1. INTRODUCTION. Anti-lock Braking System
|
|
|
- Shanon Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on which research and development has been going on for the past several year. Most of the newer vehicle models offer ABS as either standard or optional equipment.wheel lockup during braking causes skidding which in turn cause a loss of traction and vehicle control. This reduces the steering ability to change direction. So the car slides out of control. But the road wheel that is still rotating can be steered. That is what ABS is all about. With such a system, the driver can brake hard, take the evasive action and still be in control of the vehicle in any road condition at any speed and under any load. ABS does not reduce stopping distance, but compensates the changing traction or tyre loading by preventing wheel lockup. During panic braking when the wheels are about to lockup, sensors sense that the wheel has just begun turning slower than others on the vehicle. So they momentarily reduce braking force on the affected wheel. This prevents sliding of the wheels on the pavement. When the wheel resumes rolling, full braking force is again applied. ABS repeats the process until there is no longer any need for modulated braking. ABS acts faster than any driver could, pumping the brakes several times per second. Depending on the type of system, ABS adjusts the braking force at each wheel or set of wheels, whereas a driver s foot on the brake pedal operates all the brakes at once in normal braking. 1
2 2. CONCEPT OF ABS The theory behind anti-lock brakes is simple. A skidding wheel (where the tire contact patch is sliding relative to the road) has less traction than a nonskidding wheel. If the vehicle have been stuck on ice and if the wheels are spinning then the vehicle have no traction. This is because the contact patch is sliding relative to the ice. By keeping the wheels from skidding while you slow down, anti-lock brakes benefit you in two ways: You'll stop faster, and you'll be able to steer while you stop. Good drivers have always pumped the brake pedal during panic stops to avoid wheel lock up and the loss of steering control. ABS simply gets the pumping job done much faster and in much precise manner than the fastest human foot. 2
3 3. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION OF SIMPLE HYDRAULIC BRAKING SYSTEM. A simple braking system consists of a master cylinder, and four wheel cylinders. Every wheel cylinder contains two pistons which move out words when the hydraulic fluid flows from the master cylinder to the wheel cylinders through the suitable pipes or lines. Springs are used to hold the brake shoes on all four wheels. When the brake pedal is pressed the piston in the master cylinder forces the liquid out of the cylinder. This liquid presses the two pistons in the wheel cylinders outwards. These two pistons push the brake shoes out words. The brake shoes in turn press against the brake drums; this stops the brake drum which will be rotating. When the brake pedal is released the master cylinder is pushed backwords.this is done by a spring fitted in the master cylinder. The springs of 3
4 the brake shoe brings the shoes closer. The liquid in the wheel cylinder is pushed outwards through the pipes. It returns through the pipes to the master cylinder. This is how the hydraulic system of the four wheels operates 3.1 Master cylinder It consists of a reservoir feedhole, bypass port, primarypiston, secondary piston.the liquid in the reservoir flows through bypass port to the master cylinder. When the pedal is pressed the primary piston moves to the left.when it crosses the bypass port the liquid is forced along the pipe lines to the wheel cylinders. When the pedal is released the primary piston is moved back wards.it is the spring, which pushes the piston back wards. At the same time a partial vacuum is developed in the space previously occupied by the spring. 4
5 4. PRINCIPLES OF ABS The brakes of vehicle not equipped with ABS will almost immediately lock the wheels, when the driver suddenly applies the brake. In this case the vehicle slides rather than rolls to a stop. The skidding and lack of control was caused by the locking of wheels. The release and reapply of the brake pedal will avoid the locking of the wheels which in turn avoid the skidding. This is exactly what an antilock braking system does. 4.1 Pressure modulation When the brake pedal is pumped or pulsed the pressure is quickly applied and released at the wheels. This is called pressure modulation. Pressure modulation works to prevent the wheel locking. ABS can modulate the pressure to the brake as often as 15 times per seconds. By modulating the pressure to the brakes the friction between the tires and the road is maintained and the vehicle is able to come to the controllable stop. 5
6 Steering is another important consideration. As long as a tire doesn t slip it goes only in the direction in which it is turned. But once it is skid it has little or no directional stability. The Maneuverability of the vehicle is reduced if the front wheels are locked and the stability of the vehicle is reduced if the rear wheels are locked. ABS precisely controls the slip rate of the wheels to ensure maximum grip force from the tyre and it there by ensures maneuverability and stability of the vehicle. ABS control module calculates the slip rate of the wheels based on the vehicle speed and speed of the wheels, and then it controls the brake fluid pressure to attain the target slip rate. During ABS operation, the target slip rate can be from 10 to 30%. 0% slip means the wheel is rolling freely, while 100 % means the wheel is fully locked. A slip rate of 25 % means the velocity of a wheel is 25 % less than that of a freely rolling wheel at the same vehicle speed. 6
7 5. ABS COMPONENTS Many different ABS are found on today s vehicles. These designs are varied by their basic layout, operation and components. The ABS components can be divided into two categories. 1. Hydraulic components 2. Electrical/electronic components Besides these normal and conventional brake parts are part of the overall brake system. 5.1 Hydraulic components Accumulator An accumulator is used to store hydraulic fluid to maintain high pressure in the brake system and provide the residual pressure for power assisted braking. Normally the accumulator is charged with nitrogen gas and is an integral part of the modulator unit. Antilock hydraulic control valve assembly This assembly controls the release and application of the brake system pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. It may be of integral type and non integral type. In integral type the unit is combined with the power boost and master cylinder unit into one assembly. The non integral type is mounted externally from the master cylinder /power booster unit and is located between the master cylinder and wheel brake assembly. Both types generally contain solenoid valve that control the releasing, holding and applying of brake system pressure. 7
