Common rail injection system
|
|
|
- Emery Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
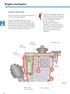
1 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel rail and protect the high-pressure fuel rail from overload. Pressure limiting valve 266_036a If the pressure inside the high-pressure fuel rail exceeds the maximum pressure of 1450 bar, the pressure limiting valve opens and the excess fuel flows to the return line. Comparison: 1450 bar is the rough equivalent of the weight of a mid-range car pressing on a surface area of one square centimetre. 26
2 Design The pressure limiting valve is a purely mechanical component. The connection to the high-pressure fuel rail is a threaded fitting. Inside is a valve with drillings. The valve is retained in its seat by a compression spring. Valve closed High pressure connection Coil spring 266_026 Valve Function If the fuel in the high-pressure fuel rail exceeds 1450 bar, the valve opens. Fuel can now escape from the high-pressure fuel rail and run into the return line via the drillings. Pressure in the high-pressure fuel rail drops. Valve open Coil spring Stop Return line Drillings 266_027 27
3 Common rail injection system Injection The fuel is injected in the combustion chambers by electromagnetically controlled injectors. To achieve the most efficient combustion possible, injection is divided into a preinjection phase and a main injection phase. Preinjection phase Before the pistons reach top dead centre (TDC), a small amount of fuel is first injected into the combustion chamber. This causes a rise in temperature and pressure in the combustion chamber. The purpose of this is to shorten the firing delay of the main injection phase and therefore reduce pressure rise and pressure peaks. The injectors are actuated once for preinjection phase and once for the main injection phase by the diesel direct injection system control unit. Main injection phase After precombustion and after a short pause in the injection cycle, the main injection quantity is injected into the combustion chamber. The level of the injection pressure remains almost identical during the entire injection cycle. The advantages of the preinjection phase are: low combustion noise low exhaust emissions Difference in pressure curve of combustion with and without preinjection phase Combustion pressure Needle lift Pressure curve with preinjection phase Pressure curve without preinjection phase Needle lift with preinjection phase Preinjection phase Pause in injection cycle Piston top dead centre Main injection phase 266_017 Time 28
4 Injectors The injectors are fitted in the cylinder head. Design Their function is to inject the right amount of fuel at the right time into the combustion chambers. They are therefore actuated by the diesel direct injection system control unit. Fuel return line to fuel tank Electrical connection Resting position In its resting position, the injector is closed. The solenoid valve is not actuated. The solenoid valve armature is pressed into its seat by the force of the solenoid valve spring. The injector needle is closed by the high pressure of the fuel due to the high ratio of the control piston surface area in relation to the injector needle. Solenoid valve armature Drain restrictor Valve control cavity Solenoid valve High-pressure connection Supply restrictor Valve control piston Injector spring Any interruption in the electrical lead to an injector or in a solenoid valve will cause the engine to shut down. Injector tip Injector needle 266_013 High-pressure return pressure 29
5 Common rail injection system Function Start of fuel injection The start of fuel injection is initiated by the diesel direct injection system control unit. It actuates the solenoid valve. When the magnetic force exceeds the closing force of the solenoid valve spring, the solenoid valve armature moves up and opens the drain restrictor. Solenoid valve spring Solenoid valve armature Drain restrictor Supply restrictor Valve control cavity Drain restrictor Valve control piston Valve control Supply restrictor cavity Valve control piston The fuel in the valve control cavity flows to the return line via the drain restrictor. The supply restrictor prevents the rapid pressure equalisation between the fuel high pressure part and the valve control cavity. The pressure acting on the valve control piston is lower at this moment than the fuel high pressure that is acting on the injector needle. This raises the injector needle and injection begins. Injector needle 266_015 30
6 End of injection The injection cycle ends when the solenoid valve is no longer actuated by the diesel direct injection system control unit. The solenoid valve is deenergised. The valve spring presses the solenoid valve armature back into the valve seat and closes the drain restrictor. In the valve control cavity, the fuel pressure rises to the pressure in the high-pressure fuel rail. The pressure in the valve control cavity is therefore exactly the same again as in the injector needle. Solenoid valve spring Solenoid valve armature Drain restrictor Valve control cavity Valve control cavity This means that the pressures in the fuel high pressure part and in the valve control cavity are again equal. The injector needle closes due to the greater surface pressure acting on the control piston. The injection cycle ends and the injector reverts back to its resting position. Valve control piston Injector spring Injector needle 266_014 31
