Objects with opposite charges attract each other, on the contrary, objects with the same charges repel each other.
|
|
|
- Oswin Hodge
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
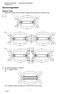
2 1. ELECTRICITY We uses enery everyday, we transfer energy in lots of ways every day. When a room is dark, we switch on the light. The light bulb transfers energy to the room. Electricity is a type of energy that can build up in one place or flow from one place to another. When electricity is in one place is called as static electricity (the word static means something that does not move); electricity that moves from one place to another is called current electricity. When a room is dark we switch on the light 1.2. Electrical charges There are two types of electrical charge: positive and negative. Negative charges can move from one place or an object to another. Objects have positive and negative charges. If an object has more negative than positive charges, it is negatively charged. If an object has more positive than negative charges, it is positively charged. If an object has the same number of positive and negative charges, it is neutral. Objects with opposite charges attract each other. Objects with the same charges repel each other Objects with opposite charges attract each other, on the contrary, objects with the same charges repel each other. By MACS 1
3 1.3. Static Electricity Static electricity often happens when we rub things together. When we rub an object with something made from a different material, we make electrical charges move, creating static electricity. Static electricity occurs with materials which are insulators. For example, if we rub a balloon onto our hair, negative charges move from our hair onto the balloon. Our hair becomes positively charged and the balloon becomes en negatively charged. When we rub an object with something made from a different material static electricity is created Electricity is a type of energy that can build up in one place or flow from one place to another. There are two types of electricity: static and current electricity. There are two types of electrical charge: positive and negative. Objects with opposite charges attract each other, on the contrary, objects with the same charges repel each other. Static electricity often happens when you rub things together. By MACS 2
4 ACTIVITIES 1. Draw on your notebook and colour to: Attract Repel 2. Complete with the words of the box negatively repel neutral positively attract Objects with the same charges.. each other. If an object has more positive charges than negative charges, it is charged. If an object has more negative charges than positive charges, it is charged. If an object has the same number of positive and negative charges, it is. Objects with opposite charges.. each other. 3. Read and complete the text. Electricity is a type of that can build up in one place or flow from one place to another. We can difference two types of electricity:.. electricity and static electricity. With respect to charges, there. also two types: positive and... An object is charged positively when has more than negative charges, on the contrary an object is charged. when has more negative than positive charges... electricity happens when we rub things together. Static electricity occurs with materials which are. By MACS 3
5 2. Electrical current Electrical current is the flow of electrical charges. It transmits energy called electricity. When electrons move, they carry electrical energy from one place to another. This is called current electricity or an electric current. A lightning bolt is one example of an electric current. Electric current passes easily through some materials. These materials are conductors. Many metals (iron, copper, steel, aluminium ) and water are good conductors. Electric current does not pass easily through other materials: air, rubber, glass, plastic and wood. These materials are insulators. Wires are made up of conductors (copper) and insulators (plastic) Conductors good conductors of electricity metals Insulators bad conductors of electricity air rubber, plastic, glass 3. Electric circuits An electric circuit is a set of different components which are connected each other to allow the flow of an electrical current. The main components of an electric circuit are: a generator, an electrical component, wires and a switch. By MACS 4
6 Generator: is the source of electricity, for example a battery. Electrical component: such as a light bulb or a motor. Wires. A switch which control the flow of electrical current. switch generator wires electrical component 3.1. Types of electric circuits There are two types of basic circuits are open and closed. A closed circuit allows the movement of electrical energy. An open circuit does not allow the electric current to flow. The two types of closed circuits are parallel and series. In a parallel circuit, there are two or more pathways for electric current to flow. If one pathway is opened, the other one still works. In a series circuit, there is only one pathway for electricity. If it is open the flow of current stops. By MACS 5
7 Series circuit Parallel circuit Electrical current is the flow of electrical charges. It transmits energy called electricity. Conductors are good conductors of electricity, insulators are bad conductors of electricity. An electric circuit is a set of different components which are connected each other to allow the flow of an electrical current, the components are: generator, wires, switch and an electrical component. There are two types of basic circuits, open and closed. The two types of closed circuits are: parallel and series. By MACS 6
8 ACTIVITIES 4. Read and write, true (T) or false (F) A closed circuit does not allow the electric current to flow. Conductors are materials that electrical energy moves through easily. Insulators are materials that allow electric current to pass easily. The main components of an electric circuit are: a generator, an electrical component, wires and a car. Examples of insulators are: plastic, rubber and water. 5. Change the false sentences into true sentences. 6. Read and match. 1. closed circuit A. is the source of electricity. 2. series circuit B. occurs when we rub an object with something made from a different material. 3. open circuit C. a circuit with two or more pathways for electric current to flow. 4. insulators D. controls the flow of electrical current. 5. parallel circuit E. is the flow of electrical charges. 6. electrical current F. are good conductors of electricity. 7. switch G. allows the movement of electrical energy. 8. conductors H. does not allow the electric current to flow. 9. generator I. are bad conductors of electricity. 10. Static electricity J. is a circuit with only one pathway for electricity. By MACS 7
