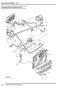
Engine Exhaust system. Engine. AMG exhaust system. The AMG sports exhaust system ends in two chrome-plated twin tailpipes bearing the AMG logo.
|
|
|
- Frederica Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 113 - Exhaust system AMG exhaust system The AMG sports exhaust system in the SLK 55 AMG satisfies the US emissions limits and is perfectly tuned in terms of function and sound to the AMG 5.5 l V8 engine. The near-engine mounted bulkhead catalytic converter is coated with palladium/rhodium while the underfloor catalytic converter is platinum/rhodium-plated. The longevity of the exhaust system is provided by the use of stainless steel throughout. The catalytic converter system incorporates one bulkhead and one underfloor catalytic converter (both made from thin-wall ceramic) in each exhaust stream. Downstream of the separation point of the two catalytic converter systems, the exhaust streams are combined in the center muffler. Further on, the exhaust flow continues in twin pipes to the two rear mufflers. The AMG sports exhaust system ends in two chrome-plated twin tailpipes bearing the AMG logo. Exhaust system 41
2 272 - Overview New V-6 engine generation 272 series Model 171 SLK350 will be the first vehicle equipped with the new engine 272. The new six cylinder V-6 engine features variable adjustment of intake and exhaust camshafts. Lightweight construction As a result of its consistent lightweight construction the weight gain in comparison to its predecessor the M 112 has been slightly reduced. This is despite the use of a solid four-valve system with four camshafts and camshaft adjustment and the two-level intake module with turbulence flaps in the inlet ports. High power With a displacement of 3498 CC the new V6 engine delivers 268 hp (200 kw) at 6000 rpm. This yields a volumetric efficiency of 57 kw/ 78 bhp a top value in this displacement class. The torque of 350 Nm is available right from 2500 rpm and remains constant up to 5000 rpm. Performance Acceleration from 0 to 100 km/h: 5.5 secs. 1) (with manual transmission) 5.6 secs. 1) (with automatic transmission) Maxuimum speed: 250 km/h (with manual or automatic transmission, electronically governed) Turbulence flaps Turbulence flaps are fitted in the intake ports. At part-throttle they are extended and increase the turbulence of the intake air in the combustion chambers. At higher revs the turbulence flaps are fully lowered in the induction pipe. Exhaust gas All the individual measures combine to yield a powerful and free-revving engine with exhaust emissions within US limits: Variable camshaft adjustment Turbulence flaps in the intake ports Internal exhaust recirculation Secondary air injection Catalytic converters fitted close to engine Internal exhaust gas recirculation The engine timing can be altered precisely by means of the variable intake and exhaust camshafts. The variable overlap times permit mixing of fresh gas and exhaust gas. Heat management An intelligent heat management system also helps to reduce fuel consumption. A new kind of electronic map-controlled thermostat, which is active in all the engine's operational modes, guides the flow of coolant into the six-cylinder engine in such a way that the engine oil and coolant always stay at the optimium temperature. A heating element allows active control of the triple-plate thermostat, causing the coolant to remain short circuited inside the engine during the warm-up period of the engine. 1) Stated rates of acceleration are based upon manufacturer's track results and may vary depending upon model, environmental and road surface conditions, driving style, elevation and vehicle load. 42 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
3 272 - Overview At-a-glance Target Comfortoptimisation through Measures Balance shaft for smooth engine running Greater rigidity in crankcase with full cross-bolting of main bearing cap Wider crankshaft bearings More rigid engine mounting with larger cross sections Reduced moving mass as result of lightweight construction throughout (pistons, con rods) Valve cover with integrated camshaft bearing Twin cartridge air filter with integrated resonators to reduce intake noise Consumptionoptimisation through Optimised combustion chamber geometry and valve arrangement Reduced friction New type of heat management in cooling cycle Performance-optimised oil and water pump drive Turbulence flaps Power steering pump with pressure regulating valve Exhaust emissions limits fulfilled through Camshaft adjustment Optimised-flow air intake with turbulence flaps Optimised combustion chamber geometry and valve arrangement Secondary air injection into the exhaust manifold ports High-volume catalytic converters close to engine 43
4 272 - Overview data M (SLK 350) M (SLK 320) designation M 272 M 112 Cylinder-arrangement/angle V6/90 V6/90 Rated power at rpm kw/hp at rpm 200/ / Rated torque at rpm Nm at rpm Max. mean pressure bar Specific power kw/l PS/l Specific torque Nm/l Compression ε 10.5:1 10.0:1 Cylinder distance mm Displacement cm Bore mm Stroke mm Con rod length mm b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
5 272 - Overview M (SLK 350) M (SLK 320) Main bearing diameter approx. mm Con rod bearing diameter approx. mm Intake/exhaust valve head diameter mm 39.5/30 36/41 Intake/exhaust valve shaft diameter mm 6 7 Valve stroke intake and exhaust valves mm Valve angle, intake valve degrees Valve angle, exhaust valve degrees Firing order Maximum continuous speed rpm Weight (approx.) kg
6 272 - Overview M P M n Power Torque rpm 46 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
7 272 - Overview i Motorenwerk Stuttgart Bad-Cannstatt The new M 272 is produced in the engine factory in Stuttgart, Bad-Cannstatt. 47
