The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
|
|
|
- Chester McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
2 Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg in 2005, the engine range is now being expanded to include the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine. Thanks to this range-topping diesel engine, Volkswagen now has a power plant that boasts excellent figures and thus superior performance with 250 kw max. at 4,000 rpm and 800 Nm as early as 1,750 rpm. This high-torque engine, which was developed by Audi and has featured in the A8 and Q7, has been adapted for use in the new Touareg. It has been possible to reach the high emissions goals for the EU5 emissions standard and, at the same time, achieve a consumption of 9.4 l/100 km with 239 g/km CO 2. This engine sets standards in terms of dynamics, driving fun, consumption and reliability while improving comfort and reducing noise. S467_002 The self-study programme portrays the design and function of new developments. The contents will not be updated. For current testing, adjustment and repair instructions, refer to the relevant service literature. Important Note 2
3 Contents Introduction Engine Mechanics Engine Management Service Test Yourself
4 Introduction The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Technical features Bosch common rail injection system with piezo injectors max. 2,000 bar injection pressure Diesel particulate filter/oxidising catalytic converter Turbochargers with speed sensors Innovative thermal management (ITM) Low-temperature exhaust gas recirculation Volumetric flow-controlled oil pump Demand-regulated fuel delivery unit Oil level/oil temperature sender with ultrasonic measurement principle S467_040 Technical data Engine code Type CKDA Displacement 4,134 cm 3 Bore Stroke Valves per cylinder 4 8-cylinder V engine 83.0 mm 95.5 mm Compression ratio 16.4 : 1 Max. output in kw Maximum torque 250 at 4,000 rpm 800 Nm at 1,750 rpm to 2,750 rpm Engine management Bosch EDC 17 Fuel Exhaust gas treatment Emissions standard EURO 5 CO 2 emission Diesel fuel complying with DIN EN590 Exhaust gas recirculation, oxidising catalytic converter, diesel particulate filter 239 g/km Torque (Nm) Output and torque graph Engine speed (rpm) Output (kw) S467_026 4
5 Engine Components Crankshaft drive The crankcase with a gap of 90 mm between the cylinders (90 V) is made from grey cast iron. The crankshaft is forged and mounted in 5 bearings. The big end bearing journals are roller burnished for strength. Roller burnishing is a non-cutting process that uses rolling tools to smoothen and strengthen material surfaces. The cast aluminium pistons with combustion cavity have a diameter of 83 mm. They are equipped with a ring carrier cooling duct for cooling the piston. Oil spray nozzles constantly spray oil onto the underside of the piston crown. Crankcase Main oil duct Bearing frame Crankshaft Oil sump S467_044 5
6 Engine Components Chain drive The chain drive has been taken from the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine as previously used at Audi, but has been improved in terms of friction and rotational vibration behaviour. The ancillary components, like the oil pump and coolant pump, are driven via the chain drive D and a gear module. Chain drive C Chain drive B Chain drive A Gear module S467_045 Chain drive D 6
7 Vibration damper The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine has been equipped with a vibration damper to dampen the vibrations caused by combustion. This results in better engine acoustics and less load on the crankshaft. Counterweight for crankshaft S467_046 Rubber track Belt track 7
8 Engine Components Camshaft drive Backlash compensation The intake and exhaust camshafts are linked via spur gear toothing with integrated backlash compensation. In this case, the spur gear on the exhaust camshaft is driven by the spur gear on the intake camshaft. Backlash compensation ensures that the camshafts are driven with little noise. Cylinder head (example left) Inlet camshaft Exhaust camshaft Spur gear on exhaust camshaft fixed moving Moving spur gear Exhaust camshaft Spur gear on inlet camshaft S467_004 Intermediate disc S467_005 Fixed spur gear Fixed spur gear Circlip Disc spring Moving spur gear Design The exhaust camshaft spur gear is split into two parts in the left-hand cylinder head. (In the right-hand cylinder head, the intake camshaft spur gear is split into two parts.) The broader part of the spur gear (fixed spur gear) is positively connected to the camshaft. Six ramps are located on the front face. The narrower part of the spur gear (moveable spur gear) can be moved radially and axially. Recesses for the six ramps are located on its rear side. S467_006 Ramps 8
9 Function Both spur gear parts are pushed together in the axial direction due to the force exerted by a disc spring. At the same time, they are rotated by the ramps. S467_007 Disc spring This rotational movement offsets the teeth of both spur gear parts and therefore leads to backlash compensation between the gear wheels on the intake and exhaust camshafts. Tooth offset S467_008 9
10 Engine Components Oil system Schematic overview of system S467_039 Legend 1 - Oil sump 2 - Oil pump 3 - Oil cooler (coolant) 4 - Oil pressure control valve 5 - Oil filter module 6 - Hydraulic camshaft adjustment 7 - Cylinder bank Cylinder bank Chain tensioner 10 - Piston cooling Coolant supply Coolant return Oil without pressure Oil under pressure 10
