ANTI-LOCK BRAKES. Section 9. Fundamental ABS Systems. ABS System Diagram
|
|
|
- Joanna Bennett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master cylinder and the wheel cylinders to control brake system hydraulic pressure. Antilock Brake Systems address two conditions related to brake application; wheel lockup and vehicle directional control. The brakes slow the rotation of the wheels, but it is actually the friction between the tire and road surface that stops the vehicle. Without ABS when brakes are applied with enough force to lock the wheels, the vehicle slides uncontrollably because there is no traction between the tires and the road surface. While the wheels are skidding, steering control is lost as well. An antilock brake system provides a high level of safety to the driver by preventing the wheels from locking, which maintains directional stability. A professional driver may be capable of maintaining control during braking by pumping the brake pedal which allows a locked wheel to turn momentarily. Whereas a professional driver may be capable of modulating the brakes approximately once per second, ABS is capable of modulating the brake pressure at a given wheel up to fifteen times per second. An ABS system does something else that no driver can do, it controls each front brake separately and the rear brakes as a pair whenever one of the wheels starts to lock. ABS helps stop a car in the shortest possible distance without wheel lockup while maintaining directional control on most types of road surface or conditions. If a Toyota ABS system malfunctions, normal braking will not be affected. ABS System Diagram ABS is combined with the conventional braking system and located between the master cylinder and the wheel cylinders. Legend: Electrical Hydraulic Toyota Brake Systems - Course
2 Tire Traction and ABS The chart below shows the slip tolerance band (shaded area) in which the most efficient braking occurs. From a slip ratio of zero (0), at which the wheel speed and the vehicle speed are equal, to a slip ratio of 10, braking is mild to moderate and good traction between the tire and the road surface is maintained. Between slip ratios of 10 to 30 the most efficient braking occurs. This is where the tires are at a point where they may begin to lose traction with the road surface. This is also the band in which ABS operation occurs. Beyond a slip ratio of 30%, braking efficiency is reduced, stopping distance is increased and directional control is lost. The amount of braking force on the left vertical line will vary based on the driver s pressure on the brake pedal and on the road surface; less braking force may be applied on wet asphalt than on dry concrete before lockup occurs, therefore the stopping distance is increased. Braking Force Chart Maximum braking force occurs between 10 to 30% slip ratio. Wheels spinning freely is 0% slip ratio. 100% slip ratio reflects a wheel completely locked up. Basic Operation Four Wheel ABS Systems use a speed sensor at each front wheel and either a single speed sensor for both rear wheels or individual speed sensors at each rear wheel. The speed sensors are monitored by a dedicated ECU. The system controls the front brakes individually and rear brakes as a pair. In a panic braking situation, the wheel speed sensors detect any sudden changes in wheel speed. The ABS ECU calculates the rotational speed of the wheels and the change in their speed, then calculates the vehicle speed. The ECU then judges the slip ratio of each wheel and instructs the actuator to provide the optimum braking pressure to each wheel. For example, the pressure to the brakes will be less on slippery pavement to reduce brake lockup. As a result, braking distance may increase but directional control will be maintained. It is also important to understand that ABS is not active during all stops. 120 TOYOTA Technical Training
3 Anti-lock Brakes The hydraulic brake actuator operates on signals from the ABS ECU to hold, reduce or increase the brake fluid pressure as necessary, to maintain the optimum slip ratio of 10 to 30% and avoid wheel lockup. Typical ABS Control System The ECU monitors the four wheel sensors, processes the data and controls the actuator solenoids and pump motor through the ABS Relay. INPUT PROCESS OUTPUT Speed Sensors Actuator Solenoids Actuator Pump Motor Battery ABS ECU Data Link Connector Stop Light Switch ABS Warning Light Toyota Brake Systems - Course
4 Types of Toyota ABS 2-Position Solenoid There are four types of ABS systems used in current Toyota models distinguished by the actuator. The four actuator types include: 2 position solenoid valves. 3 position solenoid valves with mechanical valve (Bosch). 3 position solenoid valves (Nippondenso). 2 position solenoid controlling power steering hydraulic pressure which controls brake hydraulic pressure. 2 position solenoid actuators come in configurations of six or eight solenoids. The eight solenoid configuration uses two solenoids per brake assembly. The six solenoid configuration uses two solenoids to control the rear brake assemblies while the front brake assemblies are controlled independently by two solenoids each. 2-Position Solenoid Types Controls pressure to four brake assemblies in three stages: pressure holding, increase and reduction. 122 TOYOTA Technical Training
5 Anti-lock Brakes 3-Position Solenoid and Mechanical Valve This actuator uses three, 3 position solenoid valves. Two solenoids control the front wheels independently while the third solenoid controls the right rear and the mechanical valve translates controls to the left rear. 3-Position Solenoid With Mechanical Valve The third solenoid controls the right rear and the mechanical valve translates controls to the left rear. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
