18-1. LV- HRC fuselinks HV- D- type fuselinks. D- type fusebases. Switchdisconnectorfuses. (SASIL) LV HRC system. BS system.
|
|
|
- Mervin Byrd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix
2 Semiconductor protection fuselinks / information Distribution and instrument cabinets / current carrying capacity Distribution and instrument cabinets / condensation Distribution and instrument cabinets / UV protection IP types of protection / definition Utilization categories / fuse combination units Temperaturerise limits / fuse combination units Low voltage assemblies / TTA/PTTA verification Low voltage assemblies / compartmentalization Current carrying capacity / aluminium busbars Current carrying capacity / copper busbars Current carrying capacity / correction factor for busbar/air temperatures Current carrying capacity / insulated cables Power cables / designation Cable and line protection / gl/gg fuses Cable and line protection / gl/gg fuses Transformers / nominal and shortcircuit currents Transformers, 400V / protection proposals Threephase motors / protection proposals North American conductor crosssections / conversion Sectorshaped copper conductors / dimensions Sectorshaped aluminium conductors / dimensions Circular copper conductors / dimensions Cables / outside diameters Glossary of Standard Terms Current limitation / fuselinks Current limitation / D type fuselinks Current limitation / HV Power dissipation / fuselinks fuselinks / influence of ambient temperature General Conditions of Supply and Delivery for Products and Services Certificates of Quality Contact Addresses Page LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 181 Appendix
3 Semiconductor protection fuselinks Information on semiconductor protection fuselinks Semiconductor (protection) fuselinks are fuselinks whose fusing and suppressor characteristics (fusing + suppression = breaking) are specially designed for the protection of semiconductor. Semiconductor fuselinks have lower breaking integrals than line protection fuselinks (gl; gg) or transformer protection fuselinks (gtr). Since the limit integrals of semiconductor, i.e. their maximum permissible resistive loads, have been constantly reduced, semiconductor fuselinks with ever faster characteristics (quick acting very quick acting / high speed super quick acting hyper quick acting) have been designed. The faster semiconductor fuselinks protect semiconductor only against shortcircuit currents and are not capable of breaking overload currents until a sufficient overcurrent level called miminum breaking current has been reached (partial breaking capacity). Overload currents, i.e. currents greater than the rated current and less than the minimum breaking current, must be broken by other overcurrent protective devices, which is usually easy to achieve. The power dissipation of a semiconductor fuselink is influenced by its characteristic. Semiconductor fuselinks generally have lower power dissipation values than gl/gg or gtr fuselinks, which makes it necessary to improve their heat dissipation. They are thus preferably equipped with screw or threaded contacts. When using semiconductor fuselinks with blade contacts, it must be ensured that the power dissipation of each fuselink does not exceed the rated power input of the base or fuse switchdisconnector. As a general rule, faster fuses have higher power dissipation values. The recent use of more robust semiconductor with higher limit integrals has led to applications in which the feeder cable is to be protected against overcurrents in addition to the semiconductor component, i.e. in which overload protection is required. Less fast, or slow fuselinks have therefore been developed which are capable of breaking all melting currents (full breaking capacity). Here is a general overview of all characteristics of our semiconductor fuselinks: üf2 Quick acting Overload protection gr Silica sand Art. No.: Rx2xxxxx üf1 Very quick acting Shortcircuit protection ar Silica sand Art. No.: Rx1xxxxx üf01 Super quick acting Shortcircuit protection ar Solid filler Art. No.: Rx0xxxxx üf02 Hyper quick acting Shortcircuit protection ar Solid filler Art. No.: Rx3xxxxx üf3 Slow (less fast) Overload protection gr Silica sand Art. No.: Rx5xxxxx Quick acting breaking capacity is achieved by the use of pure silver fuses with special bottleneck dimensioning and/or special quenching sand properties (e.g. solid filler). Slow fuselinks have silver fuses with solder coatings. The 5 characteristics specific of JEAN MÜLLER are summarized in the utilization categories gr (full breaking capacity) and ar (partial breaking capacity) in accordance with VDE standards. JEAN MÜLLER equivalence lists allow users to find the corresponding JM article number where the type ID of a competitor is known. Equivalence in this context means that a JM fuselink has technical data at least equivalent to those of a competitor. The rated voltage of semiconductor fuselinks is generally stated in accordance with the switching capacity tests for alternating current. The corresponding rated voltage for direct current applications, for which semiconductor fuselinks are frequently used due to their higher breaking capacity, generally must be determined by switching capacity tests. Such a test will focus on the circuit inductance, which must correspond to the application at hand, e.g. in a DC intermediate circuit or for the protection against IGBT short circuits. Higher inductance is associated with a higher time constant L/R and a lower breaking capacity or rated DC voltage. As a rule of thumb, at least % of the maximum rated AC voltage of a fuselink may be assumed for its rated DC voltage if the time constant is not greater than 20msec. A higher breaking capacity can only be guaranteed on the strength of a practical test. 182
4 Distribution and instrument cabinets Current carrying capacity of distribution and instrument cabinets for outdoor use Determination of the nominal power dissipation P v and the rated current I e of standard cable distribution cabinets, KVS/222 and KVS/10 series, equipped with stripfuseways, types L and SL. Temperaturerise tests were conducted at the standard cable distribu tion cabinet of the 10 series, size 0, type KVS010/SV/5L2, equipped with 5 size 2 (400A) stripfuseways in accordance with VDE 0660 Part 3. The load current I B was set to the limit current of the fuselinks. Temperatures were measured at the following locations: LV HV Test values: Ie Rated current 315 A T1 Surface of the central top fuselinks 120 C T2 Internal temperature of cabinet below top 75 C T3 Max. connection temperature of the central strips 60 C T4 Exhaust air temperature at cabinet C T5 Surface temperature, top, external 46 C T6 Surface temperature, door, external 36 C Room temperature 25 C 1. Nominal power dissipation P v of KVS010: 5 W. 2. Rated current I e of KVS010: 315A. Nominal power dissipation values P v for maximally equipped standard cable distribution cabinets of all sizes: KVS222 size *) Surface m 2 Nominal power dissipation P v (W) KVS 00/ KVS 0/ KVS 1/ *) DIN / T.4 KVS10 size **) Surface m 2 Nominal power dissipation P v (W) KVS KVS KVS KVS NKVS **) DIN 43629, Parts 1 and 2 D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Evaluation: The nominal power dissipation P v of equipped JEAN MÜLLER standard cable distribution cabinets is determined by the continuous loading capability of the fuses, not by overheating. If the individual power dissipation values of the builtin devices are known, the rated currents I e can be calculated. Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 183 Appendix
5 Distribution and instrument cabinets Avoiding codensation in distribution and instrument cabinets Due to the outdoor atmospheric conditions, condensed water develops in cable and distribution cabinets and precipitates at the inner surfaces. This humidity may lead to the corrosion of the metal parts and to the formation of creepage currents. Measures for avoiding excessive condensation: 1. Ventilation of the cabinet through existing ventilation slots in accordance with IP44 Upper front plate Lower front plate Approx. 300 mm Excavated soil Case Foundation Existing ground surface (digging depth) Fill zone (finegrained sand) Grid base plate to improve stability The existing ventilation slots in the lower part of the door and the rear panel and in the upper area between the top plate and door or rear panel are capable of dehumidifying the cabinet interior with the support of the heat produced by the power dissipation of fuse elements under the condition that the size of the ventilation slots is proportional to the width of the cabinet. This condition is fulfilled by the design of JEAN MÜLLER distribution and instrument cabinets, whose ventilation slots are located at the lower and upper sides of the door and rear panel. 2. Protection against ground moisture An effective dehumidification of the cabinet interior can only be achieved if the latter is protected against rising ground moisture. Such a protection can be implemented by filling in finegrained sand up to the ground surface level. Application: The foundation is filled with excavated soil up to a height of approx. 300 mm below the ground surface level. A layer of sand of approx. 300 mm height is filled above this. This sand layer effectively prevents the rising of moisture, as has been proven many times in practice. Filling crosssection of the base: see illustration 184
6 Distribution and instrument cabinets UV protection of cabinets made of glassfibrereinforced polyester Depending on the site and climatic zone, the surface of a distribution and instrument cabinet is more or less damaged by UV radiation. Such damage takes the form of surface erosion. This particularly affects surfaces facing the sun. The reduction in material thickness involved is very low ( µm in 20 years), so that the mechanical properties of the case are not impaired. After a number of years, the glass fibres immediately below the surface will be exposed. Skin contact may thus produce irritations. In addition, the increased roughness will accelerate the development of moss. Effective protection against UV radiation and thus surface erosion is provided by coating with UV varnish. 1. Surface coating is to ensure the following: a) Prevention of surface erosion of the cabinet as a consequence of UV radiation. b) UV protection as sub a) with an additional antiadhesive for spray varnishes (graffiti). c) UV protection as sub a) with an additional antiadhesive for posters. 2. Potential measures for new cabinets: a) Surface coating with a twocomponent acrylic resin: This surface coating effectively prevents the yellowing and subsequent erosion of the glassfibrereinforced polyester resin. Depending on the site, surfaces with a polyacrylic coating are protected against UV radiation for a period of 15 to 20 years. After that period, the cabinet may be revarnished if a loss of brilliance has occurred. b) Surface coating with a twocomponent acrylic resin which comprises an additional antiadhesive for spray varnishes (antigraffiti coating). This provides the same UV protection as sub a) but with an option to remove spray varnishes with a cleaning paste. c) Surface coating with a twocomponent acrylic resin which comprises an antiadhesive for posters (antiposter coating). 3. Potential measures for secondary treatment: a) Coating with a singlecomponent acrylic resin. This provides effective protection against UV radiation, but has to be repeated after a short period of time (8 10 years) because of the low durability of the varnish. b) Coating with a twocomponent acrylic resin. This provides the same protection as sub 2a). c) Surface coating with a twocomponent acrylic resin which comprises an antiadhesive for spray varnishes (antigraffiti coating). This provides the same protection as sub 2b). d) Surface coating with a twocomponent acrylic resin which comprises an antiadhesive for posters (antiposter coating). This provides the same protection as sub 2c). 4. Required surface preparation for secondary treatment: Deagreasing by washing with a detergent dissolved in water. Subsequently, removal of dirt and loose material particles with a cleaning brush or fleece. To ensure good adhesive properties of the surface coating, the varnish must be pigmented (coloured), generally light grey (RAL35), as the polyester used. Transparent varnishes are not capable of filtering UV radiation. The surface below the varnish will thus erode, which will deteriorate the adhesive properties. LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 185 Appendix
7 IP types of protection IP types of protection given to electrical equipment by cases and covers, in accordance with IEC/EN (extract) 1st numeral 2nd numeral Protection against contact Protection against foreign bodies Protection against water IP00 No special protection No special protection No special protection IP20 With fingers Solid particles, 12mm No special protection IP41 With tools etc. Solid particles, 1 mm No harmful effect from water dripping vertically IP43 With tools etc. Solid particles, 1 mm No harmful effect from spray water (any direction up to 60 from the vertical) IP54 Complete protection Harmful dust deposits in interior No harmful effect from splashing water (any direction) IP55 Complete protection Harmful dust deposits in interior No harmful effect from hosed water IP65 Complete protection Dust protection (dustproof) No harmful effect from hosed water IP66 Complete protection Dust protection (dustproof) No harmful effect from temporary flooding IP67 Complete protection Dust protection (dustproof) No harmful effect from temporary immersion IP68 Complete protection Dust protection (dustproof) No harmful effect from permanent immersion IP69 K Complete protection Dust protection (dustproof) No harmful effect from water directed against the case under very high pressure and from any direction (high pressure / steam jet hoses, bar) Protection against electric shock in accordance with IEC and VDE 0106 Part 100 IEC covers the erection of electrical equipment and its arrangement in electrical systems with rated voltages of up to 1000 VAC and 10 VDC, with regard to protection against direct contact where actuators such as pushbuttons and toggle switches are located in the vicinity of live parts. Fingerproofing relates only to the actuator, and only to the normal direction of operation. A clearance of at least 30 mm radius must be ensured from the centre point of the actuator to any live parts. Type of protection IP20 is superior to fingerproofing in that it embodies protection against contact with electrical equipment in any direction. Devices which are fingerproof and are protected to IP00 can be provided with further protection against contact in the form of covering if required. 186