11 Volumetric flow-controlled oil pump The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine uses an oil pump with two pressure levels and volumetric flow control. This is a vane cell pump that can change its delivery characteristics thanks to an eccentrically mounted adjustment ring. Engine oil pressure can be applied to the adjustment ring via two control surfaces to turn it against the force of a control spring. This changes the delivered volume. The oil pressure is measured at the main oil gallery downstream of the oil filter and, depending on the required pressure level, oil is sent to one or both control surfaces. The valve for oil pressure control N428 switches between the two pressure levels depending on the engine load, engine speed and oil temperature. The drive power of the oil pump is thus reduced considerably, above all, in the load cycles preferred by customers, like city or long-distance driving. Oil pump Vanes Delivery chamber S467_048 11
12 Engine Components Small delivery quantity The valve for oil pressure control N428 is supplied with voltage from terminal 15. The valve is connected to earth via the engine control unit. This opens the oil duct for control surface 2. Oil pressure is always supplied to control surface 1 via a second oil duct. Now both oil flows act on both control surfaces with the same pressure. The resulting forces are greater than the force of the control spring. The adjustment ring turns anti-clockwise and reduces the size of the pump delivery chamber. The small delivery quantity is switched depending on the engine speed, engine load and oil temperature. This reduces the drive power of the oil pump. Valve for oil pressure control N428 activated Crankshaft oil duct Control surface 1 Oil pressure applied from crankshaft oil duct S467_027 Vane cells Delivery chamber Control surface 2 S467_036 12
13 Large delivery quantity From an engine speed of 2,500 rpm or an increased torque (full throttle acceleration), the solenoid valve is disconnected from earth by the engine control unit. The oil duct to control surface 2 is closed. The oil pressure present only acts on control surface 1. This force is lower than the force of the control spring. The control spring rotates the adjustment ring clockwise. The adjustment ring is rotated from the centre position and thus enlarges the delivery chamber between the vane cells. More oil is delivered through the larger delivery chamber. A resistance acts through the oil holes and the bearing play of the crankshaft against the higher oil volume flow. This causes the oil pressure to rise. A volumetric flow-controlled oil pump with two pressure levels is achieved in this way. Valve for oil pressure control N428 (zero current) closed Control surface 1 Oil pressure applied from crankshaft oil duct S467_028 Vane cells Delivery chamber Control surface 2 S467_035 13
14 Engine Components Oil level and oil temperature sender G266 An electronic oil level and oil temperature sender is used in the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine for the Touareg. The conventional oil dipstick has been omitted. The sender works according to the ultrasound principle. The ultrasonic impulses emitted are reflected by the oil/air boundary layer. Ultrasound is a sound frequency that is above the range perceivable by humans. The ultrasound waves are reflected depending on the material/density of the obstacle. Air and oil have different densities. In oil, the sound waves can spread with low resistance. In air, the dispersion of the sound waves is subject to considerably greater resistance. Therefore the ultrasound waves are reflected at the oil/air boundary layer. The advantages of the ultrasound sender are: Power consumption < 0.5 A Faster sender signal, approx. 100 ms Measuring unit Seal 3-pole connector housing Sender foot with measuring electronics S467_047 14
15 Operating principle Output with pulse-width modulated signal Temperature Filling level Digital Logic Evaluation S467_043 The sender consists of the sender foot with measuring electronics, the measuring unit and the 3-pole connector housing. The ultrasound signals are processed in the measuring electronics. A map is used to calculate the oil level from the time difference between the sent and reflected signal. In addition to the oil level, the oil temperature is calculated with a PTC signal. Both values are sent to the dash panel via the engine control unit using a PWM signal (pulsewidth modulation). The display strategy of the oil level display is described in self-study programme no. 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid. 15
16 Engine Components Exhaust gas recirculation system Turbocharger with speed sender Sender for turbocharger speed G688 Aperture for speed sensor The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine is equipped with two speed-controlled turbochargers. S467_033 Features Water-cooled VGT turbocharger from Garrett High charge pressure in low rev ranges thanks to optimised compressor wheels Variable turbine geometry Turbocharger with speed sensors to monitor the speed of the turbocharger Improved software functions in engine control unit Better torque and output values Protection function against excessive speed in extreme conditions (high elevation/mountain pass driving) Speed reduction when there is a large speed difference between the two turbochargers Turbocharger speed is controlled by evaluation electronics. The turbine wheel with its guide vanes gives off a pulse for each vane. Nine pulses of the turbine wheel represent one revolution of the turbocharger. 16
17 Ventilation duct in cylinder head If there is any leakage around the copper injector seal, the combustion pressure of 180 bar will allow the air to escape from the combustion chamber via a duct. The ventilation duct is located in the cylinder head above the exhaust manifold. It prevents the excess pressure from the combustion chamber reaching the compressor side of the turbocharger, which could cause faults or damage seals. Piezo injector Access to crankcase ventilation system via the oil chamber in the cylinder head Seal Channel for glow plug S467_059 Seal to combustion chamber Ventilation duct S467_060 17
