Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5
|
|
|
- Theodore Palmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
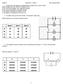
1 Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance of the lamps. 2) Two groups of pupils are investigating the electrical properties of a lamp. a) Group 1 is given the following equipment: ammeter; voltmeter; 12V dc supply ; lamp; connecting wires. Complete the circuit diagram to show how this equipment is used to measure the current through and the voltage across the lamp. b) Group 2 uses the same lamp and is only given the following equipment: lamp; ohmmeter ; connecting wires. What property of the lamp is measured by the ohmmeter? c) The results of both groups are combined and recorded in the table below. i) Use these results to complete the last two columns of the table. ii) What quantity is represented by the last two columns of the table? iii) What is the unit of this quantity?
2 3) A house owner installs a heating system under the floor of a new conservatory. The heating mats are fitted. The mats contain resistance wires and are laid underneath the floor. Each mat is designed to operate at 230V and has a power of 300W. a) State how the three mats are connected together to operate at their correct voltage. b) Calculate the current in each heating mat when switched on. c) Calculate the total resistance of the heating system when all three mats are switched on. 4) A student sets up the following circuit. a) Calculate the current in the 8Ω resistor. b) Calculate the voltage across the 8Ω resistor. c) The 24Ω resistor is replaced by one of greater resistance. How will this affect the voltage across the 8Ω resistor? Explain your answer.
3 5) A student sets up the circuit to operate two identical 12V, 36W lamps from a 48V supply. a) i) Calculate the reading on the ammeter. ii) Calculate the reading on the voltmeter. iii) Calculate the resistance of the variable resistor. b) The student sets up a second circuit using a 12V supply and the same lamps. Each lamp has a resistance of 4Ω. The resistance of the variable resistor is set at 6Ω. i) Calculate the total resistance of this circuit. ii) The variable resistor is now removed from the circuit. A) What happens to the reading on the ammeter? B) Justify your answer.
4 6) A mains electric fire has two heating elements which can be switched on and off separately. The heating elements can be switched on to produce three different heat settings: LOW, MEDIUM and HIGH. The fire also has an interior lamp which can be switched on to give a log-burning effect. The circuit diagram for the fire is shown. a) When S1 is closed, the lamp operates at its stated rating of 60W. Calculate the current in the lamp. b) Switch S1 is opened and switches S2 and S3 are closed. i) Calculate the combined resistance of both heating elements. ii) Calculate the total power developed in the heating elements when S2 and S3 are closed. iii) State and explain which switch or switches would have to be closed to produce the LOW heat setting.
5 7) The circuit shown is used to control the brightness of two identical lamps. The variable resistor is adjusted until the lamps operate at their correct voltage of 3V. a) When the lamps operate at their correct voltage, the reading on the ammeter is 1.2A. Calculate the current in one lamp. b) Calculate the resistance of one lamp. c) Calculate the combined resistance of the two lamps in this circuit. d) When the lamps operate at their correct voltage the resistance of the variable resistor is 7.5Ω. Calculate the total resistance in the circuit. e) One of the lamps is removed. i) What happens to the reading on the ammeter? ii) Justify your answer.
6 8) A householder plugs a home entertainment centre, a hi-fi, a games console and an Electric fire into a multiway adaptor connected to the mains. The householder goes on holiday for 14 days with the electric fire unplugged. All the other appliances are left on standby. On standby, these appliances operate at 9% of their power rating listed in the table. a) Calculate the total power consumption in watts of all the appliances left on standby. b) i) Calculate the number of kilowatt-hours used by these appliances during the 14 days on standby. ii) Calculate how much this will cost if it is 15p per unit of electrical energy used.
7 9) An overhead projector contains a lamp and a motor that operates a cooling fan. A technician has a choice of two lamps to fit in the projector. a) Which lamp gives a brighter light when operating at the correct voltage? Explain your answer. b) Calculate the power developed by lamp A when it is operating normally. c) The overhead projector plug contains a fuse. Draw the circuit symbol for a fuse. d) The technician builds a test circuit containing a resistor and a motor, as show in Circuit 1 below. i) State the voltage across the motor. ii) Calculate the combined resistance of the resistor and the motor.