8 Booster pump The booster pump is an assembly of an electric motor and pump. The booster pump is used to provide pressurized hydraulic fluid ABS. The pumps motor is controlled by systems control unit. Booster/Master cylinder assembly It is referred as the hydraulic unit, contains the valves and pistons needed to modulate hydraulic pressure in the wheel circuit during the ABS operations. Fluid accumulator Different than a pressure accumulator, fluid accumulator temporarily store brake fluid, that is removed from the wheel brake unit during ABS cycle. This fluid is then used by pump to build pressure for the brake hydraulic system. Hydraulic control unit This assembly contains solenoid valve, fluid accumulator, pump and electric motor. The unit may have one pump and one motor or it have one motor and two pumps. Main Valve This is a two position valve and is also controlled by ABS control module and is open only in the ABS mode. When open pressurized brake fluid from the booster circuit is directed into the master circuit to prevent excessive pedal travel. Modulator unit The modulator unit controls the flow of pressurized brake fluid to the individual wheel circuits. Normally the modulator is made up of solenoid that open and close valves, several valves that control flow of fluid to wheel brake units and electrical relays that activate or deactivate the solenoids through the 8
9 commands of the control module. This unit may also be called the hydraulic actuator, hydraulic power unit or the electro hydraulic control valve. Solenoid valves The solenoid valves are located in the modulator unit and are electrically operated by signals from the control module. The control module switches the solenoids on or off to increase, decrease, or maintain the hydraulic pressure to the individual wheel units. Wheel circuit valves Two solenoid valves are used to control each circuit or channel. One controls the inlet valve of the circuit, the controls the outlet valve.the position is determined by the control module. Outlet valves are normally closed and inlet valves are normally open. Valves are activated when abs control module switches 12 volts to the circuit solenoids. During normal driving the circuits are not activated. 5.2 Electrical\ electronic components ABS control module This small computer is normally mounted inside the trunk on the wheel housing, mounted to the master cylinder or is part of the hydraulic control unit. It monitors system operation and controls antilock function when needed. The module relies on input from the wheel speed sensors and feedback from the hydraulic unit to determine if the abs is operating correctly and to determine when the anti lock mode is required. Brake pedal sensor The antilock brake pedal sensor switch is normally closed. When the brake pedal exceeds the antilock brake pedal sensor switch setting during an antilock stop, the antilock brake control module senses that the antilock brake pedal sensor switch is open and grounds the pump motor relay coil. This 9
10 energizes the relay and turns the pump motor on. When the pump motor is running, the hydraulic reservoir is filled with high pressure brake fluid and the brake pedal will be pushed up until antilock brake pedal sensor switch closes. when the antilock brake pedal sensor switch closes, the pump motor is turned off and the brake pedal will drop some with each abs control cycle until the antilock brake pedal sensor switch opens and the pump motor is turned on again.this minimizes pedal feedback during abs cycling. Pressure differential switch It is located in the modulator unit. This switch sends a signal to the control module whenever there is an undesirable difference in the hydraulic pressures with in the brake system. Relays Relays are electromagnetic devices used to control a high current circuit with a low current switching circuit. In abs relays are used to switch motors and solenoids. A low current signal from the control module energizes the relays that complete the electrical circuit for the motor or solenoid. Toothed ring It can be located on an axle shaft, differential gear or a wheels hub. This ring is used with conjunction with the wheel speed sensor. The ring has a number of teeth around its circumference. As the ring rotates and each tooth passes by the wheel speed sensor, an ac voltage signal is generated between the sensor and tooth. Wheel speed sensor It is mounted near the different toothed ring. As the rings teeth rotate past the sensor an ac voltage is generated. as the teeth move away from the sensor, the signal is broken until the next tooth comes close to the sensor.the end result is a pulsing signal that is sent to the control module. The control module translates the signal in to wheel speed. The sensor is normally a small coil of wire with a permanent magnet in its center. 10
11 6. TYPES OF ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEMS One of the classifications of abs is integral and non integral type. Integral type they combine the master cylinder, hydraulic booster and abs hydraulic circuit in to single hydraulic assembly. In non integral type they use a conventional vacuum-assist booster and master cylinder. In addition they can be classified according to the control they provide Four channel, four sensors ABS This is the best scheme. There is speed sensor on all four wheels and a separate valve for all the four wheels. With this set up the controller monitors each wheel individually to make sure it is achieving maximum braking force Three channel, three sensor ABS This scheme is commonly found on pick up trucks with four wheels ABS, has a speed sensor and a valve for each of the front wheels, with one valve and one sensor for both rear wheels. The speed sensor for the rear wheel is located in the rear axle. This system provides individual control of the wheels, so they can both achieve maximum braking force. The rear wheels however are monitored together, they both have to start to lock up before the abs will activate on the rear. With this system, it is possible that one of the rear wheels will lock during a stop, reducing brake effectiveness. 11
