Principles of Engine Operation. Information
|
|
|
- Stewart Patterson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı Maslak Kampüsü, Ayazağa İstanbul Tel
2 Course Plan Principles of SI and CI engine operation, 2-stroke engines, 4-stroke engines Ideal standard cycles, thermal efficiencies, comparison, deviations Classification of engine fuels Characteristics of engine fuels, knock resistance, ignition tendancy, ccombustion chemistry (air excess ratio, calorific value, adiabatic flame temperature, dissociation) Real engine strokes, induction stroke, volumetric efficiency Compression stroke, combustion in SI engines and influencing parameters Abnormal combustion, parameters influencing knock and early ignition Combustion in CI engines, parameters influencing ignition delay Expension and exhaust strokes, exhaust emissions Mixture preparation in SI engines Carburator fundamentals, fuel injection, control of A/F ratio Mixture preparation in CI engines, injection pumps, injectors Fuel injection systems in Diesel engines, Atomization, combustion chamber types in Diesel engines Engine characteristics and performance. Assessment Criteria Percentage Quiz 5 x 10 = 50 % Final examination 50 % 2
3 References Textbook Heywood, J.B., Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals, McGraw Hill Book Company, New York, Soruşbay, C., IC Engine, Lecture Notes, İ.T.Ü., 2001 (soft copy). Other References Soruşbay, C. et al., İçten Yanmalı Motorlar, Birsen Yayınevi, İstanbul, Pulkrabek, W.W., Engineering Fundamentals of the Internal Combustion Engine, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, Stone, R., Introduction to Internal Combustion Engines, Macmillan, London, Other references given in the list (see web page of the course) Internal Combustion Engines MAK 493E Principles of IC Engine Operation Introduction Operation principles Classification of engines Four-stroke and two-stroke engines SI engines, CI engines 3
4 Introduction Internal Combustion Engines (IC-engines) produce mechanical power from the chemical energy contained in the fuel, as a result of the combustion process occuring inside the engine IC engine converts chemical energy of the fuel into mechanical energy, usually made available on a rotating output shaft. Chemical energy of the fuel is first converted to thermal energy by means of combustion or oxidation with air inside the engine, raising the T and p of the gases within the combustion chamber. The high-pressure gas then expands and by mechanical mechanisms rotates the crankshaft, which is the output of the engine. Crankshaft is connected to a transmission/power-train to transmit the rotating mechanical energy to drive a vehicle. Spark ignition ( SI ) engines Otto or gasoline engines Compression ignition ( CI ) engines Diesel engines Introduction Most of the internal combustion engines are reciprocating engines with a piston that reciprocate back and forth in the cylinder. Combustion process takes place in the cylinder. There are also rotary engines In external combustion engines, the combustion process takes place outside the mechanical engine system 4
5 Early History Atmospheric engines Earliest IC engines of the 17th and 18th centuries are classified as atmospheric engines. These are large engines with a single cylinder which is open on one end. Combustion is initiated at the open cylinder and immediately after combustion, cylinder would be full of hot gases at atmospheric pressure. The cylinder end is closed at this time and trapped gases are allowed to cool. As the gases are cooled, vacuum is created within the cylinder causing pressure differential across the piston (atmospheric pressure on one side and vacuum on the other side). So piston moves due to this pressure difference doing work. Early History 5
6 Early History Huygens (1673) Hautefeuille (1676) Papin (1695) Modern engines Lenoir (1860) Rochas (1862) Otto Langen (1867) Otto (1876) Clark (1878) Diesel (1892) Daimler/Maybach (1882) developed piston mechanism first concept of internal combustion engine first to use steam in piston mechaanism using same principles of operation as present engines previously no compression cycle driving the piston by the expansion of burning products - first practical engine, 0.5 HP later 4.5 kw engines with mech efficiency up to 5% four-stroke concept was proposed produced various engine improved efficiency to 11% Four-stroke engine prototype built, 8 HP and patented Two-stroke engine was developed Single cylinder, compression ignition engine Incorporated IC engine in automobile Introduction V C V D V T clearence volume displacement volume total volume D L bore stroke TDC BDC top dead center bottom dead center 6
7 Introduction A single cylinder 4-stroke engine Introduction 7
