Module 11: Antilock Brakes Systems
|
|
|
- Bridget Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1  ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for an Antilock Brake System Basic Parts of an Antilock Brake System and Their Functions ABS Brake System    Â Basic Operation of an Antilock Brake System  Two Ways to Describe Antilock Brake Systems ABS Timeline  Methods of Testing ABS Valves Most Common Problems Associated with Antilock Brake Systems Signs of Antilock Brake Failure The antilock braking system (ABS) is designed to prevent wheels locking or skidding, no matter how hard the brakes are applied or how slippery the road surface. The primary components of the ABS are as follows. The electronic control unit (ECU), which is located inside the vehicle, receives signals from the sensors in the circuit and controls the brake pressure at the road wheels according to the data analyzed by the unit. The hydraulic control unit, or modulator, receives operating signals from the ECU to apply or release the brakes under ABS conditions. The location of the hydraulic control unit varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, however some locate it under the fender or hood. The power booster and master cylinder assembly is mounted on the firewall and is activated when the driver pushes down on the brake pedal. It provides the power assistance required during braking. The wheel sensor unit consists of a tooth rotor that rotates with the road wheels and a pick-up that is located in the wheel hub. Antilock Brake System Operation Applying the brakes too hard, or on a slippery surface, can cause wheels to lock. When wheels lock, steering control is lost and, in most cases, it produces longer stopping distances. ABS prevents the wheels from locking or skidding, no matter how hard brakes are applied, or how slippery the road surface. Steering stays under control and stopping distances are generally reduced. ABS consists of the brake pedal, the master cylinder, the wheel speed sensors, the ECU, and the hydraulic control unit, also called a hydraulic modulator. The wheel speed sensor consists of a notched or toothed rotor, which rotates with each wheel, and a pickup. As the wheel turns, a small voltage pulse is induced into the pickup and sent to the ECU. When the brakes are applied, the wheel s speed of rotation changes, and this sends a new signal to the ECU. If the control unit detects that a wheel might lock, it sends a signal to the hydraulic control unit. In a three-channel system, the hydraulic control unit uses three solenoid valves to control brake pressure and prevent them from locking. The valves are in series with the brake master cylinder and the brake circuits, and one operates for each of the front wheels and one controls both rear wheels. At the start of a journey, the ABS automatically checks itself, and any failure in the system lights up a warning light in the dash panel Jones & Bartlett Learning 1
2 Principles of ABS Braking The ABS controls braking force by controlling the hydraulic pressure of the braking system, so that the wheels do not lock during braking. Braking force and the tendency of the wheels to lock up are affected by a combination of factors such as the friction coefficient of the road surface and the difference between the vehicle speed and the road wheel speed. The ABS prevents the road wheels from locking up during heavy braking by controlling the vehicle s brake system hydraulic pressure. During normal braking, as the rotational speed of the wheel falls, no electric current flows from the ECU to the hydraulic unit, and the solenoid valve is not energized. The brake master cylinder hydraulic pressure is applied to the brake unit, and the ABS is not involved. However, even though the ABS is passive during normal braking, its control module is constantly monitoring for rapid deceleration of any of the wheels. If a wheel-speed sensor signals severe wheel deceleration, which means the wheel is likely to lock up, the ECU sends a current to the hydraulic unit, and this energizes the solenoid valve. The action of the valve isolates the brake circuit from the master cylinder; this stops the braking pressure at that wheel from rising, and keeps it constant. If the sensors signal the wheel is still decelerating too rapidly, the ECU sends a larger current to the hydraulic unit. The armature moves even further and opens the valve, and it opens a passage from the brake circuit. Brake fluid is sent from the brake circuit back to the master cylinder, and pressure in the brake caliper circuit is reduced so that the wheel is braked less heavily. If the wheel sensors indicate that lowering the brake pressure is letting the wheel accelerate again, the ECU stops sending current to the hydraulic unit and de-energizes the solenoid valve. This lets the pressure increase, so that the wheel is again decelerated. This cycle repeats itself about four to six times per second. It is normal in an ABS for the valves in the hydraulic control unit to keep changing position as they change the brake pressure that s being applied, and these changes in position may cause rapid pulsations to be felt through the brake pedal. ABS Master Cylinder The tandem master cylinder transforms applied brake force into hydraulic pressure. The pressure is transferred to the wheel units through two separate circuits. Provides residual braking in the event of fluid loss The master cylinder is connected to the brake pedal via a pushrod. The ABS master cylinder is similar to the tandem master cylinder used in divided systems, and it has a primary piston and a secondary piston. The secondary piston incorporates a center valve, and it controls the opening and closing of a supply port drilling in the piston. At rest, the supply port is open and connects the reservoir with the front brake circuits, and the primary piston still has an inlet port and a compensating port. When the brake is applied, the primary piston moves, which closes its compensating port. Fluid pressure in the primary circuit rises, and it acts with the primary piston spring to move the secondary piston forward, closing the center valve. Pressure builds in the secondary circuit, and pressure keeps building in both circuits and applies the brakes in both circuits. If the secondary circuit fails, the secondary piston is forced to the end of the cylinder, and when it reaches the end, pressure builds in the primary circuit. If the primary circuit fails, the primary piston contacts the secondary piston and pushes it to operate the secondary circuit. During normal operation when the pedal is released, the springs in the master cylinder push the pistons back more quickly than the fluid can flow back from the wheel brake units. This creates a low pressure area in front of each piston, and such low-pressure areas can cause air to be drawn into the system. If the wheel sensors indicate that lowering the brake pressure is letting the wheel accelerate again, the ECU stops sending current to the hydraulic unit and de-energizes the solenoid valve. This lets the pressure increase, so that the wheel is again decelerated Jones & Bartlett Learning 2
