16 Introduction to DSC
|
|
|
- Paulina Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lateral Acceleration Sensor (Bosch 5.3) This new sensor is a major contributor of the expanded capabilities of DSC III. It is located under the drivers seat but mounted on the vertical surface of the inner rocker sill. (approximately 2 in front of the B pillar). The drivers seat and door jamb trim must be removed and the floor coverings pulled out of the way to access the lateral acceleration sensor. Sensor Operation The lateral acceleration sensor is connected to the DSC III control module by a 3 pin plug. The sensor receives operating power and ground. It return, it provides a linear voltage signal which is a measurement of side to side G-force acceleration. 1- Floor Covering 2-3 in lug 2 - Mounting Screws The voltage range is from 0.5 to 4.5 volts which corresponds to a G force range of -1.5 to +3.5 g. With the vehicle stationary on a level surface, approximately 1.7 volts is present on the signal line. This is indicative of the nominal value of 0.0g. The sensor is a capacitive type sensor. Under the effects of lateral acceleration, a moving capacitor plate moves in relation to a fixed capacitor plate. The result is a signal proportional to the effect of lateral acceleration. The signal provides additional information which enables the DSC III logic a higher level of sensing the vehicles handling characteristics. The DSC regulation is calculated from: The steering input from the desired vehicle direction from the driver The Rotation Rate sensor to determine the yaw of the vehicle The left and right front wheel speed to verify the turning rate in the corner These inputs allow the DSC logic to calculate the under/over steer while cornering, and the rate of the vehicle speed entering the corner. For this calculation, the DSC can then compensate by reducing engine torque, and applying the appropriate braking to stabilize the vehicle for safer handling. 16
2 Combined Rotation Rate/Lateral Acceleration Sensor (Bosch DSC III 5.7) On DSC III (Bosch 5.7) the Rotation Rate sensor and the Lateral Acceleration sensor have been combined into one unit. The sensor is located under the driver s seat and it is smaller in size and weight and is isolated from chassis vibrations through it s rubber mounting. The sensor provides the same information as the two spearate sensors used on DSC 5.3. It receives the same power and ground from the DSC control module. For rotational speed, the sensor produces a refernece signal of 2.5 volts and a linear voltage from 0.7 to 4.3 volts. This linear voltage input signal is used by the DSC control module as the degree of rotational rate (yaw). The sensor also produces a linear voltage signal from 0.5 to 4.5 volts. The DSC control module used this input to determine the side forces acting on the vehicle for DSC regulation 17
3 DSC Switch The system is active whenever the ignition is switched on. When pressed, the switch provides a momentary 12 volt signal to the DSC control module to switch the system off. The DSc indictator in the cluster will be illuminated to indicate that the system is off. When pressed again, the system switches back on and the DSC indicator goes off. Handbrake Switch The handbrake switch is a ground input the DSC module. MSR regulation is cancelled when there is a Handbrake On signal present. Brake Switch The brake switch is used to activate the ABS functions in the DSC III module. If the system receives a brake switch signal when in ASC mode and regulating, ASC regulation is cancelled. The ABS regulating phase is also cancelled when the brake switch signal is not present. 18
4 DSC III (BOSCH 5.3) Hydraulic System Components As mentioned at the beginning of this section, there are minor differences in the hydraulics for the 750iL compared with the 740i/iL and 540iA. The following components are the same for either variation of the system: Hydraulic Unit: Similar to DSC II hydraulic unit Modulates brake pressure during ABS, CBC, ASC and DSC control procedure. Contains: - 1 pump motor, - 2 return reciprocating pumps - 2 preload valves, - 2 changeover valves - 2 accumulator chambers - 2 damper chambers - 4 inlet valves - 4 outlet valves Master Cylinder: Master cylinder, fluid reservoir and level switch. All new components. UM MOTOR SOLENOIDS RELOAD CHANGEOVER RELOAD CHANGEOVER UM UM LEFT REAR RIGHT REAR LEFT FRONT RIGHT FRONT 19
5 To ensure sufficient brake fluid supply is always available to the hydraulic unit during ASC/ DSC hydraulic regulation, the system requires an additional pumping system not equipped on any previous ASC+T system. The pumping systems are different on the 750iL compared with the 740i/iL & 540iA and are as follows: 740i/iL & 540iA = Charge pump - located next to the master cylinder. 750iL = re-boost pump and separate charge piston. These components are also mounted next to the brake fluid master cylinder and fluid reservoir. RELOAD CHANGEOVER RELOAD CHANGEOVER UM UM LEFT REAR 20 RIGHT REAR LEFT FRONT RIGHT FRONT
6 Hydraulic Charge Existing ASC+T and DSC II systems already perform hydraulic control regulation but do not require the additional charge pump systems. Why? The reason being those systems only actuate the rear axle circuits. Obviously, the DSC III system has the capability to actuate front and rear axle circuits together which requires additional hydraulic fluid supply. For this reason, during an ASC or DSC regulation function requiring hydraulic intervention, the DSC III control module switches the electrical charge pump on to provide this additional fluid. 740i/iL & 540iA Vehicles: When activated, the Charge ump delivers a brake pressure of bar to the front axle circuit of the hydraulic unit and into the front axle circuit pressure chamber of of the master cylinder. The master cylinder piston for the front axle circuit contains a notched restrictor forward of the central valve which allows excess fluid to return to the reservoir under a restriction. The pressurized fluid also acts on the rear axle circuit of the master cylinder. This provides the hydraulic charge to the rear axle circuit of the hydraulic unit as needed. 21