8 Introduction a single cylinder, 4-stroke engine Introduction a Diesel engine 8
9 Introduction Introduction 9
10 Classification of Engines By application motorcycles, scooters, kw, SI, 2- and 4-stroke passenger cars, kw, SI and CI, 4-stroke light commercial vehicles, kw, SI and CI, 4-stroke heavy commercial vehicles, kw, Diesel, 4 zamanlı locomotives, kw, CI, 4-stroke ships, kw, CI, 2- and 4-stroke airplanes, kw, SI, 4-stroke stationary engines, kw, CI, 2- and 4-stroke Classification of Engines Basic engine design Reciprocating engines, subdivided by arrangement of cylinders Rotary engines 10
11 Classification of Engines Single-cylinder engine Otto gasoline engine Classification of Engines Single-cylinder test engine 11
12 Classification of Engines In-line engine Classification of Engines In-line engine 12
13 Classification of Engines Opposed piston engine Classification of Engines V - engine 13
14 Classification of Engines V engine Ferrari V8 90 o engine 360 Modena 3586 cc Bore/Stroke 85/79 mm 294 kw ( rpm rpm Classification of Engines Ferrari V8 90 o engine 360 Modena 3586 cc 14
15 Classification of Engines V engine Ferrari V12 65 o engine 375 kw ( rpm 550 Barchetta Pininfarina rpm Bore/Stroke 86/75 mm 5474 cc Classification of Engines Radial engine 15
16 Classification of Engines Radial engine Rotary Engines Wankel engine (Felix Wankel, prototype in 1929, patented double rotor in 1934) 16
17 Rotary Engines Rotary Engines Mazda Rx hp engine Triple rotor engine by Mazda 17
18 Classification of Engines Working cycle four-stroke cycle, complete cycle in 720 O CA naturally aspirated, supercharged, turbocharged two-stroke cycle, complete cycle in 360 O CA crankcase scavenged, supercharged, turbocharged Classification of Engines Turbocharched engine 18
19 Classification of Engines Method of ignition SI engines, mixture is uniform (conventional engines), mixture is non-uniform (stratified-charge engines) ignition is by the application of external energy (to spark plug) CI engines, ignition by compression in conventional engine (Diesel engine), pilot injection of fuel in gas engines (eg, natural gas and diesel fuel dual fuel engines) Classification of Engines Engine speed low speed engines, r.p.m. ships, stationary engines medium speed engines, r.p.m generally Diesel engines, small marine applications, stationary engines, earth moving vehicles high speed engines, r.p.m. passenger cars 19
20 Classification of Engines Method of cooling, liquid cooled, water cooled engines air cooled engines Classification of Engines Air intake process, naturally aspirated engines supercharged engines turbocharged engines crankcase compressed 20
21 Air / Air Intercooler Turbocharger with EGR system turbocharged engines Air filter Intake manifold Engine Exhaust manifold EGR valve EGR cooler Particulate trap NOx sensor p sensor Classification of Engines Fuel used, gasoline engines diesel engines natural gas (CNG and LNG), methane, LPG engines alcohol engines hydrogen engines 21
22 Classification of Engines natural gas engines Classification of Engines natural gas engines 22
23 Four-stroke SI-Engines Intake stroke Starts with the movement of the piston from TDC to BDC, while drawing fresh charge (air + fuel mixture) into the cylinder through the open inlet valve. To increase the mass inducted, inlet valve opens for a period of O CA Four-stroke SI-Engines Compression stroke when both valves are closed, the mixture inside the cylinder is compressed to a small fraction of its initial volume by the movement of the piston (12:1). Towards the end of compression stroke, combustion is initiated by a spark at the spark plug and cylinder pressure rises rapidly. At the end of compression the gas temperature is around K and pressure is MPa 23
24 Four-stroke SI-Engines Power and expansion stroke Combustion starts with the ignition of the mixture, usually before TDC. During combustion process high temperature, high pressure gases push the piston towards BDC and force the crank to rotate. Maximum temperature of K and pressure of 3 7 MPa is reached in the cylinder. Four-stroke SI-Engines Exhaust stroke The burned gases exit the cylinder through the open exhaust valve, due to the pressure difference at first and then swept by the piston movement from BDC to TDC Exhaust valve closes after TDC (stays open for O CA) At the end of exhaust stroke gas temperature is K and gas pressure MPa 24
25 Four-stroke Cycle CLOSED DIAGRAM INTAKE STROKE (1) COMPRESSION STROKE (2) POWER-EXPANSION STROKE (3) EXHAUST STROKE (4) Combustion in SI-Engines OPEN DIAGRAM 25
