National 4 Physics - Electricity and Energy Summary Notes
|
|
|
- Corey George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling iron filings on top. These line up along the magnetic field lines. The magnetic field lines for a permanent bar magnet is shown opposite. N S If two magnets are placed close to one another the magnetic field lines interact to produce a force. Two unlike poles placed near each other produce an attracting force. The field lines are as shown below. N S N S Two like poles will produce a repulsive force e.g. north and north pole or south and south pole. S N N S 1
2 An electromagnet or solenoid is created by wrapping a current carrying wire around a soft iron core such as a nail. The magnetic field produced is similar to the one for a single bar magnet. current carrying wire Applications of Magnets Magnets can be used in a range of applications. Electric motors and loudspeakers. Permanent magnets are used along with electromagnets to produce the movement in d.c. motors and loudspeakers. Refrigerator door seals. Flexible magnets in the rubber door seals of refrigerators ensure that the door seal fits tightly against the steel body of the refrigerator. Pickups on electric guitars are magnetic and the vibrating strings produces a small current which can be amplified. Audio and video tapes, although not used as much these days, use a coating on a plastic strip which is magnetised when passed over a record head. The magnetised strips can then produce small currents when passed over the playback head. Powerful electromagnets are used to pick up iron and steel in scrap yards. Turning off the current to the magnet switches off the magnet and the metal is released. Electromagnets are used in automated door locks. Relays, like the one shown opposite, can be used to switch on or off large currents or voltages with a small current or voltage. Activating the relay coil by passing a current through it attracts the pivot bar, so closing the switch contacts. relay coil with iron core coil connections iron pivot arm switch contacts switch connections 2
3 Transformers A transformer is a device which can convert a voltage from one value to another. Step-up transformers increase the voltage and step-down transformers decrease the voltage. A transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around an iron core. iron core input voltage primary coil secondary coil output voltage Transformers will only work with an alternating current (a.c.) supply. The voltage in the secondary coil will change depending on the turns ratio of the secondary coil to the primary coil. A higher number of turns of wire in the secondary means a greater voltage out of the secondary coil. Practical electrical and electronic circuits Electrical circuits Symbols are used to represent components in electrical circuits. Some of these are shown below. switch linked wires cell + battery + voltmeter V ammeter A ohmmeter resistor variable resistor light bulb 3
4 Series and parallel circuits Circuits can be series or parallel or a combination of the two. In a series circuit there is only one path through the components and back to the cell or battery. In a parallel circuit there are two or more paths around the circuit. There is at least one point in the circuit where there is a choice of paths. Voltage and Current Voltmeters are used to measure the voltage in a circuit. Voltage is measured in volts. Voltmeters are always placed in parallel or across a component. Ammeters are used to measure the current in a circuit. Current is measured in amperes. Ammeters are always placed in series or in line with a component. It does not matter if the ammeter is before or after the component the current is the same. V A Current in a circuit is the flow of electrons through the wires and components In the series circuit below the current is the same through all components. The readings on ammeters A1 and A2 will be the same. The supply voltage, V supply, is split between the components in the circuit i.e. V 1, V 2 and V 3. Vsupply A1 A2 V1 V2 V3 4
5 Ohmmeters and Resistance A resistor is a device which opposes the flow of current through a circuit. Its resistance is measured in ohms. An ohmmeter can be used to measure the resistance of a component. A length of wire will have a certain resistance. The size of the resistance will depend upon: what material the wire is made from; the length of the wire the longer it is, the more its resistance; its cross sectional area (thickness) the thinner the wire the more its resistance; its temperature the hotter the wire the higher its resistance. The resistance of a conductor can also be found by using Ohm s Law. This involves measuring the voltage across the component and the current through it using a circuit like the one opposite. A The current is measured at different voltages. The value of the resistor is the voltage divided by the current. i.e. I V will give a constant value equivalent to the resistance of the circuit. V Thus voltage, current and resistance are related in the following formula: voltage = current resistance V = I R where V = voltage measured in volts I = current measured in amperes R = resistance measured in ohms Worked example A 12 V supply is connected to lamp which draws a current of 0 5 A. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. voltage = current resistance V = I R 12 = 0 5 R 12 R = 0 5 = 24 ohms 5
6 Electronic Circuits Electronic components Electronic circuits consist of an input, a process and an output e.g. a calculator has a keyboard as the input, a microprocessor carries out the process part and the liquid crystal display is the output. Symbols are used to represent electronic components. Some of these are shown below. Input devices Output devices switch loudspeaker thermistor light emitting diode light dependent resistor + lamp microphone motor M Switches:- switches provide an on or off signal to a circuit. Thermistor:- a thermistor is a device which changes its resistance with temperature. Its resistance can decrease or increase with a rise in temperature but the commonest thermistors decrease their resistance as temperatures increase. Light dependent resistors (LDR):- the resistance of an LDR alters as the light falling on it changes. Increasing the light level decreases the resistance. Microphone:- a microphone converts sound energy into electrical energy. Loudspeaker:- a loudspeaker converts electrical energy into sound energy. Light Emitting Diode (LED):- an LED converts electrical energy into light energy. It works from a low voltage using a small current. It will only operate in a circuit if connected the right way round i.e. its negative connection must be connected to the negative terminal of the power supply. 6