9 7. Draw a circuit with its components in your notebook. 8. Look at the pictures. Write their names. Are they conductors or insulators? Never stick scissors, pens, fingers or anything else into a mains socket. Never touch switches with wet hands. Never use electrical appliances near water. Always hold the plastic part of a plug when plugging in and unplugging appliances. By MACS 8
10 4. MAGNETISM A phenomenon apparently related to electricity is magnetism. We are familiar with magnetism through the interaction of compasses with the earth s magnetic field, or through fridge magnets or magnets on children s toys. Magnets can be natural, as the mineral magnetite, or Mineral Magnetite artificial, such as different magnets manufactured from metal. A magnet is any object that has a magnetic field Magnetic forces are explained very similar to electric forces, there are two types of magnetic poles, called North and South. Like poles repel. Opposite poles attract. Magnetic forces are explained similar to electric forces 4.1. Magnetic fields Magnets create magnetic fields. A magnetic field is the space around a magnet where materials, such as iron filings, are affected by magnetic forces. A magnetic field 4.2. The uses of magnets Magnets are used to make electric motors and generators. Without these electric motors and generators we would not have telephones, lights, electric heat, television, or computers. We classify magnets according to their use: Electromagnets: they are used in televisions, computer monitors and microphones. Magnetic strips: in credit cards. Magnetic recording media: they are used in radio cassettes, floppy disks and hard disks. By MACS 9
11 Magnets can be natural or artificial. There are two types of magnetic poles, called North and South. Like poles repeal and opposite poles attract. Magnets create magnetic fields. A magnetic field is the space around a magnet where materials are affected by magnetic forces. According to their use we can classify magnets into: electromagnets, magnetic strips and magnetic recording media. ACTIVITIES 9. How can you be careful with electricity? Put in order and write sentences. fingers stick your mains Never socket or metal objects into a. switches touch hands with wet Never. use Never near appliances electrical water. part Always plastic hold the of plug a. 10. Read and write the correct word from the box. cards televisions generators field magnetic field natural South recording Magnetics scrips are used in credit. Magnets can be. and artificial. A magnet is an object that has a magnetic. There are two of magnetic poles: North and.. Magnets are used in electric motors and.. Radio cassettes, floppy disks or hard disks use magnetic.. media.is the space around a magnet where some materials, such as iron filings, are affected by magnetic forces. Electromagnets are used in, computer monitors or microphones. By MACS 10
12 11. Complete the table on your notebook. Classify these magnets. Electromagnets Magnetic strips Magnetic recording media Floppy disk video cassetted speakers memory card hard disk magnetic strip Computer monitor microphone television credit card By MACS 11
13 5. ELECTRICITY 5.1. Electricity production Human beings need to generate electricity lo live better. Electricity is produced at power plants or power stations. How is electricity generated? Water, steam or wind moves a turbine that is Coal station. Coal is used to produce energy connected to a generator, when the turbine rotates, the generator transforms mechanical energy into electricity, using a magnetic field and a conductor. We use different energy sources to move the turbine. Some power stations use non-renewable energies (coal, petrol.) and others use renewable energies (wind, water or sun). Solar station. Sunlight is used to produce energy By MACS 12
14 5.2. Electricity production The generated electricity at power stations is transmitted through conducting wires to substations near populated areas or villages. It is transmitted through tall towers called high-tension power transmission lines. A high tension power transmission line 5.3. Electricity distribution and consumption The electricity is distributed through power lines to industries, houses, offices and other places. Electricity produce different forms of energy: Heat energy: radiators, toaster Light energy: televisions, lamps Sound energy: mobile phones, radio cassettes, televisions Applicances that use different forms of energy Movement energy: cars, whisk mixer, train Electricity is generated through a turbine that is connected to a generator, when the turbine rotates, the generator transforms mechanical energy into electricity, using a magnetic field and a conductor. Electricity is transmitted through tall towers called high-tension power transmission lines. Electricity is used by different appliances to produce: heat, movement, light an sound. By MACS 13
15 6. HISTORICAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO ELECTRICITY Benjamin Franklin was a respected statesman and scientist. His scientific experiments proved that lightning is a form of electricity. Franklin also helped develop the lightning rod, a device used to protect buildings from damage during electric storms. Thomas Edison invented the incandescent light and the phonograph. He made improvements to the telephone, typewriter, electric generator, and electrically powered train. He designed the world s first electric power stations, thereby making electric power available to millions. Michael Faraday was a British physicist and chemist who discovered the principle of electromagnetic induction in He found that moving a magnet through a coil of copper wire caused an electric current to flow in the wire (induction). The electric generator and electric motor are based on this principle By MACS 14
16 ACTIVITIES 12. Explain. How is electricity generated? 13. Read and tick. Renewable or non renewable energy. By MACS 15
17 14. Read and match. 1. Solar A. heat from within the Earth 2. Coal B. energy coming from the sun 3. Wind C. oil from the Earth 4. Nuclear D. air in motion. 5. Biomass E. energy from moving water 6. Petroleum F. a sedimentary rock composed mainly of carbon 7. Natural gas G. organic materials made from plants and animals 8. Geothermal H. energy in the nucleus of a atom 9. Hydropower I. methane from the Earth 15. What type of energy do they produce? Classify. toaster television radio computer train Washing machine hairdryer radiator oven lamp mixer By MACS 16
