Buffer Stops and Restraining Devices for Dead End Tracks
|
|
|
- Candice Rodgers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Engineering (Track & Civil) Guideline Buffer Stops and Restraining Devices for Dead End Tracks ETH Applicability ARTC Network Wide Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared by Reviewed by Endorsed Approved Jul 12 Standards Manager Standards Operational Safety & Environmental Review Group Safety & Environment Committee 16/07/2012 Amendment Record Version Date Reviewed Clause Description of Amendment Jul 12 First issue of new Guideline. Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited 2012 Disclaimer: This document has been prepared by ARTC for internal use and may not be relied on by any other party without ARTC s prior written consent. Use of this document shall be subject to the terms of the relevant contract with ARTC. ARTC and its employees shall have no liability to unauthorised users of the information for any loss, damage, cost or expense incurred or arising by reason of an unauthorised user using or relying upon the information in this document, whether caused by error, negligence, omission or misrepresentation in this document. This document is uncontrolled when printed. Authorised users of this document should visit ARTC s intranet or extranet ( to access the latest version of this document.
2 Contents Contents 1 Introduction Purpose Site Specific Risk Assessments Scope Philosophy behind Site Specific Risk Assessments Relevant Procedure Responsibilities Reference Documents Definitions Specification Outcome Design Steps that should be followed when determining the most appropriate restraining device Inspection Frequency Change in Risk profile Maintenance General Repairs after usage Decommissioning APPENDICES... 9 APPENDIX A - Risk Factors... 9 APPENDIX B Calculating a Percent Slope APPENDIX C Granular (soft) arrestor bed APPENDIX D Schematic design details for a timber baulk fastened to a sleeper APPENDIX E One example of a Sliding or friction buffer stop APPENDIX F - Runaway vehicles Grade/Speed/Momentum tables Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 2 of 14
3 Introduction 1 Introduction 1.1 Purpose The ARTC Track & Civil Code of Practice (T&C CoP) stipulates that where there is a risk to people or property behind the dead end, adequate protection shall be provided. This guideline outlines a range of restraining devices (either singly or in combination) which can be used at the end of dead end tracks. These restraining devices are installed for one main purpose; to protect people and property, adjacent to or beyond the end of the dead end. Note: For dead ends where an over run will cause no appreciable damage to persons or property, then consideration should be given to minimising costs of the over run (i.e. cost of damage to the rolling stock itself as well as cost of rerailing). An example would be a site where the dead end runs towards an empty paddock or Nullarbor Plain. In this case,, an over running vehicle would not cause any damage to people or property, only to itself. It is also beneficial to be able to rerail vehicles that have over run the dead ends. 1.2 Site Specific Risk Assessments 1.3 Scope It should be stressed that this is a guideline only and each site should be assessed on its merits. Such assessments should focus primarily on the adequate protection of people and property adjacent to or beyond the end of the dead end. It should also be noted that that any effective arrestor must have some means of absorbing impacts. I.e. it is virtually impossible to stop even a very slow moving rail vehicle instantly. Energy must be absorbed over some distance, or the vehicle deflected away from danger. This guideline covers a range of restraining devices for the end of dead end tracks. The calculations, on which these guidelines are based, are primarily for runaway vehicles i.e. in most cases, they will not be adequate to restrain vehicles pushed into them by a locomotive or powered vehicle. In these locations, heavy stopping structures, engineered sliding buffer stops or a signalling system should be considered. Another factor to be considered is that some restraining devices will have to be partially or completely rebuilt every time they are struck heavily. It should be noted that the restraints in this document are for the end of dead ends only. There are other devices (such as catch points and derails) which can be used to prevent vehicles from fouling running lines. 1.4 Philosophy behind Site Specific Risk Assessments The level of restraint required for rail vehicles is based on two main considerations: 1. Where an over run has the potential to cause significant damage/injury/disruption to people, facilities or equipment, then the restraining device must have the capacity to stop the rail vehicle/s. An example of this would be a dead end that fronts onto a protected level crossing. Hence, an over running vehicle could collide with road vehicle stopped at the crossing and people and vehicles could be injured/damaged. So the over running vehicle MUST be stopped. 2. Where the consequences of overrun would be catastrophic damage to assets behind the dead end then special design of dead end stop is required. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 3 of 14
4 Introduction 1.5 Relevant Procedure This guideline supports Section 0: Track and Civil Management System of the ARTC Track & Civil Code of Practice. 1.6 Responsibilities The Manager Standards is the guideline owner and is the initial point of contact for all queries relating to this guideline. The Infrastructure Manager, Delivery Manager or nominated delegate for each Corridor is responsible for managing the application, maintenance and documentation of the process. 1.7 Reference Documents The following documents/systems support this guideline: ARTC s Safety Management System ARTC s Codes of Practice for Track Maintenance TDS 16 Light Duty Maintenance Siding Specification SDS 14 Points Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 4 of 14
5 Introduction 1.8 Definitions The following terms and acronyms are used within this document: Term or acronym Arrestor bed Away from danger Description A bed of loose material placed at the end of a dead end to stop runaway vehicles. It could consist of ballast, gravel or compacted soil. The bed may just be a compacted graded pile as shown in Appendix C. Sometimes second hand concrete sleepers are used, but they can cause damage to vehicles - see also solid buffer stop. This is where an arrestor or diversionary method is used to prevent either damage to the runway vehicle, or to rail or road vehicles on an adjoining road or railway. Or to prevent them from striking key equipment like signal cabinets, towers, buildings, etc. Baulk A rectangular piece of hardwood timber of approximately 300 by 200 mm which is bolted to the track as shown in the drawings in Appendix D. Bent track Buffer stop Dead end signal or buffer stop lights Derailer Friction sliding buffer stops Heavy stopping structure Over running vehicle Restraining device Runaway vehicle Solid sliding stop Stop block This is another means of diverting runaway vehicles away from danger be it danger to them or other facilities. The end of the dead end simply has a short curve placed in it so that it turns any runaway vehicles away from a danger zone. A structure erected across and at the end of a dead end track which is intended to stop rolling stock. Shunting signals applying to short movements from the running line to a dead end siding. Lights are usually behind the stop at a height of 1200 to 1400 mm above rail level. A mechanical device which is attached to the track and is designed to derail a wheel at a designated point by lifting and moving the wheel across the head of the rail. Usually used to protect vehicles from fouling running lines, so is not included as an option in this Guideline. These are a site specific design which are designed to slide along the rail. After use, they can easily be reset to their original position. See one example in Appendix E. A structure that weights so much that it will stop almost any vehicle even if it damages it in the process. Such structures could include a large steel framed box or gabion type structure filled with ballast or stone. If this was say 3m X 6m X 1.5m it would weight about 40 tonnes and should stop most vehicles, but it may damage them in the process. A rail vehicle that runs over the end of a dead end i.e. its wheels drop off the end of the rails. Any device or structure that controls the movement of a rail vehicle at the end of a dead end. An unattached rail vehicle (or vehicles) that travels down a dead end track out of control. This is a mass of fairly heavy material that sits on the rail. Retardation is gained by friction between the stop and the rail. It could be a mass off concrete or a stack of second concrete sleepers or a steel box full of soil, etc. Can cause damage to vehicles. A structure fixed at the termination of a running line or dead end to arrest very slow moving vehicles. Sometimes known as a Scotch Block. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 5 of 14