8 272 - Mechanical Cylinder crankcase As in the M 112, the M 272 has a cylinder angle of 90. The cylinder distance of 106 mm has also been retained. The increase in the displacement has been achieved by increasing the stroke to 86.0 mm and the bore diameter to 92.9 mm. The cylinder crankcase is made from HPDC aluminium. The crankcase is now even more rigid as a result of the cross-bolting of the bearing cap. Cylinder liners The cylinder liners are made from a spray-compacted aluminium-silicon alloy (Silitec) which has already proven its worth in the predecessor, the M 112. This yields weight savings of roughly 0.5 kg/cylinder in comparison to grey cast iron liners, while offering improved heat flow. i HPDC background information HPDC = High Pressure Die Casting In this technique the liquid metal is forced at great pressure and at high speed (between 50 and 100 m/secs.) into the casting mold. This requires careful pre planning of the casting process; this is simulated in the computer and takes the flow of the metal and the escape of the gases into consideration to prevent occlusions (local formation of shrinkage cavities, microprocessor). Advantages of this method: high degree of precision possibility to cast complex components which, using other production methods, would otherwise have to be assembled from several individual parts smooth surfaces and sharp contours reduced weight through thin-walled cast parts pre and finished casting of bore holes, slits, toothing, recesses and penetrations - plus lettering and numbering reduced post-processing costs 48 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
9 272 - Mechanical Cylinder crankcase with cross-bolted main bearing caps 49
10 272 - Mechanical Oil sump The M 272 has an oil dipstick and an oil level check switch (S43). There is no oil level sensor. The top section of the oil sump is made from aluminium. The siliconsealed bottom section of the sump is made from sheet steel. i Bottom section of oil sump To facilitate pushing the lower section down from the top section, a nut is welded onto the sheet metal sump. Switch: oil level check(s43) 1 Float housing 2 Plug contact 3 Gasket, oil sump lower section 50 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
11 272 - Mechanical Oil pump The lubricating oil is supplied in the M 272 by an internal gear pump. The oil pump is driven by a simplex chain. The advantages of this type of pump design are: smooth running thanks to "soft" tooth engagement even pump flow at sufficiently high pressure long life due to minimum running wear Internal gear pump 51
12 272 - Mechanical Crankshaft drive Crankshaft drive with balancer shaft The moving masses of the crankshaft drive have been reduced. This leads to: minimized fuel consumption less vibration more agile response Crankshaft The forged crankshaft has four bearings and four counterweights. The crankshaft bearings have been widened, thereby reducing engine vibration. The connecting rod pins are offset by 30 which permits an even firing angle of 120. Connecting rod The forged steel connecting rods weigh 20 % less, resulting in improved running characteristics. The upper con rod eye is slanted, which reduces weight. It also improves the lubrication of the piston pin. Pistons The cast pistons are made from ironcoated aluminium. In conjunction with the valve angle of 28.5 degrees the piston crown creates a combustion chamber with a high compression ratio of 10.5:1. The nitrided steel piston rings are designed for lower friction. Balancer shaft A balancer shaft is used between the cylinder banks to balance the free mass forces necessitated by the design of a V6 engine with a 90 cylinder angle. This shaft rotates counter to the crankshaft, but at the same speed as the crankshaft. 52 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
13 272 - Mechanical Cylinder head The cylinder head of the M 272 is produced using a permanent mold aluminium casting technique. The spark plugs are located centrally between the four valves. Directly above them are the coils of the mapcontrolled direct coil ignition. The bearings of the camshafts are integrated in the valve covers. If the valve covers are removed during servicing, auxiliary bearing caps are needed. Viewed from the front, the second camshaft bearing serves as the thrust bearing. The vacuum pump used in some engine versions is driven by the left intake camshaft. The right exhaust camshaft drives the centrifugal oil separator. The combustion chamber geometry is designed for fast combustion rates, especially at full-throttle. The result is lower knock sensitivity. Cylinder head M 272 (right) 1 Intake valves 2 Exhaust valves 3 Spark plug bore Auxillary bearing cap with valve cover removed (left) 1 Auxillary bearing cap 2 Thrust bearing 53
14 272 - Mechanical Valve train General A double bushing roller chain drives the intake camshafts. The exhaust camshafts are driven directly by the intake camshafts via a spring tensioned spur gear. The chain tensioner is designed as a timing chain tensioner. The valve train is designed to avoid any free chain run sections. All sections are guided by tensioning and slide rails. This has a positive impact on the dynamism and the noise response of the timing drive. The M 272 has a low-friction roller cam follower. Four valve system In contrast to the predecessor, the M 112, which had 3 valves per cylinder, the M 272 has 4 valves per cylinder. This arrangement allows the single spark plug to be positioned centrally, yielding optimum combustion. Exhaust valves made from hightemperature resistant Inconel steel. Both the intake and exhaust valves have a shaft diameter of 6 mm (M 112 has 7 mm). This only restricts the flow in the ports to a minimum extent and, as a result of fewer moving masses, this produces a low-friction and free-revving valve train. The center position of the valves differs in the various displacement versions and is adapted in line with the individual bore diameter. This means that the intake and exhaust valves can be optimally positioned for each bore diameter. i Inconel Inconel is a material consisting mainly of nickel and chrome plus the alloy components molybdenum, iron and small quanitities of aluminium and other elements. Characteristics: high degree of tensile strength, toughness and resistance to oxidation, corrosion and heat. 54 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
