Handout Activity: HA185
|
|
|
- Joshua Simon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cylinder heads Handout Activity: HA185 HA185-2 Cylinder head The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the combustion chamber. It carries the valves and, in many cases, the camshafts. The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the combustion chamber. In-line engines of light vehicles have just one cylinder head for all the cylinders. Larger in-line engines can have 2 or more. V-type and horizontally-opposed engines have a separate cylinder head for each bank of cylinders. Just as with engine blocks, cylinder heads can be made of cast iron, or aluminium alloy. A head made of aluminium alloy is lighter than if it were made of cast iron. Aluminium also conducts heat away more quickly than iron. So with an aluminium-alloy head, the heat of combustion can be conducted away into the coolant more quickly. Manufacturing the head is similar to manufacturing the block. A casting mold is made. Sand cores are put in to form any hollow areas. Depending on the engine, these can be for coolant and lubricant passages, and inlet and exhaust ports. Air-cooled engines have cooling fins cast into the cylinder head. The underside of the head is shaped to form the combustion chamber. Molten metal is poured in, and allowed to cool. The cores are broken out and removed, and the cylinder head cleaned of any sand. After casting comes machining. Surfaces that must seal are machined flat. Holes are drilled and tapped for attaching bolts and studs. In sand-cast heads, the large holes that had contained sand are machined, then fitted with soft metal plugs, called core plugs.
2 Cylinder heads HA Just as with engine blocks, cylinder heads can be made of cast iron, or alloy. 2. Air-cooled engines have cooling cast into the cylinder head. 3. The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the chamber. 4. In sand-cast heads, the large holes that had contained sand are machined, then fitted with soft metal plugs, called plugs. 5. V-type and horizontally-opposed engines have a separate head for each bank of cylinders. Score / Page 2
3 Cylinder head design Handout Activity: HA186 HA186-2 Cylinder head design Cylinder head combustion chambers are designed to help improve the swirl or turbulence of the air-fuel mixture, and prevent fuel droplets settling on the surfaces of the combustion chamber or cylinder walls. Cylinder heads are designed to help improve the swirl or turbulence of the air-fuel mixture, and prevent fuel droplets settling on the surfaces of the combustion chamber or cylinder walls. When air-fuel mixture is compressed between the piston and the flat part of the cylinder head, it produces what s called squish. That means squeezing of the gases to increase their velocity and turbulence. In gasoline engines, the three most popular combustion chamber designs are called hemispherical pent roof, bath-tub and wedge. A hemispherical, or pent-roof combustion chamber has the intake valve on one side of the chamber and the exhaust valve on the other. This provides crossflow. Air-fuel mixture enters on one side, and exhaust gases exit on the other. Positioning the valves in this way leaves room for relatively large valves and ports, and that helps the engine breathe. Breathing refers to the engine taking in the air or air-fuel mixture. Fuel starts to burn at the plug, then burning travels outward in all directions. This is called flame propagation. With the plug in the middle of the hemisphere, the flame front has less distance to travel than in some other designs, which gives rapid and effective combustion. This design is common in a lot of passenger vehicles. The bath-tub combustion chamber is oval-shaped, like an inverted bathtub. Valves are mounted vertically and side by side, making them simple to operate. The plug is to one side, and that creates a short flame path. It all helps increase turbulence. The wedge-shaped combustion chamber tapers away from the plug which is at the thick end of the wedge. The valves are in line and inclined from the vertical. This design usually has a smaller surface area than the others, with less area where fuel droplets can condense. Less fuel is left unburned after combustion, which reduces hydrocarbon exhaust emissions. And since the flame is directed toward the small end of the wedge, damage caused by detonation is reduced.
4 Cylinder head design HA In gasoline engines, the three most popular combustion chamber designs are called hemispherical pent roof, bath-tub and. 2. Less fuel is left unburned after, which reduces hydrocarbon exhaust emissions. 3. Air-fuel mixture enters on one side, and gases exit on the other. 4. When air-fuel mixture is compressed between the piston and the flat part of the cylinder head, it produces what s called. 5. The plug is to one side, and that creates a short flame path. It all helps increase. Score / Page 2
5 Diesel combustion chambers Handout Activity: HA187 HA187-2 Diesel combustion chambers Direct-injection diesels inject into the combustion chamber formed in the top of the piston. For indirect injection, the combustion chamber is a separate chamber formed in the head. Diesel combustion chambers come in 2 main types. Direct and indirect injection. Both are designed to promote turbulence, to help the compressed air and injected fuel mix well. Engines using direct injection have cylinder heads with a flat face. The combustion chamber is formed in the top of the piston. Sometimes, the rim of the piston provides squish, forcing the air to the centre of the combustion chamber. This causes turbulence as fuel is injected into the cylinder. In indirect injection, the piston is fairly flat, or has a shallow cavity. The main combustion chamber is between the cylinder head and the top of the piston, but a smaller, separate chamber is in the head. Fuel is injected into this smaller chamber. It can have various designs. A swirl chamber is spherical, and connected to the main chamber by an angled passage. Both the injector and glow plug are screwed into the head. The glow plug preheats the air inside to help start the engine. During compression, the spherical shape makes the air swirl in the chamber. This helps make a better mixture of the air and fuel, which improves combustion. This combustion chamber is divided into a main combustion chamber and an air cell, joined by a throat. The injector is in the throat. When injection commences, combustion pressure forces the air to flow from the air cell where it mixes with fuel from the injector. The rush of air from the air cell produces a rotary motion of gas in the main chamber which helps make combustion more efficient. This pre-combustion chamber is screwed into the cylinder head. The injector is mounted in the upper end. Injection occurs near the top of the compression stroke. Only part of the fuel is burned in the pre-combustion chamber because of the limited amount of air there. The high rise in pressure forces burning fuel into the main chamber. This happens very rapidly, which helps make more efficient combustion.
