second speed = distance time A car travels
VCE Systems Engineering Mechanical formula and Electrotechnology formula and worked examples - speed (m/s) or (ms distance (m) metre time (s) second ) metre per second speed = distance time A car travels
Name: New Document 1. Class: Date: 221 minutes. Time: 220 marks. Marks: Comments:
 New Document Name: Class: Date: Time: 22 minutes Marks: 220 marks Comments: Q. The diagram shows a boat pulling a water skier. The arrow represents the force on the water produced by the engine propeller.
New Document Name: Class: Date: Time: 22 minutes Marks: 220 marks Comments: Q. The diagram shows a boat pulling a water skier. The arrow represents the force on the water produced by the engine propeller.
Additional Science. Physics Unit Physics P2 PHY2H. (Jun11PHY2H01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2011.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 Written Paper General Certificate
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 Written Paper General Certificate
Calculate the current in the kettle element. (3)
 1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. N S
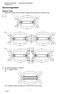 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Technology in Transportation Exam 1
 Name: 16.682 Technology in Transportation Exam 1 April 5, 2011 Question 1: Internal Combustion Engine Technology (20 points) Use the torque/rpm curve below to answer the following questions: 600 500 Horsepower
Name: 16.682 Technology in Transportation Exam 1 April 5, 2011 Question 1: Internal Combustion Engine Technology (20 points) Use the torque/rpm curve below to answer the following questions: 600 500 Horsepower
FLUID POWER TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC PUMPS APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS H1
 FLUID POWER TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC PUMPS This work covers outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS H1 The material needed for outcome 2 is very extensive so the tutorial
FLUID POWER TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC PUMPS This work covers outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS H1 The material needed for outcome 2 is very extensive so the tutorial
POE Review for Test 1 (Unit 1.1 Mechanisms and 1.2 -Energy)
 Name: Period: POE Review for Test 1 (Unit 1.1 Mechanisms and 1.2 -Energy) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Study the gear train in Figure
Name: Period: POE Review for Test 1 (Unit 1.1 Mechanisms and 1.2 -Energy) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Study the gear train in Figure
Mr. Freeze QUALITATIVE QUESTIONS
 QUALITATIVE QUESTIONS Many of the questions that follow refer to the graphs of data collected when riding Mr. Freeze with high tech data collection vests. With your I.D., you can borrow a vest without
QUALITATIVE QUESTIONS Many of the questions that follow refer to the graphs of data collected when riding Mr. Freeze with high tech data collection vests. With your I.D., you can borrow a vest without
TECHNOLOGY. Grade 8. Learner Teacher. Systems and Control (Mechanisms) Hoërskool Gerrit Maritz District D15
 TECHNOLOGY Systems and Control (Mechanisms) Hoërskool Gerrit Maritz District D15 2009 Grade 8 Learner Teacher CAPABILITY TASK In this module you are going to make a mechanism to help a disabled boom operator
TECHNOLOGY Systems and Control (Mechanisms) Hoërskool Gerrit Maritz District D15 2009 Grade 8 Learner Teacher CAPABILITY TASK In this module you are going to make a mechanism to help a disabled boom operator
Level 1 Science, 2016
 90940 909400 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Science, 2016 90940 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics 9.30 a.m. Monday 14 November 2016 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
90940 909400 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Science, 2016 90940 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics 9.30 a.m. Monday 14 November 2016 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
Work and Machines. Mr. Ahearn
 Name: Date: Per: and Machines Mr. Ahearn Key Questions: 1. When is work done on an object? 2. How do you calculate work and power? 3. How do machines make work easier? 4. What is the difference between
Name: Date: Per: and Machines Mr. Ahearn Key Questions: 1. When is work done on an object? 2. How do you calculate work and power? 3. How do machines make work easier? 4. What is the difference between
Lesson 4: Fluid Systems
 Lesson 4: Fluid Systems Even as you sleep at night, your body works to operate different hydraulic and pneumatic systems. For example, your circulatory system is pumping blood from your heart through big
Lesson 4: Fluid Systems Even as you sleep at night, your body works to operate different hydraulic and pneumatic systems. For example, your circulatory system is pumping blood from your heart through big
Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 19 November 2012
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2012 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 19 November 2012 Reading time: 9.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2012 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 19 November 2012 Reading time: 9.00
1. (s r r d v i e) These people work on buses or in taxis. They are. 2. (s s s g p n r a e e) These people ride on public transportation.
 10.1 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION 1 What s There? Circle the answers to the questions. What can you find... DICTIONARY PAGE 71 1.... inside a train station? trains tracks taxis 2.... inside a subway station?
10.1 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION 1 What s There? Circle the answers to the questions. What can you find... DICTIONARY PAGE 71 1.... inside a train station? trains tracks taxis 2.... inside a subway station?
