GeneralInformation General General. General General. General General General General General General General General General General General
|
|
|
- Clifton Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 information Information 1
2 Why die clamping systems? Cost manual die change It will pay for itself! automatic die change Innovative technology and many years of experience are the basis for our range of die clamping and changing systems. Rationalize your operation by using automatic die changing systems. Change-over operations Improved productivity More capacity thanks to reduced set-up times Less downtime e.g. due to tool breakage or reworking of dies Short test period Operating facility Operate under extreme circumstances (high temperature, spray) Die clamping in barely accessible positions Clamping using high clamping forces Dies may be changed by relatively unskilled workers Repeatable die changing process Automation Power operated elements Monitoring devices, in particular for pressure and position Short cycles thanks to automatic triggering of functions Integration with process monitoring and control Improved quality Consistent quality Repeatability of die position Low-distortion clamping Economy Short set-up times even for small batches, smaller stock of parts Simplified die change, can be carried out by the machine operator Fewer jigs and fixtures required Enhanced tool life as a result of less wear Reduced run-in period for tools and dies, fewer test pieces and less time needed Reduced rate of wear Uniform and low-distortion clamping, high clamping forces Compensating clamping force (elasticity) Repeatable positioning and clamping operation Optimum selection of clamping points 10
3 Contents Clamping principles T-slots in the press bed and slide Pages Clamping force Clamping time Pages Efficiency analysis Calculation of payback period Pages Hydraulic parameters Symbols of clamping hydraulics Pages Safety stages Power units Pages
4 Clamping principles Clamping principles Examples of clamping Clamping element Product group Die Sliding clamp, angular clamps Clamping bars, hollow piston cylinder Wedge clamps with a flat clamping edge Spring clamping cylinders Extending clamps Clamping screws 6 Pivot and pull clamp Wedge swing clamp Electromechanical clamping elements Rapid clamping system with pusher chain Hollow piston cylinder Angular clamp, electromechanical 3 5 Wedge clamp for dies with a tapered clamping edge 2 Die Double-T clamping bars Pull clamping element Swivel and pull clamps, hydraulic Swivel and pull clamps, electrical Swing-sink clamping element Swing clamping element Pull clamping element with T-slot 4 12
5 f T-slot dimensions according to DIN 650 or ANSI spec T-slot dimensions according to DIN 650 or ANSI spec Dimensions and tolerances for T-slots according to DIN 650 or ANSI spec. Applicable to machine beds, pallets or die clamping devices on presses. a (mm) 18 H8 22 H8 28 H8 36 H8 a (in) 13 / / 16 f min. (mm) f min. (in) f max. (mm) f max. (in) b (mm) b (in) c (mm) c (in) h min. (mm) h min. (in) h max. (mm) h max. (in) n max. (mm) 1,6 1,6 1,6 2,5 n max. (in) The slot depth h and the web height f must be exactly measured and checked for possible tolerances. If your T-slot is not within the specified tolerance range, customized solutions are also possible. Recommended clamping forces for T-slots acc. to DIN 650 T-slot Clamping force max. 18 mm 40 kn 22 mm 60 kn 28 mm 100 kn 36 mm 160 kn If the above clamping forces are exceeded, permanent deformation of the T-slot may be caused. Conversion factors Temperature Pressure K C F K 1 C +273,15 ( F-459,67) x 5/9 C K-273,15 1 ( F-32) x 5/9 F K x 9/5 +459,67 C x 9/ MPa 1 bar 1PSI 1 MPa ,04 1 bar 0,1 1 14,504 1 PSI 0, , K = Kelvin C = Degrees centigrade F = Degrees Fahrenheit MPa = Mega-Pascal PSI = Imperial pound per square inch Length mm inch 1 inch 25, mm 1 0,0393 inch = Imperial unit of length 13
6 Clamping force, Clamping time, Calculations Clamping force Thread, property class 8.8 Permissible test load to DIN 267 sheet 3 (kn) Max. permissible preload (utilising 2/3 of the yield point) (kn) Required tightening torque (Nm) Maximum manual clamping force* (kn) Clamping force using a clamping arm (leverage = 2 :1) (kn) Number x piston Ø for obtaining the preload specified in line 3 at 400 bar (mm) M6 M8 M10 M12 M14 M16 M20 M24 M30 M36 M42 M x16 1x20 1x25 1x32 1x40 1 x 44 2 x 32 3 x 25 1 x 55 2 x 40 3 x 32 1 x 63 2 x 50 3 x 40 1 x 80 3 x 50 4 x 40 1 x100 4 x 50 6 x 40 1 x x 80 6 x 50 1 x140 3 x 80 8 x 50 Mechanical clamping and unclamping time per clamping point ** (s) Hydraulic clamping and unclamping time per clamping point *** (s) Recommendations (50) (70) (100) 0,8 0,9 1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3 1,5 1,8 2,2 3,0 4,0 5,0 If there are several clamping points, hydraulic clamping is recommended Transition from manual to hydraulic clamping Max. permissible clamping force cannot be achieved manually; hydraulic clamping is