7 750iL Vehicles: The electric re-boost pump delivers a brake fluid pressure of 7-15 bar to the isolated chamber of the charge piston. The pre-boost pump incorporates an integral pressure relief valve which opens at 15 bar. From the isolated chamber the fluid returns to the reservoir through a restriction. The restriction causes pressure to build in the chamber which pushes the pistons outward. This immediately acts on two valves which block the normal braking circuits that flow through the charge piston ports. The pressure in the isolated chamber continues to push the pistons outward delivering the required charge pressure. CHARGE ISTON RE-BOOST UM For ABS and CBC operation, the pump systems are not switched on, only during ASC/DSC regulation requiring hydraulic intervention are the pre-boost pump or the charge pump switched on. The balance of the hydraulic system functions operate in the same familiar manor of all previous systems. The individual brake circuits can be isolated as needed to restore lateral locating forces through pressure build, hold and release phases of operation. During an ASC hydraulic intervention requiring only rear wheel brake application, the inlet valves for the front wheels are closed preventing any pressure influence from the charge pump systems. 22
8 RELOAD CHANGEOVER RELOAD CHANGEOVER UM UM LEFT REAR RIGHT REAR LEFT FRONT RIGHT FRONT 23
9 rinciple of Operation Dynamic Stability Control Systems Introduction Dynamic Stability Control (DSC III version 5.3) was introduced on the 1998 Model Year E38 and E vehicles. For Model Year 1999, the system is enhanced with additional control functions and a new combined rotational rate/lateral acceleration sensor as version 5.7. It continues to be offered as standard equipment in the E38 and E models. The new functions are titled as the Dynamic Braking System and include the: Dynamic Brake Control (DBC) Maximum Brake Control (MBC) DSC III adds a further dimension to the dynamic stability control system. DSC II has the ability to mildly correct for lateral instability and only at the rear brakes when braking control is necessary. DSC III has the ability to brake any wheel during cornering maneuvers where the control module s programmed limits for vehicle oversteer and understeer are exceeded. New sensors are added to the DSC III system to monitor the rotational rate of the vehicle around its vertical axis and a lateral acceleration sensor to monitor the side to side forces on the vehicle. The hydraulic system of the DSC II has also been modified to allow brake regulation on the front wheels and to ensure that the supply of brake fluid for DSC II regulation is maintained. Two different hydraulic systems are used on the Bosch 5.3 DSC system as follows: 740i/iL & 540iA use a charge pump for the front brake circuit. 750iL uses a boost pump and separate charge piston for both the front and rear brake circuits. The hydraulic system used on the Bosch DSC III 5.7 has changed on the E38 and E39. The 750iL now uses a similar hydraulic system tothe 740i/iL and 540i. The charge piston and pre-boost pump have been eleminated. The brake pressure sensor is now located in the hydraulic unit on all Bosch 5.7 systems. 24
10 Dynamic Stability Control (DSC III) All of the familiar braking and straight line traction control features and system communication carry over from DSC II. Based on select high/select low logic, the DSC III control module selects a vehicle stabilizing strategy based on the specific input signal values it is monitoring at the moment. For all DSC strategies this begins with engine intervention to reduce torque: For the 750iL this is handled via CAN communication, DSC III to EML to minimize the throttle angle of the DK motors (750iL). For the 740i/iL and 540iA this is handled by direct DSC III activation of the ADS II throttle housing. If additional torque reduction is necessary, DSC III informs DME over CAN to: a. Retard ignition timing b. Shut down the fuel injection to individual cylinders DSC III monitors under/oversteer conditions through the following components: The driver s desired steering angle - steering angle signal over CAN bus. Vehicle speed and speed differential at front wheels - wheel speed sensors Dynamic forces of lateral acceleration and yaw placed on the vehicle. This is possible with these two new components. The results are as follows: 25
11 The expanded hydraulic control of individual wheel circuits is apparent when stabilizing a vehicle exhibiting an oversteer condition as follows: Transmission system intervention also occurs during any ASC/DSC regulating phase. Through CAN bus communication the AGS control module is informed to delay any gear changes during regulation. This prevents any unwanted driveline dynamic changes during DSC regulation. Though DSC III provides state of the art, electronic correction of undesirable vehicle handling characteristics, it is important to remember vehicle stability is always subject to the physical laws of centrifugal force and extreme road conditions. Good judgement and common sense on the part of the driver are still required. 26
12 DSC Features Corner Braking Control (CBC) CBC is a feature of dynamic stability control that is designed to improve the vehicle s stability if the driver brakes while driving through a curve. If the vehicle is braked while driving through a curve, an unequal braking force will be applied to the wheels due to the weight shift of the vehicle to the outside of the turn. Based on the vehicle speed and the speed differential of the two front wheel speed sensors, the control module can determine if CBC needs to be activated when the driver applies the brakes. If CBC is activated, the regulation will pulse the wheel brakes on the outside of the vehicle to provide an equal braking force on all four wheels. Dynamic Braking System (DBS) The dynamic braking system is designed to enhance the braking control of the DSC for the driver of the vehicle. The dynamic braking control and maximum braking control are functions that are programmed into the control electronics of the DSC with no additional hardware changes. The Dynamic braing system features consist of DBC and MBC. Dynamic Braking Control (DBC) The DBC function is designed to provide the maximum braking force available during rapid (panic) braking situations. The DSC control module looks at the inputs from the brake pedal switch and the signal from the brake pressure sensor on the master cylinder. The criteria for activation of DBC is how rapidly is the brake pressure built up with the brake pedal depressed. The total criteria required for DBC activation includes: Brake switch ON Brake pressure build up > threshold value Vehicle road speed > 5MH Vehicle not in reverse Not all wheels in ABS regulation If the threshold for DBC activation is achieved, the DSC control module will activate a pressure build up regulation phase through the hydraulic unit. The pressure at all wheels is increased up to the ABS regulation point. This occurs even if the driver does not achieve the ABS regulation point with the pedal. The rear axle brakes are controlled with select-low regulation and the front axle brakes are controlled individually. ABS regulation will continue until the driver releases the pedal and the pressure in the master cylinder drops below the threshold value stored in the DSC control module. 27