18 Engine Components Innovative thermal management The innovative thermal management system (ITM) is being used for the first time in the new VW Touareg. It allows the flow of heat supplied by the engine to be distributed perfectly between the engine, gearbox and interior. To distribute the available heat in an ideal way, new software was developed taking the requirements and priorities of the interior, engine and gearbox into account. The centrepiece is the so-called thermal manager in the engine control unit. This guarantees a comfortable interior climate and optimum usage of the available heat to minimise friction in the engine. The air-conditioning and gearbox control unit signal their heat requirement to engine control unit via the CAN data bus. These are then weighted together with the engine heat requirement calculated by the engine control unit. The individual ITM components are then activated by the engine control unit as required. On the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine, the ITM comprises the following components: Standing coolant: The engine warms up faster during the warm-up phase resulting in lower engine friction and reduction of the HC and CO emissions. The standing coolant is made possible by an on-demand coolant pump. A vacuumoperated control shutter is pushed over the coolant pump impeller. The coolant pump continues to be driven, but coolant is not pumped. When the vacuum is removed, the control shutter is opened by a set of springs. Cylinder head temperature sensor: A coolant temperature sensor is used in the cylinder head close to the combustion chamber to monitor the critical valve bridge temperature and to avoid boiling coolant during the standing coolant mode. The coolant pump is activated using a load/engine speed-dependent map to protect components when there are large load jumps. Gearbox oil heating: Immediately after the coolant pump is switched on, the coolant that has already been heated up in the small engine circuit is made available to the gearbox oil cooler via an electrically operated directional valve. The faster heating up of the gearbox oil also reduces frictional losses in this area during the warm-up phase. Heating shut-off: If no heating is required, the complete thermal capacity of the interior heating can be switched off. As a result, the engine does not have to provide heat during the warm-up phase. 18
19 Thermal management schematic diagram The schematic diagram shows in a simplified manner how the Innovative Thermal Management system works. The heat produced by the engine is utilised in an ideal way and is passed onto the interior climate control and the gearbox as required. The individual components signal their heat requirement to the engine control unit and the components are activated depending on the priority. Electrical pump Cylinder head Gearbox Interior Main radiator Engine block Main coolant pump Thermostat S467_029 19
20 Engine Components Coolant circuit On-demand coolant pump The Innovative Thermal Management system used with the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine makes use of an on-demand coolant pump. Standing coolant When the engine is cold, the on-demand coolant pump stops the circulation of the coolant. This state is called standing coolant. The coolant circuit solenoid valve N492 pushes a vacuum-operated control shutter over the spinning vane rotor in the coolant pump. This stops the circulation of coolant. The coolant heats up more quickly and shortens the engine warm-up phase considerably. The heated coolant is sent to the automatic gearbox to also actively heat it. Heating the engine and gearbox oil more quickly reduces internal friction. This reduces the consumption and CO 2 emissions. Control shutter Guide rod Ring piston Rolling diaphragm Rod seal Friction bearing Vacuum connection By-pass seal Impeller 20 S467_030
21 Circulating coolant When no vacuum is applied, the control shutter is pressed into its resting position by return springs inside the coolant pump. The coolant circulates and heats the thermostat to activate the large cooling circuit. This ensures circulation of the coolant at all times (fail-safe). Thermostat opens from a coolant temperature of 87 C Control shutter Return spring Rolling diaphragm S467_031 21
22 Engine Components Low-temperature exhaust gas recirculation The low-temperature exhaust gas recirculation system is used to minimise nitrogen oxide (NO x ), which is formed when diesel fuel is burnt. EGR valve cylinder bank 1 Thermostat for exhaust gas recirculation cooling EGR cooler with bypass valve EGR valve cylinder bank 2 Pump for exhaust gas recirculation cooler V400 S467_013 The pump for exhaust gas recirculation cooler V400 is activated immediately upon engine start. The temperature in the exhaust gas recirculation cooler is regulated to 55 C by the thermostat. 22
23 The pump for exhaust gas recirculation cooler V400 supplies the low-temperature circuit with cold coolant directly from the main radiator. The pump is activated immediately upon engine start. The EGR cooler is integrated in its own low-temperature cooling circuit. It is no longer part of the small engine cooling circuit. Advantages Considerable increase in cooling performance Independent EGR cooling is also possible during the warm-up phase The EGR valves regulate the exhaust gas recirculation rates. A differential pressure sender is also fitted in the EGR valve. The differential pressure sender measures the pressure on the intake side. The value from the differential pressure sender and the value from the air mass meter are processed in the engine control unit. The differential pressure sender has been added because, due to the design, the air mass meter is quite far away from the actual cylinder inlet. Differential pressure sender EGR valve (cylinder bank 1) Differential pressure sender EGR valve (cylinder bank 2) S467_061 In extreme engine load conditions, engine running faults could result if only the value from the air mass meter is available. The engine control unit works with both values to avoid this. This guarantees a stable measuring value for the intake air across all engine-speed and torque ranges. Advantages More exact measured values Faster regulation is possible Almost same pressure and load relationships on both cylinder banks If the differential pressure sender signal fails, an entry is made in the fault memory and the engine control unit works with the value from the air mass meter. 23