7 Engine management system System overview Sensors Engine speed sensor G28 Hall sender G40 Air mass meter G70 Coolant temperature sender G62 Brake light switch F with brake pedal switch F47 Altitude sender F96 Clutch pedal switch F36 Accelerator pedal with accelerator position sender G79 and idling speed switch F60 Fuel pressure sender G247 Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Diagnostic connection Intake manifold pressure sender G71 and intake manifold temperature sender G72 Auxiliary input signals 32
8 Actuators Fuel pump relay J17 and fuel pump G6 Glow plug relay J52 and glow plugs 1-4 Q6 Injector solenoid valve 1-4 N30, N31, N32, N33 Solenoid valve for charge pressure control N75 Intake manifold flap change-over valve N239 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Glow period warning lamp K29 Auxiliary input signals 266_002 33
9 Engine management system Sensors Engine speed sender G28 Segment gap The engine speed sender is an inductive sender. It is attached to the timing gear housing. The sender wheel is located on the crankshaft between the flywheel and the timing gear. A segment gap on the sender wheel acts as the reference mark for the sender. Signal utilisation The signal detects the engine speed and the exact position of the crankshaft. This information helps the diesel direct injection system control unit to calculate the injection point and injection quantity. 266_019 Effect of signal failure The engine cannot run. Hall sender G40 The Hall sender is mounted in the cylinder head cover. A tooth segment on the camshaft acts as a reference mark. The sender helps to detect the position of the camshaft. Reference mark Signal utilisation The signal is required by the diesel direct injection system control unit to detect the position of the first cylinder when the engine is started. Effect of signal failure 266_018 The engine continues to run. The diesel direct injection system control unit uses the signal from the engine speed sender G28 for this. However, the engine cannot be restarted. 34
10 Air mass meter G70 The air mass meter with reverse flow recognition is located in the intake pipe and determines the intake air mass. Opening and closing the valves cause return flows of the air mass drawn into the intake pipe. The hot-film air mass meter with reverse flow recognition recognises the backflowing air mass and includes this in its signal to the diesel direct injection system control unit. Signal utilisation The signal values are used by the diesel direct injection system control unit to calculate the injection quantity. 266_073 Effect of signal failure If the signal from the air mass meter fails, the diesel direct injection system control unit calculates with a fixed substitute value. Coolant temperature sender G62 The coolant temperature sender is located in the coolant connection of the cylinder head. The sender informs the diesel direct injection system control unit about the current coolant temperature. Signal utilisation The coolant temperature is used by the diesel direct injection system control unit as a correction value to calculate the injection quantity. Effect of signal failure 266_074 If the signal fails, the diesel direct injection system control unit calculates with a fixed substitute value. 35
11 Engine management system Brake light switch F and brake pedal switch F47 The brake light switch and the brake pedal switch are located together in a single component on the foot controls. The switches help the diesel direct injection system control unit to recognise whether the brake pedal is being operated. Signal utilisation The two switches supply the diesel direct injection system control unit with the signal "brake actuated. If the accelerator position sender is defective, the engine is throttled down for safety reasons when the brake is operated. 266_078 Effect of signal failure If one of the two switches fails, the diesel direct injection system control unit reduces the fuel quantity. The engine has less power. Clutch pedal switch F36 The clutch pedal switch is located on the foot controls and is operated by the clutch pedal. It detects when the clutch pedal is depressed. Signal utilisation The signal helps the diesel direct injection system control unit to detect whether the clutch pedal is operated or not. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the injection quantity is reduced for a short period of time. This prevents engine shudder during a gearshift operation. 266_076 Effect of signal failure If the clutch pedal switch signal fails, load impacts may occur during gearshift operations. 36