18 16. What did they invented? Make sentences. Use Internet if necessary. Benjamin Franklin Thomas Edison Michael Faraday Benjamin Franklin invented Classify in renewable or non-renewable energies. petroleum solar biomass geothermal wind coal natural gas nuclear hydropower RENEWABLE ENERGY NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY 18. What can you do to save energy? Use these webpages Ask to your classmate. QUESTIONS Ask about his/her name Ask about his/her age Ask about where he/she lives YOUR CLASSMATE ANSWERS By MACS 17
19 Ask about appliances that use electricity Ask about appliances that use batteries 20. Draw a series and a parallel circuit on your notebook. Write the name of the components. 21. Put the letters in order and find the word. 1. ATCSIT 2. PLERE 3. TATRACT 4. TUCORDCON 5. LASUINTOR 6. AETNMG 7. RECNTUR 8. EOLP By MACS 18
20 22. Name these objects. Do they use electricity or a battery? computer Example: lamp electricity 23. Choose the correct answer. Final test!! 1. When electricity is in one place is called a) Current electricity b) Static electricity c) Parallel electricity By MACS 19
21 2. When electricity moves from one place to another is called a) Magnetism b) Static electricity c) Current electricity 3. If an object has more negative than positive charges a) It is positively charged b) It is negatively charged c) It is neutral 4. Objects with opposite charges a) Repel each other b) Play each other c) Attract each other 5. Static electricity often happens a) When we join two metals b) When we rub an object with something made from a different material c) When we rub two conductor materials 6. Static electricity occurs with materials which are a) Conductors b) Insulators c) Magnets 7. Insulators are a) Good conductors of electricity b) Bad conductors of electricity c) Materials that attract other materials By MACS 20
22 8. Copper is a a) Insulator material b) Conductor material c) Type of magnet 9. An electric circuit is a) Different materials which do not allow the flow of an electrical current b) a high tension power plant c) a set of different components which are connected each other to allow the flow of an electrical current 10. The components of an electric circuit are a) rubber, plastic and wood b) A generator, an electrical component, wires and a switch c) A magnet, wires, motor and a computer 11. Rubber, plastic and wood are a) Insulator materials b) Conductors materials c) Neutral materials 12. A closed circuit allows a) The movement of energy sources b) The attraction of two materials c) The movement of electrical energy 13. There are two types of closed circuits a) Open and closed circuits b) Parallel and series circuits c) Magnets and current circuits 14. In a parallel circuit a) There are two or more pathways for electric current to flow b) There is only a pathway c) There is not any pathway By MACS 21
23 15. A magnet is a) An object composed of an insulator material b) A component of an electric circuit c) An object that has a magnetic field 16. A magnetic field is a) An object that has magnetic properties b) the space around a magnet where materials are affected by magnetic forces c) A power station to produce energy 17. Credit cards are composed of a) electromagnets b) magnetic strips c) magnetic recording media 18. A radio produces a) Light energy b) Sound energy c) Heat energy 19. Renewable energies are a) Coal, nuclear and natural gas energies. b) Nuclear, biomass and solar energies. c) Solar, biomass, hydropower, wind and geothermal energies. 20. Thomas Edison invented a) The lightning rod b) The incandescent light c) The electric generator By MACS 22
24 To transfer: Plastic: Heat: To switch on: Wood: Electromagnets: Light bulb: To allow: Magnetic strips: Wind: Component: Magnetic recording media: To build up: Generator: To generate: Static electricity: Conducting wires: Power plants: Current electricity: Switch: Power Stations: Electrical charge: Closed circuit: Renewable energy: charge: Open circuit: Non-renewable energy: positive: Parallel circuit: Hydropower energy: negative: Seires circuit: Solar energy: neutral: Pathway: Biomass energy: To attract: Still: Wind energy: To repel: To work: Geothermal energy: To rub: Current: Turbine: Insulator: Never: To rotate: Conductor: Always: Energy source: Balloon: To touch: High tension: To become: To plug: Transmission line: Electrical current: To Unplug: Heat energy: To flow: Main socket: Light energy: Lightning bolt: Wet: Movement energy: To pass: Magnetism: Sound energy: Easily: Compass: Lightning rod: Iron: Magnet: Buildings: Copper: Magnetic field: Electric storm: Steel: Pole: Incandescente light: Aluminium: North: Improvement: Rubber: South: Available: Glass: Magnetic forces: Chemist: By MACS 23
Electricity All Around Us
 ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST Name: Section 1: or. Circle true or false for the following questions. 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed
ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST Name: Section 1: or. Circle true or false for the following questions. 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME
 ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
ELECTRICITY UNIT NAME Atom An atom is the smallest particle characterizing an element. All matter in the universe is made up of a combination of different atoms. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons
Electricity. Grade Level: 4 6
 Electricity Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Page page 6 Activity Page page 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Once students
Electricity Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Page page 6 Activity Page page 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Once students
What is Electricity? Lesson one
 What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
What is Electricity? Lesson one Static Electricity Static Electricity: an electrical charge that builds up on an object Most of the time, matter is electrically neutral. The same number of positive and
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS. Unit 1 Electricity and Energy. Revision Notes
 Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 PHYSICS Unit 1 Electricity and Energy Revision Notes Content Practical electrical and electronic circuits - Measurement of current, voltage and resistance using appropriate
Electricity All Around Us
 ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST ANSWER KEY Section 1: or False 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed close to water are a safety hazard. 3.