12 6.3. One channel, one sensor abs This scheme is commonly found on pick up trucks with rear wheel abs.it has one valve,which controls both rear wheels, and one speed sensor, located in the rear axle. This system operates the same as the rear end of the rear channel system. The rear wheels are monitored together and both have to start to lock up before the abs kicks in. in this system is also possible that one of the rear wheels will lock reducing brake effectiveness. 7. FOUR WHEEL SYSTEM The hydraulic circuit for this type of system is an independent four channel type. One for each wheel. The hydraulic control unit is a separate unit. Normal braking is accompanied by conventional vacuum power assist brake system. The system prevents wheel lock up during an emergency stop by modulating brake pressure. It allows the driver to maintain steering control and stop the vehicle in the shortest possible distance under most conditions. During ABS operation the driver will sense a pulsation in the brake pedal and clicking sound. 7.1 Operation The ABS control module calculates the slip rate of the wheels and control the brake fluid pressure to attain the target slip rate if the control module senses that the wheel is about to lock based on input sensor data, it pulses the normally open inlet solenoid valve closed for that circuit. This prevents any more fluid from entering that circuit. ABS control module then 12
13 looks at the sensor signal from the effected wheel again. If that wheel is still decelerating faster than other three wheels it opens the normally closed out let solenoid valve for that circuit. This dumps any pressure that is trapped between the closed inlet valve and the brake back to the master cylinder reservoir. Once the effected wheel returns to the same speed as the other wheel, the control module returns the valve to the normal condition allowing fluid flow to the effected brake. Based on the input from vehicle speed and the wheel speed sensor, the control module calculates the slip rate of each wheel, and transmits a control signal to the modulator unit solenoid valve when the slip rate is high. Wheel speed at each wheel is measured by variable reluctance sensors and sensor indicators. The sensors operate on magnetic induction principles. 13
14 As the teeth on brake sensor indicators rotate past the sensors, ac current is generated. The ac frequency changes in accordance with the wheel speed. The ABS control unit detects the wheel sensor signal frequency and there by detects wheel speed. 7.2 FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM OF FOUR CHANNEL ABS 14
15 8. ADVANCEMENTS IN ABS Some systems, which work with the ABS, are Automatic traction control and Automatic stability control, which are discussed below. 8.1 AUTOMATIC TRACTION CONTROL (ATC) Automatic traction control systems apply the brakes when a drive wheel attempts to spin and lose traction. The system works best when one drive wheel is working on a good traction surface and the other is not. The system also works well when the vehicle is accelerating on slippery road surfaces, especially when climbing hills. ATC is most helpful on four wheel or all wheel drive vehicles in which loss of traction at one wheel could hamper driver control. During road operation the ATC system uses an electronic control module to monitor the wheel speed sensors. If a wheel enters a loss of traction situation, the module applies braking force to the wheel in trouble. Loss of traction is identified by comparing the vehicle speed to the speed of the wheel. If there is a loss of traction the speed of the wheel will be greater than expected for the particular vehicle speed. ABS and ATC systems can be integral and uses the common valves. These systems are designed to reduce wheel slip and maintain traction at the drive wheels when the road is wet or snow covered. The control module monitors wheel speed. If during acceleration the module detects drive wheel slip and if brakes are not applied, the control module enters into the traction control mode. The inlet and outlet solenoid valves are pulsed and allow the brake to be quickly applied and released. 15
16 In some systems when a loss of traction is sensed, it not only cycles the brakes but signals the engine control module to retard ignition timing and partially close the throttle as well, which in turn reduces engine output. Many systems are equipped with a dash mounted warning light to alert the driver that the system is operating. There will also be a manual cut off switch so that the driver can turn off ATC operation. 16
17 8.2 AUTOMATIC STABILITY CONTROL Like ATC, the stability control systems are linked with the ABS. it can also be called Electronic Stability Programme (ESP). Stability control systems momentarily apply the brakes at any one wheel to correct over steer or under steer. The control unit receives signals from the typical sensors plus a yaw, lateral acceleration (G-force) and a steering angle sensor. The system uses the angle of the steering wheel and the speed of the four wheels to calculate the path chosen by the driver. It then looks at lateral G-forces and vehicle yaw to measure where the vehicle is going. (Yaw is defined as the natural tendency for a vehicle to rotate on its vertical center axis). So it is also called Yaw control. 17
18 Under steer is the condition in which the vehicle is slow to respond to steering changes. Over steer occurs when the rear wheels try to swing around causing the car to spin. When the system senses under steer in a turn the brake at the inside rear wheel is applied. During over steer the outside front brake is applied. Relaying on the input from the sensors and computer programming the system calculates if the vehicle is going exactly in the same direction in which it is being steered. In case of any difference between what the driver is asking and what the vehicle is doing, the system corrects the situation by applying one of the right or left brakes. 18
19 9. ADVANTAGES OF ABS It allows the driver to maintain directional stability and control over steering during braking Safe and effective Automatically changes the brake fluid pressure at each wheel to maintain optimum brake performance. ABS absorbs the unwanted turbulence shock waves and modulates the pulses thus permitting the wheel to continue turning under maximum braking pressure. Disadvantages It is very costly Maintenance cost of a car equipped with ABS is more. 19
20 10. CONCLUSION ABS has been so far developed to a system, which provides rapid, automatic braking in response to signs of incipient wheel locking by alternatively increasing and decreasing hydraulic pressure in the brake line Statistics show that approximately 40 % of automobile accidents are due to skidding. These problems commonly occur on vehicle with conventional brake system which can be avoided by adding devices called ABS If there is an ABS failure, the system will revert to normal brake operation. Normally the ABS warning light will turn on and let the driver know there is a fault 20