12 Accelerator position sender G79 with idling speed switch F60 The accelerator position sender is located in the engine compartment and is linked to the accelerator pedal by a rod linkage. The control unit recognises the position of the accelerator pedal from the signal sent by the accelerator position sender. The sender also includes an idling speed switch. Signal utilisation The accelerator pedal position acts as the main influencing factor to calculate the injection quantity. The idling speed switch helps the diesel direct injection system control unit to recognise whether the accelerator pedal is being operated or not. 266_071 Effect of signal failure Without this signal the diesel direct injection system control unit cannot recognise the accelerator pedal position. The engine will continue to run at higher idling speed. The driver can reach the nearest workshop. Altitude sender F96 The altitude sender is located in the diesel direct injection system control unit. Signal utilisation The altitude sender reports the current ambient air pressure to the diesel direct injection system control unit. The signal is dependent on the geographical altitude. The signal provides an altitude correction for charge pressure control. Effect of signal failure Altitude sender 266_077 Black smoke occurs at high altitudes. 37
13 Engine management system Fuel pressure sender G247 The fuel pressure sender is located on the high-pressure fuel rail and determines the current fuel pressure in the high-pressure section. Function Fuel pressure reaches the sensor element via the high-pressure connection. The sensor is a steel diaphragm with vapourdeposit strain gauges. When there is a change in pressure, the diaphragm shape changes as well as the resistance of the strain gauges. The evaluation electronics amplify the resistance signal and transfer it in the form of a voltage signal to the diesel direct injection system control unit. Using a characteristic curve stored there, the control unit calculates the current fuel pressure. Signal utilisation The voltage signal is an influencing parameter for the diesel direct injection system control unit to control the fuel pressure in the fuel high-pressure part. Effect of signal failure Sensor element 266_058 Electrical connection Evaluation electronics The engine cannot run. High pressure connection 266_080 If the fuel pressure sender detects a strong pressure drop or pressure rise in the high-pressure part, the engine is shut down for safety reasons. 38
14 Intake manifold pressure sender G71 and intake manifold temperature sender G72 The two senders are integrated in a single components located in the intake pipe. Intake manifold pressure sender G71 The intake manifold pressure sender detects the current pressure in the intake manifold. Signal utilisation The sender signal is required by the diesel direct injection system control unit to control the charge pressure. 266_023 Effect of signal failure If it fails, there is no substitute function. The charge pressure control is shut down and the engine power is reduced. Intake manifold temperature sender G72 The intake manifold temperature sender detects the current air temperature of the intake air. Signal utilisation The signal acts as a correction value for the diesel direct injection system control unit to calculate the charge pressure. This takes into account the effect of temperature on the density of the charge air. Effect of signal failure If the signal fails, the diesel direct injection system control unit calculates with a fixed value. This leads to reduced engine performance. 39
15 Engine management system Auxiliary input signals Road speed signal This signal is sent to the diesel direct injection system control unit by the road speed sender. It has the following functions: limits the top speed dampens engine shudder when shifting gear and checks the function of the cruise control system. Cruise control system The signal from the cruise control system switch is detected by the diesel direct injection system control unit and indicates that the cruise control system is active. Air conditioner compressor standby The diesel direct injection system control unit receives the signal from the air conditioner switch that the air conditioner compressor was switched on. It raises the engine idling speed to prevent a sharp drop in engine speed when the compressor starts. Working speed control The working speed control switch sends the signal for raising the engine speed to the diesel direct injection system control unit. Auxiliary output signals Engine speed This signal is intended as engine speed information for the rev counter in the dash panel insert. Air conditioner compressor The signal switches off the air conditioner compressor to limit engine load under certain conditions. 40
16 Actuators Charge pressure control solenoid valve N75 The charge pressure control solenoid valve is an electro-pneumatic valve and is mounted on the engine bulkhead together with the intake manifold flap change-over valve N239 in the engine compartment. The solenoid valve is clocked by the diesel direct injection system control unit and switches the control pressure to operate the vacuum box to adjust the turbocharger vanes. The charge pressure is controlled by a map stored in the diesel direct injection system control unit. Effects of failure 266_075 If the charge pressure control solenoid valve fails, engine performance drops. Intake manifold flap change-over valve N239 The intake manifold flap change-over valve switches the vacuum to operate the intake manifold flap in the intake pipe. The intake manifold flap prevents shudder when the engine is shut down. It interrupts the air supply when the engine is turned off. Less air is compressed and the engine turns off softly. Effects of failure If the intake manifold flap change-over valve fails, the intake manifold flap opens. 266_079 41