6 Diesel combustion chambers HA The injector is in the. 2. Direct and indirect injection. Both are designed to promote, to help the compressed air and injected fuel mix well. 3. Injection occurs near the top of the stroke. 4. Sometimes, the rim of the piston provides squish, forcing the air to the centre of the chamber. 5. When injection commences, combustion pressure forces the air to flow from the air cell where it mixes with fuel from the. Score / Page 2
7 Intake and exhaust passages Handout Activity: HA188 HA188-2 Intake and exhaust passages Smaller intake and exhaust passages and ports allow more torque at low engine speeds. At high speeds, smaller passages restrict airflow. Larger passages produce greater power at high engine speeds. The size of passages in the head can affect engine output. Smaller intake and exhaust passages and ports allow more torque at low engine speeds. This is because smaller passages improve mixing of air and fuel at low speeds, which causes more efficient combustion. At high speeds however, these smaller passages restrict HA187-2 airflow. To reduce the effect of this, this engine has two inlet valves. One opens at low speed and the other operates at higher engine speeds. Larger passages produce greater power at high engine speeds. Each intake and exhaust passage can be formed separately in the head. Intake passages for adjacent passages may have a common, thin wall between them. This is called siamesed. Exhaust ports in the same head can also be siamesed. When all intake and exhaust ports are on one side, it is called a counter-flow head. They can be cast separately or siamesed. When all of the intake ports are on one side and exhaust ports are on the other, it is called a cross-flow head. This allows for straighter passageways and higher efficiency.
8 Intake and exhaust passages HA At high speeds however, these smaller passages restrict. 2. When all of the intake ports are on one side and exhaust ports are on the other, it is called a head. 3. Smaller intake and exhaust passages and ports allow more at low engine speeds. 4. When all intake and exhaust ports are on one side, it is called a head. 5. Larger passages produce greater power at engine speeds. Score / Page 2
9 Gaskets Handout Activity: HA189 HA189-2 Gaskets Gaskets form a seal by being compressed between stationary parts where liquid or gas could pass. Gaskets around a rotating part would quickly wear out. Oil seals are used to seal these parts. Gaskets form a seal by being compressed between stationary parts where liquid or gas could pass. Most gaskets are made to be used only once. They can be made of soft materials such as cork, rubber, paper, asbestos. They can also be made of soft alloys and metals such as brass, copper, aluminium or soft steel sheet metal. Choosing which material and design to use depends on the substance to be sealed, the pressures and temperatures involved. And, the materials and mating surfaces to be sealed. Head gaskets seal and contain the pressures of combustion within the engine, between the cylinder head and block. They also seal oil passages between block and head. And control the flow of coolant between the block and the head. Some gaskets provide or adjust clearances. Some joints between surfaces on modern engines are being sealed with special sealants which eliminate the use of gaskets in some applications. Gaskets around a rotating part would quickly wear out and leak. To seal these parts, oil seals are needed. Many different kinds have been developed, including oil slinger rings. The most widely used is the lip type dynamic oil seal. It has a shaped dynamic rubber lip that s held in contact with the shaft to be sealed by a circular coil spring called a garter spring. A similar sealing principle is used to seal the valve stem to prevent oil entering the engine combustion chamber. Rotating or sliding shafts can also be sealed by using O rings, but generally they are not as durable in most applications as the lip-type seal. As a general rule, oil seals must be replaced when a component is overhauled.
10 Gaskets HA Gaskets around a rotating part would quickly wear out and leak. To seal these parts, seals are needed. 2. Gaskets form a by being compressed between stationary parts where liquid or gas could pass. 3. Head gaskets seal and contain the pressures of combustion within the engine, between the cylinder head and. Score / Page 2
11 Gaskets and oil seals Handout Activity: HA190 HA190-2 Gaskets and oil seals Gaskets can be made of soft materials such as cork or rubber, or they can be made of soft alloys and metals. Most gaskets are made to be used only once. Oil seals must also be replaced when a component is overhauled. Gaskets form a seal by being compressed between stationary parts where liquid or gas could pass. Most gaskets are made to be used only once. They can be made of soft materials such as cork, rubber, nitrile, paper, heat resistant materials or graphite; or they can also be made of soft alloys and metals such as brass, copper, aluminum or soft steel sheet metal. Such materials may be used individually or in some cases as blends to produce the required functional material. Choosing which material and design to use depends on the substance to be sealed, the pressures and temperatures involved, and the materials and mating surfaces to be sealed. Head gaskets seal and contain the pressures of combustion within the engine, between the cylinder head and block. Modern head gaskets have to be constructed to resist high temperatures and engine detonation. Some modern high temperature head gaskets are called anisotropic in nature. This means that the gasket is designed to conduct heat laterally to transfer heat from the engine to the coolant faster. They are normally constructed with a steel core. Special facing materials are added to both sides of the gasket core to provide a comprehensive seal under varying torque conditions. With the advent of environmental factors and a reduction in the use of asbestos, replacement materials have been developed. Some of these modern special materials that are now used for the side layers of head gaskets are designed to withstand temperatures up to 2100 degrees F or 1150 degrees C. Such materials are also designed to allow the cylinder head and block, some of which which have considerable distortion rates, to move slightly on the head gasket as they expand during engine warm-up. This feature is vital for preventing head gasket failure. Some head gaskets also incorporate stainless steel fire rings to help to contain heat and pressure within the cylinder. In addition, many head gaskets also have an added silicone based outer coating on both sides of the side material layers to provide additional cold sealing ability during start-up and warm-up. Head gaskets also seal oil passages, and control the flow of coolant between the cylinder block and head and are fitted with beads or rings to prevent leakage and corrosion. Some joints between surfaces on modern engines are being sealed with special sealants which eliminate the use of gaskets in some applications. Pure rubber, or conventional cork-rubber is unable to deal with the stresses and pressures in modern engines. Modern gasket manufacturers are producing improved material combinations such as nitrile and cork blends to deal with high tech engine demands. Such combinations are more able to deal with issues such as compressibility and wicking. Some materials are designed to swell in application and increase sealing ability. For instance when oil inside a valve cover penetrates the edge of the gasket material, it is designed to swell by approximately 30%. This swelling effect increases the sealing pressure between the head and valve cover sealing surfaces and helps to seal potential leaks. Some gasket materials are designed to have high tensile strength. They are designed to resist breakage during dismantling or installation processes. Gaskets around a rotating part would quickly wear out and leak. To seal these parts, oil seals are needed. The most widely used is the lip type dynamic oil seal. It has a shaped dynamic rubber lip that s held in contact with the shaft to be sealed by a circular coil spring called a garter spring.