6 3-Position Solenoids The 3 position solenoid valve actuator comes in three solenoid or four solenoid configurations. The four solenoid system controls hydraulic pressure to all four wheels. In the 3 solenoid system, each front wheel is controlled independently while the rear wheels are controlled in tandem. 3-Position Solenoids Controls pressure to four brake assemblies in three stages: pressure holding, pressure increase and pressure reduction. Power Steering Control The last actuator type uses power steering pressure to regulate brake pressure using a single 2 position solenoid, a cut valve and bypass valve. Brake system pressure is controlled for the rear brakes only. Power Steering Hydraulic Pressure Controls Brake Hydraulic Pressure A single 2-position solenoid regulates power steering pressure which controls brake hydraulic pressure to the two rear wheels only. 124 TOYOTA Technical Training
7 Anti-lock Brakes System Components Each ABS type shares common components which provide information to the ECU. This section will examine each of these components and then describe each of the actuator types and their operation. The components identified below are typical of most Toyota ABS systems. Speed Sensors monitor wheel speed. G Sensor monitors rate of deceleration or lateral acceleration. ABS Actuators control brake system pressure. Control Relay controls the Actuator Pump Motor and Solenoids. ABS ECU monitors sensor inputs and controls the Actuator. ABS Warning Lamp alerts the driver to system conditions. The location of components may vary by model and year, therefore, for accurate location of components, consult your EWD or Repair Manual. Typical Component Layout Component location is typical for most models: speed sensors at each wheel, actuator in engine compartment. The ECU however may require an EWD or Repair Manual to pinpoint its location. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
8 Wheel Speed Sensor A wheel speed sensor is mounted at each wheel and sends a wheel rotation signal to the ABS ECU. The front and rear wheel speed sensors consist of a permanent magnet attached to a soft iron core (yoke) and a wire wound coil. The front wheel speed sensors are mounted to the steering knuckle, and the rear speed sensors are mounted to the rear axle carrier. Serrated rotors are mounted to the drive axle shaft or brake rotor, and rotate as a unit. Wheel Speed Sensors Speed sensors monitor individual wheel speed. Early Supras including the 1993 model year and Cressidas equipped with ABS, used a single rear speed sensor mounted on the transmission extension housing to monitor rear wheel speed. 126 TOYOTA Technical Training
9 Anti-lock Brakes Operation Speed sensor operation is similar to the magnetic pick up in a distributor. When the teeth of the Sensor Rotor pass the iron core, the magnetic lines of force cut through the coil windings causing a voltage to be induced into the coil. As the tooth approaches the iron core, the magnetic field contracts causing a positive voltage to be induced in the coil. When the tooth is centered on the iron core the magnetic field does not move and zero volts are induced in the coil. As the tooth moves away from the iron core the magnetic field expands, resulting in a negative voltage. As the rotation of the sensor rotor increases, the voltage and the frequency of this signal increase, indicating to the ECU a higher wheel speed. Speed Sensor Operation Voltage is induced into the coil when the magnetic field changes each time the sensor rotor teeth pass the iron core. Deceleration Sensor The deceleration sensor is used on some systems to provide input to the ABS ECU about the vehicle s rate of deceleration to improve braking performance. In a typical ABS system, the ECU compares individual speed sensors to determine the speed of the vehicle and rate of wheel deceleration. The deceleration sensor is used on all full time 4WD vehicles equipped with ABS to determine deceleration, as the front and rear axles are connected through the transfer case and present unique braking characteristics. Models equipped with only rear wheel ABS have a single speed sensor and no means of determining the actual vehicle speed or rate of deceleration. The deceleration sensor is composed of two pairs of LEDs (light emitting diodes) and phototransistors, a slit plate, and a signal conversion circuit. The deceleration sensor senses the vehicle s rate of deceleration and sends signals to the ABS ECU. The ECU compares the rate of deceleration and vehicle speed to determine the precise road surface conditions and takes appropriate control measures. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
10 Deceleration Sensor Components The slit plate swings between the LED s and Phototransistors. Operation Both LED s are located on one side of the slit plate and both photo transistors are located on the opposite side. The LED s are ON when the ignition switch is in the ON position. When the vehicle s rate of deceleration changes, the slit plate swings in the vehicle s rear to front direction. The slits in the slit plate act to expose the light from the LEDs to the phototransistors. This movement of the slit plate switches the phototransistors ON and OFF. Deceleration Sensor Operation As the slit plate swings forward the slits expose the phototransistor to the LED. Lateral Acceleration Sensor The lateral acceleration sensor has similar construction to the deceleration sensor described above. Rather than having the slit plate swing rear to front, the sensor is mounted in such a way that the slit plate swings from side to side. This sensor is found only on the /2 and later model Supra to detect lateral forces while braking. 128 TOYOTA Technical Training
