(2) The graph below shows how the power output of a wind turbine changes over one day.
|
|
|
- Alan Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity. The graph below shows how the power output of a wind turbine changes over one day. A wind turbine does not generate electricity constantly. For how many hours did the wind turbine generate no electricity?... Time =... hours () Page of 59
2 (c) Electrical power is transferred from power stations to the National Grid. What is the National Grid? Tick one box. a system of cables and pylons a system of cables and transformers a system of cables, transformers and power stations () (d) An island has a large number of wind turbines and a coal-fired power station. The island needs to use the electricity generated by the coal-fired power station at certain times. Choose one reason why. Tick one box. Wind is a renewable energy resource. Wind turbine power output is constant. The power output of wind turbines is unpredictable. The fuel cost for wind turbines is very high. () (e) A wind turbine has an average power output of 0.60 MW. A coal-fired power station has a continuous power output of 500 MW. Calculate how many wind turbines would be needed to generate the same power output as one coal-fired power station Number of wind turbines =... Page 2 of 59
3 (f) It is important that scientists develop new energy resources. Choose one reason why. Tick one box. All energy resources are running out. All energy resources are used to generate electricity. Most energy resources have negative environmental effects. () (Total 8 marks) 2 An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current that travels directly to the component. Current that is always in the same direction. () Page 3 of 59
4 (b) The equation which links current, potential difference and resistance is: potential difference = current resistance Calculate the potential difference across the battery in the circuit in the figure above Potential difference =... V (3) (c) The equation which links current, potential difference and power is: power = current potential difference Calculate the power output of the battery in the figure above. Give your answer to one significant figure.... Power =... W (Total 6 marks) Page 4 of 59
5 3 An electrician is replacing an old electric shower with a new one. The inside of the old shower is shown in the figure below. Michael Priest (a) The electrician should not change the shower unless he switches off the mains electricity supply. Explain why Page 5 of 59
6 (b) The new shower has a power output of W when it is connected to the 230 V mains electricity supply. The equation which links current, potential difference and power is: current= Calculate the current passing through the new shower. Give your answer to two significant figures Current =... A (4) (c) The new shower has a higher power rating than the old shower. How does the power of the new shower affect the cost of using the shower? Give a reason for your answer (Total 8 marks) Page 6 of 59
7 4 An electrician is replacing an old electric shower with a new one. The inside of the old shower is shown in Figure. Figure Michael Priest (a) If the electrician touches the live wire he will receive an electric shock. Explain why (4) Page 7 of 59
8 (b) Different electrical wires need to have a cross-sectional area that is suitable for the power output. Figure 2 shows the recommended maximum power input to wires of different crosssectional areas. Figure 2 The new electric shower has a power input of 3.8 kw. Determine the minimum diameter of wire that should be used for the new shower. The diameter, d, can be calculated using the equation: A is the cross-sectional area of the wire Minimum diameter =... mm Page 8 of 59
9 (c) The charge that flows through the new shower in 300 seconds is C. The new electric shower has a power of 3.8 kw. Calculate the resistance of the heating element in the new shower. Write down any equations you use Resistance =... Ω (5) (Total marks) 5 A student finds some information about energy-saving light bulbs. (a) A 30W light bulb uses 600J of electrical energy in a certain period of time. In that time, it produces 450 J of light energy. The rest of the energy is wasted. (i) Calculate the energy wasted by the light bulb in this period of time.. Wasted energy =... J () What happens to the energy wasted by the light bulb?.. () (iii) Calculate the efficiency of this light bulb... Efficiency =... Page 9 of 59
10 (iv) Calculate the period of time, in seconds, during which the 600 J is provided to the 30 W light bulb... Time =... s (b) A company that makes light bulbs provides information about some of their products. The table shows some of this information. Power in watts Lifetime in hours Cost of bulb in Filament bulb LED bulb (i) Suggest why it is important to confirm this information independently.. () A homeowner is thinking about replacing his filament bulbs with LED bulbs. A 2 W LED bulb gives the same light output as a 60 W filament bulb. Suggest reasons why the homeowner is likely to choose LED bulbs. Use the information given in the table..... (iii) State one factor, other than efficiency, that is important when considering the choice of a bulb for lighting in the home... () (Total 0 marks) Page 0 of 59
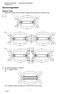
11 6 The diagram shows an a.c. generator. The coil rotates about the axis shown and cuts through the magnetic field produced by the magnets. (a) (i) A potential difference is induced between X and Y. Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. electric generator motor transformer This effect is called the... effect. () What do the letters a.c. stand for?. () (iii) Name an instrument that could be used to measure the potential difference between X and Y.. () Page of 59
12 (b) Graph shows the output from the a.c. generator. Graph (i) One of the axes on Graph has been labelled Potential difference. What should the other axis be labelled?. () The direction of the magnetic field is reversed. On Graph, draw the output from the a.c. generator if everything else remains the same. (c) The number of turns of wire on the coil is increased. This increases the maximum induced potential difference. State two other ways in which the maximum induced potential difference could be increased (Total 8 marks) Page 2 of 59
13 7 (a) A resistor is a component that is used in an electric circuit. (i) Describe how a student would use the circuit to take the readings necessary to determine the resistance of resistor R (6) Page 3 of 59
14 Explain why the student should open the switch after each reading..... (iii) In an experiment using this circuit, an ammeter reading was 0.75 A. The calculated value of the resistance of resistor R was 6 Ω. What is the voltmeter reading?.. Voltmeter reading =... V (iv) The student told his teacher that the resistance of resistor R was 6 Ω. The teacher explained that the resistors used could only have one of the following values of resistance. 0 Ω 2 Ω 5 Ω 8 Ω 22 Ω Suggest which of these resistors the student had used in his experiment. Give a reason for your answer..... Page 4 of 59
15 (b) The diagram shows a fuse. Describe the action of the fuse in a circuit (3) (Total 5 marks) 8 The current in a circuit depends on the potential difference (p.d.) provided by the cells and the total resistance of the circuit. (a) Using the correct circuit symbols, draw a diagram to show how you would connect.5 V cells together to give a p.d. of 6 V. Page 5 of 59
16 (b) Figure shows a circuit containing an 8 V battery. Two resistors, X and Y, are connected in series. X has a resistance of 3 Ω. There is a current of 2 A in X. Figure (i) Calculate the p.d. across X. P.d. across X =... V Calculate the p.d. across Y. P.d. across Y =... V (iii) Calculate the total resistance of X and Y. Total resistance of X and Y =... Ω Page 6 of 59
17 (c) Figure 2 shows a transformer. Figure 2 (i) An 8 V battery could not be used as the input of a transformer. Explain why. The transformer is 00% efficient. Calculate the output current for the transformer shown in Figure 2. Output current =... A (Total 2 marks) Page 7 of 59
18 9 The figure below shows a coil and a magnet. An ammeter is connected to the coil. The ammeter has a centre zero scale, so that values of current going in either direction through the coil can be measured. (a) A teacher moves the magnet slowly towards the coil. Explain why there is a reading on the ammeter. (6) Page 8 of 59
19 (b) The table below shows some other actions taken by the teacher. Complete the table to show the effect of each action on the ammeter reading. Action taken by teacher What happens to the ammeter reading? Holds the magnet stationary and moves the coil slowly towards the magnet Holds the magnet stationary within the coil Moves the magnet quickly towards the coil Reverses the magnet and moves it slowly towards the coil (4) (c) The magnet moves so that there is a steady reading of 0.05 A on the ammeter for 6 seconds. Calculate the charge that flows through the coil during the 6 seconds. Give the unit. Charge =... (3) (Total 3 marks) Page 9 of 59
20 0 If a fault develops in an electrical circuit, the current may become too great. The circuit needs to be protected by being disconnected. A fuse or a circuit breaker may be used to protect the circuit. One type of circuit breaker is a Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB). (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. earth live neutral A fuse is connected in the... wire. () Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. are bigger are cheaper react faster RCCBs are sometimes preferred to fuses because they.... () (iii) RCCBs operate by detecting a difference in the current between two wires. Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. earth and live earth and neutral live and neutral The two wires are the... wires. () Page 20 of 59