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS. This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module:
 FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material
time in seconds Amy leaves diving board
 1 Amy dives from the high diving board at a swimming pool. Look at the graph of her motion. speed in m / s 15 10 Amy enters water P Q 5 0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 time in seconds Amy leaves diving board (a)
1 Amy dives from the high diving board at a swimming pool. Look at the graph of her motion. speed in m / s 15 10 Amy enters water P Q 5 0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 time in seconds Amy leaves diving board (a)
GraspIT AQA GCSE Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Questions
 A. Permanent and Induced Magnetism, Magnetic Forces and Fields 1. The following question is about magnets. a. Iron is a magnetic material. Name two other magnetic elements. (2) b. Describe the effect a
A. Permanent and Induced Magnetism, Magnetic Forces and Fields 1. The following question is about magnets. a. Iron is a magnetic material. Name two other magnetic elements. (2) b. Describe the effect a
Water handling and water power devices, propeller wheel and steering device.
 SECTION VIII NOB. us 1*8 Water handling and water power devices, propeller wheel and steering device. 52 THE NEWARK MUSEUM Section VIII 113. Old oaken bucket. This is the first known method of raising
SECTION VIII NOB. us 1*8 Water handling and water power devices, propeller wheel and steering device. 52 THE NEWARK MUSEUM Section VIII 113. Old oaken bucket. This is the first known method of raising
Technology Exploration_II
 Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion
Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion
7.9.2 Potential Difference
 7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
3/19/2017 9:49 AM. Transmission Replacement. Tools Required ^ J B Cooler Quick Connect Tool ^ J Transmission Jack Adapter
 1 of 16 Transmission Replacement Tools Required ^ J 41623-B Cooler Quick Connect Tool ^ J 41160 Transmission Jack Adapter Removal Procedure 1. Remove the upper filler panel. 2. Remove the upper and lower
1 of 16 Transmission Replacement Tools Required ^ J 41623-B Cooler Quick Connect Tool ^ J 41160 Transmission Jack Adapter Removal Procedure 1. Remove the upper filler panel. 2. Remove the upper and lower
Energy Conversions Questions CfE
 Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
Draft copy. Friction and motion. Friction: pros and cons
 As you have learned, moving objects often slow down because there is a force acting on them. The force is acting in the opposite direction to the way the objects are moving. This force is called friction.
As you have learned, moving objects often slow down because there is a force acting on them. The force is acting in the opposite direction to the way the objects are moving. This force is called friction.
Intermediate 2 Momentum & Energy Past Paper questions
 Intermediate 2 Momentum & Energy Past Paper questions 2000-2010 2000 Q23. A chairlift at a ski resort carries skiers through a vertical distance of 400 m. (a) One of the skiers has a mass of 90.0 kg.
Intermediate 2 Momentum & Energy Past Paper questions 2000-2010 2000 Q23. A chairlift at a ski resort carries skiers through a vertical distance of 400 m. (a) One of the skiers has a mass of 90.0 kg.
BRAKE BOOSTER. Section 5. Brake Booster. Construction. Single Diaphragm Booster
 BRAKE BOOSTER Brake Booster The brake booster is designed to create a greater braking force from a minimum pedal effort, using a difference in atmospheric pressure and the engine s manifold vacuum. It
BRAKE BOOSTER Brake Booster The brake booster is designed to create a greater braking force from a minimum pedal effort, using a difference in atmospheric pressure and the engine s manifold vacuum. It
Exampro GCSE Physics. P2 Forces and their effects Self Study Questions Higher tier. Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 117. Marks: 117.
 Exampro GCSE Physics P2 Forces and their effects Self Study Questions Higher tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 117 Marks: 117 Comments: Page 1 of 32 Q1. (a) The stopping distance of a vehicle is made
Exampro GCSE Physics P2 Forces and their effects Self Study Questions Higher tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 117 Marks: 117 Comments: Page 1 of 32 Q1. (a) The stopping distance of a vehicle is made
2007 Pontiac G BRAKES Disc Brakes - G6
 REAR DISC BRAKE PADS REPLACEMENT Removal Procedure CAUTION: Refer to Brake Dust Caution. 1. Inspect the fluid level in the brake master cylinder reservoir. 2. If the brake fluid level is midway between
REAR DISC BRAKE PADS REPLACEMENT Removal Procedure CAUTION: Refer to Brake Dust Caution. 1. Inspect the fluid level in the brake master cylinder reservoir. 2. If the brake fluid level is midway between
units metric edition Name Newtons & Pascals
 L R E W O P D I FLU Name Set: metric units edition Newtons & Pascals This lab will provide you an understanding of: Hydraulic Systems Pneumatic Systems Cylinders Pascal s Law Liquids & Gases Pressure Kinetic
L R E W O P D I FLU Name Set: metric units edition Newtons & Pascals This lab will provide you an understanding of: Hydraulic Systems Pneumatic Systems Cylinders Pascal s Law Liquids & Gases Pressure Kinetic
Newton s First Law. Evaluation copy. Vernier data-collection interface
