Engines. ii. Explain the operation of spark ignition and compression ignition for internal combustion engines used aboard small vessels.
|
|
|
- Barry Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quartermaster 13b. i. Explain the principal features of steam turbine, turboelectric, direct reversing diesel, dieselelectric, gas turbine, nuclear, gasoline, and diesel engines and the relative advantages of each type. ii. Explain the operation of spark ignition and compression ignition for internal combustion engines used aboard small vessels. iii. Demonstrate your familiarity with the engine aboard the vessel used by your ship, including its principles of operation, fuel, lubrication, cooling and electrical systems, and their component parts. iiii. Demonstrate your ability to locate and correct minor engine troubles according to the engine manufacturer s troubleshooting guide. Engines The vast majority of boaters today operate craft that are powered by either outboard or inboard marine internal combustion engines. Since outboard engines account for about 70 percent of total engine production, let s consider them first. Outboard This is a basic, internal combustion engine consisting of an aluminum alloy block containing a crankshaft with a flywheel on top that is rotated by a rope or an electric starter. The crankshaft is rotated by pistons that move up and down within cylinders. They are driven by the expanding force of a mixture of fuel (gasoline) and air, ignited by an electric spark from spark plugs that protrude into the cylinders through the cylinder head. These spark plugs get current from a magnet. As the crankshaft is forced to rotate by the driving action of pistons, this rotation is transmitted through a drive shaft, vertically mounted, through bevel gears to a short, horizontal propeller shaft on which the propeller is mounted. The basic engine is a two-cycle engine normally using gasoline mixed with oil. The oil lubricates the internal working parts and surfaces. The oil and gas enter a carburetor, where air is mixed with the fuel. This mixture enters the crankcase through an intake valve and on into a combustion chamber. The fuel ignites at the maximum compression caused by the rising piston, and the explosion forces the piston down. Each piston goes through a cycle of two strokes. The down or power stroke rotates the drive shaft and exposes the exhaust and intake ports in the wall of the cylinder. Exhaust gases escape on one side and fresh fuel enters on the other. The upstroke covers these ports and compresses the fuel for ignition. Exhaust valves are not required. Outboard Basic Engine, Two Cycle 1. Manual starter handle 2. Manual starter pulley 3. Flywheel 4. Upper Cover 5. Magneto assembly 6. Low-speed control 7. Carburetor silencer 8. Crankcase 9. Piston 10. Cylinder 11. Head jacket 12. Spark plugs 13. Carburetor 14. Steering handle and throttle control 15. Upper motor control Spark Plug Components 16. Water intake pipe to engine 17. Shift rod 18. Lower cover 19. Driveshaft 20. Stern mounting bracket 21. Exhaust gallery 22. Water outlet 23. Lower motor mount 24. Water pump 25. Exhaust outlet 26. Water intake 27. Driveshaft pinion gear 28. Propeller-shaft gears 29. Shift lever 30. Skeg 31. Propeller The source of the igniting spark is the magnet mounted within the flywheel, which requires no outside power. (Normally, batteries are used for starting, lights, etc., but not for ignition.)
2 The motor is cooled by water picked up by a forward-facing scoop just behind the propeller. It is forced through passages around the motor by a pump and is expelled through an underwater outlet as are the exhaust fumes. The outboard motor is entirely self-contained, is secured by clamps, and should be protected by a safety chain to the stern of the boat or attached as an auxiliary by means of a bracket. Outboard motors may have two, four, or six cylinders. Their power output ranges from 3 horsepower to 100 horsepower, and although intended to be portable, these removable engines range in weight from 17 to 300 pounds. Small outboard engines (up to 18 horsepower) usually are hand-started and handcontrolled. Some have an integral fuel tank. Outboard motors generally have electric starters, equipped for remote starting, control, and steering, and have separate fuel tanks. Four-Cycle Inboard Engine (Gasoline, 4 Cylinders) 1. Piston 2. Cylinder 3. Valve 4. Rocker arm 5. Valve spring 6. Water jacket 7. Reverse gear 8. Timing gear 9. Flywheel 10. Crankcase 11. Crankshaft 12. Main bearings 13. Rod bearings 14. Camshaft 15. Valve cover 16. Valve push rods Four-Cycle Diesel Marine Engine 1. Rocker arms; valves, exhaust 2. Rocker arms; injectors 3. Push rods 4. Piston 5. Cylinder 6. Camshaft 7. Main bearings 8. Timing gear, camshaft 9. Timing gear, idler 10. Flywheel 11. Gearbox 12. Rod bearings 13. Crankcase 14. Cam followers 15. Air intake ports 16. Accessory pulley wheel 17. Water jacket Inboard The inboard engine (so called because it is located entirely inside the hull, mounted on stringers or a bed) is an internal combustion engine that develops its power by pistons driving a crankshaft. It includes a cast-iron block containing pistons, the crankshaft, and other moving parts. Attached to the block are various accessories for starting, ignition, cooling, lubricating, exhaust gas removal, fuel injection, etc. Fuel may be either gasoline (most common) or diesel fuel a less expensive fuel that is less likely to explode. Normally marine engines have two, three, four, six, or eight cylinders usually mounted in-line or, as in the V-6 and V-8 engines, in two parallel banks. The combustion principle is the same as discussed in outboard engines, except for diesel engines. Here, the fuel is ignited by the heat of air compression caused by the upstroke of the piston, thus eliminating the need for spark plugs or an ignition system. Most inboard engines are of the four-strokecycle type, commonly called four-cycle, requiring two valves for each cylinder intake and exhaust to admit fuel and dispose of burned gases. These valves are activated by a camshaft, which is geared to the crankshaft.