8 Utilization categories Utilization categories for fuse combination units in accordance with IEC/EN and VDE 0660 Part 107 AC Utilization Typical Verification of electrical endurance Verification of making and breaking capacities category applications Make Break Make Break I e I U cos I c U r cos I e I U cos I c U r cos A I e U e I e U e A I e U e I e U e AC20A(B) 1) Connecting and disconnecting 3) 2) 2) 2) 2) 2) 2) 3) 2) ) 2) ) under noload conditions AC21A(B) 1) Switching of resistive loads, 3) ) , including slight overloads AC22A(B) 1) Switching of mixed resistive 3) ) and inductive loads, including slight overloads AC23A(B) 1) Switching of motor loads and 3) ) other highly inductive loads 5) LV HV DC Utilization Typical Verification of electrical endurance Verification of making and breaking capacities category applications Make Break Make Break I e I U L/R I c U r L/R I e I U L/R I c U r L/R A I e U e ms ms A I e U e ms ms DC20A(B) 1) Connecting and disconnecting 3) 2) 2) 2) 2) 2) 2) 3) 2) ) 2) ) under noload conditions DC21A(B) 1) Switching of resistive loads, 3) ) , including slight overloads DC22A(B) 1) Switching of mixed resistive and 3) ) inductive loads, including overloads (e.g. shunt motors) DC23A(B) 1) Switching of highly inductive 3) ) loads (e.g. series motors) I = Making current I c = Breaking current I e = Rated operational current U = Voltage U e = Rated operational voltage 1 ) A: frequent actuation, B: occasional actuation. 2 ) If the switching device has a making and/or breaking capacity, the values for the current and the power factor (time constants) must be stated by the manufacturer. 3 ) All values 4) I e 100 A 5) I e 100 A I e U e I e U e D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 187 Appendix
9 Temperaturerise limits Temperaturerise limits of fuse combination units in accordance with IEC/EN and VDE 0660 Part 100 a) Temperaturerise limits of connections Connection material Copper, blank Copperzinc alloy, blank Copper or copperzinc alloy, tinplated Copper or copperzinc alloy, silverplated or tinplated Other metal parts Temperaturerise limit in K b) Temperaturerise limits of accessible parts Accessible part Manually operated actuators: Metallic Nonmetallic Parts which are touched but not gripped: Metallic Nonmetallic Parts which need not be touched during normal actuation: Outside surface of cases, near the cable inlet Metallic Nonmetallic Outside surface of cases which contain resistors Air from ventilation apertures of cases which contain resistors Temperaturerise limit in K Temperaturerise limits of low voltage assemblies in accordance with IEC/EN and VDE 0660 Part 0 Assembly Builtin equipment Conventional switchgear Electronic modules Equipment Connections for insulated conductors introduced from the outside Busbars Conductors Plugin contacts of removable parts Actuators which are accessible from the outside Metallic Insulating material External surfaces of cases or covers which are accessible from the outside Metallic Insulating material External surfaces of cases or covers which are accessible from the outside but need not be touched during normal operation Metallic Insulating material Plugin connections Temperaturerise limit in K In accordance with the relevant standards, if such standards exist, or in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications taking into account the internal temperature of the assembly. Limiting factors: Mechanical strength of the conductor materials Potential influence on neighbouring equipment Permissible temperaturerise limit of the insulating material touched by the conductor Effects of the conductor temperature on connected devices Type and surface of the contact material for plugin contacts Limiting factors are the values for the equipment of which they form part 188
10 Low voltage assemblies TTA/ PTTA verification Verification and testing of typetested and partially typetested assemblies Ser. no. Requirement TTA PTTA 1 Temperaturerise limit 2 Insulation properties Verification of compliance by (Type) testing Verification by (Type) testing Verification of compliance by (Type) testing Extrapolation/calculation in accordance with VDE 0660 Part 7; Verification by Testing or Verification of the insulation resistance LV HV D type fuselinks 3 Shortcircuit strength 4 Effectiveness of the protectiveconductor circuit Verification by (Type) testing Verification by Testing or Extrapolation of similar typetested assemblies / calculation in accordance with VDE 0660 Part 9; D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system Correct connection between the assembly and the protectiveconductor circuit Verification of correct connection between the assembly and the protectiveconductor circuit by Inspection or Resistance measuring (type testing) Verification of correct connection between the assembly and the protectiveconductor circuit by Inspection or Resistance measuring Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals Shortcircuit strength of the protectiveconductor circuit Verification by (Type) testing Verification by Testing or Corresponding design and arrangement of the protective conductor LV HRC stripfuseways 5 Clearances and creepage distances 6 Mechanical function 7 IP type of protection Verification by (Type) testing Verification by (Type) testing Verification by (Type) testing Verification by Testing Verification by Testing Verification by Testing striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases 8 Wiring and electrical function Verification by Inspection of the assembly including the wiring and electrical function testing (if required) (routine testing) Verification by Inspection of the assembly including the wiring and electrical function testing (if required) fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system 9 Insulation Verification by Insulation testing (routine testing) Verification by Insulation testing or Verification of the insulation resistance Consumer supply technology 10 Protective measures Verification by Checking of the protective measures and the continuous protectiveconductor circuits (routine testing) Verification by Checking of the protective measures Distribution and instrument cabinets 11 Insulation resistance Verification of the insulation resistance if no insulation property test has been conducted (see ser. nos. 2 and 9) Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 189 Appendix
11 Low voltage assemblies Compartmentalization of assemblies in accordance with DIN/EN : Modern low voltage assemblies must comply with operational safety and personnel protection requirements. The division of switchgear cabinets into separate function sections and their compartmentalization are prerequisites for: High availability Exchangeability of the builtin switchgear under operational conditions, i.e. while the system is energized Short downtimes for maintenance and testing. A switchgear cabinet is divided into the following function sections: Device compartment Busbar compartment (main and field distributor busbar system) Cable compartment Type of protection IP2X or above is required to prevent the ingress of solid foreign bodies from a function unit into an adjacent unit. In addition, type of protection IPXXB or above is required to prevent contact with live parts of an adjacent unit. The compartmentalization design and higher protection than described above must be agreed between the manufacturer and the user. Compartmentalization by covers or barriers Design Main characteristic Connections Image Design 1 No compartmentalization Design 2a Compartmentalization between the busbars and function units External conductor connections not separated from the busbars Design 2b Compartmentalization between the busbars and function units External conductor connections separated from the busbars Design 3a Compartmentalization between the busbars and function units and between the function units External conductor connections not separated from the busbars Design 3b Compartmentalization of the external conductor connections and function units, but no compartmentalization between the conductor connections External conductor connections not separated from the busbars Design 4a Design 4b Compartmentalization between the busbars and function units and between the function units including the external conductor connections which are an integral part of the function units. Compartmentalization between the busbars and function units and between the function units including the external conductor connections which are an integral part of the function units. External conductor connections in the same compartment as the corresponding function unit External conductor connections not in the same compartment as the corresponding function units, but in a separate enclosed and protected section or compartment. 1810
12 Current carrying capacity / aluminium busbars Continuous currents in accordance with DIN 43 6 for rectangular EAl busbars used in indoor systems at 35 C air temperature and 65 C busbar temperature Width x thickness [mm] 12 x 2 15 x 2 15 x 3 20 x 2 20 x 3 20 x 5 20 x 10 Crosssection [mm 2 ] Weight 1) [kg/m] Continuous current in A AC up to 60 Hz DC/AC up to 16 2 / 3 Hz Painted Blank Painted Blank Number of busbars Number of busbars Number of busbars Number of busbars I II I II I II I II LV HV D type fuselinks D type fusebases 25 x 3 25 x 5 30 x 3 30 x 5 30 x x 3 40 x 5 40 x Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals x 5 x x 5 60 x LV HRC stripfuseways 80 x 5 80 x striptype fuse switchdisconnectors 100 x x x fusebases 120 x x x x x x fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system 1) Weight calculated with a density of 2.7kg/dm 3 Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1811 Appendix
13 Current carrying capacity/ copper busbars Continuous currents in accordance with DIN 43 6 for rectangular ECu busbars used in indoor systems at 35 C air temperature and 65 C busbar temperature Continuous current in A AC up to 60 Hz DC/AC up to 16 2 / 3 Hz Painted Blank Painted Blank Number of busbars Number of busbars Number of busbars Number of busbars Width x thickness [mm] Crosssection [mm 2 ] Weight 2) [kg/m] I II I II I II I II 12 x 2 15 x 2 15 x x 2 20 x 3 20 x 5 20 x x 3 25 x x 3 30 x 5 30 x x 3 40 x 5 40 x x 5 x x 5 60 x x 5 80 x x x x x x ) Weight calculated with a density of 8.9 kg/dm
14 Current carrying capacity / correction factor for busbar/air temperatures Correction factor k2 for copper busbars at varied busbar and air temperatures LV Faktor Factor k 2 2, , C 10 HV 2, , D type fuselinks 1, , , , , u Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system 1, ,2 1.2 Terminals 1, ,0 1.0 LV HRC stripfuseways 0, ,8 0.8 striptype fuse switchdisconnectors 0,7 0.7 fusebases 0, ,5 0.5 fuse switchdisconnectors 0, , C 125 Busbar system Factor k 2 to determine the conductor crosssection of copper busbars at ambient temperatures u of 0 to 60 C and/or operating temperatures s up to 125 C s Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1813 Appendix
15 Current carrying capacity/ insulated cables Current carrying capacity of insulated cables in accordance with DIN VDE 0100 Part 523 Nominal crosssection [mm 2 ] Group 1 One or more singlecore cables installed in conduits Cu conductor [A] Al conductor [A] Group 2 Multicore cables, e.g. light plasticsheathed cables, pipelines, flat webbed cables and flexible cables Cu conductor [A] Cu conductor [A] Group 3 Singlecore, in free air, spacing of the cables corresponds at least to their diameter Cu conductor [A] Al conductor [A] Correction factor for cables in accordance with DIN VDE 0298 Part 4 Ambient temperature [ C] PVC VPE and EPR Isolierung PVCsheathed C sheathing Blank 105 C sheathing
16 Power cables / designation Designation of power cables Harmonized design in accordance with DIN VDE 0281 Standard code: Harmonized standard Recognized national type H A Nominal voltage U 0 /U: 300V/300V V/0V 05 4V/7V 07 LV HV Insulating material: PVC Natural caoutchouc or styrenebutadiene rubber Silicone rubber Sheath material: PVC Natural caoutchouc or styrenebutadiene rubber Polychloroprene Glassfibre braid Textile braid Design characteristics: Fanout ribbon cable Other ribbon cable V R S V R N J T H H2 D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Type of cable: Singlecore U Multicore R Flexible, for fixed installation K Flexible, for flexible cables F Highly flexible, for flexible cables H Tinsel Y Number of cores... Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors Protective conductor: Without protective conductor With protective conductor X G fusebases Nominal conductor crosssection... fuse switchdisconnectors Example (sequence as given above) H05VRHU3G1,5 Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1815 Appendix
17 Cable and line protection / gl/gg fuses Overload protection of cables and lines using gl/gg fuses in accordance with VDE 0100 Part 430 and supplement For overload protection of cables and lines, the nominal current I n of the fuse principally must be less than or equal to the current carrying capacity I z of the cable or line. The following formula applies to the tripping current I 2 of gl/gg fuses: I 2 = 1,45 I n With I 2 1,45 I z for overload protection in accordance with VDE 0100 Part 430, the following formula for the selection of the protective device "gl/gg fuse" results: I n I z! Crosssection Current carrying capacity I z gl/gg fuse Current carrying capacity I z gl/gg fuse 0.6/1kV cable 1) 2) Nominal current I n conductor 3) 2) Nominal current I n Cu Alu Cu Alu Cu Cu 1,5 mm 2 27 A 25 A 18,5 A 16 A 2,5 mm 2 36 A 35 A 25 A 25 A 4 mm 2 47 A 40 A 35 A 35 A 6 mm 2 59 A A 43 A 40 A 10 mm 2 79 A 63 A 63 A 63 A 16 mm A 100 A 81 A 80 A 25 mm A 102 A 125 A 100 A 102 A 100 A 35 mm A 123 A 160 A 100 A 126 A 125 A mm A 144 A 160 A 125 A 142 A 125 A mm A 179 A 224 A 160 A 181 A 160 A 95 mm A 215 A 2 A 200 A 219 A 200 A 120 mm A 245 A 315 A 224 A 253 A 2 A 1 mm A 275 A 355 A 2 A 185 mm A 313 A 400 A 315 A 1) Cable in earth; insulating material: PVC; 4conductor threephase cable With 3 loaded cores: VDE 0276 Part ) gl/gg fuses disconnect at 1.45 In within the normal test duration. 3) Installation method C according to Supplement 1 to VDE 0100 Part
18 Cable and line protection / gl/gg fuses Nominal current of gl/gg fuses for overload protection of cables and lines VDE 0636 and EN specify fuses of the utilization category gl/gg for cable and line protection. Taking into account the relevant standards for overheating protection of cables and lines and for the current carrying capacity of cables, the following fuse currents have been found suitable in power supply applications (urban networks and cable distribution cabinets) to protect cables and lines (low voltage circuits) against overloading using gl/gg fuses: Installation method Conductor material Crosssection mm 2 Nominal current of the gl/gg fuselinks In earth Copper 16 mm A 25 mm A 35 mm A mm A mm A 95 mm 2 2 A 120 mm A 1 mm A In earth Aluminium 25 mm 2 80 A 35 mm A mm A mm A 95 mm A 120 mm A 1 mm 2 2 A 185 mm A In air Copper 16 mm A 25 mm A 35 mm A mm A In air Aluminium 25 mm 2 80 A 35 mm A mm A mm A LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1817 Appendix
19 Transformers Nominal and shortcircuit currents of standard transformers Nominal voltage U N Shortcircuit voltage U K Rating Nominal 400V/231V 4% 6% Shortcircuit current I K Nominal 525V 4% 6% Shortcircuit current I K Nominal 690V/400V 4% 6% Shortcircuit current I K [kva] current I N [A] [A] current I N [A] [A] current I N [A] [A] I K = I N U K [%] *100 U K = Shortcircuit voltage in % 1818
20 Transformers / protection proposals Protection proposals for 400V mains transformers, 3.6kV to 36kV kv 400 V Transformer data Rating Nominal current Primary Secondary kva A A HV HRC fuse Type IKUS 3 Nominal current Minimum Maximum A A fuse Type M00M4agL/gG Nominal current Minimum Maximum A A fuse Type M2M4agTr in accordance with VDE 0636/22 kva LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system 7.2 kv 400 V Terminals Transformer data Rating Nominal current Primary Secondary kva A A HV HRC fuse Type IKUS 6 Nominal current Minimum Recom. Maximum A A A fuse Type M00M4agL/gG Nominal current Minimum Maximum A A fuse Type M2M4agTr in accordance with VDE 0636/22 kva LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Nominal currents shown in bold comply with VDE 06/402 recommendations. Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1819 Appendix