3 To prevent this, there are recuperating grooves in the primary piston and the seal, and fluid at atmospheric pressure flows through the inlet port, past these grooves. When the primary piston is returned fully, any extra fluid coming back from the brake units displaces fluid into the reservoir, through the compensating port. In the secondary circuit, fluid also at atmospheric pressure is forced back into the inlet port and the inlet port connects with the supply port drilling in the piston. Any difference in pressure lifts the center valve from its seat, lets fluid enter the chamber ahead of the secondary seal, and prevents low pressures from developing. When the piston has returned to the rest position, the seal is pulled off its seat by the action of the link and spring, and this lets fluid, still returning from the wheel units, displace fluid back to the reservoir. If braking conditions are such that the hydraulic modulator must return brake fluid to the master cylinder, then, for the front brake circuits, fluid is returned to the front section. This forces the secondary piston back, against the force of the primary piston spring and the rear brake pressure, and if enough fluid returns, the center valve opens, and allows fluid to return to the reservoir. If fluid is returned from the rear brake circuit, the secondary and primary pistons tend to be forced apart. The amount of fluid that returns to the master cylinder is determined by the degree of antilock braking control, and with approximately four to six ABS control cycles per second, the rapid changes in pressure cause pulsations that can be felt by the driver at the brake pedal. Hydraulic Control Unit The hydraulic control unit, or modulator, executes commands in the form of electrical signals from the ABS control module and uses solenoid valves to change the hydraulic pressure in the brake circuit. The ABS control module, or ECU, sends commands in the form of electrical signals to the hydraulic control unit. The hydraulic control unit executes the commands, using three solenoid valves connected in series with the master cylinder and the brake circuits one valve for each front wheel hydraulic circuit and one valve for both of the rear wheels. In normal, non-abs braking, brake pedal force is transmitted to the master cylinder, then through the solenoid valve to the brake unit at the wheel. When the signals from the wheel speed sensor show no tendency for the wheel to lock up, the ECU does not send any control current to the solenoid coil. The solenoid valve is not energized, and the hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder is supplied to the brake unit at the wheel. When the control unit detects any lock up tendency, perhaps from too rapid wheel deceleration, it sends a command current to the solenoid coil. The command current causes the armature and valve to move upward and isolate the brake circuit from the master cylinder. That keeps the pressure between the solenoid and the brake circuit constant whether or not the master cylinder hydraulic pressure rises. If the sensors signal continuing excessive wheel deceleration, the control module sends a larger current to the solenoid valve. This current lowers the braking pressure by moving the armature up further, opening a passage from the brake circuit to an accumulator, which is a temporary reservoir for any brake fluid that flows out of the wheel brake cylinders due to a fall in pressure. A return pump sends this brake fluid back to the master cylinder. If the sensors then signal that the lower pressure has allowed the wheel to speed up, the ECU stops all command current, which de-energizes the solenoid valve. The pressure rises, and the wheel is again slowed down. Whatever the phase of operation, pressure in the circuit can never rise above the master cylinder pressure Jones & Bartlett Learning 3
4 Wheel Speed Sensors Wheel speed sensors consist of a toothed rotor and a pickup, and wheel rotation sends input signals to the ECU, which processes them and controls the hydraulic control unit. A wheel sensor consists of a toothed rotor that rotates with the wheels and a pickup, and as each tooth of the rotor passes the pickup, a small voltage is induced in the pickup. These pulses are sent as input signals to the ECU, which processes them to operate the hydraulic control unit. ABS Electronic Control Unit The ECU receives signals from various sources, and the brake pedal, the ignition system, and wheel speed sensors control the hydraulic control unit and anticipate wheel lock. A switch at the brake pedal provides a brakeoperating signal, and another switch in the ignition system signals the engine is operating. This sets off the automatic check the ABS conducts every time the engine starts. Another input comes from the wheel speed sensors, and these signals are used to control the hydraulic control unit and anticipate wheel lock. If a wheel starts to lock, the ECU operates the solenoid valves to reduce hydraulic pressure appropriately. Terms and Definitions The antilock braking system (ABS) is part of the service brake system that automatically controls the amount of rotational wheel slip during braking. The coefficient of friction is the grip that a tire has on a particular surface, and the higher the number, the greater the friction and the greater the stopping ability. Some examples include low friction surfaces, such as wet, icy, or snow-covered highways, and high friction surfaces, such as dry concrete pavement. Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) are federal requirements that apply to vehicles, including their brake systems and antilock brake systems. Note: FMVSS 105 governs hydraulic and electric brakes, and FMVSS121 governs air brakes. Both standards address antilock brake systems. Jackknife is a skid condition in which the tractortrailer combination brakes at different speeds, ultimately forming a 90 bend. The light-emitting diode (LED) is an electronic device that puts out light when a voltage is applied to it, and is commonly used on electronic displays. Lock up is the condition in which the brakes have stopped the wheels, but the momentum of the moving vehicle causes it to continue to move (skid). To modulate means to adjust or regulate a value (such as wheel speed) within a desired range. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) is the federal agency that monitors highway safety and mandates safety regulations. A sensor is an electronic device that responds to a physical stimulus (such as heat, light, movement, pressure, etc.) and then transmits a signal to a control device. Skid is the continued movement of the vehicle after wheel lock up. Split-coefficient surfaces are road conditions in which one wheel s side of the lane has a very different coefficient of friction from the other wheel s side. An example would be if the left half of the lane is wet, but the right half is icy or has icy patches. Traction is the adhesive friction between the tire and the surface on which it moves. Traction control is an optional feature available on some antilock brake systems that applies a braking force to a wheel that spins as a result of low traction. Transitional surfaces are road conditions that are quickly changing from one coefficient of friction to another. Some examples include icy to wet, dry to wet, and gravel to asphalt. Wheel slip is the difference between the vehicle speed and the wheel speed, expressed as a percentage Jones & Bartlett Learning 4
5 Purposes for an Antilock Brake System There are four purposes for having ABS: 1. To prevent wheels from locking up such as during panic stops 2. To prevent wheels from skidding such as on slippery road surfaces 3. To prevent jackknives when driving a combination vehicle 4. To maintain vehicle stability and steering control Basic Parts of an Antilock Brake System and Their Functions Exciters, tone rings, or toothed wheels (various names) are rings with notches or teeth that are read or sensed by the wheel speed sensor and are generally installed in the foundation brake area on the wheel or hub shaft. Wheel speed sensors are electromagnetic devices mounted at the wheel end or inside an axle that combine with the exciter ring to measure wheel speed and transmit the information to the ECU. They consist of two sensors per sensed axle. Modulator (control) valves are solenoid-type valves actuated by the ECU. Basic Operation of an Antilock Brake System The exciter (toothed) ring rotates with the wheel. The wheel sensor works with the exciter to generate an electrical signal regarding the wheel and vehicle speed that is sent to the ECU. The ECU constantly compares the actual wheel speed signal to the ideal wheel parameter identified in the ECU. If the ECU interprets information as normal (within range), operation continues. If the ECU interprets new information as abnormal (the wheels are turning at different speeds), a new signal is sent to the modulator or relay valve at the wheel. The modulator responds to the ECU message and adjusts the braking force. Two Ways to Describe Antilock Brake Systems There are two ways we describe antilock brake systems: 1. By number of channels or the number of ABS modulators, such that a two-channel system has two ABS modulators 2. By alphanumeric descriptors or the number of sensors (S) and number of modulators (M). Some examples would be 2S/1M (2 sensors, 1 modulator), 2S/2M (2 sensors, 2 modulators), and 4S/2M (4 sensors, 2 modulators) Jones & Bartlett Learning 5
6 ABS Timeline 1974: FMVSS 121 rule takes effect requiring specific brake performance on all new airbraked vehicles. ABS is designed to meet the new requirements. 1978: The Federal Court sets aside a stopping distance requirement, thereby ending the use of firstgeneration ABS devices : NHTSA begins research on the second generation of ABS; fleet testing begins : Congress orders the Department of Transportation (DOT)/NHTSA to pursue an ABS rule. The National Transportation Safety Board recommends mandating ABS. NHTSA publishes an advanced notice of rulemaking. 1995: NHTSA issues their final ABS rule, Stability and Control Requirements for Medium and Heavy Vehicles. 1997: From March 1, all new air-braked tractors must have ABS. 1998: From March 1, all new air-braked trailers must have ABS. 1999: From March 1, all new air-braked straight trucks, buses, dollies, and trailers must have ABS. 1999: From March 1, all new hydraulically braked straight trucks and buses over 10,000-lb GVWR must have ABS. 2001: From March 1, a dash-mounted trailer ABS warning light is required. 2009: From March 1, external ABS warning lights are no longer required on new trailers and dollies. Methods of Testing ABS Valves Different methods are used to test ABS valves, and all of the tests are manufacturer-specific. Consult the appropriate manufacturer s service manual for more information. A test blow-down sequence is a quick function check of the pneumatic valves of the ABS system and is performed in the following way. Apply and hold the brake pedal while the ignition is in the OFF position. While continuing to hold the pedal down, turn the ignition to the ON position (it is not necessary to start the engine). Listen for an exhaust pop of the application valves. This cannot be performed on all systems, and even among those that do pop, not all systems pop in the same order. Check the diagnostic display. A check for fault codes stored in the ECU if the system has on-board or remote diagnostic displays or devices Involves the use of the manufacturer s fault code lists to identify specific problems May use flashing blink codes or LED bar code lights to indicate the problem or may require electronic diagnostic readers/scan tools or computers/pcs to diagnose the problem Check the dash panel light sequence or trailer indicator lamp. Observed as the ignition key is turned to the ON position Provides the driver or service technician with a quick check of the electrical components of the ABS system The light sequence varies by manufacturer and build date of the vehicle. Some examples include when the light goes on-off-on and, when the vehicle is moved, the light goes off; and when the light goes on-off each time the brake pedal is applied (trailer systems). Variations such as continuous ON or continuous OFF indicate a system fault. Most Common Problems Associated with Antilock Brake Systems Wheel sensors are out of adjustment (usually there s an excessive air gap between the exciter ring and the sensor) and may be caused by excessive wheel end play from out-of-adjustment wheel bearings, may be displaced during service on nearby parts, or may be caused by freezing/refreezing of ice and snow. A worn or damaged sensor or modulator Faulty warning indicator lights A nonfunctioning ECU 2012 Jones & Bartlett Learning 6
