Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
|
|
|
- Meagan Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated system that controls primary ignition, fuelling and idle control from within the same ECU. It is normally only fitted to 16 valve GM engines. The control unit contains three microprocessors for: general control unit operation sequential injection knock control The Motronic ignition point and injection duration are jointly processed by the ECU so that the best moment for ignition and fuelling are determined for every operating condition. The injection function of the Motronic system is based on the well tried 'L' jetronic system, although a number of refinements have improved operation. A 55 pin connector and multi-plug connects the ECU to the battery, sensors and actuators. Basic ECU operation A permanent voltage supply is made from the vehicle battery to pin 18 of the ECU. This allows the self-diagnostic function to retain data of an intermittent nature. Once the ignition is switched on, a voltage supply to the ignition coil and to ECU pin 27 is made from the ignition switch. This causes the ECU to connect pin 36 to earth, so actuating the main fuel injection relay. A relay switched voltage supply is thus made to ECU pin 37, from terminal 87 of the main fuel injection relay. The majority of sensors (other than those that generate a voltage such the CAS, KS and OS), are now provided with a 5.0 volt reference supply from a relevant pin on the ECU. When the engine is cranked or run, a speed signal from the CAS causes the ECU to earth pin 3 so that the fuel pump will run. Ignition and injection functions are also activated. All actuators (Injectors, ISCV, FTVV etc), are supplied with nbv from the main relay and the ECU completes the circuit by pulsing the relevant actuator wire to earth. Signal processing Basic Ignition timing is calculated from the ignition map and engine load determines the basic injection pulse value. Correction factors are then applied for starting, idle, deceleration, part and full-load operation. The main engine load sensor is the AFS and the main correction factor is engine temperature. Reference voltage Voltage supply from the ECU to many of the engine sensors is at a 5.0 volt reference level. This ensures a stable working voltage unaffected by variations in system voltage. The earth return connection for most engine sensors is made through an ECU pin that is not directly connected to earth. The ECU internally connects that pin to earth via one of the ECU pins that are directly connected to earth. ECU coding wires (where fitted) Some vehicles equipped with Motronic 2.5 have certain ECU pins allocated as coding earths. The open circuit voltage at these pins is either nbv or at 5.0 volt reference level. Connection of the pin to earth indicates to the ECU that the vehicle is equipped with certain equipment. The non cat vehicle has pin 20 connected to earth and the catalyst equipped vehicle has pin 20 open circuit. The vehicle with AT has pin 21 connected to earth and the vehicle with MT has pin 21 open circuit. Signal shielding To reduce RFI, a number of sensors (ie CAS, HES, KS, amplifier and OS) use a shielded cable. The shielded cable is connected to the main ECU earth wire at terminal 19 to reduce interference to a minimum. CAS The CAS consists of an inductive magnet that radiates a magnetic field and a toothed disk. The disk is attached to the crankshaft or pulley and theoretically comprises 60 teeth set at 3 intervals around its circumference; each tooth being 3 wide. At a position some distance BTDC, two teeth are omitted as a reference to TDC and so a total of 58 teeth remain on the disk. As the crankshaft spins, and the teeth are rotated in the magnetic field, an AC voltage signal is generated and delivered to the ECU to indicate speed of crankshaft rotation. In addition, as the engine spins, the missing teeth generate a variation of the signal that serves as a reference to TDC to indicate crankshaft position. The peak to peak voltage of the speed signal (when viewed upon an oscilloscope) can vary from 5 volts at idle to over 100 volts at 6000 rpm. Because computers prefer their data as on/ off signals, the ECU utilises an analogue to digital converter (ADC) to transform the AC pulse into a digital signal. Ignition Data on load (AFS), engine speed (CAS), engine temperature (CTS) and throttle position (TS) are collected by the ECU, which then refers to a three dimensional digital map stored within its microprocessor. This map contains an advance angle for each operating condition, and thus the best ignition advance angle for a particular operating condition can be determined. When the throttle switch is closed, the ECU enters base timing mode and the timing is set at 10. Amplifier The amplifier contains the circuitry for switching the coil negative terminal at the correct moment to instigate ignition. The signal received by the amplifier from the trigger is of an insufficient level to complete the necessary coil switching. The signal