3 In the complete cycle, four strokes of the piston are involved. The crankshaft makes one revolution on each two strokes. Two crankshaft revolutions equal one cycle of four piston strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. FOUR-STROKE CYCLE, GASOLINE ENGINE Power is related from the crankshaft to the drive shaft through the transmission in order to enable neutral, forward, or reverse drive. In addition, some engines are equipped with a reduction gear to reduce the crankshaft speed to a lower speed on the drive shaft in order to enable both the engine and the propeller to operate at their most efficient rates. The inboard-outboard motor combines an inboard engine connected through the transom with an outboard stern-drive unit. This gives the outboard engine s ease of maneuvering, along with the greater horsepower of an inboard engine more conveniently located aboard the boat. Other Types of Propulsion Although the internal combustion engine is by far the most widely used today, there are other types. DIAGRAM OF A RECIPROCATING STEAM ENGINE There are variations of the internal combustion model, such as the multifuel engine, which uses hydrocarbon fuel developed by the U.S. Army. This operates like a two-cycle diesel engine, requiring no valves and equipped with air cooling. STEAM LAP EXHAUST LAP PISTON STEAM EXHAUST VALVE STEAM INLET The N.S.U. Wankel rotary engine replaces cylinders and pistons with an eccentric-mounted rotor. A single spark plug ignites compressed fuel in a specially-shaped chamber containing the rotor, keeping it turning. The gas turbine engine consists of a gas producer where gasoline and air are vaporized under enormous pressure and a turbine converts the burning expanding gas into rotating shaft power. Steam Expansion Engines The source of steam power is the coal or oil-fired furnace, which heats water in a boiler to produce steam under pressure. This high-pressure steam is conducted through pipes to the cylinders of a reciprocating piston engine, where steam expansion provides the driving force that activates the pistons. A sliding valve alternates steam CROSSHEAD GUIDE ECCENTRIC ARM PISTON ROD CROSSHEAD ECCENTRIC CIRCLE CONNECTING ROD LINE ECCENTRIC ROD CRANK CIRCLE CRANK ARM VALVE STEAM ECCENTRIC CIRCLE VALVE IN MID-POSITION
4 to the top and bottom surfaces of the piston, providing up and down strokes in sequence. Piston action rotates the engine s crankshaft. In a double-expansion engine, the cylinders are mounted in pairs. A small-diameter pair operates first and then feeds steam into the larger one under less pressure. The steam provides the driving force by continuing expansion before being drawn off into a condenser that converts it back to water. The water is returned to the boiler through a preheating system. Triple- and quadruple-expansion engines are an extension of connected cylinders with each of the companion cylinders increasing in size according to a precise ratio. FOUR-CYLINDER, TRIPLE-EXPANSION STEAM ENGINE Turboelectric Drive This propulsion system is based on a steam-driven turbine wherein steam under pressure is the force that strikes the turbine blades, causing them to rotate. The blades are small at the front of the turbine and become larger toward the rear to utilize decreasing steam pressure as it moves through the turbine. This rotation is connected by a shaft to an AC or DC generator or alternator, which in turn provides power for the main, electric-propulsion engine. Diesel-Electric Drive The basic power unit is a diesel-fueled engine that provides the driving action for an electric generator or alternator, which in turn provides electric power for an AC or DC electricpropulsion motor that provides the propeller shaft driving power directly or through a system of gears. To reverse a turboelectric or diesel-electric drive, if the electric motor is operated on DC, polarity is reversed. If the motor is operating on AC, two of its three phases are reversed. Direct Reversing Diesel In this installation, a standard, heavy-duty, diesel-fueled, internal combustion engine is the basic power unit. In the reversing process, the engine is completely stopped and a camshaft device is activated, which, when the engine is restarted, causes the crankshaft to operate in reverse. In other words, the engine itself reverses its rotation, as, of course, does the drive shaft and propeller.
5 To achieve a neutral position, a clutch action separates the drive shaft, permitting the engine to continue to operate. This is a fairly standard installation on harbor tugs, river towboats, commercial, and military auxiliary vessels. Nuclear Power To date, the application of relatively small, nuclear-power reactors for ship propulsion has been developed chiefly for submarines, aircraft carriers, and other naval vessels. Only one commercial ship, the freight-passenger vessel Savannah, was equipped with nuclear power. Its keel was laid in 1958 and the vessel was retired in The Savannah was used mostly as a goodwill promotional vessel, demonstrating a peaceful use of nuclear power. The ship actually transported cargo between 1965 and Without going into the complex fission process, whereby the splitting of atoms releases fantastic amounts of energy (heat), we will simply consider its application. The power reactor consists of a heavily-shielded container (cement/lead-insulated to protect personnel from radiation) containing heavy water as a moderator. It utilizes enriched uranium or plutonium. The reactor also contains the fuel, which is an enriched solution of uranium salt. The moderator and fuel are intimately mixed. Heat generated by the resulting fission process goes into a water-filled heat exchanger, where it is converted to steam. The steam thus produced is piped into a steam turbine that rotates the drive shaft. The steam residue goes into a condenser and returns as water to the heat exchanger. In this case, uranium is substituted for conventional fuel as the energy source. From 2.2 pounds of uranium comes a power output equal to five million pounds of coal (2,500 tons). Hopefully, this type of power source for ship propulsion will increase in the years ahead. Engine Operation The proper function, dependability, and long life of any power plant depends to a large degree on the care and maintenance it gets. Safety is the first consideration. Proper safety practices include having the tanks vented overboard; being sure there are no fuel fumes in the bilge; equipping the engine with a drip pan and the carburetors with a flame arrestor; spark-proofing the electric switches; and checking for tight fuel tanks and lines, adequate engine compartment ventilation, and tight electrical connections. Your pre-starting check should include careful attention to the following: No fumes in engine compartment Oil level in crankcase at proper level (add proper grade oil, if necessary) Water level in battery (plates should be covered) Grease cups on water pump, transmission, etc., filled and tightened down Distributor wiring and spark plugs free of dirt, corrosion, and moisture All wiring with good connections Water intake open Fuel valves open Lines tight and clean Reverse gear operates freely No stuffing box leak Ventilation exhaust blower running a full five minutes before starting
