Training Service. Self-Study Programme 522. The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw. Design and function
|
|
|
- Joleen Ball
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Training Service Self-Study Programme 522 The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw Design and function
2 We would like, in this self-study program, introduced the 2.0 TSI engine the 162 kw / 169 kilowatts range EA888. This is the 3 e generation of this engine. The 2.0 TSI engine the 162 kw / 169 kilowatts, which already meets the requirements of the future EU6 emissions standard and is manufactured at the plant in Györ, Hungary. This engine is designed to be integrated in the modular transverse engine platform (MQB) and can therefore be used universally within the Volkswagen Group. s522_777 For more information on the petrol engines of 1.8 l and 2.0 l, 337 self-study programs see "The FSI engine of 2.0 liter turbocharging in" and 401 "Engine 1.8L TFSI V kilowatts." This Self-Study Programme presents the design and operation of innovations Recent techniques! Its content is not updated. For current instructions control, adjustment and repair, please refer to the documentation of Customer Service. Warning Note 2
3 At a glance Introduction Overview of technical data motor mechanics The cylinder block The moving equipment The chain drive The cylinder head 8 with switching of the valve stroke Recycling of crankcase gas and degassing the crankcase Circuit oil Overview of the oil supply The oil pump 22 to outer gear to two levels of regulation engageable piston cooling injectors Cooling system cooling system overview Innovative thermogestion thirty Air Supply and overeating Overview of the supercharging system The turbocharger feeding system Overview of the power system The packaging of the mixture engine management Overview of the system Service Special tools New component blocks Check your knowledge!
4 Introduction Key development targets for the development of the recent range of EA888 engines were fundamentally respect the EU6 emissions standard and the possibility of use of motors in modular transverse engine platform (MQB). Other development objectives were: - Reduction of CO 2 - Loss of engine weight - Decreasing friction inside the engine - Optimization of power and torque with respect to fuel consumption - Improved driving stability Overview of technical data s522_123 engine mechanics The development of the engine range 2.0 TSI is expressed in the following characteristics of the engine mechanical: - total weight gain of 7.8 kg - Cylinder head with integrated exhaust manifold - balancer shafts mounted on bearings - Journals smaller more with just four counterweights - Turbocharger with electrical actuation of the discharge valve flaps - reduced oil pressure level - separate oil sump portions (Aluminium top and bottom plastic) - Oil filter and oil cooler integrated in the support of auxiliary bodies 4
5 engine management The characteristics of the engine management engine range the 2.0 TSI are: - A timing variator shaft intake cam and exhaust - electronic switching of the valve stroke - double injection system with injectors TSI (Turbo Stratified Injection) and SRE (Saugrohreinspritzung) (combination of direct injection and multi-point injection) - Thermogestion with innovative regulation by rotary distributors (Engine temperature control actuator N493) - engageable piston cooling nozzles - adaptive lambda control - Mapping controlled ignition high voltage distribution - Intake manifold flaps - Regulating the oil pressure at two levels by oil pump external gear - Full electronic management engine with electric throttle SIMOS Power versions of 162 and 169 kilowatts are produced via engine management Technical characteristics Diagram of torque and power motor letters benchmark CHHB CHHA [Nm] [KW] Type Engine 4 cylinders in line 220 Displacement 1984 cm 3 bore Race 82.5 mm 92.8 mm Qty valves per cylinder Compression ratio 9.6: Maximum power 162 kilowatts to rev / 169 kilowatts to rev / 140 max torque min 350 Nm r / min min 350 Nm rev / min engine management SIMOS 18.1 Fuel Super unleaded 98 RON Aftertreatment of exhaust Trifunctional catalyst, oxygen gases sensor upstream wide band lambda probe voltage jumps downstream of the catalyst emissions standard Euro [Tr / min] s522_076 CHHB kilowatts CHHA kilowatts 5
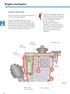
6 engine mechanics The cylinder block It was possible only at the level of the cylinder block to achieve a systematic overhaul of the architecture of the cylinder block, a weight gain of 2.4 kg over the previous model. The cylinder wall thickness was reduced by approx. 3.5 mm to approx. 3 mm. The crankcase oil coarse particle separation crankcase vent has been integrated into the cylinder block. Cylinder Block Cast gray Separation of coarse particles of oil thickness wall of the cylinder 3 mm sealing flange Part sump baffle with higher oil gear oil pump outside and to control the volumetric flow rate Insert Bee sump nest Gasket Bottom plastic oil pan s522_063 6
7 The moving equipment Measures taken on the moving described below have improved internal friction while reducing weight. the crankshaft The diameter of the pins was reduced from 52 mm to 48 mm. The number of counterweights from eight to four. The upper and lower half shells are bilayer execution and lead free. Weight gain at the crankshaft amounts to 1.6 kg. pistons The piston running clearance was enlarged to reduce friction during the engine warm-up phase. An additional carbon coating serves to reduce wear. The top piston ring is designed as segment of rectangular cross section, the central piston ring is a conical portion supported and the third piston ring a scraper ring spiral spring in two parts for scraping oil. rods The connecting rods are fractured. The connecting rod head is provided, such as pins, bilayer unleaded half shells. The bronze bushing in the connecting rod has been removed. Instead, the piston axes are equipped with a special surface coating of carbon. Bearing crankshaft bearing caps are screwed to the top of the oil sump. This results in an improvement of the motor mechanical properties in terms of acoustics and vibration resistance. piston pin with carbon coating Coated piston spiral spring scraper ring in two parts s522_108 connecting rod without bronze bushing carbon fractured connecting rod crankshaft 4 counterweights s522_005 s522_052 Half shell unleaded in the composition of the alloy Screwing the bearing caps the upper oil pan 7
8 engine mechanics The chain drive The fundamental design of the chain drive was taken from the previous model and perfected. As the engine oil needs are less important, the driving power of the chain drive could be reduced. The chain adjusters have been adapted to the reduced oil pressure. Exhaust camshaft with switching of the valve stroke Fuel pump high pressure Tree timing variator exhaust camshaft Tree timing variator Order intake cams by silent chain Chain tensioner Coolant pump drive by coolant pump belt drive chain oil pump balancer shaft with bearings oil pump external gear and to control the volumetric flow rate s522_007 8
9 One of the novelties of this engine is a control program for the diagnosis of chain elongation. The diagnosis elongation of the chain is used to detect an elongate command string in the engine. The chain elongation is detected using the camshaft sensors based on the relative displacement of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft. A check of the lengthening of the chain following a record in the log is done by visual inspection at the chain tensioner. If the offsets exceed many times a specific threshold camshaft, an entry in the log is generated. For the diagnostic functions properly once repaired, it must be updated after the following work on the engine: - Replacing the engine computer - Replacement of engine components neighbors command chain - Replacing the chain of command or the complete engine s522_109 2 rings visible = in fair condition chain chain tensioner with regard to diagnostic chain length 7 rings visible = replace the string s522_110 s522_124 Remember that the work steps for the assembly of the chain differ from the previous model. After working on the chain drive, proceed with the diagnostic drive to an adaptation of the elongation of the chain. To work on the chain drive, refer to the detailed instructions and notes provided in ELSA. 9
10 engine mechanics The balance shafts On balance shafts also, it was possible to gain weight over the previous model. The guiding in rotation of the balancer shafts is ensured in part by the bearings. This measure reduces the friction power of the balance shafts, particularly in the low operating temperature range and therefore of low oil temperature. silent chain Rolling balancer shaft Slide tensioner pad with threaded tensioner balancer shaft plain bearing intermediate gear Sprocket chain crank shaft s522_006 Slide There is a repair kit for repairing balance shafts. It consists of two balancer shafts and their bearings. Only the large central bearing may be replaced together with the balance shafts. Small rear bearings are mounted in the cylinder head and can not be replaced individually. 10