2 2 is thus amplified to a level capable of switching the coil negative terminal. Unlike earlier Vauxhall/ Motronic systems (in which the amplifier was contained in the ECU itself), Motronic 2.5 utilises a separate amplifier mounted on a heat sink plate adjacent to the coil. The ECU thus calculates the correct ignition dwell time and timing advance from data received from its sensors, and sends a signal to the amplifier which then switches the coil negative terminal. The advantage of a separate amplifier, is that if the amplifier fails, it is less costly to renew than a new ECU. Dwell operation in Motronic is based upon the principle of the 'constant energy current limiting' system. This means that the dwell period remains constant at around 4.0 to 5.0 ms, at virtually all engine running speeds. However, the dwell duty cycle, when measured in percent or degrees, will vary as the engine speed varies. A current limiting hump is not visible when viewing an oscilloscope waveform. Ignition coil The ignition coil utilises low primary resistance in order to increase primary current and primary energy. The amplifier limits the primary current to around 8 amps and this permits a reserve of energy to maintain the required spark burn time (duration). Distributor In the Motronic system, the distributor only contains secondary HT components (distributor cap, rotor and HT leads) and serves to distribute the HT current from the coil secondary terminal to each spark plug in firing order. Knock sensor The optimal ignition timing (at engine speeds greater than idle) for a given high compression engine is quite close to the point of onset of knock. However, running so close to the point of knock occurrence, means that knock will certainly occur on one or more cylinders at certain times during the engine operating cycle. Since knock may occur at a different moment in each individual cylinder, Motronic 2.5 employs the Knock Control unit - KCU (in the ECU) to pinpoint the actual cylinder or cylinders that are knocking. The Knock Sensor is mounted on the engine block and consists of a piezoceramic measuring element that responds to engine noise oscillations. This signal is converted to a voltage signal by the Knock Sensor and returned to the KCU for evaluation and action. Tests have shown that the 20XE & C20XE engines have a knocking frequency in the 15kHz frequency band. The KCU will analyse the noise from each individual cylinder and set a reference noise level for that cylinder based upon the average of the last 16 phases. If the noise level exceeds the reference level by a certain amount, the KCU identifies the presence of engine knock. Initially, timing will occur at its optimal ignition point. Once knock is identified, the Knock Control microprocessor retards the ignition timing for that cylinder or cylinders by 3ш. Approximately 2 seconds after knocking ceases (20 to 120 knock- free combustion cycles), the timing is advanced in 0.75ш increments until the reference timing value is achieved or knock occurs once more when the timing is retarded or This procedure continually occurs so that all cylinders will consistently run at their optimum timing. If a fault exists in the Knock Control processor, Knock control sensor or wiring, an appropriate code will be logged in the self-diagnostic unit and the ignition timing retarded by 10.5ш by the LOS program. Cylinder Identification In earlier Motronic systems the ECU does not recognise number one cylinder or indeed even the firing order. This is because it is actually unnecessary. When the crankshaft or distributor provides a timing signal, the correct cylinder is identified by the mechanical position of the crankshaft, camshaft, valves and ignition rotor. In systems where the injectors fire simultaneously, then the fuel will sit upon the back of an inlet valve until the valve opens. Since fuel injection occurs on an individual cylinder basis in Motronic 2.5, the ECU must be informed on which stroke a cylinder is actually on. This is achieved by a cylinder identification sensor attached to the distributor and which works on the Hall-Effect principle. The sensor identifies number one cylinder, and returns a signal to the