13 Maximum Brake Control The MBC function is also designed to enhance a driver initiated braking procedure. The MBC will build up the pressure in the rear brake circuit when the front brakes are already in an ABS regulation cycle. The additional braking pressure at the rear wheels will shorten the stopping distance. The following criteria must be met before the DSC control module will activate MBC: Both front wheel brakes in ABS regulation Vehicle speed > 5 MH Vehicle not in reverse DBC and pressure sensor initialization test OK Rear wheels not in ABS regulation 28
14 Diagnosis The following diagnostic functions are available using the DISplus or GT-1. Control Unit Functions: Expert mode diagnosis available at any time during troubleshooting. To enter: press the Control Unit Functions button at the right lower corner of the screen. The contents are: Identification Delete Fault Memory Read Fault Memory Component Activation Status queries (requests) Service Functions: rovides access to specialized test modules used as post repair procedures. To enter: Function Selection Service Functions Chassis Dynamic Stability Control The contents are: Connection Speed Sensor: A test to verify the proper wiring to the wheel speed sensors Connection Brake Lines: A test to verify the proper brake pipe connections to the hydraulic unit. Adjustment Functions: Test modules to initialize certain components after repair work is performed Steering Angle Sensor Lateral Acceleration Sensor ressure Sensors Test Modules: Faults with the DSC III system can be diagnosed using fault or symptom driven test modules. To begin diagnosis: erform the Quick Test. Select Vehicle Symptom from the Symptom Selection page. Select Test Module from Test lan page. ress the Test Schedule Button. 29
15 Coding Coding must be performed after replacement of the DSC III control module or the steering angle sensor. ZCS coding is found in the Coding and rogramming selection from the start screen or when pressing the Change button. Follow on-screen instructions for initialization of components after completing the coding process. Adjustment Functions Adjustment (initialization) is required when: Replacing the DSC III Control Unit. Replacing/Re-coding the Steering Angle Sensor. Replacing one or both Brake ressure Sensors. Replacing Lateral Acceleration Sensor. Steering Angle Sensor The steering angle sensor requires an offset adjustment after the sensor has been replaced, coded or after repairs to the steering or suspension system. The offset adjustment informs the steering angle sensor processor of the straight ahead position of the front wheels. The adjustment is performed by completing the Test Module found in Service Functions. Once the adjustment is complete the sensor sends an identification number over the CAN bus to the DSC control unit. The ID provides confirmation that the steering angle sensor is coded and has successfully completed the adjustment procedure. Special Tools Special Tools available for the DSC III system consist of: Tool # Description urpose rint Change End Services BMW Coding/programming SELECTION 1 CAR MEMORY 2 KEYMEMORY 3 ZCS CODING 4 ROGRAMMING 5 ALIGNMENT EWS-DME 6 ALIGNMENT EWS-DDE in V-Cable For B.O.B in B.O.B. For pin by pin diagnosis ressure Sensor Socket For installation and removal of hydraulic brake pressure sensor in B.O.B. For pin by pin diagnosis of Bosch DSC III 5.3 and ASC +T5 Note 30
Table of Contents. Introduction to DSC
 Table of Contents Subject Page Module Objectives...2 Overview of DSC Systems...3 Puspose of the System...4 DSC Components...9 Control Module/Hydraulic Unit... 10 Wheel Speed Sensors... 11 Hydraulic Pressure
Table of Contents Subject Page Module Objectives...2 Overview of DSC Systems...3 Puspose of the System...4 DSC Components...9 Control Module/Hydraulic Unit... 10 Wheel Speed Sensors... 11 Hydraulic Pressure
Table of Contents. Introduction to DSC
 Table of Contents Subject Page Module Objectives...2 Overview of DSC Systems...3 Puspose of the System...4 DSC Components...9 Control Module/Hydraulic Unit... 10 Wheel Speed Sensors... 11 Hydraulic Pressure
Table of Contents Subject Page Module Objectives...2 Overview of DSC Systems...3 Puspose of the System...4 DSC Components...9 Control Module/Hydraulic Unit... 10 Wheel Speed Sensors... 11 Hydraulic Pressure
SUBJECT: Automatic Stability Control with Traction Control System (ASC+T)
 Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (040) 09/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION... 35C-16 CONSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION... 35C-5
 35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL)
 35C-1 GROUP 35C TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35C-2 DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 INTRODUCTION TO TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 TCL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35C-4 DIAGNOSTIC
35C-1 GROUP 35C TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35C-2 DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 INTRODUCTION TO TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 TCL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35C-4 DIAGNOSTIC
 Page of Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Vehicle Dynamic Suspension and Operation Dynamic Suspension Component Location NOTE: Right hand drive vehicle shown 0 Front RH air spring damper module Front RH height