11 The cylinder head with switching of the valve stroke The cylinder head of the 2.0 TSI engine is a wholly new. The exhaust manifold is now integrated in the cylinder head, so that the cooling of the exhaust gas and guiding the exhaust gas is also carried out inside the cylinder head. Camshafts of intake and exhaust have a shaft of variable valve timing cam. The exhaust camshaft has an additional switching of the valve stroke, to open and / or close the valves in two different cam profiles. The coolant temperature sender G62 is screwed side box in the cylinder head. Positioned at the hottest point of the head, there can accurately record the thermal behavior and so avoids boiling coolant. Intake camshaft Tree timing variator cam continuous intake up to 60 crank angle stroke valve stroke switching Actuators fluid temperature transmitter G62 cooling Camshaft with exhaust switching valve the Exhaust manifold s522_008 breech casing Tree timing variator continuously exhaust cams of 33 to 34 crank angle valve stroke switching actuators are in the workshop documentation of the following designations: exhaust cam actuator A cylinder 1 N580, exhaust cam actuator cylinder 1 B N581, exhaust cam actuator cylinder A 2 N588, exhaust cam actuator cylinder 2 B N589, actuator A exhaust cam cylinder 3 N596, exhaust cam actuator cylinder B 3 N597, exhaust cam actuator A 4 cylinder N604, exhaust cam actuator B 4 cylinder N
12 engine mechanics The integrated exhaust manifold The temperature of the exhaust upstream of the compressor of the gas turbine is significantly reduced by the use of a turbocharger. Through the combination with a turbocharger high temperature resistant, it is possible, in particular at high speeds, to give a large part in a full-load enrichment to protect the turbine. This reduces fuel consumption and CO 2. Exhaust manifold s522_009 The exhaust channel are positioned such that the flow of exhaust gas from the cylinder occurs where the exhaust does not disturb the scanning of another cylinder. The full energy of the flow of exhaust gas is thus available for driving the turbocharger turbine. Another advantage of the integrated exhaust manifold lies in the more rapid warming of the coolant during engine warm-up phase. It is thus possible to switch to controlled cooling mode of the innovative thermogestion after a very short phase of rise in temperature. cooling channels As the lambda probe is mounted directly downstream of the integrated exhaust manifold, it also quickly reaches the optimum operating temperature. s522_080 12
13 The electrical switching of the valve stroke The electrical switching of the valve stroke on the camshaft exhaust ensures, in interaction with the variation of the timing camshaft intake and exhaust, an optimum control of the load change for each cylinder. The small cam profile is used only low speeds. The use of cam profiles is defined in a mapping. These measures: - Optimize the load change - To avoid rebreathing exhaust gas at the cylinder earlier in the exhaust phase (180 ) - Allow a higher fill rate with a time earlier admission opening - Reduce residual gas by a difference of positive pressure in the combustion chamber - Improve response - To achieve a higher torque at low revs and a higher boost pressure Exhaust camshaft Grand cam Small cam Roller rocker arm Exhaust valve Small valve stroke Piston Large valve stroke s522_118 13
14 engine mechanics Design To allow the passage from one to the other of the two different valve lift races, this camshaft has four sliding blocks multicames internal gear. Multicame Each block has two pairs of cams whose exercise is different. Switching between the two lifts is provided by electric actuators which engage in a sliding groove on each block and move multicame multicame block on the camshaft. Multicame each block and has two actuators for the passage of a lift to another. A ball calibrated spring in the camshaft helps stop multicames blocks in the limit position considered. Moving multicames blocks is limited by the sliding grooves and the axial bearings of the camshaft. Due to the double execution of the pairs of cams on a multicame block, the bearing surface of the roller rocker arms had to be reduced. multicames sliding blocks Exhaust camshaft external teeth s522_111 Attaching multicames blocks using a ball and a spring s522_082 The design and operation of the electrical switching of the valve stroke are similar to those of the active cylinder management (ACT). Consult about this Self-Study Programme 510 "Active management of the ACT cylinder TSI engine 1.4 l 103 kw". The balls and springs are available as spare parts. 14
15 The switching actuators of the valve stroke Multicame each block is moved in both directions between its two switching positions on the exhaust camshaft with two electrical actuators actuators (actuator shaft exhaust camshaft A / B cylinder 1-4 ). An actuator cylinder switches on the large valve lift, the second on the small valve stroke. The steering of each actuator is provided by the J623 engine computer via a ground signal. The power supply is provided by the main relay J271. The power consumption of the actuators is of the order of 3 A. Camshaft exhaust multicame Rod sliding block Repositioning ramp s522_084 Design Each actuator (actuator shaft cam A / B cylinder 1 to 4) consists of an electromagnet to repel down a metal rod housed in a guide tube. In the retracted position and the extended position, the metal rod is held in place by a permanent magnet located in the actuator housing. housing permanent magnet electromagnet guide tube Rod s522_079 15
16 engine mechanics Operation When the solenoid actuator is energized, the metal rod extends in the space of 18 to 22 milliseconds. The metal rod coming out then engages in the corresponding groove of the sliding block multicame on the exhaust cam shaft and the leads due to the rotation of the camshaft in the corresponding switching position. The withdrawal of the rod mechanically effected by the slide groove playing repositioning ramp role. magnet permanent The actuation of the two actuators of a multicame block is always performed so that the output of the metal rod takes place only on one of the two actuators. s522_128 rod return rod exit With repositioning of signals, the engine ECU can detect the instantaneous position of the metal rod. A reset signal is generated when the metal rod of an actuator is pushed into the guide tube to the actuator by the repositioning ramp. Next actuator delivering repositioning signals, engine management can draw conclusions about the current position of the slide unit considered. reset signal s522_129 Accordingly in case of failure The failure of an actuator enough for the valve stroke switching function can no longer be enforced. In this case, the engine management tries to switch all cylinders on the last valve stroke switching leading. If this is not feasible, all cylinders are switched to the small valve lift. The engine speed is then limited to r / min and recording takes place in the event memory. The EPC warning lamp lights up. A record in the event memory occurs even if the switch on the large valve lift can be performed. However, the scheme is not limited and the EPC warning light does not come on. 16
17 actuator rod Cam position in the lower rev range To improve the load change in the load range, the engine management moves the intake camshaft in the direction of advance and the exhaust cam shaft and towards the delay through the timing variator 'camshaft. The switching of the valve stroke comes on the exhaust cam. For this, the right actuator controls the output of the metal rod. It engages in the sliding groove and moves the multicame block toward multicame rocker pebble Gorge slide the small lift cam. Valve Block s522_085 The valves are rising and are now lower with the lower valve lift. The position slightly offset relative to the other of two small cams causes a slight shift of the opening times of the two exhaust valves of a cylinder. Both measures result, on the expulsion of exhaust gas turbocharger piston, by a lower pulsation of the exhaust stream, so that a higher boost pressure is reached at the lower rev range. The roller rocker arm moves on the small cam. Small valve stroke s522_086 17
18 engine mechanics Cam position in the range of partial load and full load actuator rod The driver accelerates and passes in the partial load range and the full load range. The cylinders of load change must then be adapted to the higher power requirement. The engine management moves the intake camshaft in the direction of advance and the exhaust camshaft in the direction of delay through the shaft of variable valve timing cam. For optimum filling of the cylinders, exhaust valves require the maximum stroke. The actuator is then driven left and takes out his metal rod. sliding groove block multicame Roller rocker arm Valve s522_087 The metal rod moves multicame block through the sliding groove toward the high cam. The exhaust valves open and now closed with the maximum stroke. In this position also, the multicames blocks are held in position by the balls tared spring in the camshaft. The roller rocker arm moves over a high cam. It is not intended for diagnosis of these actuators. Large valve stroke s522_088 18
19 The Crankcase gas and degassing the crankcase Recycling crankcase gases and degassing of the new TSI engines of 2.0 l were set for a higher pressure difference. This has a positive impact on the engine's oil consumption. To reduce the number of components required, designers have ensured that the guiding of the crankcase gases is effected as far as possible inside the engine. These engines require only one rigid pipe to convey the cleaned crankcase gases upstream of the turbocharger turbine. Recycling crankcase gas and degassing is constituted by: - The separation of coarse particles of oil in the cylinder block - A separator oil fine particles screwed into the cylinder head cover - The piping to ensure proper flow of purified crankcase gases only to the turbocharger - The return of oil in the cylinder block with check valve in the insert honeycomb oil pan - The pressure regulating valve designed for a pressure difference of -100 mbar compared with the outside air - The coupling of the carbon canister on the separator of fine oil particles Introduction of the crankcase gases into the intake manifold separation of fine oil particles Oil return Separation of crude oil particles s522_016 check valve in the pipe oil return 19