6 While in operation, the engine should be periodically checked to be sure the oil pressure and engine temperature are normal, the electric-charging rate is proper, the fuel supply is adequate, and the engine is running smoothly. Before securing the engine, slow down its operating speed to allow it to cool. Turn off the fuel valves and run all fuel out of the lines. Shut off the ignition. Recheck the engine compartment for fuel or water leaks. Consult manufacturers specifications for engines that may not require that fuel lines be drained. All engines come with an operation manual provided by the manufacturer. If you don t have one, contact the manufacturer for another copy. It includes all specifications, operating instructions, and maintenance and repair data for the engine and its accessories. Familiarize yourself with this manual and develop a checklist for prestarting, operating, winter care, lay up, and outfitting. Always keep an engine log that records the hours of operation, oil changes, repairs and adjustments made, most efficient revolutions per minute (rpms), the best operating temperature and charging rate, etc. Obviously, it makes good sense to carry a tool kit as recommended by the manufacturer. Similarly, an adequate supply of spare parts should be aboard. Electrical Systems For the most part, electrical systems on small boats are entirely self-contained. Even on the smallest powerboats and auxiliaries, electricity is needed for engine operation, running lights, etc. Battery Components Are Shown in Standard 3-Cell, 6-Volt Type The source of electrical power is usually the wet cell or lead-acid battery, which is made up of a series of cells in a plastic or hard-rubber container, electricallyconnected in series. Each cell is made up of a number of positive (lead sulfate) and negative (spongy lead) plates separated by glass, wood, or rubber inserts. Three such cells make up a 6 V battery and six cells make up a 12 V battery. They are submerged in a sulfuric acid solution. The resulting chemical reaction produces electrical energy released through positive and negative terminals to which the engine and other circuits are attached by wires. Battery care calls for careful maintenance of the electrolyte (liquid level) in the battery by the addition of distilled water as necessary. The battery s ability to deliver electrical energy should be checked periodically with a hydrometer, which measures the specific gravity of the electrolyte. The battery and, particularly, its terminals should be kept clean and free from corrosion with a solution of sodium bicarbonate, and coated with Vaseline. Maintaining a battery at or near
7 Inboard Ignition System full charge (normally a reading between and on the hydrometer) will protect it from freezing, and prolong its life. Batteries in boats should be firmly-secured and provided with a ventilated plastic cover. On many boats, a dual battery system is used, with one battery used for cabin lights, radios, etc., and the other reserved for engine starting, ignition, and equipment that is used only when the engine is in operation, such as running lights, etc. To understand the wiring of your boat and galvanic action, you will need an expert. Care of Outboard Motors Outboard motors for boats have been around for a good many years, but they are still temperamental and must be handled with tender loving care. Most of them are of two-cycle stroke, but a few are four-cycle. It is the twocycle that requires the most care and is the more popular. Such engines in the lower horsepower ranges may be either air- or water-cooled. They are very expensive and easily damaged. Owners of such engines are reluctant to loan them out for fear of damage. Never violate any of the following rules. Never run an outboard engine in salt water without flushing it in fresh water immediately after. Never connect a starting battery, if required, to the wrong polarity of the electrical system. One spark and you will have a very expensive repair bill. Never start an outboard unless the safety chain is secured to the transom. Make sure your tanks are full of the proper oil-gas mixture (Oil-Gas Mixtures chart) before casting off. As soon as the engine is started, ascertain that enough cooling water is being discharged for water-cooled engines. If no discharge is seen, shut the engine down immediately. Investigate. Never leave an engine with gas in the carburetor for more than 24 hours. If you do not need it sooner, disconnect the fuel line at the motor while it is running and let it run dry. You may want to consult the manufacturer s specifications. Periodically, check the lower transmission oil level and replenish it. Use oil as specified for two-cycle engines; others create excess carbon. Store engines in a vertical position to keep water pumps drained. Have a spare starter rope, spark plug, propeller shear pin, and cotter key, and the minimum tools for such repairs on board at all times. Accidents can happen to outboard motors. If you are cruising along and come to a sudden stop by hitting a submerged object or sandbar, your outboard engine may be pooped, or swamped by your own backwash. In such cases, you may be able to start it again. Remove the hood and use a dry towel to wipe clean all electrical systems. You may have to remove the plugs and also dry them, depending on how long the engine ran submerged. Since the carburetor is under pressure, very little water should be in it. A few squeezes on the fuel priming bulb will take care of that. On the other hand, if your engine falls overboard, for whatever reason, and can be salvaged within a few hours, it can be disassembled and restored with no great trouble by a reliable marine motor shop. Even saltwater-immersed engines may have such damage alleviated by emptying the cylinders of water and refilling them with light oil until you can get the engine back to a shop.
8 A little practice in changing shear pins from inside a boat will reward you later if you operate often in obstructed waterways. Oil-Gas Mixtures 50-to-1 Mixture Gasoline Oil U.S. Measure 1 gallon 1 / 6 pint or 3 oz 3 gallons 1 / 2 pint or 9 oz. 5 gallons 13 / 16 pint or 15 oz. 6 gallons 1 pint or 16 oz. Metric Measure 1 liter 0.02 liter or 20 cc 5 liters 0.10 liter or 100 cc 10 liters 0.20 liter or 200 cc 20 liters 0.40 liter or 400 cc
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Objectives Topics Resources & Notes GAIN ATTENTION Review homework from chapter 6 Slide 1 OBJECTIVE
 7 Outboard Engines and Stern Drives 67 COURSE LESSON TITLE PRESENTATION TIME PRESENTATION METHOD MATERIALS REQUIRED Chapter 7 Outboard Engines and Drives, and Stern Drives 2 hours Participative Lecture
7 Outboard Engines and Stern Drives 67 COURSE LESSON TITLE PRESENTATION TIME PRESENTATION METHOD MATERIALS REQUIRED Chapter 7 Outboard Engines and Drives, and Stern Drives 2 hours Participative Lecture
EM2007 Errata Student Manual 13 April 2008 Replace referenced paragraphs and homework questions with the following:
 EM2007 Errata Student Manual 13 April 2008 Replace referenced paragraphs and homework questions with the following: Paragraph 7 Internal combustion engines convert about one third of the fuel s energy
EM2007 Errata Student Manual 13 April 2008 Replace referenced paragraphs and homework questions with the following: Paragraph 7 Internal combustion engines convert about one third of the fuel s energy
Handout Activity: HA170
 Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Engine Construction and Principles of Operation
 Ch. 4 Engine Construction and Principles of Operation Gasoline Engine A gasoline fueled engine is a mechanism designed to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy It is an internal combustion engine.
Ch. 4 Engine Construction and Principles of Operation Gasoline Engine A gasoline fueled engine is a mechanism designed to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy It is an internal combustion engine.
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
Automobile section, showing different parts in detail. and miscellaneous devices.
 SECTION VII Nos. 97 112 Automobile section, showing different parts in detail. and miscellaneous devices. Hydraulic jack MECHANICAL MODELS 43 Section VII 97. Automobile engine starter. This device known
SECTION VII Nos. 97 112 Automobile section, showing different parts in detail. and miscellaneous devices. Hydraulic jack MECHANICAL MODELS 43 Section VII 97. Automobile engine starter. This device known
TKP3501 Farm Mechanization
 TKP3501 Farm Mechanization Topic 2: Internal Combustion Engines Ahmad Suhaizi, Mat Su Email: asuhaizi@upm.edu.my Outlines Internal vs external combustion engines Engine structure Combustion cycle 4 stroke
TKP3501 Farm Mechanization Topic 2: Internal Combustion Engines Ahmad Suhaizi, Mat Su Email: asuhaizi@upm.edu.my Outlines Internal vs external combustion engines Engine structure Combustion cycle 4 stroke
IC ENGINE(4 STROKE) G.H.R.I.E&M JALGAON. Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Mehta chirag Shah sagar Patel jainish talele amit
 IC ENGINE(4 STROKE) G.H.R.I.E&M JALGAON Mehta chirag Shah sagar Patel jainish talele amit Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) 9096297071 9028248697 9028913994 8087260063 1 Abstract The four stroke,
IC ENGINE(4 STROKE) G.H.R.I.E&M JALGAON Mehta chirag Shah sagar Patel jainish talele amit Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) Sec.(Mech) 9096297071 9028248697 9028913994 8087260063 1 Abstract The four stroke,
Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061
 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061 EZpdh.com All Rights Reserved Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii LIST OF TABLES...
Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061 EZpdh.com All Rights Reserved Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii LIST OF TABLES...
Installation instruction
 Installation instruction Intercalated generator CIC Reference : 60 300 143 09/2008 Complete 12V or 24V system Wet or gel battery 1 Installation instructions - Intercalated generator Table of contents Safety
Installation instruction Intercalated generator CIC Reference : 60 300 143 09/2008 Complete 12V or 24V system Wet or gel battery 1 Installation instructions - Intercalated generator Table of contents Safety
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
 Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION Section 1B - Maintenance MAINTENANCE 1 B Specifications........................... 1B-1 Special Tools........................... 1B-2 Mercury/Quicksilver Lubricants
Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION Section 1B - Maintenance MAINTENANCE 1 B Specifications........................... 1B-1 Special Tools........................... 1B-2 Mercury/Quicksilver Lubricants
Electric Trolling Motor
 Electric Trolling Motor L Series User s Manual Please read and retain this manual before using product REACH RoHS TABLE OF CONTENTS Contents GENERAL INFORMATION 4 SPECIFICATIONS 4 WIRING AND BATTERY RECOMMENDATIONS
Electric Trolling Motor L Series User s Manual Please read and retain this manual before using product REACH RoHS TABLE OF CONTENTS Contents GENERAL INFORMATION 4 SPECIFICATIONS 4 WIRING AND BATTERY RECOMMENDATIONS
FINAL EXAM. 1. Fill in the gaps with the appropriate word from the list. (30 p.) A. two points operates injecting stroke
 Merchant Marine Academy of Macedonia School of Engineers English Language Academic Year: 2011-2012 September 2012 Semester: B (Retakes) Instructor s name: NAME: A.Γ.Μ.: DATE: FINAL EXAM 1. Fill in the
Merchant Marine Academy of Macedonia School of Engineers English Language Academic Year: 2011-2012 September 2012 Semester: B (Retakes) Instructor s name: NAME: A.Γ.Μ.: DATE: FINAL EXAM 1. Fill in the
Chapter 3. Direct Current Power. MElec-Ch3-1
 Chapter 3 Direct Current Power MElec-Ch3-1 Overview Batteries Safety Precautions Marine Storage Battery Charging Systems Battery Utilization MElec-Ch3-2 Batteries Cells and Battery Battery Chemistry Primary
Chapter 3 Direct Current Power MElec-Ch3-1 Overview Batteries Safety Precautions Marine Storage Battery Charging Systems Battery Utilization MElec-Ch3-2 Batteries Cells and Battery Battery Chemistry Primary
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Objectives Topics Resources & Notes GAIN ATTENTION Review homework from Chapter 2 Slide 1 OBJECTIVE
 3 Inboard Spark Engines - Part 2 29 COURSE LESSON TITLE Chapter 3 Inboard Spark Engines Part 2 PRESENTATION TIME PRESENTATION METHOD MATERIALS REQUIRED 2 hours Participative Lecture Ch3 PPT slides, computer,
3 Inboard Spark Engines - Part 2 29 COURSE LESSON TITLE Chapter 3 Inboard Spark Engines Part 2 PRESENTATION TIME PRESENTATION METHOD MATERIALS REQUIRED 2 hours Participative Lecture Ch3 PPT slides, computer,
NILFISK BA 500 Service Manual
 NILFISK BA 500 Service Manual Model 66324400 12/94 Form Number 043023 TABLE OF CONTENTS Batteries...21 Brush Drive Belt Adjustment Or Replacement...7 Brush Drive Motor - Carbon brush Inspection... 8 Brush
NILFISK BA 500 Service Manual Model 66324400 12/94 Form Number 043023 TABLE OF CONTENTS Batteries...21 Brush Drive Belt Adjustment Or Replacement...7 Brush Drive Motor - Carbon brush Inspection... 8 Brush
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
Bronze Level Training
 Bronze Level Training Engine Principles of Operation While not everyone at the dealership needs to be a top rated service technician, it is good for all the employees to have a basic understanding of engine
Bronze Level Training Engine Principles of Operation While not everyone at the dealership needs to be a top rated service technician, it is good for all the employees to have a basic understanding of engine
Fundamentals of Small Gas Engines
 Fundamentals of Small Gas Engines Objectives: Describe the four-stroke cycle engine operation and explain the purpose of each stroke Explain the concept of valve timing Describe two-stroke engine operation
Fundamentals of Small Gas Engines Objectives: Describe the four-stroke cycle engine operation and explain the purpose of each stroke Explain the concept of valve timing Describe two-stroke engine operation
Parsun Portable 4-Stroke Outboard Motor Winterize or Storing DIY Service Guide
 Parsun Portable 4-Stroke Outboard Motor Winterize or Storing DIY Service Guide To help keep your engine in tip-top condition for years to come, it is important that you winterize your outboard for off-season
Parsun Portable 4-Stroke Outboard Motor Winterize or Storing DIY Service Guide To help keep your engine in tip-top condition for years to come, it is important that you winterize your outboard for off-season
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
 Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION Section 1B - Maintenance MAINTENANCE 1 B Specifications................................ 1B-1 Special Tools................................ 1B-2 Quicksilver Lubricant/Sealant..................
Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION Section 1B - Maintenance MAINTENANCE 1 B Specifications................................ 1B-1 Special Tools................................ 1B-2 Quicksilver Lubricant/Sealant..................