7 Lamp:- a lamp or bulb converts electrical energy into light energy. Motor:- an electric motor converts electrical energy into kinetic energy. Logic gates Logic gates are used in electronic circuits. Logic gates have one or more inputs and an output. The signals in and out of a logic gate are digital and described as being ON or OFF, HIGH or LOW or 1 or 0. Three common logic gates are shown below. A TRUTH TABLE can be completed for each one showing what the output will be for a given input. NOT gate Sometimes called an INVERTER, the output from the not gate is the opposite of the input. input output INPUT OUTPUT AND gate An AND gate has two inputs and both must be HIGH for the output to be HIGH. input A input B output INPUT A INPUT B OUTPUT OR gate An OR gate has two inputs and the output will be HIGH if either of the inputs is HIGH. input A input B output INPUT A INPUT B OUTPUT
8 Logic gates are used to control a circuit e.g. a lamp is switched on when the switch is ON and the light sensor detects that it is dark. light sensor switch AND gate lamp Light sensor gives a HIGH output when it is dark and the switch gives a HIGH output when switched on. When both inputs are HIGH the lamp is switched on. Logic gates can be combined together to provide new functions e.g. an AND gate and NOT gate can be combined to give a completely new truth table as shown. input A input B C output INPUT A INPUT B C OUTPUT Electrical Power Energy consumption Appliances in the home convert electrical energy into other forms. A television converts electrical energy into light and sound energy. A washing machine converts electrical energy into kinetic energy and heat energy. The rate at which appliances use energy is termed their power and is measured in watts. If an appliance has a power of 1 watt it uses 1 joule of energy every second. Appliances with high power ratings usually produce a lot of heat. Toasters, electric irons, kettles etc. usually have power ratings of over 1000 watts. 8
9 Calculating power The power of an appliance can be calculated using the formula below. power = energy time P = E t where P = power measured in watts E = energy measured in joules t = time measured in seconds Worked example An electric heater with an output power of 1 kw is switched on for 5 minutes. Calculate the energy output from the heater. power = P = 1000 = E = = energy time E t E joules Energy waste and efficiency The biggest usage of energy in the home is for heating the house and heating water. This may be by electricity or by using gas or oil fired boilers. Sometimes coal or wood may be used. There are ways of improving the efficiency of heating our homes. Insulate walls and loft as most heat escapes through these areas. Loft insulation should be at least 200 mm thick and is most often glass fibre or mineral wool. Air trapped in the wool stops heat escaping. Wall insulation if fitted when a house is built consists of thick foam panels with a foil backing to reflect the heat back into the house. Fit double glazing to stop heat escaping through windows. Fit insulation around the hot water storage tank even if it is already covered in foam. The money saved quickly repays the cost. Turn down room thermostats. Even a small reduction in temperature will save money. The bigger the temperature difference between the inside and outside of a house, the more quickly heat will be lost. Reduce draughts by fitting draught excluders on external doors, letterboxes etc. and around opening windows. 9
10 There are other ways in which energy can be saved such as: Turn out the lights when not in the room. Don't fill your kettle with more water than you need otherwise water is being heated which will then just cool down. Only use a dishwasher when full as every use of the dishwasher can cost up to 50 p. Don t leave appliances on standby as even the one or two watts of power consumed, if repeated for several appliances, 24 hours a day, can soon mount up. Choose energy efficient appliances. All new appliances have a sticker to show how energy efficient they are. It gives the appliance a rating from A (very efficient) to G (inefficient). Have showers instead of baths as showers use a lot less hot water. Electrical appliances have a rating plate attached which gives information on the voltage it uses and its power in watts. This is the rate at which it uses energy but the useful energy or power output will be less due to energy losses. An electric blender has a power rating of 150 watts but the useful kinetic energy it gives out is only 75 watts. 230 volts a.c. 50 hertz 150 watt Model No. N413 Made in Scotland. Its efficiency can be calculated from the formula: power out % efficiency = power in 100 In the case of the blender it is 50 % efficient. The amount of energy an appliance loses varies the greater the loss of energy, the less efficient is the appliance. Worked example A light bulb is rated at 60 watts but only produces 3 watts of useful light. Calculate the efficiency of the light bulb. power out efficiency = 100 power in 3 = = 5% 10
11 The energy input to the appliance and the energy output can also be used to calculate efficiency using the formula: energy out % efficiency = energy in 100 Worked example An electric drill is 40 % efficient. Calculate the useful energy output if uses joules in drilling a hole. % efficiency = energy out energy in 100 energy out 40 % energy out joules Sources of Energy At the present time our main sources of energy are fossil fuels coal, oil and gas. The reserves of these fuels, i.e. the quantity of them left, is limited. These fuels take millions of years to form naturally and so are not being replaced so are referred to as non-renewable energy sources. Oil and gas reserves in the North Sea will last for about another 40 years. There is a lot more coal under the UK but it is often in deep mines so harder to get at. Coal also produces more pollution when burned. Renewable sources of energy are constantly being replaced due to natural processes such as the wind, tides, rainfall etc. Renewable energy sources include wave power, solar power, geothermal power, hydroelectric power, wind power, tidal power and bio fuel. All renewable energy sources have the advantage that they are always being replaced. However, it can be expensive to gather the energy from these sources and they are not always available eg. if its not windy then wind farms are not much use. 11