8 10) A resistor is labelled: 10Ω ± 10%, 3W. This means that the resistance value could actually be between 9Ω and 11Ω. a) A student decides to check the value of resistance. Draw a circuit diagram, including a 6V battery, a voltmeter and an ammeter, for a circuit that could be used to determine resistance. b) Readings from the circuit give the voltage across the resistor as 5.7V and the current through the resistor as 0.60A. Use these values to calculate the resistance. c) During the experiment, the resistor becomes very hot and gives off smoke. Explain why this happens. d) The student states that two of these resistors would not have overheated if they were connected together in parallel with the battery. Is the student correct? Explain your answer. 11) A student has two electrical power supplies. One is ac and the other is a dc supply. a) Explain ac and dc in terms of electron flow in a circuit. b) i) Which power supply should be used to operate a transformer? ii) A transformer with an efficiency of 30% is used in a computer. Calculate the power output when the input power is 50W.
9 12) A student sets up the following circuit to investigate the resistance of resistor R. The variable resistor is adjusted and the voltmeter and ammeter readings are noted. The following graph is obtained from the experimental results. a) i) Calculate the value of resistor when the reading on the voltmeter is 4.2V. ii) Using the information from the graph, state whether the resistance of resistor R, increases, stays the same or decreases as the voltage increases. Justify your answer. b) The student is given a task to combine two resistors from a pack containing one each of 33Ω, 56Ω, 82Ω, 150Ω, 270Ω and 390Ω. Show by calculation which two resistors should be used to give: i) The largest combined resistance: ii) The smallest combined resistance.
10 13) Some resistors are labelled with a power rating as well as their resistance value. This is the maximum power at which they can operate without overheating. a) A resistor is labelled 50Ω, 2W. Calculate the maximum operating current for this resistor. b) Two resistors, each rated at 2W, are connected in parallel to a 9V dc supply. They have resistances 60Ω and 30Ω. i) Calculate the total resistance of the circuit. ii) Calculate the power produced in each resistor. iii) State which, if any, of the resistors will overheat. c) The 9V dc supply is replaced by a 9V ac supply. What affect, if any, would this have on the answers to part b) ii)?
11 14) The resistance of a length of bare uniform wire is 30Ω. The length of wire is folded into the shape of a square and the ends soldered together as shown below. What value of resistance would the ohmmeter read if it is connected as shown at the mid-points of opposite sides of the square? (You may ignore the resistance of the ohmmeter leads.) 15) A student sets up the circuit below. a) Calculate the total resistance in the circuit. b) Calculate the current reading show on the ammeter.
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4)
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
Circuits-Circuit Analysis
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below. 4. A 9-volt battery is connected to a 4-ohm resistor and a 5-ohm resistor as shown in the diagram below. A 3.0-ohm resistor,
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below. 4. A 9-volt battery is connected to a 4-ohm resistor and a 5-ohm resistor as shown in the diagram below. A 3.0-ohm resistor,
PHYSICS 6 EXTENDED PHYSICS
 PHYSICS 6 EXTENDED PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 3 PORTFOLIO TASKS 2013-2014 STS\G11\Portfolio\Extended Physics Assessment Booklet\CDAU\ADVETIVersion 1.0 2014 1 31 Unit/Topic Performance Criteria Assess Event
PHYSICS 6 EXTENDED PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 3 PORTFOLIO TASKS 2013-2014 STS\G11\Portfolio\Extended Physics Assessment Booklet\CDAU\ADVETIVersion 1.0 2014 1 31 Unit/Topic Performance Criteria Assess Event
Exam-style questions: electricity
 Exam-style questions: electricity Q. The diagram shows an electrical circuit. (a) Complete the two labels on the diagram. P and Q are meters. What is meter P measuring?... () What is meter Q measuring?...