7 Signs of Antilock Brake Failure Improper vehicle motion is when the brakes are applied on slippery surfaces; the vehicle skids, plows out, locks up, or experiences trailer swing; and the antilock brakes do not operate. Improper ABS braking is when the antilock system is activated unnecessarily, when normal braking should be possible. Visible signs of ABS damage include cracks, leaks, frayed wires, or other indications that can be seen by the driver or service technician. Instrument indicators are warning lights and diagnostic displays that alert the driver or service technician to malfunctions Jones & Bartlett Learning 7
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES. Section 9. Fundamental ABS Systems. ABS System Diagram
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master
1. INTRODUCTION. Anti-lock Braking System
 1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
Section 5 AIR BRAKES. This Section Covers. Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes
 Section 5 AIR BRAKES This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 AIR BRAKES This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking
 ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems
 Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
Automatic drain valves
 driving commercial vehicles If you notice more than a few drops of water when you drain the supply reservoir, the air dryer or compressor may need servicing. fast fact Even if the air brake system includes
driving commercial vehicles If you notice more than a few drops of water when you drain the supply reservoir, the air dryer or compressor may need servicing. fast fact Even if the air brake system includes
The parts of these systems are discussed in greater detail below.
 Section 5 Air Brakes This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
Section 5 Air Brakes This Section Covers Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting Air Brakes Using Air Brakes This section tells you about air brakes. If you want to drive a truck or bus
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM. Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
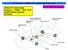
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
Anti Locking Brakes. Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK. Regd no:
 Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
Anti Locking Brakes Seminar by JYOTI RANJAN NAYAK Regd no: 0501227541 Introduction An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
SUBJECT: Automatic Stability Control with Traction Control System (ASC+T)
 Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 35B-5 INTRODUCTION TO 35B-5 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-5 DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION 35B-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 35B-5 INTRODUCTION TO 35B-5 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-5 DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION 35B-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice. Operating temperature - 40 C to 150 C - 40 C to 150 C
 489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
ENRESO.WORLD. Traction Control System. Created by Istas René - enreso.world. Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys
 ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
ATASA 5 th. ABS & Traction Control Systems. Please Read The Summary
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 51 Pages: 1506 1534 Antilock Brake Systems 59 Points Please Read The Summary Before We Begin Keeping in mind the Career Cluster of Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes. Course 105 PREVIEW ONLY PARTICIPANT GUIDE
 Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes Course 105 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Table of Contents How to Use the Participant Guide... ii MODULE 1...1 General Principles and Terminology...1 1-1 Safety Review...2
Introduction and Overview to Friction Brakes Course 105 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Table of Contents How to Use the Participant Guide... ii MODULE 1...1 General Principles and Terminology...1 1-1 Safety Review...2
ABS Operator s Manual
 ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
definition Retarders definition driving tip chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Using retarders
 chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Brake fade occurs when your brakes stop working properly because they're overheated. Your vehicle takes longer to stop, or may not stop at all if you haven't properly controlled
chapter 2 heavy vehicle braking Brake fade occurs when your brakes stop working properly because they're overheated. Your vehicle takes longer to stop, or may not stop at all if you haven't properly controlled
SD Bendix EC-14 AntiLock Controller Assembly DESCRIPTION GENERAL MOUNTING PHYSICAL
 Bendix EC-14 AntiLock Controller Assembly SD-13-4784 30 PIN WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR MOUNTING HOLES (4) DIAGSTICS WINDOW DESCRIPTION GENERAL Bendix trailer antilock systems utilizing the EC-14 electronic
Bendix EC-14 AntiLock Controller Assembly SD-13-4784 30 PIN WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR MOUNTING HOLES (4) DIAGSTICS WINDOW DESCRIPTION GENERAL Bendix trailer antilock systems utilizing the EC-14 electronic
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
 Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
Page 1 of 23 593: Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S241436824, 436824 16/7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw
Enhanced Easy-Stop TM with PLC Trailer ABS Training Program
 $2.50 Trailer ABS Enhanced Easy-Stop TM with PLC Trailer ABS Training Program Student Manual Issued 12-01 Module 1 General Information Module 2 Diagnostics and Repair Enhanced Easy-Stop with PLC Trailer
$2.50 Trailer ABS Enhanced Easy-Stop TM with PLC Trailer ABS Training Program Student Manual Issued 12-01 Module 1 General Information Module 2 Diagnostics and Repair Enhanced Easy-Stop with PLC Trailer
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES
 BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
To study about various types of braking system.