12 Generation of Electricity A voltage can be generated across a wire by moving it between the poles of a magnet. The kinetic energy of the moving wire is converted into electrical energy. If the wire is stationary then no voltage will be generated. magnets wire bar magnet S V The same effect can be created by keeping the wire stationary and moving the magnet e.g. a bar magnet can be pushed in and out of a coil of wire. V N coil of wire The voltage generated can be increased by having more coils of wire, a stronger magnet or increasing the kinetic energy of the magnet by moving it faster. Power stations use generators which are rotated by turbines. The turbines are rotated by high pressure steam. A fuel, such as coal, oil or gas, is burned to create heat to turn water into steam. The block diagram below shows a typical fossil fuel powered power station. BOILER fossil fuel burned - water turned into steam TURBINE steam at pressure causes turbine blades to rotate GENERATOR turbine turns generator which produces electricity In a conventional power station you will often see cooling towers. Water vapour or steam rises from these as hot water is cooled. 12
13 In hydro electric power stations, the turbines are rotated by water which runs downhill from behind a dam. The water has potential energy when stored behind the dam and this is changed into kinetic energy as it flows downhill. dam generating station Electricity which is generated by the power station must be transmitted to the consumers who may live many kilometres away. The output voltage from the generator is increased to hundreds of thousands of volts. This has the effect of reducing the current of the transmitted electricity which means that much smaller cables can be used. The energy losses are also much reduced. Once the electricity reaches the houses it supplies, the voltage is reduced back to a lower value by transformers in a sub-station. Gas Laws and the Kinetic Model Kinetic Model of Gases The particles of a gas can be thought of as being in constant motion. When they collide with the walls of a container they provide a small outwards force. The many, many collisions of the gas particles with the walls of a container which causes the pressure of a gas. Pressure and temperature At a high temperature the gas particles have a lot of kinetic energy and move quickly. There are many collisions with the container walls, each collision producing more force on the wall. If the temperature of the gas is reduced the gas particles move more slowly with less kinetic energy. There are fewer collisions with the container walls and with less force than before so the pressure is less. 13
14 Pressure and volume If a container holding a gas is sqeezed or compressed the pressure inside increases e.g. placing your finger over the end of a bicycle pump and pushing down the handle. In a container with a large volume there are relatively fewer collisions with the container walls as the gas particles have further to travel between walls. If the volume of the container is reduced there are more collisions with the container and so the pressure is greater. Volume and temperature Heating a container of gas will make it expand till the pressure inside is equal to the pressure outside the container. The gas particles collide with the walls of the container pushing it outwards. Air particles outside push the walls inwards so a balance is achieved. If the temperature of the gas is raised they have more kinetic energy and hit the walls more often and with more force. This pushes the container walls outwards causing till the pressure inside the container equals the pressure outside once more. 14
Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. N S
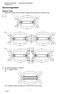 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS. Unit 1 Electricity and Energy. Revision Notes
 Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Using Electricity. Summary Notes. 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety.
 Using Electricity Summary Notes Section Content 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety. 2. Alternating and Direct Battery and transformer. Current Circuit diagrams. Current
Using Electricity Summary Notes Section Content 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety. 2. Alternating and Direct Battery and transformer. Current Circuit diagrams. Current
Electrical Energy and Power Ratings
 Section 1 - From the Wall Socket Electrical Energy and ower Ratings Batteries and the mains are sources of electrical energy. Electrical appliances can then convert this into other forms of energy. e.g.
Section 1 - From the Wall Socket Electrical Energy and ower Ratings Batteries and the mains are sources of electrical energy. Electrical appliances can then convert this into other forms of energy. e.g.
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy.
 Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Electricity All Around Us
 ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST ANSWER KEY Section 1: or False 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed close to water are a safety hazard. 3.
ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST ANSWER KEY Section 1: or False 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed close to water are a safety hazard. 3.
How is lightning similar to getting an electric shock when you reach for a metal door knob?
 How is lightning similar to getting an electric shock when you reach for a metal door knob? Electricity Electric charges are from protons, which are positive (+) and electrons, which are negative (-).
How is lightning similar to getting an electric shock when you reach for a metal door knob? Electricity Electric charges are from protons, which are positive (+) and electrons, which are negative (-).