17 Engine management system Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 The fuel pressure regulating valve N276 is located on the high-pressure pump. Its function is to regulate the fuel pressure in the high-pressure part. It is therefore activated by the diesel direct injection system control unit. The fuel pressure is regulated on the suction side in the low-pressure part. This has the advantage that the high-pressure pump only needs to generate the pressure required by the momentary operating situation. This reduces the power consumption of the high-pressure pump and avoids heating the fuel unnecessarily. 266_054 Control procedure The regulating valve N276 is activated by the control unit to control fuel pressure. Control unit J248 uses the information from the engine speed sender G28, coolant temperature sender G62, air mass meter G70, intake manifold pressure sender G71, intake manifold temperature sender G72, accelerator position sender G79 and fuel pressure sender G247 G28 G62 G70 G71 G72 G79 to calculate the fuel pressure required for injection. 42
18 The diesel direct injection system control unit then activates the regulating valve N276 using a pulse-width modulated signal: large pulse width = high pressure short pulse width = low pressure. Depending on the necessary engine load, the control unit changes the pulse width which is used to activate the regulating valve. This regulates the flow rate of the fuel to the high-pressure pump. PWM signal Regulating valve U t N276 J248 G247 RAIL The fuel pressure sender G247 reports the current fuel pressure to the control unit J _094a 43
19 Engine management system Function Low fuel pressure If less fuel pressure is required, the signal pulse width is short. The regulating piston reduces the fuel supply to the high-pressure pump. So only a small quantity of fuel reaches the high-pressure pump and generates a lower fuel pressure. Excess fuel conveyed by the gear pump is returned to the fuel tank via the return line. Drive shaft High-pressure pump Supply line PWM signals from control unit Gear pump Regulating piston Fuel pressure regulating valve Return line 266_056 U PWM signal with short pulse width t 266_106 44
20 High fuel pressure To generate high fuel pressure, the fuel pressure regulating valve is activated by a long pulse width signal. The regulating piston releases a large crosssection from the gear pump to the high-pressure pump. So a large quantity of fuel reaches the highpressure pump and generates a lower fuel pressure. Pump piston To high-pressure fuel rail Supply line Lubricating oil drilling Restrictor 266_055 U PWM signal with long pulse width t 266_107 45
21 Engine management system Glow plug system The glow plug system makes for easier starting at low temperatures. It is switched on by the diesel direct injection system control unit at a coolant temperature of under +9 o C. The glow plug relay is activated by the diesel direct injection system control unit. It then switches on the working current for the glow plugs. The system overview of the glow plug system shows you what sensors use which signals for the glow plug system and what actuators are activated. System overview of glow plug system Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Engine speed sender G28 Glow plugs Q6 Glow plug relay J52 Coolant temperature sender G62 Glow period warning lamp K29 266_064 46
22 The glow period makes a distinction between two phases: Glow phase When the ignition is switched on, the glow plugs are switched on at a temperature of under +9 o C. The warning lamp lights up in the dash panel insert for glow period. When the glow phase ends, the warning lamp goes out and the engine can start. Afterglow phase Every time the engine is started, there is an afterglow phase, irrespective of whether a glow phase took place. This lowers combustion noise, improves idling quality and reduces hydrocarbon emissions. c km/h km /min x100 P ABS ABD SRS ADR Glow period warning lamp K29 266_105c 47
23 Engine management system Function diagram (2.8 ltr. TDI engine with common rail - AUH) X J317 J52 S J17 S S S 80A M Q6 N239 G40 + N276 G6 J248 F96 N30 N31 N32 N33 t P P G79 F60 G28 G72 G71 G62 G247 E45 31 Colour codes = input signal = output signal = positive = GND = bidirectional 48
24 30 15 X Parts E45 F F36 F47 F60 F96 - Cruise control system switch - Brake light switch - Clutch pedal switch - Brake pedal switch for cruise control system/diesel direct injection system - Idling speed switch - Altitude sender S N75 M G70 G6 G28 G40 G62 G70 G71 G72 G79 G247 - Fuel pump - Engine speed sender - Hall sender - Coolant temperature sender - Air mass meter - Intake manifold pressure sender - Intake manifold temperature sender - Accelerator position sender - Fuel pressure sender J17 - Fuel pump relay J52 - Glow plug relay J248 - Diesel direct injection system control unit J317 - Voltage supply relay - Terminal 30 M9 M9 M10 - Brake light bulb, left - Brake light bulb, right M10 F36 F/F47 15 Auxiliary signals _001 N30 - Solenoid valve for injector, cylinder 1 N31 - Solenoid valve for injector, cylinder 2 N32 - Solenoid valve for injector, cylinder 3 N33 - Solenoid valve for injector, cylinder 4 N75 - Charge pressure control solenoid valve N239 - Intake manifold flap change-over valve N276 - Fuel pressure regulating valve Q6 - Glow plugs 1 Road speed signal S - Fuse Air conditioner compressor signal To glow period warning lamp K29 Engine speed signal Working speed control 49