21 Bibliography Automotive technology Jack erjavec Automobile engineering kirpal Singh 21
22 ABSTRACT Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS) are designed to maintain driver control and stability of the car during emergency braking. Locked wheels will slow a car down but will not provide steering ability. ABS allows maximum braking to be applied while retaining the ability to 'steer out of trouble' The theory behind anti-lock brakes is simple. A skidding wheel (where the tire contact patch is sliding relative to the road) has less traction than a non-skidding wheel. By keeping the wheels from skidding while you slow down, anti-lock brakes benefit you in two ways: You'll stop faster, and you'll be able to steer while you stop. An ABS system monitors four wheel speed sensors to evaluate wheel slippage. Slip can be determined by calculating the ratio of wheel speed to vehicle speed, which is continuously calculated from the four individual wheel speeds. During a braking event, the function of the control system is to maintain maximum possible wheel grip on the road - without the wheel locking - by adjusting the hydraulic fluid pressure to each brake by way of electronically controlled solenoid valves. 22
23 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION CONCEPT OF ABS HYDRAULIC BRAKING SYSTEM PRINCIPLES OF ABS Pressure modulation 5. ABS COMPONENTS Hydraulic components 5.2 Electrical\ electronic components 6. TYPES OF ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEMS Four channel, four sensors ABS 6.2. Three channel, three sensor ABS 6.3. One channel, one sensor abs 7. FOUR WHEEL SYSTEM ADVANCEMENTS IN ABS automatic traction control 8.2 automatic stability control 9. ADVANTAGES OF ABS CONCLUSION BIBLIOGRAPHY
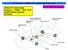
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES. Section 9. Fundamental ABS Systems. ABS System Diagram
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master
Module 11: Antilock Brakes Systems
 ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
ATASA 5 th. ABS & Traction Control Systems. Please Read The Summary
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
 Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
ENRESO.WORLD. Traction Control System. Created by Istas René - enreso.world. Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys
 ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
To study about various types of braking system.
 To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
Read on to find out more about each component of the Star Safety System and how it can be of benefit to you.
 All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems
 Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
Anti Locking Brakes. Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK. Regd no:
 Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM. Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
definition Retarders definition driving tip chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Using retarders
 chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Brake fade occurs when your brakes stop working properly because they're overheated. Your vehicle takes longer to stop, or may not stop at all if you haven't properly controlled
chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Brake fade occurs when your brakes stop working properly because they're overheated. Your vehicle takes longer to stop, or may not stop at all if you haven't properly controlled
HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice. Operating temperature - 40 C to 150 C - 40 C to 150 C
 489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages Brake Systems 49 Points. Automotive Service
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
System overview. Introduction. Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved.
 "VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
"VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking
 ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
8. Other system and brake theories
 8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
The Brake Assist System
 Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Document ID# Chevrolet/Geo Corvette
 Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
SUBJECT: Automatic Stability Control with Traction Control System (ASC+T)
 Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake
 SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch.............................................. 114 Automatic transmission.....................................
SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch.............................................. 114 Automatic transmission.....................................
COASTAL BEND COLLEGE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS (rev. Fall 2012)
 COASTAL BEND COLLEGE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS (rev. Fall 2012) AUMT 1310: Automotive Brake Systems SEMESTER HOURS: 3 TEXTBOOK Automotive Technology A systems Approach COURSE DESCRIPTION; Operation
COASTAL BEND COLLEGE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS (rev. Fall 2012) AUMT 1310: Automotive Brake Systems SEMESTER HOURS: 3 TEXTBOOK Automotive Technology A systems Approach COURSE DESCRIPTION; Operation
Safe Braking on the School Bus Advanced BrakingTechniques and Practices. Reference Guide and Test by Video Communications
 Safe Braking on the School Bus Advanced BrakingTechniques and Practices Reference Guide and Test by Video Communications Introduction Brakes are considered one of the most important items for school bus
Safe Braking on the School Bus Advanced BrakingTechniques and Practices Reference Guide and Test by Video Communications Introduction Brakes are considered one of the most important items for school bus
From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo
 newsroom History Mar 14, 2018 From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo One of the first cars to feature all-wheel drive was a Porsche, and it was a sports car: Ferdinand Porsche designed and built the
newsroom History Mar 14, 2018 From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo One of the first cars to feature all-wheel drive was a Porsche, and it was a sports car: Ferdinand Porsche designed and built the
ABS. Prof. R.G. Longoria Spring v. 1. ME 379M/397 Vehicle System Dynamics and Control
 ABS Prof. R.G. Longoria Spring 2002 v. 1 Anti-lock Braking Systems These systems monitor operating conditions and modify the applied braking torque by modulating the brake pressure. The systems try to
ABS Prof. R.G. Longoria Spring 2002 v. 1 Anti-lock Braking Systems These systems monitor operating conditions and modify the applied braking torque by modulating the brake pressure. The systems try to