21 (b) An RCCB contains an iron rocker and a coil. A student investigated how the force of attraction, between a coil and an iron rocker, varies with the current in the coil. She supported a coil vertically and connected it in an electrical circuit, part of which is shown in the figure below. She put a small mass on the end of the rocker and increased the current in the coil until the rocker balanced. She repeated the procedure for different masses. Some of her results are shown in the table below. Mass in grams Current needed for the rocker to balance in amps (i) State two extra components that must have been included in the circuit in the figure above to allow the data in the above table to be collected. Give reasons for your answers. Page 2 of 59
22 (4) A teacher said that the values of current were too high to be safe. Suggest two changes that would allow lower values of current to be used in this investigation. Change... Change 2... (Total 9 marks) (a) A company is developing a system which can heat up and melt ice on roads in the winter. This system is called energy storage. During the summer, the black surface of the road will heat up in the sunshine. This energy will be stored in a large amount of soil deep under the road surface. Pipes will run through the soil. In winter, cold water entering the pipes will be warmed and brought to the surface to melt ice. The system could work well because the road surface is black. Suggest why. () (b) (i) What is meant by specific latent heat of fusion? Page 22 of 59
23 Calculate the amount of energy required to melt 5 kg of ice at 0 C. Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = J/kg. Energy =... J (c) Another way to keep roads clear of ice is to spread salt on them. When salt is added to ice, the melting point of the ice changes. A student investigated how the melting point of ice varies with the mass of salt added. The figure below shows the equipment that she used. The student added salt to crushed ice and measured the temperature at which the ice melted. (i) State one variable that the student should have controlled. () Page 23 of 59
24 During the investigation the student stirred the crushed ice. Suggest two reasons why. Tick ( ) two boxes. Tick ( ) To raise the melting point of the ice To lower the melting point of the ice To distribute the salt throughout the ice To keep all the ice at the same temperature To reduce energy transfer from the surroundings to the ice (iii) The table below shows the data that the student obtained. Mass of salt added in grams Melting point of ice in C Describe the pattern shown in the table. () (d) Undersoil electrical heating systems are used in greenhouses. This system could also be used under a road. A cable just below the ground carries an electric current. One greenhouse system has a power output of 0.50 kw. Calculate the energy transferred in 2 minutes. Energy transferred =... J (3) Page 24 of 59
25 (e) In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. A local council wants to keep a particular section of a road clear of ice in the winter. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of keeping the road clear of ice using: energy storage salt undersoil electrical heating. Extra space... (6) (Total 8 marks) Page 25 of 59
26 2 (a) Figure shows the inside of a three-pin plug and a length of three-core cable. The cable is to be connected to the plug. Figure (i) Complete Table to show which plug terminal, A, B or C, connects to each of the wires inside the cable. Table Wire Plug terminal Live Neutral Earth Name a material that could be used to make the case of the plug. () Page 26 of 59
27 (b) Figure 2 shows an electric drill and an extension lead. The drill is used with the extension lead. Figure 2 Electric drill Extension lead (i) The drill is used for 50 seconds. In this time, joules of energy are transferred from the mains electricity supply to the drill. Calculate the power of the drill. Power =... W Page 27 of 59
28 A second drill is used with the extension lead. The power of this drill is 200 W. The instructions for using the extension lead include the following information. When in use the lead may get hot: DO NOT go over the maximum power lead wound inside the case: 820 watts lead fully unwound outside the case: 300 watts It would not be safe to use this drill with the extension lead if the lead was left wound inside the plastic case. Explain why. (3) Page 28 of 59
29 (c) Table 2 gives information about three different electric drills. Table 2 Drill Power input in watts Power output in watts X Y Z A person is going to buy one of the drills, X, Y or Z. The drills cost the same to buy. Use only the information in the table to decide which one of the drills, X, Y or Z, the person should buy. Write your answer in the box. Give a reason for your answer. () (Total 9 marks) 3 Solar panels are often seen on the roofs of houses. (a) Describe the action and purpose of a solar panel..... Page 29 of 59
30 (b) Photovoltaic cells transfer light energy to electrical energy. In the UK, some householders have fitted modules containing photovoltaic cells on the roofs of their houses. Four modules are shown in the diagram. The electricity company pays the householder for the energy transferred. The maximum power available from the photovoltaic cells shown in the diagram is W. How long, in minutes, does it take to transfer 68 kj of energy? Time =... minutes (3) Page 30 of 59
31 (c) When the modules are fitted on a roof, the householder gets an extra electricity meter to measure the amount of energy transferred by the photovoltaic cells. (i) The diagram shows two readings of this electricity meter taken three months apart. The readings are in kilowatt-hours (kwh). 2 November February Calculate the energy transferred by the photovoltaic cells during this time period.. Energy transferred =... kwh () The electricity company pays 40p for each kwh of energy transferred. Calculate the money the electricity company would pay the householder... Money paid =... (iii) The cost of the four modules is Calculate the payback time in years for the modules... Payback time =... years (3) (iv) State an assumption you have made in your calculation in part (iii)... () Page 3 of 59
32 (d) In the northern hemisphere, the modules should always face south for the maximum transfer of energy. State one other factor that would affect the amount of energy transferred during daylight hours... () (Total 3 marks) 4 (a) The diagram shows the circuit used to obtain the data needed to plot the current potential difference graph for a filament bulb. (i) Why is the component labelled J included in the circuit? () The resistance of the bulb increases as the potential difference across the bulb increases. Why? () (iii) The bulb is at full brightness when the potential difference across the bulb is 2 V. The current through the bulb is then 3 A. Calculate the power of the bulb when it is at full brightness and give the unit. Power =... (3) Page 32 of 59
33 (b) In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. The table gives data about two types of light bulb people may use in their homes. Type of light bulb Energy efficiency Cost of one light bulb Average lifetime in hours Halogen 0% Light Emitting Diode (LED) 32% Both types of light bulb produce the same amount of light. Evaluate, in terms of cost and energy efficiency, the use of the two types of light bulb. To gain full marks you must compare both types of light bulb and conclude which light bulb would be the best to use. (6) (Total marks) Page 33 of 59
34 5 The picture shows an electric cooker hob. The simplified circuit diagram shows how the four heating elements connect to the mains electricity supply. The heating elements are identical. When all four heating elements are switched on at full power the hob draws a current of 26 A from the 230 V mains electricity supply. (a) Calculate the resistance of one heating element when the hob is switched on at full power. Give your answer to 2 significant figures. Resistance =... Ω (3) Page 34 of 59
35 (b) The table gives the maximum current that can safely pass through copper wires of different cross-sectional area. Cross-sectional area in mm 2 Maximum safe current in amps The power sockets in a home are wired to the mains electricity supply using cables containing 2.5 mm 2 copper wires. Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains electricity supply by plugging them into a standard power socket. It would not be safe to connect the electric cooker hob to the mains electricity supply by plugging it into a standard power socket. Why? (c) Mains electricity is an alternating current supply. Batteries supply a direct current. What is the difference between an alternating current and a direct current? (Total 7 marks) Page 35 of 59
36 6 (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply. 230 V 2760 W 50 Hz Use the information from the plate to answer the following questions. (i) What is the frequency of the a.c. mains electricity supply? () What is the power of the electric kettle? () (b) To boil the water in the kettle, 2400 coulombs of charge pass through the heating element in 200 seconds. Calculate the current flowing through the heating element and give the unit. Choose the unit from the list below. amps volts watts Current =... (3) Page 36 of 59
37 (c) The amount of charge passing through the heating element of an electric kettle depends on the time the kettle is switched on. What pattern links the amount of charge passing through the heating element and the time the kettle is switched on? (Total 7 marks) Page 37 of 59
38 7 The diagram shows the structure of a cable. The cable is part of an undersoil heating circuit inside a large greenhouse. (a) The cable is connected to the mains electricity supply through a residual current circuit breaker. If the cable is accidentally cut the circuit breaker automatically switches the circuit off. (i) What is the frequency of the mains electricity supply in the UK? () What happens, as the cable is cut, to cause the circuit breaker to switch the circuit off? (iii) A circuit can also be switched off by the action of a fuse. Give one advantage of using a circuit breaker to switch off a circuit rather than a fuse. () (b) The 230 volt mains electricity supply causes a current of amps to flow through the cable. (i) Calculate the amount of charge that flows through the cable when the cable is switched on for 2 hours and give the unit. Charge =... (3) Page 38 of 59