ELECTRICITY ALL AROUND US, COMPLETE MODULE MATERIALS MODULE TEST ANSWER KEY Section 1: or False 1. Damaged wires can cause fires in your home. 2. Appliances placed close to water are a safety hazard. 3.
Electricity and Magnetism. Module 6
 Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? When two objects rub against each other electrons
Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? When two objects rub against each other electrons
What is represented by this BrainBat?
 What is represented by this BrainBat? What is represented by this BrainBat? Hint: Say what you see. What is represented by this BrainBat? Hint: Say what you see. Answer: Octopi Electricity and Magnetism
What is represented by this BrainBat? What is represented by this BrainBat? Hint: Say what you see. What is represented by this BrainBat? Hint: Say what you see. Answer: Octopi Electricity and Magnetism
Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses. Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current
 Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current Section 1: Magnetism Standard 6: Demonstrate an understanding of the nature,
Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current Section 1: Magnetism Standard 6: Demonstrate an understanding of the nature,
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications
 UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
UNIT 4 Electrical Applications Topic How do the sources used 4.1 to generate electrical energy compare? (Pages 244-51) Topic 4.1: How do the sources used to generate electrical energy compare? Topic 4.6:
Magnets. Unit 6. How do magnets work? In this Unit, you will learn:
 Previously From Page 220 Forces appear whenever two objects interact. From Page 225 Unbalanced forces cause the motion of a body to change. Unit 6 Magnets How do magnets work? Magnets are interesting things
Previously From Page 220 Forces appear whenever two objects interact. From Page 225 Unbalanced forces cause the motion of a body to change. Unit 6 Magnets How do magnets work? Magnets are interesting things
reflect energy: the ability to do work
 reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
reflect Have you ever thought about how much we depend on electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that runs computers, appliances, and radios. Electricity lights our homes, schools, and office buildings.
How is lightning similar to getting an electric shock when you reach for a metal door knob?
 How is lightning similar to getting an electric shock when you reach for a metal door knob? Electricity Electric charges are from protons, which are positive (+) and electrons, which are negative (-).
How is lightning similar to getting an electric shock when you reach for a metal door knob? Electricity Electric charges are from protons, which are positive (+) and electrons, which are negative (-).
Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy. Lesson 1-
 Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy Lesson 1- Most atoms have equal numbers of protons, which are positively charged, and electrons, which are negatively charged. These atoms have no charge; they
Science Part B Chapter 4- Electrical Energy Lesson 1- Most atoms have equal numbers of protons, which are positively charged, and electrons, which are negatively charged. These atoms have no charge; they
Chapter 17 Notes. Magnetism is created by moving charges.
 Chapter 17 Notes Section 17.1 Electric Current and Magnetism Hans Christian Øersted (1819), a Danish physicist and chemist - compass needle near a wire circuit and with current flowing through the wire,
Chapter 17 Notes Section 17.1 Electric Current and Magnetism Hans Christian Øersted (1819), a Danish physicist and chemist - compass needle near a wire circuit and with current flowing through the wire,
Magnets and magnetism
 Chapter 2 Electromagnetism Section 1 Magnets and magnetism Vocabulary: magnet magnetic pole magnetic force Properties of Magnets Magnetic Poles on a magnet, the magnetic poles are the locations where the
Chapter 2 Electromagnetism Section 1 Magnets and magnetism Vocabulary: magnet magnetic pole magnetic force Properties of Magnets Magnetic Poles on a magnet, the magnetic poles are the locations where the
Electricity. Grade: 1 st grade Category: Physical Science NGSS: ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems
 Electricity Grade: 1 st grade Category: Physical Science NGSS: ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems Description: In this lesson, the students will learn that some objects need electricity
Electricity Grade: 1 st grade Category: Physical Science NGSS: ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems Description: In this lesson, the students will learn that some objects need electricity
Section 1: Magnets and Magnetic Fields Section 2: Magnetism from Electric Currents Section 3: Electric Currents from Magnetism
 Section 1: Magnets and Magnetic Fields Section 2: Magnetism from Electric Currents Section 3: Electric Currents from Magnetism Key Terms Magnetic Poles Magnetic Fields Magnets The name magnet comes from
Section 1: Magnets and Magnetic Fields Section 2: Magnetism from Electric Currents Section 3: Electric Currents from Magnetism Key Terms Magnetic Poles Magnetic Fields Magnets The name magnet comes from
Understanding Electricity and Electrical Safety Teacher s Guide
 Understanding Electricity and Electrical Safety Teacher s Guide Note to Instructor: The activities and experiments in this booklet build on each other to develop a student s understanding of electricity
Understanding Electricity and Electrical Safety Teacher s Guide Note to Instructor: The activities and experiments in this booklet build on each other to develop a student s understanding of electricity
New Section: Circuits & Machines. Warm Up: 1.) How do we use electricity every day? 2.) What do you think of when you hear the word "current?