6 2 Specification 2.1 Outcome The aim of this document is to provide a series of steps for field staff to proceed through to assess sites and ensure that the aims of this procedure are met. 3 Design 3.1 Steps that should be followed when determining the most appropriate restraining device Below is a suggested sequence of steps that can be followed to try and ensure that effective, safe arresting devices are installed. Step 1: Assess the site for potential risks i.e. will an over running rail vehicle cause any damage to people or property. See Appendix A for guidelines. Step 2: Determine the average grade of the dead end - see Appendix B for measuring methods. Step 3: Determine the length that the runaway vehicle might reasonably be able to gather speed over. Note: This may be from the back of the turnout off the running line, or from a high point in the dead end. Step 4: Determine the approximate speed from table 1 below: Table 1 - Grade/Length/Speed Chart Distance in metres Grade % Speed at end of track in km/h 1 in in in in in Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 6 of 14
7 Design Step 5: Apply actions in table 2 for possible type of arrestor: Table 2 Actions to take for different types of arrestor Type of arrestor Max. speed it is effective for Is further arrestor required? Cost range Comments Secondary arrestor required if an over run may cause injury or damage Repair/replacement when significantly struck Baulk 1.5 km/h Probably Low Primarily just a marker provides little resistance Bent track 20 km/h Probably Low Simple option. Can have baulk as marker Arrestor bed as shown in Appendix C Solid sliding stop Friction sliding buffer stops Heavy stopping structure Long arrestor bed or allowing wagon to run off into paddock 15 km/h Not usually Low If no asset to be protected then allow wagon to run into paddock 5 to 15 km/h (depending on weight) 25 km/h (depending on design) Not usually Moderate depending on materials Yes in most cases Yes in most cases. Secondary arrestor likely to be required if site is dangerous Complete rebuild almost always required Should be able to just drag vehicles back onto track Unlikely Partial repair usually required grading, etc See definitions in 1.8 above Depends on design Would have to be pulled back along track No High There are many designs. Need to check with supplier and match to site. See Appendix F for indications of speed and momentum of vehicles 25 km/h No Moderate Many designs concrete structures, gabions, steel boxes filled with ballast or rock, etc >25km/h No Low Used beyond short arrestor or other device when there is no asset behind the dead end. Can build compacted earth ramp off end of track to minimise damage to rolling stock and permit easy rerailing Needs engineering design No Should just need to be reset. May require replacement friction blocks if they are worn. Probably not, but likely to damage vehicles Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 7 of 14
8 Inspection 4 Inspection 4.1 Frequency Arrestor devices should be inspected by a competent Track worker when completing normal yard inspections for points and crossings. Reporting of defects or changes in risk profiles, should be by exception. The item shall be recorded on Asset Registers and have Maintenance Service Orders created in accordance with the required inspection frequency of the Maintenance Plan. 4.2 Change in Risk profile If during the inspection, there has been some appreciable change in risk levels, then this should be reported to the appropriate Area Manager of the infrastructure. Examples of some such changes could be the following erected/installed just behind the end of the dead end: A new road or railway track A new structure, especially a building housing people A signal cabinet or column A pier or support for an overhead bridge, walkway, pipeline, etc An embankment with a steep slope, which could result in runaway vehicles accelerating down this grade Any other item which a runaway vehicle could collide with. 5 Maintenance 5.1 General It is impossible to specify limits for deterioration of all the arrestor devices that are possible under these Guidelines. However, a Competent Track worker should be able to exercise reasonable judgement in this regard. Basically the arrestor device should be maintained at a level that will enable it to perform to give an appropriate level of safety. 5.2 Repairs after usage After a runaway vehicle has been retarded by the device, in many cases it will require repairs see last column in Table. At high risk sites these repairs should be completed as soon as practicable, depending on usage. Alternatively, for high risk sites, the dead end should be closed to all traffic until repairs have been completed. Certification of the repairs by a person with appropriate competence shall be documented and kept with asset and maintenance records. 6 Decommissioning In the event of a dead being closed, in many cases the cheapest option may be to just leave the arrestor devices in place. But in some cases there could be reasons to justify their removal. Such reasons could include: Economics can the device be reused at another site? Aesthetics will the deteriorating device be an eyesore? Vandalism Risk to the public In these cases, the devices should be removed and the site cleaned up. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 8 of 14
9 APPENDICES 7 APPENDICES APPENDIX A - Risk Factors Possible risks that could be present beyond the end of a dead end and could require a secondary arrestor device. People: Pedestrian walkway Level crossing or road way Other railway tracks. Property: Signal cabinets Other railway tracks Buildings, especially those that are regularly inhabited Signal towers or structures Supports for overhead structures, bridges, walkways, pipelines, etc. Factors which increase risk level: Dead ends at the top of banks, where an over running rail vehicle could run down the bank and strike or foul roads, track, buildings etc. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 9 of 14
10 APPENDICES APPENDIX B Calculating a Percent Slope To calculate a percent slope simply, you apply the following formula: 1 metre 20 centimetres Measured over 1m (100cm) and rise of 20cm the percentage of slope is 20%. Method: Take a one metre ruler or straightedge, a spirit level and a plumb line. Put the ruler horizontally to the top of the rail checking with the level, and then write down how long is the plumb or ruler down to the lower section of rail, this distance (drop) will be the percentage. This is straightforward because 1 metre is 100 centimetres. For a 1m ruler or straightedge, slopes will be as follow: Drop Grade In cm In mm Percentage Ratio % 1 in % 1 in % 1 in % 1 in % 1 in 500 Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 10 of 14
11 APPENDICES APPENDIX C Granular (soft) arrestor bed Note: Length to depend on estimated vehicle speed from Table 1 above. As a guide, a vehicle at 15 km/h requires a length of at least 5 metres. Material can be anything that will retard vehicles. Should be soft enough for wheels to dig in. Not so hard that wheels ride over the top of the slope. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 11 of 14
12 APPENDICES APPENDIX D Schematic design details for a timber baulk fastened to a sleeper Note: Bolts to be at least 19 mm diameter and kept tight. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 12 of 14
13 APPENDICES APPENDIX E One example of a Sliding or friction buffer stop Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 13 of 14
14 APPENDICES APPENDIX F - Runaway vehicles Grade/Speed/Momentum tables Grade/Length/Speed Chart Distance in metres Grade Speed at end of track in km/h 1 in in in in in Momentum, Empty vehicle (20 tonnes mass) Distance in metres Grade Momentum in kg.m/sec x 100,000 1 in in in in in Momentum, Loaded vehicle (92 tonnes mass) Distance in metres Grade Momentum in kg.m/sec x 100,000 1 in in in in in Momentum, Loco (134 tonnes mass) Distance in metres Grade Momentum in kg.m/sec x 100,000 1 in in in in in Notes: 1) Based on formulas developed by Fred Mau (Steelcon Consultants) June ) Distance is from where vehicle commences to move, to where vehicle is restrained / strikes arresting device, etc. 3) Based on theoretical determinations see assumptions in calculation. Version 1.0 Date of last revision: 02 Jul 12 Page 14 of 14
Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Code of Practice. Clearances. Section 7. Applicability. ARTC Network wide.
 Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Code Practice Clearances Section 7 Applicability ARTC Network wide Primary Source Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared by Reviewed by Endorsed
Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Code Practice Clearances Section 7 Applicability ARTC Network wide Primary Source Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared by Reviewed by Endorsed
Maintenance of Signal Sighting and Signals
 Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard Maintenance of Signal Sighting and Signals SMP 31 Applicability New South Wales CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source RIC Standard SC 00 52 00 31 SI Version
Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard Maintenance of Signal Sighting and Signals SMP 31 Applicability New South Wales CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source RIC Standard SC 00 52 00 31 SI Version
Management of Clearances
 Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Standard Management of Clearances ETM-7-1 Applicability New South Wales CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source ARTC Standards BDS 9, BDS 11, BDS 12, BDS 13, BDS
Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Standard Management of Clearances ETM-7-1 Applicability New South Wales CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source ARTC Standards BDS 9, BDS 11, BDS 12, BDS 13, BDS
Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures
 Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures Shunting and Marshalling Rule Number: 4013 Version 1.0, 31 March 2016 Shunting and Marshalling Rule Number: 4013 Document Control Identification Document title
Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures Shunting and Marshalling Rule Number: 4013 Version 1.0, 31 March 2016 Shunting and Marshalling Rule Number: 4013 Document Control Identification Document title
Shunting and Marshalling
 Applicability NSW SMS Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 2.0 11 October 2015 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC) Disclaimer This document
Applicability NSW SMS Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 2.0 11 October 2015 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC) Disclaimer This document
Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard. Braking Distance SDS 03. Applicability. Primary Source
 Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard SDS 03 Applicability New South Wales CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source RIC Standard SC 00 13 01 03 SP Version 3.0 Document Status Version Date Reviewed
Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard SDS 03 Applicability New South Wales CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source RIC Standard SC 00 13 01 03 SP Version 3.0 Document Status Version Date Reviewed
Control, Safe Use and Operation of Road-Rail Plant
 Control, Safe Use and Operation of Page 1 of 13 Part A Synopsis A Standard detailing the requirements for the control, safe use and operation of road-rail plant in the railway environment. Approval and
Control, Safe Use and Operation of Page 1 of 13 Part A Synopsis A Standard detailing the requirements for the control, safe use and operation of road-rail plant in the railway environment. Approval and
Mechanical Trainstop Systems
 Mechanical Trainstop Systems Synopsis This document defines the functional requirements for mechanical trainstop systems and the requirements relating to their use on both track and trains. Signatures
Mechanical Trainstop Systems Synopsis This document defines the functional requirements for mechanical trainstop systems and the requirements relating to their use on both track and trains. Signatures
Control, Safe Use and Operation of Excavators, Loaders and Earth Moving Equipment
 Control, Safe Use and Operation of Excavators, Loaders and Earth Moving Equipment Page 1 of 14 Part A Synopsis A standard detailing the requirements for the control, safe use and operation of excavators,
Control, Safe Use and Operation of Excavators, Loaders and Earth Moving Equipment Page 1 of 14 Part A Synopsis A standard detailing the requirements for the control, safe use and operation of excavators,
Enterprise Services, General Manager Technical Standards. Track and Civil Code of Practice Section 7 Clearances Technical Note ETD-07-01
 TO FROM Network Wide Enterprise Services, General Manager Technical Standards DATE 09/11/2017 SUBJECT Track and Civil Code of Practice Section 7 Clearances Technical Note ETD-07-01 TITLE Technical Note
TO FROM Network Wide Enterprise Services, General Manager Technical Standards DATE 09/11/2017 SUBJECT Track and Civil Code of Practice Section 7 Clearances Technical Note ETD-07-01 TITLE Technical Note
Operating Procedures Overhead and Electrical Equipment - Procedures 1 to 11
 Operating Procedures Overhead and Electrical Equipment - Procedures 1 to 11 Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 1 07 August 2011 0 04
Operating Procedures Overhead and Electrical Equipment - Procedures 1 to 11 Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 1 07 August 2011 0 04
Track Vehicles ANWT 316. Applicability. Publication Requirement. Document Status NSW SMS. External Only September 2018.
 Applicability NSW SMS Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 3.1 16 September 2018 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC) Disclaimer This document
Applicability NSW SMS Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 3.1 16 September 2018 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC) Disclaimer This document
General Interface Requirements
 Discipline: Engineering (Rolling Stock) Category: Standard General Interface Requirements WOS 01.100 Applicability New South Wales Primary Source RIC Standard RSU 100 Series Version 2.0 Document Status
Discipline: Engineering (Rolling Stock) Category: Standard General Interface Requirements WOS 01.100 Applicability New South Wales Primary Source RIC Standard RSU 100 Series Version 2.0 Document Status
Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures
 Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures s Rule Number: 3025 Version 1.0, 31 March 2016 Temporary Speed Restrictions Rule Number: 3025 Document Control Identification Document title Number Version Date
Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures s Rule Number: 3025 Version 1.0, 31 March 2016 Temporary Speed Restrictions Rule Number: 3025 Document Control Identification Document title Number Version Date
Title High Voltage and 1500 System Earthing References and Definitions. Reference Number PDS 02 (RIC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title High Voltage and 1500 System Earthing References and Definitions Reference Number PDS 02 (RIC Standard: EP 12 00 00 01 SP) Document Control
Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title High Voltage and 1500 System Earthing References and Definitions Reference Number PDS 02 (RIC Standard: EP 12 00 00 01 SP) Document Control
WORKING SAFELY NEXT TO WEST MIDLANDS METRO
 WORKING SAFELY NEXT TO WEST MIDLANDS METRO GUIDELINES FOR BUSINESSES, CONTRACTORS, EVENT ORGANISERS & OTHERS WORKING ON OR NEAR TO WEST MIDLANDS METRO. If you own, occupy a building or other assets near
WORKING SAFELY NEXT TO WEST MIDLANDS METRO GUIDELINES FOR BUSINESSES, CONTRACTORS, EVENT ORGANISERS & OTHERS WORKING ON OR NEAR TO WEST MIDLANDS METRO. If you own, occupy a building or other assets near
Train Order System - Rules 1 to 37
 Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 1 07 August 2011 0 04 October 2015 1 01 July 2018 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC)
Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 1 07 August 2011 0 04 October 2015 1 01 July 2018 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC)
SYDNEY TRAMWAY MUSEUM TROLLEY WIRE INSPECTION PROCEDURE
 TROLLEY WIRE INSPECTION PROCEDURE JUNE 2014 1. Document Details: Name: SYDNEY TRAMWAY MUSEUM Document Control Record Number STM 6029 Version Number: 15 TrolleyWire Inspection Procedure Document Status:
TROLLEY WIRE INSPECTION PROCEDURE JUNE 2014 1. Document Details: Name: SYDNEY TRAMWAY MUSEUM Document Control Record Number STM 6029 Version Number: 15 TrolleyWire Inspection Procedure Document Status:
Guidelines when working near TasNetworks electrical assets