ECU from which the identification of all the other cylinders can be calculated. The distributor is attached to the exhaust camshaft (the engine is DOHC in configuration). Octane coding Because of the sophistication of the KCU and timing control an octane coding plug is not considered necessary for the 20XE & C20XE engines. Octane adjustment is automatically selected according to operating conditions. Motronic 2.5 is programmed with two different timing maps. These are Low Octane Number Map (more retarded timing) and High Octane Number Map (more advanced dwell angle). The KCU selects the appropriate map according to the following conditions. Once knocking combustion of more than 50 have occurred, the KCU switches to the Low Octane Map. Once approximately 8.5 minutes of knock-free operation have passed, the KCU switches to the High Octane Map. Fuel injection The ECU or vehicle computer is programmed with a basic injector map. Information is then gathered from engine sensors such as the AFS, CAS, CTS, and TS. As a result of this information, the ECU will look-up the correct injector pulse duration right across the engine rpm, load and temperature range. Fuel injection The Motronic 2.5 system is a multi-point injection system and pulses the injectors sequentially - ie in firing order and once per
3 3 engine cycle. Each injector is connected to the ECU via a separate ECU pin). Earlier Motronic systems (ie 4.1 and 1.5) pulse all injectors at the same time - ie simultaneously and twice per engine cycle. During engine start from cold, the pulse duration and number of pulses (frequency) are increased to provide a richer air/fuel mixture. Fuel injectors The fuel injector is a magnetically operated solenoid valve that is actuated by the ECU. Voltage to the injectors is applied from the main relay and the earth path is completed by the ECU for a period of time (called pulse duration) of between 1.5 and 10 milliseconds. The pulse duration is very much dependant upon engine temperature, load, speed and operating conditions. When the magnetic solenoid closes, a back EMF voltage of up to 60 volts is initiated. The fuel injectors are mounted in the inlet stubs to the engine inlet valves so that a finely atomised fuel spray is directed onto the back of each valve. Since the injectors are all pulsed simultaneously, fuel will briefly rest upon the back of a valve before being drawn into a cylinder. Hot Wire Air mass meter (AFS) Motronic 2.5 also uses a Hot Wire airflow sensor to measure the mass of air entering engine. From the air mass, an accurate fuel injection pulse can then be calculated. Hot Wire is a very accurate method of calculating the engine load (air input) and excludes the need for additional sensors to measure air temperature and air pressure. Automatic compensation for altitude is thus provided. The absence of moving parts improves reliability and lessens maintenance requirements. Essentially, the hot wire is so called because a heated wire is placed in the air intake. As air passes over the wire it has a cooling effect in proportion to the mass of air. As airmass increases or decreases according to engine load, the ECU adjusts the current flow to maintain the wire at its original resistance and temperature. By measuring the change in current flow, the ECU is able to determine the mass of air flow into the engine. As the current varies on the signal wire, so does the voltage and an indication of load can be assessed by measuring the variable voltage signal. Voltage is applied to the sensor from the system relay. If a fault exists in the Hot Wire AFS or wiring, an appropriate code will be logged in the self-diagnostic unit and a substitute value provided by the LOS program. Hot wire burn-off Over a period of time, deposits tend to build-up upon the hot wire and this can lead to contamination of the hot-wire. This is avoided with a `burn-off' function controlled by the ECU during engine shutdown. Approximately four seconds after the engine has been switched off, the ECU rapidly pulses the hot-wire terminal 4 of the AFS for 1.5 seconds. Burn-off will not occur if the engine speed has not exceeded 1000 rpm and the coolant temperature is under approximately 30 C. CO pot The CO pot mixture adjuster is a three wire potentiometer that allows small changes to be made to the idle CO. A 5.0 volt reference voltage is applied to the sensor and connected to the AFS earth return circuit. The third wire is the CO pot signal. As the CO pot adjustment screw is turned the change in resistance returns a voltage signal to the ECU that will result in a change in CO. The CO pot adjustment only