21 12 kv 400 V Transformer data Rating Nominal current Primary Secondary kva A A HV HRC fuse Type IKUS 10 Nominal current Minimum Recom. Maximum A A A fuse Type M00M4agL/gG Nominal current Minimum Maximum A A fuse Type M2M4agTr in accordance with VDE 0636/22 kva Nominal currents shown in bold comply with VDE 06/402 recommendations. 24 kv 400 V Transformer data Rating Nominal current Primary Secondary kva A A HV HRC fuse Type IKUS 20 Nominal current Minimum Recom. Maximum A A A fuse Type M00M4agL/gG Nominal current Minimum Maximum A A fuse Type M2M4agTr in accordance with VDE 0636/22 kva Nominal currents shown in bold comply with VDE 06/402 recommendations. 1820
22 36 kv 400 V Transformer data Rating Nominal current Primary Secondary kva A A HV HRC fuse Type IKUS 30 Nominal current Minimum Recom. Maximum A A A fuse Type M00M4agL/gG Nominal current Minimum Maximum A A fuse Type M2M4agTr in accordance with VDE 0636/22 kva LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Nominal currents shown in bold comply with VDE 06/402 recommendations. Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1821 Appendix
23 Threephase motors / protection proposals Minimum short circuit protection for threephase motors The maximum size is governed by the requirements of the associated switchgear or overload relay. The nominal motor currents apply to normal internally ventilated and enclosed fancooled threephase motors at 10 rpm. D.O.L. starting: Maximum starting current: 6 x nominal motor current; maximum starting time: 5 s. starting: Maximum starting current: 2 x nominal motor current; maximum starting time: 15 s. Set the overload relay in the phase lead to 0.58 x nominal motor current. Nominal fuse currents for starting also apply to threephase motors with slipring rotors. Use a larger fuse if the nominal current or starting current is higher and/or if the starting time is longer. The table applies to slow or gl/gg fuses (VDE 0636 and EN 60269). For fuses with am characteristics. select the nominal fuse current to match the nominal motor current. Motor rating 230 V 400 V 0 V 690 V Nominal Fuse Nominal Fuse Nominal Fuse Nominal Fuse motor motor motor motor current Starting current Starting current Starting current Starting D.O.L. D.O.L. D.O.L. D.O.L. kw cos % A A A A A A A A A A A A Motor rating 230 V 400 V 0 V 690 V Nominal Fuse Nominal Fuse Nominal Fuse Nominal Fuse motor motor motor motor current Starting current Starting current Starting current Starting D.O.L. D.O.L. D.O.L. D.O.L. kw cos % A A A A A A A A A A A A
24 North American conductor crosssections / conversion North American conductor crosssections Conversion into mm 2 USA/ Canada Europe USA / Canada Europe AWG mm 2 mm 2 circular mills mm 2 mm 2 (exact) (nearest standard value) (exact) (nearest standard value) , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,000, ,300, / / /0 85 4/ LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals Transformers / terminal studs Terminal studs for transformers in accordance with DIN LV HRC stripfuseways Transformer size / rating [kva] Male thread striptype fuse switchdisconnectors 100 M M12 2 M M M30 x M42 x M42 x 3 fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1823 Appendix
25 Sectorshaped copper conductors / dimensions Dimensions of stranded sectorshaped copper conductors in accordance with VDE 0295 Nominal crosssection mm 2 h Approx. value mm Nominal value mm d Permissible deviation mm b Approx. value mm r 1 Approx. value mm r 2 Approx. value mm a Approx. value mm Basic angle = ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ± Basic angle = ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ± Basic angle = ) ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ± Basic angle = ) ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ±0.8 ± ) For copper conductors 1824
26 Sectorshaped aluminium conductors / dimensions Dimensions of solid sectorshaped aluminium conductors in accordance with VDE 0295 b R2 a d h LV R1 R2 HV Nominal crosssection mm 2 h Approx. value mm d Nominal value mm Permissible deviations mm b r 1 Nominal value mm Permissible deviations mm Approx. value mm r 2 Approx. value mm a Approx. value mm D type fuselinks Basic angle = Basic angle = ±0.5 ±0.5 ±0.5 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.5 ±0.5 ±0.5 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ± ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.7 ±0.7 ±0.5 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ±0.6 ± Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1825 Appendix
27 Circular copper conductors / dimensions Diameters of circular conductors in accordance with VDE 0295 d d Solid circular copper conductors, blank or tinned, and circular aluminium conductors, blank Stranded circular copper conductors, blank or tinned, and circular aluminium conductors Nominal crosssection mm 2 Solid circular conductors Diameter Diameter d d of circular copper of circular aluminium conductors conductors Minimum mm Maximum mm Minimum mm Maximum mm Stranded circular conductors Diameter d of Diameter d of noncompacted circular compacted circular copper aluminium conductors and aluminium conductors Maximum mm Minimum mm Maximum mm Flexible circular conductors Diameter d of flexible and highly flexible copper conductors Minimum Maximum mm mm ) ) Values not specified 2) Minimum not specified 1826
28 Cables / outside diameters Outside diameters of lines and cables (average values of various brands) Cable crosssection mm 2 NYM NYY NYCY NYCWY in mm H05RRF H07RNF LV 3 x x x 4 3 x 6 3 x 10 3 x 16 3 x 35 / 16 3 x / 25 3 x / 35 3 x 95 / 3 x 120 / 3 x 1 / 3 x 185 / 95 3 x 240 / x 300 / HV D type fusebases D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system 4 x x x 4 4 x 6 4 x 10 4 x 16 4 x 25 4 x 35 4 x 4 x 4 x 95 4 x x 1 4 x x Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors 5 x x x 4 5 x 6 5 x 10 5 x fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors NYM Light plasticsheathed cable NYCWY Plasticsheathed cable with concentric rippled conductors NYY NYCY Heavy plasticsheathed cable Plasticsheathed cable with concentric conductors HO5RRF Light rubbersheathed cable HO7RNF Heavy rubbersheathed cable Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1827 Appendix
29 Glossary of Standard Terms This Glossary offers brief explanations the standard terms used in this Catalogue. However, it must not be regarded as a substitute for the actual text of the standard, especially where the new terms used in IEC/EN are concerned. Reference is therefore made alongside each such term to the relevant section of the standard, e.g. IEC/EN In addition, IEV numbers are given to enable you to find foreign language equivalents in the International Electrotechnical Vocabulary (IEC ) if required, e.g. IEV Terms Brief explanations Rated breaking capacity (see also IEC/EN ) Rated operational voltage Ue (see also IEC/EN ) Rated operational current Ie (see also IEC/EN ) Rated uninterrupted current Iu (see also IEC/EN ) Rated making capacity (see also IEC/EN ) Rated frequency (see also IEC/EN ) Rated insulation voltage Ui (see also IEC/EN ) Rated shortcircuit breaking capacity Icn (see also IEC/EN ) Rated shortcircuit making capacity Icm (see also IEC/EN ) Rated shorttime withstand current Icw (see also IEC/EN ) Motor rating (see also IEC/EN ) Rated impulsewithstand voltage Uimp (see also IEC/EN ) Protection against direct contact The r.m.s. value of the current which a switching device is capable of breaking according to its utilization category. This information refers to the rated operational voltage and the rated operational current. The switching device must be capable of breaking any value of current up to and including its rated breaking capacity stated. The voltage to which the characteristics of a switching device are referred. The maximum rated operational voltage must not be higher than the rated insulation voltage. The current which a switching device is capable of carrying taking into account the rated operational voltage, duration of operation, utilization category and ambient temperature. The current which a switching device is capable of carrying in uninterrupted duty (i.e. for weeks, months or years). The current which a switching device is capable of making in accordance with the utilization category and the rated operational voltage. The frequency for which a switching device is designed and to which the other characteristics are referred. The voltage to which insulation tests and creepage distances of a switching device are referred. The maximum rated operational voltage must not be higher than the rated insulation voltage. The maximum current which a switching device is capable of breaking at rated operational voltage and rated frequency, and without sustaining damage. It is expressed as r.m.s. value. The maximum current which a switching device is capable of making at rated operational voltage and rated frequency, and without sustaining damage. Unlike for other characteristics, this is expressed as maximum prospective peak value. The shorttime withstand current which a switching device is capable of carrying for a specified time without damage, e.g. due to excessive heating. Power output of a motor at the associated rated operational voltage. Measures the stability of the internal clearances of a switching device against overvoltage peaks. The utilization of suitable switchgear can ensure that overvoltages are prevented from transferring from the mains to deenergized system sections within it. Design measures incorporated into switching devices in order to prevent direct contact, i.e. without tools, with live parts of a system (fingerproof, backofhand proof). 1828
30 Terms Brief explanations Damp heat, constant This test subjects a switching device to an ambient temperature of 40 C at a constant humidity of 93%. At set intervals during the test, the electrical and mechanical function of the switching device are examined. Damp heat, cyclic Fingerproof Utilization category (see also IEC/EN / IEV ) Backofhand proof Altitude This test subjects a switching device to cyclically changing climatic conditions. A cycle applies 40 C ambient temperature at 93% relative humidity for 12 hours, followed by 12 hours of 25 C at 95% relative humidity. At set intervals during this test, the electrical and mechanical function of the switching device are examined. A switching device whose live parts cannot be touched by the operator during actuation is termed fingerproof. This also affects operator activity on neighbouring switching devices. The fingerproof area of a pushactuated switching device is a circular area of at least 30mm radius around the actuator, and vertical to the direction of actuation. Within this circular area, live parts must be located at no less than 80mm depth under the actuating level. A combination of specified requirements relating to the operating conditions in which a switching device or fuse fulfils its purpose, selected to represent a characteristic group of practical applications. The specified requirements may concern, for example, the values of making capacity, breaking capacity and other characteristic values, data concerning associated circuits, and the relevant conditions of use and behaviour. A switching device whose live parts cannot be touched by a sphere of mm diameter is regarded as backofhand proof. The density of air decreases with increasing altitude, and this reduces its insulating capacity as well as its heat transfer capability. The rated operational voltage and current of switching devices, conductors and motors as well as the tripping behaviour of thermal overload relays are affected by this. Upon request, JEAN MÜLLER will supply information as to the suitability or otherwise of switchgear for operation at altitudes above the 2000m limit specified by the standard. LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways Conventional thermal current Ith (see also IEC/EN ; ) Creepage distance (see also IEC/EN ; / IEV ) The maximum current which a switching device is capable of carrying for a minimum of eight hours without thermal overloading. As a rule, it corresponds to the maximum rated operational current. The shortest distance along the surface of the insulating material between two conductive parts. The creepage distance is determined by the rated insulation voltage, the pollution degree and the creep resistance of the material used. striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases Clearance (see also IEC/EN ; / IEV The distance between two conductive parts along a string stretched the shortest way between these parts. The clearance is determined by the rated impulse withstand voltage, the overvoltage category and the pollution degree. fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1829 Appendix
31 Current limitation / fuselinks Current limitation for fuselinks, 0V/690V (Table 1) Characteristic: gg Sizes 00 to 4a, 2A to 12A ) ) 12A 800A Letthrough current I s ; I D [A] A 400A 315A 2A 200A 125A 80A A 35A 25A 16A 6A 2A Prospective shortcircuit current I p [A eff ] 1) Peak shortcircuit current without DC component 2) Peak shortcircuit current with largest DC component 1830
32 Current limitation for fuselinks, 0V/690V, Table 2 Characteristic: gg Sizes 00 to 4a, 4A to 1000A LV HV 2) D type fuselinks 1) A 630A D type fusebases 425A 355A 300A 224A 160A Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system A 63A 40A 32A Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Letthrough current I s ; I D [A] A 10A 4A Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases 100 fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Prospective shortcircuit current I p [A eff ] Distribution and instrument cabinets 1) Peak shortcircuit current without DC component 2) Peak shortcircuit current with largest DC component Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1831 Appendix
33 Current limitation / D type fuselinks Current limitation for fuselinks, 0V Characteristic: gg Sizes DII/DIII, 2 to 100A ) 1) A 80A 63A A 35A 25A 20A Letthrough current I s ; I D [A] A 10A 6A 4A 2A Prospective shortcircuit current I p [A eff ] 1) Peak shortcircuit current without DC component 2) Peak shortcircuit current with largest DC component 1832
34 Current limitation / HV Current limitation for HV, 3.6 to 36kV Characteristic: in accordance with VDE 06 6A to 2A LV ) 1) HV Letthrough current I s ; I D [A] A 200A 160A 125A 100A 80A 63A A 40A 32A 25A 20A 16A 6/10A D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors 1000 fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Prospective shortcircuit current I p [A eff ] Distribution and instrument cabinets 1) Peak shortcircuit current without DC component 2) Peak shortcircuit current with largest DC component Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1833 Appendix
35 Power dissipation / fuselinks Power dissipation of fuselinks Rated DSystem current D01 gl/gg D02 gl/gg NDZ gf NDZ gt DII gl/gg DIII gl/gg DIII gl/gg DIII gf three channel slow [A] 400V 400V 0V 0V 0V 0V 690V 7V 1200V Data in watts Characteristic gg Rated system current NH00 NH1 NH2 NH3 NH4a [A] 400V 0V 690V 400V 0V 690V 400V 0V 690V 400V 0V 690V 0V 690V Data in watts 1834