Page of Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Vehicle Dynamic Suspension and Operation Dynamic Suspension Component Location NOTE: Right hand drive vehicle shown 0 Front RH air spring damper module Front RH height
2006 Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC. Chassis and Drivetrain 42
 Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
Document ID# Chevrolet/Geo Corvette
 Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
LUCAS ACE - System Overview
 LUCAS ACE - System Overview The Active Corner Enhancement system manufactured by Rover Group Lucas appears to have been produced specifically for the Land Rover Discovery series II to address the poor
LUCAS ACE - System Overview The Active Corner Enhancement system manufactured by Rover Group Lucas appears to have been produced specifically for the Land Rover Discovery series II to address the poor
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function
 GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
ABS, 4-ETS and EBP BRAKES ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 4-WHEEL ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (4-ETS) ELECTRONIC BRAKE PROPORTIONING (EBP)
 1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
In 04/2000, active cruise control (system supplier: BOSCH) was installed for the first time in a BMW as special equipment for the E38.
 10/20/2015 1/10 FTD-FTD-SBT2004-660104067 Active Cruise Control E60, E61, E63, E64, E65, E66 VIN: XXXXXXX Vehicle: 7'/E65/SEDAN/750i/N62/AUTO/USA/LL/2007/06 System Version: 3.47.10.13054 Data Version:
10/20/2015 1/10 FTD-FTD-SBT2004-660104067 Active Cruise Control E60, E61, E63, E64, E65, E66 VIN: XXXXXXX Vehicle: 7'/E65/SEDAN/750i/N62/AUTO/USA/LL/2007/06 System Version: 3.47.10.13054 Data Version:
Rear Drive Axle and Differential
 Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
System overview. Introduction. Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved.
 "VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
"VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
 Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
1. INTRODUCTION. Anti-lock Braking System
 1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
DESCRIPTION. Chrysler NCV3 Service Info Section 08 > Electronic Modules > MODULE, Transmission Control Information
 DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
Shift Solenoid "B" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S2)
 86 A750E AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM DTC P0756 Shift Solenoid "B" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S2) DESCRIPTION The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input
86 A750E AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM DTC P0756 Shift Solenoid "B" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S2) DESCRIPTION The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 35B-5 INTRODUCTION TO 35B-5 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-5 DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION 35B-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 35B-5 INTRODUCTION TO 35B-5 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-5 DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION 35B-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2................ 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................ 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2................ 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................ 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC
HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice. Operating temperature - 40 C to 150 C - 40 C to 150 C
 489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
E61, E63, E64, E70, E81, E87, E90, E91, E92, E93 BMW AG - TIS
 VS-42 es Baugruppe/Group: 32 meeknet.co.uk/e64 32 01 03 (001) Active Steering E60, E61, E63, E64, E70, E81, E87, E90, E91, E92, E93 weltweit Datum/Date: 04/2003 Update: 02/2007 Introduction Active Steering
VS-42 es Baugruppe/Group: 32 meeknet.co.uk/e64 32 01 03 (001) Active Steering E60, E61, E63, E64, E70, E81, E87, E90, E91, E92, E93 weltweit Datum/Date: 04/2003 Update: 02/2007 Introduction Active Steering
Shift Solenoid "B" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S2)
 88 A750F AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM DTC P0756 Shift Solenoid "B" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S2) DESCRIPTION The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input
88 A750F AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION AUTOMIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM DTC P0756 Shift Solenoid "B" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S2) DESCRIPTION The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input
Purpose of the System...3. System Components...3 Instrument Cluster Display...4
 meeknet.co.uk/e64 Table of Contents Active Cruise Control Workbook Subject Page Purpose of the System......................................3 System Components........................................3 Instrument
meeknet.co.uk/e64 Table of Contents Active Cruise Control Workbook Subject Page Purpose of the System......................................3 System Components........................................3 Instrument
Class 5 to 7 Truck and Bus Hydraulic Brake System
 Class 5 to 7 Truck and Bus Hydraulic Brake System Diagnostic Guide 2nd Edition www.bosch.us Important Service tes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information
Class 5 to 7 Truck and Bus Hydraulic Brake System Diagnostic Guide 2nd Edition www.bosch.us Important Service tes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information
Shift Solenoid "A" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S1)
 78 DTC P0751 Shift Solenoid "A" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S1) DESCRIPTION The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input speed sensor to detect the actual gear position (1st,
78 DTC P0751 Shift Solenoid "A" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S1) DESCRIPTION The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input speed sensor to detect the actual gear position (1st,
TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION CIRCUIT ACTYON