15 272 - Mechanical Variable valve timing The intake and exhaust camshafts can be adjusted continuously by 40 degrees. The infinitely variable adjustment of the camshafts is carried out by patented, electrohydraulically operated vane adjusters mounted on the front ends of the camshafts, with integrated control valves (similar to the 271). Camshaft adjuster i Advantages of variable valve timing Internal exhaust gas recirculation possible: less energy lost during charge change in the cylinders better exhaust emissions Good volumetric efficiency: Adjustment of valve overlap in line with revs Optimised cylinder filling Increased power and torque 55
16 272 - Mechanical Tooth backlash compensation The spur gear toothing of the exhuast camshaft adjuster is gripped between the front gear (1), the grip gear and the rear gear (2) of the main toothing. The grip force of the spring pushes the spur gears of the exhaust camshaft adjuster away from each other, thereby pressing them, free of backlash, onto the tooth flanks of the spur gear of the intake camshaft adjuster. The gripped gears help reduce engine noise, above all when idling. Tooth backlash compensation 1 Front gear 2 Rear gear 3 Pin i Note WIS repair instructions! Before removing the exhaust camshaft adjuster, a pin must be inserted in the bore of the support element. Lever and lateral forces must be avoided. Otherwise the camshaft adjuster could be damaged. 56 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
17 272 - Mechanical Pulse wheels The pulse wheels are attached to the camshaft adjusters. They are needed to register the position of the camshafts. Used pulse wheel: Shorn pins (arrows) Score marks and flattening (hatching). i Note WIS repair instructions! Pulse wheels should only ever be fitted once! Otherwise there is a risk of the pins shearing off. 57
18 272 - Mechanical Timing chain tensioner i Note WIS repair instructions! If the assembly sequence of the timing chain tensioner described in the WIS is not observed, this can result in engine damage through torn timing chains. Timing chain tensioner (exploded view, not the assembly sequence!) 1 End piece 2 O-ring 3 Filler piece 4 Compression spring 5 Chain tensioner housing 6 O-ring 7 Locking spring 8 Pressure bolt 9 Timing cover 58 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
19 272 - Mechanical venting Oil separation 1 Centrifugal oil separator 2 Full-throttle vent line 3 Throttle valve 4 Air guide housing 5 Mass airflow meter (MAF) 6 Scavenging line connection 7 Part-throttle vent line 8 Oil separator The oil separator (8) is responsible for part-throttle venting. The oil vapor contained in the blow-by gas are separated in its labyrinth. The part-throttle vent line (7) leads to the air guide housing (4) behind the throttle valve (3). At higher load levels the centrifugal oil separator (1) is responsible for the venting. The full-throttle vent line (2) leads between the throttle valve (3) and the mass airflow meter (5) to the induction pipe (4). The air which has had oil mist removed from it is not measured by the MAF. 59
20 272 - Mechanical A centrifugal oil separator is used in the M 272 which is driven by the right exhaust camshaft. Vapor containing oil mist flows from the crankcase into the centrifuge (5), which rotates at the same speed as the camshaft. This starts the vapor rotating. The oil separates out and drips through the screen filter (4) back into the crankcase. The purified air flows via the full-throttle vent line (2) to the air guide housing. Ventilation of crankcase In no load and part load more blowby gas is taken out via the hose from the crankcase than enters from the combustion process. The volume difference flows over the full load hose into the crankcase (fresh air ventilation). The location of the part load and full load ventilation provides for a diagonal flow of air through the motor with fresh air. In full load operation the throttle plate is wide open. Thereby the throttling effect is lost and vacuum decreases. Centrifugal oil separator 1 Line to induction pipe 2 Full-throttle vent line 3 Cap 4 Screen filter 5 Centrifuge i Ventilation of crankcase Ventilation of the crankcase with fresh air has a positive effect on the oil quality: the high throughput of vapor removes more water and fuel from the engine oil. 60 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
21 272 - Mechanical Belt drive Belt routing M 272 Number of ribs: 6 1 Pulley, crankshaft 2 Generator 3 Coolant pump 4 Steering roller 5 Steering roller 6 Idler 7 Power steering pump 8 A/C compressor 61
22 272 - Combustion Intake manifold Intake manifold 1 Diaphragm unit routing flaps, right cylinder bank The housing of the intake manifold is made from magnesium die cast parts which are joined and bonded using a tongue and groove system. In contrast to plastic, magnesium has the advantage of greater rigidity and dimensional stability which provides improved sealing in the port. 2 Diaphragm unit turbulence flaps 3 Diaphragm unit, routing flaps, left cylinder bank The intake pipes to the air filter are made from sound-absorbent nylon and, in contrast to the smooth surface plastic used up to now, has the advantage of making the material sound-absorbent, thereby significantly reducing the intake noise level. 4 Mass airflow meter 5 Turbulence flaps 6 Routing flaps 62 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