preferred Manual clamping is no longer appropriate; hydraulic clamping only * Clamping force that can be achieved manually using a wrench to DIN 894, by applying a manual force of 150N and a coefficient of friction of ** Total time required in case of mechanical clamping and unclamping to obtain the clamping force specified in line 5, without taking account of time required for providing single components. Clamping stroke = 6 mm When working overhead or when using clamping claws, the clamping and unclamping time must be increased by about 50%. *** Total time required for hydraulic clamping and unclamping to obtain the clamping force specified in line 3. Electric power unit with solenoid valves. Pump delivery 40 cm 3 /s at 400 bar. Clamping stroke = 6 mm. Clamping time for other clamping strokes Time for mechanical clamping = Time for hydraulic clamping = t = Clamping time specified in lines 8 and 9 h = Clamping stroke (mm) m = Stroke factor 0.8 for stroke >6 mm Stroke factor 1.2 for stroke <6 mm t x h 6 t x h x m 6 (s) (s) Calculations Clamping time, t t = Piston velocity, v v = q x s x z 16 x Q 160 x Q A x z [s] [mm/s] Pump delivery, Q = q x s x z 16 x t [l/min] Motor power on continuous duty, P P = 2,7 x n x V x p [W] Pressure loss in pipes, Δp Δp = 1 x L 4 x d x v 2 [bar] t = Clamping time [sec] q = Oil required per 1 mm piston stroke acc. to catalogue [cm 3 /mm] s = Clamping stroke [mm] z = Number of clamping cylinders Q = Pump delivery [l/min] A = Piston area [cm 2 ] n = Motor speed [rpm] V = Pump delivery (l/min.) p = Operating pressure [bar] Assumed: = 0,055, p = 700 Ns 2 /m 4 y, volumetric efficiency 0.96, motor efficiency 0.88 L = Pipe length [m] (straight, smooth pipe) d = Pipe inner diameter [mm] v = Flow velocity [m/s] v max. = 6 m/s for pressure pipes, 2 m/s for return pipes F = force F = A x p A = surface p = pressure 14
7 Determination of clamping force The clamping force to be applied for upper and lower die depends on: the stripping force on the slide the ejection force the acceleration force the die weight The total clamping force to be produced by the clamping elements must be higher than the greatest of all forces acting in a specific case. In general, the following approximate value may be assumed as the total clamping force for the upper or the lower die Total clamping force = 10 % - 20 % of the pressing force Based on the total clamping force, the required number of clamping elements is determined taking account of their clamping force and local conditions (symmetry, clearance, etc.) Stripping force on the slide This is the force acting on the die s clamping points after deduction of losses due to friction and acceleration. In the case of die casting machines, this force is referred to as the opening force. In a specific case it must be checked whether this force has to be taken into consideration when designing the clamping elements. Under normal operating conditions, the full machine potential is not utilized. Often it only becomes evident when the die halves have become stuck. The clamping elements must be designed in such a way that they are not damaged or broken in such cases of emergency. (Approximate values as per VDI guidelines 3145, see below.) Ejection force If ejectors are used, the maximum ejection force must be taken into account. The ejection force acts on the die, if the ejector cylinders do not move against their own stops but when the die is used as stop. Thus, ejection forces must be considered in any case. (Approximate values as per VDI guidelines 3145, see below.) Approximate values as per VDI guidelines 3145 Stripping force on the slide: 5 % 20 % of the pressing force Ejection force in the bed: 5 % 20% of the pressing force Ejection force in the slide: 1 % 10 % of the pressing force Acceleration force The acceleration force must be taken into consideration when using very heavy dies and/or in case of high slide acceleration. The acceleration depends on the press drive, on the mechanical properties (elasticity, rigidity) of the press frame and on the operations being carried out. The following approx. values may be assumed: approx. 50 g for high-speed automatic punching presses approx. 30 g for open-front presses approx. 6 g for car body presses For determining the occurring acceleration force, the die weight must be known. The interrelation is shown in the diagram below: Acceleration force (kn) Weight of the die in the slide (kg) Example of calculation Hydraulic double-column press, without drawing operation, max. stripping force 400 kn; weight of upper and lower dies: 1000 kg each. Approximate value for the total clamping force per die half: Determination on the basis of the acceleration force: 20% of the pressing force = approx. 400 kn. with an acceleration of 10 g and a weight of 1000 kg, the acceleration force (as per diagram) is approx. 100 kn. In view of the low acceleration force, the clamping force is determined on the basis of the stripping force. Thus, the required total clamping force is 400 kn. 15