20 engine mechanics particle separation from crude oil The separation of coarse oil particles is an integral part of the cylinder block. crankcase gases through the separator of crude oil particles by changing direction several times. The relatively large size of the oil droplets are separated at the deflectors of the coarse particles of oil separator and returned to the oil sump via a return channel. The coarsely cleaned crankcase gases are guided through channels in the cylinder block and cylinder head in the direction of fine oil particle separator. Separation of coarse particles of oil in the crankcase Oil return s522_071 s522_125 20
21 The separation of fine oil particles The gases are routed through a channel in the crankcase to the separator of fine oil particles on the cylinder head cover. They cross at first a bypass valve before arriving in a cyclone separator. The bypass valve opens mechanically in case of excessive flow of crankcase gases at very high engine speeds to prevent damage to the joints. In the cyclone separator, the crankcase gases are rotated up to r / min. The finer oil droplets are then separated. They are redirected to the oil sump by a return channel in the cylinder block. At the end of the return channel, a check valve is located in the oil sump. It prevents oil from being sucked through the return channel in the oil separation in the case of unfavorable pressure conditions and high lateral accelerations. cleaned crankcase gases are guided downstream of the cyclone separator through a pressure control valve at one level. The pressure regulating valve is designed for a -100 bar pressure difference with the outside air. Depending on the pressure conditions prevailing in the charge air system, the introduction of cleaned crankcase gases takes place in the intake manifold (air mode) or in the turbocharger (boost mode). connector regulating valve pressure Bypass Valve Input gas housing in the separation of fine oil particles s522_017 Routing purified crankcase gases towards the turbocharger charcoal canister cyclone Oil return 21
22 Oil System Overview of the oil supply The following points were imperative in the development of the oil supply: - Regulation of the two levels to oil pressure - Reduction gear oil pump regulated low pressure - Reduction in oil pressure at low pressure - higher speed range at - Use of piston cooling nozzles with electrical engagement - Filter screwed oil and oil cooler on the auxiliary support members The support of ancillary units It is found on the support of attachments, in addition to the oil cooler and oil filter: - The pressure switch of F22 oil - The oil pressure switch to control the reduced pressure F378 - The control valve for N522 piston cooling nozzles - The automatic tensioner for multitrack belt drive ancillaries Oil pressure switch to control the F378 reduced pressure ( bar) F22 Oil pressure switch ( bar) N522 control valve for piston cooling nozzles Support of secondary units Oil pressure regulating valve N428 Oil pressure switch, level 3 F447 gear oil pump outside and to control the volumetric flow rate s522_018 The oil pressure switches F22, F378 and F447 must be replaced after loosening. 22
23 The oil pump external gear to two stages of regulation The gear pump was reduced compared to that of the oil pump of the previous engine, so that the pump runs slowly. The displacement of the sliding unit is carried out via a control piston and control channels within the oil pump. The training continues to be insured through a separate chain from the crankshaft. The control piston directs the oil flow from the left or right side of the sliding unit, which then moves longitudinally along the oil pressure. The sliding unit within the pump is characteristic of the oil pump external gear to two levels of regulation. It allows a reciprocal sliding of the two pump gears in the longitudinal direction and therefore the control of the pump power at two levels. When the two gears are the same height, the pump delivers the maximum power; when the two gears are offset relative to each other, the pump is handling with a reduced power. The regulating piston is driven by the N428 oil pressure control valve. Switching the low discharge level up discharge level applicable depending on the load and / or speed. Below this threshold, the pump is at a pressure of 1.5 bar. When the regime r / min is reached, the pump is at a pressure of 3.75 bar. Up to a mileage of 1000 km, the motor operates only at high pressure level. control channels Piston Training Sliding control unit pump housing Gear pump Nozzle inlet s522_020 The oil pump is essentially identical to the regulated oil pump range of EA211 engines. A detailed description of the design and operation of the oil pump external gear with two levels of regulation in the Self-Study Programme 511 "The new range of petrol engines EA211." 23
24 Oil System Electrical components for regulating the oil pressure The pressure switch of F22 oil F22 Oil pressure switch is screwed to the support of ancillary units, below the oil filter. Using the signal and function The engine management checks, among others, with this sensor if the oil pump delivers the high level of oil pressure. s522_045 Accordingly in case of failure If the oil pressure switch fails, a default is recorded in the event memory of the engine ECU and the oil warning light comes on. F22 Oil pressure switch Support of secondary units Oil pressure regulating valve N428 The switching valve is screwed beneath the support of secondary units to the front face of the cylinder block. Function and operation The switching valve is controlled by the engine computer for switching the gear oil pump outside a level of regulation to another. There is for this, depending on the switching state, applying an oil pressure on the regulating piston housed in the oil pump. The position of the regulating piston then carries out the switching pressure. Accordingly in case of failure When the valve fails, it is closed. The oil pump delivers the higher pressure level. s522_048 pressure regulating valve N428 of oil 24
25 piston cooling injectors engageable A cooling plunger heads is not necessary in all situations of The engagement of piston cooling nozzles can take place at higher pressure level as the lower level of pressure of the oil circuit. A engine operation. This is why the TSI engines of 2.0 l of this range are equipped with engageable piston cooling nozzles. contactor of additional oil pressure, oil pressure switch, level 3 F447, registers the oil pressure in the additional oil gallery and to monitor the operation of cooling the piston. The control valve for N522 piston cooling nozzles is controlled based on a mapping. A mechanical switching valve opens at a higher than 0.9 bar oil pressure. The control valve and the switching valve are mounted in the support and auxiliary bodies connected by a control channel. The oil pressure switch closes to an oil pressure between 0.3 and 0.6 bar. Oil pressure switch for control reduced pressure F378 Feeding the oil gallery and the piston cooling nozzles control valve for cooling injectors of N522 piston control channel s522_021 switching valve mechanical 25
26 Oil System The activation of piston cooling nozzles control strategy The steering control valve is performed by the engine computer using a mapping. To calculate the mapping, engine calculator uses engine torque, engine speed and temperature of the oil. At a temperature of the oil below 50 C, the piston cooling nozzles remain inactivated in a mapping range between 1000 and 6600 rev / min and a load of approx. 30 Nm. At a temperature of oil of greater than 50 C, the piston cooling nozzles remain inactivated in a engine speed range between 1000 and 3000 rev / min and a load range between 30 and 100 Nm. the injectors are disabled in all the other beaches in the mapping. piston cooling off (Oil temperature <50 C) off piston cooling s522_113 (Oil temperature> 50 C) Monitoring the operation of piston cooling nozzles The oil pressure switch, level 3 F447 and the ability to diagnose control valve N522 for piston cooling nozzles, to monitor the correct operation of piston cooling nozzles and ensure adequate cooling of the pistons. Defects can be recognized: Impact without piston cooling: - No pressure oil in the piston cooling nozzles despite the request - Couple and limited diet - Absence of low oil pressure range - Oil pressure switch, level 3 defective F447 - Witness EPC lit in the instrument cluster - Message that the regime is limited to r / min - oil pressure despite the presence of the cut-off piston cooling nozzles - cable cut = piston cooling nozzles permanently activated - Short circuit to ground = piston cooling nozzles disabled - Short circuit to positive = piston cooling nozzles activated 26
27 activated piston cooling nozzles F447 N522 closed oil gallery with injectors piston cooling mechanical switching valve Spring s522_090 In the absence of current, the control valve for N522 piston cooling nozzles is closed. Therefore, the control channel between the control valve and the switching valve is also closed. There then applying an oil pressure to one side of the switching valve, which is moved by overcoming the force exerted by a return spring until the channel in the direction of the piston cooling nozzles is released. The oil reaches the switching valve in the additional oil gallery and from there to the piston cooling nozzles. The injectors are then engaged. The engine computer recognizes from the oil pressure switch signal, level 3 F447, the piston cooling nozzles are activated. disabled piston cooling nozzles F447 oil gallery with injectors To disable the piston cooling nozzles, the pilot motor of the calculator control valve for cooling injectors N522 piston. piston cooling In the switched state, the control valve for piston cooling N522 injectors releases the control channel direction of the switching valve. An oil pressure is now applied to both sides of the switching valve. The force exerted by the return spring when the wins and the switching valve is pushed. open N522 control channel mechanical switching valve Spring s522_089 The connecting channel with the oil gallery is interrupted and the piston cooling injectors are disabled. The engine computer recognizes from the oil pressure switch signal, level 3 F447, the piston cooling nozzles are disabled. 27