23 272 - Combustion Mass airflow meter (MAF) Like the entire intake manifold, the housing of the enhanced mass airflow meter (MAF 62) has been optimized in terms of flow. The housing of the mass airflow meter has a modified grating with low air resistance. Routing flaps The routing flaps inside the intake manifold vary the length of the intake channels. The routing flaps are opened or closed depending on the load. At low revs the routing flaps are closed which increases the length of the intake channels. The length is calculated so that the pressure waves in the induction pipe move the combustion air towards the intake valve during the intake stroke. This increases the cylinder charge, in turn optimizing the torque band and lowering the fuel consumption and the emissions. The routing flaps open from around 3500 rpm allowing the air to flow directly into the combustion chambers. The length of the intake channels is calculated to ensure a "supercharging" effect, even at high revs. This yields high performance at high revs. Routing flaps closed, long intake channels 1 Routing flap 2 Turbulence flap 3 Injection valve Routing flaps open, short intake channels 63
24 272 - Combustion Turbulence flaps Charge movements 1 Turbulence flap A Turbulence flaps lowered at higher engine load B Turbulence flaps pivoted out at part-throttle Turbulence flaps Electropneumatically activated turbulence flaps are installed at the end of each intake port. The turbulence flaps have two positions: lowered or pivoted out When pivoted out at part-throttle, the turbulence flaps increase the flow speed of the incoming air. The resulting turbulence of the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber yields a more even distribution of the mixture and therefore better and faster combustion. At part-throttle, when the mixture is leaner due to the exhaust gas recirculation, the increased combustion speed helps provide lower fuel consumption. At higher revs the turbulence flaps are fully lowered in the induction pipe; the intake process is unaffected. 64 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
25 272 - Combustion i Charge movement There are two different charge movements in the cylinder swirl and turbulence. The swirl mirrors the action of the cylinder axle whereas the turbulence motion is perpendicular to this. The upwards movement of the piston converts the turbulence movement into self-amplifying, complex turbulence. This leads to good ignition and burnthrough conditions in the mixture. The results are: good ignition of the mixture made leaner by the internal EGR, faster and more complete combustion lower fuel consumption smoother running. Charge movement in the cylinder A B Swirl Turbulence Turbulence flap in the intake manifold 1 Turbulence flap 65
26 272 - Combustion Secondary Air Injection (AIR) The excellent exhaust emissions of the M 272 is achieved in part by secondary air injection with increased throughput. Secondary air injection in the ports of the cavity-insulated exhaust manifold results in after burning of uncombusted gas. This raises the exhaust port temperature, bringing the catalytic converters more quickly up to operating temperature as a result. The injection points have been determined on the basis of the flow patterns in the exhaust ports of the cylinder head. This ensures more even distribution of the air to all exhaust ports in the cylinder head. Each cylinder has one injection point per exhaust valve. Secondary air injection 1 Secondary air injection combi-valve 2 Electric AIR pump Injection points in the cylinder head 1 Air duct 2 Injection points 66 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
27 272 - Combustion Emission controls Environment The elaborate measures taken for emission controls including monolith coating of the catalytic converters fulfil the LEV II limits. The exhaust manifold has a doubleflow design with two walls (cavity insulated). Catalytic converters Catalytic converters fitted close to the engine, each with 1.4 l volume, have the following benefits: Improved light-off in the catalytic converters, Long catalytic service life Reduction of high-frequency structure-borne noise. Oxygen sensors Each of the two catalytic converters has a control sensor and a guide sensor. Thanks to the linear control of the control sensor they supply the engine control module with precise data about the exhaust gas composition immediately after a cold start. The engine control module then adjusts the ignition timing so that the catalytic converters quickly reach their operating temperature. Catalytic converter mounted close to engine 1 Oxygen-guide sensor 2 Oxygen-control sensor 67
28 272 - Cooling and lubrication lubrication Lubricating oil circulation A Oil sump B Timing cover C Crankcase D Cylinder head, right E Cylinder head, right F Special units 1 Oil pump 2 oil cooler 3 oil filter 4 Timing chain tensioner 5 Main oil duct 6 Balancer shaft bearing 7 Crankshaft and con rod bearing 8 Oil injection jets, piston 9 Camshaft adjuster 10 Camshaft (intake/exhaust) bearing 11 Hydraulic valve lifters 12 Bearing lubrication, vacuum pump The camshaft is hollow inside and uses this cavity to supply the camshaft adjusters and their two center bearing points with lubricating oil. The rear bearing position is supplied via a bore hole in the cylinder head. Lubricating oil is taken from the left cylinder head for the bearings of the vacuum pump which is fitted in some engine versions. 68 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
29 272 - Cooling and lubrication cooling Triple-plate thermostat The new heat management system contributes to the lower fuel consumption of the M 272. A new type of electronic mapcontrolled triple-plate thermostat controls the flow of coolant around the engine in all operating conditions. The opening temperature of the triple-plate thermostat can be actively controlled by a heating element in the expansion cartridge. Triple-plate thermostat Triple-plate thermostat (Y110) 1 Heating element with electrical connection 69