12 Gaskets and oil seals HA190-2 A similar sealing principle Engines: is used to Motive seal the Power valve stem Types: to prevent oil entering the engine combustion chamber. Rotating or sliding shafts can also be sealed by using O rings, but generally they are not as durable in most applications as the lip-type seal. Various materials are used in modern oil seals, some being impregnated with special coating materials that are designed to increase their sealing ability on worn shafts. As a general rule, oil seals must be replaced when a component is overhauled. 1. This swelling effect increases the sealing between the head and valve cover sealing surfaces and helps to seal potential leaks. 2. Gaskets around a rotating part would quickly wear out and leak. To seal these parts, seals are needed. 3. With the advent of environmental factors and a reduction in the use of, replacement materials have been developed. 4. Rotating or sliding shafts can also be sealed by using rings, but generally they are not as durable in most applications as the lip-type seal. 5. Modern head gaskets have to be constructed to resist high and engine detonation. Score / Page 2
13 Head gaskets Handout Activity: HA191 HA191-2 Head gaskets Head gaskets seal and contain the pressures of combustion within the engine, between the cylinder head and the block. Head gaskets seal and contain the pressures of combustion within the engine, between the cylinder head and the block. Some high temperature head gaskets are called anisotropic in nature. This means that the gasket is designed to conduct heat laterally to transfer heat from the engine to the coolant faster. They are normally constructed with a steel core. Special facing materials are added to both sides of the gasket core to provide a comprehensive seal under varying torque conditions. Some head gaskets incorporate stainless steel fire rings to help to contain heat and pressure within the cylinder. Many head gaskets also have an added silicone based outer coating on both sides of the side material layers to provide additional cold sealing ability during start-up and warm-up. Head gaskets also seal oil passages, and control the flow of coolant between the cylinder block and head and are fitted with beads or rings to prevent leakage and corrosion. Gasket manufacturers have produced improved material combinations such as nitrile and cork blends because pure rubber, or conventional cork-rubber, is unable to deal with the stresses and pressures of high tech engines. Such combinations are more able to deal with issues such as compressibility and wicking. Some materials are designed to swell in application and increase sealing ability. For instance when oil inside a valve cover penetrates the edge of the gasket material, it is designed to swell by approximately 30%. This swelling effect increases the sealing pressure between the head and valve cover sealing surfaces and helps to seal potential leaks. Some materials are also designed to allow the cylinder head and block, some of which have considerable distortion rates, to move slightly on the head gasket as they expand during engine warm-up. This feature can be vital for preventing head gasket failure.
14 Head gaskets HA Gasket manufacturers have produced improved material combinations such as nitrile and cork blends because pure rubber, or conventional cork-rubber, is unable to deal with the stresses and pressures of high tech engines. Such combinations are more able to deal with issues such as compressibility and. 2. Head gaskets seal and contain the pressures of combustion within the engine, between the cylinder and the block. 3. Some materials are designed to swell in application and sealing ability. 4. This means that the gasket is designed to conduct heat laterally to transfer heat from the engine to the faster. 5. Some head gaskets incorporate stainless steel rings to help to contain heat and pressure within the cylinder. Score / Page 2
15 Turbulence Handout Activity: HA192 HA192-2 Turbulence Turbulence refers to the swirling motion of a liquid or a gas. Turbulence refers to the swirling motion of a liquid or a gas. It helps to maximise the mixing of air and fuel, which helps make sure the combustion process occurs efficiently. Without turbulence, the air-fuel mixture can form local areas of high pressure and temperature that can cause detonation during combustion. A high level of turbulence can prevent this. 1. Turbulence refers to the swirling motion of a or a gas. 2. Without turbulence, the air-fuel mixture can form local areas of high and temperature that can cause detonation during combustion. Score / 2
Handout Activity: HA170
 Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Engine Construction and Principles of Operation
 Ch. 4 Engine Construction and Principles of Operation Gasoline Engine A gasoline fueled engine is a mechanism designed to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy It is an internal combustion engine.