Braking system. Basic requirement of a braking system
 Braking system The most vital factor in the running and control of the modern vehicle is the braking system. In order to bring the moving vehicle to rest or slow down, the energy of the vehicle processed
Braking system The most vital factor in the running and control of the modern vehicle is the braking system. In order to bring the moving vehicle to rest or slow down, the energy of the vehicle processed
ABS, 4-ETS and EBP BRAKES ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 4-WHEEL ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (4-ETS) ELECTRONIC BRAKE PROPORTIONING (EBP)
 1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes
 A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes Study Guide TMT-040701 Study Guide International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes TMT-040701 2007 International
A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes Study Guide TMT-040701 Study Guide International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes TMT-040701 2007 International
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
POWER TRAIN 2-1 CONTENTS AYC SYSTEM... 9 CLUTCH... 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS... 4 FRONT AXLE... 5 REAR AXLE... 6
 2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (5AT)
 (5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
(5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES
 BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
Brake System Operation
 Brake System Brake System Operation Donald Jones Brookhaven College Master cylinder Brake lines Hydraulic valves Disc brakes Drum brakes Power assist unit Parking brake Antilock system Brake System Functions
Brake System Brake System Operation Donald Jones Brookhaven College Master cylinder Brake lines Hydraulic valves Disc brakes Drum brakes Power assist unit Parking brake Antilock system Brake System Functions
ESCONDIDO FIRE DEPT TRAINING MANUAL Section DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 Pumps and Accessory Equipment Revised
 DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
2006 Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC. Chassis and Drivetrain 42
 Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
 TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
DESCRIPTION. Chrysler NCV3 Service Info Section 08 > Electronic Modules > MODULE, Transmission Control Information
 DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
SD Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly DESCRIPTION M-21 MODULATOR M-22 MODULATOR
 SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
ABS Operator s Manual
 ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
Brake Systems. Introduction
 Brake Systems Figure 1. A Typical Brake System Introduction The brake system (Figure 1) is designed to slow and halt the motion of a vehicle. To do that, various components within a hydraulic brake system
Brake Systems Figure 1. A Typical Brake System Introduction The brake system (Figure 1) is designed to slow and halt the motion of a vehicle. To do that, various components within a hydraulic brake system
Appendix A: Motion Control Theory
 Appendix A: Motion Control Theory Objectives The objectives for this appendix are as follows: Learn about valve step response. Show examples and terminology related to valve and system damping. Gain an
Appendix A: Motion Control Theory Objectives The objectives for this appendix are as follows: Learn about valve step response. Show examples and terminology related to valve and system damping. Gain an
Road Safety Factsheet
 Road Safety Factsheet Electronic Braking Systems Factsheet August 2017 Brake Assist Brake Assist (BA) is a technology that ensures that the maximum pressure is applied by the brakes to stop a vehicle in
Road Safety Factsheet Electronic Braking Systems Factsheet August 2017 Brake Assist Brake Assist (BA) is a technology that ensures that the maximum pressure is applied by the brakes to stop a vehicle in
Automatic drain valves
 driving commercial vehicles If you notice more than a few drops of water when you drain the supply reservoir, the air dryer or compressor may need servicing. fast fact Even if the air brake system includes
driving commercial vehicles If you notice more than a few drops of water when you drain the supply reservoir, the air dryer or compressor may need servicing. fast fact Even if the air brake system includes
motion table of contents: squarebot assembly 3.2 concepts to understand 3.3 subsystems interfaces 3.21 motion subsystem inventory 3.
 The subsystem of the robot is responsible for exactly that,. It includes both the motors that generate, and the wheels and gears that transfer and transform that into the desired forms. With the structural
The subsystem of the robot is responsible for exactly that,. It includes both the motors that generate, and the wheels and gears that transfer and transform that into the desired forms. With the structural
1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION
 4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. BD20B (with Differential Lock Actuator)
 6 4RUNNER NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES DIFFERENTIAL (OFF-ROAD PACKAGE MODELS) 1. General The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. Rear Differential Lock Actuator 233CH46
6 4RUNNER NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES DIFFERENTIAL (OFF-ROAD PACKAGE MODELS) 1. General The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. Rear Differential Lock Actuator 233CH46
Torsen Differentials - How They Work and What STaSIS Does to Improve Them For the Audi Quattro
 Torsen Differentials - How They Work and What STaSIS Does to Improve Them For the Audi Quattro One of the best bang-for-your buck products that STaSIS has developed is the center differential torque bias
Torsen Differentials - How They Work and What STaSIS Does to Improve Them For the Audi Quattro One of the best bang-for-your buck products that STaSIS has developed is the center differential torque bias
Dealing with customer concerns related to electronic throttle bodies By: Bernie Thompson
 Dealing with customer concerns related to electronic throttle bodies By: Bernie Thompson In order to regulate the power produced from the gasoline internal combustion engine (ICE), a restriction is used
Dealing with customer concerns related to electronic throttle bodies By: Bernie Thompson In order to regulate the power produced from the gasoline internal combustion engine (ICE), a restriction is used
2012 MKT Workshop Manual. REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 06/13/2011