 311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION...... 17-3 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS.................. 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION...... 17-3 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS.................. 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION
 4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6
 35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
POWER TRAIN 2-1 CONTENTS AYC SYSTEM... 9 CLUTCH... 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS... 4 FRONT AXLE... 5 REAR AXLE... 6
 2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
RIDE AND HANDLING OPTIMIZATION
 PUBLISHED: 26-JAN-2015 2013.0 RANGE ROVER SPORT (LS), 204-06 RIDE AND HANDLING OPTIMIZATION DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Terrain Response - Component Location ITEM DESCRIPTION 1 Terrain Response control and
PUBLISHED: 26-JAN-2015 2013.0 RANGE ROVER SPORT (LS), 204-06 RIDE AND HANDLING OPTIMIZATION DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Terrain Response - Component Location ITEM DESCRIPTION 1 Terrain Response control and
SECTION Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination
 413-00-i Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination 413-00-i SECTION 413-00 Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination CONTENTS PAGE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination... 413-00-2
413-00-i Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination 413-00-i SECTION 413-00 Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination CONTENTS PAGE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Instrument Cluster and Panel Illumination... 413-00-2
1GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM
 1GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 299 P2120 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit P2122 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit Low Input P2123 Throttle / Pedal Position
1GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 299 P2120 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit P2122 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit Low Input P2123 Throttle / Pedal Position
ACTIVE SKID CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)
 35C-1 GROUP 35C ACTIVE SKID CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...35C-4 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS...35C-6...35C-7 INTRODUCTION TO ASC...35C-7 ASC DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY...35C-7
35C-1 GROUP 35C ACTIVE SKID CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...35C-4 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS...35C-6...35C-7 INTRODUCTION TO ASC...35C-7 ASC DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY...35C-7
Brakes Objectives of the Module...2 Purpose of the System...3
 Table of Contents Subject Page Brakes Objectives of the Module.....................................2 Purpose of the System.......................................3 Service Brakes System Components........................................
Table of Contents Subject Page Brakes Objectives of the Module.....................................2 Purpose of the System.......................................3 Service Brakes System Components........................................
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-4
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-4
8.1 4MATIC Contents. b Diagnostic Manual Chassis and Drivetrain 03/ MATIC C/ Model 124.2
 8.1 4MATIC Contents 8.1 Model 124.2 Page Diagnosis Function Test................................... 11/1 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Memory................ 12/1 Complaint Related Diagnostic Chart...................
8.1 4MATIC Contents 8.1 Model 124.2 Page Diagnosis Function Test................................... 11/1 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Memory................ 12/1 Complaint Related Diagnostic Chart...................
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
Function description of roll-over bar
 91-800 Function description of roll-over bar Roll-over bar system, model 129 (version up to approx. 05/95) P91.50-0203-59 A1e29 Roll-over bar warning lamp (RB) S68/7 Front left seat belt buckle/seat belt
91-800 Function description of roll-over bar Roll-over bar system, model 129 (version up to approx. 05/95) P91.50-0203-59 A1e29 Roll-over bar warning lamp (RB) S68/7 Front left seat belt buckle/seat belt
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM. Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
10.1 Electronic Stability Program (ESP) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents
 10.1 lectronic Stability Program (SP) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 10.1 Models 129 (with engine 104, 119) up to M.Y. 1999, Model 129 (with engine 120), 140, 210 as of M.Y. 1996 Page
10.1 lectronic Stability Program (SP) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 10.1 Models 129 (with engine 104, 119) up to M.Y. 1999, Model 129 (with engine 120), 140, 210 as of M.Y. 1996 Page
Function Description Of Roll-over Bar
 Function Description Of Roll-over Bar General The U-shaped roll-over bar is mounted on two main bearings on the left and right center pillars. In the retracted state the roll-over bar is positioned in
Function Description Of Roll-over Bar General The U-shaped roll-over bar is mounted on two main bearings on the left and right center pillars. In the retracted state the roll-over bar is positioned in
GROUP 17 CONTENTS WARNINGS REGARDING SERVICING OF SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) EQUIPPED VEHICLES
 17-1 GROUP 17 CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-4 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 17-4 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 17-4 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 17-4 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING
17-1 GROUP 17 CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-4 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 17-4 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 17-4 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 17-4 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Document ID# Buick LeSabre
 http://127.0.0.1:9001/servlets/blobshtml?shtmlfile=633088&evc=sm&pubid=262&cellid... Page 1 of 3 Document ID# 633088 DTC C1214 Circuit Description The system relay is energized when the ignition is ON.