39 Calculate the energy transferred from the cable to the soil in 2 hours. Energy transferred =... J (c) The heating circuit includes a thermistor. The thermistor is buried in the soil and acts as a thermostat to control the increase in the temperature of the soil. Describe how an increase in the temperature of the soil affects the thermistor. (Total marks) 8 The pictures show six different household appliances. (a) Four of the appliances, including the fan heater, are designed to transform electrical energy into heat. Name the other three appliances designed to transform electrical energy into heat. 2 3 (3) Page 39 of 59
40 (b) The bar chart shows the power of three electric kettles, X, Y and Z. Kettle (i) In one week, each kettle is used for a total of 30 minutes. Which kettle costs the most to use? Put a tick ( ) next to your answer. X Y Y () A new express boil kettle boils water faster than any other kettle. Draw a fourth bar on the chart to show the possible power of an express boil kettle. () Page 40 of 59
41 (c) The graph shows how the time to boil water in an electric kettle depends on the volume of water in the kettle. Volume of water in litres A householder always fills the electric kettle to the top, even when only enough boiling water for one small cup of coffee is wanted. Explain how the householder is wasting money. (3) (Total 8 marks) Page 4 of 59
42 9 (a) The diagram shows the inside of an incorrectly wired three-pin plug. (i) What two changes need to be made so that the plug is wired correctly? The fuse inside a plug is a safety device. Explain what happens when too much current passes through a fuse. Page 42 of 59
43 (b) Each of these pictures shows an electrical appliance being used in a bathroom. Using the hairdryer in picture A is dangerous. However, it is safe to use the batteryoperated radio in picture B. Explain why. (Total 6 marks) 20 (a) Describe the difference between an alternating current (a.c.) and a direct current (d.c.). Page 43 of 59
44 (b) The diagram shows how the electric supply cable is connected to an electric kettle. The earth wire is connected to the metal case of the kettle. If a fault makes the metal case live, the earth wire and the fuse inside the plug protect anyone using the kettle from an electric shock. Explain how. (Total 4 marks) 2 (a) The diagram shows the traces produced on an oscilloscope when it is connected across different electricity supplies. Which of the traces could have been produced by the mains electricity supply? Give a reason for your answer. Page 44 of 59
45 (b) The picture shows two adaptors being used to plug five electrical appliances into the same socket. Explain why it is dangerous to have all five appliances switched on and working at the same time. (Total 4 marks) 22 (a) The diagram shows a piece of two-core cable and a piece of three-core cable. (i) Which one of the wires inside a three-core cable is missing from a two-core cable? Draw a ring around your answer. earth wire live wire neutral wire () Page 45 of 59
46 Use a word from the box to complete the following sentence. double extra totally A pottery table lamp fitted with a two-core cable is safe to use because it is... insulated. () (b) The cables connecting the power sockets in a building contain wires.8 mm thick. The maximum current that can safely pass through these wires is 20 amps. A fuse is included in the circuit to protect the wiring. Explain how a fuse protects the wiring of a circuit. (3) (Total 5 marks) Page 46 of 59
47 23 (a) The picture shows a person using a set of electronic Body Fat Scales. When the person stands on the scales, a small, harmless, electric current passes through the person s body. The scales then calculate the resistance of the person s body and convert the resistance into a prediction of body fat content. (i) The scales contain two 3 V cells joined in series. Calculate the resistance of a person s body, if when he stands on the scales, a current of 0.2 ma passes through his body. 000 ma = A Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Resistance =... (3) The scales can only produce a prediction of body fat content and not an accurate measurement. Suggest why. () Page 47 of 59
48 (iii) It is recommended that the scales are not used immediately after a person has drunk a large amount of water. Suggest why. (b) The diagram shows how someone could get an electric shock from accidentally cutting into an electric cable. If this happens, and a Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) is being used, the circuit will switch off automatically. (i) A faulty appliance or circuit can be switched off by a RCCB or a fuse. Compare the action of a RCCB with the action of a fuse. The graph shows how the severity of an electric shock depends on the size of the current and the time that the current flows through the body. Page 48 of 59
49 Using the RCCB helps prevent an electric shock seriously injuring the person using the hedge trimmers. Using information from both the diagram and the graph explain how. (Total 0 marks) Page 49 of 59
50 24 (a) The diagram shows the energy transformations produced by a television. When the television is working, 200 joules of energy are supplied to the television every second. The useful energy transferred by the television is 720 joules every second. (i) Use the equation in the box to calculate the efficiency of the television. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Efficiency =... Use one word from the diagram to complete the following sentence. The electrical energy that is not usefully transformed by the television is wasted as.... () Page 50 of 59
51 (b) A homeowner is sent an electricity bill every 3 months. The total amount of electrical energy used during one 3-month period was 800 kilowatt-hours. Electrical energy costs 5p per kilowatt-hour. Use the equation in the box to calculate the cost of the energy transferred from the mains electricity supply. total cost = number of kilowatt-hours cost per kilowatt-hour Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Cost =... (Total 5 marks) Page 5 of 59
52 25 The diagram shows a helicopter being used to rescue a person from the sea. (a) (i) The mass of the rescued person is 72 kg. Use the equation in the box to calculate the weight of the rescued person. weight = mass gravitational field strength gravitational field strength = 0 N/kg Show clearly how you work out your answer. Weight =... N An electric motor is used to lift the person up to the helicopter. The motor lifts the person at a constant speed. State the size of the force, T, in the cable. Force T =... N () Page 52 of 59
53 (b) To lift the person up to the helicopter, the electric motor transformed joules of energy usefully. (i) Use a form of energy from the box to complete the following sentence. gravitational potential heat sound The electric motor transforms electrical energy to kinetic energy. The kinetic energy is then transformed into useful... energy. () It takes 50 seconds for the electric motor to lift the person up to the helicopter. Use the equation in the box to calculate the power of the electric motor. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Choose the unit from the list below. coulomb (C) hertz (Hz) watt (W) Power =... (3) (Total 7 marks) Page 53 of 59
54 26 The diagram shows an electric circuit used in a dolls house. The switches are 2-way switches; this means that each switch has a connecting wire that can be in one of two positions. (a) (i) With the connecting wire in each switch in the position shown in the diagram, the lamp is off. Why? () When switched on, the lamp has a resistance of 8 Ω and draws a current of 0.5 A from the power supply. Use the equation in the box to calculate the potential difference of the power supply used in the circuit. potential difference = current resistance Show clearly how you work out your answer. Potential difference =... V Page 54 of 59
55 (iii) A second, identical lamp is added to the circuit. The two lamps are joined in series. Calculate the total resistance of the two lamps. Total resistance =... Ω () (b) This type of circuit is also used in real houses. One of the switches is at the top of the stairs, and the other switch is at the bottom of the stairs. What is the advantage of using this circuit to switch a lamp on or off, rather than using a more simple circuit that has only one switch? () (c) The diagram shows an old type of metal lamp fitting. The cable has been connected to the lamp fitting in a way that makes the lamp fitting unsafe. (i) What is the possible risk to someone touching the lamp fitting while the lamp is switched on? () Page 55 of 59
56 What should be done to make this lamp fitting safe to use? () (Total 7 marks) 27 The diagrams show the inside of a 3 amp plug. (a) (i) Which one of the plugs, A, B, C or D, is correctly wired? Write your answer, A, B, C or D, in the box. A B C D The plug that is correctly wired is () What material is the outside casing of a plug made from? () Page 56 of 59
57 (b) An electric drill draws a current of 2 amps from the 230 volt mains electricity supply. Use the equation in the box to calculate the power of the drill. power = current potential difference Show clearly how you work out your answer. Power... watts (c) A householder needs to replace a damaged plug. Most replacement plugs are sold with a 3 amp fuse fitted inside. The householder thinks it would be better for shops to sell the plugs without a fuse. He could then buy either a 3 A, 5 A or 3 A fuse to fit inside the plug. Explain an advantage of selling plugs without a fuse, rather than with a 3 amp fuse fitted. (Total 6 marks) Page 57 of 59
58 28 A set of lights consists of 20 lamps connected in series to the 230 V mains electricity supply. (a) When the lights are switched on and working correctly, the current through each lamp is 0.25 A. (i) What is the total current drawn from the mains supply? () Calculate the charge passing through one of the lamps in 5 minutes. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Total charge =... (3) Page 58 of 59