25 ABS Auxiliary functions Power take-off Optionally, the LT can be equipped with a power take-off to drive additional devices. The power take-off permits the operation of auxiliary devices such as a tipping body or a loading platform. The power take-off is driven by the manual gearbox. Warning lamp switch lamp Shift cylinder Power take-off shaft 266_083 The power take-off is switched on by the power take-off switch in the dash panel. 266_103 When the power take-off is activated, the warning lamp in the dash panel insert lights up. c km/h km /min x100 6 P ABD SRS ADR 266_105b Warning lamp When operating the auxiliary device, make sure the manufacturer's operating instructions are adhered to. 50
26 System overview of power take-off Power take-off valve Vacuum reservoir Converter Hydraulic pressure Power take-off switch Vacuum Power take-off warning lamp switch Shift cylinder Driver Control unit for Diesel direct injection system Engine (engine speed) Power take-off Power take-off shaft 266_084 Function The power take-off is activated by the rocker switch in the dash panel. The power take-off valve then opens and applies a vacuum to the converter. The converter builds up a hydraulic pressure which switches the power take-off reduction gear via a shift cylinder and the driver. The warning lamp switch on the shift cylinder switches the warning lamp for the power take-off in the dash panel insert. The warning lamp remains lit as long as the power take-off is on. 51
27 Auxiliary functions Converter The converter converts the vacuum into a hydraulic pressure. The oil pressure operates the shift cylinder. Power take-off not on Power take-off on Port open Piston Port closed Brake fluid expansion tank Vacuum reservoir Power take-off valve (closed) 266_100 Power take-off valve (open) Vacuum to converter 266_101 As long as the power take-off valve is closed, pressure equalisation exists between the brake fluid expansion tank and the power take-off shift cylinder. When the power take-off is switched on, the power take-off valve opens. This applies a vacuum to the converter. The piston moved down. The piston moving down closes the opening between the expansion tank and the shift cylinder. A hydraulic pressure is built up between the converter and the shift cylinder. This pressure causes the shift cylinder to switch the power take-off on. The power take-off shaft starts to turn. 52
28 ABS Working speed control The working speed of the power take-off is controlled using the engine speed by the diesel direct injection system control unit. A warning lamp for the automatic engine speed control (ASC) is located in the dash panel insert. If there is a fault in the automatic engine speed control, the ASC warning lamp flashes. Automatic engine speed control To prevent a drop in engine speed when the power take-off is switched on, an automatic engine speed control is activated. It is controlled by the diesel direct injection system control unit. Depending on the type of power take-off, a - variable working speed control or a - fixed working speed control can be used. c P km/h /min 0 12 x100 km ABD SRS ASC warning lamp ADR ADR 266_0105a Variable working speed control In this type of control, the working speed is changed by pressing the power take-off switch up or down. The maximum engine speed is adjustable within a range of 1000 rpm to 3000 rpm using the VAS 5051 Vehicle Diagnostic, Testing and Information System. Power take-off speed switch 266_093 Fixed working speed control In this type of control the working speed does not change when the power take-off is active. The fixed speed is adjustable within a range of 1000 rpm to 3000 rpm using the VAS 5051 Vehicle Diagnostic, Testing and Information System. You will find instructions for adapting the variable or fixed working speed control in the Workshop Manual. 53
29 Test your knowledge What are the correct answers? One or more, or even all, answers may be correct. 1. Using what gear of the toothed belt drive can the backlash be adjusted? a) Camshaft gear wheel. b) Intermediate camshaft gear. c) Adjustment is possible using all gears. 2. What is the maximum possible pressure in the high-pressure fuel rail? The maximum possible pressure is... bar. 3. What components are responsible for controlling the fuel pressure in the high-pressure circuit of the common rail injection system? a) The pressure limiting valve. b) The fuel pressure sender G247. c) The injectors. 4. What component of the high-pressure pump is responsible for moving the three pump pistons up and down? The up and down movements of the three pump pistons is performed by the... on the
30 5. Why is phased injection performed in the common rail injection system (pre- and post-injection)? a) To inject the greatest possible fuel quantity into the combustion chamber. b) To shorten the firing delay of the main injection phase. c) To avoid combustion noise. 6. What is the injection quantity of the injectors dependent on? a) The control duration of the solenoid valve on the Injector. b) Pressure in the rail. c) The pressure limiting valve. 1. b; bar; 3. b; 4. Eccentric cams, input shaft; 5. b, c; 6. a. b; Answers: 55
31 Service. 266 For internal use only. VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights reserved. Technical specifications subject to change without notice Technical status 03/02 This paper is produced from non-chlorine-bleached pulp.