 SECTION 205-05: Rear Drive Halfshafts REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 06/13/2011 Halfshaft Special Tool(s) Axle Seal Protector 205-816 Front Hub Remover 205-D070 (D93P-1175-B) or equivalent
SECTION 205-05: Rear Drive Halfshafts REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 06/13/2011 Halfshaft Special Tool(s) Axle Seal Protector 205-816 Front Hub Remover 205-D070 (D93P-1175-B) or equivalent
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS
 Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-6 Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch with steering lock Automatic transmission Manual transmission Four-wheel drive system
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-6 Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch with steering lock Automatic transmission Manual transmission Four-wheel drive system
Adaptive Cruise Control System Overview
 5th Meeting of the U.S. Software System Safety Working Group April 12th-14th 2005 @ Anaheim, California USA 1 Introduction Adaptive Cruise System Overview Adaptive Cruise () is an automotive feature that
5th Meeting of the U.S. Software System Safety Working Group April 12th-14th 2005 @ Anaheim, California USA 1 Introduction Adaptive Cruise System Overview Adaptive Cruise () is an automotive feature that
TECHNICAL PAPER 1002 FT. WORTH, TEXAS REPORT X ORDER
 I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
Hydro-Max Hydraulic Brake Booster and Master Cylinder. Technical Manual
 Hydro-Max Hydraulic Brake Booster and Master Cylinder Technical Manual * 5+0 Important Service Notes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information presented in
Hydro-Max Hydraulic Brake Booster and Master Cylinder Technical Manual * 5+0 Important Service Notes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information presented in
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Antilock Brakes, Vehicle Stability Control, and Power Assist
 C H A P T E R 1 6 Antilock Brakes, Vehicle Stability Control, and Power Assist Chapter Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter you should be able to: Explain the purpose and operation of antilock
C H A P T E R 1 6 Antilock Brakes, Vehicle Stability Control, and Power Assist Chapter Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter you should be able to: Explain the purpose and operation of antilock
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor
 Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor Mohammad A Obeidat Abstract In this paper an electrical braking system is proposed. The force on
Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor Mohammad A Obeidat Abstract In this paper an electrical braking system is proposed. The force on
Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes. Course 105 PREVIEW ONLY PARTICIPANT GUIDE
 Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes Course 105 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Table of Contents How to Use the Participant Guide... ii MODULE 1...1 General Principles and Terminology...1 1-1 Safety Review...2
Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes Course 105 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Table of Contents How to Use the Participant Guide... ii MODULE 1...1 General Principles and Terminology...1 1-1 Safety Review...2
Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period
 Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period Basic Brake System Matching 1. Metal tubing and rubber hose that transmit pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. 2. Mechanical system for applying
Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period Basic Brake System Matching 1. Metal tubing and rubber hose that transmit pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. 2. Mechanical system for applying
AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES
 Section 5 AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES AIR BRAKES/Section 5 SECTION 5: AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION COVERS Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting
Section 5 AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES AIR BRAKES/Section 5 SECTION 5: AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION COVERS Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting
SD Bendix Gen 4 and Gen 5 ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses GEN 4 AND GEN 5 ABS INTRODUCTION
 SD-- Bendix Gen and Gen ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses Cab-Mounted Models Frame-Mounted Model FIGURE - Bendix ABS Controller Assemblies GEN AND GEN ABS INTRODUCTION This manual describes both the
SD-- Bendix Gen and Gen ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses Cab-Mounted Models Frame-Mounted Model FIGURE - Bendix ABS Controller Assemblies GEN AND GEN ABS INTRODUCTION This manual describes both the
Emergency driving and its procedures
 Emergency driving and its procedures Prepared By (Name of the student) Enrol Number: ( ) Date: ( ) (Name of the school) How to Avoid Vehicle Malfunction Although some vehicle malfunctions may not be avoidable,
Emergency driving and its procedures Prepared By (Name of the student) Enrol Number: ( ) Date: ( ) (Name of the school) How to Avoid Vehicle Malfunction Although some vehicle malfunctions may not be avoidable,
three different ways, so it is important to be aware of how flow is to be specified
 Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Step Motor. Mechatronics Device Report Yisheng Zhang 04/02/03. What Is A Step Motor?
 Step Motor What is a Step Motor? How Do They Work? Basic Types: Variable Reluctance, Permanent Magnet, Hybrid Where Are They Used? How Are They Controlled? How To Select A Step Motor and Driver Types of
Step Motor What is a Step Motor? How Do They Work? Basic Types: Variable Reluctance, Permanent Magnet, Hybrid Where Are They Used? How Are They Controlled? How To Select A Step Motor and Driver Types of
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
Electromagnetic Braking
 I J C T A, 9(37) 2016, pp. 563-567 International Science Press Electromagnetic Braking An Innovative Approach Abhay Singh Rajput * and Utkarsh Sharma ** Abstract: This paper focuses on use of electromagnetic
I J C T A, 9(37) 2016, pp. 563-567 International Science Press Electromagnetic Braking An Innovative Approach Abhay Singh Rajput * and Utkarsh Sharma ** Abstract: This paper focuses on use of electromagnetic
1998 E-Series Workshop Manual
 SECTION 206-09A: Anti-Lock Control Rear DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 02/08/2000 Anti-Lock Control Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42, Speed Control for schematic and connector information.