 Guidelines when working near TasNetworks electrical assets About TasNetworks Tasmanian Networks Pty Ltd (ACN 167 357 299) ( TasNetworks ) is the owner and operator of the regulated electricity network
Guidelines when working near TasNetworks electrical assets About TasNetworks Tasmanian Networks Pty Ltd (ACN 167 357 299) ( TasNetworks ) is the owner and operator of the regulated electricity network
Risk Management of Rail Vehicle Axle Bearings
 Railway Group Standard Risk Management of Rail Vehicle Axle Bearings Synopsis This Railway Group Standard mandates that there shall be riskbased processes to minimise and detect failures of rail vehicle
Railway Group Standard Risk Management of Rail Vehicle Axle Bearings Synopsis This Railway Group Standard mandates that there shall be riskbased processes to minimise and detect failures of rail vehicle
Inspection of Points and Crossings: Procedure
 Division / Business Unit: Function: Document Type: Enterprise Services Engineering (Track & Civil) Standard Inspection of Points and Crossings: Procedure Applicability ARTC Network Wide SMS Publication
Division / Business Unit: Function: Document Type: Enterprise Services Engineering (Track & Civil) Standard Inspection of Points and Crossings: Procedure Applicability ARTC Network Wide SMS Publication
Minimum Operating Standards for. Rolling Stock WOS 01
 Discipline Engineering Standard Category Rolling Stock Minimum Operating Standards for Rolling Stock WOS 01 Applicability ARTC Network wide New South Wales Western Jurisdiction Victoria Primary Source
Discipline Engineering Standard Category Rolling Stock Minimum Operating Standards for Rolling Stock WOS 01 Applicability ARTC Network wide New South Wales Western Jurisdiction Victoria Primary Source
Working of Trains - Rules 1 to 45
 Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 1 07 August 201 0 04 October 2015 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC) Disclaimer This
Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 1 07 August 201 0 04 October 2015 Australian Rail Track Corporation Limited (ARTC) Disclaimer This
Equipotential Bonding of Rail Vehicles to Running Rail Potential
 Railway Group Standard Equipotential Bonding of Rail Vehicles to Running Rail Potential Synopsis This standard mandates the requirements for equipotenial bonding of rail vehicles to comply with the Electricity
Railway Group Standard Equipotential Bonding of Rail Vehicles to Running Rail Potential Synopsis This standard mandates the requirements for equipotenial bonding of rail vehicles to comply with the Electricity
Title Low Voltage Distribution and Installations Earthing References and Definitions. Reference Number PDS 03 (ARTC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Low Voltage Distribution and Installations Earthing References and Definitions Reference Number PDS 03 (ARTC Standard: EP 12 00 00 02 SP) Document
Discipline Engineering Standard NSW Category Electrical Title Low Voltage Distribution and Installations Earthing References and Definitions Reference Number PDS 03 (ARTC Standard: EP 12 00 00 02 SP) Document
Permissible Track Forces for Railway Vehicles
 British Railways Board Page 1 of 11 Part A Synopsis This document prescribes design and maintenance requirements for traction and rolling stock and for on track plant to ensure that interactive forces
British Railways Board Page 1 of 11 Part A Synopsis This document prescribes design and maintenance requirements for traction and rolling stock and for on track plant to ensure that interactive forces
CPCS renewal test factsheet
 CPCS renewal test factsheet Introduction to the CPCS renewal test The industry-led CPCS Management Committee has determined that key safety-related knowledge must be checked on each category prior to the
CPCS renewal test factsheet Introduction to the CPCS renewal test The industry-led CPCS Management Committee has determined that key safety-related knowledge must be checked on each category prior to the
SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL. Estimation and Costing & Utilization of Electrical Energy
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Estimation and Costing & Utilization of Electrical Energy Estimation and Costing & Utilization of electrical Energy Estimation
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Estimation and Costing & Utilization of Electrical Energy Estimation and Costing & Utilization of electrical Energy Estimation
Document Control Identification. Document History. Authorisation
 Document Control Identification Document History Authorisation Rail Safety Manager Brookfield Rail 1 October 2016 Table of Contents Glossary for this Rule... 4... 9... 9... 9... 10... 11... 12... 13...
Document Control Identification Document History Authorisation Rail Safety Manager Brookfield Rail 1 October 2016 Table of Contents Glossary for this Rule... 4... 9... 9... 9... 10... 11... 12... 13...
Track Circuit Assister Configuration for Rail Vehicles
 Track Circuit Assister Configuration for Rail Synopsis This Standard mandates where TCAs shall be fitted onto a vehicle and how they shall be set up. It also contains the requirements for testing a TCA.
Track Circuit Assister Configuration for Rail Synopsis This Standard mandates where TCAs shall be fitted onto a vehicle and how they shall be set up. It also contains the requirements for testing a TCA.
Module M4. Floods and snow. GE/RT M4 Rule Book. Issue 1. June 2003
 GE/RT8000 - M4 Rule Book Module M4 Floods and snow Issue 1 June 2003 Comes into force 6 December 2003 Issue Date Comments Comes into force 1 June 2003 Initial issue 6 December 2003 Copyright 2003 Railway
GE/RT8000 - M4 Rule Book Module M4 Floods and snow Issue 1 June 2003 Comes into force 6 December 2003 Issue Date Comments Comes into force 1 June 2003 Initial issue 6 December 2003 Copyright 2003 Railway
Centralised Traffic Control System - Rules 1 to 17
 Centralised Traffic Control System - Rules 1 to 17 Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 2 13 May 2012 0 04 October 2015 Australian Rail
Centralised Traffic Control System - Rules 1 to 17 Applicability VIC Publication Requirement External Only Document Status Issue/Revision # Effective from 2 13 May 2012 0 04 October 2015 Australian Rail
Title Requirements for Electric Aerials Crossing ARTC Infrastructure. Reference Number PYS 02 - (RIC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard - NSW Category Electrical Title Requirements for Electric Aerials Crossing ARTC Infrastructure Reference Number PYS 02 - (RIC Standard: EP 10 01 00 05 SP) Document Control
Discipline Engineering Standard - NSW Category Electrical Title Requirements for Electric Aerials Crossing ARTC Infrastructure Reference Number PYS 02 - (RIC Standard: EP 10 01 00 05 SP) Document Control
Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures
 Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures Setting Back or Propelling on Running Lines Rule Number: 4015 Version 1.0, 31 March 2016 Setting Back or Propelling on Running Lines Rule Number: 4015 Document
Network Safeworking Rules and Procedures Setting Back or Propelling on Running Lines Rule Number: 4015 Version 1.0, 31 March 2016 Setting Back or Propelling on Running Lines Rule Number: 4015 Document
Substation Lightning Protection. Document Number: 1-11-FR-11
 Substation Lightning Protection Document Number: 1-11-FR-11 VERSION 1.0 June 2018 This functional requirements document is in line with the organisation's 1-11-ACS-11 Substation Lightning Protection Asset
Substation Lightning Protection Document Number: 1-11-FR-11 VERSION 1.0 June 2018 This functional requirements document is in line with the organisation's 1-11-ACS-11 Substation Lightning Protection Asset
Interface between Rail Vehicle Weights and Underline Bridges
 Interface between Rail Vehicle Weights and Synopsis This document sets out the requirements for managing the risk of overloading of underline bridges by rail vehicles Submitted by Signatures removed from
Interface between Rail Vehicle Weights and Synopsis This document sets out the requirements for managing the risk of overloading of underline bridges by rail vehicles Submitted by Signatures removed from
Position Paper. Telehandler Use: Lifting Suspended Loads
 Position Paper Telehandler Use: Lifting Suspended Loads The following paper reflects the considered opinion on the Crane Association of New Zealand (Inc.) This document has been prepared by the Technical