Ch. 4 Engine Construction and Principles of Operation Gasoline Engine A gasoline fueled engine is a mechanism designed to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy It is an internal combustion engine.
LECTURE NOTES INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION
 LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
 CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION CYLINDER BLOCKS, HEADS, AND CRANKCASES The cylinder, or the engine block, is the basic foundation of virtually all liquid-cooled engines. The block is a solid casting made
CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION CYLINDER BLOCKS, HEADS, AND CRANKCASES The cylinder, or the engine block, is the basic foundation of virtually all liquid-cooled engines. The block is a solid casting made
Lecture 5. Abnormal Combustion
 Lecture 5 Abnormal Combustion Abnormal Combustion The Abnormal Combustion:- When the combustion gets deviated from the normal behavior resulting loss of performance or damage to the engine. It is happened
Lecture 5 Abnormal Combustion Abnormal Combustion The Abnormal Combustion:- When the combustion gets deviated from the normal behavior resulting loss of performance or damage to the engine. It is happened
Name Date. True-False. Multiple Choice
 Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Cylinder Head Servicing Dye penetrant Magnetic Flux
 Cylinder Head Servicing To prevent warpage of cylinder heads, damaged bolts, threads and gasket leakage, even, consistent and adequate clamping of cylinder heads is necessary. An earlier technique for
Cylinder Head Servicing To prevent warpage of cylinder heads, damaged bolts, threads and gasket leakage, even, consistent and adequate clamping of cylinder heads is necessary. An earlier technique for
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
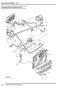 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
California State University, Bakersfield. Signals and Systems. Kristin Koehler. California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013
 Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Heat Transfer in Engines. Internal Combustion Engines
 Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions
 Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions People who are familiar with the functioning of a gasoline aircraft engine need not have any difficulty in understanding how a high speed Diesel aircraft
Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions People who are familiar with the functioning of a gasoline aircraft engine need not have any difficulty in understanding how a high speed Diesel aircraft
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
unit 10 lubricating systems
 FUEL TANK unit 10 lubricating systems An engine needs oil between its moving parts. The oil keeps the parts from rubbing on each other. When the parts do not rub on each other they do not wear out as quickly.
FUEL TANK unit 10 lubricating systems An engine needs oil between its moving parts. The oil keeps the parts from rubbing on each other. When the parts do not rub on each other they do not wear out as quickly.
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines
 Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Combustion. T Alrayyes
 Combustion T Alrayyes Fluid motion with combustion chamber Turbulence Swirl SQUISH AND TUMBLE Combustion in SI Engines Introduction The combustion in SI engines inside the engine can be divided into three
Combustion T Alrayyes Fluid motion with combustion chamber Turbulence Swirl SQUISH AND TUMBLE Combustion in SI Engines Introduction The combustion in SI engines inside the engine can be divided into three
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Engine Design Classifications
 Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC - F02F - 2014.07 - Interleaved - page 1 CPC COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION F02F CYLINDERS, PISTONS OR CASINGS, FOR COMBUSTION ENGINES; ARRANGEMENTS OF SEALINGS IN COMBUSTION ENGINES ( specially
CPC - F02F - 2014.07 - Interleaved - page 1 CPC COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION F02F CYLINDERS, PISTONS OR CASINGS, FOR COMBUSTION ENGINES; ARRANGEMENTS OF SEALINGS IN COMBUSTION ENGINES ( specially
TKP3501 Farm Mechanization
 TKP3501 Farm Mechanization Topic 2: Internal Combustion Engines Ahmad Suhaizi, Mat Su Email: asuhaizi@upm.edu.my Outlines Internal vs external combustion engines Engine structure Combustion cycle 4 stroke
TKP3501 Farm Mechanization Topic 2: Internal Combustion Engines Ahmad Suhaizi, Mat Su Email: asuhaizi@upm.edu.my Outlines Internal vs external combustion engines Engine structure Combustion cycle 4 stroke
Normal vs Abnormal Combustion in SI engine. SI Combustion. Turbulent Combustion
 Turbulent Combustion The motion of the charge in the engine cylinder is always turbulent, when it is reached by the flame front. The charge motion is usually composed by large vortexes, whose length scales
Turbulent Combustion The motion of the charge in the engine cylinder is always turbulent, when it is reached by the flame front. The charge motion is usually composed by large vortexes, whose length scales
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
Module 7: Cooling System Components
 Â ÂÂ Â Basic Cooling System Components Radiators Common Types of Radiators Coolant Hoses Water Pumps Centrifugal Force Types of Drives for Water Pumps Types of Drive Belts Basic Cooling System Components
 Â  Basic Cooling System Components Radiators Common Types of Radiators Coolant Hoses Water Pumps Centrifugal Force Types of Drives for Water Pumps Types of Drive Belts Basic Cooling System Components
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
Small Engines CDE Test Bank B
 Small Engines CDE Test Bank B Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following would not be found in the crankcase? a. oil c. camshaft
Small Engines CDE Test Bank B Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following would not be found in the crankcase? a. oil c. camshaft
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
HALDERMAN
 HALDERMAN WWW.JAMESHALDERMAN.COM 1. Diesel fuel ignition in a warm engine is being discussed. Technician A says diesel fuel is ignited by the heat of the compression. Technician B says diesel fuel is ignited
HALDERMAN WWW.JAMESHALDERMAN.COM 1. Diesel fuel ignition in a warm engine is being discussed. Technician A says diesel fuel is ignited by the heat of the compression. Technician B says diesel fuel is ignited
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 13 & 14 Pages Engine Construction 52 Points
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 13 & 14 Pages 182-216 Engine Construction 52 Points Automotive Service 1. The engine top end includes the cylinder, valve cover and intake & exhaust. Head, Manifolds
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 13 & 14 Pages 182-216 Engine Construction 52 Points Automotive Service 1. The engine top end includes the cylinder, valve cover and intake & exhaust. Head, Manifolds
LANLEO11 - SQA Unit Code F9GV 04 Service and repair engines on land-based equipment
 Service and repair engines on land-based equipment Overview This standard covers the construction and operating principles of two-stroke and four-stroke spark ignition and compression ignition engines
Service and repair engines on land-based equipment Overview This standard covers the construction and operating principles of two-stroke and four-stroke spark ignition and compression ignition engines
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER
 AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
DESCRIPTION FUEL AND VACUUM PUMP REMOVE AND REPLACE FUEL PUMP-OVERHAUL 6B PONTIAC SHOP MANUAL. S. Install battery and connect cables.