59 (b) One of the lamps in the set is a fuse lamp. This contains a filament which melts if a fault occurs. A short time after the lights are switched on, a fault causes the filament inside the fuse lamp to melt and all the lamps go out. The householder cannot find another fuse lamp so connects a piece of aluminium foil across the contacts inside the fuse lamp holder. When switched on, the nineteen remaining lamps work. What the householder has done is dangerous. Explain why. (Total 6 marks) 29 Diagram shows a hairdryer. Diagram 2 shows how the heaters and fan of the hairdryer are connected to a 3-pin plug. The hairdryer does not have an earth wire. (a) What colour is the insulation around the wire connected to the live pin inside the plug?... () Page 59 of 59
60 (b) Why does the hairdryer not need an earth wire? () (c) All the switches are shown in the OFF position. (i) Which switch or switches have to be ON to make: () only the fan work;... heater 2 work?... The heaters can only be switched on when the fan is also switched on. Explain why. Page 60 of 59
61 (d) The table shows the current drawn from the 230 volt mains electricity supply when different parts of the hairdryer are switched on. Current in amps Fan only.0 Fan and heater 4.4 Fan and both heaters 6.5 Calculate the maximum power of the hairdryer. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Maximum power =... (3) (Total 9 marks) Page 6 of 59
62 30 The diagram shows a strain gauge, which is an electrical device used to monitor a changing force. Applying a force to the gauge causes it to stretch. This makes the electrical resistance of the wire change. (a) (i) Using the correct symbols, add to the diagram to show how a battery, an ammeter and a voltmeter can be used to find the resistance of the strain gauge drawn above. When in use, the strain gauge is always connected to a d.c. power supply, such as a battery. How is a d.c. (direct current) power supply different from an a.c. (alternating current) power supply? () (b) Before any force is applied, the unstretched gauge, correctly connected to a 3.0 V battery, has a current of A flowing through it. (i) Calculate the resistance of the unstretched gauge. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Resistance =... Ω Page 62 of 59
63 Stretching the gauge causes the current flowing through the gauge to decrease. What happens to the resistance of the gauge when it is stretched? () (iii) What form of energy is stored in the gauge when a force is applied and the gauge stretches? () (Total 7 marks) 3 The picture shows a new washing machine. When the door is closed and the machine switched on, an electric motor rotates the drum and washing. (a) What happens to the energy wasted by the electric motor? () Page 63 of 59
64 (b) The diagram shows the label from the new washing machine. An A rated washing machine is more energy efficient than a C rated washing machine. Explain what being more energy efficient means. Page 64 of 59
65 (c) The graph shows that washing clothes at a lower temperature uses less energy than washing them at a higher temperature. Using less energy will save money. (i) Electricity costs 2 p per kilowatt-hour (kwh). The temperature setting is turned down from 40 C to 30 C. Use the graph and equation in the box to calculate the money saved each wash cycle. total cost = number of kilowatt-hours cost per kilowatt-hour Show clearly how you work out your answer. Money saved =... p Suggest why reducing the amount of energy used by washing machines could reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere. () (Total 6 marks) Page 65 of 59
66 32 (a) The diagram shows the inside of an incorrectly wired three-pin plug. (i) What two changes need to be made so that the plug is wired correctly? Which one of the wires inside a plug is there to make an appliance with a metal case safer to use? () (iii) The fuse inside a plug is a safety device. Explain what happens when too much current passes through a fuse. Page 66 of 59
67 (b) Each of these pictures shows an electrical appliance being used in a bathroom. A Using the hairdryer in picture A is dangerous. However, it is safe to use the batteryoperated radio in picture B. Explain why. (Total 7 marks) Page 67 of 59
68 33 An oscilloscope is connected to an alternating current (a.c.) supply. The diagram shows the trace produced on the oscilloscope screen. Each horizontal division on the oscilloscope screen represents s. (a) Calculate the frequency of the alternating current supply. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Frequency =... (3) (b) What is the frequency of the a.c. mains electricity supply in the UK? () (Total 4 marks) 34 A homeowner has installed electric underfloor heating in the kitchen. When the heating is switched on, an electric current flows through wires running under the tiled floor surface. (a) What is an electric current? () Page 68 of 59
69 (b) The graph shows how the power output of an underfloor heating system depends on the area of the floor that is heated. The area of the homeowner s kitchen floor is 9.0 m 2. Calculate, using the graph, the current drawn from the 230 V mains supply by the heating system. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Current =... (4) (Total 5 marks) Page 69 of 59
70 35 (a) Use numbers given in the box to complete the following sentences In the UK, the mains electricity supply is... volts. The frequency of the UK mains electricity supply is... hertz. (b) The diagram shows a hairdryer designed to be used with the UK mains supply. The cable connecting the hairdryer to the plug does not have an earth wire. Plastic cover (i) Why does the hairdryer not need a cable with an earth wire? () Which one of the following materials are the two wires inside the cable made from? Draw a ring around your answer. aluminium copper steel () (Total 4 marks) Page 70 of 59
71 36 (a) Describe the difference between an alternating current (a.c.) and a direct current (d.c.) (b) The diagram shows the information plate on the bottom of an electric wallpaper steamer. (i) Calculate the current used by the steamer. Show clearly how you work out your answer Current... A Which one of the following fuses should be used inside the plug of the steamer? Draw a ring around your answer. A 3 A 5 A 0 A 3 A () (Total 5 marks) Page 7 of 59
72 37 The diagram shows someone accidentally touching the live wire inside a dismantled 230 volt mains electricity socket. A current flows through the person giving him an electric shock. (a) (i) Calculate the current that will flow through the person. Show clearly how you work out your answer Current =... A Rubber is a good insulator. Explain why it is a good idea for electricians to wear rubber soled boots when working Page 72 of 59
73 (b) If the current flowing through a person is too high, the person cannot let go of the electrical source. Different people were tested to see whether the ability to let go of an electrical source depended on the frequency of the current. The results of the test are shown in the graph. (i) What is the frequency of the mains electricity supply in the UK?... () From a safety point of view, is the frequency of the UK mains electricity supply suitable? Give a reason for your answer () Page 73 of 59
74 (c) The diagram shows how the electric supply cable is connected to an electric kettle. The earth wire is connected to the metal case of the kettle. If a fault makes the metal case live, the earth wire and the fuse inside the plug protect anyone using the kettle from an electric shock. Explain how (Total 8 marks) Page 74 of 59
75 38 (a) Each letter A, B, C, D and E represents an energy transformation. A electrical to gravitational potential B electrical to heat C electrical to kinetic D electrical to light E electrical to sound Match each of the following devices to the useful energy transformation that it is designed to make. Write the correct letter, A, B, C, D or E, in the box below the device. Use each letter once or not at all. (3) (b) The bar chart shows the power of three electric kettles. (i) What is the power of kettle Y?... () Page 75 of 59
76 In one week each kettle is used for a total of 30 minutes. Which kettle costs the most to use?... () (iii) A new express boil kettle boils water faster than any other kettle. Draw a fourth bar on the chart to show the possible power of an express boil kettle. () (c) Some friends are going on holiday. They want to be able to boil water to make their own hot drinks. They cannot decide which to take, a travel kettle or a small portable immersion heater that can be placed in a mug. Travel Kettle k W element Holds litre Works on 0V or 230V Washable water filter Immersion heater 0.4 k W element Heates up to 0.5 litres of water Works on 230 V only Small compact size (i) Give one advantage of taking the travel kettle () Page 76 of 59
77 Give one advantage of taking the immersion heater () (Total 8 marks) 39 (a) Look at this electrical safety information poster. (i) Complete the table to show which size fuse, 3 A or 3 A, should be fitted to each of the appliances. Appliance Power rating Fuse Hairdryer 600 W Electric saw 350 W Food mixer 200 W The plug of an electric kettle has been wrongly fitted with a 3 A fuse. What will happen to the fuse when the kettle is switched on? () Page 77 of 59
78 (b) The drawing shows a toaster, which takes a current of 4 A from the 230 V mains electricity supply. (i) Use the equation in the box to calculate the power of the toaster. Power (watt, W) = current (ampere, A) potential difference (volt, V) Show clearly how you work out your answer Power =... W A householder rewires the toaster with a new cable and plug. The diagram shows how the new cable has been connected to the plug. Explain why the toaster may not be safe to use Page 78 of 59
79 (c) The diagram shows the oscilloscope traces produced by four different electricity supplies. The settings on the oscilloscope are the same for each electricity supply. (i) Which two supplies give a direct current (d.c.)?... and... () Supply K provides a peak potential difference of 6 V. What is the peak potential difference provided by supply M?... () (Total 9 marks) 40 (a) The diagram shows the inside of a correctly wired three-pin plug. (i) What colour is the insulation on the wire labelled X? Draw a ring around your answer. blue brown green/yellow () What name is given to the wire labelled Y? Draw a ring around your answer. earth live neutral () Page 79 of 59