http://127.0.0.1:9001/servlets/blobshtml?shtmlfile=633088&evc=sm&pubid=262&cellid... Page 1 of 3 Document ID# 633088 DTC C1214 Circuit Description The system relay is energized when the ignition is ON.
9.1 Traction Systems (ASR, ETS) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents
 9.1 Traction Systems (ASR, TS) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 9.1 Models 129, 140 as of 06/94 up to 08/95 Page Diagnosis Function Test (ASR only).......................... 11/1 Diagnostic
9.1 Traction Systems (ASR, TS) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 9.1 Models 129, 140 as of 06/94 up to 08/95 Page Diagnosis Function Test (ASR only).......................... 11/1 Diagnostic
Module 11: Antilock Brakes Systems
 ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
A750E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION: AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM (for 1GR-FE)... Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM000000XP101WX
 Last Modified: 4-26-2007 Service Category: Drivetrain 1.6 C Section: Automatic Transmission/Transaxle Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM000000XP101WX Title: A750E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION: AUTOMATIC
Last Modified: 4-26-2007 Service Category: Drivetrain 1.6 C Section: Automatic Transmission/Transaxle Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM000000XP101WX Title: A750E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION: AUTOMATIC
GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 HYDRAULIC BRAKE BOOSTER (HBB) DIAGNOSIS...
 35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6 SYMPTOM CHART...................
35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6 SYMPTOM CHART...................
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 CRUISE CONTROL CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. HANDLING PRECAUTION FOR CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM (a) Turn the cruise control main switch OFF when not using the cruise control system.
CRUISE CONTROL CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. HANDLING PRECAUTION FOR CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM (a) Turn the cruise control main switch OFF when not using the cruise control system.
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 Negative (-) Battery Terminal CRUISE CONTROL CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM Cable System name METER / GAUGE SYSTEM D033496E01 CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. DISCONNECT AND RECONNECT CABLE OF NEGATIVE BATTERY
Negative (-) Battery Terminal CRUISE CONTROL CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM Cable System name METER / GAUGE SYSTEM D033496E01 CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. DISCONNECT AND RECONNECT CABLE OF NEGATIVE BATTERY
A750F AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION: AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEM (for 1GR-FE)... Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM000000W80023X
 Last Modified: 4-26-2007 Service Category: Drivetrain 1.6 C Section: Automatic Transmission/Transaxle Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM000000W80023X Title: A750F AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION: AUTOMATIC
Last Modified: 4-26-2007 Service Category: Drivetrain 1.6 C Section: Automatic Transmission/Transaxle Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM000000W80023X Title: A750F AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION: AUTOMATIC
Injector Solenoid - Test
 Injector Solenoid - Test System Operation Description: Use this procedure to troubleshoot the electrical system if a problem is suspected with the injectors or if any one of the diagnostic codes in Table
Injector Solenoid - Test System Operation Description: Use this procedure to troubleshoot the electrical system if a problem is suspected with the injectors or if any one of the diagnostic codes in Table
Table of Contents. E70 Lateral Dynamics Systems
 Table of Contents Subject Page Lateral Dynamics..............................................3 Active Steering (AS)............................................3 Active Front Steering (AFS)......................................4
Table of Contents Subject Page Lateral Dynamics..............................................3 Active Steering (AS)............................................3 Active Front Steering (AFS)......................................4
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
Driving dynamics GENERAL INFORMATION WINTER MODE. JaguarDrive Control
 GENERAL INFORMATION Driving dynamics It remains the driver's responsibility to drive safely, according to the prevailing conditions and within the law. JaguarDrive Control JaguarDrive Control is a selectable
GENERAL INFORMATION Driving dynamics It remains the driver's responsibility to drive safely, according to the prevailing conditions and within the law. JaguarDrive Control JaguarDrive Control is a selectable
CRUISE CONTROL WITH ELECTRIC ACTUATOR. Group 61 - Chassis Electrics
 CRUISE CONTROL WITH ELECTRIC ACTUATOR Group 61 - Chassis Electrics Produced By: BMW of North America, Inc Issued 7/83 61-09 CRUISE CONTROL WITH ELECTRIC ACTUATOR The electric actuator type cruise control