36 fuselinks/ influence of ambient temperature Influence of ambient temperature on the function of fuselinks in accordance with EN :1998 (Annex D) D.1 Influence of an increase in ambient temperature D.1.1 On the rated current Where fuses must operate at full load and for long periods of time at ambient temperatures whose average value exceeds the value specified in section 3.1, it may be necessary to reduce the nominal current. The reduction factor should be agreed between the the manufacturer and the user taking into account all conditions of use. D.1.2 On heating An increase in the average ambient temperature causes relatively low heating. D.2 Influence of a decrease in ambient temperature A decrease in ambient temperature below the value specified in section 3.1 may allow an increase in the rated current, but it may also cause an increase in the conventional fusing and nonfusing current and in melting times in the event of small overcurrents. The extent of the individual increases depends of the actual temperature and the design of the fuselink. Relevant information must be obtained from the manufacturer. D.3 Influence of fitting conditions Fitting conditions such as: a) Fitting in a box or open fitting; b)properties of the mounting area; c) Number of fuses fitted in a box; d) Crosssection and insulation of connections may influence the functional conditions and should therefore be taken into account. LV HV D type fusebases D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system Influence of ambient temperature on the rated current of fuselinks of the characteristic gg Correction factor C I / I e 1,3 1,2 1,1 1,0 0,9 0,8 0,7 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,3 0,2 0,1 Melting temperature 200 C 0, Ambient temperature of fuselink [ C] Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1835 Appendix
37 1836
38 General conditions for the supply of products and services of the electrical and electronics industry *) (Model form recommended by the Zentralverband Elektrotechnikund Elektronikindustrie (ZVEI) e.v.) June 1997 I. General conditions 1. The scope of the supplies or services (hereinafter called supplies ) shall be defined by the written declarations of both parties to the contract. General terms and conditions of the purchaser shall apply only where expressly accepted in writing by the supplier or service provider (hereinafter called supplier ). 2. For cost estimates, drawings and other documents (hereinafter called documents ), the supplier reserves all rights, right, title and interest in the property and the copyright. Such documents may not be made available to third parties without the prior consent of the supplier and they shall, upon request, be immediately returned to the supplier if he is not awarded the contract. Sentences 1 and 2 shall apply reciprocally to purchaser s documents; however, these may be made available to those third parties to whom the supplier may transfer supplies. 3. The purchaser shall have the nonexclusive right to use standard software in unchanged form with the stipulated performance characteristics for the agreed equipment. The purchaser is allowed to make two backup copies without the supplier s express consent. 4. Partial supplies shall be permissible where they can be reasonably expected of the supplier. II. Prices and terms of payment 1. Prices shall be ex works and exclude packing and shall exclude the sales tax payable under the applicable law. 2. If the supplier has undertaken the assembly or erection, the purchaser shall bear all required incidental costs in addition to the agreed contract price unless otherwise agreed. 3. Payments shall be made free at supplier s paying office. 4. The purchaser may set off only those claims that are undisputed or have been finally determined in a legally binding manner. III. Retention of titel 1. The items of supplies (Secured Goods) shall remain the property of the supplier until each and every claim against the purchaser to which the supplier is entitled under this business relationship has been duly satisfied. If the value of all security rights of the supplier exceeds the value of all secured claims by more than 20 percent, the supplier shall release a corresponding part of the security rights at the purchaser s request. 2. For the duration of the retention of title, the purchaser is prohibited from giving the items of supplies in pledge or as security, and resale shall be permissible only to resellers in the ordinary course of business and only on condition that the reseller receives payment from his customer or retains title so that the property is transferred to the customer only after fulfilment of his obligation to pay. 3. In case of seizure or other acts or interventions by third parties, the supplier shall be immediately informed thereof in writing by the purchaser. 4. In cases of fundamental nonperformance of contractual obligations by the purchaser, especially a delay in payment, the supplier shall be entitled to take back the goods following a demand for payment. The purchaser shall be obliged to return the purchased goods. The taking back, the assertion of the retention of title or the seizure of the Secured Goods by the supplier does not mean termination of the contract except if expressly stated by the supplier. IV. Time for delivery and delay 1. Observance of the stipulated time for delivery is conditional upon the timely receipt of all documents, necessary permits and releases, especially of plans to be provided by the purchaser, as well as fulfilment of the agreed terms of payment and other obligations by the purchaser. Unless these conditions are fulfilled on time, the time for delivery will be extended accordingly except where the supplier is responsible for the delay. 2. If nonobservance of the time for delivery is due to force majeure such as mobilization, war, riot, or similar events, e.g. strike or lockout, such time shall be extended accordingly. 3. If the supplier is responsible for a delay in delivery, the purchaser who can establish credibly that he suffered a loss from such delay may claim agreed compensation of 0.5 percent for every completed week of delay but in no event shall the aggregate of such compensation exceed a total of 5 percent of the price of that part of the supplies which, because of the delay, could not be LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1837 Appendix
39 0put to the intended use. 4. purchaser s claims for compensation which exceed the limits specified in clause IV para 3 shall be excluded in all cases of delayed delivery even after expiry of an extension of time that may have been granted to the supplier. This exclusion shall not apply where in cases of wilful misconduct or gross negligence there is a legally binding liability on the part of the supplier. No change in the burden of proof to the detriment of the purchaser is involved. purchaser s right to terminate the contract shall remain unaffected after the expiry of an extension granted to the supplier that did not result in delivery. 5. If dispatch or delivery is delayed at purchaser s request by more than one month after notice was given of the readiness for dispatch, the purchaser may be charged storage costs for each month thereafter to the amount of 0.5 percent of the price of the supplied goods but in no event shall the aggregate storage charges exceed a total of 5 percent of the price. The parties to the contract are at liberty to furnish proof of higher or lower storage costs. V. Transfer of risk 1. Even where carriage paid delivery has been agreed, the risk shall pass to the purchaser as follows: a) If the supply does not include assembly or erection, when goods have been delivered to or picked up by carrier. At the purchaser s request and expense, supplies shall be insured by the supplier against the ordinary risks of transport. b) If the supply includes assembly or erection, the day on which they are taken over into purchaser s own service or, if so stipulated, after a satisfactory trial run. 2. If the dispatch, the delivery, the beginning or completion of assembly or erection, the taking over into purchaser s own service or the trial run is delayed for reasons within the purchaser s responsibility, or if the purchaser has failed for other reasons to accept delivery, the risk shall pass to the purchaser. VI. Assembly and electition Unless otherwise agreed in writing, assembly, and erection shall be subject to the following provisions: 1. The purchaser shall provide at his own expense and in a timely manner: a) all earthmoving and construction work and other ancillary services not specific to the sup plier s trade as well as the necessary skilled and unskilled labour, materials, and tools, b) the equipment and materials necessary for assembly, erection, and commissioning such as scaffolds, lifting equipment etc., fuels, and lubricants, c) energy and water at the point of use, including connections, heating, and lighting, d) suitable, dry, and lockable rooms of sufficient size at the site for the storage of machine parts, apparatus, materials, tools etc. and adequate working and recreation rooms for the assembly personnel including appropriate sanitary facilities. Furthermore, the purchaser shall take all measures he would take for the protection of his own property to safeguard the property of the supplier and of the assembly personnel, e) protective clothing and protective devices which are needed because of particular conditions on the site. 2. Before the start of assembly or erection, the purchaser shall make available of his own accord all necessary information concerning the location of concealed electric power, gas and water lines or of similar installations as well as the required data concerning statics and underlying conditions of the site. 3. Before the beginning of assembly or erection, the necessary materials and equipment to start work must be provided at the site and all preparations must have advanced to such a point that the assembly or erection can be started as agreed and carried out without interruption. Access roads and the site itself must be level and clear. 4. If the assembly, erection or commissioning is delayed by circumstances for which the supplier is not responsible, the purchaser shall bear an appropriate amount of the costs of waiting periods and of any additional travelling of the supplier or the assembly personnel that may be necessary. 5. The purchaser shall attest to the supplier at weekly intervals the hours worked by the assembly personnel and he shall immediately confirm in writing the completion of assembly, erection or commissioning. 6. If, after completion, the supplier requests acceptance of the supplies, it shall be carried out by the purchaser within two weeks of the supplier s request, 1838
40 failing which acceptance is deemed to have taken place. Acceptance is also deemed to have taken place if after completion of any agreed test phase the supplies are put to use. VII. Taking delivery Deliveries, even with minor defects, have to be accepted by the purchaser. VIII. Warranty For defects which include the absence of expressly warranted characteristics, the supplier shall be liable as follows: 1. The supplier shall, at his option and expense, repair, replace, or newly provide any parts or services whose usefulness is impaired more than insignificantly within 12 months from the date of the transfer of risk regardless of the period of operation owing to circumstances that existed before the transfer of risk. 2. Warranty claims are subject to a limitation period of 12 months after notification of the defect. Notice in writing shall be given to the supplier immediately after discovery of the defect. 3. In case of notification of a defect, purchaser s payments may be withheld in reasonable proportion to the noticed defect. If the contract pertains to the conduct of a purchaser s business, the purchaser can withhold payments only if the legitimacy of the asserted complaint can be established beyond doubt. 4. The supplier shall be given adequate time and opportunity to remedy the defect. If he is refused these, the supplier shall have no liability for the defect. 5. If an adequate extension granted to the supplier expires without the defect being remedied, the purchaser shall have the right to demand cancellation of the contract or a reduction of the purchase price. 6. The warranty does not cover natural wear and tear or damage arising, after the transfer of risk, from faulty or negligent handling, excessive strain, unsuitable equipment, defective workmanship, inappropriate foundation soil or from particular external influences not assumed under the contract, or from nonreproducible software errors. The warranty does not cover modifications or repairs carried out improperly by the purchaser or by third parties. 7. The warranty period for repairs or replacement supplies (of goods or services) shall be 6 months. It shall be the later of: (1) 6 months from the date of repair or replacement; or (2) the remaining length of the original warranty period for the supplies. For those parts which cannot be put to the intended use because of the interruption of service, the warranty period shall be extended by the period of service interruption caused by the repair or replacement supply. 8. The periods specified in paras 1, 2 and 7 shall not apply where longer periods are provided by law according to 638 BGB. 9. Except as provided above, any other warranty claims of the purchaser against the supplier and the supplier s agent shall be excluded. However, clause XI (Further liability) shall remain unaffected. IX. Industrial property rights and copyright 1. If a third party, because of an infringement of an industrial property right or copyright (hereinafter called Property Rights ) by products furnished by the supplier and used in conformity with the contract, asserts legitimate claims against the purchaser, the supplier shall be liable to the purchaser as follows: a) At his own option and expense, the supplier shall either obtain a right to use the product, modify the product so as not to infringe the Property Rights or replace the product. If this is not possible to the supplier on acceptable terms, he shall have to take back the product and refund the purchase price. b) supplier s aforesaid obligations shall exist only on condition that the purchaser immediately notifies the supplier in writing of the claims asserted by the third party, that he does not acknowledge an infringement and that all countermeasures and settlement negotiations are reserved to the supplier. If the purchaser stops using the product to reduce the damage or for other important reasons, he shall be obliged to make it clear to the third party that the suspended use does not mean acknowledgment of an infringement of Property Rights. 2. Claims of the purchaser shall be excluded if he is responsible for an infringement of Property Rights. 3. Claims of the purchaser shall also be excluded if the infringement of Property Rights was caused by specific demands of the purchaser, by a use of the product not foreseeable by the supplier or by the product being altered by the LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1839 Appendix