26 Four-stroke CI-Engines Intake stroke Starts with the movement of the piston from TDC to BDC, while drawing only air into the cylinder through the open inlet valve. The cylinder pressure is MPa To increase the mass inducted, inlet valve opens for a period of O CA Compression stroke When both valves are closed, cylinder contents are compressed (14:1 24:1). At the end of compression the gas temperature is around K and pressure is MPa Four-stroke CI-Engines Power and expansion stroke Combustion starts with the injection of the fuel spray into the combustion chamber, usually before TDC with certain injection advance. There is ignition delay before combustion starts. During combustion process high temperature, high pressure gases push the piston towards BDC and force the crank to rotate. Maximum temperature of K and pressure of 4 8 MPa (IDI engines) and 7 10 MPa (DI engines) is reached in the cylinder. Exhaust stroke Exhaust valve opens and combustion products exit cylinder. The stay open for O CA. The gas temperature is around K and pressure is MPa 26
27 Combustion in CI-Engines Two-stroke Cycle COMPRESSION STROKE (1) POWER-EXPANSION STROKE (2) 27
28 Two-stroke Engine Two-stroke Engine 28
29 Two-stroke Engine Two-stroke Engine 29
Spark Ignition Engine Combustion
 Spark Ignition Engine Combustion MAK 652E Introduction to Combustion Process in Engines Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University - Automotive Laboratories Contents Course information Combustion
Spark Ignition Engine Combustion MAK 652E Introduction to Combustion Process in Engines Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University - Automotive Laboratories Contents Course information Combustion
Internal Combustion Engine. Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST
 Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Internal Combustion Engines
 Introduction Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will learn about: Definition of internal combustion Development of the internal combustion engine Different engine classifications We will also draw
Introduction Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will learn about: Definition of internal combustion Development of the internal combustion engine Different engine classifications We will also draw
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
Introduction. Internal Combustion Engines
 Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines A heat engine that converts chemical energy in a fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy first converted into thermal energy (Combustion)
Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines A heat engine that converts chemical energy in a fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy first converted into thermal energy (Combustion)
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
Kul Internal Combustion Engine Technology. Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5
 Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Kul-14.4100 Internal Combustion Engine Technology Definition & Classification, Characteristics 2015 Basshuysen 1,2,3,4,5 Definitions Combustion engines convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Combustion engines. Combustion
 Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1. Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Template for the Storyboard stage
 Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
I.C ENGINES. CLASSIFICATION I.C Engines are classified according to:
 I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, April/May-2017 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts
2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines
 Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
AME 436. Energy and Propulsion. Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters
 AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
AME 436. Energy and Propulsion. Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters
 AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
AME 436 Energy and Propulsion Lecture 6 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 1: Basic operating principles, design & performance parameters Outline Classification of unsteady-flow engines Basic operating
Internal Combustion Engines
 Lecture-19 Prepared under QIP-CD Cell Project Internal Combustion Engines Ujjwal K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati 1 Background The power output
Lecture-19 Prepared under QIP-CD Cell Project Internal Combustion Engines Ujjwal K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati 1 Background The power output
EEN-E2002 Internal Combustion Definitions and Characteristics, lecture 3. January 2017, Martti Larmi
 EEN-E2002 Internal Combustion Definitions and Characteristics, lecture 3 January 2017, Martti Larmi Textbooks on Internal Combustion Internal combustion engine handbook : basics, components, systems, and