Position Paper Telehandler Use: Lifting Suspended Loads The following paper reflects the considered opinion on the Crane Association of New Zealand (Inc.) This document has been prepared by the Technical
Installation Manual. Talon Series. Portable Vehicle Scale by Fairbanks Scales, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Installation Manual Talon Series Portable Vehicle Scale 2007-2012 by Fairbanks Scales, Inc. All rights reserved 51158 Revision 5 12/12 Disclaimer Every effort has been made to provide complete and accurate
Installation Manual Talon Series Portable Vehicle Scale 2007-2012 by Fairbanks Scales, Inc. All rights reserved 51158 Revision 5 12/12 Disclaimer Every effort has been made to provide complete and accurate
CPCS renewal test factsheet
 CPCS renewal test factsheet Introduction to the CPCS renewal test The industry-led CPCS Management Committee has determined that key safety-related knowledge must be checked on each category prior to the
CPCS renewal test factsheet Introduction to the CPCS renewal test The industry-led CPCS Management Committee has determined that key safety-related knowledge must be checked on each category prior to the
CER/EIM Position Paper Ballast Pick-up due to Aerodynamic Effects. October Version 1.0
 CER/EIM Position Paper Ballast Pick-up due to Aerodynamic Effects October 2015 Version 1.0 Introduction Aerodynamic loads on the trackbed generated by the passing of trains at high speed may cause individual
CER/EIM Position Paper Ballast Pick-up due to Aerodynamic Effects October 2015 Version 1.0 Introduction Aerodynamic loads on the trackbed generated by the passing of trains at high speed may cause individual
SECTION 11 INTERMODAL EQUIPMENT
 SECTION 11 INTERMODAL EQUIPMENT ROA MANUAL SCHEDULE OF AMENDMENTS SECTION 11 AMENDMENT NUMBER PAGES AMENDED AMENDMENT SUMMARY DATE ISSUED TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Description Page No. 11.1 SCOPE... 11-1
SECTION 11 INTERMODAL EQUIPMENT ROA MANUAL SCHEDULE OF AMENDMENTS SECTION 11 AMENDMENT NUMBER PAGES AMENDED AMENDMENT SUMMARY DATE ISSUED TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Description Page No. 11.1 SCOPE... 11-1
Route Access Condition Notice
 Route Access Condition Notice 13-00039 Distributed To: ARTC Website Distribution Date: 04/04/14 Requested By: Subject: Effective Period: Amendment Type: ARTC General Review by Rules Team Until Published
Route Access Condition Notice 13-00039 Distributed To: ARTC Website Distribution Date: 04/04/14 Requested By: Subject: Effective Period: Amendment Type: ARTC General Review by Rules Team Until Published
Rapid Response. Lineside Signal Spacing. Railway Group Standard GK/RT0034 Issue Three Date September 1998
 Rapid Response Railway Group Standard Lineside Signal Spacing Synopsis This Standard specifies the minimum distance that must be provided between the first signal displaying a cautionary aspect and the
Rapid Response Railway Group Standard Lineside Signal Spacing Synopsis This Standard specifies the minimum distance that must be provided between the first signal displaying a cautionary aspect and the
Appendix 3. DRAFT Policy on Vehicle Activated Signs
 Appendix 3 DRAFT Policy on Vehicle Activated Signs Ealing Council has been installing vehicle activated signs for around three years and there are now 45 across the borough. These signs help to reduce
Appendix 3 DRAFT Policy on Vehicle Activated Signs Ealing Council has been installing vehicle activated signs for around three years and there are now 45 across the borough. These signs help to reduce
Lineside Signal Spacing and Speed Signage
 Document comes into force and supersedes GKRT0075 Iss 3 on 05/12/15 With effect from 03/03/18 parts of this document have been superseded by Date September 15 Lineside Signal Spacing and Speed Synopsis
Document comes into force and supersedes GKRT0075 Iss 3 on 05/12/15 With effect from 03/03/18 parts of this document have been superseded by Date September 15 Lineside Signal Spacing and Speed Synopsis
Signalling Rolling Stock Interface
 Division / Business Unit: Function: Document Type: Enterprise Services Signalling Standard Signalling Rolling Stock Interface Applicability ARTC Network Wide SMS Publication Requirement Internal / External
Division / Business Unit: Function: Document Type: Enterprise Services Signalling Standard Signalling Rolling Stock Interface Applicability ARTC Network Wide SMS Publication Requirement Internal / External
PRINTOUT MAY NOT BE UP-TO-DATE; REFER TO METRO INTRANET FOR THE LATEST VERSION
 Engineering Specification Track L1-CHE-SPE-064 Ballast Supply Version: 1 Issued: October 2015 Owner: Engineering Group Approved By: Gordon Djurdjevic Track Engineering Manager PRINTOUT MAY NOT BE UP-TO-DATE;
Engineering Specification Track L1-CHE-SPE-064 Ballast Supply Version: 1 Issued: October 2015 Owner: Engineering Group Approved By: Gordon Djurdjevic Track Engineering Manager PRINTOUT MAY NOT BE UP-TO-DATE;
Locomotive Hauled Passenger Vehicle Specific Interface Requirements WOS
 Discipline Engineering Standard Category Rolling Stock Locomotive Hauled Passenger Vehicle Specific Interface Requirements WOS 01.500 Applicability ARTC Network wide New South Wales Western Jurisdiction
Discipline Engineering Standard Category Rolling Stock Locomotive Hauled Passenger Vehicle Specific Interface Requirements WOS 01.500 Applicability ARTC Network wide New South Wales Western Jurisdiction
Module SP. Speeds. GE/RT8000/SP Rule Book. Issue 5. September 2015
 GE/RT8000/SP Rule Book Module SP Speeds Issue 5 September 2015 Comes into force 05 December 2015 Published by: RSSB The authoritative version of this document is available at www.rssb.co.uk/rgsonline Contents
GE/RT8000/SP Rule Book Module SP Speeds Issue 5 September 2015 Comes into force 05 December 2015 Published by: RSSB The authoritative version of this document is available at www.rssb.co.uk/rgsonline Contents
Australian/New Zealand Standard
 AS/NZS 3845:1999 Australian/New Zealand Standard Road safety barrier systems AS/NZS 3845:1999 This Joint Australian/New Zealand Standard was prepared by Joint Technical Committee CE/33, Road Safety Barrier
AS/NZS 3845:1999 Australian/New Zealand Standard Road safety barrier systems AS/NZS 3845:1999 This Joint Australian/New Zealand Standard was prepared by Joint Technical Committee CE/33, Road Safety Barrier
Rail safety statistics Six monthly statistics for the period ended 30 June August 2015
 Rail safety statistics Six monthly statistics for the period ended 30 June 2015 August 2015 Disclaimer All reasonable endeavours are made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this report. However,
Rail safety statistics Six monthly statistics for the period ended 30 June 2015 August 2015 Disclaimer All reasonable endeavours are made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this report. However,
Port of Oulu Ltd. 8 Dec PERIOD OF VALIDITY AND INFORMING OF CHANGES RAIL NETWORK... 2
 1 NETWORK STATEMENT for the 2019 timetable period (Link to Finnish version) Contents 1 PERIOD OF VALIDITY AND INFORMING OF CHANGES... 2 1.1 INFORMING OF CHANGES... 2 2 RAIL NETWORK... 2 2.1 DESCRIPTION,
1 NETWORK STATEMENT for the 2019 timetable period (Link to Finnish version) Contents 1 PERIOD OF VALIDITY AND INFORMING OF CHANGES... 2 1.1 INFORMING OF CHANGES... 2 2 RAIL NETWORK... 2 2.1 DESCRIPTION,
Handbook 15. Issue 5. Duties of the machine controller (MC) and ontrack plant operator. GERT8000-HB15 Rule Book
 GERT8000-HB15 Rule Book Duties of the machine controller (MC) and ontrack plant operator Handbook 15 Issue 5 September 2017 Comes into force 02 December 2017 Published by: RSSB The authoritative version
GERT8000-HB15 Rule Book Duties of the machine controller (MC) and ontrack plant operator Handbook 15 Issue 5 September 2017 Comes into force 02 December 2017 Published by: RSSB The authoritative version
SUBSTATION INTERLOCKING SCHEMES
 SUBSTATION INTERLOCKING SCHEMES This document is for internal and contract specific use only. Disclaimer NGG and NGET or their agents, servants or contractors do not accept any liability for any losses
SUBSTATION INTERLOCKING SCHEMES This document is for internal and contract specific use only. Disclaimer NGG and NGET or their agents, servants or contractors do not accept any liability for any losses
Transportation Engineering II UNIT - I
 Transportation Engineering II UNIT - I I. Components of a Permanent Way: A. Rails: Rails are the I-section members of a track laid in two parallel lines to provide a level surface for the movement of trains.