28 Oil System The electrical components of the piston cooling The oil pressure switch, level 3 F447 The oil pressure switch, level 3 F447 is screwed to the crankcase, below the intake manifold. Using the signal and function The oil pressure switch monitors oil pressure in the oil gallery which feeds the piston cooling nozzles. The signal from the oil pressure switch, level 3 F447 allows the engine management to determine the presence of a malfunction of the piston cooling nozzles, such as lack of oil pressure in spite of an activated oil pressure switch, Level 3 F447 s522_046 piston cooling or for oil pressure despite a disabled piston cooling. Accordingly in case of failure The oil pressure switch is suitable for diagnosis. In case of failure of the sensor signal, the piston cooling remains activated. The oil pressure switch to control the reduced pressure F378 The oil pressure switch is also screwed to the support of ancillary units, below the oil filter. Using the signal and function Via the oil pressure switch for control of the F378 reduced pressure, the engine management system monitors the pump pressure regulating oil external gear at two levels. s522_127 Accordingly in case of failure Without the signal of the oil pressure switch for monitoring the reduced pressure F378, regulation at two levels of the oil pressure is not possible. When the oil pressure switch fails, a default is recorded in the event memory and the oil warning light comes on. The oil pump stops working at higher pressure level. Support of secondary units Oil pressure switch for pressure control reduced F378 28
29 Cooling system Cooling System Overview Cooling systems depend on the operator and the equipment of a vehicle. We have therefore shown here an example of a simplified cooling circuit corresponding to an equipment without dual-clutch gearbox, to illustrate the cooling system of the basic structure. Main characteristics of the cooling circuit, in particular as regards the innovative thermogestion are integrated exhaust manifold into the cylinder head and a new rotary distributors module. 3 N422 V51 2 G62 N493 N V7 V177 7 G83 1 Legend s522_022 G62 coolant temperature sender G83 V51 recirculation pump V177 coolant coolant temperature transmitter N82 radiator outlet 2 fan radiator 1 heat exchanger heating 2 liquid cutoff valve N422 cooling liquid cutoff valve Climatronic cooling N493 transmission oil cooler (optional) 3 Expansion tank 4 rotary distributors module with coolant pump 5 V7 engine temperature control actuator gas turbocharger exhaust 6 Radiator fan Oil radiator 7 Radiator water main 29
30 Cooling system The innovative thermogestion The innovative thermogestion (ITM - Innovative thermal management) is a smart program cold start and engine warm-up and the gearbox. It allows variable control of the engine temperature by targeted control of the coolant flow. The centerpiece is the engine temperature control actuator N493 (rotary distributors module). It is screwed to the motor housing inlet side below the cylinder head. temperature control of the actuator motor N493 with coolant pump Pinion for driving the coolant pump toothed belt fixing screw left hand thread Pinion drive on the balancer shaft s522_025 Cache of the toothed belt drive When replacing the rotary distributors module or the water pump, please consider the repair manual. thirty
31 The engine temperature control actuator (Rotary distributor module). It contains: - The coolant pump - Two rotary distributors - a thermostat - The N493 engine temperature regulating actuator for regulating coolant flow - A gear with angle of rotation sensor The drive of the coolant pump is provided from the balance shaft by a toothed belt. Design The main characteristic of rotary distributors module consists of two rotary distributors elements housed within the module, electrically The rotary distributor 2 is moved via an intermediate gear (time in teeth) by a toothed slides on the rotating distributor 1. actuated by the control actuator N493 engine temperature. The rotary valve 1 is directly driven via a shaft by N493 engine temperature control actuator. Rotary distributors 1 and 2 are thus mechanically coupled and move in relation to each other. An additional thermostat wax plug serves as a safety device (thermostat for degraded mode) and opens in case of failure at 113 C. rotary distributors module housing rotary distributor 2 Drive the coolant pump control actuator engine temperature N493 coolant pump Gear with sensor rotation angle drive shaft rotary distributor 1 Thermostat degraded mode s522_024 31
32 Cooling system Operation of rotary distributors module The electric motor of the actuator causes the rotary valve 1 via a gear. It controls the coolant flow between the oil cooler, engine and main water radiator. More heat from the engine increases, the rotary feeder 1 is rotated by the electric motor of the actuator. A rotation angle sensor (Hall sender) mounted on the control board communicates the positions of the rotary distributor to the engine computer. After stopping the engine and the end of the recirculation phase, the rotary distributor is set on an angular position of 40. In case of failure in the system, it is possible, in this angular range, performing an engine start via the thermostat for degraded mode. If the engine is started in the presence of a defect, the rotary distributor is set The rotary valve 2 is driven via an intermediate gear via a toothed to the angular position of 160. slides on the rotating distributor 1. connecting pipe for supply to the radiator Manifold for Engine radiator connection Electric motor Drive shaft Distributor rotary 2 Control board with angle sensor rotation gearing intermediate gear toothed slides Housing rotary distributor 1 Thermostat degraded mode s522_091 connecting tubing the return of the radiator 32
33 The actuator control is performed by the motor computer using maps. Targeted control of rotary distributors can achieve different switching positions for quick heat-up phase and to keep the engine at a variable temperature between 86 C and 107 C. It is possible to distinguish between three basic control ranges: - A temperature rise range - A temperature control range - A recirculation beach The toothed slides over the rotary valve 1 is designed so that the rotary distributor 2 mates with the angular position of 145. The coolant flows to the cylinder head is open and increases with the rotation of the rotary distributor 2. At an angle of 85 on the rotary feeder 1, the rotary valve 2 is disengaged after reaching its maximum angle of rotation and to have fully open the coolant flows to the cylinder block. The temperature rise range is in turn divided into three control phases. adjustment angle Rise in temperature regulation and 160 total Recirculation of 95 total temperature control range partial load and full rise beach temperature Beach recirculation charge Activation of the oil cooler engine minimum flow rate Liquid of stagnant cooling s522_107 The course of the control starting with the temperature rise range, continuing with the temperature control range and ending with the recirculation phase is described by way of example the following pages. A very simplified representation of rotary distributors module and the engine cooling circuit is used for this purpose. The electric drive of the two rotary distributors Rotary distributors module and toothed belt drive of the coolant pump are not considered in this form of representation. 33
34 Cooling system Flow regulation During the temperature rise, the engine passes through the three phases: - stagnant coolant - minimum flow rate - Enabling the engine oil cooler The different phases differ in the positions of the two rotary distributors and succeed each other continuously. The objective is optimal exploitation of the heat generated by the combustion of fuel in the cylinders for the engine warm. Then it is already possible, from the "stagnant coolant" phase, to provide thermal energy to the passenger compartment in a biasing of the heating by the vehicle occupants. Turbocharger exhaust gas check valves exhaust manifold Heat exchanger heating and air conditioning Cylinder Block gradient to integrated recirculating pump V51 Coolant Oil Cooler Coolant shutoff valve N422 of the Climatronic rotary distributor 2 rotary distributor 1 Thermostat for fashion Cylinder coolant pump rotary distributors module Radiator water main s522_092 34
35 Rise in temperature with liquid stagnant cooling To keep the heat generated by the combustion in the engine, the rotary valve 2 is closed. The flow outlet of the coolant pump is thus interrupted. The rotary distributor 1 blocks the return of the engine oil cooler and the return of the main water radiator. Engine block V51 The cut-off valve of the N422 Climatronic coolant stops the coolant flow to the heater and air conditioner. The electric recirculation pump V51 coolant is cut. N422 rotary distributor 2 1 rotary distributor s522_092 Radiator water main Turbocharger exhaust gas Temperature rise with volume flow minimal This allows regulation phase in the temperature rise range, to protect the head and the turbocharger overheating due to the exhaust manifold in the case of stagnant coolant. When the angular position of the rotary valve 1 is 145, the rotary distributor 2 mates and begins to slightly open the coolant flow to the cylinder block. A small amount of coolant through the cylinder head and now the turbocharger and is then redirected to the rotary distributor module to the coolant pump. This avoids heat accumulation and overheating of the cylinder head and turbocharger. rotary distributor 2 1 rotary distributor s522_093 35