affects idle CO. On catalyst equipped models, the CO pot has no effect and the CO is thus non-adjustable. CTS The CTS is immersed in the coolant system and contains a variable resistance that operates on the NTC principle. When the engine is cold, the resistance is quite high. Once the engine is started and begins to warm-up, the coolant becomes hotter and this causes a change in the CTS resistance. As the CTS becomes hotter, the resistance of the CTS reduces (NTC principle) and this returns a variable voltage signal to the ECU based upon the coolant temperature. The open circuit supply to the sensor is at a 5.0 volt reference level and this voltage reduces to a value that depends upon the resistance of the CTS resistance. Normal operating temperature is usually from 80 to 100 C. The ECU uses the CTS signal as a main correction factor when calculating ignition timing and injection duration. Throttle switch A throttle switch with dual contacts is provided to inform the ECU of idle position, deceleration, cruising and full-load (WOT) conditions. When the engine is at idle the idle contact is closed and the full-load contact is open. As the throttle is moved to the fully open position, the full-load contact closes and the idle contact becomes open. Under cruising conditions with a part-open throttle, both contacts are open. During full-load operation, the ECU provides additional enrichment. During closed throttle operation above a certain rpm (deceleration), the ECU will cut-off fuel injection. Injection will be reintroduced once the rpm returns to idle or the throttle is opened. ISCV The ISCV is a solenoid controlled actuator that the ECU uses to automatically control idle speed during normal idle and during engine warm-up. The ISCV is located in a hose that connects the inlet manifold to the air filter side of the throttle plate. When an electrical load, such as headlights or heater fan etc are switched on, the idle speed would tend to drop. The ECU will sense the load and rotate the ISCV against spring tension to increase the air flow through the valve and thus increase the idle
4 4 speed. When the load is removed, the ECU will pulse the valve so that the air flow is reduced. Normal idle speed should be maintained under all cold and hot operating conditions. If the ISCV fails it will fail in a fail-safe position with the aperture almost closed. This will provide a basic idle speed. Relays relay diagram The Motronic electrical system is controlled by a single system relay with dual contacts. A permanent voltage supply is made to relay terminals 30 and 86 from the battery positive terminal. When the ignition is switched on, the ECU earths terminal 85 through ECU terminal number 36 which energises the first relay winding. This causes the first relay contacts to close and terminal 30 is connected to the output circuit at terminal 87. A voltage supply is thus output at terminal 87. Terminal 87 supplies voltage to the injectors, ECU terminal 37, ISCV and the FTVV when fitted. In addition voltage is supplied to the second relay contact. When the ignition is switched on. the ECU briefly earths relay contact 85b at ECU terminal 3. This energises the second relay winding, which closes the second relay contact and connects voltage from terminal 30 to terminal 87b, thereby providing voltage to the fuel pump circuit. After approximately one second, the ECU opens the circuit and the pump stops. This brief running of the fuel pump allows pressure to build within the fuel pressure lines, and provides for an easier start. The second circuit will then remain open until the engine is cranked or run. Once the ECU receives a speed signal from the CAS, the second winding will again be energised by the ECU, and the fuel pump will run until the engine is stopped. Fuel pressure system A roller type fuel pump, driven by a permanent magnet electric motor mounted close to the fuel tank, draws fuel from the tank and pumps it to the fuel rail via a fuel filter. The pump is of the 'wet' variety in that fuel actually flows through the pump and the electric motor. There is no actual fire risk because the fuel drawn through the pump is not in a combustible condition. Mounted upon the armature shaft is an eccentric rotor holding a number of pockets arranged around the circumference - each pocket containing a metal roller. As the pump is actuated, the rollers are flung outwards by centrifugal force to act as seals. The fuel between the rollers is forced to the pump pressure outlet. Fuel pressure in the fuel rail is maintained at a constant 2.5 bar by a fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pump