Magnetism Ch Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance
 Magnetism Ch 21 22.1 Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance 1 Magnets attract & repel other magnets. The attraction between the north pole of a magnet and the south pole of another magnet is based
Magnetism Ch 21 22.1 Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance 1 Magnets attract & repel other magnets. The attraction between the north pole of a magnet and the south pole of another magnet is based
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 One mark for each of: when the pressure switch (A) is pushed, a current flows the electromagnet (B) is activated/switched on the armature (C) is attracted to the electromagnet the clapper
QUESTIONSHEET 1 One mark for each of: when the pressure switch (A) is pushed, a current flows the electromagnet (B) is activated/switched on the armature (C) is attracted to the electromagnet the clapper
Parts of an atom. Protons (P + ) Electrons (e - ) Neutrons. Have a positive electric charge. Have a negative electric charge
 Electricity Parts of an atom Protons (P + ) Have a positive electric charge Electrons (e - ) Have a negative electric charge Neutrons Are neutral Have no charge Electric Charge In most atoms, the charges
Electricity Parts of an atom Protons (P + ) Have a positive electric charge Electrons (e - ) Have a negative electric charge Neutrons Are neutral Have no charge Electric Charge In most atoms, the charges
Current Electricity. 3 rd Years
 Current Electricity 3 rd Years Comparing: Flow of electricity to flow of water. Electric Current An electric current is a flow of electric charge. An electric current is caused by the flow of electrons
Current Electricity 3 rd Years Comparing: Flow of electricity to flow of water. Electric Current An electric current is a flow of electric charge. An electric current is caused by the flow of electrons
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy
 Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
ELECTROMAGNETISM. 1. the number of turns. 2. An increase in current. Unlike an ordinary magnet, electromagnets can be switched on and off.
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Unlike an ordinary magnet, electromagnets can be switched on and off. A simple electromagnet consists of: - a core (usually iron) - several turns of insulated copper wire When current
ELECTROMAGNETISM Unlike an ordinary magnet, electromagnets can be switched on and off. A simple electromagnet consists of: - a core (usually iron) - several turns of insulated copper wire When current
Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere. electric current. resistor battery.
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
KS3 Revision. 8J Magnets and Electromagnets
 KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED?
 ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
What is Electricity? Lesson one
 What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
Electricity concepts teacher backgrounder
 Electricity concepts teacher backgrounder What is electricity, where does it come from and what do we use it for? Scientifically, electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. This
Electricity concepts teacher backgrounder What is electricity, where does it come from and what do we use it for? Scientifically, electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. This
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction
 Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
Electricity All Around Us
 ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST Name: Section 1: or. Circle true or false for the following questions. 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed
ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST Name: Section 1: or. Circle true or false for the following questions. 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy. Lesson 1-
 Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy Lesson 1- Most atoms have equal numbers of protons, which are positively charged, and electrons, which are negatively charged. These atoms have no charge; they
Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy Lesson 1- Most atoms have equal numbers of protons, which are positively charged, and electrons, which are negatively charged. These atoms have no charge; they
Electricity. Chapter 20
 Electricity Chapter 20 Types of electric charge Protons + charge Electrons - charge SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) Interactions between charges Like charges repel Opposite charges attract
Electricity Chapter 20 Types of electric charge Protons + charge Electrons - charge SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) Interactions between charges Like charges repel Opposite charges attract
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Physical Science Lecture Notes Chapter 13
 Physical Science Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Section 13-1 Electricity, Magnetism & Motion A. Electrical & mechanical energy 1. Magnetic forces repel when alike and attract when opposite 2. Electric current
Physical Science Lecture Notes Chapter 13 I. Section 13-1 Electricity, Magnetism & Motion A. Electrical & mechanical energy 1. Magnetic forces repel when alike and attract when opposite 2. Electric current
Magnets and magnetism
 Chapter 2 Electromagnetism Section 1 Magnets and magnetism Vocabulary: magnet magnetic pole magnetic force Properties of Magnets Magnetic Poles on a magnet, the magnetic poles are the locations where the
Chapter 2 Electromagnetism Section 1 Magnets and magnetism Vocabulary: magnet magnetic pole magnetic force Properties of Magnets Magnetic Poles on a magnet, the magnetic poles are the locations where the
Energy Conversions Questions CfE
 Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
1 A strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. core. current. coil. pins. What happens when the current in the coil is halved?
 1 strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. current core pins coil What happens when the current in the coil is halved? No pins are attracted. Some pins are attracted, but not as many. The same number
1 strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. current core pins coil What happens when the current in the coil is halved? No pins are attracted. Some pins are attracted, but not as many. The same number
Like poles repel, unlike poles attract can be made into a magnet
 Topic 7 Magnetism and Electromagnetism 7.1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields A permanent magnet has its own magnetic field : region in which a magnetic force is felt Poles are the places where the magnetic force
Topic 7 Magnetism and Electromagnetism 7.1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields A permanent magnet has its own magnetic field : region in which a magnetic force is felt Poles are the places where the magnetic force
4 Electricity and Magnetism
 4 Electricity and Magnetism 1. Simple phenomena of magnetism 2. Electrical quantities 3. Electrical circuits 4. Dangers of electricity 5. Electromagnetic effects 6. Cathode ray oscilloscope 1. The diagram
4 Electricity and Magnetism 1. Simple phenomena of magnetism 2. Electrical quantities 3. Electrical circuits 4. Dangers of electricity 5. Electromagnetic effects 6. Cathode ray oscilloscope 1. The diagram
Objects with opposite charges attract each other, on the contrary, objects with the same charges repel each other.