 New Section: Circuits & Machines. Warm Up: 1.) How do we use electricity every day? lights, computers, electronics, tvs, microwaves, etc... new, flowing...? 2.) What do you think of when you hear the word
New Section: Circuits & Machines. Warm Up: 1.) How do we use electricity every day? lights, computers, electronics, tvs, microwaves, etc... new, flowing...? 2.) What do you think of when you hear the word
a) Understand the conditions for lighting a light bulb by connecting it to batteries with wires to make it illuminate.
 This area deals with simple electric circuits and electromagnets. In this area, students learn about electricity for the first time and build an electromagnet and a simple circuit to compare the brightness
This area deals with simple electric circuits and electromagnets. In this area, students learn about electricity for the first time and build an electromagnet and a simple circuit to compare the brightness
LET S FIND... ENERGY WORLD: Electricity around us ELECTRICAL APPLIANCES IN THE SCHOOL. What appliance? Who found it?? Who uses it?
 1 LET S FIND... ELECTRICAL APPLIANCES IN THE SCHOOL Who found it?? What appliance? What is it for? Where does it get electricity from? Who uses it? Alex clock know time batteries everybody What electrical
1 LET S FIND... ELECTRICAL APPLIANCES IN THE SCHOOL Who found it?? What appliance? What is it for? Where does it get electricity from? Who uses it? Alex clock know time batteries everybody What electrical
Electricity. An atom with more protons than electrons has a positive charge.
 Electricity Lesson 1 How Are Electricity and Magnetism Related? Electricity Have you used electricity in the past hour? Did you turn on a lamp? Did you watch TV? Did you get something cold to drink from
Electricity Lesson 1 How Are Electricity and Magnetism Related? Electricity Have you used electricity in the past hour? Did you turn on a lamp? Did you watch TV? Did you get something cold to drink from
National 4 Physics - Electricity and Energy Summary Notes
 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found around any permanent or electromagnet. They are normally invisible but can be shown up by placing a sheet of paper over the magnet and sprinkling
LETTER TO PARENTS SCIENCE NEWS. Dear Parents,
 LETTER TO PARENTS Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Parents, SCIENCE NEWS Our class is beginning a new science unit using the FOSS Magnetism and Electricity Module. We
LETTER TO PARENTS Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Parents, SCIENCE NEWS Our class is beginning a new science unit using the FOSS Magnetism and Electricity Module. We
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes)
 Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Parts of an atom. Protons (P + ) Electrons (e - ) Neutrons. Have a positive electric charge. Have a negative electric charge
 Electricity Parts of an atom Protons (P + ) Have a positive electric charge Electrons (e - ) Have a negative electric charge Neutrons Are neutral Have no charge Electric Charge In most atoms, the charges
Electricity Parts of an atom Protons (P + ) Have a positive electric charge Electrons (e - ) Have a negative electric charge Neutrons Are neutral Have no charge Electric Charge In most atoms, the charges
Lesson 2: Electrical Safety Ladders can become electrified if they come into contact with electric wires. Don't raise a ladder close to electric
 Lesson 2: Electrical Safety Ladders can become electrified if they come into contact with electric wires. Don't raise a ladder close to electric lines. Never touch hanging or broken wires. Don't trim trees
Lesson 2: Electrical Safety Ladders can become electrified if they come into contact with electric wires. Don't raise a ladder close to electric lines. Never touch hanging or broken wires. Don't trim trees
3 Electricity from Magnetism
 CHAPTER 2 3 Electricity from Magnetism SECTION Electromagnetism BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can a magnetic field make an electric current?
CHAPTER 2 3 Electricity from Magnetism SECTION Electromagnetism BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can a magnetic field make an electric current?
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
Question 2: Around the bar magnet draw its magnetic fields. Answer:
 Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Solutions
 Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Solutions 2015 Question 12 (d) [Ordinary Level] A solenoid (long coil of wire) is connected to a battery as shown. (i) Copy the diagram into your
Ordinary Level Physics ANSWERS : ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Solutions 2015 Question 12 (d) [Ordinary Level] A solenoid (long coil of wire) is connected to a battery as shown. (i) Copy the diagram into your
Post-Show ELECTRICITY. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show ELECTRICITY After the Show We recently presented an electricity show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic.
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show ELECTRICITY After the Show We recently presented an electricity show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic.
Chapter 18 Magnetism Student Notes
 Chapter 18 Magnetism Student Notes Section 18.1 Magnets and Magnet Fields Magnets More than discovered deposits of a that was a. The mineral is now called. These magnets were used by the ancient peoples
Chapter 18 Magnetism Student Notes Section 18.1 Magnets and Magnet Fields Magnets More than discovered deposits of a that was a. The mineral is now called. These magnets were used by the ancient peoples
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT. To understand Magnetic effects of Electric current, first we should know what is the Magnet?