 6B-74 1955 PONTIAC SHOP MANUAL DESCRIPTION FUEL AND VACUUM PUMP All models are equipped with a combination fueland double acting vacuum pump operated by an eccentric bolted to the front end of the engine
6B-74 1955 PONTIAC SHOP MANUAL DESCRIPTION FUEL AND VACUUM PUMP All models are equipped with a combination fueland double acting vacuum pump operated by an eccentric bolted to the front end of the engine
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages Engine Fundamentals 62 Points
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages 145-161 Engine Fundamentals 62 Points 1. The is the area between the top of the piston & the cylinder head. Combustion Chamber Cylinder Chamber Chamber of
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages 145-161 Engine Fundamentals 62 Points 1. The is the area between the top of the piston & the cylinder head. Combustion Chamber Cylinder Chamber Chamber of
Brake Systems. Introduction
 Brake Systems Figure 1. A Typical Brake System Introduction The brake system (Figure 1) is designed to slow and halt the motion of a vehicle. To do that, various components within a hydraulic brake system
Brake Systems Figure 1. A Typical Brake System Introduction The brake system (Figure 1) is designed to slow and halt the motion of a vehicle. To do that, various components within a hydraulic brake system
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS
 Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Module7:Advanced Combustion Systems and Alternative Powerplants Lecture 32:Stratified Charge Engines
 ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING SECTION
 PURPOSE OF IGNITION SYSTEM The ignition system supplies high-voltage surges as high as 47,000 volts (in some electronic systems) to the spark plugs in the engine cylinders. These surges produce electric
PURPOSE OF IGNITION SYSTEM The ignition system supplies high-voltage surges as high as 47,000 volts (in some electronic systems) to the spark plugs in the engine cylinders. These surges produce electric
TYPE E Main Valve Sizes 3 /8 through 12
 Technical Data SD 3001E PRINTED IN U.S.A. SD 3001E/9709 SPENCE ENGINEERING COMPANY, INC. 150 COLDENHAM ROAD, WALDEN, NY 12586-2035 A B TYPE E MAIN VALVE FACE TO FACE DIMENSIONS C D E DIMENSIONS (inches)
Technical Data SD 3001E PRINTED IN U.S.A. SD 3001E/9709 SPENCE ENGINEERING COMPANY, INC. 150 COLDENHAM ROAD, WALDEN, NY 12586-2035 A B TYPE E MAIN VALVE FACE TO FACE DIMENSIONS C D E DIMENSIONS (inches)
AT AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK
 AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
2) Rich mixture: A mixture which contains less air than the stoichiometric requirement is called a rich mixture (ex. A/F ratio: 12:1, 10:1 etc.
 Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
CH. 48 ENGINE MECHANICAL PROBLEMS TEST
 TERRY FOX AUTOMOTIVE CH. 48 ENGINE MECHANICAL PROBLEMS TEST WHEN YOU ARE DONE THIS TEST GUESS WHAT YOU THINK YOU WILL RECEIVE FOR A MARK BELOW. IF YOU ARE WITHIN 2 MARKS YOU WILL RECEIVE 2 BONUS MARKS.
TERRY FOX AUTOMOTIVE CH. 48 ENGINE MECHANICAL PROBLEMS TEST WHEN YOU ARE DONE THIS TEST GUESS WHAT YOU THINK YOU WILL RECEIVE FOR A MARK BELOW. IF YOU ARE WITHIN 2 MARKS YOU WILL RECEIVE 2 BONUS MARKS.
E-TVCS. Technology for the clean age.