8 Analysis of economic value Assistance in reaching a decision When does an investment pay for itself? The subject of quick die changing on forming presses and injection molding machines should not be interpreted too closely. The term clamping includes the complete part of the process which is capable of being automated, i.e. feeding to and positioning in the machine, clamping and transporting outside the machine and, in a broader sense, also storage of dies. Hilma-Roemheld offers system solutions which are suitable for adaptation to customers specific needs. There may be many reasons for automation, the degree being dependent of the criteria prevailing in a company with respect to production and to the workplace. A decision for automation may be influenced by the following criteria: improving productivity minimizing set-up times increasing flexibility rationalization measures humanization of work safety This means that the decision for an automation of the die changing process is not only taken on the basis of a cost-benefit analysis but it is also influenced by workplacerelated optimizing approaches. In order to approach a solution by taking account of both quantity- and quality-related aspects, the so-called efficiency analysis may be applied. This method for an alternative assessment offers the possibility of including also those criteria which cannot be expressed in units of money. In addition to the fixed and variable costs of an investment, quality-related features such as guaranteed conditions availability of spare parts safety service life advice and training ease of operation compatibility with the environment, etc. can also be taken into account. For each criterion included an evaluation is determined which reflects the importance of the criterion concerned. In the second step, each alternative relevant for the decision is assigned a mark, based on its compliance with the various criteria. By multiplying these dimensionless figures, a partial efficiency is obtained for each criterion. Addition of the partial efficiency obtained for the alternative under consideration will give the overall efficiency. In the example, two alternative solutions for press automation are at choice. Using this model of an analysis of the efficiency (scoring model) decisions can also be made taking account of quality criteria. Die changing system A Die changing system B Criterion Evaluation % Degree of compliance 2) Efficiency Degree of compliance Efficiency Acquisition costs Maintenance Safety Operation Spare parts Training Overall efficiency ,00 3 0, ,80 6 1, ,50 9 2, , , ,40 9 0, ,06 9 0, ,06 7,05 2) The degree of compliance is expressed in marks between 1 and 10, 10 being the best. Although the price of die changing system B does not meet with expectations (assigned degree of compliance = 3), this alternative has a higher overall efficiency. For more details, we recommend reference to examples on the Internet, catchword: Analysis of efficiency. When simply comparing costs, only the investment costs of two or more alternatives are compared with the anticipated benefit. 16
9 Calculation of payback period Calculation of payback period In this method, the acquisition costs (purchase price, calculatory depreciation and interest), the operating costs (energy, maintenance, expenses for the room where the machine is installed, follow-up costs for dies) as well as wage costs (set-up times, run-in period after die change) are calculated and, related to the planned die changing frequency, compared with the savings in time and costs. Example of calculation Using the example of an existing press, two alternative proposals for die changing are compared. The production conditions are as follows: 2-shift operation, 810 min./day one die change per shift the dies are being used in the press roller bars and support consoles for loading the die are already fitted to the press Example A Die change is carried out using ten M24 mechanical clamping screws on the slide and six M24 clamping screws on the bed. The acquisition costs are negligible compared with alternative B. Example B On the slide, die change is carried out using quick clamping systems from product group 3, i.e. hollow piston cylinders type HILMA (8x). On the bed, die change is carried out using clamping bars of product group 2 type HILMA (4x). Clamping bar Hollow piston cylinder 17