Transportation Engineering II UNIT - I I. Components of a Permanent Way: A. Rails: Rails are the I-section members of a track laid in two parallel lines to provide a level surface for the movement of trains.
file://c:\users\salearners\desktop\e-books2\road Signs Two K53 Learners Licenc...
 Page 1 of 15 ROAD SIGNS TWO >> 1) What does this sign tell motorists: [A] The right lane is coming to an end in 200m [B] A highway is beginning in 200m [C] The left lane is coming to an end in 200m 2)
Page 1 of 15 ROAD SIGNS TWO >> 1) What does this sign tell motorists: [A] The right lane is coming to an end in 200m [B] A highway is beginning in 200m [C] The left lane is coming to an end in 200m 2)
TE-II (10CV63) Ballast
 Lecture-09 10CV63 TE-II Introduction Ballast The ballast is a layer of broken stones, gravel, moorum, or any other granular material placed and packed below and around sleepers for distributing load from
Lecture-09 10CV63 TE-II Introduction Ballast The ballast is a layer of broken stones, gravel, moorum, or any other granular material placed and packed below and around sleepers for distributing load from
Inspection and Assessment of Track Geometry
 Purpose This document defines requirements for inspection and assessment of track geometry. This document applies to all infrastructure on the Victorian Regional Infrastructure Lease managed by V/Line
Purpose This document defines requirements for inspection and assessment of track geometry. This document applies to all infrastructure on the Victorian Regional Infrastructure Lease managed by V/Line
PRINTOUT MAY NOT BE UP-TO-DATE; REFER TO METRO INTRANET FOR THE LATEST VERSION
 Engineering Standard Track Vehicles Version: 8 Issued: December 2016 Owner: Chief Engineer Approved By: Phil Ellingworth Chief Engineer PRINTOUT MAY NOT BE UP-TO-DATE; REFER TO METRO INTRANET FOR THE LATEST
Engineering Standard Track Vehicles Version: 8 Issued: December 2016 Owner: Chief Engineer Approved By: Phil Ellingworth Chief Engineer PRINTOUT MAY NOT BE UP-TO-DATE; REFER TO METRO INTRANET FOR THE LATEST
NZQA registered unit standard version 1 Page 1 of 5. Apply and remove portable earths in an electricity supply system
 Page 1 of 5 Title Apply and remove portable earths in an electricity supply system Level 4 Credits 7 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: demonstrate knowledge of earthing and bonding
Page 1 of 5 Title Apply and remove portable earths in an electricity supply system Level 4 Credits 7 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: demonstrate knowledge of earthing and bonding
Locating Ground Mounted Equipment
 Network Asset Technical Document Locating Ground Mounted Equipment Original issue: April 2008 Prepared by: Lee Chan & Robert Rogerson This revision: Original Issue Date for next review: April 2013 Copyright
Network Asset Technical Document Locating Ground Mounted Equipment Original issue: April 2008 Prepared by: Lee Chan & Robert Rogerson This revision: Original Issue Date for next review: April 2013 Copyright
9 Locomotive Compensation
 Part 3 Section 9 Locomotive Compensation August 2008 9 Locomotive Compensation Introduction Traditionally, model locomotives have been built with a rigid chassis. Some builders looking for more realism
Part 3 Section 9 Locomotive Compensation August 2008 9 Locomotive Compensation Introduction Traditionally, model locomotives have been built with a rigid chassis. Some builders looking for more realism
TOC Waiver. ARTC website
 TOC Waiver Reference Number 12475 Distributed To: ARTC website Distribution Date: 05/06/2014 Requested By: Subject: Effective Period: ARTC RAS Manual Stage 1 implementation for the ARTC in New South Wales
TOC Waiver Reference Number 12475 Distributed To: ARTC website Distribution Date: 05/06/2014 Requested By: Subject: Effective Period: ARTC RAS Manual Stage 1 implementation for the ARTC in New South Wales
Safe use of portable ladders
 Safe use of portable ladders A portable ladder is primarily used for gaining access to areas above or below the ground, or other levels that are not provided with permanent access. The potential for injury
Safe use of portable ladders A portable ladder is primarily used for gaining access to areas above or below the ground, or other levels that are not provided with permanent access. The potential for injury
Australian Standard. Cranes, hoists and winches Safe use. Part 10: Mobile elevating work platforms AS AS
 AS 2550.10 2006 AS 2550.10 2006 Australian Standard Cranes, hoists and winches Safe use Part 10: Mobile elevating work platforms This Australian Standard was prepared by Committee ME-005, Cranes. It was
AS 2550.10 2006 AS 2550.10 2006 Australian Standard Cranes, hoists and winches Safe use Part 10: Mobile elevating work platforms This Australian Standard was prepared by Committee ME-005, Cranes. It was
SECTION 14: AERIAL LIFT PROGRAM
 SECTION 14: AERIAL LIFT PROGRAM Fisher Auto Parts is committed to promoting a safe and healthy environment for all employees and customers. Protection from accidental loss of any resources, especially
SECTION 14: AERIAL LIFT PROGRAM Fisher Auto Parts is committed to promoting a safe and healthy environment for all employees and customers. Protection from accidental loss of any resources, especially
CPCS renewal test factsheet
 CPCS renewal test factsheet Introduction to the CPCS renewal test The industry-led CPCS Management Committee has determined that key safety-related knowledge must be checked on each category prior to the
CPCS renewal test factsheet Introduction to the CPCS renewal test The industry-led CPCS Management Committee has determined that key safety-related knowledge must be checked on each category prior to the
Road Signs. 1) Which one of the following is correct when encountering this sign:
 Road Signs 1) Which one of the following is correct when encountering this sign: Maintain speed and continue driving Decrease speed and give right of way to vehicles on your left Decrease speed and give
Road Signs 1) Which one of the following is correct when encountering this sign: Maintain speed and continue driving Decrease speed and give right of way to vehicles on your left Decrease speed and give
Australian 5" Gauge Track Notes
 Australian 5" Gauge Track Notes Track gauge The track gauge is normally specified as 5" with a tolerance of -0 / + 1 / 32 " or 127mm -0 / +0.8mm. The rail is generally made from rectangular bar (25 x 10
Australian 5" Gauge Track Notes Track gauge The track gauge is normally specified as 5" with a tolerance of -0 / + 1 / 32 " or 127mm -0 / +0.8mm. The rail is generally made from rectangular bar (25 x 10
safedirection.com.au Ref: PM 017/02
 DISTRIBUTOR 0 Product Manual Ref: PM 017/02 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 3 2.0 The... 3 3.0 How the Functions... 4 4.0 Crash Test Performance... 4 5.0 Characteristics of Terminals... 5 5.1 Gating