Exam-style questions: electricity Q. The diagram shows an electrical circuit. (a) Complete the two labels on the diagram. P and Q are meters. What is meter P measuring?... () What is meter Q measuring?...
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Review for formula, circuit and resistance test
 Review for formula, circuit and resistance test 1. Fill in the table giving the symbol and unit(s) for each. Current intensity Potential difference Voltage Resistance Power Energy Time 2. Give the formula
Review for formula, circuit and resistance test 1. Fill in the table giving the symbol and unit(s) for each. Current intensity Potential difference Voltage Resistance Power Energy Time 2. Give the formula
Current, resistance and potential difference
 Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
Circuit Analysis Questions A level standard
 1. (a) set of decorative lights consists of a string of lamps. Each lamp is rated at 5.0 V, 0.40 W and is connected in series to a 230 V supply. Calculate the number of lamps in the set, so that each lamp
1. (a) set of decorative lights consists of a string of lamps. Each lamp is rated at 5.0 V, 0.40 W and is connected in series to a 230 V supply. Calculate the number of lamps in the set, so that each lamp
7.9.2 Potential Difference
 7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
Unit P.2, P2.3. Currents in electric circuits E ½. F Fuel gauge indicator. Fuel tank. Ammeter. Float. Battery. Sliding contact. Pivot 12V.
 Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Name: Base your answer to the question on the information below and on your knowledge of physics.
 Name: Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information below and on your knowledge of physics. A student constructed a series circuit consisting of a 12.0-volt battery, a 10.0-ohm lamp, and
Name: Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information below and on your knowledge of physics. A student constructed a series circuit consisting of a 12.0-volt battery, a 10.0-ohm lamp, and
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 22.
 Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Lab 4. DC Circuits II
 Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A.
 High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
2. A student sets up the circuit shown. The switch is open (off). Which lamps are on and which lamps are off?
 1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
Physics - Chapters Task List
 Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics
 Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Electrical power. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/27/14
 Electrical power Objectives Use the equation for electrical power to solve circuit problems. Understand basic concepts for home electricity usage and wiring. Calculate the power used by electric circuit
Electrical power Objectives Use the equation for electrical power to solve circuit problems. Understand basic concepts for home electricity usage and wiring. Calculate the power used by electric circuit
Academic Year
 EXCELLENCE INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL First Term, Work sheet (1) Grade (9) Academic Year 2014-2015 Subject: quantities Topics:- Static electricity - Eelectrical NAME: DATE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1 - A circuit
EXCELLENCE INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL First Term, Work sheet (1) Grade (9) Academic Year 2014-2015 Subject: quantities Topics:- Static electricity - Eelectrical NAME: DATE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1 - A circuit
7. How long must a 100-watt light bulb be used in order to dissipate 1,000 joules of electrical energy? 1) 10 s 3) 1,000 s 2) 100 s 4) 100,000 s
 1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction
 Name: Class: Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction In this experiment, you will investigate how different materials affect the brightness of a bulb in a simple electric circuit. 1. Take a battery holder,
Name: Class: Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction In this experiment, you will investigate how different materials affect the brightness of a bulb in a simple electric circuit. 1. Take a battery holder,
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits
 Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits Name(s) Obtain an Electro-Trainer and wire it exactly as shown (Be sure to use the 100 ohm resistor) 1) Record the volt drop and current flow for the Switch, the Resistor and
Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits Name(s) Obtain an Electro-Trainer and wire it exactly as shown (Be sure to use the 100 ohm resistor) 1) Record the volt drop and current flow for the Switch, the Resistor and
EPSE Project 1: Sample Diagnostic Questions - Set 3
 EPSE Project 1: Sample Diagnostic Questions - Set 3 Circuit behaviour These questions probe pupils understanding of the behaviour of simple electric circuits. Most are about series circuits, and check
EPSE Project 1: Sample Diagnostic Questions - Set 3 Circuit behaviour These questions probe pupils understanding of the behaviour of simple electric circuits. Most are about series circuits, and check
Chapter 21 Practical Electricity
 Chapter 21 Practical Electricity (A) Electrical Power 1. State four applications of the heating effect of electricity. Home: o Used in electric kettles o Used in electric irons o Used in water heaters
Chapter 21 Practical Electricity (A) Electrical Power 1. State four applications of the heating effect of electricity. Home: o Used in electric kettles o Used in electric irons o Used in water heaters
Name: Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK. National 4/5 Physics. Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets
 Name: National 4/5 Physics Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets USING ELECTRICITY Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you
Name: National 4/5 Physics Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets USING ELECTRICITY Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you
What is included in a circuit diagram?