10 Calculation of payback period Comparison of costs Example A Example B data Transfer press (existing) number 1 1 Existing dies number 5 5 Planned dies number 3 3 If die change is carried out once per shift, about 500 die changes are carried out per year. Die change Number/year 500* 500 Costs / change 126,87 38,47 Cost advantage /change 88,40 Amortisation of die change ~ 347 die changes ( / 88,40) this corresponds to approx. 8,33 months * 500 die changes/year = 2 die changes/day x 250 working days Die changing system Clamping elements on the slide Clamping elements on the bed Power unit (including controls) Installation / Commissioning Rework of existing dies Costs of the die changing system Set-up times Die clamping on the slide min. 6,5 0,5 Die clamping on the bed min. 3,9 0,5 Die unclamping on the slide min. 6,5 0,5 Die unclamping on the bed min. 3,9 0,5 Die transport min. 4,0 4,0 Die set-up times min. 24,8 6,0 Under the given marginal conditions, an investment of 30,700 quoted as an example in alternative B will have paid off after approx months or 347 die changes. The production time gained by the reduction in the set-up times has not been taken into account. Die changing Die changes / shift number 1 1 Manpower / number of die changes number 1 1 Set-up time / month h 17,3 4,2 Hourly machine rate /h Set-up costs / month Set-up costs / year /year Hourly wage /h 25,56 25,56 Wage costs / year Calculatory depreciation years /year Calculated interests /year Sum of costs /year
11 Calculation of payback period Rough calculation As a first approach, the following formula can be used for determining the payback period with sufficient accuracy: Payback period = costs benefit = investment (quick die clamping) - investment (conventional) saving of time x hourly machine rate x die change Parameters: Investment costs (quick die clamping/changing system B) [ ] Investment costs (conventional clamping/changing system A) [ ] Saving of time = quick die clamping [min] - conventional clamping [min] Hourly machine rate [ /min] Die change [changes/month] Payback period [months] For the above example, a rough calculation gives the following results: Payback period = ( ) (24,8-6) x (280/60) x (500/12) = 8,39 months The payback period of 8.39 months determined by this method is almost identical with the payback period determined by way of calculation and thus is sufficiently accurate. Costs/benefit in Manual clamping cost benefit Quick die clamping system, hydraulic Break-even point 347 die changes = ^ 8,39 months Die change 19
12 Hydraulic parameters and recommendations Data contained in the catalog: All parameters are quoted in accordance with the VDI Guidelines 3267 to Designations and symbols according to ISO Dimensions in SI units, according to DIN Dimensions without tolerance indication: DIN 7168, medium. Clamping elements: Constant working pressure: see catalog sheets Ambient temperature: -10 C to 70 C (other temperatures on request) Mounting position: any, unless otherwise stated Piston velocity: 0.01 to 0.25 m/s Oil leakage rate: at 400 bar 20 C hydraulic oil HLP 32 - dynamic: g per double stroke (Ø = 32, stroke = 40, V = 0.1 m/s) g per double stroke (Ø = 40, stroke = 40, V = 0.1 m/s) - static: 0.03 g in 24 hours Oil recommendation: Oil temperature Designation Viscosity ( C) acc. to DIN acc. to DIN HLP 22 ISOVG HLP 32 ISOVG HLP 46 ISOVG 46 (Other hydraulic fluids are available on request) Influence of temperature: Fluids expand differently under the influence of increasing temperatures. If no space is available for expansion, the change results in a pressure increase. Since the clamping system is a closed system, there will be a pressure increase. Conversely, a decrease in temperature results in a decrease in pressure. As a rule of thumb one can say that a 10 C increase in temperature results in a 100 bar increase in pressure. In the case of a significant decrease in temperature, e.g. during the night in unheated workshops, the pressure will decrease accordingly. It is therefore recommended that systems which are isolated from the pressure generator are fitted with a pressure accumulator, in order to reduce any decrease in pressure. Pipe fittings: According to DIN screwed plugs type B to DIN 3852, sheet 2 (sealing by sealing edge) should be used. Do not use additional sealing materials such as Teflon tape! Connecting threads: Whitworth pipe threads type X to DIN 3852, sheet 2 (for cylindrical screwed plugs). Piping: Seamless, plain ended steel pipes as per DIN 2391 NBK. Preferably: Outer 0 (mm) Wall thickness (mm) Hydraulic pressure (bar) Fitting 8 1,5 400 G 1/4 8 2,0 500 G 1/4 12 2,5 400 G 3/8 12 3,0 500 G 3/8 16 3,0 400 G 1/2 (inch) (inch) (psi) 1/ ,650 G 1/4 5/ ,250 G 1/4 3/ ,900 G 3/8 Pipe runs should be as short as possible. The length of pipes for single-acting cylinders with a spring return should not exceed 5 m, pipes for double-acting cylinders may be longer. Make sure that pipes are installed with a large bending radius. Hose connections: For connection of the clamping elements we recommend high-pressure hoses with 4 x safety factor at an operating pressure of 500 bar. Special designs should be used for hoses subject to constant movement, e.g. hoses for oil supply to the slide. Observe the minimum radius bends. Starting the system, maintenance: Read the operating instructions before starting the system. Use clean and fresh oil. Bleed the complete system by operating the pump at low pressure (~20 bar) until the oil which emerges at the highest point is free from bubbles (rinsing). Since