41 purchaser or being used together with products not provided by the supplier. 4. Further claims against the supplier shall be excluded. However, clause XI (Further liability) shall remain unaffected and so shall be purchaser s right to terminate the contract. X. Impossibility of performance, contract adaptation 1. If it is impossible for the supplier to carry out the supplies for reasons for which he is responsible, the purchaser shall be entitled to claim damages but the purchaser s claim for damages shall be limited to 10 percent of the value of that part of the supplies which, owing to the impossibility, cannot be put to the intended use. This shall not apply where in cases of wilful misconduct, of gross negligence or of initial impossibilitiy, there is a legally binding liability. No change in the burden of proof to the detriment of the purchaser is involved. purchaser s right to terminate the contract shall remain unaffected. 2. Where unforeseeable events as described in clause IV para 2, substantially change the economic importance or the contents of the supplies or considerably affect the supplier s business, the contract shall be adapted accordingly with due regard to the principle of good faith. Where this is not economically reasonable, the supplier shall have the right to terminate the contract. If the supplier wants to make use of this right of termination, he shall notify the purchaser in writing immediately after becoming aware of the significance of the event. This shall apply even where at first an extension of the delivery time had been agreed with the purchaser. XI. Further liability Except as provided herein, any other claims for damages of the purchaser shall be excluded regardless of whether they are based on positive breach of contractual obligations, violation of obligations in contract negotiations, breach of warranty, tort or other legal theory. This exclusion shall not apply where e.g. under the product liability law or in cases of wilful misconduct, of gross negligence, of the absence of warranted characteristics, or of the fundamental nonperformance of contractual obligations, there is a legally binding liability. However, liability for damages arising from the fundamental nonperformance of contractual obligations shall be limited to the foreseeable damage normally covered by a contract except in cases of wilful misconduct or gross negligence. This limitation does not imply a change in the burden of proof to the detriment of the purchaser. XII. Choise of forum 1. If the purchaser is a businessman, the sole forum for all disputes arising directly or indirectly out of the contract shall be the place of the supplier s head or branch office at the supplier s option. 2. All relations arising out of the contract shall be governed by German law not including the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG). XIII. Validity of the contract Even in case of legal invalidity of individual items, the remaining parts of the contract shall remain binding save where adherence to the contract would mean an undue hardship on one of the parties. *) Translation of the German edition of June 1997 published in the Bundesanzeiger Nr. 115, , by the Bundeskartellamt (Federal Cartel Office) as a recommendation of the Zentralverband Elektrotechnik und Elektronikindustrie (ZVEI) e.v. (German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers Association) 1840
42 Certificates LV HV D type fuselinks Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) system D type fusebases Switchdisconnectorfuses (SASIL) BS system Terminals LV HRC stripfuseways striptype fuse switchdisconnectors fusebases fuse switchdisconnectors Busbar system Consumer supply technology Distribution and instrument cabinets Electronic monitoring devices Measurement data acquisition systems Software 1841 Appendix
43 Contact Addresses JEAN MÜLLER Company Headquarters and Offices Agents Sales Offices IGVG IndustriegüterVertriebsGmbH KaiserWilhelmStraße 17 D12247 Berlin (Lankwitz) Tel.: +49 (30) Fax: +49 (30) Bremen Hamburg Neubrandenburg Berlin Vertriebsbüro Nord (VBN) Riepener Straße 19 D31542 Bad Nenndorf Tel.: +49 (57 25) Fax: +49 (57 25) Dieter Eidt GmbH Im Gäuchen 3 D65604 Elz Tel.: +49 (64 31) Fax: +49 (64 31) eidtgmbh@tonline.de Köln Osnabrück Kassel Erfurt Leipzig Vertriebsbüro Leipzig (VBL) Wurzner Straße 151 D04318 Leipzig Tel.: +49 (3 41) Fax: +49 (3 41) vbl@jeanmueller.de Dresden IngenieurBüro Henry Wollschläger Seckacher Straße 158 D68259 Mannheim Tel.: +49 (6 21) Fax: +49 (6 21) hwollschlaeger@jeanmueller.de Trier Regensburg Vertriebsbüro West (VBW) Lerchenstraße 44 D58285 Gevelsberg Tel.: +49 (23 32) Fax: +49 (23 32) tkrugmann@jeanmueller.de jschweitzer@jeanmueller.de Fritz Huber Technische Vertretungen Weidenstraße 20 D72666 Neckartailfingen Tel.: +49 (71 27) Fax: +49 (71 27) fhuber@jeanmueller.de Freiburg Vertriebsbüro Bayern (VBB) Poinger Straße 18 D85551 Kirchheim Heimstetten Tel.: +49 (89) Fax: +49 (89) vbb@jeanmueller.de Company Headquarters Jean Müller GmbH Elektrotechnische Fabrik Friedrichstraße 21 D65343 Eltville am Rhein P.O. Box D65333 Eltville am Rhein Tel.: +49 (6123) Fax: +49 (6123) sales@jeanmueller.de 1842
Standardized fuse characteristics
 Product family "Fuses offer unique advantages compared to other protective devices." Standardized fuse characteristics and high current limitation guarantee easy and reliable coordination between HV HRC
Product family "Fuses offer unique advantages compared to other protective devices." Standardized fuse characteristics and high current limitation guarantee easy and reliable coordination between HV HRC
Product family. D type fuse-links
 Product family D type fuse-links Fuses offer unique advantages compared to other protective devices. 3-0 Due to their compact dimensions, D type fuses from JEAN MÜLLER provide economical overcurrent protection
Product family D type fuse-links Fuses offer unique advantages compared to other protective devices. 3-0 Due to their compact dimensions, D type fuses from JEAN MÜLLER provide economical overcurrent protection
6-0. Product family. LV HRC strip-fuseways
 Product family strip-fuseways strip-fuseways in accordance with DIN 43623 are mainly used for power distribution in cable distribution cabinets and low voltage power supply distribution systems. They are
Product family strip-fuseways strip-fuseways in accordance with DIN 43623 are mainly used for power distribution in cable distribution cabinets and low voltage power supply distribution systems. They are
mainly used for power distribution
 Product family strip type fuse-switch-disconnector strip type fuseswitch-disconnectors are mainly used for power distribution in low voltage assemblies in accordance with IEC/EN 60439-1. The strips are
Product family strip type fuse-switch-disconnector strip type fuseswitch-disconnectors are mainly used for power distribution in low voltage assemblies in accordance with IEC/EN 60439-1. The strips are
2013 JEAN MÜLLER Products
 2013 JEAN MÜLLER Products Company JEAN MÜLLER JEAN MÜLLER was founded in 1897 in Germany, when the applications of electricity were still in their very early days. The company chose as its basic activity
2013 JEAN MÜLLER Products Company JEAN MÜLLER JEAN MÜLLER was founded in 1897 in Germany, when the applications of electricity were still in their very early days. The company chose as its basic activity
20 HUBER+SUHNER RADOX SOLAR
 All our cables fully comply with the European directives 76/769/EWG, 2003/11/EG, 2000/53/EG, 2003/53/EG and 2002/95/EG (RoHS) and the requirements of REACH Nr. EC1907/2006. 20 RADOX SOLAR cables RADOX
All our cables fully comply with the European directives 76/769/EWG, 2003/11/EG, 2000/53/EG, 2003/53/EG and 2002/95/EG (RoHS) and the requirements of REACH Nr. EC1907/2006. 20 RADOX SOLAR cables RADOX
NH-Fuse system Low voltage
 38103-FER NH-fuses A4-engl 22.10.2003 15:50 Uhr Seite 3 NH-Fuse system Low voltage 38103-FER NH-fuses A4-engl 22.10.2003 14:01 Uhr Seite 2 Utilization NH-fuses gg am gtr NH-fuses Utilization Categories
38103-FER NH-fuses A4-engl 22.10.2003 15:50 Uhr Seite 3 NH-Fuse system Low voltage 38103-FER NH-fuses A4-engl 22.10.2003 14:01 Uhr Seite 2 Utilization NH-fuses gg am gtr NH-fuses Utilization Categories
3NP1 Fuse Switch Disconnectors up to 630 A
 Switch Disconnectors 3NP1 Fuse Switch Disconnectors up to 630 A Introduction Overview All key product features at a glance available for all sizes Connection of circular conductors and laminated conductors
Switch Disconnectors 3NP1 Fuse Switch Disconnectors up to 630 A Introduction Overview All key product features at a glance available for all sizes Connection of circular conductors and laminated conductors
NXPLUS C Single busbar. Maintenance-free for lifetime
 NXPLUS C Single busbar Maintenance-free for lifetime Energy Distribution Welcome! Page 2 Content Overview Technical data Typicals Panel design Circuit-Breaker panel Busbar Operation Metering Low-voltage
NXPLUS C Single busbar Maintenance-free for lifetime Energy Distribution Welcome! Page 2 Content Overview Technical data Typicals Panel design Circuit-Breaker panel Busbar Operation Metering Low-voltage
General notes. Operating conditions
 1 General notes Wöhner busbar systems and components are the result of expert development based on many years of experience. They have been exhaustively tested and hold many approvals. The correct selection
1 General notes Wöhner busbar systems and components are the result of expert development based on many years of experience. They have been exhaustively tested and hold many approvals. The correct selection
FUSES. Safety through quality
 Safety through quality HH HIGH VOLTAGE Over many decades SIBA has developed a global product line of High Voltage Fuses that are comprehensive for any and all applications. Superior engineering, advanced
Safety through quality HH HIGH VOLTAGE Over many decades SIBA has developed a global product line of High Voltage Fuses that are comprehensive for any and all applications. Superior engineering, advanced
Step 1: Collection of required data
 Step 1: Collection of required data If the relevant parameters of the interfaces are known, it is possible to dimension ASSEMBLIES 3 Installation and environmental conditions 4 Operating and servicing
Step 1: Collection of required data If the relevant parameters of the interfaces are known, it is possible to dimension ASSEMBLIES 3 Installation and environmental conditions 4 Operating and servicing
Menu. Home About this portal Latest updates. Print Save Resource detail Citations. Table of Contents
 Menu Home About this portal Latest updates Print Save Email Resource detail Citations AS/NZS 60898.1:2004 Electrical accessories - Circuit-breakers for overcurrent protection for household and similar
Menu Home About this portal Latest updates Print Save Email Resource detail Citations AS/NZS 60898.1:2004 Electrical accessories - Circuit-breakers for overcurrent protection for household and similar
The University of New South Wales. School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications. Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Topic 2
 The University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Topic 2 SWITCHBOARDS Overview Also called Switchgear and Controlgear Assembly
The University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Topic 2 SWITCHBOARDS Overview Also called Switchgear and Controlgear Assembly
OLIVER ONLINE VOLTAGE REGULATION
 CAST-RESIN TRANSFORMERS ACCORDING TO IEC/EN 60076, VDE 0532, DIN 42523, DIN EN 50541-1, EU NR. 548/2014 OLIVER ONLINE VOLTAGE REGULATION With Ruhstrat transformers you provide the right voltage for the
CAST-RESIN TRANSFORMERS ACCORDING TO IEC/EN 60076, VDE 0532, DIN 42523, DIN EN 50541-1, EU NR. 548/2014 OLIVER ONLINE VOLTAGE REGULATION With Ruhstrat transformers you provide the right voltage for the
B kv T&D GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR
 GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR B 105 170 300 kv The increasing demand for electrical power in cities and industrial centers necessitates the installation of a compact and efficient distribution and transmission
GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR B 105 170 300 kv The increasing demand for electrical power in cities and industrial centers necessitates the installation of a compact and efficient distribution and transmission
Utilisation category gl/gg 500VAC with combi indicator
 DIN-fuse-links DIN fuse-links are used for the protection of electrical installations and equipment and are common for a wide area of applications. Standardised characteristics, technical data and dimensions
DIN-fuse-links DIN fuse-links are used for the protection of electrical installations and equipment and are common for a wide area of applications. Standardised characteristics, technical data and dimensions
HV DIN FUSE-LINKS FOR TRANSFORMER PROTECTION. March 2017
 HV DIN FUSE-LINKS FOR TRANSFORMER PROTECTION March 2017 HV FUSE-LINKS IN THE WORLD UL STANDARD E OR R RATED: AMERICAN STANDARD DIN STANDARD: GERMAN STANDARD FR STANDARD: FRENCH STANDARD BS STANDARD: BRITISH
HV DIN FUSE-LINKS FOR TRANSFORMER PROTECTION March 2017 HV FUSE-LINKS IN THE WORLD UL STANDARD E OR R RATED: AMERICAN STANDARD DIN STANDARD: GERMAN STANDARD FR STANDARD: FRENCH STANDARD BS STANDARD: BRITISH
Motor-protectivecircuit-breaker,3p,Ir=2.5-4A. Product range PKZM01 motor protective circuit-breakers up to 16 A with pushbutton actuation
 Motor-protectivecircuit-breaker,3p,Ir=2.5-4A Partno. PKZM01-4 Articleno. 278482 CatalogNo. XTPB004BC1 Deliveryprogramme Product range PKZM01 motor protective circuit-breakers up to 16 A with pushbutton
Motor-protectivecircuit-breaker,3p,Ir=2.5-4A Partno. PKZM01-4 Articleno. 278482 CatalogNo. XTPB004BC1 Deliveryprogramme Product range PKZM01 motor protective circuit-breakers up to 16 A with pushbutton
FUSOMAT Visible breaking and tripping fuse switches from 250 to 1250 A
 Fuse protection The solution for > Motor load break > Protection of industrial cabinet > Electrical distribution fusom_063_b_1_cat Strong points > Tripping upon overload > High breaking capacity > Improved
Fuse protection The solution for > Motor load break > Protection of industrial cabinet > Electrical distribution fusom_063_b_1_cat Strong points > Tripping upon overload > High breaking capacity > Improved
Page. Circuit-Breakers M4 2 for motor protection. Auxiliary contacts 3 Signalling switch Auxiliary releases
 Circuit Breakers M4 Page Circuit-Breakers M4 2 for motor protection Auxiliary contacts 3 Signalling switch Auxiliary releases Insulated 3-pole busbar system 4 Terminal block DIN-rail adapters 5 Busbar
Circuit Breakers M4 Page Circuit-Breakers M4 2 for motor protection Auxiliary contacts 3 Signalling switch Auxiliary releases Insulated 3-pole busbar system 4 Terminal block DIN-rail adapters 5 Busbar
FAQ S. Main Switchboard Design Criteria. ENGINEERED SOLUTIONS FOR ALL YOUR SWITCHBOARD NEEDS
 FAQ S Main Switchboard Design Criteria h ENGINEERED SOLUTIONS FOR ALL YOUR SWITCHBOARD NEEDS www.electricalswitchboards.com.au Main switchboard Design criteria Q: What is the Australian standard for main
FAQ S Main Switchboard Design Criteria h ENGINEERED SOLUTIONS FOR ALL YOUR SWITCHBOARD NEEDS www.electricalswitchboards.com.au Main switchboard Design criteria Q: What is the Australian standard for main
BETA Switching Switches and Light Indicators
 Siemens AG 2008 BETA Switching /2 Product overview /3 5TE8 control switches / 5TE4 pushbuttons /2 5TE5 light indicators /5 5TE8 ON/OFF switches /22 5TE9 busbars /24 5TE switch disconnectors Siemens ET
Siemens AG 2008 BETA Switching /2 Product overview /3 5TE8 control switches / 5TE4 pushbuttons /2 5TE5 light indicators /5 5TE8 ON/OFF switches /22 5TE9 busbars /24 5TE switch disconnectors Siemens ET
Switch Disconnectors. SENTRON 3NP5 Fuse Switch Disconnectors up to 630 A. Introduction. 7/106 Siemens LV
 Switch Disconnectors Introduction Siemens AG 2010 Overview 3NP5 0 3NP5 2 3NP5 fuse disconnector range 3NP5 4 SENTRON 3NP5 fuse disconnectors are controls for the occasional manual ing/isolating of loads
Switch Disconnectors Introduction Siemens AG 2010 Overview 3NP5 0 3NP5 2 3NP5 fuse disconnector range 3NP5 4 SENTRON 3NP5 fuse disconnectors are controls for the occasional manual ing/isolating of loads
INTRODUCTION. The plug-in connection on the cables and lightning arrestors, allows for easy installation and replacement.