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT To understand Magnetic effects of Electric current, first we should know what is the Magnet? Magnet A Magnet is an object which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT To understand Magnetic effects of Electric current, first we should know what is the Magnet? Magnet A Magnet is an object which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy
 Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Electricity. Chapter 20
 Electricity Chapter 20 Types of electric charge Protons + charge Electrons - charge SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) Interactions between charges Like charges repel Opposite charges attract
Electricity Chapter 20 Types of electric charge Protons + charge Electrons - charge SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) Interactions between charges Like charges repel Opposite charges attract
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Answer: A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet,
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Answer: A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet,
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets More than 2,000
8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets More than 2,000
3/31/2016. Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources. Magnets. Magnets. Magnetic Force. Magnetic Field. Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses
 8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: and Its Uses : : Electricity and : Magnets More than 2,000 years ago Greeks discovered deposits of a mineral that was a natural
8 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: and Its Uses : : Electricity and : Magnets More than 2,000 years ago Greeks discovered deposits of a mineral that was a natural
Student book answers Chapter 1
 Physics P2 Unit Opener Picture Puzzler: Key Words Picture Puzzler: Close up Everest, newtonmeter, Earth, remote, gear, yellow The key word is energy. copper wires P2 1.1 Charging up In-text A positive,
Physics P2 Unit Opener Picture Puzzler: Key Words Picture Puzzler: Close up Everest, newtonmeter, Earth, remote, gear, yellow The key word is energy. copper wires P2 1.1 Charging up In-text A positive,
Electromagnetism Junior Science. Easy to read Version
 Electromagnetism Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a Electricity is a form of Energy Electricity is a type of energy. It can be transformed from many other types of energy; kinetic, chemical, nuclear
Electromagnetism Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a Electricity is a form of Energy Electricity is a type of energy. It can be transformed from many other types of energy; kinetic, chemical, nuclear
Fourth Grade Physical Science. Magnetism and Electricity. Written By: Hortencia Garcia Christina Mavaro Kathleen Tomscha
 Fourth Grade Physical Science Magnetism and Electricity Written By: Hortencia Garcia Christina Mavaro Kathleen Tomscha Developed in Conjunction with K-12 Alliance/WestED Table of Contents 1 Conceptual
Fourth Grade Physical Science Magnetism and Electricity Written By: Hortencia Garcia Christina Mavaro Kathleen Tomscha Developed in Conjunction with K-12 Alliance/WestED Table of Contents 1 Conceptual
LETTER TO FAMILY. Science News. Cut here and glue letter onto school letterhead before making copies.
 LETTER TO FAMILY Cut here and glue letter onto school letterhead before making copies. Science News Dear Family, Our class is beginning a new science unit using the. We will investigate energy, build electric
LETTER TO FAMILY Cut here and glue letter onto school letterhead before making copies. Science News Dear Family, Our class is beginning a new science unit using the. We will investigate energy, build electric
1. What type of material can be induced to become a temporary magnet? A) diamagnetic B) ferromagnetic C) monomagnetic D) paramagnetic
 Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A.
 High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets Magnetism Magnetism:
8 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses 8.1: Magnetism 8.2: Electricity and Magnetism 8.3: Producing Electric Current 8.1 Magnets Magnetism Magnetism:
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy.
 Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Electromagnets ENERGY USE AND DELIVERY LESSON PLAN 3.3. Public School System Teaching Standards Covered
 ENERGY USE AND DELIVERY LESSON PLAN 3.3 Electromagnets This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven
ENERGY USE AND DELIVERY LESSON PLAN 3.3 Electromagnets This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven
Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current
 Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current Physical Science Georgia Performance Standards: SPS10a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction. SPS10b. Explain
Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current Physical Science Georgia Performance Standards: SPS10a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction. SPS10b. Explain
Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary
 Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary Term Definition Coil Solenoid Electric Motor Parts of an electric motor: Rotor commutator armature brushes Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law of Induction Generator
Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary Term Definition Coil Solenoid Electric Motor Parts of an electric motor: Rotor commutator armature brushes Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law of Induction Generator
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707
 FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 DC I Lesson Objectives: 1. What is Electricity? 2. Discover the Electron 3. Learn about Conductors and Insulators 4. Learn about Voltage and Current 5. Learn the difference
FUN! Protected Under 18 U.S.C. 707 DC I Lesson Objectives: 1. What is Electricity? 2. Discover the Electron 3. Learn about Conductors and Insulators 4. Learn about Voltage and Current 5. Learn the difference
Is it Magnetic? 1. Fill in each table. List things ATTRACTED by a magnet on the LEFT and things NOT ATTRACTED on the RIGHT.
 Is it Magnetic? 1. Fill in each table. List things ATTRACTED by a magnet on the LEFT and things NOT ATTRACTED on the RIGHT. MAGNETIC NON-MAGNETIC # Object Made from check # Object Made from check --- ------------
Is it Magnetic? 1. Fill in each table. List things ATTRACTED by a magnet on the LEFT and things NOT ATTRACTED on the RIGHT. MAGNETIC NON-MAGNETIC # Object Made from check # Object Made from check --- ------------
(d) The magnetic field lines, produced around a straight current-carrying conductor, are concentric circles. Their centres lie on the wire.