 1. ELECTRICITY We uses enery everyday, we transfer energy in lots of ways every day. When a room is dark, we switch on the light. The light bulb transfers energy to the room. Electricity is a type of energy
1. ELECTRICITY We uses enery everyday, we transfer energy in lots of ways every day. When a room is dark, we switch on the light. The light bulb transfers energy to the room. Electricity is a type of energy
3 Electricity from Magnetism
 CHAPTER 2 3 Electricity from Magnetism SECTION Electromagnetism BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can a magnetic field make an electric current?
CHAPTER 2 3 Electricity from Magnetism SECTION Electromagnetism BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can a magnetic field make an electric current?
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 22.
 Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Chapter 17 Notes. Magnetism is created by moving charges.
 Chapter 17 Notes Section 17.1 Electric Current and Magnetism Hans Christian Øersted (1819), a Danish physicist and chemist - compass needle near a wire circuit and with current flowing through the wire,
Chapter 17 Notes Section 17.1 Electric Current and Magnetism Hans Christian Øersted (1819), a Danish physicist and chemist - compass needle near a wire circuit and with current flowing through the wire,
Section 1: Magnets and Magnetic Fields Section 2: Magnetism from Electric Currents Section 3: Electric Currents from Magnetism
 Section 1: Magnets and Magnetic Fields Section 2: Magnetism from Electric Currents Section 3: Electric Currents from Magnetism Key Terms Magnetic Poles Magnetic Fields Magnets The name magnet comes from
Section 1: Magnets and Magnetic Fields Section 2: Magnetism from Electric Currents Section 3: Electric Currents from Magnetism Key Terms Magnetic Poles Magnetic Fields Magnets The name magnet comes from
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets More than 2,000
8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets More than 2,000
3/31/2016. Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources. Magnets. Magnets. Magnetic Force. Magnetic Field. Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses
 8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: and Its Uses : : Electricity and : Magnets More than 2,000 years ago Greeks discovered deposits of a mineral that was a natural
8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: and Its Uses : : Electricity and : Magnets More than 2,000 years ago Greeks discovered deposits of a mineral that was a natural
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME
 ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
Electromagnetic Induction
 Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper Level ubject Exam oard Unit Topic ooklet O Level Physics ambridge International Examinations Electricity and Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper
Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper Level ubject Exam oard Unit Topic ooklet O Level Physics ambridge International Examinations Electricity and Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper
ELECTRICAL. CDTA Technical Training Center
 ELECTRICAL ATOMIC STRUCTURE Protons positive charge Electron negative charge Neutron - neutral Electricity is the movement of electrons from atom to atom ELECTRON FLOW CONDUCTOR - Materials which have
ELECTRICAL ATOMIC STRUCTURE Protons positive charge Electron negative charge Neutron - neutral Electricity is the movement of electrons from atom to atom ELECTRON FLOW CONDUCTOR - Materials which have
I.E.S. Cristo Del Socorro de Luanco. Magnetism
 Magnetism Magnetism is a force of attraction or repulsion that acts at a distance. It is due to a magnetic field, which is caused by moving electrically charged particles or is inherent in magnetic objects
Magnetism Magnetism is a force of attraction or repulsion that acts at a distance. It is due to a magnetic field, which is caused by moving electrically charged particles or is inherent in magnetic objects
ANSWER KEY. Using Electricity and Magnetism. Chapter Project Worksheet 1
 Using Electricity and Magnetism Using Electricity and Magnetism Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1 6. Students data will vary greatly depending on the appliances and devices they examine as well as on the size
Using Electricity and Magnetism Using Electricity and Magnetism Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1 6. Students data will vary greatly depending on the appliances and devices they examine as well as on the size
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets Magnetism Magnetism:
8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets Magnetism Magnetism:
WORKSHOP MANUAL ELECTRICITY
 WORKSHOP MANUAL ELECTRICITY GB reference : 754282 DC/ATR 04/2000 1. Electric units:...2 2. Key formulae to remember:...2 3. Definitions:...3 4. Elements:...4 Resistances:...4 Lights:...5 Condensers:...5
WORKSHOP MANUAL ELECTRICITY GB reference : 754282 DC/ATR 04/2000 1. Electric units:...2 2. Key formulae to remember:...2 3. Definitions:...3 4. Elements:...4 Resistances:...4 Lights:...5 Condensers:...5
HSC Physics. Module 9.3. Motors and. Generators
 HSC Physics Module 9.3 Motors and Generators 9.3 Motors and Generators (30 indicative hours) Contextual Outline Electricity is a convenient and flexible form of energy. It can be generated and distributed
HSC Physics Module 9.3 Motors and Generators 9.3 Motors and Generators (30 indicative hours) Contextual Outline Electricity is a convenient and flexible form of energy. It can be generated and distributed
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters
 16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707
 FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 DC I Lesson Objectives: 1. What is Electricity? 2. Discover the Electron 3. Learn about Conductors and Insulators 4. Learn about Voltage and Current 5. Learn the difference