11 Anti-lock Brakes Deceleration Rate The combinations formed by these phototransistors switching ON and OFF distinguish the rate of deceleration into four levels, which are sent as signals to the ABS ECU. The chart below indicates the rate of deceleration based on input from the two phototransistors. For example: when the No. 1 and No. 2 photo transistors are both blocked and turned OFF, the deceleration rate is medium. Deceleration Rate Level Deceleration Rate Level Rate of deceleration No. 1 Photo Transistor No. 2 Photo Transistor Low-1 Low-2 Medium High ON OFF OFF ON ON ON OFF OFF Position of Slit Plate No. 1 Photo Transistor (ON) No. 1 Photo Transistor (ON) (OFF) (ON) (OFF) (OFF) (ON) (OFF) Semiconductor Deceleration Sensor A new style deceleration sensor was introduced in the WD RAV4 only. The sensor consisted of two semiconductor sensors. They are mounted at 90 to one another and installed so that each has an angle of 45 to the centerline of the vehicle. Each semiconductor sensor is provided with a mass which exerts pressure based on the deceleration force applied to the vehicle. The sensor converts the force into electronic signals, and outputs the signals to the ABS ECU. Semiconductor Deceleration Sensor Toyota Brake Systems - Course
12 Actuator 2-Position Solenoid Type The actuator controls hydraulic brake pressure to each disc brake caliper or wheel cylinder based on input from the system sensors, thereby controlling wheel speed. These solenoids provide three operating modes during ABS operation: Pressure Holding. Pressure Reduction. Pressure Increase. The two position solenoid actuator was first used on the 1993 Corolla and subsequently on all Toyota models by 1997 except Land Cruiser. Consult the ABS Comparison Chart on page 225 of this publication for the specific model application. The actuator consists of six or eight 2 position solenoid valves, a pump and reservoir. Each hydraulic circuit is controlled by a single set of solenoids: pressure holding solenoid. pressure reduction solenoid. Aside from the 2 position solenoid valves, the basic construction and operation of this system is the same as the 3 position solenoid system: four speed sensors provide input to the ECU which controls the operation of the solenoids and prevent wheel lock up. the two front wheels are controlled independently and the two rear wheels are controlled simultaneously for three channel control. Supra has four channel control where the two rear wheels are controlled independently just like the front wheels. 2-Position Solenoid Hydraulic Circuit The actuator consists of six or eight 2-position solenoids. Two solenoids are used to control each wheel hydraulic circuit. 130 TOYOTA Technical Training
13 Anti-lock Brakes Pressure Holding Valve The pressure holding valve controls (opens and closes) the circuit between the brake master cylinder and the wheel cylinder. The valve is spring loaded to the open position (normally open). When current flows in the coil the valve closes. A spring loaded check valve provides an additional release passage when pressure from the master cylinder drops. Pressure Holding Valve Controls the circuit between the brake master cylinder and the wheel cylinder. Pressure Reduction Valve The pressure reduction valve controls (opens and closes) the circuit between the wheel cylinder and the actuator reservoir. The valve is spring loaded in the closed position (normally closed). When current flows through the coil, the valve compresses the spring and opens the valve. Pressure Reduction Valve Controls the circuit between the wheel cylinder and the actuator reservoir. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
14 Operation During Normal Braking (ABS Not Activated) During normal braking the solenoids are not energized so the pressure holding valve remains open and the pressure reduction valve remains closed. When the brake pedal is depressed, the master cylinder fluid passes through the pressure holding valve to the wheel cylinder. The pressure reduction valve prevents fluid pressure from going to the reservoir. As a result normal braking occurs. Normal Braking Mode During normal braking the solenoids are not energized so the pressure holding valve remains open and the pressure reduction valve remains closed. 132 TOYOTA Technical Training
15 Anti-lock Brakes Pressure Holding Mode When any wheel begins to lock, the ABS ECU initially goes to hold mode to prevent any additional increase in pressure. The ECU turns OFF the Pressure Reduction Valve and turns the Pressure Holding Valve ON. The pressure reduction valve closes, preventing hydraulic fluid from going to the reservoir. The pressure holding valve remains closed so no additional fluid pressure can reach the wheel cylinder. Pressure Holding Mode The pressure reduction valve closes, preventing hydraulic fluid from going to the reservoir. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
16 Pressure Reduction Mode After the initial hold mode operation, the ABS ECU energizes both the holding valve and the reduction valve. The pressure holding valve closes and blocks pressure from the master cylinder. The open reduction valve allows hydraulic pressure from the wheel cylinder circuit into the reservoir, reducing brake pressure. The pump is also energized to direct hydraulic fluid back to the master cylinder. This causes brake pedal feedback and alerts the driver to ABS operation. Pressure Reduction Mode When the slip ratio of any wheel exceeds 30%, the ABS ECU energizes both the holding valve and the reduction valve. 134 TOYOTA Technical Training