36 Cooling system Temperature rise with volume flow minimum and biasing the heating If a request from the heating takes place in this phase, the N422 exchanger Heat from the heater Climatronic coolant shut-off valve V51 is opened and the coolant recirculation pump begins to convey. The rotary distributor 2 pauses the coolant flows to the cylinder block. The coolant then passes through the cylinder head, the turbocompressor and heat exchanger of the heating. Engine temperature up phase is prolonged. Engine block V51 Even in the following control ranges, solicitation heating is always accompanied by a steering the coolant shut-off valve of the Climatronic N422 and pump for recirculating the coolant V51. N422 The coolant flows to the engine block was then, as required, reduced rotary distributor 2 or blocked by the rotary distributor 2. s522_094 Rise in temperature radiator with engine switched During the further course of the temperature rise phase, the engine oil cooler is activated in turn. For this, the rotary distributor is brought to an angular position of 120, releasing the coolant connection from the oil cooler. As the rotary valve 2 is always coupled, it also continues to rotate and increases the coolant flow through the cylinder block. There is thus a strong heat distribution in the engine block and the excess heat is removed via the oil cooler. Engine block Oil radiator tor rotary distributor 2 1 rotary distributor s522_095 36
37 the temperature control range The temperature rise range, the innovative thermogestion passes without transition to the temperature control range. Again, regulation of rotary distributors module is performed dynamically as a function of the engine load. To vent excess heat, driving towards the main water heater is released by the rotary distributors module. N493 The engine temperature control actuator then causes the rotary valve 1 to an angular position between 0 and 85 according to the importance of heat to be removed. At an angular position of the rotary distributor 1 of 0, the line to the main water heater is fully open. rotary distributor 2 rotary distributor 1 s522_096 Radiator water main If the engine runs with low stress load and speed (partial load range), the rule thermogestion the coolant temperature to 107 C. The total power of the radiator is not required, the rotary valve 1 closes temporarily driving towards the main water radiator. If the temperature exceeds this threshold, driving with the main water heater is reopened. It follows a succession of opening and closing to maintain the temperature of 107 C as constant as possible. When the load and speed increase, coolant temperature is lowered to 85 C (full load range) for complete opening of the pipe with the main water radiator. rotary distributor 2 1 rotary distributor s522_102 Radiator water main 37
38 Cooling system recirculation beach after engine shutdown To prevent boiling of coolant in the cylinder head and the turbocharger after the engine is stopped, the engine ECU starts a cartographic recirculation function. This function can be activated for up to 15 minutes after switching off the engine. For the recirculation function, the rotary valve 1 is supplied by the engine temperature control actuator N493 at an angular position between 160 and 255. V51 More recirculation load, the higher the angular position is high. At 255, the connection of the return of the main water heater is fully open and a maximum heat is evacuated. N422 Position in recirculation, the rotary distributor 2 is not coupled to the rotary distributor 1. Delivered by the pump recirculation V51 coolant, the coolant then flows into two partial flows in the cooling circuit. s522_106 Radiator water main rotary distributor 2 rotary distributor 1 A partial flow is rerouted via the cylinder head towards the recirculation pump of the V51 engine coolant. A second partial flow flows through the turbocharger by the rotary valve 1 toward the main water heater and also returns to the recirculation pump of the V51 engine coolant. Position in recirculation, the cylinder block is not crossed by the cooling fluid. 38
39 Strategy in degraded mode If the temperature in the rotary distributors module exceeds 113 C, the thermostat for degraded mode opens a bypass towards the main water radiator. Due to this measure in the construction, continued operation of the vehicle in case of default of the rotary distributors module is only possible with restrictions. If the engine computer receives no feedback signal of position of the temperature control actuator N493 motor, it controls the rotary distributor to ensure maximum cooling of the engine, independently of the load and temperature of the momentary engine. V51 N422 Other measures in the event of malfunction of rotary distributors module, for example in case of failure of the electric motor or gear jammed rotary distributor are: Thermostat degraded mode s522_097 rotary distributor 2 rotary distributor 1 - Display an error message in the porteinstruments, accompanied by a limitation of the regime to r / min. An acoustic alarm and ignition of the EPC witness also attract the driver's attention on the situation. In case of failure of the position signal of the rotational angle sensor, the motor driver calculator, as a precaution, the rotary distributors to select the maximum cooling function. - Digital display of the actual temperature of the coolant C in the porteinstruments - Opening of the coolant shutoff valve N422 - Activation of the recirculation pump of the V51 cooling liquid for the maintenance of the cylinder head cooling - Registering an event in the event memory of the engine ECU TSI engines of 2.0 l 162/169 kw DSG dual clutch If the engine is associated with a dual-clutch shift gearbox, the cooling circuit is expanded by the radiator transmission oil, the cutoff valve N82 coolant and an additional heater. The various steps of the regulation of thermogestion are identical to those motors without DSG dual clutch. s522_101 additional radiator cut the N82 coolant valve Radiator transmission oil 39
40 air and boost supply Overview of the supercharging system B C AT D E V465 N249 F N316 G31 G336 G GX3 GX9 s522_034 legend GX9 Intake manifold with transmitter: G31 G71 Boost pressure transmitter G42 Air temperature transmitter admission of tubing pressure transmitter inlet N249 air recirculation valve N316 Turbocharger V465 with intake manifold flap valve Boost pressure actuator A exhaust flow B Turbocharger exhaust gas C. Air filter D GX3 G186 throttle control unit with: throttle drive (Electric throttle control) G187 angle transmitter 1 of the throttle drive (electric throttle control) G188 Angle transmitter 2 of the throttle drive (electric throttle control) G336 Potentiometer of J338 Intake manifold flap throttle control unit fresh air flow E wastegate flap F Charge Air Cooler G Intake manifold flaps exhaust Air intake (depression) Air Boost (Boost pressure) Recirculation deceleration (Boost pressure) 40
41 the turbocharger A recent design turbocharger with electric actuator pressure turbocharging, team new TSI engines of 2.0 l. It is screwed directly to the exhaust manifold integrated in the cylinder head. Other features of the new turbocharger are: - Electric adjustment of the relief valve with boost pressure actuator V465 and the position transmitter of the boost pressure actuator G581 - lambda probe GX10 (with lambda probe G39 and lambda probe heater Z19) upstream of the turbocharger - Cast steel turbine housing compact dual stream execution - compressor housing with integrated resonator and muffler air recirculation valve N249 Turbocharger - steel turbine wheel special alloy resistant to temperatures up to 980 C - Housing bearing with standardized connections for the oil and the coolant s522_037 41
42 air and boost supply Design Housing and turbine wheel turbine compressor housing and wheel compressor To achieve resistance to high temperature of 980 C, the turbine housing is made of cast steel of a new type. The guide by dual channel flow of the exhaust outlet of the exhaust manifold gas is retained in the turbocharger until shortly before the turbine. The compressor housing is made of cast aluminum. It was strengthened due to high actuating forces exerted by the boost pressure actuator. A muffler resonator is located directly on the compressor casing. The air recirculation valve N249 of the turbocharger controls the air flow towards the resonator silencer. This results in optimum separation of the ignition sequence. The power boost of the turbine has been improved in the range of high speeds in particular. The connecting flange for introduction of crankcase venting gas is integrated in the compressor casing. Lambda probe GX10 Lambda probe GX10 is a broadband probe. It is directly screwed to the connecting flange of the turbocharger to the cylinder head. With this close arrangement of the engine, the sensor acquires the exhaust gas of each cylinder individually. This allows a much earlier end of the dew point and thus rapid validation of the lambda control, approx. 6 seconds after the engine starts. lambda probe GX10 Compressor housing V465 boost pressure actuator turbine housing Linkage air recirculation valve N249 Turbocharger discharge valve flap wheel Turbine resonator quiet compressor s522_036 42