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 DC I Lesson Objectives: 1. What is Electricity? 2. Discover the Electron 3. Learn about Conductors and Insulators 4. Learn about Voltage and Current 5. Learn the difference
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Energy and Electricity
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Energy and Electricity Moulsham High School 1 1. A domestic electricity bill for the Smith family is shown. The unit of electricity is the kilowatt
Materials can be classified 3 ways
 Magnetism Magnetism A magnet is an object that can attract other objects containing iron, cobalt, or nickel. Magnetic substances are created when electrons from within the atom or from another atom spins
Magnetism Magnetism A magnet is an object that can attract other objects containing iron, cobalt, or nickel. Magnetic substances are created when electrons from within the atom or from another atom spins
English for Electrical Engineers
 University of Kurdistan Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering English for Electrical Engineers H. Bevrani October, 2017 1 Contents Unit 1. Current, voltage and resistance... 3 Unit 2. Electrical
University of Kurdistan Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering English for Electrical Engineers H. Bevrani October, 2017 1 Contents Unit 1. Current, voltage and resistance... 3 Unit 2. Electrical
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM
 CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1: MAGNETIC EFFECT OF A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR Electromagnets 1. Conductor is a material that can flow.. current 2. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between.and
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1: MAGNETIC EFFECT OF A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR Electromagnets 1. Conductor is a material that can flow.. current 2. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between.and
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online Tuition Pakistan Pakistan Online Tutor Magnet and Electromagnetism
 Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online Tuition Pakistan Pakistan Online Tutor Magnet and Electromagnetism DEFINITION: A substance having ability to attract magnetic materials is called magnet. The properties
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online Tuition Pakistan Pakistan Online Tutor Magnet and Electromagnetism DEFINITION: A substance having ability to attract magnetic materials is called magnet. The properties
Electrical Circuits Discussion Questions:
 Electrical Circuits Discussion Questions: 1) What is electricity? 2) How does an electrical circuit work? 3) What types of materials conduct electrical energy? 4) How is electrical energy measured? 5)
Electrical Circuits Discussion Questions: 1) What is electricity? 2) How does an electrical circuit work? 3) What types of materials conduct electrical energy? 4) How is electrical energy measured? 5)
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS
 ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications
 UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
45 Current Electricity. February 09, Current Electricity. What we will learn, Arc Attack. Electric Man. 1
 Current Electricity What we will learn, Arc Attack Electric Man www.mrcjcs.com 1 Conductors and Insulators An electric current is a flow of electric charge. Set up a simple electrical circuit and insert
Current Electricity What we will learn, Arc Attack Electric Man www.mrcjcs.com 1 Conductors and Insulators An electric current is a flow of electric charge. Set up a simple electrical circuit and insert
Current Electricity. GRADE 10 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Robyn Basson CAPS
 Current Electricity GRADE 10 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Robyn Basson CAPS What is current electricity? The flow of moving charge, usually carried by moving electrons in a wire. Circuits A path in which charges continually
Current Electricity GRADE 10 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Robyn Basson CAPS What is current electricity? The flow of moving charge, usually carried by moving electrons in a wire. Circuits A path in which charges continually
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE
 Electromagnetism Observation sheet Name VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs Electromagnetism Spring 2016 (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap Circuits
Electromagnetism Observation sheet Name VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs Electromagnetism Spring 2016 (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap Circuits
Electromagnetism Junior Science. Easy to read Version
 Electromagnetism Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a Electricity is a form of Energy Electricity is a type of energy. It can be transformed from many other types of energy; kinetic, chemical, nuclear
Electromagnetism Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a Electricity is a form of Energy Electricity is a type of energy. It can be transformed from many other types of energy; kinetic, chemical, nuclear
Class X Chapter 09 Electrical Power and Household circuits Physics
 EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
$3-5/speaker 60 min Magnet Wire - Sandpaper
 DIY Speakers Topic Area(s) Cost Time Grade Level Supplies Electromagnetism Sound Electrical Circuits Prototyping & Making $3-5/speaker 60 min 6-9 - Magnet Wire - Sandpaper - D-cell battery (or similar
DIY Speakers Topic Area(s) Cost Time Grade Level Supplies Electromagnetism Sound Electrical Circuits Prototyping & Making $3-5/speaker 60 min 6-9 - Magnet Wire - Sandpaper - D-cell battery (or similar
The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them.