17 Anti-lock Brakes Pressure Increase Mode As pressure inside the wheel cylinder is reduced and the speed sensor sends a signal indicating that the speed is above the target level, the ECU turns OFF both the Pressure Reduction Valve and the Pressure Holding Valve. The pressure reduction valve closes, preventing hydraulic fluid from going to the reservoir. The pressure holding valve opens so additional pressure enters the wheel cylinder if the driver maintains pedal pressure. The operation is the same as Normal Mode except the pump is on. Pressure Increase Mode The ECU turns OFF both the Pressure Reduction Valve and the Pressure Holding Valve. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
18 ABS ECU The ABS ECU senses the rotational speed of the wheels as well as the vehicle speed based on signals from the wheel speed sensors. During braking, the deceleration rate will vary depending on pedal pressure, the vehicle speed during braking, and the road surface conditions. For example, the deceleration rate is much greater on dry asphalt, compared to a wet or icy surface. The ECU judges the slip condition between the wheels and the road surface by monitoring the change in the wheel s rotational speed during braking. The ECU controls the ABS actuator to deliver the optimum hydraulic pressure to the brake cylinder to precisely control the speed of the wheels, maintaining maximum brake force with a 10 to 30% slip ratio. ABS Wiring Diagram The ECU controls the ABS actuator to deliver the optimum hydraulic pressure to the disc brake cylinder to precisely control the speed of the wheels. 136 TOYOTA Technical Training
19 Anti-lock Brakes Solenoid Relay Control The Solenoid Relay supplies power to the solenoids. The ECU turns the Solenoid Relay ON when the following conditions are met: Ignition switch ON. The Initial Check Function is completed properly. The ECU turns the solenoid relay OFF if any of the above conditions are not met. ABS Control Relay The motor relay switches voltage to the pump motor. The solenoid relay switches voltage to the actuator solenoids. Pump Motor Relay Control The Pump Motor Relay supplies power to the ABS pump motor located in the Actuator. The ECU turns the relay ON when the following conditions are met: During ABS operation or during the Initial Check. When the Solenoid Relay is ON. The ECU turns the pump motor relay OFF when any of the above conditions are not met. Toyota Brake Systems - Course
20 Wheel Speed Control The ECU continuously receives wheel speed signals from the speed sensors and deceleration sensor. By calculating the speed and deceleration of each wheel, the ECU estimates the vehicle speed. When the brake pedal is depressed, the hydraulic pressure in each disc brake cylinder begins to increase and the wheel speed begins to decrease. If any of the wheels are near a lock up condition the ECU goes into pressure hold mode to stop the increase of hydraulic pressure in the disc brake cylinder of that wheel. SECTION A The ECU sets the solenoid valves to the pressure reduction mode based on wheel speed, thus reducing the hydraulic pressure in the disc brake cylinder. After the pressure drops, the ECU switches the solenoid valves to the Holding Mode then monitors the change in wheel speed. If the ECU judges that the hydraulic pressure needs to be reduced further, it will return to reduction mode. SECTION B When the hydraulic pressure inside the disc brake cylinder decreases (section A), the hydraulic pressure applied to the wheel falls. This allows the wheel that was locking up to speed up. However, if the hydraulic pressure is held down, the braking force acting on the wheel will become too low. To prevent this, the ECU sets the solenoid valves to the pressure increase mode and holding mode alternately as the wheel which was locking up, recovers speed. SECTION C As the hydraulic pressure is gradually increased in the brake cylinder by the ECU actuator (section B), the wheel tends to lock up again. In response, the ECU again switches the solenoid valves to the pressure reduction mode to reduce the hydraulic pressure inside the disc brake cylinder. SECTION D Since the hydraulic pressure in the brake cylinder is decreased again (section C), the ECU starts to increase the pressure again as in section B. The cycle of Hold, Reduce and Increase is repeated many times until the wheels are no longer outside the 30% slip ratio. 138 TOYOTA Technical Training
21 Anti-lock Brakes Wheel Speed Control Chart Toyota Brake Systems - Course
22 140 TOYOTA Technical Training
1. INTRODUCTION. Anti-lock Braking System
 1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
Module 11: Antilock Brakes Systems
 ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
ABS, 4-ETS and EBP BRAKES ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 4-WHEEL ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (4-ETS) ELECTRONIC BRAKE PROPORTIONING (EBP)
 1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice. Operating temperature - 40 C to 150 C - 40 C to 150 C
 489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
Anti Locking Brakes. Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK. Regd no:
 Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM. Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 SENSORS..................... 35B-6 BRAKE MODULATOR (ABS-ECU).. 35B-9 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35B-10
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 SENSORS..................... 35B-6 BRAKE MODULATOR (ABS-ECU).. 35B-9 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35B-10
HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING
 2005 BRAKES Anti-Lock Brake System With Electronic Brake Force Distribution (EBD) - Diagnostics - RAV4 HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING Troubleshoot in accordance with the following procedures. Fig.