SECTION 206-09A: Anti-Lock Control Rear DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 02/08/2000 Anti-Lock Control Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42, Speed Control for schematic and connector information.
Model PRO 9649 Owner s Manual
 Model PRO 9649 Owner s Manual 3 Button Remote Security System with Starter Disable, & Keyless Entry IMPORTANT! In order to provide the highest possible level of security to your vehicle, this system is
Model PRO 9649 Owner s Manual 3 Button Remote Security System with Starter Disable, & Keyless Entry IMPORTANT! In order to provide the highest possible level of security to your vehicle, this system is
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function
 GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS BIG ROTOR / CALIPER RELOCATION REAR KIT SUM-BK1423 1999-2009 GM 1/2 Ton Trucks & SUVs Thank you for choosing SUMMIT RACING for your braking needs. Pleases take the time to read
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS BIG ROTOR / CALIPER RELOCATION REAR KIT SUM-BK1423 1999-2009 GM 1/2 Ton Trucks & SUVs Thank you for choosing SUMMIT RACING for your braking needs. Pleases take the time to read
6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (040) 09/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
SD Bendix EC-14 AntiLock Controller Assembly DESCRIPTION GENERAL MOUNTING PHYSICAL
 Bendix EC-14 AntiLock Controller Assembly SD-13-4784 30 PIN WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR MOUNTING HOLES (4) DIAGSTICS WINDOW DESCRIPTION GENERAL Bendix trailer antilock systems utilizing the EC-14 electronic
Bendix EC-14 AntiLock Controller Assembly SD-13-4784 30 PIN WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR MOUNTING HOLES (4) DIAGSTICS WINDOW DESCRIPTION GENERAL Bendix trailer antilock systems utilizing the EC-14 electronic
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
BRAKE ASSISTED DIFFERENTIAL LOCKING SYSTEM
 BRAKE ASSISTED DIFFERENTIAL LOCKING SYSTEM GMK Sandeep 1, P. Gopi 2, V Chandra Sekhara Reddy 3 1,2,3 PG Scholar,Vignans University, Vadlamudi, Guntur, (India) ABSTRACT In this paper it takes 8,460 bolts
BRAKE ASSISTED DIFFERENTIAL LOCKING SYSTEM GMK Sandeep 1, P. Gopi 2, V Chandra Sekhara Reddy 3 1,2,3 PG Scholar,Vignans University, Vadlamudi, Guntur, (India) ABSTRACT In this paper it takes 8,460 bolts
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)
 23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Diamante 1993 BRAKES Mitsubishi - Anti-Lock Brake System Diamante DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) is designed to prevent wheel lock-up during heavy braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Diamante 1993 BRAKES Mitsubishi - Anti-Lock Brake System Diamante DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) is designed to prevent wheel lock-up during heavy braking.
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
 DN SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO....2 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES...2 BRAKE LAMP
DN SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO....2 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES...2 BRAKE LAMP
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM
 200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL USER MANUAL
 DRAG-SPORTSMAN N2O For ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL USER MANUAL TELEPHONE 828.645.1505 FAX 828.645.1525 WWW.MORETRACTION.COM US PATENT 6,577,944 Disclaimer...2 Introduction... 3 How Does It Work. 4 Installation...
DRAG-SPORTSMAN N2O For ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL USER MANUAL TELEPHONE 828.645.1505 FAX 828.645.1525 WWW.MORETRACTION.COM US PATENT 6,577,944 Disclaimer...2 Introduction... 3 How Does It Work. 4 Installation...
16 Introduction to DSC
 Lateral Acceleration Sensor (Bosch 5.3) This new sensor is a major contributor of the expanded capabilities of DSC III. It is located under the drivers seat but mounted on the vertical surface of the inner
Lateral Acceleration Sensor (Bosch 5.3) This new sensor is a major contributor of the expanded capabilities of DSC III. It is located under the drivers seat but mounted on the vertical surface of the inner
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS BIG ROTOR / CALIPER RELOCATION FRONT KITS SUM-BK1422, BK1423, BK1424 1999-2006 GM 1/2 Ton Trucks & SUVs Thank you for choosing SUMMIT RACING for your braking needs. Pleases take
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS BIG ROTOR / CALIPER RELOCATION FRONT KITS SUM-BK1422, BK1423, BK1424 1999-2006 GM 1/2 Ton Trucks & SUVs Thank you for choosing SUMMIT RACING for your braking needs. Pleases take
2006 MINI Cooper S GENINFO Starting - Overview - MINI
 MINI STARTING SYSTEM * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * 2002-07 GENINFO Starting - Overview - MINI For information on starter removal and installation, see the following articles. For Cooper, see STARTER WITH
MINI STARTING SYSTEM * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * 2002-07 GENINFO Starting - Overview - MINI For information on starter removal and installation, see the following articles. For Cooper, see STARTER WITH
ELECTROMAGNETIC BRAKING SYSTEM
 ELECTROMAGNETIC BRAKING SYSTEM 1 Krunal Prajapati, 2Rahul Vibhandik, 3Devendrasinh Baria, 4Yash Patel Student, Automobile department, Laxmi institute of Technology, Sarigam-Valsad. Gujarat Corresponding
ELECTROMAGNETIC BRAKING SYSTEM 1 Krunal Prajapati, 2Rahul Vibhandik, 3Devendrasinh Baria, 4Yash Patel Student, Automobile department, Laxmi institute of Technology, Sarigam-Valsad. Gujarat Corresponding
Power Distribution. systems work. look at how these. Series sedan. Let s. introduced a 4WD 3. few years ago BMW. decade now, and a.