EEN-E2002 Internal Combustion Definitions and Characteristics, lecture 3 January 2017, Martti Larmi Textbooks on Internal Combustion Internal combustion engine handbook : basics, components, systems, and
L34: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Introduction to Gas Cycles Definitions
 Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Page L: Internal Combustion Engine Cycles: Otto, Diesel, and Dual or Gas Power Cycles Review of Carnot Power Cycle (gas version) Air-Standard Cycles Internal Combustion (IC) Engines - Otto and Diesel Cycles
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines
 Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
LECTURE NOTES INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION
 LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
2. Discuss the effects of the following operating variables on detonation
 Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: RR220303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2006 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF MECHANICAL AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION By Desta Lemma (BSc, MSc) Introduction
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF MECHANICAL AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION By Desta Lemma (BSc, MSc) Introduction
ACTUAL CYCLE. Actual engine cycle
 1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
Al-Balqa Applied University
 تا سست عام 997 Specialization Common Course Number 202073 Course Title Internal Combustion Engines Credit Hours 3 Theoretical Hours 3 Practical Hours 0 صفحة () من (0) تا سست عام 997 Brief Course Description:
تا سست عام 997 Specialization Common Course Number 202073 Course Title Internal Combustion Engines Credit Hours 3 Theoretical Hours 3 Practical Hours 0 صفحة () من (0) تا سست عام 997 Brief Course Description:
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]
![(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16] (a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]](/thumbs/79/80273804.jpg) Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
2.61 Internal Combustion Engines
 Due: Thursday, February 19, 2004 2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Problem Set 2 Tuesday, February 10, 2004 1. Several velocities, time, and length scales are useful in understanding what goes on inside
Due: Thursday, February 19, 2004 2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Problem Set 2 Tuesday, February 10, 2004 1. Several velocities, time, and length scales are useful in understanding what goes on inside
Engine Cycles. T Alrayyes
 Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Engine Cycles T Alrayyes Introduction The cycle experienced in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is very complex. The cycle in SI and diesel engine were discussed in detail in the previous
Internal Combustion Engines
 Engine Cycles Lecture Outline In this lecture we will: Analyse actual air fuel engine cycle: -Stroke cycle -Stroke cycle Compare these cycles to air standard cycles Actual Engine Cycle Although air standard
Engine Cycles Lecture Outline In this lecture we will: Analyse actual air fuel engine cycle: -Stroke cycle -Stroke cycle Compare these cycles to air standard cycles Actual Engine Cycle Although air standard
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines
 Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines Aravind. I. Garagad. Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College of Engineering and Technology, Dharwad, Karnataka, India. ABSTRACT Large reductions
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines Aravind. I. Garagad. Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College of Engineering and Technology, Dharwad, Karnataka, India. ABSTRACT Large reductions
COMBUSTION in SI ENGINES
 Internal Combustion Engines MAK 493E COMBUSTION in SI ENGINES Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Internal Combustion Engines MAK 493E Combustion in SI Engines Introduction Classification
Internal Combustion Engines MAK 493E COMBUSTION in SI ENGINES Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Internal Combustion Engines MAK 493E Combustion in SI Engines Introduction Classification
Air Cooled Engine Technology. Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94
 Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94 1. The of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to another. Either TDC to BDC (downstroke) or BDC to TDC (upstroke). Identified
Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94 1. The of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to another. Either TDC to BDC (downstroke) or BDC to TDC (upstroke). Identified
Which are the four important control loops of an spark ignition (SI) engine?