 INTRODUCTION The Power Systems 44 kv MiniSub TM is the most compact system at this voltage available. Utilizing a deadfront termination and lightning arrestor setup, it eliminates the line top or side
INTRODUCTION The Power Systems 44 kv MiniSub TM is the most compact system at this voltage available. Utilizing a deadfront termination and lightning arrestor setup, it eliminates the line top or side
Type SIMOPRIME A4, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Switchgear
 Circuit-Breaker www.siemens.com/energy Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME A4, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Switchgear s Technology Circuit-Breaker Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME, up to 17.5 kv, Air-Insulated
Circuit-Breaker www.siemens.com/energy Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME A4, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Switchgear s Technology Circuit-Breaker Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME, up to 17.5 kv, Air-Insulated
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF 11KV SF6 / VCB METAL ENCLOSED, INDOOR (PANEL TYPE) / OUTDOOR RING MAIN UNIT (RMU). (IEC standard equipment)
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF 11KV SF6 / VCB METAL ENCLOSED, INDOOR (PANEL TYPE) / OUTDOOR RING MAIN UNIT (RMU). (IEC standard equipment) 1 SCOPE OF SUPPLY This specification covers design, manufacture, shop
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF 11KV SF6 / VCB METAL ENCLOSED, INDOOR (PANEL TYPE) / OUTDOOR RING MAIN UNIT (RMU). (IEC standard equipment) 1 SCOPE OF SUPPLY This specification covers design, manufacture, shop
ELECTRIC TRACTION.
 ELECTRIC TRACTION www.koncar.hr MODERNISATION ELECTRIC TRACTION VEHICLES Company KON AR - ELECTRIC VEHICLES Inc. upgrades electric locomotives, electric multiple unit and electric tramcars. Upgrading proceedings
ELECTRIC TRACTION www.koncar.hr MODERNISATION ELECTRIC TRACTION VEHICLES Company KON AR - ELECTRIC VEHICLES Inc. upgrades electric locomotives, electric multiple unit and electric tramcars. Upgrading proceedings
Catalog HA Edition up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated, Extendable. Medium-Voltage Switchgear. siemens.com/simosec
 Catalog HA 41.43 Edition 2018 Switchgear Type SIMOSEC, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated, Extendable Medium-Voltage Switchgear siemens.com/simosec Application Typical uses R-HA41-135.tif R-HA40-112.tif R-HA41-115.tif
Catalog HA 41.43 Edition 2018 Switchgear Type SIMOSEC, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated, Extendable Medium-Voltage Switchgear siemens.com/simosec Application Typical uses R-HA41-135.tif R-HA40-112.tif R-HA41-115.tif
2.1 Warnings & Agency Approvals Electrical Connections - Specifications Standard Wiring Configurations...2 4
 CHAPTER ELECTRICAL 2 INSTALLATION Contents of this Chapter... 2.1 Warnings & Agency Approvals..................2 2 2.1.1 Isolation..............................................2 2 2.1.2 Electrical Power
CHAPTER ELECTRICAL 2 INSTALLATION Contents of this Chapter... 2.1 Warnings & Agency Approvals..................2 2 2.1.1 Isolation..............................................2 2 2.1.2 Electrical Power
Cast resin transformers
 Product catalogue Cast resin transformers according to IEC/EN 60076, VDE 0532, DIN 42523 Power range up to 8 MVA Voltage range up to 36 kv Conductor material: copper or aluminum Protection types: IP 00
Product catalogue Cast resin transformers according to IEC/EN 60076, VDE 0532, DIN 42523 Power range up to 8 MVA Voltage range up to 36 kv Conductor material: copper or aluminum Protection types: IP 00
SWITCHBOARDS (LV and MV)
 ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems SWITCHBOARDS (LV and MV) 1. Introduction Depending on the size of the building or factory site and whether the supply is high voltage or low voltage, there
ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems SWITCHBOARDS (LV and MV) 1. Introduction Depending on the size of the building or factory site and whether the supply is high voltage or low voltage, there
1ZSE EN, REV. 4. Wall bushings type GSA-AA Technical guide
 1ZSE 2750-112 EN, REV. 4 Wall bushings type GSA-AA Technical guide Original instruction The information provided in this document is intended to be general and does not cover all possible applications.
1ZSE 2750-112 EN, REV. 4 Wall bushings type GSA-AA Technical guide Original instruction The information provided in this document is intended to be general and does not cover all possible applications.
INNOZED D0 fuse-bases with touch protection
 D0 fusebases with touch protection D0 fusebases with touch protection FUSE HOLDERS, FUSE BASES AND SUPPORTS IEC D0 & D FUSE BASES FEATURES & BENEFITS is a fuse base for D0 fuselinks, sizes D0 and D02.
D0 fusebases with touch protection D0 fusebases with touch protection FUSE HOLDERS, FUSE BASES AND SUPPORTS IEC D0 & D FUSE BASES FEATURES & BENEFITS is a fuse base for D0 fuselinks, sizes D0 and D02.
3TM Vacuum Contactors
 Catalog Extract HG 11.23 Edition 2016 Catalog Extract Medium-Voltage Equipment siemens.com/3tm R-HG11-343.psd 2 Siemens HG 11.23 2016 Contents Medium-Voltage Equipment Catalog Extract HG 11.23 2016 Contents
Catalog Extract HG 11.23 Edition 2016 Catalog Extract Medium-Voltage Equipment siemens.com/3tm R-HG11-343.psd 2 Siemens HG 11.23 2016 Contents Medium-Voltage Equipment Catalog Extract HG 11.23 2016 Contents
HHD HIGH VOLTAGE FUSES GERMAN DIN STANDARD. The temperature limiting function of the fuse striker pin. Design and construction.
 HHD HIGH VOLTAGE GERMAN DIN STANDARD FOR AIR & GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEARS OUTDOOR SWITCHGEARS The striker pin system is connected by means of a high resistance parallel conductor. After melting the main
HHD HIGH VOLTAGE GERMAN DIN STANDARD FOR AIR & GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEARS OUTDOOR SWITCHGEARS The striker pin system is connected by means of a high resistance parallel conductor. After melting the main
Application Mini Contactors for Motors and Resistive Loads
 Delivery program Contactor, 4p, 4kW/400V/AC3 Part no. DILEM4-G(24VDC) Catalog No. 012701 Eaton Catalog No. XTMF9A00TD Product range Contactors Application Mini Contactors for Motors and Resistive Loads
Delivery program Contactor, 4p, 4kW/400V/AC3 Part no. DILEM4-G(24VDC) Catalog No. 012701 Eaton Catalog No. XTMF9A00TD Product range Contactors Application Mini Contactors for Motors and Resistive Loads
SION Vacuum Circuit-Breakers. Answers for energy. Medium-Voltage Equipment Selection and Ordering Data. Catalog HG
 Medium-Voltage Equipment Selection and Ordering Data Catalog HG 11.02 2011 Answers for energy. R-HG11-172.tif 2 Siemens HG 11.02 2011 Contents SION Vacuum Circuit-Breakers Medium-Voltage Equipment Catalog
Medium-Voltage Equipment Selection and Ordering Data Catalog HG 11.02 2011 Answers for energy. R-HG11-172.tif 2 Siemens HG 11.02 2011 Contents SION Vacuum Circuit-Breakers Medium-Voltage Equipment Catalog
3RT14 Contactors with 3 Main Contacts
 3RT14 Contactors with 3 Main Contacts for Switching Resistive Loads Contactor Size 3RT14 46 Mechanical endurance Oper. 10 million Electrical endurance Oper. 0.5 million C-1 utilization category at I e
3RT14 Contactors with 3 Main Contacts for Switching Resistive Loads Contactor Size 3RT14 46 Mechanical endurance Oper. 10 million Electrical endurance Oper. 0.5 million C-1 utilization category at I e
BETA Fuses and Fuse Systems
 Introduction Overview Application LV HRC fuses are used for installation systems in non-residential, commercial and industrial buildings as well as in the switchboards of power supply companies. Fuses
Introduction Overview Application LV HRC fuses are used for installation systems in non-residential, commercial and industrial buildings as well as in the switchboards of power supply companies. Fuses
Contactors KNL A 68 KNL6, KNL9, KNL12, KNL16, KNL18, KNL22, KNL30. Dimensional drawing of KNL KNL6, KNL9, KNL12, KNL16, KNL18 KNL22, KNL30
 Contactors KNL KNL6, KNL9, KNL12, KNL16, KNL18, KNL22, KNL30 Adaptable to various control requirements with ability of mounting from one to four additional auxiliary contacts. Versatile product capable
Contactors KNL KNL6, KNL9, KNL12, KNL16, KNL18, KNL22, KNL30 Adaptable to various control requirements with ability of mounting from one to four additional auxiliary contacts. Versatile product capable
vertical fuse switch disconnectors
 SWITCHGEAR ARS vertical fuse switch disconnectors - touch protection IP 30 from the front - fibre glass extra strenghtened, self extinguishing thermoplastics - double clearance between open contacts -
SWITCHGEAR ARS vertical fuse switch disconnectors - touch protection IP 30 from the front - fibre glass extra strenghtened, self extinguishing thermoplastics - double clearance between open contacts -
Motor-drive mechanism, type BUL. Technical guide
 Motor-drive mechanism, type BUL Technical guide This Technical Guide has been produced to allow transformer manufacturers, and their designers and engineers, access to all the technical information required
Motor-drive mechanism, type BUL Technical guide This Technical Guide has been produced to allow transformer manufacturers, and their designers and engineers, access to all the technical information required
Miniature Circuit-Breakers (MCBs)
 Product Overview Miniature Circuit-Breakers (MCBs) Design Tripping characteristics Rated current I n Rated breaking capacity Power supply company product range 5SP3 E 16 - A Standard product range 5SQ2
Product Overview Miniature Circuit-Breakers (MCBs) Design Tripping characteristics Rated current I n Rated breaking capacity Power supply company product range 5SP3 E 16 - A Standard product range 5SQ2
with Vacuum Circuit Breaker HAF
 M E T A L - C L A D S W I T C H G E A R Safety and Reliability with Vacuum Circuit Breaker HAF Flexible Design and Compact with Vacuum Circuit Breaker HVF Easy Installation and Maintenance We build a better
M E T A L - C L A D S W I T C H G E A R Safety and Reliability with Vacuum Circuit Breaker HAF Flexible Design and Compact with Vacuum Circuit Breaker HVF Easy Installation and Maintenance We build a better
photovoltaic NEW Safe product solutions conforming to standards for Industrial Electrical Power Distribution Systems with extended product range
 Professional Photovoltaic Distributors NEW with extended product range 10 11 Safe product solutions conforming to standards for photovoltaic plants Industrial Electrical Power Distribution Systems Solar
Professional Photovoltaic Distributors NEW with extended product range 10 11 Safe product solutions conforming to standards for photovoltaic plants Industrial Electrical Power Distribution Systems Solar
Switchgear Type SIMOSEC, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated, Extendable
 www.siemens.com/medium-voltage-switchgear Switchgear Type SIMOSEC, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated, Extendable Medium-Voltage Switchgear Catalog HA 41.43 2012 Answers for infrastructure and cities. Neue Bilder
www.siemens.com/medium-voltage-switchgear Switchgear Type SIMOSEC, up to 24 kv, Air-Insulated, Extendable Medium-Voltage Switchgear Catalog HA 41.43 2012 Answers for infrastructure and cities. Neue Bilder
9-0. Product family. LV HRC fuse switch-disconnectors. Surface mounting Busbar mounting
 Product family fuse switch-disconnectors The 9 series fuse switch-disconnectors of the DIN sizes 00-4a are suitable for surface mounting on mounting plates and for direct mounting on busbars. The different
Product family fuse switch-disconnectors The 9 series fuse switch-disconnectors of the DIN sizes 00-4a are suitable for surface mounting on mounting plates and for direct mounting on busbars. The different
Data sheet chainflex CF210.UL
 For detailed overview please see design table 1. Outer jacket: Pressure extruded, oil-resistant PVC mixture 2. Overall shield: Bending-resistant braiding made of tinned copper wires. 3. Banding: Plastic
For detailed overview please see design table 1. Outer jacket: Pressure extruded, oil-resistant PVC mixture 2. Overall shield: Bending-resistant braiding made of tinned copper wires. 3. Banding: Plastic
Vertical fuse disconnects
 THE NAME FOR SAFETY Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects are designed to receive NH fuse links. Hinged fusecarriers enable opening and closing operation in electric