2005 BRAKES Anti-Lock Brake System With Electronic Brake Force Distribution (EBD) - Diagnostics - RAV4 HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING Troubleshoot in accordance with the following procedures. Fig.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
 TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems
 Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
2006 Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC. Chassis and Drivetrain 42
 Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
8. Other system and brake theories
 8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
ABS. Prof. R.G. Longoria Spring v. 1. ME 379M/397 Vehicle System Dynamics and Control
 ABS Prof. R.G. Longoria Spring 2002 v. 1 Anti-lock Braking Systems These systems monitor operating conditions and modify the applied braking torque by modulating the brake pressure. The systems try to
ABS Prof. R.G. Longoria Spring 2002 v. 1 Anti-lock Braking Systems These systems monitor operating conditions and modify the applied braking torque by modulating the brake pressure. The systems try to
Read on to find out more about each component of the Star Safety System and how it can be of benefit to you.
 All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR - NIPPONDENSO
 ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR - NIPPONDENSO 1988 Toyota Celica 1988 ELECTRICAL Alternators & Regulators - Nippondenso Camry, Celica, Corolla, Cressida, Land Cruiser, MR2, Pickup, Supra, Tercel, Van, 4Runner DESCRIPTION
ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR - NIPPONDENSO 1988 Toyota Celica 1988 ELECTRICAL Alternators & Regulators - Nippondenso Camry, Celica, Corolla, Cressida, Land Cruiser, MR2, Pickup, Supra, Tercel, Van, 4Runner DESCRIPTION
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Self-diagnosis. Self-diagnosis BR-44 FUNCTION SELF-DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE ABS
 Self-diagnosis ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Self-diagnosis FUNCTION NABR0095 NABR0095S01 When a problem occurs in the, the warning lamp on the instrument panel comes on. To start the self-diagnostic
Self-diagnosis ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Self-diagnosis FUNCTION NABR0095 NABR0095S01 When a problem occurs in the, the warning lamp on the instrument panel comes on. To start the self-diagnostic
1999 Toyota RAV BRAKES Disc & Drum - Trucks & Vans
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION 1999-2000 BRAKES Disc & Drum - Trucks & Vans WARNING: For warnings and procedures regarding vehicles equipped with Anti-Lock Brake Systems (ABS), see appropriate ANTI-LOCK article.
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION 1999-2000 BRAKES Disc & Drum - Trucks & Vans WARNING: For warnings and procedures regarding vehicles equipped with Anti-Lock Brake Systems (ABS), see appropriate ANTI-LOCK article.
 Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION
 4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking
 ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
GF1A TRANSFER / 4WD / AWD: DYNAMIC TORQUE CONTROL AWD SYSTEM: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 MY RAV4 [10/ /2016]
![GF1A TRANSFER / 4WD / AWD: DYNAMIC TORQUE CONTROL AWD SYSTEM: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 MY RAV4 [10/ /2016] GF1A TRANSFER / 4WD / AWD: DYNAMIC TORQUE CONTROL AWD SYSTEM: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 MY RAV4 [10/ /2016]](/thumbs/92/109878214.jpg) 11/29/2017 Dynamic Torque System - System Description - [10/2015-08/2016] (Transfer Case) - ALLDATA 2016 Toyota Truck RAV4 4WD L4-2.5L (2AR-FE) Vehicle > Transmission and Drivetrain > Transfer Case > Description
11/29/2017 Dynamic Torque System - System Description - [10/2015-08/2016] (Transfer Case) - ALLDATA 2016 Toyota Truck RAV4 4WD L4-2.5L (2AR-FE) Vehicle > Transmission and Drivetrain > Transfer Case > Description
The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. BD20B (with Differential Lock Actuator)
 6 4RUNNER NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES DIFFERENTIAL (OFF-ROAD PACKAGE MODELS) 1. General The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. Rear Differential Lock Actuator 233CH46
6 4RUNNER NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES DIFFERENTIAL (OFF-ROAD PACKAGE MODELS) 1. General The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. Rear Differential Lock Actuator 233CH46
POWER TRAIN 2-1 CONTENTS AYC SYSTEM... 9 CLUTCH... 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS... 4 FRONT AXLE... 5 REAR AXLE... 6
 2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
Automatic drain valves
 driving commercial vehicles If you notice more than a few drops of water when you drain the supply reservoir, the air dryer or compressor may need servicing. fast fact Even if the air brake system includes
driving commercial vehicles If you notice more than a few drops of water when you drain the supply reservoir, the air dryer or compressor may need servicing. fast fact Even if the air brake system includes
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
 DN SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO....2 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES...2 BRAKE LAMP
DN SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO....2 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES...2 BRAKE LAMP
ATASA 5 th. ABS & Traction Control Systems. Please Read The Summary
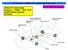 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages Brake Systems 49 Points. Automotive Service
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
BRAKE SYSTEM Article Text 1996 Toyota RAV4 For Copyright 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC Wednesday, September 13, :30PM
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 BRAKES Toyota - Disc & Drum RAV4 * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * WARNING: For warnings and procedures regarding vehicles equipped with Anti-Lock Brake Systems (ABS), see
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 BRAKES Toyota - Disc & Drum RAV4 * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * WARNING: For warnings and procedures regarding vehicles equipped with Anti-Lock Brake Systems (ABS), see
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General CH-16 CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
7. ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle Control System-intelligent)
 5 7. ETCS-i (Electronic System-intelligent) General The ETCS-i is used, providing excellent throttle control in all the operating ranges. In the new 1GR-FE engine, the accelerator cable has been discontinued,
5 7. ETCS-i (Electronic System-intelligent) General The ETCS-i is used, providing excellent throttle control in all the operating ranges. In the new 1GR-FE engine, the accelerator cable has been discontinued,
ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-3 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-4............ 35B-5 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-3 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-4............ 35B-5 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
SUBJECT: Automatic Stability Control with Traction Control System (ASC+T)
 Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
System overview. Introduction. Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved.