30 272 - Cooling and lubrication Triple-plate thermostat operating modes Short-circuited coolant In a cold start when the duo or heating cut-off valve (depending on type) is closed, the coolant remains short-circuited in the engine in the coolant cycle. The coolant pump "stirs" the coolant. Advantage: The engine achieves its operating temperature more quickly. Raised coolant temperature In a warm engine at part-throttle the coolant temperature can be raised to around 100 C. At full-throttle and in temperature-critical operating conditions the coolant temperature is lowered (80 C in summer / 90 C in winter). Advantage: The engine is designed to run at the optimum temperature, even at very low or very high loads. Reducible engine short circuit The triple-plate thermostat reduces the coolant flow through the engine to allow a greater quantity to flow through the heating system heater. Advantage: A highly effective heating system which reacts quickly. Triple-plate thermostat operating modes A Full reduction B Short-circuit mode C Mixed mode D Radiator mode 1 to the radiator 2 from the engine 3 to coolant pump (short/circuit) 70 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
31 272 - Cooling and lubrication Schematic coolant cycle, based on R 171 (radiator mode shown) 1 Coolant pump 2 cooling, radiator 3 Check valve 4 Coolant recovery bottle with silica gel 5 Electric coolant pump, heating circulation 6 Triple-plate thermostat 7 Washer water heating 8 Duo valve 9 Heating system heat exchanger 10 Plug coupling 11 Shut-off valve 12 Cylinder crankcase with cylinder heads 13 oil cooler A B C D E F G Coolant return Coolant feed Venting Full reduction Short-circuit mode Mixed mode Radiator mode Full reduction To speed up warming of the engine, the connections to the radiator and the coolant pump (short-circuit) are fully closed. The coolant remains stationary. Short-circuit mode During the warm-up phase, the connection to the coolant pump is gradually opened until it is 100 % open. Mixed mode The connections to the radiator and the coolant pump are partially opened depending on the degree of cooling required. Radiator mode For maximum cooling the connection to the radiator is opened 100 %, the connection to the coolant pump is closed. Duo valve/heating shut-off valve A duo or a heating shut-off valve (not shown) is fitted, depending on the engine type. These valves interrupt the supply of coolant to the heating system heat exchanger to warm up the engine more quickly. 71
32 272 - electrical/electronics control management of the M272 is done by the engine control module, the ME 9.7. To help achieve short electrical paths, the engine control module is mounted on the induction pipe of the engine, i.e. it is an integral part of the engine design. The mounting of the control module on the engine also offers benefits in production. As with the M 271, the M 272 also features a two-computer design engine control module. Knock sensor Two knock sensors, one per cylinder bank, detect any combustion knock. The sensors are piezoceramic and correct the ignition timing as required. control module mounted on intake manifold 1 Knock sensors 72 b Model Year 2005 I Model 171
33 272 - electrical/electronics Coil Individual coils with integrated ignition output stage are used in the M 272 The coils are controlled by the engine control module via a dedicated control lead. Generator interface The generator communicates with the engine control module via the LIN bus. This means that the engine control module can influence the control action of the generator by prescribing a target control voltage. Conversely, the generator also signals any errors to the engine control module. 1 Coil i LIN-bus LIN stands for Local Interconnect Network. The LIN bus is a bi-directional single-wire interface with a maximum transmission rate of 20 kbit/s. The LIN bus links up intelligent engine components which do not require high data transmission rates. 73
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED
 SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE
 EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system, the DIS (Direct Ignition System), and a plastic intake manifold have been used on the
EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system, the DIS (Direct Ignition System), and a plastic intake manifold have been used on the
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
This information covers the design and function of the intake and exhaust systems for the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED
 Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED 185HP & MASSIVE TORQUE iame41-1.doc 29Mar03 Page 1 of 2 Another Sea-Doo watercraft first and only. Introducing the 185hp, GTX 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED PWC. The 4-TEC
Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED 185HP & MASSIVE TORQUE iame41-1.doc 29Mar03 Page 1 of 2 Another Sea-Doo watercraft first and only. Introducing the 185hp, GTX 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED PWC. The 4-TEC
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
2AZ-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL
 ENGINE 2Z-FE ENGINE MECHNICL EG-33 2Z-FE ENGINE MECHNICL ENGINE COVER The engine cover is made of nylon resin, and sound insulation material (urethane foam) is placed between the engine cover and the cylinder
ENGINE 2Z-FE ENGINE MECHNICL EG-33 2Z-FE ENGINE MECHNICL ENGINE COVER The engine cover is made of nylon resin, and sound insulation material (urethane foam) is placed between the engine cover and the cylinder
Objectives of the Module...2 Purpose of the System...3 Technical Data... 4
 Table of Contents N73B60 Engine - Workbook Subject Page N73B60 Engine Objectives of the Module...2 Purpose of the System...3 Technical Data... 4 Disassembly - Components Intake Manifold... 6 Cylinder Head
Table of Contents N73B60 Engine - Workbook Subject Page N73B60 Engine Objectives of the Module...2 Purpose of the System...3 Technical Data... 4 Disassembly - Components Intake Manifold... 6 Cylinder Head
Handout Activity: HA170
 Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Product Information. N57 Engine.
 Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Heat Transfer in Engines. Internal Combustion Engines
 Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
SOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
 SECTION 1B SOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
SECTION 1B SOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
CHAPTER 1 MECHANICAL ARRANGEMENT
 CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 MECHANICAL ARRANGEMENT CONTENTS PAGE Basic Principals 02 The Crankshaft 06 Piston Attachment 08 Major Assemblies 10 Valve Gear 12 Cam Drive 18 Mechanical Arrangement - Basic Principals
CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 MECHANICAL ARRANGEMENT CONTENTS PAGE Basic Principals 02 The Crankshaft 06 Piston Attachment 08 Major Assemblies 10 Valve Gear 12 Cam Drive 18 Mechanical Arrangement - Basic Principals
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Lower Intake Manifold Replacement
 Lower Intake Manifold Replacement Removal Procedure 1. Turn OFF all the lamps and the accessories. 2. Ensure the ignition switch is in the OFF position. 3. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
Lower Intake Manifold Replacement Removal Procedure 1. Turn OFF all the lamps and the accessories. 2. Ensure the ignition switch is in the OFF position. 3. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
SECTION A Engine 3.7L
 303-01A-i Engine 3.7L 303-01A-i SECTION 303-01A Engine 3.7L CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01A-2 Engine Identification... 303-01A-2 Engine Code Information Label... 303-01A-2 Engine
303-01A-i Engine 3.7L 303-01A-i SECTION 303-01A Engine 3.7L CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01A-2 Engine Identification... 303-01A-2 Engine Code Information Label... 303-01A-2 Engine
Engine Exhaust system. Engine
 Engine Engine 272 - Exhaust system The engine of the 6-cylinder version satisfies the US exhaust emissions limits. To meet these limits the monolith coating of the catalytic converters has been modified
Engine Engine 272 - Exhaust system The engine of the 6-cylinder version satisfies the US exhaust emissions limits. To meet these limits the monolith coating of the catalytic converters has been modified
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
N62B44 Engine...1. Objectives of the Module...1. Purpose of the System...2. Technical Data...3. Engine Views...5
 Table of Contents Subject Page N62B44 Engine.............................................1 Objectives of the Module.....................................1 Purpose of the System.......................................2
Table of Contents Subject Page N62B44 Engine.............................................1 Objectives of the Module.....................................1 Purpose of the System.......................................2
ACTUAL CYCLE. Actual engine cycle
 1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins
 Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins Introduction The bi-fuel system modifies standard heavy-duty diesel engines to operate on diesel and gas simultaneously. The gas is used as main fuel and
Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins Introduction The bi-fuel system modifies standard heavy-duty diesel engines to operate on diesel and gas simultaneously. The gas is used as main fuel and
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
ENGINE MECHANICAL <134>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Swirl Flaps. A = Non swirl not active. B = Swirl active
 Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
A. Perform a vacuum gauge test to determine engine condition and performance.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
TECHNICAL DATA. COMPRESSION RATUI 9,5/1 WEIGHT ready to fly CONSUMPTION at 5400RPM 5,6litres/h POWER at 6200RPM
 VICTOR 1 SUPER This handbook aims to bring to the attention of key technical, functional and maintenance of your motor VICTOR 1. Read carefully the following pages, will be synonymous with safety, reliability
VICTOR 1 SUPER This handbook aims to bring to the attention of key technical, functional and maintenance of your motor VICTOR 1. Read carefully the following pages, will be synonymous with safety, reliability
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Workshop Manual. System Description & Operation
 Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine. Month XX, 20XX
 EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine Month XX, 20XX EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine PRESENTER S NAME PRESENTER S POSITION TRADITION OF ENGINE INNOVATION MX, EU PX DD575 PR MX, NA MX 11, EU 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine Month XX, 20XX EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine PRESENTER S NAME PRESENTER S POSITION TRADITION OF ENGINE INNOVATION MX, EU PX DD575 PR MX, NA MX 11, EU 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
Engine Dismantle and Assemble ( )
 Engine Dismantle and Assemble ( 34 8) Special Tools 5 053 Slide hammer 47 Vibration damper remover 47 5053 00 Splined head socket, cylinder head bolts 87 Mounting stand with geared drive 00 059C Installer
Engine Dismantle and Assemble ( 34 8) Special Tools 5 053 Slide hammer 47 Vibration damper remover 47 5053 00 Splined head socket, cylinder head bolts 87 Mounting stand with geared drive 00 059C Installer
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
2012 BMW 135i. ENGINE N55 - Service Information. N55 - Service Information
 ENGINE N55 - Service Information INTRODUCTION The N55 engine is the successor to the N54, Re-engineering and modifications have made it possible to now use only one exhaust turbocharger. Against the backdrop
ENGINE N55 - Service Information INTRODUCTION The N55 engine is the successor to the N54, Re-engineering and modifications have made it possible to now use only one exhaust turbocharger. Against the backdrop
The TL Series is available with either a 3.2-liter V-6 or a 2.5-liter, inline fivecylinder,
 OVERVIEW The TL Series is available with either a 3.2-liter V-6 or a 2.5-liter, inline fivecylinder, engine. The 3.2TL engine, like all other Acura engines, is made of aluminum alloy and is equipped with
OVERVIEW The TL Series is available with either a 3.2-liter V-6 or a 2.5-liter, inline fivecylinder, engine. The 3.2TL engine, like all other Acura engines, is made of aluminum alloy and is equipped with
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment kw at 2100 rpm
 2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
Toothed belt, removing and installing
 Toothed belt, removing and installing Special Tools and Equipment ^ 3212 spanner wrench ^ 3387 pin wrench ^ T40011 pin ^ T40026 locking pin ^ T40028 socket ^ T40030 camshaft adjuster gauge Removing Lock
Toothed belt, removing and installing Special Tools and Equipment ^ 3212 spanner wrench ^ 3387 pin wrench ^ T40011 pin ^ T40026 locking pin ^ T40028 socket ^ T40030 camshaft adjuster gauge Removing Lock
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
This page contains the BMW S38B38 Technical Info. It is actually the official BMW AG training centre documentation for the dealers.