24 Engine Components Low-pressure fuel system Fuel system The fuel system is divided into three pressure areas 1 - Fuel delivery unit GX1 High pressure up to 2000 bar Return pressure from the injectors 10 bar Supply pressure, return pressure 2 - Pressure-resistant fuel filter 3 - Fuel temperature sender G81 In the fuel supply system, the fuel is delivered by the fuel delivery unit from the fuel tank through the fuel filter to the high-pressure pump as required. The fuel delivery unit supplies the fuel pressure as required. The engine control unit calculates the current fuel requirement from the accelerator position, torque, engine temperature etc. and sends a corresponding signal to the fuel pump control unit. The fuel pump runs fast or slow accordingly. The high fuel pressure required for injection is generated in the high-pressure pump and is fed into the high-pressure accumulator (rail). The fuel reaches the injectors from the high-pressure accumulator. The pressure retention valve in the overflow diesel oil line maintains the injector return pressure at 10 bar. This pressure is important for operation of the piezo injectors. Calculates the current fuel temperature. 4 - High-pressure pump Generates the high fuel pressure required for injection. 5 - Fuel metering valve N290 Controls the quantity of fuel to be pressurised as required. 6 - Pressure retention valve Maintains the return pressure of the injectors at approx. 10 bar. This pressure is required for the injectors to work. 2 High pressure Supply pressure 11 Return pressure 1 Return from the injectors 24
25 7 - Engine control unit J Fuel pressure sender G247 Measures the current fuel pressure in the highpressure area. 9 - Fuel pressure regulating valve N Injectors 11 - Fuel pump control unit J High-pressure accumulator (rail) Stores the fuel required for injection into all cylinders under high pressure. Sets the fuel pressure in the high-pressure area Cylinder bank Cylinder bank S467_042 25
26 Engine Components Fuel delivery unit GX1 The fuel pump is an electrically driven annular gear pump and produces a fuel pressure of 3.5 to 6 bar at a maximum of 220 l/h. The fuel pressure is regulated according to requirements. Function The engine control unit calculates the current fuel requirement from the accelerator position, torque, engine temperature etc. and sends a PWM signal to the fuel pump control unit J538. The fuel pump control unit is mounted on the fuel tank. The control unit sends a corresponding command (signal) to the fuel pump. As a result, the fuel pump runs faster or slower and supplies the requested volume of fuel. Thanks to the fuel pump being activated on demand, an additional pre-supply pump is no longer required and has been omitted. Fuel line for auxiliary heating Fuel return Fuel supply system Electrical connection Fuel delivery unit Fuel pump S
27 Functional diagram CAN data bus Legend S GX1 Fuel delivery unit G1 Fuel gauge G3 Coolant temperature gauge J285 Control unit in dash panel insert J538 Fuel pump control unit J623 Engine control unit K29 Glow period warning lamp K132 Electronic power control fault lamp K231 Diesel particulate filter warning lamp Input signal Output signal Positive Ground CAN data bus 27
28 Engine Components Common rail fuel injection system Basic explanation The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine in the Touareg is equipped with a Bosch common rail injection system for mixture preparation. In this system, pressure generation and fuel injection are separate. The high-pressure pump generates the high fuel pressure required for injection. The common rail fuel injection system is controlled by the Bosch EDC 17 engine management system. The injection pressure is instantly available and is adapted to the current engine operating status Flexible fuel injection process, with several pilot and secondary injection processes. Fuel line to high-pressure accumulator (rail) Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 High-pressure pump High-pressure accumulator (rail) cylinder bank 1 Fuel metering valve N290 High-pressure accumulator (rail) cylinder bank 2 Fuel distributor between the rails Fuel pressure sender G247 S467_055 Injectors Injectors 28
29 Restrictors in the rail When the injector is closed and during subsequent injections, a pressure wave from the injector is built up. This continues up to the rail and is reflected from there again. To dampen the pressure waves, restrictors are fitted in the fuel supply from the high-pressure pump to the high-pressure accumulators (rails), on the highpressure accumulators (rails) for cylinder banks 1 and 2 and in the rails in front of each injector. The correct tightening torque must be used when tightening the injector fuel line and also the line connecting the two rails. High-pressure line Deformed or damaged high-pressure lines may not be used again they have to be replaced. Union nut Restrictor Rail S467_066 29
30 Engine Components High-pressure pump The high-pressure pump is a 2-piston pump. The pump is driven by a toothed belt. It generates the high fuel pressure of up to 2000 bar that is required for injection. Design of high-pressure pump Intake valve Fuel metering valve N290 Outlet valve Pump plunger Connection to rail Fuel inlet Plunger spring Fuel return Roller Overflow valve Drive shaft Drive cam S467_049 30
31 Design of high-pressure pump schematic Intake valve Outlet valve Fuel metering valve N290 Connection to rail Pump plunger Plunger spring Fine filter Overflow valve Roller Drive shaft with cam Fuel return Fuel inlet S467_053 31