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages Engine Fundamentals 62 Points
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages 145-161 Engine Fundamentals 62 Points 1. The is the area between the top of the piston & the cylinder head. Combustion Chamber Cylinder Chamber Chamber of
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages 145-161 Engine Fundamentals 62 Points 1. The is the area between the top of the piston & the cylinder head. Combustion Chamber Cylinder Chamber Chamber of
Engine Project. These engines are typically used in lawn mowers, snow blowers, go-carts, etc
 Engine Project Your team is going to dissect and assemble a 3.5 HP single cylinder, 4 cycle engine, made by Briggs and Stratton in Milwaukee, Wisconsin These engines are typically used in lawn mowers,
Engine Project Your team is going to dissect and assemble a 3.5 HP single cylinder, 4 cycle engine, made by Briggs and Stratton in Milwaukee, Wisconsin These engines are typically used in lawn mowers,
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1. Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
FORZA BOLT OUTBOARD MOTOR OWNER S MANUAL
 FORZA BOLT OUTBOARD MOTOR OWNER S MANUAL Table Of Contents 1.Introduction...1 2.Safety Information.1 3.Refuelling Information...1 4.Safety Matters 2 5.Preparation.3 6.Operation.3 7.Maintenance...4 8.Storage...5
FORZA BOLT OUTBOARD MOTOR OWNER S MANUAL Table Of Contents 1.Introduction...1 2.Safety Information.1 3.Refuelling Information...1 4.Safety Matters 2 5.Preparation.3 6.Operation.3 7.Maintenance...4 8.Storage...5
CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES
 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Bthird, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the
 third, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the piston reaches DC it enters the fourth cycle. The exhaust valve opens and the piston rises forcing burned gases from the combustion chamber in what
third, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the piston reaches DC it enters the fourth cycle. The exhaust valve opens and the piston rises forcing burned gases from the combustion chamber in what
Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines
 Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions
 Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions People who are familiar with the functioning of a gasoline aircraft engine need not have any difficulty in understanding how a high speed Diesel aircraft
Chapter 2 How the Diesel Aircraft Engine Functions People who are familiar with the functioning of a gasoline aircraft engine need not have any difficulty in understanding how a high speed Diesel aircraft
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4.
 THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? WE KNOW ABOUT:- WHICH WE KNOW AS:- LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4. EXHAUST SQUEEZE BANG BLOW Inlet valve
THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? WE KNOW ABOUT:- WHICH WE KNOW AS:- LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4. EXHAUST SQUEEZE BANG BLOW Inlet valve
Inside a typical car engine. Almost all cars today use a reciprocating internal combustion engine because this engine is:
 Tech Torque HOW PETROL ENGINES WORK The Basics The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline
Tech Torque HOW PETROL ENGINES WORK The Basics The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
 Table of Contents Safety... 2 Specifications... 3 Functions... 4 Operation... 5 Maintenance... 7 Warranty... 7 SAFETY SPECIFICATIONS OPERATION MAINTENANCE WARNING SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS This is the safety
Table of Contents Safety... 2 Specifications... 3 Functions... 4 Operation... 5 Maintenance... 7 Warranty... 7 SAFETY SPECIFICATIONS OPERATION MAINTENANCE WARNING SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS This is the safety
Today, we re going to talk about battery safety. We ll discuss all the key issues associated with using batteries safely, including battery hazards,
 Today, we re going to talk about battery safety. We ll discuss all the key issues associated with using batteries safely, including battery hazards, battery charging, and battery maintenance. Although
Today, we re going to talk about battery safety. We ll discuss all the key issues associated with using batteries safely, including battery hazards, battery charging, and battery maintenance. Although
Unit D: Agricultural Equipment Systems. Lesson 1: Understanding Applications of Fluids and Lubricants in Agricultural Equipment
 Unit D: Agricultural Equipment Systems Lesson 1: Understanding Applications of Fluids and Lubricants in Agricultural Equipment 1 Terms Ash content bottom dead center cloud point compression ratio coolant
Unit D: Agricultural Equipment Systems Lesson 1: Understanding Applications of Fluids and Lubricants in Agricultural Equipment 1 Terms Ash content bottom dead center cloud point compression ratio coolant
A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
MerCruiser & Mercury Diesel Logbook R02
 MerCruiser & Mercury Diesel Logbook 90-889160R02 04/2015 IMPORTANT Maintenance must be completed by a Mercury Marine/Brunswick Marine in EMEA authorized dealer. At the completion of any maintenance check-up
MerCruiser & Mercury Diesel Logbook 90-889160R02 04/2015 IMPORTANT Maintenance must be completed by a Mercury Marine/Brunswick Marine in EMEA authorized dealer. At the completion of any maintenance check-up
CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
 CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION CYLINDER BLOCKS, HEADS, AND CRANKCASES The cylinder, or the engine block, is the basic foundation of virtually all liquid-cooled engines. The block is a solid casting made
CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION CYLINDER BLOCKS, HEADS, AND CRANKCASES The cylinder, or the engine block, is the basic foundation of virtually all liquid-cooled engines. The block is a solid casting made
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
THE T IN DETAIL
 STEP 37 THE T-34-85 IN DETAIL The B-2 [Kharkiv model V-2] engine consisted of a crankcase; two cylinder blocks; a crank rod mechanism; transmission; power system; lubricating, cooling and starting mechanisms.
STEP 37 THE T-34-85 IN DETAIL The B-2 [Kharkiv model V-2] engine consisted of a crankcase; two cylinder blocks; a crank rod mechanism; transmission; power system; lubricating, cooling and starting mechanisms.
DISSECTION OF AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
 DISSECTION OF AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE Purpose: The purpose of this dissection is to familiarize you with the construction and operation of a Briggs & Stratton model 80232 one cylinder, four-stroke,
DISSECTION OF AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE Purpose: The purpose of this dissection is to familiarize you with the construction and operation of a Briggs & Stratton model 80232 one cylinder, four-stroke,
FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS
 Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
What is a GLOW engine?