 E-TVCS Technology for the clean age. Kubota's proprietary TVCS (Three Vortex Combustion System) obtains an optimum air/fuel mixture by generating three intense swirling air flows (vortexes) within the
E-TVCS Technology for the clean age. Kubota's proprietary TVCS (Three Vortex Combustion System) obtains an optimum air/fuel mixture by generating three intense swirling air flows (vortexes) within the
CYLINDER HEAD OVERHAUL
 ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION -2011 Mercedes-... Page 1 of 20 CYLINDER HEAD OVERHAUL * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * Examples used in this article are general in nature and do not necessarily
ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION -2011 Mercedes-... Page 1 of 20 CYLINDER HEAD OVERHAUL * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * Examples used in this article are general in nature and do not necessarily
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
Design/Modeling and Thermal Analysis on Cylinder Head of I.C Engine
 Design/Modeling and Thermal Analysis on Cylinder Head of I.C Engine G.Bahadur Vali Department of Mechanical, Chebrolu Engineering College. Abstract: A cylinder head is made of box type of section of considerable
Design/Modeling and Thermal Analysis on Cylinder Head of I.C Engine G.Bahadur Vali Department of Mechanical, Chebrolu Engineering College. Abstract: A cylinder head is made of box type of section of considerable
AE 1005 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES COMBUSTION IN SI ENGINES
 AE 1005 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES COMBUSTION IN SI ENGINES Syllabus Combustion in premixed and diffusion flames - Combustion process in IC engines. Stages of combustion - Flame propagation - Flame velocity and
AE 1005 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES COMBUSTION IN SI ENGINES Syllabus Combustion in premixed and diffusion flames - Combustion process in IC engines. Stages of combustion - Flame propagation - Flame velocity and
2. Air Line AIR LINE FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL B: MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR FU(H4DOTC)-3
 W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
Figure 1: The spray of a direct-injecting four-stroke diesel engine
 MIXTURE FORMATION AND COMBUSTION IN CI AND SI ENGINES 7.0 Mixture Formation in Diesel Engines Diesel engines can be operated both in the two-stroke and four-stroke process. Diesel engines that run at high
MIXTURE FORMATION AND COMBUSTION IN CI AND SI ENGINES 7.0 Mixture Formation in Diesel Engines Diesel engines can be operated both in the two-stroke and four-stroke process. Diesel engines that run at high
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 9:Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd.
 Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd. The Lecture Contains: HC from Lubricating Oil Film Combustion Chamber Deposits HC Mixture Quality and In-Cylinder Liquid Fuel HC from Misfired Combustion
Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd. The Lecture Contains: HC from Lubricating Oil Film Combustion Chamber Deposits HC Mixture Quality and In-Cylinder Liquid Fuel HC from Misfired Combustion
SIDEWINDER COURSE PREREQUISITE MANUAL
 SIDEWINDER COURSE PREREQUISITE MANUAL The S&S engine class is designed for the seasoned tech or shop owner. A certain level of knowledge and understanding is required for your success. We will be covering
SIDEWINDER COURSE PREREQUISITE MANUAL The S&S engine class is designed for the seasoned tech or shop owner. A certain level of knowledge and understanding is required for your success. We will be covering
Workshop Manual. F-Super Duty : Powertrain. 03: Engine
 Workshop Manual 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 3: Powertrain 03: Engine 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 Contents/Index GROUP 03: Engine SECTION 303-00: Engine System General Information SECTION 303-01A: Engine 5.4L
Workshop Manual 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 3: Powertrain 03: Engine 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 Contents/Index GROUP 03: Engine SECTION 303-00: Engine System General Information SECTION 303-01A: Engine 5.4L
Chapter 4 ANALYTICAL WORK: COMBUSTION MODELING
 a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST
 SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST 1. Position two 3 x 6 x ¼ steel plates in the flat position for a butt weld. The weld joint should be 6 long. 2. Select to either bevel the metal
SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST 1. Position two 3 x 6 x ¼ steel plates in the flat position for a butt weld. The weld joint should be 6 long. 2. Select to either bevel the metal
Technical Service Bulletin
 TSB: MO-2004-04-03 Technical Service Bulletin Date: 05/05/04 Product Description: All Motor Oils / Oil Analysis Subject: Engine Oil Consumption Description: REASONS FOR MOTOR OIL CONSUMPTION provides explanations
TSB: MO-2004-04-03 Technical Service Bulletin Date: 05/05/04 Product Description: All Motor Oils / Oil Analysis Subject: Engine Oil Consumption Description: REASONS FOR MOTOR OIL CONSUMPTION provides explanations
GLOSSARY. Block. Cylinders
 Engine The power source for any farm tractor is the engine. The engine provides the muscle for the power train and the hydraulic system. The typical modern farm tractor has a diesel engine ranging from
Engine The power source for any farm tractor is the engine. The engine provides the muscle for the power train and the hydraulic system. The typical modern farm tractor has a diesel engine ranging from