 This page contains the BMW S38B38 Technical Info. It is actually the official BMW AG training centre documentation for the dealers. This article was originally given to me in Dutch, and, with a lot of
This page contains the BMW S38B38 Technical Info. It is actually the official BMW AG training centre documentation for the dealers. This article was originally given to me in Dutch, and, with a lot of
Cooling System Description and Operation
 Page 1 of 5 2008 Holden VE Sedan VE, WM, Caprice, Statesman, Lumina, Omega, VXR8 Service Manual Engine Engine Cooling Description and Operation Document ID: 1990377 Cooling System Description and Operation
Page 1 of 5 2008 Holden VE Sedan VE, WM, Caprice, Statesman, Lumina, Omega, VXR8 Service Manual Engine Engine Cooling Description and Operation Document ID: 1990377 Cooling System Description and Operation
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies. Turbochargers
 Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Engine. External View GENERAL TECHNICAL FEATURES. file://c:\users\duncan Capewell\Documents\Data Files - DCapewell\Mydocs\Disco3...
 Page 1 of 32 Published : May 7, 2004 Engine External View GENERAL The TdV6 engine is a 2.7 litre, direct injection, six-cylinder diesel engine having two banks of three cylinders, arranged at 60 degrees
Page 1 of 32 Published : May 7, 2004 Engine External View GENERAL The TdV6 engine is a 2.7 litre, direct injection, six-cylinder diesel engine having two banks of three cylinders, arranged at 60 degrees
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
Volkswagen New Beetle 2.0 Liter 4-cyl General, Engine (Engine Code AEG) 13 Engine-Crankshaft, Cylinder block (Page GR-13)
 13 Engine-Crankshaft, Cylinder block (Page GR-13) Engine, disassembly and assembly 10-222 A/21 guide from 10-222 A support tool, modifying Ribbed belt, removing and installing Semi-automatic toothed belt
13 Engine-Crankshaft, Cylinder block (Page GR-13) Engine, disassembly and assembly 10-222 A/21 guide from 10-222 A support tool, modifying Ribbed belt, removing and installing Semi-automatic toothed belt
Handout Activity: HA185
 Cylinder heads Handout Activity: HA185 HA185-2 Cylinder head The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the combustion chamber. It carries the valves and, in many
Cylinder heads Handout Activity: HA185 HA185-2 Cylinder head The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the combustion chamber. It carries the valves and, in many
Name Date. True-False. Multiple Choice
 Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
AfterSales Training. Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C
 AfterSales Training Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C Porsche AfterSales Training Student Name: Training Center Location: Instructor Name: Date: Important Notice: Some of the contents of this AfterSales
AfterSales Training Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C Porsche AfterSales Training Student Name: Training Center Location: Instructor Name: Date: Important Notice: Some of the contents of this AfterSales
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
2002 Mustang Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 13 SECTION 303-01B: Engine 4.6L (2V) 2002 Mustang Workshop Manual REMOVAL Procedure revision date: 01/02/2003 Cylinder Heads Special Tool(s) Remover, Crankshaft Vibration Damper 303-009 (T58P-6316-D)
Page 1 of 13 SECTION 303-01B: Engine 4.6L (2V) 2002 Mustang Workshop Manual REMOVAL Procedure revision date: 01/02/2003 Cylinder Heads Special Tool(s) Remover, Crankshaft Vibration Damper 303-009 (T58P-6316-D)
2005 Escape Workshop Manual Cylinder block
 22 6010 Cylinder block Cylinder Head Item Part Number Description 1 12A366 Coil-on-plug assembly (4 req'd) 2 6M293 Valve cover 3 12K073 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor 4 6766 Oil filler cap 5 6M293 Valve
22 6010 Cylinder block Cylinder Head Item Part Number Description 1 12A366 Coil-on-plug assembly (4 req'd) 2 6M293 Valve cover 3 12K073 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor 4 6766 Oil filler cap 5 6M293 Valve
H35/40G(V) /7 Call Center. Engine Power Plant Sales Dep t Tel : 86)
 http://www.soarpower.com http://www.soarpower.com H35/40G(V) Copyright 2014 Hyundai Heavey Industries Engine Power Plant Sales Dep t Tel : 86) 4006-690 588 E-mail : sale@soar.hk 24/7 Call Center 9 +8-4008111308
http://www.soarpower.com http://www.soarpower.com H35/40G(V) Copyright 2014 Hyundai Heavey Industries Engine Power Plant Sales Dep t Tel : 86) 4006-690 588 E-mail : sale@soar.hk 24/7 Call Center 9 +8-4008111308
A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install
 Page 1 of 46 Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install Remove 1. Open the bonnet. 2. Disconnect the battery. 3. Open the engine cover (1). 4. Detach the engine cover. 6 bolts (2) and (3) 5. Release
Page 1 of 46 Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install Remove 1. Open the bonnet. 2. Disconnect the battery. 3. Open the engine cover (1). 4. Detach the engine cover. 6 bolts (2) and (3) 5. Release
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