 Micro engines What is a GLOW engine? R/C models get power from various modes. Gliders, for example, do not need a power source other than what nature provides. But they are the exception. Normally all
Micro engines What is a GLOW engine? R/C models get power from various modes. Gliders, for example, do not need a power source other than what nature provides. But they are the exception. Normally all
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines
 Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
#9040 FUEL TANK SWEEPER
 #9040 FUEL TANK SWEEPER INSTRUCTION MANUAL FILTERS AND REMOVES FINE BIO-CONTAMINANTS, ALGAE, ETC. SWEEPING PROCESS REMOVES LARGE CONTAMINANTS FROM OIL TANKS SUCH AS RUST, WATER, CRUDE AND DIRT CIRCULATES
#9040 FUEL TANK SWEEPER INSTRUCTION MANUAL FILTERS AND REMOVES FINE BIO-CONTAMINANTS, ALGAE, ETC. SWEEPING PROCESS REMOVES LARGE CONTAMINANTS FROM OIL TANKS SUCH AS RUST, WATER, CRUDE AND DIRT CIRCULATES
AIR-COOLED DIESEL GENERATOR OWNERʼS MANUAL. This manual contains important safety information. TDG2500E TDGW7000E TDG7000SE TDG4500E
 AIR-COOLED DIESEL GENERATOR OWNERʼS MANUAL This manual contains important safety information. TDG2500E TDGW7000E TDG7000SE TDG4500E TDG8000-3 TDG7000SE-3 TDG7000E TDG8000E TDGW7000SE TDG7000E3 TDGW8000E
AIR-COOLED DIESEL GENERATOR OWNERʼS MANUAL This manual contains important safety information. TDG2500E TDGW7000E TDG7000SE TDG4500E TDG8000-3 TDG7000SE-3 TDG7000E TDG8000E TDGW7000SE TDG7000E3 TDGW8000E
Deep Cycle Battery Safety. First. Battery Handling, Maintenance & Test Procedures
 Deep Cycle Battery Safety. First. Battery Handling, Maintenance & Test Procedures Crown deep cycle batteries employ a low-maintenance design. They do require periodic maintenance and effective charging
Deep Cycle Battery Safety. First. Battery Handling, Maintenance & Test Procedures Crown deep cycle batteries employ a low-maintenance design. They do require periodic maintenance and effective charging
A SYSTEMATIC SEQUENCE FOR PM INSPECTIONS
 A SYSTEMATIC SEQUENCE FOR PM INSPECTIONS TYPE OF INSPECTION UNDER THE HOOD GASOLINE AND DIESEL 1 Fuel, oil, exhaust leaks - inspect 2 Oil and fuel lines inspect for kinks and wear 3 Automatic transmission
A SYSTEMATIC SEQUENCE FOR PM INSPECTIONS TYPE OF INSPECTION UNDER THE HOOD GASOLINE AND DIESEL 1 Fuel, oil, exhaust leaks - inspect 2 Oil and fuel lines inspect for kinks and wear 3 Automatic transmission
Outboard Engines This sneak preview of your study material has been prepared in advance of the book's actual online release.
 Study Unit Outboard Engines This sneak preview of your study material has been prepared in advance of the book's actual online release. iii Preview An outboard engine is a special type of small engine
Study Unit Outboard Engines This sneak preview of your study material has been prepared in advance of the book's actual online release. iii Preview An outboard engine is a special type of small engine
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Electrical Systems. Introduction
 Electrical Systems Figure 1. Major Components of the Car s Electrical System Introduction Electricity is used in nearly all systems of the automobile (Figure 1). It is much easier to understand what electricity
Electrical Systems Figure 1. Major Components of the Car s Electrical System Introduction Electricity is used in nearly all systems of the automobile (Figure 1). It is much easier to understand what electricity
Owner s/operator s Manual
 Water Pump MP2533E2 Owner s/operator s Manual Completely read and understand this manual before using this product. Foreword This Owner s/ Operator s Manual is designed to familiarize the operator with
Water Pump MP2533E2 Owner s/operator s Manual Completely read and understand this manual before using this product. Foreword This Owner s/ Operator s Manual is designed to familiarize the operator with
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
Owner s Manual & Safety Instructions
 Owner s Manual & Safety Instructions Save This Manual Keep this manual for the safety warnings and precautions, assembly, operating, inspection, maintenance and cleaning procedures. Write the product s
Owner s Manual & Safety Instructions Save This Manual Keep this manual for the safety warnings and precautions, assembly, operating, inspection, maintenance and cleaning procedures. Write the product s
DISPLACEMENT: The maximum displacement that may be achieved in the Ski Superstock Class is 1500 cc.
 SKSS.1 SUPERSTOCK CLASS COMPETITION Competitors in this class are allowed modifications to gain maximum machine and engine performance while restricting the build costs by prohibiting aftermarket hulls
SKSS.1 SUPERSTOCK CLASS COMPETITION Competitors in this class are allowed modifications to gain maximum machine and engine performance while restricting the build costs by prohibiting aftermarket hulls
1 Name any 5stationary parts and moving partsof a large 2-stroke diesel engine?
 2 Marks question Bank for ME 802 General & Motor 1 Name any 5stationary parts and moving partsof a large 2-stroke diesel engine? 2 Why in certain engine the bottom half of crosshead bearing is of single
2 Marks question Bank for ME 802 General & Motor 1 Name any 5stationary parts and moving partsof a large 2-stroke diesel engine? 2 Why in certain engine the bottom half of crosshead bearing is of single
MAIN PROPULSION ENGINE INTERMEDIATE GENERAL FOR MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS 3-1 LANDING CRAFT UTILITY (LCU) INDEX-1
 TECHNICAL MANUAL UNIT, INTERMEDIATE DIRECT INTRODUCTION 1-1 SUPPORT AND INTERMEDIATE GENERAL SUPPORT UNIT MAINTENANCE 2-1 MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS INSTRUCTIONS MAIN PROPULSION ENGINE INTERMEDIATE GENERAL
TECHNICAL MANUAL UNIT, INTERMEDIATE DIRECT INTRODUCTION 1-1 SUPPORT AND INTERMEDIATE GENERAL SUPPORT UNIT MAINTENANCE 2-1 MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS INSTRUCTIONS MAIN PROPULSION ENGINE INTERMEDIATE GENERAL
Internal Combustion Engines.