 1 polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth. polythene rod cloth The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them. The rod becomes negatively charged. Which diagram shows how the rod
1 polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth. polythene rod cloth The rod and the cloth both become charged as electrons move between them. The rod becomes negatively charged. Which diagram shows how the rod
Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses. Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current
 Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current Section 1: Magnetism Standard 6: Demonstrate an understanding of the nature,
Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current Section 1: Magnetism Standard 6: Demonstrate an understanding of the nature,
BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS
 CHAPTER 13 BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle is based on the
CHAPTER 13 BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle is based on the
A direct current (DC) circuit. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC power
![A direct current (DC) circuit. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC power A direct current (DC) circuit. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] Alternating Current (AC) Direct Current DC. AC power](/thumbs/75/71489894.jpg) L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit simple electrical circuits direct current DC Alternating current (AC) vs direct current (DC) electric power distribution household electricity
L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [4] A direct current (DC) circuit simple electrical circuits direct current DC Alternating current (AC) vs direct current (DC) electric power distribution household electricity
Single Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX
 Single Phase Induction Motor Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX Application :- The single-phase induction machine is the most frequently used motor for refrigerators, washing machines, clocks, drills,
Single Phase Induction Motor Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX Application :- The single-phase induction machine is the most frequently used motor for refrigerators, washing machines, clocks, drills,
Electricity and Hydrogen: The energy carriers. Energy and Power for Electricity Electrical Distribution Hydrogen not a source, a carrier
 Electricity and Hydrogen: The energy carriers Energy and Power for Electricity Electrical Distribution Hydrogen not a source, a carrier Unit 07 Electricity - Slide 1 Quiz The wheels of a 5000kg truck place
Electricity and Hydrogen: The energy carriers Energy and Power for Electricity Electrical Distribution Hydrogen not a source, a carrier Unit 07 Electricity - Slide 1 Quiz The wheels of a 5000kg truck place
(2) The graph below shows how the power output of a wind turbine changes over one day.
 Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources... 2.. (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity.
Energy resources can be renewable or non-renewable. (a) Coal is a non-renewable energy resource. Name two other non-renewable energy resources... 2.. (b) Wind turbines are used to generate electricity.
Student book answers Chapter 1
 Physics P2 Unit Opener Picture Puzzler: Key Words Picture Puzzler: Close up Everest, newtonmeter, Earth, remote, gear, yellow The key word is energy. copper wires P2 1.1 Charging up In-text A positive,
Physics P2 Unit Opener Picture Puzzler: Key Words Picture Puzzler: Close up Everest, newtonmeter, Earth, remote, gear, yellow The key word is energy. copper wires P2 1.1 Charging up In-text A positive,
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism
 7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
Electrical Systems. Introduction
 Electrical Systems Figure 1. Major Components of the Car s Electrical System Introduction Electricity is used in nearly all systems of the automobile (Figure 1). It is much easier to understand what electricity
Electrical Systems Figure 1. Major Components of the Car s Electrical System Introduction Electricity is used in nearly all systems of the automobile (Figure 1). It is much easier to understand what electricity
Handout Activity: HA773
 Charging system HA773-2 Handout Activity: HA773 Charging system The charging system allows for a means to recharge the battery and allow for electrical usage of components in the vehicle. The charging
Charging system HA773-2 Handout Activity: HA773 Charging system The charging system allows for a means to recharge the battery and allow for electrical usage of components in the vehicle. The charging
Introduction: Electromagnetism:
 This model of both an AC and DC electric motor is easy to assemble and disassemble. The model can also be used to demonstrate both permanent and electromagnetic motors. Everything comes packed in its own
This model of both an AC and DC electric motor is easy to assemble and disassemble. The model can also be used to demonstrate both permanent and electromagnetic motors. Everything comes packed in its own
JSUNIL TUTORIAL PUNJABI COLONY GALI 01
 10 th Electricity Numerical 1. The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it? 2. An electric iron of resistance 20 ohm draws a current of 5 amperes.
10 th Electricity Numerical 1. The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it? 2. An electric iron of resistance 20 ohm draws a current of 5 amperes.