 To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION... 35C-16 CONSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION... 35C-5
 35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL)
 35C-1 GROUP 35C TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35C-2 DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 INTRODUCTION TO TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 TCL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35C-4 DIAGNOSTIC
35C-1 GROUP 35C TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35C-2 DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 INTRODUCTION TO TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35C-4 TCL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35C-4 DIAGNOSTIC
SECTION 4A BRAKE SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS
 SECTION 4A BRAKE SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS Description and Operation... 4A-2 Braking System Testing... 4A-2 Hydraulic Brake System... 4A-2 Brake Pedal... 4A-2 Master Cylinder... 4A-2 Brake Booster... 4A-3
SECTION 4A BRAKE SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS Description and Operation... 4A-2 Braking System Testing... 4A-2 Hydraulic Brake System... 4A-2 Brake Pedal... 4A-2 Master Cylinder... 4A-2 Brake Booster... 4A-3
AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES
 Section 5 AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES AIR BRAKES/Section 5 SECTION 5: AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION COVERS Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting
Section 5 AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES AIR BRAKES/Section 5 SECTION 5: AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION COVERS Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting
REV F2.0. User's Manual. Hydraulic ABS (HABS) Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) Page 1 of 28
 REV F2.0 User's Manual Hydraulic ABS (HABS) Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) Page 1 of 28 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...4 Starting TOOLBOX Software... 5 MAIN MENU...6 System Setup... 6 Language... 7 Select
REV F2.0 User's Manual Hydraulic ABS (HABS) Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) Page 1 of 28 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...4 Starting TOOLBOX Software... 5 MAIN MENU...6 System Setup... 6 Language... 7 Select
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
System overview. Introduction. Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved.
 "VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
"VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
MASTER CYLINDER. Section 2. Lesson Objectives
 MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
 TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
SD Bendix MC-12 Modulator Controller Assembly DESCRIPTION
 SD-13-4762 Bendix MC-12 Modulator Controller Assembly EC-12 CONTROLLER DIAGSTIC DISPLAY DIAGSTIC DISPLAY M-12 MODULATOR DELIVERY PORTS (4 VERTICAL) 14 PIN CONNECTOR CONTROL PORT DELIVERY PORTS (2 VERTICAL
SD-13-4762 Bendix MC-12 Modulator Controller Assembly EC-12 CONTROLLER DIAGSTIC DISPLAY DIAGSTIC DISPLAY M-12 MODULATOR DELIVERY PORTS (4 VERTICAL) 14 PIN CONNECTOR CONTROL PORT DELIVERY PORTS (2 VERTICAL
Department of Transportation. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. [Docket No. NHTSA ; Notice 2]
![Department of Transportation. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. [Docket No. NHTSA ; Notice 2] Department of Transportation. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. [Docket No. NHTSA ; Notice 2]](/thumbs/93/111796957.jpg) This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 04/04/2012 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2012-08000, and on FDsys.gov Department of Transportation National
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 04/04/2012 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2012-08000, and on FDsys.gov Department of Transportation National
Drive Right Chapter 5 Study Guide
 3/23/2008 Define Gravity. Define Center of Gravity. Define Energy of Motion Define Friction. Define Traction. How does gravity affect your car going uphill? What is Tread, and how is it affected when the
3/23/2008 Define Gravity. Define Center of Gravity. Define Energy of Motion Define Friction. Define Traction. How does gravity affect your car going uphill? What is Tread, and how is it affected when the
ABS, 4-ETS and EBP BRAKES ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 4-WHEEL ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (4-ETS) ELECTRONIC BRAKE PROPORTIONING (EBP)
 1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
8. Other system and brake theories
 8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
SD Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC Controllers (Standard & Premium Models) Frame and Cab Mount INTRODUCTION. Standard Frame Standard Cab.