32 Engine Components High-pressure fuel system Fuel metering valve N290 The fuel metering valve N290 is integrated into the high-pressure pump. The valve regulates the fuel quantity that is required to produce high pressure. The advantage of this is that the high-pressure pump only has to pressurise the amount of fuel that is required for the current operating conditions. This reduces the power consumption of the high-pressure pump and avoids unnecessary fuel heating. To compression chamber Control plunger Inlet from inside of pump S467_052 Function When no current is supplied, the fuel metering valve is open. To reduce the quantity flowing to the compression chamber, the valve is actuated by the engine control unit with a pulse-width modulated (PWM) signal. The fuel metering valve is pulsed closed by the PWM signal. The quantity of fuel flowing into the compression chamber of the high-pressure pump varies in relation to the PWM signal. 32
33 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 The fuel pressure regulating valve is located on the high-pressure accumulator (rail) for cylinder bank 1. The fuel pressure is set in the high-pressure area by opening and closing the regulating valve. To do this, the regulating valve is actuated by the engine control unit with a pulse-width-modulated signal. High-pressure accumulator (rail)- cylinder bank 1 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 S467_058 Design Electrical connection High-pressure accumulator (rail) Solenoid Valve needle Valve armature S467_051 Return to the fuel tank Valve spring 33
34 Engine Components Function Regulating valve in resting position (engine off ) If the regulating valve is not actuated, the pressure regulating valve is opened by the valve springs. The high-pressure area is connected to the fuel return line. This ensures a volume balance between the fuel highpressure and low-pressure area. Vapour bubbles, which can form in the high-pressure accumulator (rail) during the cooling process after the engine is switched off, are avoided and the starting behaviour of the engine is thus improved. S467_015 Regulating valve actuated (engine "on") Valve springs To attain an operating pressure of 230 to 2,000 bar in the high-pressure accumulator, the regulating valve is actuated by the engine control unit J623 using a pulse-width modulated (PWM) signal. This creates a magnetic field in the solenoid. The valve armature is attracted and presses the valve needle into its seat. The fuel pressure in the high-pressure accumulator is therefore opposed by a magnetic force. Depending on the on-off ratio of actuation, the flow to the return line and therefore the quantity flowing back is varied. This also enables pressure fluctuations in the highpressure accumulator to be compensated for. Engine control unit J623 S467_016 Effects upon failure The engine will not run if the fuel pressure regulating valve fails because it is not possible to build up sufficient fuel pressure for fuel injection. 34
35 Regulation of the high-pressure fuel In the common rail injection system, the high-pressure fuel is regulated with a so-called dual-regulation design. The fuel pressure regulating valve N276 and the fuel metering valve N290 are actuated by the engine control unit using a pulse-width modulated signal (PWM signal) for this purpose. Depending on the operating status of the engine, the high fuel pressure is regulated by one of the two valves. The other valve is then only controlled by the engine control unit. Regulation by the fuel pressure regulating valve N276 When the engine is started and the fuel needs warming, the high fuel pressure is regulated by the fuel pressure regulating valve N276. To warm up the fuel quickly, the high-pressure pump delivers and pressurises more fuel than is required. The excess fuel is returned to the fuel return line by the fuel pressure regulating valve N276. Regulation by the fuel metering valve N290 When there are large injection quantities and high rail pressures, the high fuel pressure is regulated by the fuel metering valve N290. This results in ondemand control of the high fuel pressure. The power consumption of the high-pressure pump is reduced and unnecessary fuel heating is avoided. Control by both valves During idling and overrun and when there are small injection quantities, the fuel pressure is regulated by both valves at the same time. This allows precise regulation, which improves the idling quality and the transition to overrun. Schematic diagram of dual-regulation design Regulation of the high pressure fuel by the fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Injection quantity Regulation of the high-pressure fuel by the fuel metering valve N290 Regulation by both valves Engine speed S467_054 35
36 Engine Components Injectors Piezo-controlled injectors are used in the common rail injection system for the Touareg 4.2 l TDI engine. The injectors are controlled via a piezo actuator. This results in the following advantages: Very short switching times Several injections per working cycle are possible Precise proportional injection quantities Electrical connection Fuel inlet (high-pressure connection) Pin-type filter Fuel return Piezo actuator Connecting plunger Valve plunger Valve plunger spring Switching valve Restrictor plate Nozzle spring Seal Nozzle needle S467_014 36