 "VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
"VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES
 BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
A proportioning valve is used to regulate brake pressure between front and rear brakes. Rear brakes on all models are self-adjusting.
 Page 1 of 21 ARTICLE BEGINNING DESCRIPTION & OPERATION WARNING: For warnings and procedures regarding vehicles equipped with Anti- Lock Brake Systems (ABS), see ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM article in the BRAKES
Page 1 of 21 ARTICLE BEGINNING DESCRIPTION & OPERATION WARNING: For warnings and procedures regarding vehicles equipped with Anti- Lock Brake Systems (ABS), see ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM article in the BRAKES
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Diamante 1993 BRAKES Mitsubishi - Anti-Lock Brake System Diamante DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) is designed to prevent wheel lock-up during heavy braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Diamante 1993 BRAKES Mitsubishi - Anti-Lock Brake System Diamante DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) is designed to prevent wheel lock-up during heavy braking.
ENRESO.WORLD. Traction Control System. Created by Istas René - enreso.world. Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys
 ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
Section 5 AIR BRAKES. This Section Covers. Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes
 Section 5 AIR BRAKES This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 AIR BRAKES This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL)
 35C-1 GROUP 35C TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35C-2 DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 INTRODUCTION TO TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 TCL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35C-4 DIAGNOSTIC
35C-1 GROUP 35C TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35C-2 DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 INTRODUCTION TO TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 TCL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35C-4 DIAGNOSTIC
Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Velocity Prediction by Observer System)
 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) 15-1 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) - Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Prediction by Observer System) by Sean RITHY *1
Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) 15-1 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) - Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Prediction by Observer System) by Sean RITHY *1
ABS Operator s Manual
 ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1992 Infiniti G20 1990-92 BRAKES Infiniti Anti-Lock Brake System Infiniti; G20, M30, Q45 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) prevents wheel lock-up during abrupt
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1992 Infiniti G20 1990-92 BRAKES Infiniti Anti-Lock Brake System Infiniti; G20, M30, Q45 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) prevents wheel lock-up during abrupt
To study about various types of braking system.
 To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-4 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-5............ 35B-6 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-4 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-5............ 35B-6 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the physics principles.
 489201 103 SYSTEM 489201 1. GENERAL INFORMATION The aim of the is to mmaintain steerability and driving stability and to take the burden off the driver. If the stopping distance is shorter on some road
489201 103 SYSTEM 489201 1. GENERAL INFORMATION The aim of the is to mmaintain steerability and driving stability and to take the burden off the driver. If the stopping distance is shorter on some road
INTRODUCTION TO SENSORS, TRANSDUCERS & ACTUATORS
 INTRODUCTION Transducers play a major role in mechatronics engineering & technology. These are the basic elements that convert or transform one form of energy to another form. Let us change the word energy
INTRODUCTION Transducers play a major role in mechatronics engineering & technology. These are the basic elements that convert or transform one form of energy to another form. Let us change the word energy
The parking brake is an electrically actuated system that operates drum brakes integrated into the rear brake discs. The
 Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)
 23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
ELECTRICAL. Contents - Wiring Diagrams
 Contents - Wiring Diagrams T-Bar (Floating Deck - Hydro)............................................ 8-16 T-Bar (Fixed Deck - Gear)............................................... 8-17 T-Bar (Fixed Deck
Contents - Wiring Diagrams T-Bar (Floating Deck - Hydro)............................................ 8-16 T-Bar (Fixed Deck - Gear)............................................... 8-17 T-Bar (Fixed Deck
Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor
 Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor Mohammad A Obeidat Abstract In this paper an electrical braking system is proposed. The force on
Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor Mohammad A Obeidat Abstract In this paper an electrical braking system is proposed. The force on
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. - Cruise Control Systems Celica DESCRIPTION Cruise control system consists of Cruise Control Electronic
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. - Cruise Control Systems Celica DESCRIPTION Cruise control system consists of Cruise Control Electronic
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (5AT)
 (5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
(5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
1998 E-Series Workshop Manual
 SECTION 206-09A: Anti-Lock Control Rear DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 02/08/2000 Anti-Lock Control Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42, Speed Control for schematic and connector information.
SECTION 206-09A: Anti-Lock Control Rear DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 02/08/2000 Anti-Lock Control Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42, Speed Control for schematic and connector information.