 Circuit Diagrams What is included in a circuit diagram? Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent parts of a circuit, including a source of electrical energy and devices that are run by the electrical
Circuit Diagrams What is included in a circuit diagram? Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent parts of a circuit, including a source of electrical energy and devices that are run by the electrical
PHA3/W PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 3 Current Electricity and Elastic Properties of Solids
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA3/W Unit 3 Current
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA3/W Unit 3 Current
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Energy and Electricity
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above?
 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Series and Parallel Circuits 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are series and parallel circuits? 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Circuit components can
Series and Parallel Circuits 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Series and Parallel Circuits 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are series and parallel circuits? 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Circuit components can
Chapter 26 DC Circuits
 Chapter 26 DC Circuits Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does have a small internal resistance,
Chapter 26 DC Circuits Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does have a small internal resistance,
Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits
 Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Chapter 26 DC Circuits. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 DC Circuits 26-1 EMF and Terminal Voltage Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does
Chapter 26 DC Circuits 26-1 EMF and Terminal Voltage Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does
Lab 4. DC Circuits II
 Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
2. Four 20-Ω resistors are connected in parallel and the combination is connected to a 20- V emf device. The current in any one of the resistors is:
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_27 Sunday, February 03, 2008 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. By using only two resistors, R1 and R2, a student is able to obtain resistances of 3 Ω, 4 Ω, 12 Ω, and 16
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_27 Sunday, February 03, 2008 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. By using only two resistors, R1 and R2, a student is able to obtain resistances of 3 Ω, 4 Ω, 12 Ω, and 16
11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY. Electrochemical Cells (the energy source) pg Wet Cell. Dry Cell. Positive. Terminal. Negative.
 Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them.
 1 polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth. polythene rod cloth The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them. The rod becomes negatively charged. Which diagram shows how the rod
1 polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth. polythene rod cloth The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them. The rod becomes negatively charged. Which diagram shows how the rod
to allow a current in one circuit to operate a switch in another circuit to protect a circuit by melting if the current becomes too large
 1 What is the function of a relay? to allow a current in one circuit to operate a switch in another circuit to prevent an electric shock by earthing a metal case to protect a circuit by melting if the
1 What is the function of a relay? to allow a current in one circuit to operate a switch in another circuit to prevent an electric shock by earthing a metal case to protect a circuit by melting if the
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS
 PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 A plastic rod is rubbed with a cloth and becomes negatively charged. (a) Explain how the rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed with a cloth... [2] (b) An uncharged metal-coated
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 A plastic rod is rubbed with a cloth and becomes negatively charged. (a) Explain how the rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed with a cloth... [2] (b) An uncharged metal-coated
CHAPTER 3 DOMESTIC ELECTRICITY
 CHAPTER 3 DOMESTIC ELECTRICITY 1 Electrical Power How to calculate power drawn from a source? Three equivalent expressions of power [HKCEE] [Power] Calculate the power dissipated in the 10Ω resistor. Page
CHAPTER 3 DOMESTIC ELECTRICITY 1 Electrical Power How to calculate power drawn from a source? Three equivalent expressions of power [HKCEE] [Power] Calculate the power dissipated in the 10Ω resistor. Page
4.2 Electrical Quantities
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 4.2 Electrical Quantities Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 4.2 Electrical Quantities Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International
Unit 9. (Filled In) Draw schematic circuit diagrams for resistors in series and in parallel
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 9 Series & Parallel Circuits (Filled In) Essential Questions: Does adding resistors to a circuit always reduce current? Does adding more light bulbs to a circuit always make them
Name: Date: Period: Unit 9 Series & Parallel Circuits (Filled In) Essential Questions: Does adding resistors to a circuit always reduce current? Does adding more light bulbs to a circuit always make them
SNC1D PHYSICS 4/6/2013. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P ) Electrical Resistance. Electrical Resistance
 SNC1D PHYSICS THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P.441-443) Electrical Resistance Have you ever noticed that when you recharge your cellphone, MP3 player, or laptop computer, the
SNC1D PHYSICS THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P.441-443) Electrical Resistance Have you ever noticed that when you recharge your cellphone, MP3 player, or laptop computer, the
The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch bulb.
 Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Electronics Questions NAT 5
 Electronics Questions NAT 5 1) A radio and a computer mouse are examples of electronic systems. a) An electronic system can be represented by a block diagram as shown. Complete the block diagram by filling
Electronics Questions NAT 5 1) A radio and a computer mouse are examples of electronic systems. a) An electronic system can be represented by a block diagram as shown. Complete the block diagram by filling
Electrical Energy and Power Ratings
 Section 1 - From the Wall Socket Electrical Energy and ower Ratings Batteries and the mains are sources of electrical energy. Electrical appliances can then convert this into other forms of energy. e.g.
Section 1 - From the Wall Socket Electrical Energy and ower Ratings Batteries and the mains are sources of electrical energy. Electrical appliances can then convert this into other forms of energy. e.g.
APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat, sand paper, connecting wires.
 ACTIVITIES ACTIVITY 1 AIM To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat, sand paper,
ACTIVITIES ACTIVITY 1 AIM To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Resistor, ammeter, (0-1.5A) voltmeter (0-5V ), battery, one way key, rheostat, sand paper,
HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED?
 ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
Section 6 HOW ARE VALUES OF CIRCUIT VARIABLES MEASURED?
 Section 6 HOW RE VUES OF CIRCUIT VRIBES MESURED? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow
Section 6 HOW RE VUES OF CIRCUIT VRIBES MESURED? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS AND CONSTRUCTION NQF LEVEL 2 NOVEMBER 2009
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS AND CONSTRUCTION NQF LEVEL 2 NOVEMBER 2009 (12041032) 12 November (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 This question paper consists of 6 pages. (12041032) -2- NC710(E)(N12)V
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS AND CONSTRUCTION NQF LEVEL 2 NOVEMBER 2009 (12041032) 12 November (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 This question paper consists of 6 pages. (12041032) -2- NC710(E)(N12)V
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
Q1. (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply.
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply. 230 V 2760 W 50 Hz Use the information from the plate to answer the
Q1. (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply. 230 V 2760 W 50 Hz Use the information from the plate to answer the
Special resistors. Book page Syllabus
 Special resistors Book page 84 87 Syllabus2.12 2.13 Multiple-choice quiz What am I? LDR, LED or thermistor? Starter LDR s and thermistors are both types of resistor which can change their resistances.
Special resistors Book page 84 87 Syllabus2.12 2.13 Multiple-choice quiz What am I? LDR, LED or thermistor? Starter LDR s and thermistors are both types of resistor which can change their resistances.
Chapter 19. DC Circuits
 Ch-19-1 Chapter 19 Questions DC Circuits 1. Explain why birds can sit on power lines safely, even though the wires have no insulation around them, whereas leaning a metal ladder up against a power line
Ch-19-1 Chapter 19 Questions DC Circuits 1. Explain why birds can sit on power lines safely, even though the wires have no insulation around them, whereas leaning a metal ladder up against a power line
INVESTIGATION ONE: WHAT DOES A VOLTMETER DO? How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured?