Cooling System Description and Operation
 Page 1 of 5 2008 Holden VE Sedan VE, WM, Caprice, Statesman, Lumina, Omega, VXR8 Service Manual Engine Engine Cooling Description and Operation Document ID: 1990377 Cooling System Description and Operation
Page 1 of 5 2008 Holden VE Sedan VE, WM, Caprice, Statesman, Lumina, Omega, VXR8 Service Manual Engine Engine Cooling Description and Operation Document ID: 1990377 Cooling System Description and Operation
MASTER CYLINDER. Section 2. Lesson Objectives
 MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
 Page 1 of 7 1965 Ford Mustang 4.7L Eng VIN A Base Service Manual: 221", 260", 289" V8 ENGINES Print Date: ENGINE NOTES 1962-65 COOLANT LOSS OR WATER PUMP & FRONT COVER CORROSION CORRECTION: May be caused
Page 1 of 7 1965 Ford Mustang 4.7L Eng VIN A Base Service Manual: 221", 260", 289" V8 ENGINES Print Date: ENGINE NOTES 1962-65 COOLANT LOSS OR WATER PUMP & FRONT COVER CORROSION CORRECTION: May be caused
Mechanical Engineering Design of a Split-Cycle Combustor. Experimental Fluid-Mechanics Research Group
 Mechanical Engineering Design of a Split-Cycle Combustor Dr Daniel D Coren Dr Nicolas D D Miché Experimental Fluid-Mechanics Research Group University of Brighton, March 2015 mechanical design considerations
Mechanical Engineering Design of a Split-Cycle Combustor Dr Daniel D Coren Dr Nicolas D D Miché Experimental Fluid-Mechanics Research Group University of Brighton, March 2015 mechanical design considerations
Bearings. Rolling-contact Bearings
 Bearings A bearing is a mechanical element that limits relative motion to only the desired motion and at the same time it reduces the frictional resistance to the desired motion. Depending on the design
Bearings A bearing is a mechanical element that limits relative motion to only the desired motion and at the same time it reduces the frictional resistance to the desired motion. Depending on the design
PIERBURG. Carburetor: 2E3
 PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Chapter 7: Combustion Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Outline In this lecture we will discuss the combustion process: The characteristics of the process. The different
Chapter 7: Combustion Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Outline In this lecture we will discuss the combustion process: The characteristics of the process. The different
NATIONAL HOMOLOGATION FORM KARTING ENGINE
 NATIONAL HOMOLOGATION FORM KARTING ENGINE Manufacturer BRIGGS & STRATTON Make BRIGGS & STRATTON Model 206-124332 Validity of the homologation 6 years Number of pages 25 This Homologation Form reproduces
NATIONAL HOMOLOGATION FORM KARTING ENGINE Manufacturer BRIGGS & STRATTON Make BRIGGS & STRATTON Model 206-124332 Validity of the homologation 6 years Number of pages 25 This Homologation Form reproduces
GIOUP 11 EXHAUST SYSTEM
 EXHAUST SYSTEM 11-1 GIOUP 11 EXHAUST SYSTEM CONTENTS Page Exhaust Manifold...... -4 Exhaust Pipes, Mufflers and Tail Pipes... 5 -Intake Manifold... 4 Manifold Heat Control Valve... 5 Manifold Heat Control
EXHAUST SYSTEM 11-1 GIOUP 11 EXHAUST SYSTEM CONTENTS Page Exhaust Manifold...... -4 Exhaust Pipes, Mufflers and Tail Pipes... 5 -Intake Manifold... 4 Manifold Heat Control Valve... 5 Manifold Heat Control
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
Internal Combustion Engines.
 Internal Combustion Engines. Here's a quick description of a typical internal combustion engine, along with basic vocabularies that describe the components and their functions. This stuffs serve as a quick
Internal Combustion Engines. Here's a quick description of a typical internal combustion engine, along with basic vocabularies that describe the components and their functions. This stuffs serve as a quick
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE GUIDE SERVICE
 CHAPTER 22 CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE GUIDE SERVICE OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 22, the reader will be able to: 1. Prepare for Engine Repair (A1) ASE certification test content area B (Cylinder Head
CHAPTER 22 CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE GUIDE SERVICE OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 22, the reader will be able to: 1. Prepare for Engine Repair (A1) ASE certification test content area B (Cylinder Head
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
Shay Engine. Nelson Riedel, 1/14/2003, last updated 06/05/2004. Shay Engine
 Shay Engine Nelson Riedel, Nelson@NelsonsLocomotive.com 1/14/2003, last updated 06/05/2004 The following shows the various parts of the engine for the Shay locomotive. Rough Castings: I started with the
Shay Engine Nelson Riedel, Nelson@NelsonsLocomotive.com 1/14/2003, last updated 06/05/2004 The following shows the various parts of the engine for the Shay locomotive. Rough Castings: I started with the
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Focus on Training Section: Unit 2
 All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
Short Block Contains. Long Block. Crankshaft Connecting Rods Pistons Camshaft Timing Gears. Same as short block plus. Cylinder heads Lifters Push Rods
 Short Block Short Block Contains Crankshaft Connecting Rods Pistons Camshaft Timing Gears Long Block Same as short block plus Cylinder heads Lifters Push Rods Displacement Volume of all cylinders swept.
Short Block Short Block Contains Crankshaft Connecting Rods Pistons Camshaft Timing Gears Long Block Same as short block plus Cylinder heads Lifters Push Rods Displacement Volume of all cylinders swept.