 Newton s First Law Experiment 3 INTRODUCTION Everyone knows that force and motion are related. A stationary object will not begin to move unless some agent applies a force to it. But just how does the
Newton s First Law Experiment 3 INTRODUCTION Everyone knows that force and motion are related. A stationary object will not begin to move unless some agent applies a force to it. But just how does the
[2] [2]
![[2] [2] [2] [2]](/thumbs/88/114953460.jpg) High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 A jet aircraft is taking off from an international airport. Its mass, including passengers and fuel is 150,000 kg. Its take-off speed is 100 ms -1. The maximum thrust
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 A jet aircraft is taking off from an international airport. Its mass, including passengers and fuel is 150,000 kg. Its take-off speed is 100 ms -1. The maximum thrust
Exploration 4: Rotorcraft Flight and Lift
 Exploration 4: Rotorcraft Flight and Lift Students use appropriate terminology to describe the various stages of flight and discover that the lift force changes with the amount of air moved by the rotor
Exploration 4: Rotorcraft Flight and Lift Students use appropriate terminology to describe the various stages of flight and discover that the lift force changes with the amount of air moved by the rotor
Activity 3: Electricity
 Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Chapter 14 Learning Objectives-Study this for TEST. Chapter 14 Work and Power. Chapter 14 Learning Objectives-Study this for TEST
 Chapter 14 Work and Power GOAL: Students will be able to compare and contrast work and power qualitatively and quantitatively. Standard: SC.912.P.10.3 Students will: Level Scale 4 design and conduct experiments
Chapter 14 Work and Power GOAL: Students will be able to compare and contrast work and power qualitatively and quantitatively. Standard: SC.912.P.10.3 Students will: Level Scale 4 design and conduct experiments
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
UNIT 2: MECHANICAL SYSTEMS UNIT NOTEBOOK. SCIENCE 8 Mr. Anderson
 UNIT 2: MECHANICAL SYSTEMS UNIT NOTEBOOK SCIENCE 8 Mr. Anderson Section 1 Notes 1.1 Simple Machines - Meeting Human Needs Machines help people use energy more efficiently. A machine helps us do work. The
UNIT 2: MECHANICAL SYSTEMS UNIT NOTEBOOK SCIENCE 8 Mr. Anderson Section 1 Notes 1.1 Simple Machines - Meeting Human Needs Machines help people use energy more efficiently. A machine helps us do work. The
1 of 11 4/11/ :35 AM
 1 of 11 4/11/2015 11:35 AM Rear Disc Brake Pads Replacement Special Tools * KM-6007 Resetting Tool * KM-6007-30 Adaptor Removal Procedure 2 of 11 4/11/2015 11:35 AM Caution: Refer to Brake Dust Caution
1 of 11 4/11/2015 11:35 AM Rear Disc Brake Pads Replacement Special Tools * KM-6007 Resetting Tool * KM-6007-30 Adaptor Removal Procedure 2 of 11 4/11/2015 11:35 AM Caution: Refer to Brake Dust Caution
A.M. MONDAY, 19 January minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 241/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER PHYSICS 2 A.M. MONDAY, 19 January 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 241/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER PHYSICS 2 A.M. MONDAY, 19 January 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT EDULABZ. the mere presence of magnet, is called...
 Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
7.9.1 Circuits. 123 minutes. 170 marks. Page 1 of 56
 7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
Exploration 2: How Do Rotorcraft Fly?
 Exploration 2: How Do Rotorcraft Fly? Students choose a model and use it to explore rotorcraft flight. They use a fair test and conclude that a spinning rotor is required for a rotorcraft to fly. Main
Exploration 2: How Do Rotorcraft Fly? Students choose a model and use it to explore rotorcraft flight. They use a fair test and conclude that a spinning rotor is required for a rotorcraft to fly. Main
reflect energy: the ability to do work
 reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
Work and Simple Machines
 Work and Simple Machines What is work? The scientific definition of work is: using a force to move an object a distance Measured in Joules W=FD Work = Force x Distance Calculate: If a man pushes a concrete
Work and Simple Machines What is work? The scientific definition of work is: using a force to move an object a distance Measured in Joules W=FD Work = Force x Distance Calculate: If a man pushes a concrete
4. Picture yourself riding a bicycle in a race. Describe how energy is transferred from your body to the bicycle wheels.
 CHECK AND REFLECT 1. What is the difference between a simple and a complex machine? 2. What improvements have been made to bicycle designs over the last century? 3. a) Your body is made up of several simple
CHECK AND REFLECT 1. What is the difference between a simple and a complex machine? 2. What improvements have been made to bicycle designs over the last century? 3. a) Your body is made up of several simple
IT'S MAGNETIC (1 Hour)
 IT'S MAGNETIC (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will create a simple electromagnet using a nail, a battery, and copper wire. They will
IT'S MAGNETIC (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will create a simple electromagnet using a nail, a battery, and copper wire. They will
1. What type of material can be induced to become a temporary magnet? A) diamagnetic B) ferromagnetic C) monomagnetic D) paramagnetic
 Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