GAS/PETROL THE ALTERNATIVE: ENGINES LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER AND MORE COMPACT ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY 22,0 6,6 431,1
 THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
Module7:Advanced Combustion Systems and Alternative Powerplants Lecture 32:Stratified Charge Engines
 ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions
 Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions People who are familiar with the functioning of a gasoline aircraft engine need not have any difficulty in understanding how a high speed Diesel aircraft
Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions People who are familiar with the functioning of a gasoline aircraft engine need not have any difficulty in understanding how a high speed Diesel aircraft
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
ENGINE MECHANICAL <2.0L ENIGNE>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 This model is equipped with a newly developed 4B11 engine. It is a 4-cylinder,
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 This model is equipped with a newly developed 4B11 engine. It is a 4-cylinder,
COMPONENT LOCATOR > DISASSEMBLED VIEWS
 Page 1 of 45 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8L Eng Base Service Manual: ENGINE MECHANICAL - 3.8L COMPONENT LOCATOR > DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Fig 1: Engine Block Component Views Callout Component Name 100 Engine
Page 1 of 45 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8L Eng Base Service Manual: ENGINE MECHANICAL - 3.8L COMPONENT LOCATOR > DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Fig 1: Engine Block Component Views Callout Component Name 100 Engine
PIERBURG. Carburetor: 2E3
 PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER
 A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS
 2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry. 1 Introduction Preface Model-Building Simulation... 5 References...
 Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
1996 ACURA 3.5RL POWERTRAIN
 - - - n- _n - --- OVERVIEW The 3.5 RL is powered by a 3.5-liter,all-aluminum, single-overhead camshaft, 90-degree V-6 engine which produces 210 horsepower at 5200rpm and 2241bsft of torque at a very low
- - - n- _n - --- OVERVIEW The 3.5 RL is powered by a 3.5-liter,all-aluminum, single-overhead camshaft, 90-degree V-6 engine which produces 210 horsepower at 5200rpm and 2241bsft of torque at a very low
STIH) Technical Information New cut-off machine STIHL TS 700 Series 4224
 STIH) Technical Information 52.2004 New cut-off machine STIHL TS 700 Series 4224 Contents 1. Technical description 2. Technical data 3. Accessories 4. Service accessories 5. Repairs 6. Spare parts englisch
STIH) Technical Information 52.2004 New cut-off machine STIHL TS 700 Series 4224 Contents 1. Technical description 2. Technical data 3. Accessories 4. Service accessories 5. Repairs 6. Spare parts englisch
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
THERMODYNAMICS. T85D - Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed
 THERMODYNAMICS T85D - Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed 1. General Didacta s T85D Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed has been specially designed for use in testing laboratories, and to ensure the greatest
THERMODYNAMICS T85D - Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed 1. General Didacta s T85D Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed has been specially designed for use in testing laboratories, and to ensure the greatest
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
2004 Volvo C70 L5-2.4L Turbo VIN 63 B5244T7 Cylinder Head Assembly Service and Repair, Removal and Replacement: Cylinder Head/Gasket, Replacing
 1 of 25 8/18/2011 6:10 PM 2004 Volvo C70 L5-2.4L Turbo VIN 63 B5244T7 Cylinder Head Assembly Service and Repair, Removal and Replacement: Cylinder Head/Gasket, Replacing Cylinder head/gasket, replacement
1 of 25 8/18/2011 6:10 PM 2004 Volvo C70 L5-2.4L Turbo VIN 63 B5244T7 Cylinder Head Assembly Service and Repair, Removal and Replacement: Cylinder Head/Gasket, Replacing Cylinder head/gasket, replacement
gas passes through baffle plates in cylinder oil separator inlet port. Separated oil returns The first separation will happen when blowby
 2 05 LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW Lubrication System PCV Oil Separator Cylinder head cover (oil + gas) Blow-by gas (air duct hose) Inlet port Oil (oil gauge pipe) The first separation will happen when blowby gas
2 05 LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW Lubrication System PCV Oil Separator Cylinder head cover (oil + gas) Blow-by gas (air duct hose) Inlet port Oil (oil gauge pipe) The first separation will happen when blowby gas
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
Intake Components 1117
 Item Part Number Description 1 W705654 Bolt 2 N807309 Bolt (2 req'd) 3 9F460 Bracket 4 N807071 Bolt (5 req'd) 5 9A448 Intake manifold (upper) 6 9E498 Vacuum harness 7 9F792 Fuel injection supply manifold
Item Part Number Description 1 W705654 Bolt 2 N807309 Bolt (2 req'd) 3 9F460 Bracket 4 N807071 Bolt (5 req'd) 5 9A448 Intake manifold (upper) 6 9E498 Vacuum harness 7 9F792 Fuel injection supply manifold