hydraulic valves are very sensitive to dirt, make sure that no impurities are carried into the hydraulic oil. A change of oil should be carried out once a year. Dynamic pressure in the hydraulic system: Due to friction in pipes, screw fittings, valves and cylinders a pressure of 1 2 bar is necessary for proper oil circulation. The retracting springs in cylinders with a spring return are designed for a maximum dynamic pressure of 2 bar. If the cylinders move slowly, or if they do not retract properly, the dynamic pressure must be reduced (larger pipe diameter, shorter pipes, fewer screw fittings, connection in parallel rather than in series, reduced weight on the piston). In applications with double-acting cylinders dynamic pressure is likely to occur when pressure is applied to the rod side and the larger oil volume from the piston side must flow back to the oil reservoir through narrow pipes and valves. Normally, dynamic pressure has no negative effect. However, if in applications with swing clamps and swing sink clamps the drop is in excess of 50 bar, this may cause premature wear of the swing mechanism and result in a malfunction (see catalog sheets). 20
13 Symbols and designations used in hydraulic clamping systems Pressure generators Valves Constant displacement pump Variable displacement pump 2/2-way valve with shut-off in neutral position Manual operation in general Two-stage pump Hand-operated pump 2/2-way valve with flow in neutral position 3/2-way valve with shut-off in neutral position by button by lever Air pump Electric pump 3/2-way valve with flow in neutral position Check valve by pushbutton by spring Pressure intensifier, pneum.-hydr. Pressure intensifier, hydr.-hydr. Check valve with spring Check valve pilot controlled by solenoid by hydr. pressure Hydraulic cylinders Pressure relief valve Cylinder, single-acting Cylinder, single-acting with spring return Hollow piston cylinder, single-acting with spring return Spring clamping cylinder, pulling Sequence valve Cylinder, double-acting Pull cylinder, single-acting with spring return Spring clamping cylinder, pressing Swing sink clamping element, double-acting Pressure regulator valve Throttle valve, non-adjustable Throttle valve, adjustable Hollow piston cylinder, single-acting Swing clamping element, double-acting One way restrictor Energy transmission Hydraulic oil supply and accessories Other equipment Pressure source Operating line Control line Flexible line Electric line Line interconnection Line crossing Bleeding point Outlet with pipe connection Pressure connection Screw coupling Quick connect coupling Rotary coupling, 1-way Rotary coupling, 3-way Reservoir Pressure accumulator Filter Cooler Pressure reducer unit Pressure gauge Differential pressure gauge Thermometer Flow meter Pressure sensor Pressure switch Excerpt from ISO 1219, DIN
14 Safety levels Safety levels are determined by different safety requirements and manufacturing technologies. Based on the state of technical development, hydraulic die clamping systems can be classified into one of three safety levels. Safety level no. 1: Preferably for presses with column-guided dies: Pressure switches in every clamping circuit for controlling the clamping force, used for machine safety. Two independent hydraulic circuits. Clamping circuit Safety circuit = 50% of the clamping elements in bed and slide = 50% of the clamping elements in bed and slide If one circuit fails, the upper or lower die is still clamped with 50% of the total clamping power. Clamping circuit Safety circuit Unclamping circuit Pressure switch Clamping element Safety level no. 2: For presses with dies which are not column-guided A check valve (pilot controlled) maintains pressure in the clamping and safety circuits even when the pressure drops in the remaining system. Clamping circuit Safety circuit Unclamping circuit Check valve (pilot controlled) Safety level no. 3: For power presses and car body presses with dies which are not column-guided. All clamping elements are secured by pilot controlled check valves. If pressure drops by more than 20% of the operating pressure, the pressure switch stops the press. The check valves maintain the clamping force for many days. Clamping circuit Unclamping circuit 22
15 Hydraulic power units Hydraulic power units used for clamping applications need low oil volumes but high pressures, other than those used for applications involving motion. The power unit operates intermittently under automatic pressure control, i.e. when the set pressure of 400 bar is reached the motor is automatically switched off. If the pressure drops below 360 bar, the pressure switch causes the motor to start again. The valves used are of the seat-valve type. This ensures that oil loss in each clamping circuit is restricted to a minimum. The solenoids of the valves are designed for a 24V DC supply and for continuous duty. They are idle when the clamping elements are clamped. In addition to a high service life, this ensures that even in the case of power failure the clamping force is maintaine For power units of this design only small oil reservoirs are required, since the oil is only slightly heated up. The energy balance is very favorable. Modular system enables individual solutions Frame-type unit for 3 forging presses: 12 clamping circuits with pressure reduction for compensation of temperature high-pressure 4.2 l/min., 400 bar cooling return 45 l/min., 10 bar Power unit, series 7: 2.8 l/min., max. 400 bar Power unit, 4.2 l/min., max. 400 bar ready for connection and immediate use For more technical information on power units, please refer to product group 7. 23