THE NAME FOR SAFETY Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects are designed to receive NH fuse links. Hinged fusecarriers enable opening and closing operation in electric
CONTENTS 1 GENERAL 2 STANDARDS. 3 TECHNICAL FEATURES 3.1 Basic Technical Data 3.2 Standard Accessories 3.3 Tolerances
 CONTENTS 1 GENERAL 2 STANDARDS 3 TECHNICAL FEATURES 3.1 Basic Technical Data 3.2 Standard Accessories 3.3 Tolerances 4 MOTOR DESIGN 4.1 Stator Casing 4.2 Stator Core with Winding 4.3 Stator Winding 4.4
CONTENTS 1 GENERAL 2 STANDARDS 3 TECHNICAL FEATURES 3.1 Basic Technical Data 3.2 Standard Accessories 3.3 Tolerances 4 MOTOR DESIGN 4.1 Stator Casing 4.2 Stator Core with Winding 4.3 Stator Winding 4.4
sa B-CABLES nv PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWOEU.../3E Medium Voltage Flexible Cables for Use in Water with Copper Core Shield sa B-CABLES nv ENERGY
 PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWOEU.../3E Medium Voltage Flexible Cables for Use in Water with Copper Core Shield ENERGY Technical Data Electrical Thermal Type Type designation PROTOLON (ST) NTSCGECEWÖU.../3E Approvals/
PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWOEU.../3E Medium Voltage Flexible Cables for Use in Water with Copper Core Shield ENERGY Technical Data Electrical Thermal Type Type designation PROTOLON (ST) NTSCGECEWÖU.../3E Approvals/
Benefits, typical uses
 R-HA26-013. eps Switchgear Type 8BT1, up to 24kV,Air-Insulated Contents Application Page Application Benefits 2 Typical uses 2 and 3 Technical Data Ratings 4 Classification, dimensions, 5 room planning
R-HA26-013. eps Switchgear Type 8BT1, up to 24kV,Air-Insulated Contents Application Page Application Benefits 2 Typical uses 2 and 3 Technical Data Ratings 4 Classification, dimensions, 5 room planning
NEOZED D0 fuse-links gg 400/440VAC
 NEOZED D0 fuse-links gg 400/440VAC LOW VOLTAGE IEC FUSES DIN LV FUSE-LINKS D0 FEATURES & BENEFITS The D0 fuse-system is installed in low voltage distribution units, where fuse-links are accessible to non
NEOZED D0 fuse-links gg 400/440VAC LOW VOLTAGE IEC FUSES DIN LV FUSE-LINKS D0 FEATURES & BENEFITS The D0 fuse-system is installed in low voltage distribution units, where fuse-links are accessible to non
CONTENTS 1 GENERAL 2 STANDARDS. 3 TECHNICAL FEATURES 3.1 Basic Design Data 3.2 Standard Accessories 3.3 Tolerances
 CONTENTS 1 GENERAL 2 STANDARDS 3 TECHNICAL FEATURES 3.1 Basic Design Data 3.2 Standard Accessories 3.3 Tolerances 4 MOTOR DESIGN 4.1 Stator Casing 4.2 Stator Core with Winding 4.3 Stator Winding and Insulation
CONTENTS 1 GENERAL 2 STANDARDS 3 TECHNICAL FEATURES 3.1 Basic Design Data 3.2 Standard Accessories 3.3 Tolerances 4 MOTOR DESIGN 4.1 Stator Casing 4.2 Stator Core with Winding 4.3 Stator Winding and Insulation
Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors
 Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors NV Strip type fuse-switch-disconnector sizes 00, 1, 2, Characteristics of the NV Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors The NV Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors are
Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors NV Strip type fuse-switch-disconnector sizes 00, 1, 2, Characteristics of the NV Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors The NV Strip type fuse-switch-disconnectors are
D509E. Manual Motor - Starters
 D509E Manual Motor - Starters Index Page Manual Motors Starters 182 Auxilliary Contact Blocks 182 Trip Alarm Aux. Switch 182 Shunt Release 182 Under-voltage Release 183 Accessories 183 Busbar Connectors
D509E Manual Motor - Starters Index Page Manual Motors Starters 182 Auxilliary Contact Blocks 182 Trip Alarm Aux. Switch 182 Shunt Release 182 Under-voltage Release 183 Accessories 183 Busbar Connectors
Circuit-Breaker Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME, up to 17.5 kv, Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Switchgear.
 Circuit-Breaker Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME, up to 17.5 kv, Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Switchgear www.siemens.com/energy Technology s Contents Application Page Benefits 2 Typical uses 2 and 3 Technical
Circuit-Breaker Switchgear Type SIMOPRIME, up to 17.5 kv, Air-Insulated Medium-Voltage Switchgear www.siemens.com/energy Technology s Contents Application Page Benefits 2 Typical uses 2 and 3 Technical
020: 2013 CEB SPECIFICATION MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER (MCB)
 020: 2013 CEB SPECIFICATION MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER (MCB) CEYLON ELECTRICITY BOARD SRI LANKA Telephone: +94 11 232 0953 Fax: +94 11 232 3935 CONTENTS Page 1.0 Scope 3 2.0 System Parameters 3 3.0 Service
020: 2013 CEB SPECIFICATION MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER (MCB) CEYLON ELECTRICITY BOARD SRI LANKA Telephone: +94 11 232 0953 Fax: +94 11 232 3935 CONTENTS Page 1.0 Scope 3 2.0 System Parameters 3 3.0 Service
Switchgear Type 8BT1, up to 24 kv, air-insulated. Medium Voltage Switchgear Catalog HA 26.
 www.siemens.com/medium-voltage-switchgear Switchgear Type 8BT1, up to 24 kv, air-insulated Medium Voltage Switchgear Catalog HA 26.31 2012 Answers for infrastructure and cities. R-HA26-013. eps Contents
www.siemens.com/medium-voltage-switchgear Switchgear Type 8BT1, up to 24 kv, air-insulated Medium Voltage Switchgear Catalog HA 26.31 2012 Answers for infrastructure and cities. R-HA26-013. eps Contents
Vertical fuse disconnects
 Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects are designed to receive NH fuse links. Hinged fuse-carriers enable opening and closing operation in electric circuits under
Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects are designed to receive NH fuse links. Hinged fuse-carriers enable opening and closing operation in electric circuits under
Chapter 6 Generator-Voltage System
 Chapter 6 Generator-Voltage System 6-1. General The generator-voltage system described in this chapter includes the leads and associated equipment between the generator terminals and the low-voltage terminals
Chapter 6 Generator-Voltage System 6-1. General The generator-voltage system described in this chapter includes the leads and associated equipment between the generator terminals and the low-voltage terminals
Current Carrying Capacity of RADOX Solar cables
 Current Carrying Capacity of RADOX Solar cables Content: 1. Scope 2 2. Definitions 2 3. General remarks 2 4. Current rating under service conditions 3 4.1 Standard conditions for current rating 3 4.2 Reduction
Current Carrying Capacity of RADOX Solar cables Content: 1. Scope 2 2. Definitions 2 3. General remarks 2 4. Current rating under service conditions 3 4.1 Standard conditions for current rating 3 4.2 Reduction
General_technical_data Series
 Slow-make switching element Switching system The double-break, slow-make switching element is equipped with one or two independent contact systems, acting as normally open or normally closed contact. The
Slow-make switching element Switching system The double-break, slow-make switching element is equipped with one or two independent contact systems, acting as normally open or normally closed contact. The
NPS/003/010 - Technical Specification for 400V Assemblies (LVAC Boards) utilised in Major Substations
 Version:- 3.0 Date of Issue:- Dec 2013 Page 1 of 13 NPS/003/010 - Technical Specification for 400V Assemblies (LVAC Boards) utilised in Major Substations 1. Purpose This document is the technical specification
Version:- 3.0 Date of Issue:- Dec 2013 Page 1 of 13 NPS/003/010 - Technical Specification for 400V Assemblies (LVAC Boards) utilised in Major Substations 1. Purpose This document is the technical specification
Operating Manual (Edition 04/2004) sinamics. Braking Module / Braking Resistor SINAMICS G130
 Operating Manual (Edition 04/2004) sinamics Braking Module / Braking Resistor SINAMICS G130 04/04 Contents Contents 1 Safety Information 1-1 2 General 2-1 3 Mechanical Installation 3-1 4 Connection 4-1
Operating Manual (Edition 04/2004) sinamics Braking Module / Braking Resistor SINAMICS G130 04/04 Contents Contents 1 Safety Information 1-1 2 General 2-1 3 Mechanical Installation 3-1 4 Connection 4-1
sa B-CABLES nv PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWOEU Medium Voltage Flexible Cables for Use In Water sa B-CABLES nv ENERGY
 PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWOEU Medium Voltage Flexible Cables for Use In Water ENERGY Technical Data Electrical Thermal Type Type designation PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWÖU Approvals/ standards DIN VDE 0250 part 813
PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWOEU Medium Voltage Flexible Cables for Use In Water ENERGY Technical Data Electrical Thermal Type Type designation PROTOLON(ST) NTSCGEWÖU Approvals/ standards DIN VDE 0250 part 813
Key features. DESIGNS: - Conservator type - Hermetically sealed
 Package Substations OTDS manufactures a large range of oil filled hermitically sealed and conservator type transformers to be used in conjunction with our package substations. We are able to utalise the
Package Substations OTDS manufactures a large range of oil filled hermitically sealed and conservator type transformers to be used in conjunction with our package substations. We are able to utalise the
34-SDMS-02 SPECIFICATIONS FOR
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR M V & L V FUSE LINKS This specification is property of SEC and subject to change or modification without any notice TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE 3 2.0 CROSS REFERENCES 3 3.0 APPLICABLE
SPECIFICATIONS FOR M V & L V FUSE LINKS This specification is property of SEC and subject to change or modification without any notice TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE 3 2.0 CROSS REFERENCES 3 3.0 APPLICABLE
Index. Manual Motor Starters 1. Auxiliary Contact Blocks 1. Trip Alarm Auxiliary 1. Switch. Shunt Release 1. Under-voltage Release 2.
 Index Index Page Manual Motor Starters 1 Auxiliary Contact Blocks 1 Trip Alarm Auxiliary 1 Switch Shunt Release 1 Under-voltage Release 2 Accessories 2 Busbar Connectors 2 Enclosures 2 Leistung, kw C mv
Index Index Page Manual Motor Starters 1 Auxiliary Contact Blocks 1 Trip Alarm Auxiliary 1 Switch Shunt Release 1 Under-voltage Release 2 Accessories 2 Busbar Connectors 2 Enclosures 2 Leistung, kw C mv
Data sheet chainflex CF6
 1. Outer jacket: Pressure extruded, oil-resistant PVC mixture 2. Overall shield: Extremely bending-stable braid made of tinned copper wires 3. Inner jacket: Pressure extruded, gusset-filling PVC mixture
1. Outer jacket: Pressure extruded, oil-resistant PVC mixture 2. Overall shield: Extremely bending-stable braid made of tinned copper wires 3. Inner jacket: Pressure extruded, gusset-filling PVC mixture
Power distribution. General remarks
 When developing the Rittal busbar systems and their components, Rittal drew on the latest state of the art and the currently valid standards and regulations. These applications are used by specialist companies
When developing the Rittal busbar systems and their components, Rittal drew on the latest state of the art and the currently valid standards and regulations. These applications are used by specialist companies
Size 00-4a LV HRC fusebases. plates and for direct mounting on busbars. In addition, they serve as bases for LV HRC fuselinks
 Product family fuse-bases Size 00-4a fusebases are suitable for surface mounting on mounting plates and for direct mounting on busbars. In addition, they serve as bases for fuselinks in accordance with
Product family fuse-bases Size 00-4a fusebases are suitable for surface mounting on mounting plates and for direct mounting on busbars. In addition, they serve as bases for fuselinks in accordance with
INNOZED D0 fuse-bases with touch protection
 INNOZED D0 fusebases with touch protection INNOZED D0 fusebases with touch protection FUSE HOLDERS, FUSE BASES AND SUPPORTS IEC D0 & D FUSE BASES FEATURES & BENEFITS INNOZED is a fuse base for D0 fuselinks,
INNOZED D0 fusebases with touch protection INNOZED D0 fusebases with touch protection FUSE HOLDERS, FUSE BASES AND SUPPORTS IEC D0 & D FUSE BASES FEATURES & BENEFITS INNOZED is a fuse base for D0 fuselinks,
LV Capacitor CLMD03 Power Module Instruction manual
 LV Capacitor CLMD03 Power Module Instruction manual Table of Contents 1 Safety... 3 2 Upon reception... 3 2.1 Inspection on reception... 3 2.2 Storage- transportation handling... 3 3 Hardware Description...