80 (iii) What material would be suitable for the case of the plug?... () (iv) Which one of the following is the correct circuit symbol for a fuse? Draw a ring around your answer. () (b) A householder does not have enough electric sockets in the kitchen. To overcome the problem, the householder uses two adaptors to plug five appliances into a single electric socket. Explain why this is dangerous (Total 6 marks) Page 80 of 59
81 4 The diagram shows two oscilloscope traces, A and B. Trace A shows how the potential difference between the live and neutral terminals of an electricity supply changes with time. (a) Describe how the potential of the live terminal varies with respect to the neutral terminal of the electricity supply (b) What does trace B show? () (c) Each horizontal division on the oscilloscope represents s. (i) What is the period of this electricity supply?... Period =... seconds () Calculate the frequency of the supply.... Frequency =... hertz () (Total 5 marks) Page 8 of 59
82 42 The diagram shows the inside of a mains plug. (a) Complete the table. Wire Colour of insulation Earth Live Neutral (3) Page 82 of 59
83 (b) The diagram shows a washing machine without an earth connection. The live wire has become loose and is touching the metal case of the washing machine. (i) Draw on the diagram the path taken by the electricity when the person touches the metal case of the machine. Describe how the path of the electricity would change if the washing machine had an earth connection () Page 83 of 59
84 (c) Some electrical appliances use a cable which does not have an earth wire. Which one of the following appliances can safely use this type of cable? hairdrier iron refrigerator... Give a reason for your answer (Total 8 marks) 43 The information plate on a hairdrier is shown. (a) What is the power rating of the hairdrier?... () (b) (i) Write down the equation which links current, power and voltage.... () Calculate the current in amperes, when the hairdrier is being used. Show clearly how you work out your answer Current =... amperes (iii) Which one of the following fuses, 3A, 5A or 3A, should you use with this hairdrier?... () Page 84 of 59
85 (c) The hairdrier transfers electrical energy to heat energy and kinetic energy. Calculate the efficiency of the hairdrier in transferring electrical energy into heat energy Efficiency =... (Total 7 marks) 44 (a) The diagram shows a 3 amp plug. Page 85 of 59
86 (i) What is wrong with the way this plug has been wired? () Why do plugs have a fuse? () (b) The diagram shows an immersion heater which can be used to boil water in a mug. (i) Which part of the immersion heater should be connected to the earth pin of the plug?... () (Total 3 marks) Page 86 of 59
87 45 (a) The diagram shows an electric fence, designed to keep horses in a field. When a horse touches the wire the horse receives a mild electric shock. Explain how (b) The diagram shows how a person could receive an electric shock from a faulty electrical appliance. Using a residual circuit breaker (RCB) can help to protect the person against receiving a serious shock. Current to earth (i) Compare the action of an RCB to that of a fuse Page 87 of 59
88 The graph illustrates how the severity of an electric shock depends upon both the size of the current and the time for which the current flows through the body. Within how long must the RCB cut off the current if the person using the lawnmower is to be in no danger of serious injury? Time =... milliseconds (Total 6 marks) Page 88 of 59
89 46 (a) An adaptor can be used to connect up to four appliances in parallel to one 230 V mains socket. The adaptor is fitted with a 3 A fuse. The table gives a list of appliances and the current they draw from a mains socket. Appliance computer hairdryer heater iron television Current A 4 A 8 A 6 A 2 A (i) What current will flow to the adaptor when the television, computer and hairdryer are plugged into the adaptor?... Current =... A () Write down the equation which links current, electrical power and voltage.... () Page 89 of 59
90 (iii) Calculate the electrical power used when the television, computer and hairdryer are plugged into the adaptor. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit Electrical power =... (iv) What would happen to the fuse if the heater is also plugged into the adaptor? Give a reason for your answer (b) The diagram shows two of the appliances. (i) For safety reasons, it is important that the iron has an earth wire connected to its outer metal case. Explain why Page 90 of 59
91 The hairdryer does not have an earth wire. It is safe to use because it is double insulated. Explain what the term double insulated means (Total 0 marks) 47 The diagram below shows an electric mains plug. (a) Name the parts of the plug labelled A and B. A... B... (b) Name the colour of each of the wires X, Y and Z. X... Y... Z... (3) (c) Name a suitable material for the case of the plug.... () Page 9 of 59
92 (d) Electric fires have three wires connected in the plug. One is the live wire to feed electric current in, another is the neutral (return) wire. (i) What is the third wire called?... () Why is it important that the third wire is also connected? () (e) The diagram below shows a badly wired mains plug. Look at the plug carefully. What four changes should be made to make the plug safe? (4) (Total 2 marks) Page 92 of 59
93 48 The circuit diagram below shows a circuit used to supply electrical energy to the two headlights of a car. The current through the filament of one car headlight is 3.0 A. The potential difference across each of the two headlights is 2 V. (a) Suggest a suitable fuse for the circuit.... () (b) Calculate the resistance of the headlight filament when in use Answer... W (c) Calculate the power supplied to the two headlights of the car Answer... W Page 93 of 59
94 (d) The fully charged car battery can deliver 72 kj of energy at 2 V. How long can the battery keep the headlights fully on? Answer... s (Total 7 marks) 49 (a) The picture below shows the bathroom in a house. Describe three examples of dangerous practice in the use of mains electricity in this bathroom (3) Page 94 of 59
95 (b) In the table below three electrical appliances are listed with their power ratings and the number of hours they are used each week. ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE POWER RATINGS (W) TIME USED EACH WEEK (h) k Wh USED EACH WEEK TV Kettle Toaster 000 Cooker (i) Complete the table by inserting the number of kwh used by each appliance each week. Which appliance would cost the least to run per week?... (iii) The cost of running a toaster is 8p per week. How much does it cost to run the kettle each week? (6) (Total 9 marks) Page 95 of 59
96 50 When a mains lamp is switched on it takes 0.5 seconds for the filament to reach its normal operating temperature. The way in which the current changes during the first second after switching on is shown in the sketch graph below. Mains voltage is 240 V. (a) Calculate the resistance of the filament whilst the lamp is drawing the maximum current (3) (b) Describe how the resistance of the lamp changes after the current has reached its maximum value (c) Calculate the maximum power taken by the lamp Page 96 of 59
97 (d) Calculate the power of the lamp in normal use (e) Calculate the energy used by the lamp in six hours of normal use (3) (Total 2 marks) 5 (a) The diagram below shows the three pins in a mains plug. The pins connect with the live, neutral and earth terminals in a socket. On the diagram, label each pin to show which is: the live pin, the neutral pin, the earth pin. (3) Page 97 of 59
98 (b) The diagram below shows the inside of a mains plug. (i) Name one material which could be used for the part labelled X.... Complete the sentences below. The part labelled Y is called the.... This is used to hold the... firmly in place. The component labelled Z is the.... (iii) The plug is used with an electric fire. Which part of the electric fire is connected to the earth pin?... (5) (Total 8 marks) 52 The diagrams show a hair-dryer and the circuit inside the hair-dryer. Page 98 of 59
99 (a) Switches S, S 2 and S 3 are all shown in the OFF position. Which switch or switches have to be ON to make: (i) only the fan work?... both heaters work?... (b) (i) What happens to the current in the circuit when the heaters are switched on?... Suggest why it is important to have the fan working when the heaters are switched on (3) (c) This hair-dryer has a plastic case. It is connected to a mains socket by a 3-pin plug. The cable connecting the hair-dryer to the plug contains only two wires. (i) Write down the colour of the insulation on the wires. Wire... Wire 2... Which of the usual three wires is not needed?... (iii) This hair-dryer is safe to use without the third wire. Explain why (5) (d) The following information is stamped on the hair-dryer. Page 99 of 59
100 (i) Which number tells us how fast the hair-dryer uses energy?... On what else does the energy used by the hair-dryer depend?... (Total 2 marks) 53 The diagram shows a fan heater. (a) Complete this sentence. The fan heater is designed to transfer electrical energy as... energy and... energy. (b) The fan heater is connected to the mains by a three core cable. (i) Why are the wires in the cable made out of copper?... Why are the wires in the cable covered by plastic?... (c) You may find this equation useful when answering this part of the question energy transferred (kwh) = power (kilowatt, kw) time (hour, h) Page 00 of 59
101 (i) The power of the fan heater is 2.75 kw. Calculate how many kilowatt hours (kwh) of energy are transferred when the fan heater is used for 6 hours Number of kilowatt hours... How much will it cost to use the fan heater for 6 hours if one Unit of electricity costs 7p? Cost... p (d) A fault caused a much higher than normal current to flow in the heater. Describe what happened to the wire in the fuse (Total 0 marks) 54 (a) The diagram shows a fan heater. Page 0 of 59