 Internal Combustion Engines. Here's a quick description of a typical internal combustion engine, along with basic vocabularies that describe the components and their functions. This stuffs serve as a quick
Internal Combustion Engines. Here's a quick description of a typical internal combustion engine, along with basic vocabularies that describe the components and their functions. This stuffs serve as a quick
SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST
 SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST 1. Position two 3 x 6 x ¼ steel plates in the flat position for a butt weld. The weld joint should be 6 long. 2. Select to either bevel the metal
SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST 1. Position two 3 x 6 x ¼ steel plates in the flat position for a butt weld. The weld joint should be 6 long. 2. Select to either bevel the metal
Operation and Maintenance Instructions for the RAPTOR 178
 WWW.SKYTOY.COM Operation and Maintenance Instructions for the RAPTOR 178 See www.skytoy.com for updates and service bulletins. 2/1/2011 1. Parts Schematic:... 3 2. Muffler Assembly Diagram:... 4 3. Muffler
WWW.SKYTOY.COM Operation and Maintenance Instructions for the RAPTOR 178 See www.skytoy.com for updates and service bulletins. 2/1/2011 1. Parts Schematic:... 3 2. Muffler Assembly Diagram:... 4 3. Muffler
T erm STI2D. The process by which a car works is a lot simpler than you may think. When a driver turns a key in the ignition:
 1. How a car engine Works The process by which a car works is a lot simpler than you may think. When a driver turns a key in the ignition: The car battery powers up sending Power to the starter motor,
1. How a car engine Works The process by which a car works is a lot simpler than you may think. When a driver turns a key in the ignition: The car battery powers up sending Power to the starter motor,
Using Multiple Cylinder Engines
 Lesson A6 6 Using Multiple Cylinder Engines Unit A. Mechanical Systems and Technology Problem Area 6. Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 6. Using Multiple Cylinder Engines New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Lesson A6 6 Using Multiple Cylinder Engines Unit A. Mechanical Systems and Technology Problem Area 6. Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 6. Using Multiple Cylinder Engines New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems. Lesson 6: Using Multiple Cylinder Engines
 Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 6: Using Multiple Cylinder Engines Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 6: Using Multiple Cylinder Engines Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Air Cooled Engine Technology. Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94
 Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94 1. The of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to another. Either TDC to BDC (downstroke) or BDC to TDC (upstroke). Identified
Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94 1. The of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to another. Either TDC to BDC (downstroke) or BDC to TDC (upstroke). Identified
SECTION 3.00 WARNING WARNING ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION
 SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
Operate propulsion questions
 Operate propulsion questions SECTION 1 - Mechanical From the list below, identify the fourth internal combustion engine operation. Combustion, Exhaust, Induction and: Suction Expansion Compression Suppression
Operate propulsion questions SECTION 1 - Mechanical From the list below, identify the fourth internal combustion engine operation. Combustion, Exhaust, Induction and: Suction Expansion Compression Suppression
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
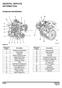 GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION Component Identification Figure 31 Reference Description Number 1 Lifting Eye (Flywheel End) 2 Turbocharger* 3 Lifting Eye ( Cooling Fan End) 4 Coolant Pump 5 Cooling Fan 6
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION Component Identification Figure 31 Reference Description Number 1 Lifting Eye (Flywheel End) 2 Turbocharger* 3 Lifting Eye ( Cooling Fan End) 4 Coolant Pump 5 Cooling Fan 6
Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED
 Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED 185HP & MASSIVE TORQUE iame41-1.doc 29Mar03 Page 1 of 2 Another Sea-Doo watercraft first and only. Introducing the 185hp, GTX 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED PWC. The 4-TEC
Introducing the Sea-Doo 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED 185HP & MASSIVE TORQUE iame41-1.doc 29Mar03 Page 1 of 2 Another Sea-Doo watercraft first and only. Introducing the 185hp, GTX 4-TEC SUPERCHARGED PWC. The 4-TEC
Ag. Systems Management 374 Test What are the two common valve angles? A. 75ø and 90ø B. 15ø and 65ø C. 30ø and 45ø D.
 Ag. Systems Management 374 Test 1-1. What are the two common valve angles? A. 75ø and 90ø B. 15ø and 65ø C. 30ø and 45ø D. 15ø and 45ø 2. Which of the following would be the best choice for measuring a
Ag. Systems Management 374 Test 1-1. What are the two common valve angles? A. 75ø and 90ø B. 15ø and 65ø C. 30ø and 45ø D. 15ø and 45ø 2. Which of the following would be the best choice for measuring a
OBJECTIVE: GENERAL ASPECTS ABOUT ENGINES MECHANISM:
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle
 The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
TM &P TECHNICAL MANUAL
 TM 5-3895-355-14&P TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR'S, ORGANIZATIONAL, DIRECT SUPPORT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL (INCLUDING REPAIR PARTS INFORMATION AND SUPPLEMENTAL MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PARTS INSTRUCTIONS)
TM 5-3895-355-14&P TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR'S, ORGANIZATIONAL, DIRECT SUPPORT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL (INCLUDING REPAIR PARTS INFORMATION AND SUPPLEMENTAL MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PARTS INSTRUCTIONS)
Service Bulletin Winter Storage. All Carbureted Engines. 1. Stabilize Fuel. 2. Change Engine Oil and Filter 3.
 Service Bulletin Volvo Penta of the Americas 1300 Volvo Penta Drive Chesapeake, Virginia 23320-9810 Distribution: M Date: 12-1996 Binder: C Group Number Version 17-3 5 02 Winter Storage All Gasoline Engines
Service Bulletin Volvo Penta of the Americas 1300 Volvo Penta Drive Chesapeake, Virginia 23320-9810 Distribution: M Date: 12-1996 Binder: C Group Number Version 17-3 5 02 Winter Storage All Gasoline Engines
TD-POWER marine. TDME series marine diesel engine Operation manual. Jiangyan Xinyang Machine-building Co., Ltd
 TD-POWER marine 2003/44/EC APPROVED TDME series marine diesel engine Operation manual Jiangyan Xinyang Machine-building Co., Ltd East Xingjiang Road Private Economic Center, jiangyan City, Jiangsu, China
TD-POWER marine 2003/44/EC APPROVED TDME series marine diesel engine Operation manual Jiangyan Xinyang Machine-building Co., Ltd East Xingjiang Road Private Economic Center, jiangyan City, Jiangsu, China
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
ROYAL CANADIAN AIR CADETS PROFICIENCY LEVEL TWO INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 3 EO M EXPLAIN THE CYCLES OF A FOUR-STROKE PISTON-POWERED ENGINE
 ROYAL CANADIAN AIR CADETS PROFICIENCY LEVEL TWO INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 3 EO M232.03 EXPLAIN THE CYCLES OF A FOUR-STROKE PISTON-POWERED ENGINE Total Time: 60 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS
ROYAL CANADIAN AIR CADETS PROFICIENCY LEVEL TWO INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 3 EO M232.03 EXPLAIN THE CYCLES OF A FOUR-STROKE PISTON-POWERED ENGINE Total Time: 60 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS
Introduction. Internal Combustion Engines
 Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines A heat engine that converts chemical energy in a fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy first converted into thermal energy (Combustion)
Introduction Internal Combustion Engines Internal Combustion Engines A heat engine that converts chemical energy in a fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy first converted into thermal energy (Combustion)
Arrow Shark TS760-Marine Onboard E-Starter. Owner Manual
 Arrow Shark TS760-Marine Onboard E-Starter Owner Manual The TS760-Marine Onboard E-Starter has concluded years of experience Arrow Shark has on RC boat onboard E-Starter, it will work for about all brands
Arrow Shark TS760-Marine Onboard E-Starter Owner Manual The TS760-Marine Onboard E-Starter has concluded years of experience Arrow Shark has on RC boat onboard E-Starter, it will work for about all brands
ENTEC WEST, INC. Marine Diesel Generators. Operating Instructions. Table of Contents SW 72nd Portland, Oregon (503)
 Operating Instructions ENTEC WEST, INC. Marine Diesel Generators Table of Contents How to Use this Manual................................................ 2 System Descriptions Fuel System..........................................................