DISTRIBUTOR 0 Product Manual Ref: PM 017/02 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 3 2.0 The... 3 3.0 How the Functions... 4 4.0 Crash Test Performance... 4 5.0 Characteristics of Terminals... 5 5.1 Gating
Road Safety Problems Documented On April 23, 2012
 Road Safety Problems Documented On April 23, 2012 Posting Date: 23 April 2012 This is a chronicle of a single morning's drive through the rural outskirts of London, Ontario, Canada, and the safety-related
Road Safety Problems Documented On April 23, 2012 Posting Date: 23 April 2012 This is a chronicle of a single morning's drive through the rural outskirts of London, Ontario, Canada, and the safety-related
Locomotive Specific Interface Requirements WOS
 Discipline Engineering Standard Category Rolling Stock Locomotive Specific Interface Requirements WOS 01.300 Applicability ARTC Network wide New South Wales Western Jurisdiction Victoria Primary Source
Discipline Engineering Standard Category Rolling Stock Locomotive Specific Interface Requirements WOS 01.300 Applicability ARTC Network wide New South Wales Western Jurisdiction Victoria Primary Source
Health, Safety, Security and Environment
 Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
Ensure staff are trained in use of equipment
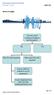 Work at height Can you avoid working at height in the first place? No Yes Plan the task required Risk assess the task required Ensure staff are trained in use of equipment Ensure equipment has been correctly
Work at height Can you avoid working at height in the first place? No Yes Plan the task required Risk assess the task required Ensure staff are trained in use of equipment Ensure equipment has been correctly
Operating instructions
 Operating instructions Digital tank contents indicator DTA 10 DTA 10 DTA 10 0 4.0 m fuel oil 0 3.5 m water Read instructions before using device! Observe all safety information! Keep instructions for future
Operating instructions Digital tank contents indicator DTA 10 DTA 10 DTA 10 0 4.0 m fuel oil 0 3.5 m water Read instructions before using device! Observe all safety information! Keep instructions for future
ROAD TRANSPORT AND DISTRIBUTION AWARD 2010
 ROAD TRANSPORT AND DISTRIBUTION AWARD 2010 This summary has been prepared as an easy reading guide for Members of the Timber Trade Industrial Association. It is not intended to replace the award but to
ROAD TRANSPORT AND DISTRIBUTION AWARD 2010 This summary has been prepared as an easy reading guide for Members of the Timber Trade Industrial Association. It is not intended to replace the award but to
Ballast Usually stone chippings, or similar material, which support the sleepers and hold them in place on the ground.
 Model Rail Terminology Alternating Current/AC The electric current that flows alternately through each wire in a rapid sequence called a cycle. The normal mains electricity supply is powered by Alternating
Model Rail Terminology Alternating Current/AC The electric current that flows alternately through each wire in a rapid sequence called a cycle. The normal mains electricity supply is powered by Alternating
Caltex Australia comments on Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper February 2009
 Caltex Australia comments on Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper February 2009 Upstream Point of Liability - Fuel Tax Package Outline of scheme The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme (CPRS) White
Caltex Australia comments on Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper February 2009 Upstream Point of Liability - Fuel Tax Package Outline of scheme The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme (CPRS) White
Requirements for the Application of Standard Vehicle Gauges
 Synopsis This document defines standard vehicle gauges and the associated application rules for rolling stock and for infrastructure. [This document contains one or more pages which contain colour] Copyright
Synopsis This document defines standard vehicle gauges and the associated application rules for rolling stock and for infrastructure. [This document contains one or more pages which contain colour] Copyright
Shoulder Ballast Cleaner Work Method Statement
 Shoulder Ballast Cleaner Specific to SBC34 Warning You cannot undertake this activity in the rail corridor unless you have completed a pre work brief and work site protection plan. Reference should also
Shoulder Ballast Cleaner Specific to SBC34 Warning You cannot undertake this activity in the rail corridor unless you have completed a pre work brief and work site protection plan. Reference should also
Controlling the Speed of Tilting Trains Through Curves
 Controlling the Speed of Tilting Trains Through Curves Synopsis This document mandates the means by which Tilting Trains may be operated at higher speeds than nontilting trains around curves. Signatures
Controlling the Speed of Tilting Trains Through Curves Synopsis This document mandates the means by which Tilting Trains may be operated at higher speeds than nontilting trains around curves. Signatures
Port of Oulu Ltd. 9 Dec 2016
 1 NETWORK STATEMENT Replaces the safety instruction for rail network traffic and rail work of the that entered into force on 1 June 2016. Contents 1 PERIOD OF VALIDITY AND INFORMING OF CHANGES... 2 1.1
1 NETWORK STATEMENT Replaces the safety instruction for rail network traffic and rail work of the that entered into force on 1 June 2016. Contents 1 PERIOD OF VALIDITY AND INFORMING OF CHANGES... 2 1.1
SYDNEY TRAMWAY MUSEUM
 DISABLED TRAMCARS Instruction Manual For Retrieving Disabled Tramcars Prepared for Traffic Officers-in-Charge Disabled Tramcars Manual STM 6152 Version 1 19/5/08 1. Document Details: Name: SYDNEY TRAMWAY
DISABLED TRAMCARS Instruction Manual For Retrieving Disabled Tramcars Prepared for Traffic Officers-in-Charge Disabled Tramcars Manual STM 6152 Version 1 19/5/08 1. Document Details: Name: SYDNEY TRAMWAY
PROCEDURE. Operative Date: 22/12/2016 Department: HSEC. Revision: Author: D Steel CONTENTS
 Title: Cranes - Inspection and Maintenance PROCEDURE Procedure No: P314.422 Issue: 1 Revision: 0 Operative Date: 22/12/2016 Department: HSEC Sect./Classification: Safety / Gear & Equipment Author: D Steel
Title: Cranes - Inspection and Maintenance PROCEDURE Procedure No: P314.422 Issue: 1 Revision: 0 Operative Date: 22/12/2016 Department: HSEC Sect./Classification: Safety / Gear & Equipment Author: D Steel
Uncontrolled When Printed Supersedes GERT8000-DC Iss 2 on 01/03/2014. Module DC. GE/RT8000/DC Rule Book. DC electrified lines. Issue 3.
 GE/RT8000/DC Rule Book Module DC DC electrified lines Issue 3 March 2014 Comes into force 07 June 2014 Conventions used in the Rule Book Example A black line in the margin indicates a change to that rule
GE/RT8000/DC Rule Book Module DC DC electrified lines Issue 3 March 2014 Comes into force 07 June 2014 Conventions used in the Rule Book Example A black line in the margin indicates a change to that rule
Hydraulic power is the key to the utility of many excavators.