CRUISE CONTROL WITH ELECTRIC ACTUATOR Group 61 - Chassis Electrics Produced By: BMW of North America, Inc Issued 7/83 61-09 CRUISE CONTROL WITH ELECTRIC ACTUATOR The electric actuator type cruise control
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
Audi A6 Current Flow Diagram No. 14 / 1 Edition
 Стр. 1 из 7 Audi A6 Current Flow Diagram No. 14 / 1 Edition 01.1998 Anti-lock brake system (ABS) with electronic differential lock (EDL), traction control system (ASR/TCS) and electronic stability program
Стр. 1 из 7 Audi A6 Current Flow Diagram No. 14 / 1 Edition 01.1998 Anti-lock brake system (ABS) with electronic differential lock (EDL), traction control system (ASR/TCS) and electronic stability program
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
Electronic Engine Power Control (EPC) (E-Gas), checking
 Page 1 of 51 24-113 Electronic Engine Power Control (EPC) (E-Gas), checking E-Gas system, function For E-Gas, the throttle valve is not operated by a cable from the accelerator pedal. There is no mechanical
Page 1 of 51 24-113 Electronic Engine Power Control (EPC) (E-Gas), checking E-Gas system, function For E-Gas, the throttle valve is not operated by a cable from the accelerator pedal. There is no mechanical
ATASA 5 th. ABS & Traction Control Systems. Please Read The Summary
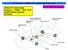 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
Anti Locking Brakes. Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK. Regd no:
 Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
CS1000 Fault Code Scanner
 CS1000 Fault Code Scanner BMW Instructions Engine (DME) - AirBag (SRS) Transmission (EGS) Service Interval Reset OB15-9 OB15-3 OB15-5 Model Years 1988-98 Baum Tools Unlimited Inc January 20, 1999 BMW Code
CS1000 Fault Code Scanner BMW Instructions Engine (DME) - AirBag (SRS) Transmission (EGS) Service Interval Reset OB15-9 OB15-3 OB15-5 Model Years 1988-98 Baum Tools Unlimited Inc January 20, 1999 BMW Code
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM
 1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
Automated Control Electronics (ACE ) System Operation and Diagnostics
 Commercial Products Automated Control Electronics (ACE ) System Operation and Diagnostics PART NO. 98962SL This page is intentionally blank. Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Controller Operation and
Commercial Products Automated Control Electronics (ACE ) System Operation and Diagnostics PART NO. 98962SL This page is intentionally blank. Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Controller Operation and
POWER MIRROR SYSTEMS
 WJ POWER MIRROR SYSTEMS 8T - 1 POWER MIRROR SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS OUTSIDE POWER MIRRORS... 1 INSIDE POWER MIRRORS... 6 OUTSIDE POWER MIRRORS TABLE OF CONTENTS AND POWER MIRROR SYSTEM...1 POWER MIRROR....2
WJ POWER MIRROR SYSTEMS 8T - 1 POWER MIRROR SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS OUTSIDE POWER MIRRORS... 1 INSIDE POWER MIRRORS... 6 OUTSIDE POWER MIRRORS TABLE OF CONTENTS AND POWER MIRROR SYSTEM...1 POWER MIRROR....2
P0088-FUEL RAIL PRESSURE TOO HIGH
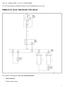 2008 - KA - DODGE NITRO - 2.8L 4 CYL TURBO DIESEL 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Engine Control (ECM)/Diagnosis and Testing P0088- RAIL TOO HIGH BATT A0 30 RELAY- AUTO SHUT DOWN MODULE- TOTALLY INTEGRATED
2008 - KA - DODGE NITRO - 2.8L 4 CYL TURBO DIESEL 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Engine Control (ECM)/Diagnosis and Testing P0088- RAIL TOO HIGH BATT A0 30 RELAY- AUTO SHUT DOWN MODULE- TOTALLY INTEGRATED
 Page 1 of 29 Section 04-05: Suspension, Computer Controlled 1997 Town Car Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 05/16/2000 Suspension, Computer Controlled Inspection and Verification
Page 1 of 29 Section 04-05: Suspension, Computer Controlled 1997 Town Car Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 05/16/2000 Suspension, Computer Controlled Inspection and Verification
REV F2.0. User's Manual. Hydraulic ABS (HABS) Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) Page 1 of 28
 REV F2.0 User's Manual Hydraulic ABS (HABS) Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) Page 1 of 28 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...4 Starting TOOLBOX Software... 5 MAIN MENU...6 System Setup... 6 Language... 7 Select
REV F2.0 User's Manual Hydraulic ABS (HABS) Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) Page 1 of 28 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...4 Starting TOOLBOX Software... 5 MAIN MENU...6 System Setup... 6 Language... 7 Select
TECHNICAL PAPER 1002 FT. WORTH, TEXAS REPORT X ORDER
 I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
Troubleshooting Guide
 Troubleshooting Guide diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG P/N 0191681 May, 1999 An ISO 9001 Registered Company P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317
Troubleshooting Guide diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG P/N 0191681 May, 1999 An ISO 9001 Registered Company P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Montero 1993 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Mitsubishi Cruise Control Systems Montero DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The cruise control system is electronically and vacuum controlled.