 How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
Electric Circuits Lab
 Electric Circuits Lab Purpose: To construct series and parallel circuits To compare the current, voltage, and resistance in series and parallel circuits To draw schematic (circuit) diagrams of various
Electric Circuits Lab Purpose: To construct series and parallel circuits To compare the current, voltage, and resistance in series and parallel circuits To draw schematic (circuit) diagrams of various
Activity 3: Electricity
 Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Circuit Notes. Def: 1. Power supply:
 Circuit Notes Def: Parts of a circuit 1. Power supply: Types: 1- photovoltaic cell: generates current when exposed to light. ex: solar calculator or watch. 2- Batteries and generators. 2. Wires: 3. Switch
Circuit Notes Def: Parts of a circuit 1. Power supply: Types: 1- photovoltaic cell: generates current when exposed to light. ex: solar calculator or watch. 2- Batteries and generators. 2. Wires: 3. Switch
Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h)
 Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h) Introduction A simple electric circuit can be made from a voltage source (batteries), wires through which current flows and a resistance,
Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h) Introduction A simple electric circuit can be made from a voltage source (batteries), wires through which current flows and a resistance,
13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ
 13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ In Activity 13.2, you observed that when the two lamps were connected in series, the brightness of the lamps was less than when the lamps were connected in
13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ In Activity 13.2, you observed that when the two lamps were connected in series, the brightness of the lamps was less than when the lamps were connected in
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
Essential Electricity Homework Exercise 1
 Homework Exercise 1 1. For each of the following electrical symbols, copy the symbol into you jotter and label it using the words below. Word bank resistor, voltmeter, battery, ammeter, bulb V A 2. State
Homework Exercise 1 1. For each of the following electrical symbols, copy the symbol into you jotter and label it using the words below. Word bank resistor, voltmeter, battery, ammeter, bulb V A 2. State
PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS
 GRADE: 10 PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS 1 The number of division in ammeter of range 2A is 10 and voltmeter of range 5 V is 20. When the switch of the circuit given below is closed, ammeter reading
GRADE: 10 PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS 1 The number of division in ammeter of range 2A is 10 and voltmeter of range 5 V is 20. When the switch of the circuit given below is closed, ammeter reading
1 A strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. core. current. coil. pins. What happens when the current in the coil is halved?
 1 strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. current core pins coil What happens when the current in the coil is halved? No pins are attracted. Some pins are attracted, but not as many. The same number
1 strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. current core pins coil What happens when the current in the coil is halved? No pins are attracted. Some pins are attracted, but not as many. The same number
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 1 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 1 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
Sensing Devices. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. International A Level. Exam Board. Current of Electricity.
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Sensing evices Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic Paper Type ooklet International Level Physics IE urrent
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Sensing evices Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic Paper Type ooklet International Level Physics IE urrent
Higher Homework One Part A. 1. Four resistors, each of resistance 20Ω, are connected to a 60V supply as shown.
 Higher Homework One Part A 1. Four resistors, each of resistance 20Ω, are connected to a 60V supply as shown. a) Calculate the total resistance of the circuit. b) Calculate the current drawn from the supply.
Higher Homework One Part A 1. Four resistors, each of resistance 20Ω, are connected to a 60V supply as shown. a) Calculate the total resistance of the circuit. b) Calculate the current drawn from the supply.
(2) The graph below shows how the power output of a wind turbine changes over one day.
 Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources... 2.. (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity.
Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources... 2.. (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity.
Series circuits. The ammeter
 Series circuits D o you remember how the parts of the torch on pages 272 3 were connected together? The circuit contained several components, connected one after the other. Conductors, like the metal strip
Series circuits D o you remember how the parts of the torch on pages 272 3 were connected together? The circuit contained several components, connected one after the other. Conductors, like the metal strip
Circuits. What are circuits?
 Circuits Circuits What are circuits? A closed loop made of a conducting substance that allows electrons to flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal Parts of a Circuit 1 Power Supply Provides
Circuits Circuits What are circuits? A closed loop made of a conducting substance that allows electrons to flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal Parts of a Circuit 1 Power Supply Provides
A device that measures the current in a circuit. It is always connected in SERIES to the device through which it is measuring current.