The parts of these systems are discussed in greater detail below.
 Section 5 Air Brakes This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 Air Brakes This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
ABS and Tire Pressure Warning System
 S and Tire Pressure arning System D Data Link 3 * : utomatic /C * : Except * SIL TC TS 7 3 8 K 9 L P- 4 K 0 L 7 S Speed Sensor Rear LH 8 S Speed Sensor Rear RH 3 0 7 3 I 5 I IL IL - R - R P- R G LG L -
S and Tire Pressure arning System D Data Link 3 * : utomatic /C * : Except * SIL TC TS 7 3 8 K 9 L P- 4 K 0 L 7 S Speed Sensor Rear LH 8 S Speed Sensor Rear RH 3 0 7 3 I 5 I IL IL - R - R P- R G LG L -
1999 Toyota RAV ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4
 1999 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4 DESCRIPTION WARNING: Deactivate air bag system before performing any service operation. See AIR BAG RESTRAINT SYSTEMS article. DO NOT apply electrical
1999 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4 DESCRIPTION WARNING: Deactivate air bag system before performing any service operation. See AIR BAG RESTRAINT SYSTEMS article. DO NOT apply electrical
MOTORS. Part 2: The Stepping Motor July 8, 2015 ELEC This lab must be handed in at the end of the lab period
 MOTORS Part 2: The Stepping Motor July 8, 2015 ELEC 3105 This lab must be handed in at the end of the lab period 1.0 Introduction The objective of this lab is to examine the operation of a typical stepping
MOTORS Part 2: The Stepping Motor July 8, 2015 ELEC 3105 This lab must be handed in at the end of the lab period 1.0 Introduction The objective of this lab is to examine the operation of a typical stepping
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM
 200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
DISC BRAKES. Section 4. Components and Operation of Disc Brakes. Disc Brake Assembly
 DISC BRAKES Components and Operation of Disc Brakes A disc brake assembly consists of a: cast iron disc (disc rotor) that rotates with the wheel. caliper assembly attached to the steering knuckle. friction
DISC BRAKES Components and Operation of Disc Brakes A disc brake assembly consists of a: cast iron disc (disc rotor) that rotates with the wheel. caliper assembly attached to the steering knuckle. friction
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 35B-5 INTRODUCTION TO 35B-5 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-5 DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION 35B-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 35B-5 INTRODUCTION TO 35B-5 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-5 DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION 35B-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
Electric cars: Technology
 In his lecture, Professor Pavol Bauer explains all about how power is converted between the various power sources and power consumers in an electric vehicle. This is done using power electronic converters.
In his lecture, Professor Pavol Bauer explains all about how power is converted between the various power sources and power consumers in an electric vehicle. This is done using power electronic converters.
2017 National HDT Rally
 2017 National HDT Rally Importance of Trailer Brakes When te DOT certifies a GCWR, the assumption is that the towed vehicle is supplying it own stopping power. A Class 8 truck is generally considered a
2017 National HDT Rally Importance of Trailer Brakes When te DOT certifies a GCWR, the assumption is that the towed vehicle is supplying it own stopping power. A Class 8 truck is generally considered a
three different ways, so it is important to be aware of how flow is to be specified
 Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
AN ANALYSIS OF HYDRAULIC BRAKING SYSTEM RELIABILITY. Stanisław Walusiak, Mieczysław Dziubiński, Wiktor Pietrzyk
 TEKA Kom. Mot. Energ. oln., 2005, 5, 217 225 AN ANALYSIS OF HYDAULIC BAKING SYSTEM ELIABILITY Lublin University of Technology Summary. For the purpose of improving driving safety, vehicles are equipped
TEKA Kom. Mot. Energ. oln., 2005, 5, 217 225 AN ANALYSIS OF HYDAULIC BAKING SYSTEM ELIABILITY Lublin University of Technology Summary. For the purpose of improving driving safety, vehicles are equipped
RX400h. New Technology
 RX400h New Technology Model Outline Performance Power Train 3MZ-FE engine [3MZ-FE] V6 3.3-liter, 24-valve, DOHC, w/vvt-i gasoline engine 155 kw @ 5,600 rpm 288 N m @ 4,400 rpm 2 Model Outline Performance
RX400h New Technology Model Outline Performance Power Train 3MZ-FE engine [3MZ-FE] V6 3.3-liter, 24-valve, DOHC, w/vvt-i gasoline engine 155 kw @ 5,600 rpm 288 N m @ 4,400 rpm 2 Model Outline Performance
1994 Mazda MX-5 Miata. ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1994 BRAKES Mazda - Anti-Lock
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1994 BRAKES Mazda - Anti-Lock DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) control unit senses reductions in front and rear wheel speed and modulates hydraulic pressure to the brakes
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1994 BRAKES Mazda - Anti-Lock DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) control unit senses reductions in front and rear wheel speed and modulates hydraulic pressure to the brakes
SECTION 3 INFORMATION BEFORE DRIVING YOUR TOYOTA
 INFORMATION BEFORE DRIVING YOUR TOYOTA SECTION 3 Off road vehicle precautions................................. 130 Break in period............................................ 131 Operation in foreign countries................................