Welcome to the SEI presentation on the basics of electricity
 Welcome to the SEI presentation on the basics of electricity 1 Electricity is a secondary energy source, meaning that it is produced from other, primary, energy sources. There are several primary sources
Welcome to the SEI presentation on the basics of electricity 1 Electricity is a secondary energy source, meaning that it is produced from other, primary, energy sources. There are several primary sources
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
Electricity and Magnetism. Module 6
 Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? When two objects rub against each other electrons
Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? When two objects rub against each other electrons
MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO A CURRENT CARRYING CONDUCTOR
 Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor 1. A current carrying straight conductor behaves as a magnet. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the Right-Hand Thumb Rule. The
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor 1. A current carrying straight conductor behaves as a magnet. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the Right-Hand Thumb Rule. The
Name: Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK. National 4/5 Physics. Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets
 Name: National 4/5 Physics Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets USING ELECTRICITY Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you
Name: National 4/5 Physics Paisley Grammar Physics Department UNIT 2 USING ELECTRICITY PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets USING ELECTRICITY Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you
Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Solutions
 Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Solutions 2015 Question 12 (d) [Ordinary Level] A solenoid (long coil of wire) is connected to a battery as shown. (i) Copy the diagram into your
Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Solutions 2015 Question 12 (d) [Ordinary Level] A solenoid (long coil of wire) is connected to a battery as shown. (i) Copy the diagram into your
L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S
 L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S What is charge? How does a charge form? Electricity What is an electric current? Y E A R 1 0 C H A P T E R 1 2 What are conductors, insulators and semiconductors? How does
L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S What is charge? How does a charge form? Electricity What is an electric current? Y E A R 1 0 C H A P T E R 1 2 What are conductors, insulators and semiconductors? How does
Electrical Measuring Instruments
 UNIT 12 Electrical Measuring Instruments Learning Objectives After studying this unit, the student will be able Understand different measuring instruments used in electricity Understand the working of
UNIT 12 Electrical Measuring Instruments Learning Objectives After studying this unit, the student will be able Understand different measuring instruments used in electricity Understand the working of
Unit 32 Three-Phase Alternators
 Unit 32 Three-Phase Alternators Objectives: Discuss the operation of a three-phase alternator. Explain the effect of rotation speed on frequency. Explain the effect of field excitation on output voltage.
Unit 32 Three-Phase Alternators Objectives: Discuss the operation of a three-phase alternator. Explain the effect of rotation speed on frequency. Explain the effect of field excitation on output voltage.
Electricity and Magnetism (Demo Version) The pictures show different arrangements of a battery, a light bulb, and a piece of copper wire.
 Read each question carefully. 1) The pictures show different arrangements of a battery, a light bulb, and a piece of copper wire. Which arrangement will light the bulb? 1 2) In which of the following circuits
Read each question carefully. 1) The pictures show different arrangements of a battery, a light bulb, and a piece of copper wire. Which arrangement will light the bulb? 1 2) In which of the following circuits
CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Compass needle:- It is a small bar magnet, whose north end is pointing towards north pole and south end is pointing towards south pole of earth..hans Oersted
CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Compass needle:- It is a small bar magnet, whose north end is pointing towards north pole and south end is pointing towards south pole of earth..hans Oersted
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes)
 Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Circuit Basics and Components
 Circuit Basics Electric circuits are arrangements of conductors and components that permit electrical current to flow. A circuit can be as simple as a battery and lamp or as sophisticated as a computer.
Circuit Basics Electric circuits are arrangements of conductors and components that permit electrical current to flow. A circuit can be as simple as a battery and lamp or as sophisticated as a computer.
DISSECTIBLE TRANSFORMER - large
 DESCRIPTION: DISSECTIBLE TRANSFORMER - large Cat: EM1660-001 220/240V.AC. 50/60Hz. The IEC Dissectible Transformer is a very useful instrument for the teaching of transformer theory and many other AC phenomena.
DESCRIPTION: DISSECTIBLE TRANSFORMER - large Cat: EM1660-001 220/240V.AC. 50/60Hz. The IEC Dissectible Transformer is a very useful instrument for the teaching of transformer theory and many other AC phenomena.
If the magnetic field is created by an electromagnet, what happens if we keep it stationary but vary its strength by changing the current through it?
 If a moving electron in a magnetic field experiences a force pushing on it at right angles to its motion, what happens when we take a copper wire (with lots of easily dislodged electrons in it) and move
If a moving electron in a magnetic field experiences a force pushing on it at right angles to its motion, what happens when we take a copper wire (with lots of easily dislodged electrons in it) and move
INDUCTANCE FM CHAPTER 6
 CHAPTER 6 INDUCTANCE INTRODUCTION The study of inductance is a very challenging but rewarding segment of electricity. It is challenging because at first it seems that new concepts are being introduced.
CHAPTER 6 INDUCTANCE INTRODUCTION The study of inductance is a very challenging but rewarding segment of electricity. It is challenging because at first it seems that new concepts are being introduced.
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
Generating Electricity
 Generating Electricity The dynamo effect An electric current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil of wire in a circuit. The direction of the current is reversed when the magnet is moved out of
Generating Electricity The dynamo effect An electric current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil of wire in a circuit. The direction of the current is reversed when the magnet is moved out of
1. What type of material can be induced to become a temporary magnet? A) diamagnetic B) ferromagnetic C) monomagnetic D) paramagnetic
 Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY. Electrochemical Cells (the energy source) pg Wet Cell. Dry Cell. Positive. Terminal. Negative.
 Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
7. How long must a 100-watt light bulb be used in order to dissipate 1,000 joules of electrical energy? 1) 10 s 3) 1,000 s 2) 100 s 4) 100,000 s
 1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1012-Electrical Diagrams
 Term Absolute Pressure 1012-Electrical Diagrams Definition Total or true pressure. Gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute that includes the atmospheric pressure in its reading. This sensor
Term Absolute Pressure 1012-Electrical Diagrams Definition Total or true pressure. Gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute that includes the atmospheric pressure in its reading. This sensor