102 (i) A current of A flows when the fan heater is working normally. Fuses of value 3A, 5A, 0A and 3A are available. Which one should be used in the plug of the fan heater?... () A fault caused a much higher than normal current to flow in the heater. Describe what happened to the wire in the fuse (b) You may find this equation useful when answering this part of the question energy transferred (kwh) = power (kilowatt, kw) time (hour, h) (i) The power of the fan heater is 2.75 kw. Calculate how many kilowatt hours of energy are transferred when the fan heater is used for 6 hours Number of kilowatt hours... How much will it cost to use the fan heater for 6 hours if one Unit of electricity costs 7p? Cost... p (Total 7 marks) Page 02 of 59
103 55 The diagram shows the inside of a 3-pin plug. (a) What colour wire should be connected to each terminal? Terminal E... Terminal N... Terminal L... (3) (b) Name two parts inside the 3-pin plug which help to make it safe (Total 5 marks) 56 (i) Write the equation which shows the relationship between the electric current, the power and the voltage () Page 03 of 59
104 Calculate the power if the current is 5 A and the voltage is V. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit Power =... (Total 3 marks) 57 In a hairdryer circuit there is a heater and a motor. It is important that the motor is always running when the heater is switched on. (a) Using the symbols shown below only once each, draw a circuit for a hairdryer. (b) Modern hairdryers are described as double insulated. Explain what this term means (c) On a modern hairdryer handle it states: 600 W 230 V 50 Hz (i) [A] Write an equation which shows the relationship between current, power and voltage.... () Page 04 of 59
105 [B] Calculate the current in the hairdryer when it is on full power. Show clearly how you get your answer Current =... A [A] Write an equation which shows the relationship between current, resistance and voltage.... () [B] The resistance of the heater is 20 ohms. Calculate the resistance of the motor. Show clearly how you get your answer Resistance =... ohms (Total 0 marks) 58 The diagram shows a type of electric immersion heater in a hot water tank. These hot water tanks are normally found in airing cupboards. Information on the immersion heater states: 230 V 0 A Page 05 of 59
106 (a) (i) What is the equation which shows the relationship between power, current and voltage?... () Calculate the power of the heater. Show clearly how you get to your answer and give the units.... Power =... (b) (i) What rating of fuse should be in the immersion heater circuit?... () There are three wires in the cable to the immersion heater. Two of the wires are connected to the immersion heater. The third wire is connected to the copper tank. Explain the function of this third wire and the fuse in the circuit (3) (c) (i) What is the equation which shows the relationship between resistance, current and voltage?... () Calculate the resistance of the heater. Show clearly how you get to your answer and give the units.... Resistance =... (Total 0 marks) Page 06 of 59
107 59 The diagram shows the inside of a mains plug. (a) Label the earth, live and neutral pins. (3) (b) (i) Explain how the earth wire and the fuse protect a person from an electric shock when there is a short circuit to the metal case of an appliance (4) What is the most appropriate size fuse rating for a fuse in a television? Circle the correct answer. 3 A 5 A 3 A () (Total 8 marks) Page 07 of 59
The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch bulb.
 Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Q1. A small torch uses a single cell to make the bulb light up. (a) The graphs show the voltage across two different types of cell as they transfer the last bit of their stored energy through the torch
Q1. (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply.
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply. 230 V 2760 W 50 Hz Use the information from the plate to answer the
Q1. (a) The diagram shows the information plate on an electric kettle. The kettle is plugged into the a.c. mains electricity supply. 230 V 2760 W 50 Hz Use the information from the plate to answer the
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A.
 High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
Electrical Energy and Power Ratings
 Section 1 - From the Wall Socket Electrical Energy and ower Ratings Batteries and the mains are sources of electrical energy. Electrical appliances can then convert this into other forms of energy. e.g.
Section 1 - From the Wall Socket Electrical Energy and ower Ratings Batteries and the mains are sources of electrical energy. Electrical appliances can then convert this into other forms of energy. e.g.
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Energy and Electricity
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS
 PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 A plastic rod is rubbed with a cloth and becomes negatively charged. (a) Explain how the rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed with a cloth... [2] (b) An uncharged metal-coated
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 A plastic rod is rubbed with a cloth and becomes negatively charged. (a) Explain how the rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed with a cloth... [2] (b) An uncharged metal-coated
Calculate the current in the kettle element. (3)
 1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
1 (a) A man monitors how much money he spends on electricity. He uses a device which calculates the cost of electrical energy used. He connects his 2.9 kw electric kettle to the 230 V mains supply. (i)
Using Electricity. Summary Notes. 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety.
 Using Electricity Summary Notes Section Content 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety. 2. Alternating and Direct Battery and transformer. Current Circuit diagrams. Current
Using Electricity Summary Notes Section Content 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety. 2. Alternating and Direct Battery and transformer. Current Circuit diagrams. Current
Class X Chapter 09 Electrical Power and Household circuits Physics
 EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
Name: Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK. National 4/5 Physics. Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets
 Name: National 4/5 Physics Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets USING ELECTRICITY Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you
Name: National 4/5 Physics Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets USING ELECTRICITY Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4)
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
Unit P.2, P2.3. Currents in electric circuits E ½. F Fuel gauge indicator. Fuel tank. Ammeter. Float. Battery. Sliding contact. Pivot 12V.
 Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
7.9.2 Potential Difference
 7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
Energy Conversions Questions CfE
 Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
kwh. 6 February
 14 10 The Robinson family have an electricity meter. The diagram shows their meter on two different dates. 28182 kwh 6 January 2 9 030 kwh 6 February (a) Use the meters to find the number of kilowatt hours
14 10 The Robinson family have an electricity meter. The diagram shows their meter on two different dates. 28182 kwh 6 January 2 9 030 kwh 6 February (a) Use the meters to find the number of kilowatt hours
A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater.
 Q1.(a) A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater. (i) Before starting the experiment, the student drew Graph A. Graph A shows how the student expected
Q1.(a) A student used the apparatus drawn below to investigate the heating effect of an electric heater. (i) Before starting the experiment, the student drew Graph A. Graph A shows how the student expected
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS. Unit 1 Electricity and Energy. Revision Notes
 Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. N S
 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Paper Reference(s) Edexcel GCSE Science (5009) Physics (5045) P1a Topics 9 and 10 Foundation and Higher Tier
 Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 59 545 Edexcel GSE Science (59) Physics (545) P1a Topics 9 and 1 Foundation and Higher Tier Friday 21 November 28 Morning Time: 2 minutes Materials required
Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 59 545 Edexcel GSE Science (59) Physics (545) P1a Topics 9 and 1 Foundation and Higher Tier Friday 21 November 28 Morning Time: 2 minutes Materials required
12.7 Power in Electric Circuits
 1.7 1.7 Power in Electric Circuits To predict the amount of energy used by an electrical device, such as a radio, stove, lights, or television, we first need to know the amount of time the device will
1.7 1.7 Power in Electric Circuits To predict the amount of energy used by an electrical device, such as a radio, stove, lights, or television, we first need to know the amount of time the device will
HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED?
 ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
Chapter 21 Practical Electricity
 Chapter 21 Practical Electricity (A) Electrical Power 1. State four applications of the heating effect of electricity. Home: o Used in electric kettles o Used in electric irons o Used in water heaters
Chapter 21 Practical Electricity (A) Electrical Power 1. State four applications of the heating effect of electricity. Home: o Used in electric kettles o Used in electric irons o Used in water heaters
National 4 Physics - Electricity and Energy Summary Notes
 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
1. Which of these shows the correct units for both energy and power? A kilowatt joule B joule kilojoule C kilojoule watt D watt kilowatt
 Multiple choice 1. Which of these shows the correct units for both energy and power? Energy Power A kilowatt joule B joule kilojoule C kilojoule watt D watt kilowatt 2. Which of these could cause an electrical
Multiple choice 1. Which of these shows the correct units for both energy and power? Energy Power A kilowatt joule B joule kilojoule C kilojoule watt D watt kilowatt 2. Which of these could cause an electrical
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 22.
 Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY
 CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY These components are used in electric circuits. TASK: Draw how you could make this lamp light. Electricity will only flow through a complete circuit. The battery, wires
CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY These components are used in electric circuits. TASK: Draw how you could make this lamp light. Electricity will only flow through a complete circuit. The battery, wires
Ordinary Level Physics SOLUTIONS: EFFECTS OF AN ELECTRIC CURRENT
 Ordinary Level Physics SOLUTIONS: EFFECTS OF AN ELECTRIC CURRENT Safety Features and kilowatt hours The unit of energy is called the kilowatt hour One kilowatt hour is the amount of energy used by a 1000
Ordinary Level Physics SOLUTIONS: EFFECTS OF AN ELECTRIC CURRENT Safety Features and kilowatt hours The unit of energy is called the kilowatt hour One kilowatt hour is the amount of energy used by a 1000
INVESTIGATION ONE: WHAT DOES A VOLTMETER DO? How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured?
 How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 1 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 1 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS
 ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S
 L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S What is charge? How does a charge form? Electricity What is an electric current? Y E A R 1 0 C H A P T E R 1 2 What are conductors, insulators and semiconductors? How does
L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S What is charge? How does a charge form? Electricity What is an electric current? Y E A R 1 0 C H A P T E R 1 2 What are conductors, insulators and semiconductors? How does
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity
 Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
Activity 3: Electricity
 Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
7.9.1 Circuits. 123 minutes. 170 marks. Page 1 of 56
 7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
PHYSICS 6 EXTENDED PHYSICS
 PHYSICS 6 EXTENDED PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 3 PORTFOLIO TASKS 2013-2014 STS\G11\Portfolio\Extended Physics Assessment Booklet\CDAU\ADVETIVersion 1.0 2014 1 31 Unit/Topic Performance Criteria Assess Event
PHYSICS 6 EXTENDED PHYSICS GRADE 11 TERM 3 PORTFOLIO TASKS 2013-2014 STS\G11\Portfolio\Extended Physics Assessment Booklet\CDAU\ADVETIVersion 1.0 2014 1 31 Unit/Topic Performance Criteria Assess Event
Exam-style questions: electricity
 Exam-style questions: electricity Q. The diagram shows an electrical circuit. (a) Complete the two labels on the diagram. P and Q are meters. What is meter P measuring?... () What is meter Q measuring?...
Exam-style questions: electricity Q. The diagram shows an electrical circuit. (a) Complete the two labels on the diagram. P and Q are meters. What is meter P measuring?... () What is meter Q measuring?...
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
A direct current (DC) circuit. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC power
![A direct current (DC) circuit. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC power A direct current (DC) circuit. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC power](/thumbs/75/71489894.jpg) L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit simple electrical circuits direct current DC Alternating current (AC) vs direct current (DC) electric power distribution household electricity
L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit simple electrical circuits direct current DC Alternating current (AC) vs direct current (DC) electric power distribution household electricity
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism
 7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications
 UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
9. Effects of an electric current
 Leaving Cert Physics Long Questions 2017-2002 9. Effects of an electric current Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Contents Ordinary
Leaving Cert Physics Long Questions 2017-2002 9. Effects of an electric current Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Contents Ordinary
Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere. electric current. resistor battery.
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
Additional Science. Physics Unit Physics P2 PHY2H. (Jun11PHY2H01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2011.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 Written Paper General Certificate
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 Written Paper General Certificate
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
A direct current (DC) circuit. Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC current. L 27 Electricity and Magnetism [4]
![A direct current (DC) circuit. Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC current. L 27 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit. Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC current. L 27 Electricity and Magnetism [4]](/thumbs/91/106941594.jpg) L 27 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit simple electrical circuits direct current DC Alternating current (AC) vs direct current (DC) electric power distribution household electricity
L 27 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit simple electrical circuits direct current DC Alternating current (AC) vs direct current (DC) electric power distribution household electricity
Review for formula, circuit and resistance test
 Review for formula, circuit and resistance test 1. Fill in the table giving the symbol and unit(s) for each. Current intensity Potential difference Voltage Resistance Power Energy Time 2. Give the formula
Review for formula, circuit and resistance test 1. Fill in the table giving the symbol and unit(s) for each. Current intensity Potential difference Voltage Resistance Power Energy Time 2. Give the formula
JSUNIL TUTORIAL PUNJABI COLONY GALI 01
 10 th Electricity Numerical 1. The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it? 2. An electric iron of resistance 20 ohm draws a current of 5 amperes.
10 th Electricity Numerical 1. The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it? 2. An electric iron of resistance 20 ohm draws a current of 5 amperes.
4 Electricity and Magnetism
 4 Electricity and Magnetism 1. Simple phenomena of magnetism 2. Electrical quantities 3. Electrical circuits 4. Dangers of electricity 5. Electromagnetic effects 6. Cathode ray oscilloscope 1. The diagram
4 Electricity and Magnetism 1. Simple phenomena of magnetism 2. Electrical quantities 3. Electrical circuits 4. Dangers of electricity 5. Electromagnetic effects 6. Cathode ray oscilloscope 1. The diagram
Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction
 Name: Class: Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction In this experiment, you will investigate how different materials affect the brightness of a bulb in a simple electric circuit. 1. Take a battery holder,
Name: Class: Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction In this experiment, you will investigate how different materials affect the brightness of a bulb in a simple electric circuit. 1. Take a battery holder,
English for Electrical Engineers
 University of Kurdistan Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering English for Electrical Engineers H. Bevrani October, 2017 1 Contents Unit 1. Current, voltage and resistance... 3 Unit 2. Electrical
University of Kurdistan Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering English for Electrical Engineers H. Bevrani October, 2017 1 Contents Unit 1. Current, voltage and resistance... 3 Unit 2. Electrical
Electricity concepts teacher backgrounder
 Electricity concepts teacher backgrounder What is electricity, where does it come from and what do we use it for? Scientifically, electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. This
Electricity concepts teacher backgrounder What is electricity, where does it come from and what do we use it for? Scientifically, electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. This
Unit D: Electrical Principles and Technologies
 Focusing Questions: Unit D: Electrical Principles and Technologies 1. How do we obtain and use electrical energy? 2. What significant principles are involved in developing, selecting, and using energyconsuming
Focusing Questions: Unit D: Electrical Principles and Technologies 1. How do we obtain and use electrical energy? 2. What significant principles are involved in developing, selecting, and using energyconsuming
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics
 Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race.
 Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
MS.RAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3
 MSRAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3 1- In Fig 91, A and B are two conductors on insulating stands Both A and B were initially uncharged X Y A B Fig 91 (a) Conductor A is given the positive charge shown
MSRAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3 1- In Fig 91, A and B are two conductors on insulating stands Both A and B were initially uncharged X Y A B Fig 91 (a) Conductor A is given the positive charge shown
Parts of an atom. Protons (P + ) Electrons (e - ) Neutrons. Have a positive electric charge. Have a negative electric charge
 Electricity Parts of an atom Protons (P + ) Have a positive electric charge Electrons (e - ) Have a negative electric charge Neutrons Are neutral Have no charge Electric Charge In most atoms, the charges
Electricity Parts of an atom Protons (P + ) Have a positive electric charge Electrons (e - ) Have a negative electric charge Neutrons Are neutral Have no charge Electric Charge In most atoms, the charges
Electrical Principles & Technologies Topic 3.3-Measuring Energy Input and Output
 Electrical Principles & Technologies Topic 3.3-Measuring Energy Input and Output Page 332-342 Name: Power 1. A Scottish inventor James Watt who invented the steam engine did a tremendous amount of work
Electrical Principles & Technologies Topic 3.3-Measuring Energy Input and Output Page 332-342 Name: Power 1. A Scottish inventor James Watt who invented the steam engine did a tremendous amount of work
Work done and Moment. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift.
 Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Electrical power. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/27/14
 Electrical power Objectives Use the equation for electrical power to solve circuit problems. Understand basic concepts for home electricity usage and wiring. Calculate the power used by electric circuit
Electrical power Objectives Use the equation for electrical power to solve circuit problems. Understand basic concepts for home electricity usage and wiring. Calculate the power used by electric circuit
Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above?