43 The boost pressure actuator V465 The supercharge pressure actuator V465, actuating the turbocharger wastegate flap is assured by an electric motor and a gear which moves the push rod towards the discharge valve flap. The electric motor drive enables rapid and precise regulation of the boost pressure and in addition provides the following benefits: - The opening of the discharge valve flap during the heating of the - Piloting the discharge valve is made possible regardless of the applied boost pressure. catalyst results in a temperature of the exhaust gas of 10 C higher upstream of the catalyst. - The high holding force of the discharge valve component helps This helps lower emissions during the cold start. achieve a maximum torque of 350 Nm at an engine speed of 1500 rev / min. - The high setting speed of the boost pressure actuator results in immediate removal of the boost pressure during changes in load - The opening of the discharge valve flap in the partial load and deceleration. range lowers the basic boost pressure. It follows a reduction in emissions CO 2 of the order of 1.2 g / km. Drive with electric motor and reducer Linkage to discharge valve flap Position transmitter of the pressure actuator suralimenta- G581 tion housing cover with control board and position transmitter s522_126 The position transmitter of the supercharging pressure actuator G581 The boost pressure actuator G581 position sensor is a Hall sensor, which is integrated into the housing of the supercharging pressure actuator. A magnet support with two permanent magnets is connected to the mechanical box. They perform the same longitudinal displacement of the push rod. The displacement of the magnets is recorded by the Hall sensor and transmitted to the engine ECU. The engine computer thus records the position of the discharge valve flap. The boost pressure actuator V465 can not be replaced individually. For more information on the resonator silencer, see Self-Study Programme 401 "Engine 1.8L TFSI V kilowatts." 43
44 Fuel System Overview of the power system G410 D N532-N535 N276 C G247 E N30-N33 AT B G6 J538 s522_040 Legend G6 fuel pump (frontloading pump) G247 AT Fuel filter B G410 Fuel Pressure Transmitter fuel tank C Fuel pressure transmitter, low pressure J538 high pressure fuel pump D fuel pump calculator N276 fuel pressure control valve N30- N33 low-pressure fuel rail E Rail high-pressure fuel Injectors for cylinders 1-4 N535 high pressure fuel system / low pressure N532- Injectors 2 Cylinder 1-4 system actuator / sensor output / input signal 44
45 The conditioning of the mixture The new TSI engines of 2.0 l have a double injection system. This means that the conditioning of the mixture can be done in two different ways. One of them is injected directly into the cylinder with the IST high-pressure injection system and the other to use as injection system multipoint injection (SRE). (SRE = Saugrohreinspritzung - multipoint injection). The use of multipoint injection has greatly reduced emissions of fine soot particles. Other objectives of the development of dual injection system are: - Increasing the pressure in the high pressure system of 150 to 200 bar - Achievement of limit values for particulate emissions from the new EU6 standard for particulate mass and particle number - Reduction of CO 2 - Reduced consumption in the partial load range - Intervention with a multipoint injection system - Improved engine acoustics multipoint injection SRE in the intake manifold fuel pressure transmitter, low pressure G410 s522_041 control shaft high pressure injection system directly in the cylinder head intake manifold flap snap The intake manifold intake of the control shaft tubing flaps are made trough-shaped. This form reduces the vibrational excitation of the shutters by the airflow. Flap position is detected by the G336 intake manifold flap potentiometer. Actuation of the drive shaft is assured by the N316 intake manifold flap valve. The switching points are stored in a map, depending on the torque and speed. 45
46 Fuel System The SRE multipoint injection system The feeding of SRE injection system is provided by flushing of connection on the high pressure fuel pump. The scan connection is part of the low pressure feed system. Scanning fitting, fuel flows to the low pressure fuel rail, and thence to the SRE injectors which inject fuel into the intake manifold. With the low pressure transmitter G410 fuel, SRE injection system has its own pressure sensor to the fuel supply monitoring. The discharge of the fuel takes place only via the fuel pump (frontloading pump) G6 in the fuel tank, not via the high pressure fuel pump. The use of scanning coupling of the high pressure fuel pump for supplying the fuel provides the scanning and therefore the cooling of the high pressure fuel pump even SRE mode. In SRE mode, the discharge of the high pressure pump can be reduced via the pressure regulating valve N276 Fuel. SRE injector s522_043 The multipoint injection is mainly used in the partial load range. Fuel droplets can sufficient time to be gasified and mixed with air. fuel packaging long before the inflammation leads: - A reduction in the mass of particles and soot formation - A reduction in CO 2 - A decrease in fuel consumption The high injection system pressure The higher fuel pressure up to 200 bar required adaptation of the design of the high-pressure supply system. High pressure injectors were acoustically decoupled from the cylinder head through the use of sealing washers. The position of the injectors has been slightly postponed. This improved the packaging of the mixture and reduce the thermal stress of the injectors. The high-pressure fuel rail was decoupled acoustically from the intake s522_042 manifold. 46
47 Operating Modes The control concept for executing the operation modes has been standardized using a mapping. The mapping determines if and when the engine can be operated SRE mode and when it can operate in high pressure mode. It distinguishes between the following operating modes: - Single injection SRE - single high-pressure injection - Double high-pressure injection - Triple high-pressure injection The engine switches between different operating modes depending on the temperature, the load and the engine speed. Starting the engine Motor operating in full load range In cold engine and a temperature of the coolant below 45 C and at each engine start, a triple direct injection takes place during the compression stroke through the high pressure injection system. Because of the high power requirement, the system returns to high pressure mode. A double direct injection takes place during the intake and compression time. temperature and catalyst heating climb degraded mode operation In case of failure of one of the two injection systems, the engine is During this phase, a double direct injection takes place during the intake and compression time. The ignition point is shifted slightly towards the "delay". intake manifold flaps are closed. driven only with the remaining system by the engine computer. The vehicle thus remains operational. The red light engine in the instrument cluster lights up. Motor operating in partial load range When the motor temperature exceeds 45 C and the engine operates in the partial load range, there SRE switching mode. Intake manifold flaps remain largely closed. To eliminate the pressure in the injection system, the engine must be running and the connector on the N276 Fuel pressure regulating valve must be disconnected. A residual pressure of the fuel pump (frontloading pump) G6 remains. Information given indications in ELSA! 47
48 engine management Overview of the system sensors throttle control unit J338 angle transmitter 1 & 2 of the drive (Electric throttle control) G187, clutch position transmitter Brake light F Contactor clutch pedal F36 Clutch pedal switch for Position transmitter throttle engine start F194 Transmitter 2 of throttle position Knock sensor 1 G61 butterfly G188 G476 G79 G185 Fault Indicator Power accelerator Witness cleanup K83 K132 Fuel pressure transmitter, low pressure G410 Transmitter Hall G40, transmitter fluid temperature transmitter cooling G62 Hall 3 G300 coolant temperature transmitter radiator outlet G83 Calculator in the instrument cluster J285 Engine speed sender G28 Level transmitter and temperature Potentiometer manifold flap tubing pressure transmitter Air temperature transmitter Fuel Pressure Transmitter G247 inlet G336 oil G266 inlet G71 inlet G42 Boost pressure transmitter Lambda probe G39 G31 engine calculator J623 lambda sensor downstream of the catalyst G130 Oil pressure switch F22 Oil pressure switch for control Oil pressure switch, level 3 F447 of the reduced pressure F378 indicator of level transmitter Transmitter 2 level indicator driving program button E598 device button start / stop setting fuel G fuel G614 Eve E693 Position transmitter of the pressure actuator overeating G581 Input signals additional Transmitter neutral box speeds G701 48
49 actuators control valve for piston cooling nozzles N522 DSG dual clutch mechatronic Ignition Coils 1-4 with power output stage N70, N127, N291, N292 J743 butterfly drive (throttle control electric) G186 Computer board network J519 2 cylinder injector 1-4 N cylinder injectors 1-4 N30-33 Coolant cutoff valve N82 Diagnostic interface the data bus J533 air recirculation valve Turbocharger N249 Valve of the intake manifold flap N316 cut-off valve of the Climatronic coolant N422 coolant recirculation pump V51 Variable valve solenoid 1 N205 1 solenoid valve variable valve in the exhaust N318 cooling pump of the supercharging air V188 fuel metering valve N290 oil pressure regulating valve N428 fuel pressure control valve N276 exhaust cam actuator A / B for cylinders 1-4 N580, N581, N588, N589, N596, N597, N604, N605 fuel pump calculator J538 fuel pump (pump frontloading) G6 engine temperature control actuator N493 lambda probe heater Z19 Heating of the lambda probe 1, downstream of the catalyst Z29 Boost pressure actuator V465 Calculator radiator fan J293 Radiator fan V7 2 radiator fan V177 s522_077 Additional output signals Solenoid 1 carbon canister N80 49
50 Service special tools Designation Tool use T10133 / 16A Removal tool Dismantling of high pressure injectors. This tool replaces the old removal tool T10133 / 16 s522_112 T10133 / 18 socket Dismantling of high-pressure injectors s522_056 T The sink Installation tool crankshaft tensioner s522_057 T40267 wedging tool crankshaft tensioner blocking command string s522_058 T40274 Hook extraction Removing the ring seal crankshaft s522_059 T40270 Socket XZN 12 Removing and installing the supports of the motor-box s522_060 50