 SD-13-4863 Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC Controllers (Standard & Premium Models) Frame and Cab Mount Standard Frame Standard Cab Premium Frame Premium Cab INTRODUCTION Bendix EC-60 controllers are members of
SD-13-4863 Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC Controllers (Standard & Premium Models) Frame and Cab Mount Standard Frame Standard Cab Premium Frame Premium Cab INTRODUCTION Bendix EC-60 controllers are members of
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
Service Manual Trucks
 Service Manual Trucks Group 593 502 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) MERITOR WABCO with E Version ECU VN/VHD PV776-TSP154520 Foreword The descriptions and service procedures contained in this manual are based
Service Manual Trucks Group 593 502 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) MERITOR WABCO with E Version ECU VN/VHD PV776-TSP154520 Foreword The descriptions and service procedures contained in this manual are based
1998 E-Series Workshop Manual
 SECTION 206-09A: Anti-Lock Control Rear DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 02/08/2000 Anti-Lock Control Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42, Speed Control for schematic and connector information.
SECTION 206-09A: Anti-Lock Control Rear DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 02/08/2000 Anti-Lock Control Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42, Speed Control for schematic and connector information.
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Self-diagnosis. Self-diagnosis BR-44 FUNCTION SELF-DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE ABS
 Self-diagnosis ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Self-diagnosis FUNCTION NABR0095 NABR0095S01 When a problem occurs in the, the warning lamp on the instrument panel comes on. To start the self-diagnostic
Self-diagnosis ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Self-diagnosis FUNCTION NABR0095 NABR0095S01 When a problem occurs in the, the warning lamp on the instrument panel comes on. To start the self-diagnostic
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function
 GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1992 Infiniti G20 1990-92 BRAKES Infiniti Anti-Lock Brake System Infiniti; G20, M30, Q45 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) prevents wheel lock-up during abrupt
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1992 Infiniti G20 1990-92 BRAKES Infiniti Anti-Lock Brake System Infiniti; G20, M30, Q45 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) prevents wheel lock-up during abrupt
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Diamante 1993 BRAKES Mitsubishi - Anti-Lock Brake System Diamante DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) is designed to prevent wheel lock-up during heavy braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1993 Mitsubishi Diamante 1993 BRAKES Mitsubishi - Anti-Lock Brake System Diamante DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) is designed to prevent wheel lock-up during heavy braking.
SECTION 4A HYDRAULIC BRAKES
 SECTION 4A HYDRAULIC BRAKES CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical
SECTION 4A HYDRAULIC BRAKES CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical
C. Brake pads Replaceable friction surfaces that are forced against the rotor by the caliper piston.
 BRAKES UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BRAKE SYSTEMS LESSON 1: FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF BRAKE SYSTEMS I. Terms and definitions A. Brake fading Loss of brakes, usually due to heat. B. Brake lining Material mounted
BRAKES UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BRAKE SYSTEMS LESSON 1: FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF BRAKE SYSTEMS I. Terms and definitions A. Brake fading Loss of brakes, usually due to heat. B. Brake lining Material mounted
SD Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC Controllers (Standard & Premium) Standard Frame. Standard Cab
 SD-13-4863 Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC Controllers (Standard & Premium) Frame Mount Cab Mount Standard Frame Standard Cab Two Connectors Are Used Premium Frame Premium Cab Three Connectors Are Used. (If all
SD-13-4863 Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC Controllers (Standard & Premium) Frame Mount Cab Mount Standard Frame Standard Cab Two Connectors Are Used Premium Frame Premium Cab Three Connectors Are Used. (If all
ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-3 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-4............ 35B-5 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-3 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-4............ 35B-5 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2................ 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................ 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2................ 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................ 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC
ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-4 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-5............ 35B-6 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-4 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-5............ 35B-6 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
Document ID# Chevrolet/Geo Corvette
 Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
SD Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly DESCRIPTION M-21 MODULATOR M-22 MODULATOR
 SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
SD-13-4793 Bendix M-21 and M-22 AntiLock Modulator Assembly CONNECTOR DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #3) DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #2) (CAST-IN ID #1) DELIVERY DELIVERY (CAST-IN ID #1) CONNECTOR MOUNTING
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION The Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is designed to aid the driver to maintain a gap from the vehicle ahead or a set road speed if there is no slower
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION The Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is designed to aid the driver to maintain a gap from the vehicle ahead or a set road speed if there is no slower
Module 6: Air Foundation Brakes
 Air Brakes Terms and Definitions Basic Components That Make Up Air Foundation Brakes Types of Air Foundation Brakes Parts of a Cam Foundation Brake Parts of a Wedge Foundation Brake Parts of a Disc Foundation
Air Brakes Terms and Definitions Basic Components That Make Up Air Foundation Brakes Types of Air Foundation Brakes Parts of a Cam Foundation Brake Parts of a Wedge Foundation Brake Parts of a Disc Foundation
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM
 200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION E94163 It is the drivers responsibility to stay alert, drive safely and be in control of the vehicle at all times. Keep the front of the vehicle free
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION E94163 It is the drivers responsibility to stay alert, drive safely and be in control of the vehicle at all times. Keep the front of the vehicle free
COVER. Bendix ATR-6 Antilock. Traction Relay Valves DELIVERY PORTS (6) FIGURE 1 - BENDIX ATR-6 (AND ATR-3 ) ANTILOCK TRACTION RELAY VALVES
 SD-13-4861 Bendix ATR-6 and ATR-3 Antilock Traction Relay Valves 2 PIN SOLENOID CONNECTOR Bendix ATR-3 Antilock Traction Relay Valves CONTROL SOLENOID CONTROL PORT COVER Bendix ATR-6 Antilock Traction
SD-13-4861 Bendix ATR-6 and ATR-3 Antilock Traction Relay Valves 2 PIN SOLENOID CONNECTOR Bendix ATR-3 Antilock Traction Relay Valves CONTROL SOLENOID CONTROL PORT COVER Bendix ATR-6 Antilock Traction
2006 Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC. Chassis and Drivetrain 42
 Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6
 35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 HYDRAULIC BRAKE BOOSTER (HBB) DIAGNOSIS...