LV Capacitor CLMD03 Power Module Instruction manual Table of Contents 1 Safety... 3 2 Upon reception... 3 2.1 Inspection on reception... 3 2.2 Storage- transportation handling... 3 3 Hardware Description...
1ZSE en, Rev. 3. Wall bushings, type GSA-AA Technical guide
 1ZSE 2750-112 en, Rev. 3 Wall bushings, type GSA-AA Technical guide Original instruction The information provided in this document is intended to be general and does not cover all possible applications.
1ZSE 2750-112 en, Rev. 3 Wall bushings, type GSA-AA Technical guide Original instruction The information provided in this document is intended to be general and does not cover all possible applications.
Circuit-Breakers M4 166 for motor protection. Auxiliary contacts 167 Signalling switch Auxiliary releases
 Index Page Circuit-Breakers M4 166 for motor protection Auxiliary contacts 167 Signalling switch Auxiliary releases Insulated 3-pole busbar system 168 Terminal block DIN-rail adapters 169 Busbar adapters
Index Page Circuit-Breakers M4 166 for motor protection Auxiliary contacts 167 Signalling switch Auxiliary releases Insulated 3-pole busbar system 168 Terminal block DIN-rail adapters 169 Busbar adapters
Appendix: Safety and application notes for... 15
 Contents Safety... 2 Warnings... 2 Symbols used in this manual... 2 Operator s safety... 2 Avoid filter module damage... 2 DC-link resonance... 2 Description... 3 Description... 3 Ordering numbers, 380-415
Contents Safety... 2 Warnings... 2 Symbols used in this manual... 2 Operator s safety... 2 Avoid filter module damage... 2 DC-link resonance... 2 Description... 3 Description... 3 Ordering numbers, 380-415
Low Voltage Fuses. Safety in Focus. ZVEI.ppt / / 1
 Low Voltage Fuses Safety in Focus ZVE.ppt / 05.01 / 1 Applications, Product Advantages Fuses protect Human life Electrical circuits Electrical products Electronics Cables and conductors Product advantages
Low Voltage Fuses Safety in Focus ZVE.ppt / 05.01 / 1 Applications, Product Advantages Fuses protect Human life Electrical circuits Electrical products Electronics Cables and conductors Product advantages
This standard covers the requirements of lighting chains. This standard covers only the safety requirements.
 FOREWORD (Formal clause will be added later) This standard covers the requirements of lighting chains. This standard covers only the safety requirements. This standard (Part 5/Section 7) is one among the
FOREWORD (Formal clause will be added later) This standard covers the requirements of lighting chains. This standard covers only the safety requirements. This standard (Part 5/Section 7) is one among the
B kv Gas-insulated Substations
 72.5 145 kv Gas-insulated Substations The increasing demand for electrical power in cities and industrial centres requires the installation of a compact and efficient distribution and transmission network.
72.5 145 kv Gas-insulated Substations The increasing demand for electrical power in cities and industrial centres requires the installation of a compact and efficient distribution and transmission network.
TIDALFLUX 2300 F Quick Start
 Quick Start Electromagnetic flow sensor for partially filled pipes The documentation is only complete when used in combination with the relevant documentation for the signal converter. KROHNE CONTENTS
Quick Start Electromagnetic flow sensor for partially filled pipes The documentation is only complete when used in combination with the relevant documentation for the signal converter. KROHNE CONTENTS
SECTION. Watertight & Dust-Tight Plugs & Connectors
 SECTION Watertight & ust-tight Wetguard Product Line Section Contents LIFETIME Wetguard Plugs, Connectors & Straight Blade 2-Pole 3-Wire 2-Pole 3-Wire 3-Pole 4-Wire 3-Pole 3-Wire Non- 4-Pole 4-Wire Non-
SECTION Watertight & ust-tight Wetguard Product Line Section Contents LIFETIME Wetguard Plugs, Connectors & Straight Blade 2-Pole 3-Wire 2-Pole 3-Wire 3-Pole 4-Wire 3-Pole 3-Wire Non- 4-Pole 4-Wire Non-
Approved Standards. Motor Contactor. Main contactor. Accessoires. 21 Motor Contactor J7KN
 Motor Contactor Main contactor AC & DC operated Integrated auxiliary contacts Screw fixing and snap fitting (35 mm DIN rail) up to 45 kw Range from 4 to 110 kw (AC 3, 380/415V) Finger proof ( VBG 4) Accessoires
Motor Contactor Main contactor AC & DC operated Integrated auxiliary contacts Screw fixing and snap fitting (35 mm DIN rail) up to 45 kw Range from 4 to 110 kw (AC 3, 380/415V) Finger proof ( VBG 4) Accessoires
HHD. High Voltage Fuses German DIN Standard. The temperature limiting function of the fuse striker pin. Design and construction.
 HHD High Voltage Fuses German DIN Standard For Air & Gas Insulated Switchgear Indoor and Outdoor Application The striker pin system is connected by means of a high resistance parallel conductor. After
HHD High Voltage Fuses German DIN Standard For Air & Gas Insulated Switchgear Indoor and Outdoor Application The striker pin system is connected by means of a high resistance parallel conductor. After
General information about motor protection
 Application guide General information about motor protection Typical construction of a motor starter Disconnect Switch UL 98 - UL489 CSA C22.2 # 4 CSA C22.2 # 5 Fuses SIRCO Non-Fusible Disconnect Switch
Application guide General information about motor protection Typical construction of a motor starter Disconnect Switch UL 98 - UL489 CSA C22.2 # 4 CSA C22.2 # 5 Fuses SIRCO Non-Fusible Disconnect Switch
TGK Prefabricated Substation Technical Data
 TGK Prefabricated Substation Technical Data Ref Item Data 1 General Technical 1.1 Frequency (Hz) 50 1.2 Transformer Rating (kva) 315/750 1.3 Transformer Primary Voltage (kv) 11 1.4 Transformer Secondary
TGK Prefabricated Substation Technical Data Ref Item Data 1 General Technical 1.1 Frequency (Hz) 50 1.2 Transformer Rating (kva) 315/750 1.3 Transformer Primary Voltage (kv) 11 1.4 Transformer Secondary
PIX-H Metal-clad switchgear up to 17.5kV
 AIR INSULATED SWITCHGEAR PIX-H Metal-clad switchgear up to 17.5kV for high rated applications Technical Specifications AREVA T&D Summary - Technical description... 3 - Standards... 6 - PIX in detail...
AIR INSULATED SWITCHGEAR PIX-H Metal-clad switchgear up to 17.5kV for high rated applications Technical Specifications AREVA T&D Summary - Technical description... 3 - Standards... 6 - PIX in detail...
AF series contactors (9 2650)
 R E32527 R E39322 contactors General purpose and motor applications AF series contactors (9 2650) 3- & 4-pole contactors General purpose up to 2700 A Motor applications up to 50 hp, 900 kw NEMA Sizes 00
R E32527 R E39322 contactors General purpose and motor applications AF series contactors (9 2650) 3- & 4-pole contactors General purpose up to 2700 A Motor applications up to 50 hp, 900 kw NEMA Sizes 00
Cable category. B Multi-core cables for domestic/handheld equipment Rubber insulation PVC insulation TPE insulation 0.
 Table 12-1: current rating Technical Tables T12 Current ratings basic table ÖLFLEX For cables with a nominal voltage of up to 1000 V and for heat-resistant cables at an ambient temperature of +30 C. You
Table 12-1: current rating Technical Tables T12 Current ratings basic table ÖLFLEX For cables with a nominal voltage of up to 1000 V and for heat-resistant cables at an ambient temperature of +30 C. You
D4DS. Compact Interlock Safety Door Switch. Compact Safety Switch Saves Space and is Ideal for a Variety of Doors. Refer to Precautions on page 9.
 Compact Interlock Safety Door Switch Compact Safety Switch Saves Space and is Ideal for a Variety of Doors Positive opening mechanism and double insulation approved by TÜV and BIA. Five-direction Operation
Compact Interlock Safety Door Switch Compact Safety Switch Saves Space and is Ideal for a Variety of Doors Positive opening mechanism and double insulation approved by TÜV and BIA. Five-direction Operation
8DJ. Maintenance-free for lifetime
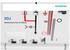 8DJ Maintenance-free for lifetime Energy Distribution Welcome! Page 2 October 1 st 2008 8DJ Main Applications for Medium-Voltage Switchgear Power generation Power stations G Power transmission High and
8DJ Maintenance-free for lifetime Energy Distribution Welcome! Page 2 October 1 st 2008 8DJ Main Applications for Medium-Voltage Switchgear Power generation Power stations G Power transmission High and
Control Circuit Protection
 Contents 5SJ4 Branch Circuit Protectors 5SY4 Supplementary Protectors 5SY6 Supplementary Protectors 16/19 5SJ4 Page Selection and ordering data 1-pole up to 63A 16/4 1-pole, 2-pole, 16/5 3-pole, 240VAC
Contents 5SJ4 Branch Circuit Protectors 5SY4 Supplementary Protectors 5SY6 Supplementary Protectors 16/19 5SJ4 Page Selection and ordering data 1-pole up to 63A 16/4 1-pole, 2-pole, 16/5 3-pole, 240VAC
PowerLogic High Density Metering System 4-Meter Enclosure Installation Guide
 PowerLogic High Density Metering System 4-Meter Enclosure Installation Guide 7002-0289-00 Instruction Bulletin HAZARD CATEGORIES AND SPECIAL SYMBOLS Read these instructions carefully and look at the equipment
PowerLogic High Density Metering System 4-Meter Enclosure Installation Guide 7002-0289-00 Instruction Bulletin HAZARD CATEGORIES AND SPECIAL SYMBOLS Read these instructions carefully and look at the equipment
3VU13, 3VU16 Circuit-Breakers
 3VU3, 3VU6 Circuit-Breakers Description The 3VU3, 3VU6 circuit-breakers are compact circuit-breakers for currents up to 80 A which operate according to the current limiting principle. The devices are used
3VU3, 3VU6 Circuit-Breakers Description The 3VU3, 3VU6 circuit-breakers are compact circuit-breakers for currents up to 80 A which operate according to the current limiting principle. The devices are used
Vertical fuse disconnects
 THE NAME FOR SAFETY Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects are designed to receive NH fuse links. Hinged fuse-carriers enable opening and closing operation in electric
THE NAME FOR SAFETY Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects Vertical fuse disconnects are designed to receive NH fuse links. Hinged fuse-carriers enable opening and closing operation in electric
OTEC Transfer switch open transition
 Specification sheet OTEC Transfer switch open transition 40 1200 amp Description OTEC transfer switches are designed for operation and switching of electrical loads between primary power and Standby generator
Specification sheet OTEC Transfer switch open transition 40 1200 amp Description OTEC transfer switches are designed for operation and switching of electrical loads between primary power and Standby generator
DATASHEET - DILMC9-10(24VDC) Technical data General. Contactor, 3p+1N/O, 4kW/400V/AC3. Catalog No Eaton Catalog No. XTCEC009B10TD.
 DATASHEET - DILMC9-10(24VDC) Technical data General Contactor, 3p+1N/O, 4kW/400V/AC3 Part no. DILMC9-10(24VDC) Catalog No. 277468 Eaton Catalog No. XTCEC009B10TD EL-Nummer 4110305 (Norway) Standards IEC/EN
DATASHEET - DILMC9-10(24VDC) Technical data General Contactor, 3p+1N/O, 4kW/400V/AC3 Part no. DILMC9-10(24VDC) Catalog No. 277468 Eaton Catalog No. XTCEC009B10TD EL-Nummer 4110305 (Norway) Standards IEC/EN
Current carrying capacity
 of RADOX 125 single core and multi core cables Scope The following tables referring to RADOX connecting leads and multicore cables give easy and fast support for the layout of apparatus and components.
of RADOX 125 single core and multi core cables Scope The following tables referring to RADOX connecting leads and multicore cables give easy and fast support for the layout of apparatus and components.
I r A short-circuit protective device: Observe the maximum permissible fuse of the contactor with direct device mounting.
 DATASHEET - ZB12-2,4 Delivery program Overload relay, 1.6-2.4 A, 1N/O+1N/C Part no. ZB12-2,4 Catalog No. 278437 Eaton Catalog No. XTOB2P4BC1 EL-Nummer 0004131832 (Norway) Product range Overload relay ZB
DATASHEET - ZB12-2,4 Delivery program Overload relay, 1.6-2.4 A, 1N/O+1N/C Part no. ZB12-2,4 Catalog No. 278437 Eaton Catalog No. XTOB2P4BC1 EL-Nummer 0004131832 (Norway) Product range Overload relay ZB