37 Injection process The very short switching times of the piezo-controlled injectors allow flexible and precise control of the injection phases and injection quantities. As a result, the injection process can be adapted to the relevant operating requirements of the engine. Up to five partial injections can be carried out per injection process. Initialisation voltage (V) Injection (rate of injection) Time Pilot injection Main injection Secondary injection S467_050 Pilot injection A small quantity of fuel is injected into the combustion chamber prior to main injection. This leads to a rise in temperature and pressure in the combustion chamber. The main injection ignition time lag is therefore shortened, thereby reducing the rise in pressure and pressure peaks in the combustion chamber. The results are low combustion noise and low exhaust gas emissions. The number, time and injection quantities of the pilot injection processes are dependent on the engine operating status. When the engine is cold and at low engine speeds, two pilot injections are carried out for acoustic reasons. At higher loads and engine speeds, only one pilot injection is carried out in order to reduce exhaust emissions. No pilot injection is carried out at full throttle and high engine speeds because a large quantity of fuel has to be injected to achieve a high level of efficiency. Main injection Following pilot injection, the main injection quantity is injected into the combustion chamber following a brief injection pause. The injection pressure level remains virtually constant throughout the entire injection process. Secondary injection Two secondary injection processes are carried out to regenerate a diesel particulate filter. These secondary injections increase the exhaust gas temperature, which is necessary to combust the soot particles in the diesel particulate filter. 37
38 Engine Management System overview Sensors Air mass meter G70 Charge pressure sender G31 Intake air temperature sender G42 Engine speed sender G28 Coolant temperature sender G62 Oil temperature sender G8 Glow period warning lamp K29 Exhaust emissions warning lamp K83 Diesel particulate filter warning lamp K231 Fuel temperature sender G81 Fuel pressure sender G247 Radiator outlet coolant temperature sender G83 Hall sender G40 Control unit in dash panel insert J285 Engine control unit J623 (master) CAN HIGH CAN LOW Powertrain CAN data bus Accelerator position sender G79 Accelerator position sender 2 G185 Elevation sender Exhaust gas pressure sensor 1 G450 Engine control unit J623 (slave) Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 G Lambda probe G39 Catalytic converter temperature sensor 1 G20 Exhaust gas temperature sender 3 G495 Exhaust gas temperature sender 4 G648 Oil level and oil temperature sender G266 Brake light switch F Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 for bank 2 G236 Air mass meter 2 G246 Exhaust gas temperature sender 3 for bank 2 G497 Catalytic converter check temperature sensor 2 G29 Lambda probe 2 G108 Exhaust gas pressure sensor 2 G451
39 Actuators Injectors for cylinders 1, 4, 6, 7 N30, N33, N84, N85 Automatic glow period control unit J179/ Glow plugs for cylinders 1, 4, 6, 7 Q10, Q13, Q15, Q16 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Throttle valve module J338 Intake manifold flap motor V157 Exhaust gas recirculation control motor V338 Fuel metering valve N290 Exhaust gas recirculation cooler changeover valve N345 Engine component current supply relay J757 Fuel pump control unit J538 Fuel delivery unit GX1 Diagnostic connector T16 Lambda probe heater Z19 Coolant circulation pump V50 Pump for exhaust gas recirculation cooler V400 Turbocharger 1 control unit J724 Turbocharger 2 control unit J725 Injectors for cylinders 2, 3, 5, 8 N31, N32, N83, N86 Lambda probe heater 2 Z28 Intake manifold flap 2 motor V275 Glow period control unit 2 J703/ glow plugs for cylinders 2, 3, 5, 8 Q11, Q12, Q14, Q17 Exhaust gas recirculation control motor 2 V339 S467_017 Throttle valve module 2 J544 39
40 Service Special tools Designation Tool Application T40094 Camshaft fitting tool T40094/1 Mount T40094/2 Mount T40094/9 Mount T40094/10 Mount T40094/11 Cap T40094/12 Mount For removing and fitting the camshafts S467_062 T40095 Camshaft fitting tool For removing and fitting the camshafts S467_063 40
41 Designation Tool Application T40096 Camshaft fitting tool For fitting the camshafts S467_064 T40178 Oil gauge tester For checking the oil level when there are system errors S467_065 41
42 Test Yourself Which answers are correct? One or several of the given answers may be correct. 1. Which statement about the oil pump is correct? a) The oil pump works with only one pressure level. b) The oil pump can change its delivery characteristics via an eccentrically mounted adjustment ring. c) The oil pump generates up to 4 pressure levels depending on the load. 2. Which statement about the oil level and oil temperature sender G266 is correct? a) The sender operates according to the Hall principle. b) The sender uses the heat conduction method. c) The sender operates according to the ultrasound principle. 3. What is the advantage of the innovative thermal management system? a) The heat produced by the engine is distributed optimally among the components. b) The heat produced by the engine is always passed on first to the gearbox. c) The heat produced by the engine is always passed on first to the interior heating. 4. Where is the fuel pressure in the low pressure area of up to 6 bar regulated on the 4.2 l V8 TDI? a) In the high-pressure pump b) In the pre-supply pump c) In the fuel delivery unit 42
43 5. What is the purpose of camshaft spur gear backlash compensation? a) Backlash compensation ensures that the camshafts are driven with little noise. b) Backlash compensation ensures that the intake camshaft is adjusted at high engine speeds. c) Backlash compensation ensures rigid engine speed compensation between the gears on the intake and exhaust camshafts. 6. Which statement about the turbocharger with speed sender is correct? a) Lower torque and output values b) Speed reduction when there is a large speed difference between the two turbochargers c) Fixed turbine geometry Answers 1. b); 2. c); 3. a), b); 4. c); 5. a); 6. b) 43
44 467 VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights and rights to make technical alterations reserved Technical status Volkswagen AG After Sales Qualifizierung Service Training VSQ-1 Brieffach 1995 D Wolfsburg This paper was manufactured from pulp bleached without the use of chlorine.
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
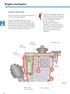 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service Training. Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 365