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Montero 1993 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Mitsubishi Cruise Control Systems Montero DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The cruise control system is electronically and vacuum controlled.
2010 Flex Workshop Manual. REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 12/10/2010
 SECTION 501-12: Instrument Panel and Console REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 12/10/2010 Refrigerator Rear console Item Part Number Description 1 04567 Front finish panel 2 045A90B Bottom
SECTION 501-12: Instrument Panel and Console REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 12/10/2010 Refrigerator Rear console Item Part Number Description 1 04567 Front finish panel 2 045A90B Bottom
 TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
The parking brake is an electrically actuated system that operates drum brakes integrated into the rear brake discs. The
 Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
Ride and Handling Optimization
 Page 1 of 6 Published: Feb 23, 2009 Ride and Handling Optimization COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Terrain Response rotary control OVERVIEW The Terrain Response system allows the driver
Page 1 of 6 Published: Feb 23, 2009 Ride and Handling Optimization COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Terrain Response rotary control OVERVIEW The Terrain Response system allows the driver
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
 08 5 ECU According to input signals from various sensors, engine ECU calculates driver s demand (position of the accelerator pedal) and then controls overall operating performance of engine and vehicle
08 5 ECU According to input signals from various sensors, engine ECU calculates driver s demand (position of the accelerator pedal) and then controls overall operating performance of engine and vehicle
VEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMS
 ZG VEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMS 8Q - 1 VEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMS CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION ARMING... 1 DISARMING... 2 INTRODUCTION... 1 POWER-UP MODE... 2 TAMPER ALERT... 2 DESCRIPTION AND
ZG VEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMS 8Q - 1 VEHICLE THEFT/SECURITY SYSTEMS CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION ARMING... 1 DISARMING... 2 INTRODUCTION... 1 POWER-UP MODE... 2 TAMPER ALERT... 2 DESCRIPTION AND
SI B Intermediate and Special Transmission. September 2015 Technical Service
 SI B27 04 15 Intermediate and Special Transmission September 2015 Technical Service SUBJECT Shudder from the Driveline on Vehicles with xdrive MODEL E90 (3 Series xdrive Sedan) E91 (3 Series xdrive Sports
SI B27 04 15 Intermediate and Special Transmission September 2015 Technical Service SUBJECT Shudder from the Driveline on Vehicles with xdrive MODEL E90 (3 Series xdrive Sedan) E91 (3 Series xdrive Sports
Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Description and Operation COMPONENT LOCATION Published: 18-Dec-2013
 Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Description and Operation Published: 18Dec2013 COMPONENT LOCATION Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Part Number Description RH (right hand) front spring
Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Vehicle Dynamic Suspension Description and Operation Published: 18Dec2013 COMPONENT LOCATION Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Part Number Description RH (right hand) front spring
Active On demand Coupling (AOC) Clutch unit and control module Signals
 Page 1 of 5 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 26/3/2013 PRINT 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) Active On demand Clutch
Page 1 of 5 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 26/3/2013 PRINT 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) Active On demand Clutch
DTC P0657 Actuator Supply Voltage Circuit / Open
 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 277 DTC P0657 Actuator Supply Voltage Circuit / Open MONITOR DCRIPTION The ECM monitors the output voltage to the throttle actuator. This self-check ensures that the
1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 277 DTC P0657 Actuator Supply Voltage Circuit / Open MONITOR DCRIPTION The ECM monitors the output voltage to the throttle actuator. This self-check ensures that the
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) <2WD> ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM
 35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
ESCONDIDO FIRE DEPT TRAINING MANUAL Section DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 Pumps and Accessory Equipment Revised
 DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
SECTION 5 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)
 5 1. DTC MEMORY SECTION 5 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are logged in a list in TCM memory. The DTCs contained in the list have information recorded as shown in Table 5 1 (DTC example). The TCM is capable
5 1. DTC MEMORY SECTION 5 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are logged in a list in TCM memory. The DTCs contained in the list have information recorded as shown in Table 5 1 (DTC example). The TCM is capable
POWER LOCK SYSTEMS 8P - 1 POWER LOCK SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 AN POWER LOCK SYSTEMS 8P - 1 POWER LOCK SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION INTRODUCTION...1 POWER LOCK SYSTEM...1 REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM...1 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION CENTRAL TIMER
AN POWER LOCK SYSTEMS 8P - 1 POWER LOCK SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION INTRODUCTION...1 POWER LOCK SYSTEM...1 REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM...1 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION CENTRAL TIMER
Test Which component has the highest Energy Density? A. Accumulator. B. Battery. C. Capacitor. D. Spring.
 Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
SD Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly DESCRIPTION M-21 MODULATOR M-22 MODULATOR
 SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