 feature Power Distribution Getting all that awesome BMW power to the ground is no easy task. The 4WD BMW X5 has been around for a decade now, and a few years ago BMW introduced a 4WD 3 Series sedan. Let
feature Power Distribution Getting all that awesome BMW power to the ground is no easy task. The 4WD BMW X5 has been around for a decade now, and a few years ago BMW introduced a 4WD 3 Series sedan. Let
Mercedes-Benz Service. Brake System Modifications and New Features Model 374, 375, , , ,
 Mercedes-Benz Service Brake System Modifications and New Features Model 374, 375, 930-934, 940-944, 950-954, 970-976 Mercedes-Benz Service Brake System Modifications and New Features Model 374, 375, 930-934,
Mercedes-Benz Service Brake System Modifications and New Features Model 374, 375, 930-934, 940-944, 950-954, 970-976 Mercedes-Benz Service Brake System Modifications and New Features Model 374, 375, 930-934,
MASTER CYLINDER. Section 2. Lesson Objectives
 MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
MANTECH ELECTRONICS. Stepper Motors. Basics on Stepper Motors I. STEPPER MOTOR SYSTEMS OVERVIEW 2. STEPPING MOTORS
 MANTECH ELECTRONICS Stepper Motors Basics on Stepper Motors I. STEPPER MOTOR SYSTEMS OVERVIEW 2. STEPPING MOTORS TYPES OF STEPPING MOTORS 1. VARIABLE RELUCTANCE 2. PERMANENT MAGNET 3. HYBRID MOTOR WINDINGS
MANTECH ELECTRONICS Stepper Motors Basics on Stepper Motors I. STEPPER MOTOR SYSTEMS OVERVIEW 2. STEPPING MOTORS TYPES OF STEPPING MOTORS 1. VARIABLE RELUCTANCE 2. PERMANENT MAGNET 3. HYBRID MOTOR WINDINGS
The parts of these systems are discussed in greater detail below.
 Section 5 Air Brakes This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 Air Brakes This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 AIR BRAKES. This Section Covers. Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes
 Section 5 AIR BRAKES This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 AIR BRAKES This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
2013 Scion FR-S Quick Reference Guide
 2013 Scion FR-S Quick Reference Guide 2013 Scion FR-S This Quick Reference Guide is a summary of basic vehicle operations. It contains brief descriptions of fundamental operations so you can locate and
2013 Scion FR-S Quick Reference Guide 2013 Scion FR-S This Quick Reference Guide is a summary of basic vehicle operations. It contains brief descriptions of fundamental operations so you can locate and
Chapter 13: Application of Proportional Flow Control
 Chapter 13: Application of Proportional Flow Control Objectives The objectives for this chapter are as follows: Review the benefits of compensation. Learn about the cost to add compensation to a hydraulic
Chapter 13: Application of Proportional Flow Control Objectives The objectives for this chapter are as follows: Review the benefits of compensation. Learn about the cost to add compensation to a hydraulic
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
Volkswagen New Beetle Brake System ABS, ABS/EDL 45 Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) (Page GR-45)
 45 Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) (Page GR-45) Anti-lock brake system (ABS) and anti-lock brake system with electronic differential lock (ABS/EDL) ITT Mark 20 IE Differences between ABS ITT Mark 20 IE and
45 Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) (Page GR-45) Anti-lock brake system (ABS) and anti-lock brake system with electronic differential lock (ABS/EDL) ITT Mark 20 IE Differences between ABS ITT Mark 20 IE and
TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION CIRCUIT ACTYON
 311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
AN ANALYSIS OF HYDRAULIC BRAKING SYSTEM RELIABILITY. Stanisław Walusiak, Mieczysław Dziubiński, Wiktor Pietrzyk
 TEKA Kom. Mot. Energ. oln., 2005, 5, 217 225 AN ANALYSIS OF HYDAULIC BAKING SYSTEM ELIABILITY Lublin University of Technology Summary. For the purpose of improving driving safety, vehicles are equipped
TEKA Kom. Mot. Energ. oln., 2005, 5, 217 225 AN ANALYSIS OF HYDAULIC BAKING SYSTEM ELIABILITY Lublin University of Technology Summary. For the purpose of improving driving safety, vehicles are equipped
DRIVING TIPS AND SAFE DRIVING
 High Speed Driving 8-1 Driving on Hills 8-1 Driving on Slippery Roads 8-2 Driving on Wet Roads 8-2 Do's and Don'ts for Safe Driving 8-3 73 8-1 70F-06-001 Wear Your Seat Belts at All Times. The driver and
High Speed Driving 8-1 Driving on Hills 8-1 Driving on Slippery Roads 8-2 Driving on Wet Roads 8-2 Do's and Don'ts for Safe Driving 8-3 73 8-1 70F-06-001 Wear Your Seat Belts at All Times. The driver and
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