INFORMATION BEFORE DRIVING YOUR TOYOTA SECTION 3 Off road vehicle precautions................................. 130 Break in period............................................ 131 Operation in foreign countries................................
Just what is an alternator?
 Just what is an alternator? An alternator is the device used to produce the electricity the car needs to run and to keep the battery charged. The battery is the heart of your electrical system. But you
Just what is an alternator? An alternator is the device used to produce the electricity the car needs to run and to keep the battery charged. The battery is the heart of your electrical system. But you
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) <2WD> ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM
 35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
The Brake Assist System
 Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Document ID# Chevrolet/Geo Corvette
 Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
Battery Operation. Battery Construction. Battery State Of Charge. Battery Load Test. Battery Rating Systems 2/14/12
 Battery Operation Batteries, Charging and Donald Jones Brookhaven College Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy During discharge the battery s plate composition is changed During charging
Battery Operation Batteries, Charging and Donald Jones Brookhaven College Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy During discharge the battery s plate composition is changed During charging
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE. Destination New Model Previous Model Change (from previous model)
 CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes. Course 105 PREVIEW ONLY PARTICIPANT GUIDE
 Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes Course 105 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Table of Contents How to Use the Participant Guide... ii MODULE 1...1 General Principles and Terminology...1 1-1 Safety Review...2
Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes Course 105 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Table of Contents How to Use the Participant Guide... ii MODULE 1...1 General Principles and Terminology...1 1-1 Safety Review...2
SD Bendix Gen 4 and Gen 5 ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses GEN 4 AND GEN 5 ABS INTRODUCTION
 SD-- Bendix Gen and Gen ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses Cab-Mounted Models Frame-Mounted Model FIGURE - Bendix ABS Controller Assemblies GEN AND GEN ABS INTRODUCTION This manual describes both the
SD-- Bendix Gen and Gen ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses Cab-Mounted Models Frame-Mounted Model FIGURE - Bendix ABS Controller Assemblies GEN AND GEN ABS INTRODUCTION This manual describes both the
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) DIAGNOSIS.................... 35B-3 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) DIAGNOSIS.................... 35B-3 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................
Prepared By: Ahmad Firdaus Bin Ahmad Zaidi
 Prepared By: Ahmad Firdaus Bin Ahmad Zaidi A stepper motor is an electromechanical device which converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical rotational movements. Stepper motor mainly used when
Prepared By: Ahmad Firdaus Bin Ahmad Zaidi A stepper motor is an electromechanical device which converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical rotational movements. Stepper motor mainly used when
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6
 35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING
 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING UNIT 4 BRAKES & SUSPENSION TYPES OF BRAKES The two main types of friction brake are drum brake and disc brake. In both types a fixed (non-rotating) shoe or pad rubs against a moving
AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING UNIT 4 BRAKES & SUSPENSION TYPES OF BRAKES The two main types of friction brake are drum brake and disc brake. In both types a fixed (non-rotating) shoe or pad rubs against a moving
definition Retarders definition driving tip chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Using retarders
 chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Brake fade occurs when your brakes stop working properly because they're overheated. Your vehicle takes longer to stop, or may not stop at all if you haven't properly controlled
chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Brake fade occurs when your brakes stop working properly because they're overheated. Your vehicle takes longer to stop, or may not stop at all if you haven't properly controlled
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy.
 Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
Photographs of large cities, such as Seattle, Washington, are visible reminders of how much people rely on electrical energy. Generating Electric Current How is voltage induced in a conductor? According
PRE-CHECK ABS Warning Light BRAKE Warning Light USA: USA: Canada: Canada: VSC Warning Light SLIP Indicator Light. TRAC OFF Indicator Light
 ABS Warning Light BRAKE Warning Light USA: Canada: USA: Canada: VSC Warning Light SLIP Indicator Light TRAC Indicator Light F45096 PRECHECK 05765 05H3Y02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Check the warning lights.
ABS Warning Light BRAKE Warning Light USA: Canada: USA: Canada: VSC Warning Light SLIP Indicator Light TRAC Indicator Light F45096 PRECHECK 05765 05H3Y02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Check the warning lights.
Automatic Transmission Basics
 Section 1 Automatic Transmission Basics Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication
Section 1 Automatic Transmission Basics Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION... 35C-16 CONSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION... 35C-5
 35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES
 ASSIS U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES -41 U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES DESCRIPTION The new model uses 2 types (U340E, U441E) of automatic transaxle. A U340E automatic transaxle is provided
ASSIS U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES -41 U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES DESCRIPTION The new model uses 2 types (U340E, U441E) of automatic transaxle. A U340E automatic transaxle is provided
SD Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly DESCRIPTION M-21 MODULATOR M-22 MODULATOR
 SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