 Page 240»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire? (a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire (b) The field
Page 240»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire? (a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire (b) The field
Electricity and Magnetism (Demo Version) The pictures show different arrangements of a battery, a light bulb, and a piece of copper wire.
 Read each question carefully. 1) The pictures show different arrangements of a battery, a light bulb, and a piece of copper wire. Which arrangement will light the bulb? 1 2) In which of the following circuits
Read each question carefully. 1) The pictures show different arrangements of a battery, a light bulb, and a piece of copper wire. Which arrangement will light the bulb? 1 2) In which of the following circuits
Page 1 of 19. Website: Mobile:
 Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with
Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with
Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
 Intext Exercise 1 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact
Intext Exercise 1 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? When two objects rub against each other, electrons transfer
Electricity and Magnetism What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? When two objects rub against each other, electrons transfer
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT EDULABZ. the mere presence of magnet, is called...
 Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
KS3 Revision. 8J Magnets and Electromagnets
 KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. N S
 Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
Electromagnetism Magnetic fields 1. Place the magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkle iron filings on top. 2. (a) N S (b) N S N S (c) S N N S 3. (a) Electromagnet or solenoid (b) A magnetic field. (c)
CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Compass needle:- It is a small bar magnet, whose north end is pointing towards north pole and south end is pointing towards south pole of earth..hans Oersted
CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Compass needle:- It is a small bar magnet, whose north end is pointing towards north pole and south end is pointing towards south pole of earth..hans Oersted
8.2 Electric Circuits and Electrical Power
 8.2 Electric Circuits and Electrical Power Every electrical device uses current to carry energy and voltage to push the current. How are electrical devices designed? What types of parts are used in an
8.2 Electric Circuits and Electrical Power Every electrical device uses current to carry energy and voltage to push the current. How are electrical devices designed? What types of parts are used in an
CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY
 CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY These components are used in electric circuits. TASK: Draw how you could make this lamp light. Electricity will only flow through a complete circuit. The battery, wires
CHAPTER 6.3: CURRENT ELECTRICITY These components are used in electric circuits. TASK: Draw how you could make this lamp light. Electricity will only flow through a complete circuit. The battery, wires
Construction Set: Smart Grid System
 Construction Set: Smart Grid System Curriculum for Grades 3-5 Student Edition Center for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Illinois State University 2017 www.smartgridforschools.org Look around your
Construction Set: Smart Grid System Curriculum for Grades 3-5 Student Edition Center for Mathematics, Science, and Technology Illinois State University 2017 www.smartgridforschools.org Look around your
DC motor theory. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 DC motor theory This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
DC motor theory This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA Class X MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 1. Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor (a) Nature of magnetic field: The magnetic field lines due
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA Class X MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 1. Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor (a) Nature of magnetic field: The magnetic field lines due
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT
 Magnet A magnet is an object, which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel and cobalt. Naturally Occurring Magnet Lodestone is a naturally occurring magnet. It is actually a black coloured, oxide ore of
Magnet A magnet is an object, which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel and cobalt. Naturally Occurring Magnet Lodestone is a naturally occurring magnet. It is actually a black coloured, oxide ore of
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED?
 ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
ELECTRICITY HOW IS ELECTRICITY PRODUCED? All electricity is produced from other sources of energy. Hydroelectricity is produced from the stored energy of water held back by a dam. As the water runs downhill
Magnetism - General Properties
 Magnetism - General Properties A magnet, when suspended from a string, will align itself along the north - south direction. Two like poles of a magnet will repel each other, while opposite poles will attract.
Magnetism - General Properties A magnet, when suspended from a string, will align itself along the north - south direction. Two like poles of a magnet will repel each other, while opposite poles will attract.
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... ELECTROMAGNETISM 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1 1. Fran has a balancing game.
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education NAME:.... SCHOOL: DATE:... ELECTROMAGNETISM 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer ALL questions in this paper in the spaces provided. 1 1. Fran has a balancing game.
How are lightning and the shock your brother gives you after rubbing his feet on the carpet the same and how are they different?
 Standard IV, Objective I Fifth Grade Compare and Contrast How are lightning and the shock your brother gives you after rubbing his feet on the carpet the same and how are they different? You re a thoughtful
Standard IV, Objective I Fifth Grade Compare and Contrast How are lightning and the shock your brother gives you after rubbing his feet on the carpet the same and how are they different? You re a thoughtful
ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions
 CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2A Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 8 MAKING USE OF ELECTRICITY Part A Sectional Exercise 8.1 & 8.2 Concept checking p.35 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True Questions
$3-5/speaker 60 min Magnet Wire - Sandpaper
 DIY Speakers Topic Area(s) Cost Time Grade Level Supplies Electromagnetism Sound Electrical Circuits Prototyping & Making $3-5/speaker 60 min 6-9 - Magnet Wire - Sandpaper - D-cell battery (or similar
DIY Speakers Topic Area(s) Cost Time Grade Level Supplies Electromagnetism Sound Electrical Circuits Prototyping & Making $3-5/speaker 60 min 6-9 - Magnet Wire - Sandpaper - D-cell battery (or similar
Science Test Revision
 John Buchan Middle School Science Test Revision 4F Circuits and Conductors 39 min 38 marks Name John Buchan Middle School 1 Level 3 1. Conducting electricity (a) Year 6 are testing objects to see if they
John Buchan Middle School Science Test Revision 4F Circuits and Conductors 39 min 38 marks Name John Buchan Middle School 1 Level 3 1. Conducting electricity (a) Year 6 are testing objects to see if they
11/2/2011. Magnetic field =surrounds a magnet and can exert magnetic forces.