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Caddy Current Flow Diagram No. 86 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 9 Caddy Current Flow Diagram No. 86 / 1 Edition 09.2003 1.9 l/47 kw Naturally aspirated diesel engine with direct injection, engine code AYQ From May 2000 Relay locations 3 - Terminal 30 voltage
Page 1 of 9 Caddy Current Flow Diagram No. 86 / 1 Edition 09.2003 1.9 l/47 kw Naturally aspirated diesel engine with direct injection, engine code AYQ From May 2000 Relay locations 3 - Terminal 30 voltage
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (-40 )
 149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Transporter Current Flow Diagram No. 80 / 1 Edition
 Side 1 av 13 Transporter Current Flow Diagram No. 80 / 1 Edition 05.2003 2.5 l/65 kw direct injection turbo diesel, engine code AJT From May 1999 2.5 l/75 kw direct injection turbo diesel, engine codes
Side 1 av 13 Transporter Current Flow Diagram No. 80 / 1 Edition 05.2003 2.5 l/65 kw direct injection turbo diesel, engine code AJT From May 1999 2.5 l/75 kw direct injection turbo diesel, engine codes
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
Full list of fault codes and events
 Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
MERCEDES P1XXX CODES Gas and Diesel
 MERCEDES P1XXX CODES 4/27/2000 Gasoline Engines Mercedes Pcode P0801 P1031 P1131 P1132 P1137 P1138 P1146 MERCEDES P1XXX CODES Gas and Diesel OBD-II Pcode Definition Engine/Climate control electric cooling
MERCEDES P1XXX CODES 4/27/2000 Gasoline Engines Mercedes Pcode P0801 P1031 P1131 P1132 P1137 P1138 P1146 MERCEDES P1XXX CODES Gas and Diesel OBD-II Pcode Definition Engine/Climate control electric cooling
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B
 Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine. And how it works
 Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Swirl Flaps. A = Non swirl not active. B = Swirl active
 Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA
 Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
 PE07.61-P-2001-60DB Legend of block diagram of ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system ENGINE 271 in MODEL 211 Code Designation Coordinate A1 Instrument cluster 43E A1p13 Multifunction display 42F A7/3
PE07.61-P-2001-60DB Legend of block diagram of ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system ENGINE 271 in MODEL 211 Code Designation Coordinate A1 Instrument cluster 43E A1p13 Multifunction display 42F A7/3
ENGINE GENERAL ENGINE GENERAL GENERAL OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. STRUCTURE...
 GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4
 Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4 1. Which of these sensors directly measures engine load? a. Manifold absolute pressure sensor. b. Coolant sensor (ECT). c. Vehicle speed sensor.
Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4 1. Which of these sensors directly measures engine load? a. Manifold absolute pressure sensor. b. Coolant sensor (ECT). c. Vehicle speed sensor.
HFM Gasoline Injection and Ignition System
 07.5-0030 HFM Design and Function HFM Gasoline Injection and Ignition System A. General The HFM gasoline injection and ignition system is a further development of the LH and EZL. The basic system of the
07.5-0030 HFM Design and Function HFM Gasoline Injection and Ignition System A. General The HFM gasoline injection and ignition system is a further development of the LH and EZL. The basic system of the
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
ISC, QSC8.3, and ISL (FIS )
 Fault Information System... 1 FIS Usage Recommendations... 2 FIS Usage Recommendations... 2 Diagnostic Methods... 9 Troubleshooting Fault Codes... 9 Information Fault Codes... 3 (fc211) Fault Code 211...
Fault Information System... 1 FIS Usage Recommendations... 2 FIS Usage Recommendations... 2 Diagnostic Methods... 9 Troubleshooting Fault Codes... 9 Information Fault Codes... 3 (fc211) Fault Code 211...