normally provides much more fuel than is required, and surplus fuel is thus returned to the fuel tank via a return pipe. In fact, a maximum fuel pressure in excess of 5 bar is possible in this system. To prevent pressure loss in the supply system, a non-return valve is provided in the fuel pump outlet. When the ignition is switched off, and the fuel pump ceases operation, pressure is thus maintained for some time. Fuel pressure regulator The pressure regulator is fitted on the outlet side of the fuel rail and maintains an even pressure of 2.5 bar in the fuel rail. The pressure regulator consists of two chambers separated by a diaphragm. The upper chamber contains a spring which exerts pressure upon the lower chamber and closes off the outlet diaphragm. Pressurised fuel flows into the lower chamber and this exerts pressure upon the diaphragm. Once the pressure exceeds 2.5 bar, the outlet diaphragm is opened and excess fuel flows back to the fuel tank via a return line. A vacuum hose connects the upper chamber to the inlet manifold so that variations in inlet manifold pressure will not affect the amount of fuel injected. This means that the pressure in the rail is always at a constant pressure above the pressure in the inlet manifold. The quantity of injected fuel thus depends solely on injector opening time, as determined by the ECU, and not on a variable fuel pressure. At idle speed with the vacuum pipe disconnected, or with the engine stopped and the pump running, or at WOT the system fuel pressure will be approximately 2.5 bar. At idle speed (vacuum pipe connected), the fuel pressure will be approximately 0.5 bar under the system pressure. Self Diagnostic function The Motronic 1.5 system has a self-test capability that regularly examines the signals from engine sensors and internally logs a code in the event of a fault being present. This code can be extracted from the Motronic serial port by a suitable Fault Code Reader. When the ECU detects that a fault is present, it earths pin 17 and the warning lamp on the dash will light. The lamp will stay lit until the fault is no longer present. If the fault clears, the code will remain logged until wiped clean with a suitable FCR, or until the engine has been started for more than 20 times when the fault code is self initialising. An ECU that retains codes for faults of an intermittent nature is a valuable aid to fault diagnosis. In addition to the self-test capability, Motronic 1.5 has full limp home facilities. In the event of a serious fault in one or more of the sensors, the EMS will substitute a fixed default value in place of the defective sensor. This means that the engine may actually run quite well with failure of one or more minor sensors. Since the substituted values are those of a hot engine, cold starting and running during the warm-up period may be less than satisfactory. Also, failure of a major sensor, ie the AFS, will tend to make driving conditions less easy. Catalytic Converter and emission control Versions with a Catalytic Converter will also be fitted with an oxygen sensor so that closed loop control of emissions can be implemented. The OS is heated so that it will reach optimum operating temperature as quickly as possible after the engine is started. The OS heater supply is made from the fuel injection relay terminal number 87b. This ensures that the heater will only
5 5 operate whilst the engine is running. An FTVV and activated carbon canister are also be employed to aid evaporative emission control. The carbon canister stores fuel vapours until the FTVV is opened by the EMS under certain operating conditions. Once the FTVV is actuated by the EMS, fuel vapours are drawn into the inlet manifold to be burnt by the engine during normal combustion. Testing Because of the difficulty in access to many of the sensors, a BOB is deemed necessary to make voltage, resistance, duty cycle and oscilloscope tests. < END >
Motronic September 1998
 The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS
 2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT
 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
4.0L CEC SYSTEM Jeep Cherokee DESCRIPTION OPERATION FUEL CONTROL DATA SENSORS & SWITCHES
 4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Non-Turbo>
 13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13A-2 FUEL INJECTI CTROL...... 13A-6 IDLE SPEED CTROL (ISC)..... 13A-7 IGNITI TIMING AND DISTRIBUTI CTROL........
13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13A-2 FUEL INJECTI CTROL...... 13A-6 IDLE SPEED CTROL (ISC)..... 13A-7 IGNITI TIMING AND DISTRIBUTI CTROL........