 151-0567-00 Engine Systems (HS 2017) Exercise 1 Topic: Lecture 1 Johannes Ritzmann (jritzman@ethz.ch), Raffi Hedinger (hraffael@ethz.ch); October 13, 2017 Problem 1 (Control Systems) Why do we use control
151-0567-00 Engine Systems (HS 2017) Exercise 1 Topic: Lecture 1 Johannes Ritzmann (jritzman@ethz.ch), Raffi Hedinger (hraffael@ethz.ch); October 13, 2017 Problem 1 (Control Systems) Why do we use control
A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE
 A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE Prakash Kumar Sen 1, Lalit Kumar 2, Shailendra Kumar Bohidar 3 1 Student of M.Tech. Manufacturing Management, BITS Pilani (India) 2 Student of Mechanical
A REVIEW OF SCAVENGING PROCESS OF TWO STROKE ENGINE Prakash Kumar Sen 1, Lalit Kumar 2, Shailendra Kumar Bohidar 3 1 Student of M.Tech. Manufacturing Management, BITS Pilani (India) 2 Student of Mechanical
California State University, Bakersfield. Signals and Systems. Kristin Koehler. California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013
 Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS
 Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
4. With a neat sketch explain in detail about the different types of fuel injection system used in SI engines. (May 2016)
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
Lecture 5. Abnormal Combustion
 Lecture 5 Abnormal Combustion Abnormal Combustion The Abnormal Combustion:- When the combustion gets deviated from the normal behavior resulting loss of performance or damage to the engine. It is happened
Lecture 5 Abnormal Combustion Abnormal Combustion The Abnormal Combustion:- When the combustion gets deviated from the normal behavior resulting loss of performance or damage to the engine. It is happened
Combustion Systems What we might have learned
 Combustion Systems What we might have learned IMechE ADSC, 6 December 2012 Chris Whelan Contents Engines Big & Small Carnot, Otto & Diesel Thermodynamic Cycles Combustion Process & Systems Diesel & Otto
Combustion Systems What we might have learned IMechE ADSC, 6 December 2012 Chris Whelan Contents Engines Big & Small Carnot, Otto & Diesel Thermodynamic Cycles Combustion Process & Systems Diesel & Otto
MEL345 I.C. ENGINES. Course Instructor : Prof. J.P. Subrahmanyam. II Next to I.C. Engines Laboratory.
 MEL345 I.C. ENGINES Course Instructor : Prof. J.P. Subrahmanyam II-154 - Next to I.C. Engines Laboratory jp_sub@yahoo.com jpsm@mech.iitd.ernet.in Course Coordinator : Prof. M.R. Ravi II 257; ravimr@iitd.ac.in
MEL345 I.C. ENGINES Course Instructor : Prof. J.P. Subrahmanyam II-154 - Next to I.C. Engines Laboratory jp_sub@yahoo.com jpsm@mech.iitd.ernet.in Course Coordinator : Prof. M.R. Ravi II 257; ravimr@iitd.ac.in
OBJECTIVE: GENERAL ASPECTS ABOUT ENGINES MECHANISM:
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
COURSE NUMBER & COURSE TITLE: ME 300 Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engine
 COURSE NUMBER & COURSE TITLE: ME 300 Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engine INSTRUCTOR: Xingcai Lu, Xinqi Credits: 3 Qiao REQUIRED COURSE OR ELECTIVE COURSE: Required COURSE STRUCTURE/SCHEDULE: 1.
COURSE NUMBER & COURSE TITLE: ME 300 Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engine INSTRUCTOR: Xingcai Lu, Xinqi Credits: 3 Qiao REQUIRED COURSE OR ELECTIVE COURSE: Required COURSE STRUCTURE/SCHEDULE: 1.
Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes:
 Classification of thermodynamics cycles Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes: Gas and vapor cycles - Gas cycle: the working
Classification of thermodynamics cycles Thermodynamics cycles can be classified into different categories depending on fluid used or the different processes: Gas and vapor cycles - Gas cycle: the working
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles
 Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
Assignment-1 Air Standard Cycles 1. What do u mean by air standard cycle? List assumptions for air standard cycle & give reasons why air standard cycle differs from actual cycle. 2. Derive an equation
Assignment-1 Introduction
 Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Assignment-1 Introduction 1. Compare S.I. engines with C.I engines. 2. Explain with the help of neat sketch, the working of a 2-stroke petrol engine. 3. Derive an equation of efficiency, work output and
Engine Design Classifications
 Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Chapter 4 ANALYTICAL WORK: COMBUSTION MODELING
 a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
AT AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK
 AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
AT6301 - AUTOMOTIVE ENGINES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: CONSTRUCTION & WORKING PRINCIPLE OF IC ENGINES 1. State the application of CI engines? 2. What is Cubic capacity of an engine? 3. What is the purpose of
SELECTION OF PROPULSION SYSTEMS FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS. Pierre Duysinx LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic Year
 SELECTION OF PROPULSION SYSTEMS FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS Pierre Duysinx LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic Year 2015-2016 1 Bibliography R. Bosch. «Automotive Handbook». 5th edition. 2002. Society
SELECTION OF PROPULSION SYSTEMS FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS Pierre Duysinx LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic Year 2015-2016 1 Bibliography R. Bosch. «Automotive Handbook». 5th edition. 2002. Society
New Polytechnic, Kolhapur
 01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 16 marks Content 1.1 Introduction 4 Marks Definition of I C engine. Engine nomenclature. 1.2 The working principle of Engine 6 Marks Four-Stroke
01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 01. Fundamentals of I.C. Engine 16 marks Content 1.1 Introduction 4 Marks Definition of I C engine. Engine nomenclature. 1.2 The working principle of Engine 6 Marks Four-Stroke
Topic Page: Internal Combustion Engine
 Topic Page: Internal Combustion Engine Definition: internal combustion engine from Dictionary of Energy Transportation. an engine in which the process of combustion takes place in a cylinder or cylinders
Topic Page: Internal Combustion Engine Definition: internal combustion engine from Dictionary of Energy Transportation. an engine in which the process of combustion takes place in a cylinder or cylinders
CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES
 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
IC ENGINES. Differences between SI and CI engines: Petrol is fuel, which has a high self ignition temperature
 IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
IC ENGINES SI Engines work at constant volume. They have a compression ratio of around 6-10. But CI engines work at constant pressure and has a compression ratio of 16-20. In four stroke engines, one power
Heat Transfer in Engines. Internal Combustion Engines
 Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
SUPERCHARGER AND TURBOCHARGER
 SUPERCHARGER AND TURBOCHARGER 1 Turbocharger and supercharger 2 To increase the output of any engine more fuel can be burned and make bigger explosion in every cycle. i. One way to add power is to build
SUPERCHARGER AND TURBOCHARGER 1 Turbocharger and supercharger 2 To increase the output of any engine more fuel can be burned and make bigger explosion in every cycle. i. One way to add power is to build
REVIEW STUDY ON EXHAUST OF A DIESEL ENGINE THERMAL STORAGE
 REVIEW STUDY ON EXHAUST OF A DIESEL ENGINE THERMAL STORAGE Prateek Jain 1, Sushil Yadav 2, Durgesh Singh 3 1,2 B.Tech. Scholar, 3 Assistant Professor, Vedant College of Engineering and Technology, Bundi,
REVIEW STUDY ON EXHAUST OF A DIESEL ENGINE THERMAL STORAGE Prateek Jain 1, Sushil Yadav 2, Durgesh Singh 3 1,2 B.Tech. Scholar, 3 Assistant Professor, Vedant College of Engineering and Technology, Bundi,
density ratio of 1.5.
 Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Problem 1: An 8cyl 426 ci Hemi motor makes 426 HP at 5500 rpm on a compression ratio of 10.5:1. It is over square by 10% meaning that it s stroke is 10% less than it s bore. It s volumetric efficiency
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Week 10. Gas Power Cycles. ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1
 Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Week 10 Gas Power Cycles ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Today s Outline Gas power cycles Internal combustion engines Four-stroke cycle Thermodynamic cycles Ideal cycle ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Gas Power
Gas Power System. By Ertanto Vetra
 Gas Power System 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Otto Cycles Diesel Cycles Gas Turbine Cycles Gas Turbine Based Combined Cycles Gas Turbines for Aircrafts Turbojets
Gas Power System 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Otto Cycles Diesel Cycles Gas Turbine Cycles Gas Turbine Based Combined Cycles Gas Turbines for Aircrafts Turbojets
Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Air-standard cycles Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje CH. 2 ۱ Cold-air-standard assumptions: When the working fluid is considered to be air with constant specific heats at room temperature (25 C). Air-standard
Air-standard cycles Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje CH. 2 ۱ Cold-air-standard assumptions: When the working fluid is considered to be air with constant specific heats at room temperature (25 C). Air-standard
COMBUSTION AND EXHAUST EMISSION IN COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINES WITH DUAL- FUEL SYSTEM
 COMBUSTION AND EXHAUST EMISSION IN COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINES WITH DUAL- FUEL SYSTEM WLADYSLAW MITIANIEC CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINE-EXPO 2008 OPEN TECHNOLOGY FORUM STUTTGAT, 7 MAY 2008 APPLICATIONS
COMBUSTION AND EXHAUST EMISSION IN COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINES WITH DUAL- FUEL SYSTEM WLADYSLAW MITIANIEC CRACOW UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINE-EXPO 2008 OPEN TECHNOLOGY FORUM STUTTGAT, 7 MAY 2008 APPLICATIONS
INFLUENCE OF INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON HCCI COMBUSTION PROCESS USING BIOETHANOL
 ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 2.-27..216. INFLUENCE OF INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON HCCI COMBUSTION PROCESS USING BIOETHANOL Kastytis Laurinaitis, Stasys Slavinskas
ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 2.-27..216. INFLUENCE OF INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON HCCI COMBUSTION PROCESS USING BIOETHANOL Kastytis Laurinaitis, Stasys Slavinskas
EEN-E2002 Combustion Technology 2017 LE 3 answers
 EEN-E2002 Combustion Technology 2017 LE 3 answers 1. Plot the following graphs from LEO-1 engine with data (Excel_sheet_data) attached on my courses? (12 p.) a. Draw cyclic pressure curve. Also non-fired
EEN-E2002 Combustion Technology 2017 LE 3 answers 1. Plot the following graphs from LEO-1 engine with data (Excel_sheet_data) attached on my courses? (12 p.) a. Draw cyclic pressure curve. Also non-fired
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle
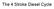 The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
Experimental Investigation of Performance and Emissions of a Stratified Charge CNG Direct Injection Engine with Turbocharger
 MATEC Web of Conferences 1, 7 (17 ) DOI:1.11/matecconf/1717 ICTTE 17 Experimental Investigation of Performance and Emissions of a Stratified Charge CNG Direct Injection Engine with charger Hilmi Amiruddin
MATEC Web of Conferences 1, 7 (17 ) DOI:1.11/matecconf/1717 ICTTE 17 Experimental Investigation of Performance and Emissions of a Stratified Charge CNG Direct Injection Engine with charger Hilmi Amiruddin
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies. Turbochargers
 Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 320 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged, Lean-burn, Hydrogen-fuelled, Direct Injection Engines
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 29 (2012 ) 455 462 World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2012 Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 29 (2012 ) 455 462 World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2012 Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged,
Evaluation Of Parameters Affecting The Performance Of Spark-Ignition Engine BY Bello Lawal And Dr. Isa Garba
 Evaluation Of Parameters Affecting The Performance Of Spark-Ignition Engine BY Bello Lawal And Dr. Isa Garba ABSTRACT This paper focused on the performance of a spark-ignition (engine, which is affected
Evaluation Of Parameters Affecting The Performance Of Spark-Ignition Engine BY Bello Lawal And Dr. Isa Garba ABSTRACT This paper focused on the performance of a spark-ignition (engine, which is affected
Internal Combustion Engines
 Air and Fuel Induction Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss the following: A/F mixture preparation in gasoline engines using carburetion. Air Charging technologies: Superchargers Turbochargers
Air and Fuel Induction Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss the following: A/F mixture preparation in gasoline engines using carburetion. Air Charging technologies: Superchargers Turbochargers