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Kul Internal Combustion Engine Technology. Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5
 Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
The TL Series is available with either a 3.2-liter V-6 or a 2.5-liter, inline fivecylinder,
 OVERVIEW The TL Series is available with either a 3.2-liter V-6 or a 2.5-liter, inline fivecylinder, engine. The 3.2TL engine, like all other Acura engines, is made of aluminum alloy and is equipped with
OVERVIEW The TL Series is available with either a 3.2-liter V-6 or a 2.5-liter, inline fivecylinder, engine. The 3.2TL engine, like all other Acura engines, is made of aluminum alloy and is equipped with
Inside a typical car engine. Almost all cars today use a reciprocating internal combustion engine because this engine is:
 Tech Torque HOW PETROL ENGINES WORK The Basics The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline
Tech Torque HOW PETROL ENGINES WORK The Basics The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline
Bthird, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the
 third, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the piston reaches DC it enters the fourth cycle. The exhaust valve opens and the piston rises forcing burned gases from the combustion chamber in what
third, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the piston reaches DC it enters the fourth cycle. The exhaust valve opens and the piston rises forcing burned gases from the combustion chamber in what
ENGINE MECHANICAL <134>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
Analysis of Combustion Chambers in Internal Combustion Engine
 Global Science and Technology Journal Vol. 2 No.1 March 2014. Pp. 12-21 Analysis of Combustion Chambers in Internal Combustion Engine Ariz Ahmad* Abstract: The main objective of this paper is to study
Global Science and Technology Journal Vol. 2 No.1 March 2014. Pp. 12-21 Analysis of Combustion Chambers in Internal Combustion Engine Ariz Ahmad* Abstract: The main objective of this paper is to study
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES)
 REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
Ignition System Fundamentals
 Ignition System Fundamentals Chapter 37 Objectives Describe the functions of ignition system parts Explain the operation of points, electronic, and computer ignition systems Give an overview of the different
Ignition System Fundamentals Chapter 37 Objectives Describe the functions of ignition system parts Explain the operation of points, electronic, and computer ignition systems Give an overview of the different
Mikuni RS Carburetor Conversion
 Mikuni RS Carburetor Conversion After putting your carbies on the bench or the kitchen table if the wife is out, you will see that the linkages may be in different positions depending on which brand of
Mikuni RS Carburetor Conversion After putting your carbies on the bench or the kitchen table if the wife is out, you will see that the linkages may be in different positions depending on which brand of
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS & SERVICE MANUAL BLUE MAX II HYDROSTATIC TEST PUMP
 PAGE 1 OF 10 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS & SERVICE MANUAL BLUE MAX II HYDROSTATIC TEST PUMP EFFICIENT, EASY OPERATION Air operated pump Wide range of pressures and volumes Easy to operate controls Output pressure
PAGE 1 OF 10 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS & SERVICE MANUAL BLUE MAX II HYDROSTATIC TEST PUMP EFFICIENT, EASY OPERATION Air operated pump Wide range of pressures and volumes Easy to operate controls Output pressure
NZQA unit standard version 5 Page 1 of 6. Demonstrate knowledge of engine design factors and machining practices
 Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate knowledge of engine design factors and machining practices Level 4 Credits 20 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to demonstrate knowledge of engine design
Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate knowledge of engine design factors and machining practices Level 4 Credits 20 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to demonstrate knowledge of engine design
Engine Heat Transfer. Engine Heat Transfer
 Engine Heat Transfer 1. Impact of heat transfer on engine operation 2. Heat transfer environment 3. Energy flow in an engine 4. Engine heat transfer Fundamentals Spark-ignition engine heat transfer Diesel
Engine Heat Transfer 1. Impact of heat transfer on engine operation 2. Heat transfer environment 3. Energy flow in an engine 4. Engine heat transfer Fundamentals Spark-ignition engine heat transfer Diesel
Study on Liquid Cooled 2 Stroke Engine
 Study on Liquid Cooled 2 Stroke Engine Abhishek toppo, Sumnat Pandey, Gopikahnu Tudu Mr. Sunil Rout Department of mechanical engineering, GIET GUNUPUR Email: giet12me072@gmail.com Abstract- A cooling system
Study on Liquid Cooled 2 Stroke Engine Abhishek toppo, Sumnat Pandey, Gopikahnu Tudu Mr. Sunil Rout Department of mechanical engineering, GIET GUNUPUR Email: giet12me072@gmail.com Abstract- A cooling system
Valve Selection. 1. Function and service considerations
 1. Function and service considerations Valve Selection Selection Valves serve the purpose of controlling the fluids in building services piping. Valves are produced in a variety of design types and materials.
1. Function and service considerations Valve Selection Selection Valves serve the purpose of controlling the fluids in building services piping. Valves are produced in a variety of design types and materials.
ENGINE 6G74 3.5L-SOHC-24 VALVE
 11A ENGINE General Information/Service Specifications ENGINE 6G74 3.5L-SOHC-24 VALVE GENERAL INFORMATION Items Specifications Type V-type, Over Head Camshaft Number of cylinders 6 Bore mm 93.0 Stroke mm
11A ENGINE General Information/Service Specifications ENGINE 6G74 3.5L-SOHC-24 VALVE GENERAL INFORMATION Items Specifications Type V-type, Over Head Camshaft Number of cylinders 6 Bore mm 93.0 Stroke mm
General Installation Manual for American Gas Lamp Works Gas & Electric Lamps, Torches & Posts
 General Installation Manual for American Gas Lamp Works Gas & Electric Lamps, Torches & Posts 1 Table of Contents Item #s 1800, 1900, 2000, 2300 & 2301 Post Mount 3 Item #s 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600 & 2900
General Installation Manual for American Gas Lamp Works Gas & Electric Lamps, Torches & Posts 1 Table of Contents Item #s 1800, 1900, 2000, 2300 & 2301 Post Mount 3 Item #s 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600 & 2900
CARTER DOWNDRAFT CARBURETOR Terraplane All Models. Technical Information
 CARTER DOWNDRAFT CARBURETOR 1934 Terraplane All Models Technical Information . Carter W-1 Downdraft Carburetors 1934 Terraplane Challenger, Model KS NOTE: Terraplane Models. Carburetor fitted with Anti-
CARTER DOWNDRAFT CARBURETOR 1934 Terraplane All Models Technical Information . Carter W-1 Downdraft Carburetors 1934 Terraplane Challenger, Model KS NOTE: Terraplane Models. Carburetor fitted with Anti-
Service and Repair CAMSHAFT
 Service and Repair CAMSHAFT Removal and Installation REMOVAL 1. Remove front timing chain case, camshaft sprocket, timing chain and rear timing chain case. Refer to "REMOVAL". 2. Remove camshaft position
Service and Repair CAMSHAFT Removal and Installation REMOVAL 1. Remove front timing chain case, camshaft sprocket, timing chain and rear timing chain case. Refer to "REMOVAL". 2. Remove camshaft position