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Turbo>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Timing is everything with internal combustion engines By: Bernie Thompson
 Timing is everything with internal combustion engines By: Bernie Thompson As one goes through life, it is said that timing is everything. In the case of the internal combustion engine, this could not be
Timing is everything with internal combustion engines By: Bernie Thompson As one goes through life, it is said that timing is everything. In the case of the internal combustion engine, this could not be
Lotus Service Notes Section EMR
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Setup Tabs. Basic Setup: Advanced Setup:
 Setup Tabs Basic Setup: Password This option sets a password that MUST be entered to re-enter the system. Note: ProEFI can NOT get you into the calibration if you lose this password. You will have to reflash
Setup Tabs Basic Setup: Password This option sets a password that MUST be entered to re-enter the system. Note: ProEFI can NOT get you into the calibration if you lose this password. You will have to reflash
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF) B B B
 5. Specified Data A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen heater Engine coolant temperature Signal
5. Specified Data A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen heater Engine coolant temperature Signal
Ignition control. The ignition system tasks. How is the ignition coil charge time and the ignition setting regulated?
 1 Ignition control The ignition system tasks To transform the system voltage (approximately 14 V) to a sufficiently high ignition voltage. In electronic systems this is normally above 30 kv (30 000 V).
1 Ignition control The ignition system tasks To transform the system voltage (approximately 14 V) to a sufficiently high ignition voltage. In electronic systems this is normally above 30 kv (30 000 V).
Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator
 Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator Introduction Some of the notes here are repetitious in order to review the components
Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator Introduction Some of the notes here are repetitious in order to review the components
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
51. absolute pressure sensor
 51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En
 02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system
 5B 1 Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system Contents Distributor - removal and refitting.............................4 Ignition HT coil(s) - removal, testing and refitting.................3 Ignition system
5B 1 Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system Contents Distributor - removal and refitting.............................4 Ignition HT coil(s) - removal, testing and refitting.................3 Ignition system
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control
 The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Fuel control. The fuel injection system tasks. Starting fuel pump (FP)
 1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal S008526
 5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal S008526 A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION S008526A08 1. MT VEHICLES S008526A0801 B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal S008526 A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION S008526A08 1. MT VEHICLES S008526A0801 B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DTC Description P0010 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1) P0020 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DTC Description P0010 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1) P0020 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)
 13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
Stop Lamp Switch. STP or BRK. Stop Lamps
 WORKSHEET 2 1 Position/Mode Switches and Circuits (Instructor Copy) Vehicle Year/Prod. Date Engine Transmission Technician Objectives With this worksheet, you will learn to test position/mode circuits
WORKSHEET 2 1 Position/Mode Switches and Circuits (Instructor Copy) Vehicle Year/Prod. Date Engine Transmission Technician Objectives With this worksheet, you will learn to test position/mode circuits
Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank
 Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
Ignition System Fundamentals
 Ignition System Fundamentals Chapter 37 Objectives Describe the functions of ignition system parts Explain the operation of points, electronic, and computer ignition systems Give an overview of the different
Ignition System Fundamentals Chapter 37 Objectives Describe the functions of ignition system parts Explain the operation of points, electronic, and computer ignition systems Give an overview of the different
Chrysler Electronic Ignition System
 1 of 11 1/6/2010 11:02 PM Chrysler Electronic Ignition System Classic Winnebago's Post by: DaveVA78Chieftain on August 13, 2009, 10:15 PM Components The Chrysler Electronic Ignition System consists of
1 of 11 1/6/2010 11:02 PM Chrysler Electronic Ignition System Classic Winnebago's Post by: DaveVA78Chieftain on August 13, 2009, 10:15 PM Components The Chrysler Electronic Ignition System consists of
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table
 Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
Fig.11 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
 2003 Dodge or Ram Truck Caravan V6-3.3L VIN R Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Computers and Control Systems > Engine Control Module >
2003 Dodge or Ram Truck Caravan V6-3.3L VIN R Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Computers and Control Systems > Engine Control Module >
9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor
 9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1. Troubles 1. The signal line is short to ground (Abnormally low signal voltage : below 0.5 [volt]) Cause of trouble Counter action Engine state Signal