Operating Instructions ENTEC WEST, INC. Marine Diesel Generators Table of Contents How to Use this Manual................................................ 2 System Descriptions Fuel System..........................................................
Fuel Systems GASOLINE FUEL SYSTEMS
 Fuel Systems I - 1 GASOLINE FUEL SYSTEMS Gasoline fuel systems used in Four Winns boats are designed to meet or exceed the requirements of the US Coast Guard, the National Marine Manufacturers Association,
Fuel Systems I - 1 GASOLINE FUEL SYSTEMS Gasoline fuel systems used in Four Winns boats are designed to meet or exceed the requirements of the US Coast Guard, the National Marine Manufacturers Association,
IT 0335 US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES
 SUBCOURSE IT 0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES Subcourse Number IT0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER FORT HUACHUCA,
SUBCOURSE IT 0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES Subcourse Number IT0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER FORT HUACHUCA,
MECHANICAL SCIENCE Module 1 Diesel Engine Fundamentals
 Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook MECHANICAL SCIENCE Module 1 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook MECHANICAL SCIENCE Module 1 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii
IT 0335 US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES
 SUBCOURSE IT 0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES Subcourse Number IT0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER FORT HUACHUCA,
SUBCOURSE IT 0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES INTRODUCTION TO CELLS AND BATTERIES Subcourse Number IT0335 EDITION B US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER FORT HUACHUCA,
3-71, 4-71 & 6-71 Series Engines Volume 1 of 2
 Detroit Diesel Service Manual 3-71, 4-71 & 6-71 Series Engines Volume 1 of 2 Service Manual THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF DETROIT DIESEL OR IT S SUCCESSORS. DETROIT
Detroit Diesel Service Manual 3-71, 4-71 & 6-71 Series Engines Volume 1 of 2 Service Manual THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF DETROIT DIESEL OR IT S SUCCESSORS. DETROIT
Everything Leading Up to Nuclear Cars. next 150 years is to have a car that runs on the splitting of atoms. This will be a clean and
 Ethan Brunet-Bailey Everything Leading Up to Nuclear Cars Engineering is why we have cars, electronics, and everything around us. The car that we have in 2016-2017 runs off of fossil fuels and some are
Ethan Brunet-Bailey Everything Leading Up to Nuclear Cars Engineering is why we have cars, electronics, and everything around us. The car that we have in 2016-2017 runs off of fossil fuels and some are
LINCOLN. Continental 1
 3154_U01.qxd 8/1/03 7:28 AM Page 1 Continental 1 BRAKES...1-27 DRIVE TRAIN...1-21 ENGINE REPAIR...1-7 FUEL SYSTEM...1-20 PRECAUTIONS...1-7 SPECIFICATION CHARTS...1-2 STEERING AND SUSPENSION...1-22 A Air
3154_U01.qxd 8/1/03 7:28 AM Page 1 Continental 1 BRAKES...1-27 DRIVE TRAIN...1-21 ENGINE REPAIR...1-7 FUEL SYSTEM...1-20 PRECAUTIONS...1-7 SPECIFICATION CHARTS...1-2 STEERING AND SUSPENSION...1-22 A Air
03. Fuel and Air Feed System
 Page 11 of 03. Fuel and Air Feed System Content (16 Marks) 3.1 Petrol fuel supply system. 8 Marks Conventional Petrol Engine: Gravity feed, Pump feed (Layout,Function of Components and location). Construction
Page 11 of 03. Fuel and Air Feed System Content (16 Marks) 3.1 Petrol fuel supply system. 8 Marks Conventional Petrol Engine: Gravity feed, Pump feed (Layout,Function of Components and location). Construction
Chapter 4 Ignition & Electrical Systems
 Chapter 4 Ignition & Electrical Systems Chapter 4 Section A Study Aid Questions Fill in the Blanks 1. Ignition systems can be divided into two classifications: systems or systems for reciprocating engines.
Chapter 4 Ignition & Electrical Systems Chapter 4 Section A Study Aid Questions Fill in the Blanks 1. Ignition systems can be divided into two classifications: systems or systems for reciprocating engines.
OUTBOARD MOTORS FOR PACIFIC ISLAND MARINERS RESTRICTED CLASS 6-MASTER/ENGINEER SPC O22C LEARNER S GUIDE
 OUTBOARD MOTORS FOR PACIFIC ISLAND MARINERS RESTRICTED CLASS 6-MASTER/ENGINEER SPC O22C LEARNER S GUIDE SECRETARIAT OF THE PACIFIC COMMUNITY GOVERNMENT OF TAIWAN/ROC TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
OUTBOARD MOTORS FOR PACIFIC ISLAND MARINERS RESTRICTED CLASS 6-MASTER/ENGINEER SPC O22C LEARNER S GUIDE SECRETARIAT OF THE PACIFIC COMMUNITY GOVERNMENT OF TAIWAN/ROC TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
California State University, Bakersfield. Signals and Systems. Kristin Koehler. California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013
 Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Mfg. No: E1
 Parts Manual Mfg. No: 120312-0143-E1 Copyright Briggs and Stratton. All Rights reserved 05-Jan-2018 Model Components Table Of Contents Page Air Cleaner, Exhaust System...........................................................................
Parts Manual Mfg. No: 120312-0143-E1 Copyright Briggs and Stratton. All Rights reserved 05-Jan-2018 Model Components Table Of Contents Page Air Cleaner, Exhaust System...........................................................................
BSS Examination Record Form for Privately Owned and Managed Vessels
 BSS Examination Record Form for Privately Owned and Managed Vessels [Edition 1.04 April 2013] Current boat name Former name Reg. number or index Length (m) Berths Hull material Hull colour Superstructure
BSS Examination Record Form for Privately Owned and Managed Vessels [Edition 1.04 April 2013] Current boat name Former name Reg. number or index Length (m) Berths Hull material Hull colour Superstructure
DATA FOR AUTOMATIC AND REMOTE CONTROL OF MACHINERY SYSTEM
 DATA-DF(2004.6) SHIPBUILDER: HULL NO.: DATA FOR AUTOMATIC AND REMOTE CONTROL OF MACHINERY SYSTEM Diesel Ship NIPPON KAIJI KYOKAI Summary of Description 1. If the ships are designed in accordance with description
DATA-DF(2004.6) SHIPBUILDER: HULL NO.: DATA FOR AUTOMATIC AND REMOTE CONTROL OF MACHINERY SYSTEM Diesel Ship NIPPON KAIJI KYOKAI Summary of Description 1. If the ships are designed in accordance with description