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
(3) (4) (6) (5) (10) (9) (8) (7)
 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition
 Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Fault Code List OBD1 X X X X X X X X X 1. Page 1 of 12 MALFUNCTION DESCRIPTION. Dec Hex DDE1 DDE2 DME. Siemens MS40 (VANOS) M50 DME 3.3.
 1.1, 1.2 & 1.7, 1.7.1 & 1.7.2...1 0 0 1 01 1 01 1 01 1 01 1 01 2 02 2 02 2 02 2 02 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Undefined Fault. Fault in the Control Unit - Reset and run vehicle. If code returns replace Fuel Pump
1.1, 1.2 & 1.7, 1.7.1 & 1.7.2...1 0 0 1 01 1 01 1 01 1 01 1 01 2 02 2 02 2 02 2 02 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Undefined Fault. Fault in the Control Unit - Reset and run vehicle. If code returns replace Fuel Pump
Onboard power supply management
 Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
D. Functions in the KE control unit. a) General
 D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table
 Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP(SEBP ) - Document Structure. Media Number -RENR Publication Date -01/02/2008 Date Updated -07/02/2008
 Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
AD07.61-P-4000AC ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory Possible cause Note Fault code description
 Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
2. Air Line AIR LINE FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL B: MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR FU(H4DOTC)-3
 W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
Function of Preglow System
 15-0705 Function of Preglow System General On a diesel engine, combustion occurs when the fuel is injected into the highly compressed and thus greatly heated combustion air and selfignites. When the engine
15-0705 Function of Preglow System General On a diesel engine, combustion occurs when the fuel is injected into the highly compressed and thus greatly heated combustion air and selfignites. When the engine
Caddy/Polo Classic. Current Flow Diagram No. 3 / 1. Edition Glow plug relay (104)
 Page 1 of 6 Current Flow Diagram No. 3 / 1 Edition 09.1998 1.9 l/47 kw Cat diesel engine, engine code 1Y From November 1996 For alternatives to relay and fuse positions as well as multi-pin connector wiring
Page 1 of 6 Current Flow Diagram No. 3 / 1 Edition 09.1998 1.9 l/47 kw Cat diesel engine, engine code 1Y From November 1996 For alternatives to relay and fuse positions as well as multi-pin connector wiring
EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
 Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Acura Plus Comprehensive & Major Component Coverage
 Acura Plus Comprehensive & Major Component Coverage ENGINE Cylinder block and all internal parts Cylinder heads and all internal parts Engine mounts Engine seals and gaskets Flywheel Intake and exhaust
Acura Plus Comprehensive & Major Component Coverage ENGINE Cylinder block and all internal parts Cylinder heads and all internal parts Engine mounts Engine seals and gaskets Flywheel Intake and exhaust
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited
 Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
Transmission Electronic Control System
 SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 5R55S 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 05/23/2008 Transmission Electronic Control System Electronic System
SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 5R55S 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 05/23/2008 Transmission Electronic Control System Electronic System
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
Intake manifold change-over
 Page 1 of 10 24-67 Intake manifold change-over This test should only be performed if there is a performance deficiency. The intake manifold switches from the long intake path to the short one at approx.
Page 1 of 10 24-67 Intake manifold change-over This test should only be performed if there is a performance deficiency. The intake manifold switches from the long intake path to the short one at approx.