 Goals of this second circuit lab packet: 1 to learn to use voltmeters an ammeters, the basic devices for analyzing a circuit. 2 to learn to use two devices which make circuit building far more simple:
Goals of this second circuit lab packet: 1 to learn to use voltmeters an ammeters, the basic devices for analyzing a circuit. 2 to learn to use two devices which make circuit building far more simple:
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY
 CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY These components are used in electric circuits. TASK: Draw how you could make this lamp light. Electricity will only flow through a complete circuit. The battery, wires
CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY These components are used in electric circuits. TASK: Draw how you could make this lamp light. Electricity will only flow through a complete circuit. The battery, wires
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS. Unit 1 Electricity and Energy. Revision Notes
 Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Calculate the current in the kettle element. (3)
 1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
Name Period. (c) Now replace the round bulb(s) with long bulb(s). How does the brightness change?
 Name Period P Phys 1 Discovery Lesson Electric Circuits 2.1 Experiment: Charge Flow Strength & Resistors circuit is an unbroken loop of conductors. Charge (q) can flow continuously in a circuit. If an
Name Period P Phys 1 Discovery Lesson Electric Circuits 2.1 Experiment: Charge Flow Strength & Resistors circuit is an unbroken loop of conductors. Charge (q) can flow continuously in a circuit. If an
Section 3 Electric Circuits
 Section 3 Electric Circuits As You Read What You'll Learn Explain how voltage, current, and resistance are related in an electric circuit. Investigate the difference between series and parallel circuits.
Section 3 Electric Circuits As You Read What You'll Learn Explain how voltage, current, and resistance are related in an electric circuit. Investigate the difference between series and parallel circuits.
Circuits. Now put the round bulb in a socket and set up the following circuit. The bulb should light up.
 Name: Partner(s): 1118 section: Desk # Date: Purpose Circuits The purpose of this lab is to gain experience with setting up electric circuits and using meters to measure voltages and currents, and to introduce
Name: Partner(s): 1118 section: Desk # Date: Purpose Circuits The purpose of this lab is to gain experience with setting up electric circuits and using meters to measure voltages and currents, and to introduce
Work done and Moment. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift.
 Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Cabrillo College Physics 10L. LAB 7 Circuits. Read Hewitt Chapter 23
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 7 Circuits Read Hewitt Chapter 23 What to learn and explore Every electrical circuit must have at least one source (which supplies electrical energy to the circuit)
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 7 Circuits Read Hewitt Chapter 23 What to learn and explore Every electrical circuit must have at least one source (which supplies electrical energy to the circuit)
34.5 Electric Current: Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE. Purpose. Required Equipment and Supplies. Discussion. Procedure
 Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Electric Circuits Exam
 Electric Circuits Exam 1. The diagram below represents a lamp, a 10-volt battery, and a length of nichrome wire connected in series. 4. Which circuit has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) B) As the
Electric Circuits Exam 1. The diagram below represents a lamp, a 10-volt battery, and a length of nichrome wire connected in series. 4. Which circuit has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) B) As the
V=I R P=V I P=I 2 R. E=P t V 2 R
 Circuit Concepts Learners should be able to: (a) draw, communicate and analyse circuits using standard circuit symbols using standard convention (b) apply current and voltage rules in series and parallel
Circuit Concepts Learners should be able to: (a) draw, communicate and analyse circuits using standard circuit symbols using standard convention (b) apply current and voltage rules in series and parallel
Class X Chapter 09 Electrical Power and Household circuits Physics
 EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
Electricity Notes 3. Objectives
 Electricity Notes 3 Objectives Series Circuit There is only one path for the current to travel. bulbs connected in series; when one goes out, they all go out. As you add more bulbs, the brightness of the
Electricity Notes 3 Objectives Series Circuit There is only one path for the current to travel. bulbs connected in series; when one goes out, they all go out. As you add more bulbs, the brightness of the
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK (SUMMER