 CHAPTER Construction Planning, Equipment, and Methods EXCAVATORS Sixth Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 8 By Dr. Ibrahim Assakkaf ENCE 420 Construction
CHAPTER Construction Planning, Equipment, and Methods EXCAVATORS Sixth Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 8 By Dr. Ibrahim Assakkaf ENCE 420 Construction
Level Crossing Equipment
 Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard Level Crossing Equipment ESC-03-01 Applicability ARTC Network Wide CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source SC 03 01 Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared
Discipline: Engineering (Signalling) Category: Standard Level Crossing Equipment ESC-03-01 Applicability ARTC Network Wide CRIA (NSW CRN) Primary Source SC 03 01 Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared
LOAD SAFETY SERIES Information Sheet
 LOAD SAFETY SERIES Information Sheet March 2016 What the Law requires Under Health and Safety Legislation, a vehicle is a place of work. The law requires that workplaces are maintained in a condition that
LOAD SAFETY SERIES Information Sheet March 2016 What the Law requires Under Health and Safety Legislation, a vehicle is a place of work. The law requires that workplaces are maintained in a condition that
The West Lancashire Light Railway OPERATING RULE BOOK
 The West Lancashire Light Railway OPERATING RULE BOOK Revision 4-5th November 2008 This supersedes any previous versions of the Rule Book CONTENTS 1 Definitions and Abbreviations 2 Method of Operation
The West Lancashire Light Railway OPERATING RULE BOOK Revision 4-5th November 2008 This supersedes any previous versions of the Rule Book CONTENTS 1 Definitions and Abbreviations 2 Method of Operation
Transport by road overweight and overdimension loads that do not require a pilot or overdimension permit
 Page 1 of 7 Transport by road overweight and overdimension loads that do not require a pilot or overdimension permit Level 4 Credits 9 Purpose This unit standard is for drivers who transport overweight
Page 1 of 7 Transport by road overweight and overdimension loads that do not require a pilot or overdimension permit Level 4 Credits 9 Purpose This unit standard is for drivers who transport overweight
Rubber Tyred Vehicles Technical Bulletin
 Rubber Tyred Vehicles Technical Bulletin Bulletin Number: TB0906 Date: 17/06/2009 Subject: TBS Design Registration 130 Purpose To inform the industry of the registration of the Transport Braking System
Rubber Tyred Vehicles Technical Bulletin Bulletin Number: TB0906 Date: 17/06/2009 Subject: TBS Design Registration 130 Purpose To inform the industry of the registration of the Transport Braking System
REFERENCE CP_TSSPEC_138 0 DATE: JUNE 2006 PAGE: 1 OF 17 TITLE SPECIFICATION FOR POLE- MOUNTED AUTO-RECLOSERS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TITLE SPECIFICATION FOR POLE- MOUNTED DATE: JUNE 2006 PAGE: 1 OF 17 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page FOREWORD...2 INTRODUCTION...3 1 SCOPE...3 2 NORMATIVE S...3 3 DEFINITIONS AND ABBIATIONS...3 4 REQUIREMENTS...3
TITLE SPECIFICATION FOR POLE- MOUNTED DATE: JUNE 2006 PAGE: 1 OF 17 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page FOREWORD...2 INTRODUCTION...3 1 SCOPE...3 2 NORMATIVE S...3 3 DEFINITIONS AND ABBIATIONS...3 4 REQUIREMENTS...3
Structural Requirements For Drawgear And Buffers On Railway Vehicles
 Structural Requirements For Drawgear And Buffers On Railway Vehicles Submitted by D. Boocock Nominated Responsible Manager Synopsis This standard prescribes the strength requirements for drawgear and buffers
Structural Requirements For Drawgear And Buffers On Railway Vehicles Submitted by D. Boocock Nominated Responsible Manager Synopsis This standard prescribes the strength requirements for drawgear and buffers
UCKFIELD MODEL RAILWAY CLUB BENTLEY MINIATURE RAILWAY TRACK SAFETY REGULATIONS
 UCKFIELD MODEL RAILWAY CLUB BENTLEY MINIATURE RAILWAY TRACK SAFETY REGULATIONS (revised July 2005) (amended April 2012) REFERENCE DOCUMENTS These Regulations should be read in conjunction with the following
UCKFIELD MODEL RAILWAY CLUB BENTLEY MINIATURE RAILWAY TRACK SAFETY REGULATIONS (revised July 2005) (amended April 2012) REFERENCE DOCUMENTS These Regulations should be read in conjunction with the following
Protecting Workers on the Track
 Transport for London London Underground Access Protecting Workers on the Track Train Movements Learning information booklet Effective April 2014 Issue 1 MAYOR OF LONDON Contents Section page 1 Introduction
Transport for London London Underground Access Protecting Workers on the Track Train Movements Learning information booklet Effective April 2014 Issue 1 MAYOR OF LONDON Contents Section page 1 Introduction
Uncontrolled When Printed Document to be superseded on 01/12/2012 Superseded by GERT8000-HB15 Iss 2 published on 01/09/2012
 GE/RT8000/HB15 Rule Book Handbook 15 Duties of the machine controller (MC) and on-track plant operator Handbook 15 Issue 1 Valid from June 2011 Published by: RSSB Block 2 Angel Square 1 Torrens Street
GE/RT8000/HB15 Rule Book Handbook 15 Duties of the machine controller (MC) and on-track plant operator Handbook 15 Issue 1 Valid from June 2011 Published by: RSSB Block 2 Angel Square 1 Torrens Street
A Guide to Key Railroad Terminology for the Northeast Corridor
 A Guide to Key Railroad Terminology for the Northeast Corridor Index of terms Approach signal, 8 Diverging route, 5 Ladder, 6 Section break, 12, 13 Tie replacement, 7 Ballast, 3, 4, 7 Double slip switch,
A Guide to Key Railroad Terminology for the Northeast Corridor Index of terms Approach signal, 8 Diverging route, 5 Ladder, 6 Section break, 12, 13 Tie replacement, 7 Ballast, 3, 4, 7 Double slip switch,
Applicable standards in HS Infrastructure subsystem TSI (2008/217/EC)
 Applicable standards in HS Infrastructure subsystem TSI (2008/217/EC) ERA 1.0 Page 1/8 Standards or other documents referred to in the HS infrastructure TSI (and therefore mandatory) TSI Sections Characteristics
Applicable standards in HS Infrastructure subsystem TSI (2008/217/EC) ERA 1.0 Page 1/8 Standards or other documents referred to in the HS infrastructure TSI (and therefore mandatory) TSI Sections Characteristics
SECTION 23 CLASSIFICATION AND NUMBERING OF FREIGHT VEHICLES
 SECTION 23 CLASSIFICATION AND NUMBERING OF FREIGHT VEHICLES ROA MANUAL SCHEDULE OF AMENDMENTS SECTION 23 AMENDMENT NUMBER PAGES AMENDED AMENDMENT SUMMARY DATE ISSUED TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Description
SECTION 23 CLASSIFICATION AND NUMBERING OF FREIGHT VEHICLES ROA MANUAL SCHEDULE OF AMENDMENTS SECTION 23 AMENDMENT NUMBER PAGES AMENDED AMENDMENT SUMMARY DATE ISSUED TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Description
INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
 SUMP TANKS INSTALLATION GUIDELINES Thank you for purchasing a quality SumpTank. In order to gain the maximum benefit from your purchase, we have outlined the following instructions for the installation
SUMP TANKS INSTALLATION GUIDELINES Thank you for purchasing a quality SumpTank. In order to gain the maximum benefit from your purchase, we have outlined the following instructions for the installation