51 Designation Tool use T40191 / 1 spacers Illustration: W Installation of the ball on the exhaust camshaft with scenes s522_117 T40266 Adapter To rotate the camshafts s522_073 T40271 Restraint system Blocking sprockets on the camshafts s522_061 51
52 Service New blocks of components The development of electronic components used to group various sensors and actuators block components. The following table provides information on the new designations of the blocks and the sensors and actuators that make them. Block components Module GX2 accelerator throttle control unit GX3 Sensors and actuators in part position transmitter of the G79 and accelerator transmitter 2 of throttle position G185 throttle control unit J338, driving the throttle valve electrically controlled G186, angle transmitter 1 of the drive of the throttle valve (electric throttle control) G187 and angle transmitter 2 of the drive of the butterfly ( electric throttle control) G188 Lambda probe 1 downstream of the catalyst GX7 lambda sensor downstream of the catalyst and G130 Heating Lambda probe 1 downstream of the catalyst Z29 Intake manifold transmitter GX9 Intake manifold pressure sender G71 and intake air temperature sender G42 lambda probe 1 upstream of the catalyst GX10 Instrument cluster KX2 Radiator fan VX57 lambda probe G39 and lambda probe heater Z19 Calculator in the J285-door instruments radiator fan J293 calculator, radiator fan V7 and V177 Radiator fan 2 Command module in the console EX23 driving program button E598 and device button start / stop standby E693 52
53 Check your knowledge! What are the correct answers? Among answers indicated, there may be one or more correct answers. 1. The valve of electric discharge allows... a) higher clamping forces. b) temperatures higher exhaust gas upon heating of the catalyst. c) removing the supercharging pressure in case of load changes. 2. What are the important points about the rotary distributors module? a) It regulates the coolant flows to the heat exchanger heating. b) temperature control actuator also includes a thermostat which opens when emergency. c) screwing the drive gear on the balancer shaft has a left-hand thread. 3. piston cooling injectors are... a) mechanically controlled in the case of high oil pressure level. b) controlled by the oil pressure switch, level 3 F447. c) controlled via a control valve on the support of auxiliary bodies. 4. In air mode of the engine, the crankcase gases are... a) moved upstream of the turbocharger. b) fed into the intake manifold. c) re-routed to the engine housing via the separator of fine oil particles. 53
54 Check your knowledge! 5. What is the advantage of switching the valve stroke? a) The load change is optimized for high speeds. b) The re-suction of the exhaust gas cylinder on the previously exhaust stroke is avoided. c) Residual gases are reduced by a positive pressure difference in the combustion chamber. 6. Which statements concerning dual injection system is accurate? a) In the case of multipoint injection and direct injection, a higher power is available. b) During multipoint injection, the fuel droplets have more time to gasify. c) mode of multipoint injection, double injection is also possible to reduce the mass of particles. 7. What are the important points about the command chain? a) There is a diagnosis of elongation of the chain. b) The extension of the chain is recognized by the rings on the chain tensioner. c) A diagnostic chain extender should be performed after the removal and installation of the cylinder head. R é p o not se s : 1. at), b ) c ); 2. b ), c ); 3. c ); 4. b ); 5. b ), c ); 6. b ); 7. at), b ), c ) 54
55 55
56 522 VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights and technical changes reserved Last updated 08/2013 Volkswagen AG Qualification After-sales Service Training VSQ-2 Brieffach 1995 D Wolfsburg This paper is made from bleached without chlorine.
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Section 10 Chapter 7
 Section 10 Chapter 7 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Troubleshooting Symptoms Identification Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have
Section 10 Chapter 7 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Troubleshooting Symptoms Identification Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Diesel Technology: Engines
 Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel
 Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED
 Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED 185HP & MASSIVE TORQUE iame41-1.doc 29Mar03 Page 1 of 2 Another Sea-Doo watercraft first and only. Introducing the 185hp, GTX 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED PWC. The 4-TEC
Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED 185HP & MASSIVE TORQUE iame41-1.doc 29Mar03 Page 1 of 2 Another Sea-Doo watercraft first and only. Introducing the 185hp, GTX 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED PWC. The 4-TEC
HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE
 16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Oregon Fuel Injection
 Cummins PT Fuel Pump Diagnostic No Start, with no smoke 1. This could be caused by the fuel pump not turning or a seized gear pump. Remove the fuel supply hose and the fuel inlet fitting from the gear
Cummins PT Fuel Pump Diagnostic No Start, with no smoke 1. This could be caused by the fuel pump not turning or a seized gear pump. Remove the fuel supply hose and the fuel inlet fitting from the gear
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
1983 BMW 320i. 1.8L 4-CYL 1983 Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder
 ENGINE IDENTIFICATION 1.8L 4-CYL 1983 Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder For engine repair procedures not covered in this article, see ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION article in the GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION 1.8L 4-CYL 1983 Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder For engine repair procedures not covered in this article, see ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION article in the GENERAL INFORMATION
DISASSEMBLED VIEWS. Disassembled Views. Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW or LFX)
 2012 Cadillac CTS Wagon AWD V6-3.0L Vehicle > Engine, Cooling and Exhaust > Engine > Locations > Components DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Disassembled Views Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW
2012 Cadillac CTS Wagon AWD V6-3.0L Vehicle > Engine, Cooling and Exhaust > Engine > Locations > Components DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Disassembled Views Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
COMPONENT LOCATOR > DISASSEMBLED VIEWS
 Page 1 of 45 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8L Eng Base Service Manual: ENGINE MECHANICAL - 3.8L COMPONENT LOCATOR > DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Fig 1: Engine Block Component Views Callout Component Name 100 Engine
Page 1 of 45 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8L Eng Base Service Manual: ENGINE MECHANICAL - 3.8L COMPONENT LOCATOR > DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Fig 1: Engine Block Component Views Callout Component Name 100 Engine
Exhaust After-Treatment System. This information covers design and function of the Exhaust After-Treatment System (EATS) on the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 1.2007 258 44 1(6) Exhaust After-Treatment System Design and Function D16F Exhaust After-Treatment System W2005772
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 1.2007 258 44 1(6) Exhaust After-Treatment System Design and Function D16F Exhaust After-Treatment System W2005772
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
Installation Manual. Model T675A Engine Brakes. For Mack 6 Cylinder, 2 valve Head ENDT-673, 675, 676 & E6 Series Engines.
 Engine Brakes Installation Manual Model T675A Engine Brakes For Mack 6 Cylinder, 2 valve Head ENDT-673, 675, 676 & E6 Series Engines TecBrake P.O. Box 27822 Houston, Texas 77227 INSTALLATION MANUAL TECBRAKE
Engine Brakes Installation Manual Model T675A Engine Brakes For Mack 6 Cylinder, 2 valve Head ENDT-673, 675, 676 & E6 Series Engines TecBrake P.O. Box 27822 Houston, Texas 77227 INSTALLATION MANUAL TECBRAKE
Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (-40 )
 149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual
 Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual DOWNLOAD HERE "Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual Signature
Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual DOWNLOAD HERE "Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual Signature
Product Information. N57 Engine.
 Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
SOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
 SECTION 1B SOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
SECTION 1B SOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
AD07.61-P-4000AC ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory Possible cause Note Fault code description
 Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED
 SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
ENGINE <4G6> 1-1 CONTENTS OVERVIEW... 2 COOLING SYSTEM... 4 MAIN UNIT... 2 INTAKE AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS... 4 LUBRICATION SYSTEM... 2 FUEL SYSTEM...
 1-1 ENGINE CONTENTS OVERVIEW.............................. 2 MAIN UNIT.............................. 2 Pistons.................................... 2 LUBRICATION SYSTEM.................. 2 Oil Pan....................................
1-1 ENGINE CONTENTS OVERVIEW.............................. 2 MAIN UNIT.............................. 2 Pistons.................................... 2 LUBRICATION SYSTEM.................. 2 Oil Pan....................................
TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR S, UNIT, INTERMEDIATE (DS) AND INTERMEDIATE (GS) MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR
 TM 5-2815-232-14 TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR S, UNIT, INTERMEDIATE (DS) AND INTERMEDIATE (GS) MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR ENGINE, DIESEL, CATERPILLAR, MODEL 3508 NSN 2815-01-216-0938 HEADQUARTERS, DEPARTMENT
TM 5-2815-232-14 TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR S, UNIT, INTERMEDIATE (DS) AND INTERMEDIATE (GS) MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR ENGINE, DIESEL, CATERPILLAR, MODEL 3508 NSN 2815-01-216-0938 HEADQUARTERS, DEPARTMENT
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
4 Stroke Diesel. Oil type SAE 15 W40/E 3
 MARCH 2006 TECHNICAL DATA 2.33 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS Cycle Air supply Injection 4 Stroke Diesel naturally aspirated direct Number of cylinders 4 in line 6 in line Bore mm 104 Stroke mm 132 Total displacement
MARCH 2006 TECHNICAL DATA 2.33 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS Cycle Air supply Injection 4 Stroke Diesel naturally aspirated direct Number of cylinders 4 in line 6 in line Bore mm 104 Stroke mm 132 Total displacement
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
SECTION A Engine 3.7L
 303-01A-i Engine 3.7L 303-01A-i SECTION 303-01A Engine 3.7L CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01A-2 Engine Identification... 303-01A-2 Engine Code Information Label... 303-01A-2 Engine
303-01A-i Engine 3.7L 303-01A-i SECTION 303-01A Engine 3.7L CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01A-2 Engine Identification... 303-01A-2 Engine Code Information Label... 303-01A-2 Engine
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
ENGINE GENERAL ENGINE GENERAL GENERAL OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. STRUCTURE...
 GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Page 1 of 10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION AIR DELIVERY DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The air delivery description and operation is divided into five areas: HVAC Control Components Air Speed Air Delivery Recirculation
Page 1 of 10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION AIR DELIVERY DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The air delivery description and operation is divided into five areas: HVAC Control Components Air Speed Air Delivery Recirculation
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP(SEBP ) - Document Structure. Media Number -RENR Publication Date -01/02/2008 Date Updated -07/02/2008
 Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES)
 REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 KENR6225-01 April 2008 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 402D-403D-404D Industrial Engine GG (Engine) GH (Engine) GJ (Engine) GK (Engine) GL (Engine) GM (Engine) GN (Engine) GP (Engine) GQ (Engine)
KENR6225-01 April 2008 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 402D-403D-404D Industrial Engine GG (Engine) GH (Engine) GJ (Engine) GK (Engine) GL (Engine) GM (Engine) GN (Engine) GP (Engine) GQ (Engine)
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS MONITORING
 Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS MONITORING Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 2 Description Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII
Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS MONITORING Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 2 Description Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT
 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
TMT121336EN 8355 R EPA, 2013 N13 Engine Aftertreatment System Overview for Technicians Study Guide
 TMT121336EN 8355 R1 2010 EPA, 2013 N13 Engine Aftertreatment System Overview for Technicians Study Guide 2010 EPA, 2013 N13 Engine Aftertreatment System STUDY GUIDE 2014 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive,
TMT121336EN 8355 R1 2010 EPA, 2013 N13 Engine Aftertreatment System Overview for Technicians Study Guide 2010 EPA, 2013 N13 Engine Aftertreatment System STUDY GUIDE 2014 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive,
PIERBURG. Carburetor: 2E3
 PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
This information covers the design and function of the intake and exhaust systems for the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
2. Turbocharger System
 INTAKE (INDUCTION) 2. Turbocharger System A: GENERAL The turbocharger system consists of a water-cooled turbocharger, air-cooled intercooler, wastegate control solenoid valve, etc. The turbine rotated
INTAKE (INDUCTION) 2. Turbocharger System A: GENERAL The turbocharger system consists of a water-cooled turbocharger, air-cooled intercooler, wastegate control solenoid valve, etc. The turbine rotated
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
1988 Ford F-350 PICKUP
 1988 Ford F-350 PICKUP Submodel: Engine Type: V8 Liters: 7.5 Fuel Delivery: FI Fuel: GAS 1987 93 4.9L Engine The intake and exhaust manifolds on these engines are known as combination manifolds and are
1988 Ford F-350 PICKUP Submodel: Engine Type: V8 Liters: 7.5 Fuel Delivery: FI Fuel: GAS 1987 93 4.9L Engine The intake and exhaust manifolds on these engines are known as combination manifolds and are
UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE DIRECT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE REPAIR PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS LIST FOR
 TECHNICAL MANUAL TM 55-1905-223-24P-1 UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE DIRECT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE REPAIR PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS LIST FOR LANDING CRAFT UTILITY (LCU 2000) (NSN 1905-01-154-1191) This copy
TECHNICAL MANUAL TM 55-1905-223-24P-1 UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE DIRECT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE REPAIR PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS LIST FOR LANDING CRAFT UTILITY (LCU 2000) (NSN 1905-01-154-1191) This copy
Five-digit error code First position: P - is for powertrain codes B - is for body codes C - is for chassis codes
 https://www.automotive-manuals.net Five-digit error code First position: P - is for powertrain codes B - is for body codes C - is for chassis codes The second position: 0 - the total for the OBD-II code
https://www.automotive-manuals.net Five-digit error code First position: P - is for powertrain codes B - is for body codes C - is for chassis codes The second position: 0 - the total for the OBD-II code
Full list of fault codes and events
 Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Technician Turbocharger Guide for the L Power Stroke Engine
 Technician Turbocharger Guide for the 2003.25 6.0L Power Stroke Engine Vanes VGT Actuator Piston Turbine Wheel Shaft Seal Compressor Wheel VGT Control Valve TURBOCHARGER DESCRIPTION AND BASIC OPERATION
Technician Turbocharger Guide for the 2003.25 6.0L Power Stroke Engine Vanes VGT Actuator Piston Turbine Wheel Shaft Seal Compressor Wheel VGT Control Valve TURBOCHARGER DESCRIPTION AND BASIC OPERATION
LANDING CRAFT UTILITY (LCU 2000)
 TECHNICAL MANUAL TM 55-1905-223-24P-3 UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE DIRECT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE REPAIR PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS LIST FOR LANDING CRAFT UTILITY (LCU 2000) (NSN 1905-01-154-1191) Approved
TECHNICAL MANUAL TM 55-1905-223-24P-3 UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE DIRECT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE REPAIR PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS LIST FOR LANDING CRAFT UTILITY (LCU 2000) (NSN 1905-01-154-1191) Approved
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER
 AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
Handout Activity: HA170
 Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
gas passes through baffle plates in cylinder oil separator inlet port. Separated oil returns The first separation will happen when blowby
 2 05 LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW Lubrication System PCV Oil Separator Cylinder head cover (oil + gas) Blow-by gas (air duct hose) Inlet port Oil (oil gauge pipe) The first separation will happen when blowby gas
2 05 LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW Lubrication System PCV Oil Separator Cylinder head cover (oil + gas) Blow-by gas (air duct hose) Inlet port Oil (oil gauge pipe) The first separation will happen when blowby gas
Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT
 A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
ENGINE MECHANICAL <134>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
TECHNICAL FORM SEAT LEON CUP RACER MK3 1. GENERAL. Homologation N. Extension N. Model: LEON CUP RACER MK3. Make: SEAT SPORT
 Model: LEON CUP TECHNICAL FORM Certification valid as from: 26 MARCH 215 SEAT 1. GENERAL 11. MANUFACTURER SEAT 12. MODEL AND TYPE a) Model and type LEON CUP b) Typical chassis number VSSMK35F4XSSPXXXX
Model: LEON CUP TECHNICAL FORM Certification valid as from: 26 MARCH 215 SEAT 1. GENERAL 11. MANUFACTURER SEAT 12. MODEL AND TYPE a) Model and type LEON CUP b) Typical chassis number VSSMK35F4XSSPXXXX
THERMODYNAMICS. T85D - Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed
 THERMODYNAMICS T85D - Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed 1. General Didacta s T85D Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed has been specially designed for use in testing laboratories, and to ensure the greatest
THERMODYNAMICS T85D - Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed 1. General Didacta s T85D Internal Combustion Engine Test Bed has been specially designed for use in testing laboratories, and to ensure the greatest
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION
 SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION A -- Ground G -- Fuel Pump B -- Diagnostic Terminal H -- Brake Sense Speed Input F -- TCC M -- Serial Data (special tool needed - Do Not Use) For ECM Trouble Codes,
SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION A -- Ground G -- Fuel Pump B -- Diagnostic Terminal H -- Brake Sense Speed Input F -- TCC M -- Serial Data (special tool needed - Do Not Use) For ECM Trouble Codes,
Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install
 Page 1 of 46 Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install Remove 1. Open the bonnet. 2. Disconnect the battery. 3. Open the engine cover (1). 4. Detach the engine cover. 6 bolts (2) and (3) 5. Release
Page 1 of 46 Pistons and Connecting Rods, Remove and Install Remove 1. Open the bonnet. 2. Disconnect the battery. 3. Open the engine cover (1). 4. Detach the engine cover. 6 bolts (2) and (3) 5. Release
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