 Notice NO: GAIS/2016-17/007 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK (SUMMER 2016-2017) Grade X(CIE) HINDI Grade 10 Hindi Holiday Homework -2016-17 Solve IGSCE Hindi papers of last 5 years. The papers can be downloaded from cie.org.uk
Notice NO: GAIS/2016-17/007 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK (SUMMER 2016-2017) Grade X(CIE) HINDI Grade 10 Hindi Holiday Homework -2016-17 Solve IGSCE Hindi papers of last 5 years. The papers can be downloaded from cie.org.uk
Series and Parallel Circuits Virtual Lab
 Series and Parallel Circuits Virtual Lab Learning Goals: Students will be able to Discuss basic electricity relationships Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits Build series,
Series and Parallel Circuits Virtual Lab Learning Goals: Students will be able to Discuss basic electricity relationships Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits Build series,
Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism
 Name: Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism 1. An electron, travelling with a constant velocity, enters a region of uniform magnetic field. Which of the following is not a possible pathway? 2. A bar magnet
Name: Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism 1. An electron, travelling with a constant velocity, enters a region of uniform magnetic field. Which of the following is not a possible pathway? 2. A bar magnet
Current Score: 0/20. Due: Mon Feb :15 PM EST. Question Points. 0/40/100/40/10/1 Total 0/20. Description
 1 of 5 2/4/2010 3:35 PM Current Score: 0/20 Due: Mon Feb 15 2010 10:15 PM EST Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 0/40/100/40/10/1 Total 0/20 Description This assignment is worth 20 points. Each part is worth 1
1 of 5 2/4/2010 3:35 PM Current Score: 0/20 Due: Mon Feb 15 2010 10:15 PM EST Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 0/40/100/40/10/1 Total 0/20 Description This assignment is worth 20 points. Each part is worth 1
2: The resistivity of copper is Ω.m. Determine the resistance of a copper wire that is 1.3 m long and has a diameter of 2.1 mm.
 Chapter 20 Discussion January-03-15 8:58 PM Electric Circuits Discussion Questions 1: A current of 12 A flows for 2.5 minutes to charge a battery. How much charge is transferred to the battery in this
Chapter 20 Discussion January-03-15 8:58 PM Electric Circuits Discussion Questions 1: A current of 12 A flows for 2.5 minutes to charge a battery. How much charge is transferred to the battery in this
Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere. electric current. resistor battery.
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
What does the measure? I
 TOP 17 urrent Electricity 1 Which of the following is a correct unit for electrical energy? 5 The diagrams show the symbols and ranges of five meters. ampere Which meter should be used to measure a current
TOP 17 urrent Electricity 1 Which of the following is a correct unit for electrical energy? 5 The diagrams show the symbols and ranges of five meters. ampere Which meter should be used to measure a current
4.5 Dangers of Electricity
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 4.5 angers of Electricity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 4.5 angers of Electricity Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (0625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International
Mark Scheme Q1. Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Question Number. (a) B (1) Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Question Number
 Mark Scheme Q1. (a) B (b) voltmeter symbol connected across battery (c)(i) substitution 2.5 12 evaluation 30 give full marks for correct answer, no (W) working (c)(ii) substitution 12 2.5 evaluation 4.8
Mark Scheme Q1. (a) B (b) voltmeter symbol connected across battery (c)(i) substitution 2.5 12 evaluation 30 give full marks for correct answer, no (W) working (c)(ii) substitution 12 2.5 evaluation 4.8
45 Current Electricity. February 09, Current Electricity. What we will learn, Arc Attack. Electric Man. 1
 Current Electricity What we will learn, Arc Attack Electric Man www.mrcjcs.com 1 Conductors and Insulators An electric current is a flow of electric charge. Set up a simple electrical circuit and insert
Current Electricity What we will learn, Arc Attack Electric Man www.mrcjcs.com 1 Conductors and Insulators An electric current is a flow of electric charge. Set up a simple electrical circuit and insert
Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab
 Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab 1 Current and moving charges Atypical currentinanelectronic devicemightbe5.0 10 3 A.Determinethenumber of electrons that pass through the device
Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab 1 Current and moving charges Atypical currentinanelectronic devicemightbe5.0 10 3 A.Determinethenumber of electrons that pass through the device