9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1. Troubles 1. The signal line is short to ground (Abnormally low signal voltage : below 0.5 [volt]) Cause of trouble Counter action Engine state Signal
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (-40 )
 149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (continued) SAE Defined Codes
 78 SAE Defined Codes P01XX Fuel and Air Metering P0100 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Problem P0101 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Range or Performance Problem P0102 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Low
78 SAE Defined Codes P01XX Fuel and Air Metering P0100 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Problem P0101 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Range or Performance Problem P0102 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Low
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
AUTRONIC SM3 ECU Specifications
 AUTRONIC SM3 ECU Specifications Microcomputer Power Supply - Voltage Normal operation Operational limits Intel 16 bit 20MHz 12v to 15v DC 6.2v to 18v DC continuous Power Supply - Current Survival limits
AUTRONIC SM3 ECU Specifications Microcomputer Power Supply - Voltage Normal operation Operational limits Intel 16 bit 20MHz 12v to 15v DC 6.2v to 18v DC continuous Power Supply - Current Survival limits
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
16.01 Theory Module INPUTS
 16.01 Theory Module INPUTS Crankshaft position sensor Camshaft position sensor Knock sensor (some engine types) Barometric pressure sensor Intake air temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor
16.01 Theory Module INPUTS Crankshaft position sensor Camshaft position sensor Knock sensor (some engine types) Barometric pressure sensor Intake air temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
FUEL 13-1 CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)... 2 FUEL SUPPLY ON-VEHICLE SERVICE GENERAL SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 4 SEALANT...
 13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL............................... 2 Outline of Change......................... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 4 SEALANT...............................
13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL............................... 2 Outline of Change......................... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 4 SEALANT...............................
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
FUEL 13-1 CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 3 SEALANT... 3 SPECIAL TOOLS...
 13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION................ 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 3 SEALANT............................... 3 SPECIAL TOOLS........................
13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION................ 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 3 SEALANT............................... 3 SPECIAL TOOLS........................
1.2 HFM Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection/Ignition System (HFM-SFI) Engine 111
 Diagnosis - Diagnostic Trouble Code () Memory Preliminary work:........................ Engine Test, djustment, Engines, Volume 1 Note regarding diagnostic trouble code () readout: The engine control module
Diagnosis - Diagnostic Trouble Code () Memory Preliminary work:........................ Engine Test, djustment, Engines, Volume 1 Note regarding diagnostic trouble code () readout: The engine control module
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system - transistorised type
 5B 1 Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system - transistorised type Contents Coil - testing........................................... 9 Distributor - overhaul..................................... 7 Distributor
5B 1 Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system - transistorised type Contents Coil - testing........................................... 9 Distributor - overhaul..................................... 7 Distributor
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING SECTION
 PURPOSE OF IGNITION SYSTEM The ignition system supplies high-voltage surges as high as 47,000 volts (in some electronic systems) to the spark plugs in the engine cylinders. These surges produce electric
PURPOSE OF IGNITION SYSTEM The ignition system supplies high-voltage surges as high as 47,000 volts (in some electronic systems) to the spark plugs in the engine cylinders. These surges produce electric
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
The Bosch LH 2.4 Jetronic System is used on the models (and later non-turbo/non-odbii models)
 The Bosch LH 2.4 Jetronic System is used on the 89-93 models (and later non-turbo/non-odbii models) 1-1-1 No faults. 1-1-2 Control unit fault. 1-1-3 Fuel injectors - Injector cable break or blocked injector;
The Bosch LH 2.4 Jetronic System is used on the 89-93 models (and later non-turbo/non-odbii models) 1-1-1 No faults. 1-1-2 Control unit fault. 1-1-3 Fuel injectors - Injector cable break or blocked injector;
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS 2009 CORVETTE LS - 9 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR LS 9 The following instructions are intended as an aid to assist in harness installation. More in depth information can be obtained
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS 2009 CORVETTE LS - 9 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR LS 9 The following instructions are intended as an aid to assist in harness installation. More in depth information can be obtained
Lotus Service Notes Section EMD
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited
 Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4
 Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4 1. Which of these sensors directly measures engine load? a. Manifold absolute pressure sensor. b. Coolant sensor (ECT). c. Vehicle speed sensor.
Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4 1. Which of these sensors directly measures engine load? a. Manifold absolute pressure sensor. b. Coolant sensor (ECT). c. Vehicle speed sensor.
Unit MC07K Knowledge of Diagnosis and Rectification of Motorcycle Engine Faults
 Assessment Requirements Unit MC07K Knowledge of Diagnosis and Rectification of Motorcycle Engine Faults Content: Single cylinder and multi-cylinder fuel injection systems a. The operation and construction
Assessment Requirements Unit MC07K Knowledge of Diagnosis and Rectification of Motorcycle Engine Faults Content: Single cylinder and multi-cylinder fuel injection systems a. The operation and construction
Powertrain DTC Summaries OBD II
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
H - TESTS W/O CODES Nissan 240SX INTRODUCTION TROUBLE SHOOTING SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS WILL NOT START
 H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components
 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
AD07.61-P-4000AC ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory Possible cause Note Fault code description
 Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
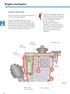 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace
 Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION
 SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION A -- Ground G -- Fuel Pump B -- Diagnostic Terminal H -- Brake Sense Speed Input F -- TCC M -- Serial Data (special tool needed - Do Not Use) For ECM Trouble Codes,
SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION A -- Ground G -- Fuel Pump B -- Diagnostic Terminal H -- Brake Sense Speed Input F -- TCC M -- Serial Data (special tool needed - Do Not Use) For ECM Trouble Codes,
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
G - TESTS W/CODES Volvo 960 INTRODUCTION SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics
 G - TESTS W/CODES 1994 Volvo 960 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics 960 INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES, proceed with SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.
G - TESTS W/CODES 1994 Volvo 960 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics 960 INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES, proceed with SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
Glossary. 116
 Sequential Fuel Injection Sequential means that each injector for each cylinder is triggered only one time during the engine s cycle. Typically the injector is triggered only during the intake stroke.
Sequential Fuel Injection Sequential means that each injector for each cylinder is triggered only one time during the engine s cycle. Typically the injector is triggered only during the intake stroke.
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Cylinder Numbering 2 Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Cylinder Numbering 2 Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. System Sensors
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
Function description
 30-0006 Function description Electronic accelerator (EA) Block diagram Overvoltage protection EA control relay, Models 124, 202 (power supply) Idle speed control Base, Models (ISC) 129,140, 124.034/036
30-0006 Function description Electronic accelerator (EA) Block diagram Overvoltage protection EA control relay, Models 124, 202 (power supply) Idle speed control Base, Models (ISC) 129,140, 124.034/036
POLESTAR HS Management System
 POLESTAR HS Management System Installation Instructions This document contains the information needed to install and adjust the POLESTAR HS Engine Management System. It assumes that the system already
POLESTAR HS Management System Installation Instructions This document contains the information needed to install and adjust the POLESTAR HS Engine Management System. It assumes that the system already
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
DTC Summaries. NipponDenso V12 Engine Management
 DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART 05 35 HINT: As for the vehicle for MEXICO, refer to Repair Manual 2003 COROLLA MATRIX (Pub. No. RM940U). Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART 05 35 HINT: As for the vehicle for MEXICO, refer to Repair Manual 2003 COROLLA MATRIX (Pub. No. RM940U). Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your
1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen System & Component Testing - Digifant. EuroVan
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen System & Component Testing - Digifant EuroVan INTRODUCTION Since many computer-controlled and monitored components set a trouble code if
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen System & Component Testing - Digifant EuroVan INTRODUCTION Since many computer-controlled and monitored components set a trouble code if
Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65).
 DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