 35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6 SYMPTOM CHART...................
35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6 SYMPTOM CHART...................
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages Brake Systems 49 Points. Automotive Service
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
ESCONDIDO FIRE DEPT TRAINING MANUAL Section DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 Pumps and Accessory Equipment Revised
 DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
TREAD and TRACTION. Tread- The grooved surface of a tire that grips the road.
 1 NAME: HOUR: DATE: NO: Chapter 5: Natural Laws and Car Control GRAVITY- Is the force that pulls all things to Earth. UPHILL DRIVING- Gravity will decrease your car down when going uphill, unless you use
1 NAME: HOUR: DATE: NO: Chapter 5: Natural Laws and Car Control GRAVITY- Is the force that pulls all things to Earth. UPHILL DRIVING- Gravity will decrease your car down when going uphill, unless you use
Antilock Brake System (ABS) Inspections
 Summary Created: May 19, 2010 Revised: Sept. 19, 2013 Revised: April 27, 2017 This Inspection Bulletin provides guidance for inspecting the antilock brake system (ABS) on a bus, truck, truck tractor, trailer
Summary Created: May 19, 2010 Revised: Sept. 19, 2013 Revised: April 27, 2017 This Inspection Bulletin provides guidance for inspecting the antilock brake system (ABS) on a bus, truck, truck tractor, trailer
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
SD Bendix Gen 4 and Gen 5 ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses GEN 4 AND GEN 5 ABS INTRODUCTION
 SD-- Bendix Gen and Gen ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses Cab-Mounted Models Frame-Mounted Model FIGURE - Bendix ABS Controller Assemblies GEN AND GEN ABS INTRODUCTION This manual describes both the
SD-- Bendix Gen and Gen ABS for Trucks, Tractors, and Buses Cab-Mounted Models Frame-Mounted Model FIGURE - Bendix ABS Controller Assemblies GEN AND GEN ABS INTRODUCTION This manual describes both the
Installation Guide. Installing the FRK Hydraulic Compact Unit (HCU) with Parking Brake Valve on International School Buses
 Revised 09-18 Installation Guide Revised 1 Technical 09-18 Bulletin Installing the FRK 08-10086 Hydraulic Compact Unit (HCU) with Parking Brake Valve on International School Buses Hazard Alert Messages
Revised 09-18 Installation Guide Revised 1 Technical 09-18 Bulletin Installing the FRK 08-10086 Hydraulic Compact Unit (HCU) with Parking Brake Valve on International School Buses Hazard Alert Messages
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) <2WD> ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM
 35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (5AT)
 (5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
(5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
POWER TRAIN 2-1 CONTENTS AYC SYSTEM... 9 CLUTCH... 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS... 4 FRONT AXLE... 5 REAR AXLE... 6
 2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-4
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 35B-2 DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35B-4 ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 35B-4
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) DIAGNOSIS.................... 35B-3 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................
35B-1 GROUP 35B ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) DIAGNOSIS.................... 35B-3 INTRODUCTION TO ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS................