Approved by AICTE, Government of India & affiliated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
Experiment No. - 1 Object: Study and working of four stroke petrol engine. Apparatus Required: S. No. Name of Apparatus Specifications Model of Four stroke petrol engine NA Figure 1: Working of four stroke
A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
California State University, Bakersfield. Signals and Systems. Kristin Koehler. California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 6 July 23 rd, 2013
 Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 6 July 23 rd, 2013 1 Outline Review (2 and 4 stroke engines) Diesel Engines 2 stroke 4 stroke Benefits of diesel Uses of diesel engines
Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 6 July 23 rd, 2013 1 Outline Review (2 and 4 stroke engines) Diesel Engines 2 stroke 4 stroke Benefits of diesel Uses of diesel engines
Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines
 Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems. Lesson 1: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engines
 Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 1: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engines 1 Terms Compression Compression stroke Connecting rod Crankshaft Cycle Cylinder Diesel
Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 1: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engines 1 Terms Compression Compression stroke Connecting rod Crankshaft Cycle Cylinder Diesel
State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal Combustion Engines
 State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal Combustion Engines July 1997 State of New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Air Quality Permitting Program State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal
State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal Combustion Engines July 1997 State of New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Air Quality Permitting Program State of the Art (SOTA) Manual for Internal
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems
 Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy : Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy : Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES
 CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
CHAPTER I GAS POWER CYCLES 1.1 AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard
COMBUSTION in SI ENGINES
 Internal Combustion Engines ME422 COMBUSTION in SI ENGINES Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Internal Combustion Engines Combustion in SI Engines Introduction Classification of the combustion process Normal combustion
Internal Combustion Engines ME422 COMBUSTION in SI ENGINES Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Internal Combustion Engines Combustion in SI Engines Introduction Classification of the combustion process Normal combustion
ABSTRACT. Electronic fuel injection, Microcontroller, CNG, Manifold injection. Manifold injection with uniflow scavenging.
 ABSTRACT Key Words: Electronic fuel injection, Microcontroller, CNG, Manifold injection. Manifold injection with uniflow scavenging. Manifold injection with uniflow stratified scavenging. Direct CNG injection.
ABSTRACT Key Words: Electronic fuel injection, Microcontroller, CNG, Manifold injection. Manifold injection with uniflow scavenging. Manifold injection with uniflow stratified scavenging. Direct CNG injection.
Model Question Papers
 QUESTION CARRIES 2 MARKS Model Question Papers 1. Define engine. Give their classification? 6 th Semester I.C. ENGINE [ME-604] UNIT -1 2. Define the performance parameters of IC engine ie indicated power,
QUESTION CARRIES 2 MARKS Model Question Papers 1. Define engine. Give their classification? 6 th Semester I.C. ENGINE [ME-604] UNIT -1 2. Define the performance parameters of IC engine ie indicated power,
Scheme - G. Sample Test Paper-I. Course Name : Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Code : ME Semester : Fifth Subject Title : Power Engineering
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour Q1. Attempt any Three 3X3=9 a) Define i) Mean Effective Pressure ii) Piston Speed iii) Swept Volume b) Draw Carnot cycle on P-V and T-S Diagram c) State the need
Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE)
 Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) Editor s Note: Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) includes
Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) Editor s Note: Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) includes
Selected aspects of the use of gaseous fuels blends to improve efficiency and emission of SI engine
 D.O.M. G Kubica Selected aspects of the use of gaseous fuels blends to improve efficiency and emission of SI engine Grzegorz Kubica, Marek Flekiewicz, Paweł Fabiś, Paweł Marzec Silesian University of Technology,
D.O.M. G Kubica Selected aspects of the use of gaseous fuels blends to improve efficiency and emission of SI engine Grzegorz Kubica, Marek Flekiewicz, Paweł Fabiś, Paweł Marzec Silesian University of Technology,
Chapter 6. NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE)
 Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) Editor s Note: Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) was written
Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) Editor s Note: Chapter 6 NOx Formation and Reduction in Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) was written