 Service Training Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 365 In 1999, the 3.3 l A8 (1994) was installed for the first time with a V8 TDI engine, followed in the new A8
Service Training Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 365 In 1999, the 3.3 l A8 (1994) was installed for the first time with a V8 TDI engine, followed in the new A8
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Service Training. Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System. Self-Study Programme 412
 Service Training Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System Self-Study Programme 412 In this booklet we explain to you the design and function of the 2.0 l 125 kw four-valve TDI engine, focussing
Service Training Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System Self-Study Programme 412 In this booklet we explain to you the design and function of the 2.0 l 125 kw four-valve TDI engine, focussing
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
Training Service. Self-Study Programme 522. The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw. Design and function
 Training Service Self-Study Programme 522 The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw Design and function We would like, in this self-study program, introduced the 2.0 TSI engine the 162 kw / 169 kilowatts
Training Service Self-Study Programme 522 The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw Design and function We would like, in this self-study program, introduced the 2.0 TSI engine the 162 kw / 169 kilowatts
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED
 SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
51. absolute pressure sensor
 51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Service. Self-Study Programme 248. The W Engine Concept. Design and Function
 Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty
 PRESS info P07901EN / Per-Erik Nordström 5 September 2007 Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty As the first heavy vehicle manufacturer, Scania achieves Euro
PRESS info P07901EN / Per-Erik Nordström 5 September 2007 Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty As the first heavy vehicle manufacturer, Scania achieves Euro
Workshop Manual. System Description & Operation
 Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Product Information. N57 Engine.
 Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant. After-Threatment
 EURO4-5 Common Rail EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant After-Threatment 1 Exhaust gas recirculation EGR fundamentals: AFR: Air to Fuel Ratio. This parameter is used to define the ratio between fuel (petrol,
EURO4-5 Common Rail EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant After-Threatment 1 Exhaust gas recirculation EGR fundamentals: AFR: Air to Fuel Ratio. This parameter is used to define the ratio between fuel (petrol,
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine. And how it works
 Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator
 Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
DASH RETRIEVED FAULT CODES C ONVENTIONAL FS65 SAF T LINER C2, C2E H YBRID SAF T LINER HDX, HD, ER SAF T LINER EF, EFX A LL Y EARS
 DASH RETRIEVED FAULT CODES C ONVENTIONAL FS65 SAF T LINER C2, C2E H YBRID SAF T LINER HD, HD, ER SAF T LINER EF, EF A LL Y EARS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK TABLE OF CONTENTS EARLY PRODUCTS: J1587/J1708
DASH RETRIEVED FAULT CODES C ONVENTIONAL FS65 SAF T LINER C2, C2E H YBRID SAF T LINER HD, HD, ER SAF T LINER EF, EF A LL Y EARS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK TABLE OF CONTENTS EARLY PRODUCTS: J1587/J1708
3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP(SEBP ) - Document Structure. Media Number -RENR Publication Date -01/02/2008 Date Updated -07/02/2008
 Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
6-speed automatic transmission 09D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Fuel control. The fuel injection system tasks. Starting fuel pump (FP)
 1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
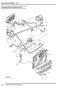 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install
 Page 1 of 46 Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install Remove 1. Open the bonnet. 2. Disconnect the battery. 3. Open the engine cover (1). 4. Detach the engine cover. 6 bolts (2) and (3) 5. Release
Page 1 of 46 Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install Remove 1. Open the bonnet. 2. Disconnect the battery. 3. Open the engine cover (1). 4. Detach the engine cover. 6 bolts (2) and (3) 5. Release
Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT
 A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment ,9 kw hp at rpm
 The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
Exhaust After-Treatment System. This information covers design and function of the Exhaust After-Treatment System (EATS) on the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 1.2007 258 44 1(6) Exhaust After-Treatment System Design and Function D16F Exhaust After-Treatment System W2005772
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 1.2007 258 44 1(6) Exhaust After-Treatment System Design and Function D16F Exhaust After-Treatment System W2005772
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment kw at 2100 rpm
 2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg
 Service Training Self-Study Programme 331 Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg Design and Function The running gear is a key component of the entire vehicle. It transmits all the forces acting between
Service Training Self-Study Programme 331 Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg Design and Function The running gear is a key component of the entire vehicle. It transmits all the forces acting between
Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry. 1 Introduction Preface Model-Building Simulation... 5 References...
 Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE
 16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
Rear Drive Axle and Differential
 Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA
 Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Engine Exhaust system. Engine. AMG exhaust system. The AMG sports exhaust system ends in two chrome-plated twin tailpipes bearing the AMG logo.
 113 - Exhaust system AMG exhaust system The AMG sports exhaust system in the SLK 55 AMG satisfies the US emissions limits and is perfectly tuned in terms of function and sound to the AMG 5.5 l V8 engine.
113 - Exhaust system AMG exhaust system The AMG sports exhaust system in the SLK 55 AMG satisfies the US emissions limits and is perfectly tuned in terms of function and sound to the AMG 5.5 l V8 engine.
VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION. Layout. EGR valve. Turbocharger actuator. Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump. Turbocharger vacuum modulator
 42 04 VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION Layout Turbocharger actuator EGR valve Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump Turbocharger vacuum modulator EGR vacuum modulator Vacuum Modulator for VGT Turbocharger Actuator
42 04 VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION Layout Turbocharger actuator EGR valve Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump Turbocharger vacuum modulator EGR vacuum modulator Vacuum Modulator for VGT Turbocharger Actuator
The Construction Equipment Engine kw hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 The Construction Equipment Engine 50 85 kw 67 114 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes ranging
The Construction Equipment Engine 50 85 kw 67 114 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes ranging
 Page 1 of 6 2008 Ford Pickup 6.4L Eng F250 Super Duty ENGINE CONTROLS - DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION - F250-F550 SUPER DUTY 6.4L (DIESEL ) FUEL SYSTEM The fuel system includes the following: low pressure
Page 1 of 6 2008 Ford Pickup 6.4L Eng F250 Super Duty ENGINE CONTROLS - DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION - F250-F550 SUPER DUTY 6.4L (DIESEL ) FUEL SYSTEM The fuel system includes the following: low pressure
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition
 Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM TURBOCHARGER TC 1
 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM TURBOCHARGER TC1 TC2 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM Description DESCRIPTION Systems which increase the amount of air sent to the engine are either turbocharger type (using exhaust gas to turn
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM TURBOCHARGER TC1 TC2 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM Description DESCRIPTION Systems which increase the amount of air sent to the engine are either turbocharger type (using exhaust gas to turn
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
A. Perform a vacuum gauge test to determine engine condition and performance.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
Technical Specification
 Technical Specification including performance data Project 3 x 9CM25 rev 2. consisting of 3 Caterpillar Diesel Generator sets Type 9CM25 with site output of: 2475 bkw at each engine flywheel rated 750
Technical Specification including performance data Project 3 x 9CM25 rev 2. consisting of 3 Caterpillar Diesel Generator sets Type 9CM25 with site output of: 2475 bkw at each engine flywheel rated 750
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Oregon Fuel Injection
 2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
FORD ECOSPORT SPECIFICATIONS
 FORD ECOSPORT SPECIFICATIONS PERFORMANCE AND ECONOMY 1.0-litre EcoBoost (5-speed manual) 1.5-litre Duratec Ti-VCT (6-speed automatic) 1.5-litre Duratorq TDCi (5-speed manual) Power (PS) CO 2 (g/km) Urban
FORD ECOSPORT SPECIFICATIONS PERFORMANCE AND ECONOMY 1.0-litre EcoBoost (5-speed manual) 1.5-litre Duratec Ti-VCT (6-speed automatic) 1.5-litre Duratorq TDCi (5-speed manual) Power (PS) CO 2 (g/km) Urban
Diesel Technology: Engines
 Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