 It is a substance that contains a magnetic field. There are three primary types of magnets; Ferromagnetic- A substance that is naturally and permanently magnetic like iron. Paramagnetic- which becomes
It is a substance that contains a magnetic field. There are three primary types of magnets; Ferromagnetic- A substance that is naturally and permanently magnetic like iron. Paramagnetic- which becomes
L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S
 L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S What is charge? How does a charge form? Electricity What is an electric current? Y E A R 1 0 C H A P T E R 1 2 What are conductors, insulators and semiconductors? How does
L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S What is charge? How does a charge form? Electricity What is an electric current? Y E A R 1 0 C H A P T E R 1 2 What are conductors, insulators and semiconductors? How does
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4)
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism
 7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
Ch. 3 Magnetism and Electromagnetism
 Ch. 3 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet a. are only perpendicular
Ch. 3 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet a. are only perpendicular
Materials can be classified 3 ways
 Magnetism Magnetism A magnet is an object that can attract other objects containing iron, cobalt, or nickel. Magnetic substances are created when electrons from within the atom or from another atom spins
Magnetism Magnetism A magnet is an object that can attract other objects containing iron, cobalt, or nickel. Magnetic substances are created when electrons from within the atom or from another atom spins
Introduction. Lamplighters It was a lamplighter s job to light the gas streetlights.
 Introduction Do you need some light so that you can read? Flip a switch. Would you like a piece of toast? Drop a slice of bread into the toaster. Do you want to know what s going on in the world? Turn
Introduction Do you need some light so that you can read? Flip a switch. Would you like a piece of toast? Drop a slice of bread into the toaster. Do you want to know what s going on in the world? Turn
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
Unit 6: Electricity and Magnetism
 Objectives Unit 6: Electricity and Magnetism Identify the factors influencing the electric force between objects. Explain the interaction between charged and uncharged objects. Design, construct, and explain
Objectives Unit 6: Electricity and Magnetism Identify the factors influencing the electric force between objects. Explain the interaction between charged and uncharged objects. Design, construct, and explain
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS
 ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
Paper Reference(s) Edexcel GCSE Science (5009) Physics (5045) P1a Topics 9 and 10 Foundation and Higher Tier
 Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 59 545 Edexcel GSE Science (59) Physics (545) P1a Topics 9 and 1 Foundation and Higher Tier Friday 21 November 28 Morning Time: 2 minutes Materials required
Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 59 545 Edexcel GSE Science (59) Physics (545) P1a Topics 9 and 1 Foundation and Higher Tier Friday 21 November 28 Morning Time: 2 minutes Materials required
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online Tuition Pakistan Pakistan Online Tutor Magnet and Electromagnetism
 Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online Tuition Pakistan Pakistan Online Tutor Magnet and Electromagnetism DEFINITION: A substance having ability to attract magnetic materials is called magnet. The properties
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online Tuition Pakistan Pakistan Online Tutor Magnet and Electromagnetism DEFINITION: A substance having ability to attract magnetic materials is called magnet. The properties
Unit 4 Electricity and Media
 Unit 4 Electricity and Media Lesson 16: Lesson 17: Lesson 18: Lesson 19: Lesson 20: What is Electricity? Electromagnet Electric Power from Different Energy Sources Using Electricity Safely Science and
Unit 4 Electricity and Media Lesson 16: Lesson 17: Lesson 18: Lesson 19: Lesson 20: What is Electricity? Electromagnet Electric Power from Different Energy Sources Using Electricity Safely Science and
ELECTRIC CURRENT AND ITS EFFECT
 14 ELECTRIC CURRENT AND ITS EFFECT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. Draw in your notebook the symbols to represent the following components of electrical circuits, connecting wires, switch in
14 ELECTRIC CURRENT AND ITS EFFECT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. Draw in your notebook the symbols to represent the following components of electrical circuits, connecting wires, switch in
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
 1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? The needle of a compass is a small magnet. That s why when a compass needle is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? The needle of a compass is a small magnet. That s why when a compass needle is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines
Electricity Electric Current current. ampere. Sources of Current
 Electricity The basis for the study of electricity begins with the electron. It is a small, negatively charged particle located outside the nucleus in all atoms. The nucleus of the atom is positively charged
Electricity The basis for the study of electricity begins with the electron. It is a small, negatively charged particle located outside the nucleus in all atoms. The nucleus of the atom is positively charged
Electrical Safety World Video Teacher s Guide
 Electrical Safety World Video Teacher s Guide The Electrical Safety World video explains electric science concepts and how to use electricity safely in daily life. The content addresses many state and
Electrical Safety World Video Teacher s Guide The Electrical Safety World video explains electric science concepts and how to use electricity safely in daily life. The content addresses many state and