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Function description
 30-0006 Function description Electronic accelerator (EA) Block diagram Overvoltage protection EA control relay, Models 124, 202 (power supply) Idle speed control Base, Models (ISC) 129,140, 124.034/036
30-0006 Function description Electronic accelerator (EA) Block diagram Overvoltage protection EA control relay, Models 124, 202 (power supply) Idle speed control Base, Models (ISC) 129,140, 124.034/036
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
E60, E61, E63, E64, E65, E66, E70 BMW AG - TIS
 VS-42 je Baugruppe/Group: 11 meeknet.co.uk/e64 11 03 05 (142) 8-cylinder spark-ignition engine N62TU E60, E61, E63, E64, E65, E66, E70 weltweit Datum/Date: 04/2007 Update: 04/2007 Introduction The N62TU
VS-42 je Baugruppe/Group: 11 meeknet.co.uk/e64 11 03 05 (142) 8-cylinder spark-ignition engine N62TU E60, E61, E63, E64, E65, E66, E70 weltweit Datum/Date: 04/2007 Update: 04/2007 Introduction The N62TU
Motronic September 1998
 The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
 08 5 ECU According to input signals from various sensors, engine ECU calculates driver s demand (position of the accelerator pedal) and then controls overall operating performance of engine and vehicle
08 5 ECU According to input signals from various sensors, engine ECU calculates driver s demand (position of the accelerator pedal) and then controls overall operating performance of engine and vehicle
3. Fuel System FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-7
 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
DASH RETRIEVED FAULT CODES C ONVENTIONAL FS65 SAF T LINER C2, C2E H YBRID SAF T LINER HDX, HD, ER SAF T LINER EF, EFX A LL Y EARS
 DASH RETRIEVED FAULT CODES C ONVENTIONAL FS65 SAF T LINER C2, C2E H YBRID SAF T LINER HD, HD, ER SAF T LINER EF, EF A LL Y EARS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK TABLE OF CONTENTS EARLY PRODUCTS: J1587/J1708
DASH RETRIEVED FAULT CODES C ONVENTIONAL FS65 SAF T LINER C2, C2E H YBRID SAF T LINER HD, HD, ER SAF T LINER EF, EF A LL Y EARS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK TABLE OF CONTENTS EARLY PRODUCTS: J1587/J1708
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
Electronic control system
 Electronic control system Date 28 March 2013 Vico de Bres Customer Service Department Yanmar Europe B.V. Content 1. Overview 2. ECU connections 3. Sensors Page1 Overview Page2 Engine sensors and actuators
Electronic control system Date 28 March 2013 Vico de Bres Customer Service Department Yanmar Europe B.V. Content 1. Overview 2. ECU connections 3. Sensors Page1 Overview Page2 Engine sensors and actuators
VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION. Layout. EGR valve. Turbocharger actuator. Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump. Turbocharger vacuum modulator
 42 04 VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION Layout Turbocharger actuator EGR valve Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump Turbocharger vacuum modulator EGR vacuum modulator Vacuum Modulator for VGT Turbocharger Actuator
42 04 VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION Layout Turbocharger actuator EGR valve Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump Turbocharger vacuum modulator EGR vacuum modulator Vacuum Modulator for VGT Turbocharger Actuator
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE DESCRIPTION ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE
 39 ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The new MR2 has the 2.0 liter, 16 valve, DOHC 3S GTE engine with turbocharger which is used in the Celica All Trac/4WD models and has been well received. The 3S GTE
39 ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The new MR2 has the 2.0 liter, 16 valve, DOHC 3S GTE engine with turbocharger which is used in the Celica All Trac/4WD models and has been well received. The 3S GTE
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
EGR System, Design and Function. This information covers design and function of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system on a Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 254 59 1(6) EGR System Design and Function D16F EGR System, Design and Function W2005836 This information
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 254 59 1(6) EGR System Design and Function D16F EGR System, Design and Function W2005836 This information
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)
 13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Turbo>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
CUMMINS ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC CODES
 ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS GROUP 105 CUMMINS ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC CODES 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 TROUBLESHOOTING CODES... 1 1 INTRODUCTION. This group provides information on the engine fault codes that could potentially
ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS GROUP 105 CUMMINS ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC CODES 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 TROUBLESHOOTING CODES... 1 1 INTRODUCTION. This group provides information on the engine fault codes that could potentially
Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65).
 DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
SECTION 9A BODY WIRING SYSTEM
 SECTION 9A BODY WIRING SYSTEM Caution: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical
SECTION 9A BODY WIRING SYSTEM Caution: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
Heater capacity 250W 13.5V Injector System pressure 1800 bar High pressure fuel pump. Normal operating temperature. Operating temperature
 221001 033 1. SPECIFICATIONS Description Fuel Specification Diesel Fuel filter Type Fuel heater + priming pump + water separator integrated type Filter type Changeable filter element type Change interval
221001 033 1. SPECIFICATIONS Description Fuel Specification Diesel Fuel filter Type Fuel heater + priming pump + water separator integrated type Filter type Changeable filter element type Change interval
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Fig.11 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
 2003 Dodge or Ram Truck Caravan V6-3.3L VIN R Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Computers and Control Systems > Engine Control Module >
2003 Dodge or Ram Truck Caravan V6-3.3L VIN R Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Computers and Control Systems > Engine Control Module >
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank
 Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