 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
to allow a current in one circuit to operate a switch in another circuit to protect a circuit by melting if the current becomes too large
 1 What is the function of a relay? to allow a current in one circuit to operate a switch in another circuit to prevent an electric shock by earthing a metal case to protect a circuit by melting if the
1 What is the function of a relay? to allow a current in one circuit to operate a switch in another circuit to prevent an electric shock by earthing a metal case to protect a circuit by melting if the
ELECTRICAL SERVICE TECHNICIAN EXAMINATION 22 November 2014 QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOKLET
 EST 2063 Candidate Code No. For Board Use Only Result Date Result Date Int ELECTRICAL SERVICE TECHNICIAN EXAMINATION 22 November 2014 QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOKLET Time Allowed: Two Hours INSTRUCTIONS READ
EST 2063 Candidate Code No. For Board Use Only Result Date Result Date Int ELECTRICAL SERVICE TECHNICIAN EXAMINATION 22 November 2014 QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOKLET Time Allowed: Two Hours INSTRUCTIONS READ
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME
 ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
INFO. SHEET: E1:1 INSPECTION & TESTING OF ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
 INFO. SHEET: E1:1 INSPECTION & TESTING OF ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to carry out User Checks, Formal Visual Inspections and combined Inspection and Tests on portable
INFO. SHEET: E1:1 INSPECTION & TESTING OF ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to carry out User Checks, Formal Visual Inspections and combined Inspection and Tests on portable
CHAPTER 3 DOMESTIC ELECTRICITY
 CHAPTER 3 DOMESTIC ELECTRICITY 1 Electrical Power How to calculate power drawn from a source? Three equivalent expressions of power [HKCEE] [Power] Calculate the power dissipated in the 10Ω resistor. Page
CHAPTER 3 DOMESTIC ELECTRICITY 1 Electrical Power How to calculate power drawn from a source? Three equivalent expressions of power [HKCEE] [Power] Calculate the power dissipated in the 10Ω resistor. Page
7. How long must a 100-watt light bulb be used in order to dissipate 1,000 joules of electrical energy? 1) 10 s 3) 1,000 s 2) 100 s 4) 100,000 s
 1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
V=I R P=V I P=I 2 R. E=P t V 2 R
 Circuit Concepts Learners should be able to: (a) draw, communicate and analyse circuits using standard circuit symbols using standard convention (b) apply current and voltage rules in series and parallel
Circuit Concepts Learners should be able to: (a) draw, communicate and analyse circuits using standard circuit symbols using standard convention (b) apply current and voltage rules in series and parallel
Electricity Merit Badge
 Electricity Merit Badge Class 4 Safety at Home June 13, 2017 Electricity Merit Badge Class 4 2017 National Scout Jamboree 1 Classes Class 1 Basics Electricity Class 2 Magnetism Class 3 Electric Power,
Electricity Merit Badge Class 4 Safety at Home June 13, 2017 Electricity Merit Badge Class 4 2017 National Scout Jamboree 1 Classes Class 1 Basics Electricity Class 2 Magnetism Class 3 Electric Power,
Student book answers Chapter 1
 Physics P2 Unit Opener Picture Puzzler: Key Words Picture Puzzler: Close up Everest, newtonmeter, Earth, remote, gear, yellow The key word is energy. copper wires P2 1.1 Charging up In-text A positive,
Physics P2 Unit Opener Picture Puzzler: Key Words Picture Puzzler: Close up Everest, newtonmeter, Earth, remote, gear, yellow The key word is energy. copper wires P2 1.1 Charging up In-text A positive,
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance.
 Q1. (a) A driver may have to make an emergency stop. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance. Give three different factors which affect the thinking distance or the braking distance. In
Q1. (a) A driver may have to make an emergency stop. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance. Give three different factors which affect the thinking distance or the braking distance. In
Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in.
 Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in. (a) Choose from the following words to complete the sentences below. distance energy force speed time You
Q1. To get a bobsleigh moving quickly, the crew push it hard for a few metres and then jump in. (a) Choose from the following words to complete the sentences below. distance energy force speed time You
Alternating Current (AC) Electricity
 Alternating Current (AC) Electricity Alternating current or AC electricity is the type of electricity commonly used in homes and businesses throughout the world. While the flow of electrons through a wire
Alternating Current (AC) Electricity Alternating current or AC electricity is the type of electricity commonly used in homes and businesses throughout the world. While the flow of electrons through a wire
Physics - Chapters Task List
 Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 20 November 2017
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them.
 1 polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth. polythene rod cloth The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them. The rod becomes negatively charged. Which diagram shows how the rod
1 polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth. polythene rod cloth The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them. The rod becomes negatively charged. Which diagram shows how the rod
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5
 Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
Objects with opposite charges attract each other, on the contrary, objects with the same charges repel each other.
 1. ELECTRICITY We uses enery everyday, we transfer energy in lots of ways every day. When a room is dark, we switch on the light. The light bulb transfers energy to the room. Electricity is a type of energy
1. ELECTRICITY We uses enery everyday, we transfer energy in lots of ways every day. When a room is dark, we switch on the light. The light bulb transfers energy to the room. Electricity is a type of energy
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters
 16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
Sustainability. How to get the most from your solar photovoltaic (PV) system
 Sustainability How to get the most from your solar photovoltaic (PV) system Solar photovoltaic energy in your home If you are a WDH tenant with solar panels on your roof you can make use of the free electricity
Sustainability How to get the most from your solar photovoltaic (PV) system Solar photovoltaic energy in your home If you are a WDH tenant with solar panels on your roof you can make use of the free electricity
LETTER TO PARENTS SCIENCE NEWS. Dear Parents,
 LETTER TO PARENTS Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Parents, SCIENCE NEWS Our class is beginning a new science unit using the FOSS Magnetism and Electricity Module. We
LETTER TO PARENTS Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Parents, SCIENCE NEWS Our class is beginning a new science unit using the FOSS Magnetism and Electricity Module. We
Mr Cooke s Physics Notes IGCSE Triple Physics 2011 Vers Electricity
 Electricity Introduction... 2 Charge, Current, Voltage and Potential Difference... 2 Charge... 2 Current... 2 Voltage... 3 Mains Electricity... 4 Hazards of Electricity... 5 Safety measures... 5 Heating
Electricity Introduction... 2 Charge, Current, Voltage and Potential Difference... 2 Charge... 2 Current... 2 Voltage... 3 Mains Electricity... 4 Hazards of Electricity... 5 Safety measures... 5 Heating
Electricity All Around Us
 ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST Name: Section 1: or. Circle true or false for the following questions. 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed
ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST Name: Section 1: or. Circle true or false for the following questions. 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed
The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance.
 FORCES AND BRAKING Q1. The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed.
FORCES AND BRAKING Q1. The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and the braking distance. The table below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance vary with speed.
4.2 Electrical Quantities
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 4.2 Electrical Quantities Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 4.2 Electrical Quantities Question Paper Level IGSE Subject Physics (625) Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet ambridge International
Using your Digital Multimeter
 Using your Digital Multimeter The multimeter is a precision instrument and must be used correctly. The rotary switch should not be turned unnecessarily. To measure Volts, Milliamps or resistance, the black
Using your Digital Multimeter The multimeter is a precision instrument and must be used correctly. The rotary switch should not be turned unnecessarily. To measure Volts, Milliamps or resistance, the black
Boardworks Ltd Mains Electricity
 1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mains Electricity Mains Electricity 2 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Direct current 3 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2016 There are two main types of electric current: direct current (DC)
1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mains Electricity Mains Electricity 2 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Direct current 3 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2016 There are two main types of electric current: direct current (DC)
7J Electrical circuits Multiple-choice main test
 For each question, circle the correct answer. Question 1 A switch turns off a torch by... A) breaking the circuit B) making the circuit C) shorting the circuit D) turning a series circuit into a parallel
For each question, circle the correct answer. Question 1 A switch turns off a torch by... A) breaking the circuit B) making the circuit C) shorting the circuit D) turning a series circuit into a parallel
What is Electricity? Lesson one
 What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... ELECTROMAGNETISM 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1 1. Fran has a balancing game.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... ELECTROMAGNETISM 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1 1. Fran has a balancing game.
reflect energy: the ability to do work
 reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
Current, resistance and potential difference
 Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
Question 2: Around the bar magnet draw its magnetic fields. Answer:
 Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Circuit Analysis Questions A level standard
 1. (a) set of decorative lights consists of a string of lamps. Each lamp is rated at 5.0 V, 0.40 W and is connected in series to a 230 V supply. Calculate the number of lamps in the set, so that each lamp
1. (a) set of decorative lights consists of a string of lamps. Each lamp is rated at 5.0 V, 0.40 W and is connected in series to a 230 V supply. Calculate the number of lamps in the set, so that each lamp