R and R Meritor WABCO Enhanced Easy-Stop Trailer ABS Replacement Kits for Easy-Stop ECU/Modulator Valve Assembly Part Number
 Issued 06-03 Installation Guide Hazard Alert Messages Read and observe all Warning and Caution hazard alert messages in this publication. They provide information that can help prevent serious personal
Issued 06-03 Installation Guide Hazard Alert Messages Read and observe all Warning and Caution hazard alert messages in this publication. They provide information that can help prevent serious personal
International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes
 A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes Study Guide TMT-040701 Study Guide International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes TMT-040701 2007 International
A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes Study Guide TMT-040701 Study Guide International Medium Duty Full Power Hydraulic Brakes TMT-040701 2007 International
1994 Mazda MX-5 Miata. ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1994 BRAKES Mazda - Anti-Lock
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1994 BRAKES Mazda - Anti-Lock DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) control unit senses reductions in front and rear wheel speed and modulates hydraulic pressure to the brakes
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 1994 BRAKES Mazda - Anti-Lock DESCRIPTION The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) control unit senses reductions in front and rear wheel speed and modulates hydraulic pressure to the brakes
Battery Operation. Battery Construction. Battery State Of Charge. Battery Load Test. Battery Rating Systems 2/14/12
 Battery Operation Batteries, Charging and Donald Jones Brookhaven College Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy During discharge the battery s plate composition is changed During charging
Battery Operation Batteries, Charging and Donald Jones Brookhaven College Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy During discharge the battery s plate composition is changed During charging
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
three different ways, so it is important to be aware of how flow is to be specified
 Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION
 4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
COASTAL BEND COLLEGE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS (rev. Fall 2012)
 COASTAL BEND COLLEGE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS (rev. Fall 2012) AUMT 1310: Automotive Brake Systems SEMESTER HOURS: 3 TEXTBOOK Automotive Technology A systems Approach COURSE DESCRIPTION; Operation
COASTAL BEND COLLEGE AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS (rev. Fall 2012) AUMT 1310: Automotive Brake Systems SEMESTER HOURS: 3 TEXTBOOK Automotive Technology A systems Approach COURSE DESCRIPTION; Operation
DESCRIPTION. Chrysler NCV3 Service Info Section 08 > Electronic Modules > MODULE, Transmission Control Information
 DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
How Regenerative Braking Works
 Feature How Regenerative Braking Works The regenerative braking systems on Nissan hybrid vehicles can be confusing and misunderstood. Let s take a look at how these systems really work. 26 Nissan TechNews
Feature How Regenerative Braking Works The regenerative braking systems on Nissan hybrid vehicles can be confusing and misunderstood. Let s take a look at how these systems really work. 26 Nissan TechNews
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION WARNING Adaptive Cruise Control is not a collision warning or avoidance system. Additionally, Adaptive Cruise Control will not detect: stationary or
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION WARNING Adaptive Cruise Control is not a collision warning or avoidance system. Additionally, Adaptive Cruise Control will not detect: stationary or
 8803214-8803999 DIODE BOARD The diode board is located inside the lower control box. D15 D8 D7 D14 D5 D13 ART_2181 J1 14 8 D9 D10 7 1 R2 R1 R3 R4 TB1 8601 D11 D3 D12 D4 D1 D2 J1 Plug Pin Identification
8803214-8803999 DIODE BOARD The diode board is located inside the lower control box. D15 D8 D7 D14 D5 D13 ART_2181 J1 14 8 D9 D10 7 1 R2 R1 R3 R4 TB1 8601 D11 D3 D12 D4 D1 D2 J1 Plug Pin Identification
 DIODE BOARD The diode board is located inside the lower control box. D15 D8 D7 D14 D5 D13 ART_2181 J1 14 8 D9 D10 7 1 R2 R1 R3 R4 TB1 8601 D11 D3 D12 D4 D1 D2 J1 Plug Pin Identification PIN # WIRE # SIGNAL
DIODE BOARD The diode board is located inside the lower control box. D15 D8 D7 D14 D5 D13 ART_2181 J1 14 8 D9 D10 7 1 R2 R1 R3 R4 TB1 8601 D11 D3 D12 D4 D1 D2 J1 Plug Pin Identification PIN # WIRE # SIGNAL
Hydro-Max Hydraulic Brake Booster and Master Cylinder. Technical Manual
 Hydro-Max Hydraulic Brake Booster and Master Cylinder Technical Manual * 5+0 Important Service Notes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information presented in
Hydro-Max Hydraulic Brake Booster and Master Cylinder Technical Manual * 5+0 Important Service Notes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information presented in
NATEF Task List - Medium/Heavy Duty Truck Brakes
 The first task in is to listen to and verify the operator s concern, review past maintenance and repair documents, and determine necessary III. BRAKES A. Air 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. Air Supply and
The first task in is to listen to and verify the operator s concern, review past maintenance and repair documents, and determine necessary III. BRAKES A. Air 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. Air Supply and
Read on to find out more about each component of the Star Safety System and how it can be of benefit to you.
 All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
 DN SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO....2 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES...2 BRAKE LAMP
DN SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO....2 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES...2 BRAKE LAMP
Ch 4 Motor Control Devices
 Ch 4 Motor Control Devices Part 1 Manually Operated Switches 1. List three examples of primary motor control devices. (P 66) Answer: Motor contactor, starter, and controller or anything that control the
Ch 4 Motor Control Devices Part 1 Manually Operated Switches 1. List three examples of primary motor control devices. (P 66) Answer: Motor contactor, starter, and controller or anything that control the
Air Brake Manual. Training & Reference Guide. For vehicles with air brake systems.
 Air Brake Manual Training & Reference Guide 2007 For vehicles with air brake systems A supplement to the Basic Licence Driver s Handbook www.dot.gov.nt.ca Table of Contents CHAPTER Brakes and Braking Heat-energy-traction-friction....
Air Brake Manual Training & Reference Guide 2007 For vehicles with air brake systems A supplement to the Basic Licence Driver s Handbook www.dot.gov.nt.ca Table of Contents CHAPTER Brakes and Braking Heat-energy-traction-friction....