16 QUICK DIE CHANGE Automatic or Manual Hilma has been safely clamping dies for more than 50 years. We work with you to develop an automatic or manual die change system to suit your needs. We provide the products and support to keep you competitive in today s manufacturing environment. Manual Clamping Nut See Section 6 New Automatic Flexline Traveling Clamp See Section 3 24
/2017. Swing sink clamping element double-acting
 Applications: integrated in press rams integrated in press beds in machine tools and equipment when the available space is limited when temperatures may reach 70 C For power units please see product group
Applications: integrated in press rams integrated in press beds in machine tools and equipment when the available space is limited when temperatures may reach 70 C For power units please see product group
Hydraulic clamping elements
 Hydraulic clamping elements hydraulic 3 Contents Product group 3 Hollow piston cylinder single-acting 3.1403 3.2130 Sliding clamp single-acting compact classic 3.2202 3.2204 Angular clamping element single
Hydraulic clamping elements hydraulic 3 Contents Product group 3 Hollow piston cylinder single-acting 3.1403 3.2130 Sliding clamp single-acting compact classic 3.2202 3.2204 Angular clamping element single
Ball Rail Systems RE / The Drive & Control Company
 Ball Rail Systems RE 82 202/2002-12 The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems
Ball Rail Systems RE 82 202/2002-12 The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems
Wedge clamps
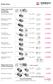 Wedge clamps Wedge clamps for dies with tapered clamping edge Without position monitoring up to 160 C* 2.24000 With position monitoring lateral fastening up to 100 C** 2.24001 With position monitoring
Wedge clamps Wedge clamps for dies with tapered clamping edge Without position monitoring up to 160 C* 2.24000 With position monitoring lateral fastening up to 100 C** 2.24001 With position monitoring
...components in motion. Miniature Linear Guideways
 ...components in motion Miniature Linear Introduction Miniature linear guideway systems are widely used throughout industry for precise, compact applications. Precise and Stainless The gothic arch shape
...components in motion Miniature Linear Introduction Miniature linear guideway systems are widely used throughout industry for precise, compact applications. Precise and Stainless The gothic arch shape
Die changing technique
 Die changing Die changing 8 Contents Product group 8 Roller bar, hydraulically lifted for heavy loads (400 bar), lifting of the complete roller bar for medium loads (120 bar), lifting of individual rollers
Die changing Die changing 8 Contents Product group 8 Roller bar, hydraulically lifted for heavy loads (400 bar), lifting of the complete roller bar for medium loads (120 bar), lifting of individual rollers
/2017. Hollow piston cylinder, single-acting spring clamping hydraulic unclamping
 , single-acting spring clamping hydraulic unclamping Applications: un-pressurized long-term clamping of dies or fixtures on press beds and rams when the space available is limited T-bolt Spring clamping
, single-acting spring clamping hydraulic unclamping Applications: un-pressurized long-term clamping of dies or fixtures on press beds and rams when the space available is limited T-bolt Spring clamping
Miniature Ball Rail Systems
 R310EN 2210 (2004.06) The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature-BRS R310EN 2210 (2004.06) Linear Motion Systems Ball Rail System Standard Ball Rail
R310EN 2210 (2004.06) The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature-BRS R310EN 2210 (2004.06) Linear Motion Systems Ball Rail System Standard Ball Rail
Profi le rail guides LLR
 Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Vane pump, direct operated
 Vane pump, direct operated RE 1/8.8 Replaces: 1. 1/18 Type PV7 A Nominal sizes 1 to Series 1X / X Maximum operating pressure 1 bar Displacement volume 1 to cm 3 H17 H9 Overview of contents Features Contents
Vane pump, direct operated RE 1/8.8 Replaces: 1. 1/18 Type PV7 A Nominal sizes 1 to Series 1X / X Maximum operating pressure 1 bar Displacement volume 1 to cm 3 H17 H9 Overview of contents Features Contents
Test Which component has the highest Energy Density? A. Accumulator. B. Battery. C. Capacitor. D. Spring.
 Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
Variable Vane Pump, Direct Controlled PV7...A Series 1X / 2X
 Variable Vane Pump, Direct Controlled PV7...A Series 1X / X RE 1 Issue: 1.13 Replaces: 8.8 Sizes 1 to Maximum pressure 1 bar Displacement volume 1 to cm 3 Features Very short control times Low noise Mounting
Variable Vane Pump, Direct Controlled PV7...A Series 1X / X RE 1 Issue: 1.13 Replaces: 8.8 Sizes 1 to Maximum pressure 1 bar Displacement volume 1 to cm 3 Features Very short control times Low noise Mounting
R310EN 2211 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 eline Ball Rail Systems R310EN 2211 (2006.04) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball
eline Ball Rail Systems R310EN 2211 (2006.04) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball
Courtesy of CMA/Flodyne/Hydradyne Motion Control Hydraulic Pneumatic Electrical Mechanical (800)
 01_1 Miniature st Headline_36 Ball Rail pt/14.4 Systems mm second line 2 Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts
01_1 Miniature st Headline_36 Ball Rail pt/14.4 Systems mm second line 2 Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts
Steering unit LAGZ. Data sheet. Series 2 x
 Steering unit LAGZ Data sheet Nominal sizes 125 620 Series 2 x Maximum flow 50 l / min HE 11868 / 09.2017 2 LAGZ HE 11868 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering details Function,
Steering unit LAGZ Data sheet Nominal sizes 125 620 Series 2 x Maximum flow 50 l / min HE 11868 / 09.2017 2 LAGZ HE 11868 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering details Function,
TRANSLATION (OR LINEAR)
 5) Load Bearing Mechanisms Load bearing mechanisms are the structural backbone of any linear / rotary motion system, and are a critical consideration. This section will introduce most of the more common
5) Load Bearing Mechanisms Load bearing mechanisms are the structural backbone of any linear / rotary motion system, and are a critical consideration. This section will introduce most of the more common
TPV Variable Displacement Closed Loop System Axial Piston Pump THE PRODUCTION LINE OF HANSA-TMP HT 16 / M / 852 / 0815 / E
 HYDRAULIC COMPONENTS HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSIONS GEARBOXES - ACCESSORIES Certified Company ISO 9001-14001 ISO 9001 Via M. L. King, 6-41122 MODENA (ITALY) Tel: +39 059 415 711 Fax: +39 059 415 729 / 059 415
HYDRAULIC COMPONENTS HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSIONS GEARBOXES - ACCESSORIES Certified Company ISO 9001-14001 ISO 9001 Via M. L. King, 6-41122 MODENA (ITALY) Tel: +39 059 415 711 Fax: +39 059 415 729 / 059 415
Shaft-Hub-Connections
 Stand: 14.01.2010 Shaft-Hub-Connections Shrink Discs Cone Clamping Elements Star Discs 36 Edition 2012/2013 RINGSPANN Eingetragenes Warenzeichen der RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg Table of Contents Introduction
Stand: 14.01.2010 Shaft-Hub-Connections Shrink Discs Cone Clamping Elements Star Discs 36 Edition 2012/2013 RINGSPANN Eingetragenes Warenzeichen der RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg Table of Contents Introduction
Round Fine Centering for the mold construction. The development. Advantages
 Round Fine Centering for the mold construction The development Advantages Durability: for mass production Backlash-free for very precise mold alignment Shorter cycle times High initial load capacity at
Round Fine Centering for the mold construction The development Advantages Durability: for mass production Backlash-free for very precise mold alignment Shorter cycle times High initial load capacity at
R310EN 2302 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 R31EN 232 (26.4) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball Screw Drives Linear Motion Systems Basic Mechanical
R31EN 232 (26.4) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball Screw Drives Linear Motion Systems Basic Mechanical
Steering unit LAGC. Data sheet
 Steering unit LAGC Data sheet Nominal sizes Series Maximum flow HE 14365 / 09.2017 40 1000 1 x and 2 x 80 l / min 2 LAGC HE 14365 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering details
Steering unit LAGC Data sheet Nominal sizes Series Maximum flow HE 14365 / 09.2017 40 1000 1 x and 2 x 80 l / min 2 LAGC HE 14365 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering details
HYDRAULIC JACKS & TOOLS
 HYDRAULIC JACKS & TOOLS 323 Why hydraulics? Hydraulics is the kind of power transmission which allows the greatest density of forces. There is no other kind of power transmission that will transmit comparable
HYDRAULIC JACKS & TOOLS 323 Why hydraulics? Hydraulics is the kind of power transmission which allows the greatest density of forces. There is no other kind of power transmission that will transmit comparable
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 General Nomenclature Spherical Roller Bearings The spherical roller bearing is a combination radial and thrust bearing designed for taking misalignment under load When loads are heavy, alignment of housings
General Nomenclature Spherical Roller Bearings The spherical roller bearing is a combination radial and thrust bearing designed for taking misalignment under load When loads are heavy, alignment of housings
Spring hangers, spring supports
 Spring hangers, spring supports 2 spring Spring hangers, supports PRODUCT 2 GROUP Spring hangers, spring supports Contents Page Field of application...2.1 Overview of spring hangers and spring supports...2.3
Spring hangers, spring supports 2 spring Spring hangers, supports PRODUCT 2 GROUP Spring hangers, spring supports Contents Page Field of application...2.1 Overview of spring hangers and spring supports...2.3
Features of the LM Guide
 Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
three different ways, so it is important to be aware of how flow is to be specified
 Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
PISTON MOTORS FOR CLOSED LOOP SYSTEMS types HMF/A/V/R-02
 1-control optional swashing to 0 cc /rev 2-swash plate hydrostatic bearing 3-piston-slipper assembly 21 swash angle 4-housing monoshell for high rigidity 5-valve plate housing highly integrated 6-control
1-control optional swashing to 0 cc /rev 2-swash plate hydrostatic bearing 3-piston-slipper assembly 21 swash angle 4-housing monoshell for high rigidity 5-valve plate housing highly integrated 6-control
Is Low Friction Efficient?
 Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
TuffCam Swing Clamps C-1. Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions C-1 When do you recommend the use of TuffCam Swing Clamps over the standard product? Applications where speed is essential, massive arms are required, or position sensing is
Frequently Asked Questions C-1 When do you recommend the use of TuffCam Swing Clamps over the standard product? Applications where speed is essential, massive arms are required, or position sensing is
Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FM
 Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FM RE 91001/06.2012 1/46 Replaces: 09.07 Data sheet Series 6 Size Nominal pressure/maximum pressure 5 315/350 bar 10 to 200 400/450 bar 250 to 1000 350/400 bar Open and closed
Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FM RE 91001/06.2012 1/46 Replaces: 09.07 Data sheet Series 6 Size Nominal pressure/maximum pressure 5 315/350 bar 10 to 200 400/450 bar 250 to 1000 350/400 bar Open and closed
ELGOGLIDE maintenance-free spherical plain bearings and plain bushes
 Not everything that is presented on paper as giving very high performance actually fulfils the expectations raised in practice. Nothing is more annoying than promises that cannot then be kept in technical
Not everything that is presented on paper as giving very high performance actually fulfils the expectations raised in practice. Nothing is more annoying than promises that cannot then be kept in technical
MINIRAIL Profiled miniature guideway
 MINIRAIL Profiled miniature guideway Table of Contents 1 Product overview and technical informations MINIRAIL a range of high-precision products.... 2 MINIRAIL overview accuracy classes:.... 3 MINIRAIL
MINIRAIL Profiled miniature guideway Table of Contents 1 Product overview and technical informations MINIRAIL a range of high-precision products.... 2 MINIRAIL overview accuracy classes:.... 3 MINIRAIL
RE / STAR Tolerance Rings STAR Ball Knobs, Knob and Lever Type Handles
 RE 2 970/.99 STAR Tolerance Rings STAR Ball Knobs, Knob and Lever Type Handles STAR Tolerance Rings Product Overview Tolerance rings are made of hard, embossed spring steel strip and belong to the class
RE 2 970/.99 STAR Tolerance Rings STAR Ball Knobs, Knob and Lever Type Handles STAR Tolerance Rings Product Overview Tolerance rings are made of hard, embossed spring steel strip and belong to the class
Directional servo-valve of 4-way design
 Courtesy of CM/Flodyne/Hydradyne Motion Control Hydraulic Pneumatic Electrical Mechanical (0) 426-54 www.cmafh.com Directional servo-valve of 4-way design Type 4WSE3E 32 Size 32 Component series 5X Maximum
Courtesy of CM/Flodyne/Hydradyne Motion Control Hydraulic Pneumatic Electrical Mechanical (0) 426-54 www.cmafh.com Directional servo-valve of 4-way design Type 4WSE3E 32 Size 32 Component series 5X Maximum
Fixed displacement radial piston pump
 Fixed displacement radial piston pump RE 11263/05.13 Replaces: 10.05 1/16 Type R4 izes 1.60 to 20.00 cm 3 Component series 3X Maximum operating pressure 700 bar H7322 2R4-3X/4,00-700RK01M01+AZF8 H7321
Fixed displacement radial piston pump RE 11263/05.13 Replaces: 10.05 1/16 Type R4 izes 1.60 to 20.00 cm 3 Component series 3X Maximum operating pressure 700 bar H7322 2R4-3X/4,00-700RK01M01+AZF8 H7321
Axial Piston Fixed Pump A17FNO Series 10
 Axial Piston Fixed Pump A17FNO Series 10 RE 91510 Issue: 06.2012 Replaces: 03.2010 Size 125 Nominal pressure 250 bar Maximum pressure 300 bar For commercial vehicles Open circuit Features Fixed pump with
Axial Piston Fixed Pump A17FNO Series 10 RE 91510 Issue: 06.2012 Replaces: 03.2010 Size 125 Nominal pressure 250 bar Maximum pressure 300 bar For commercial vehicles Open circuit Features Fixed pump with
Chapter B-3. Chapter 3. Actuators and output devices. Festo Didactic TP101
 155 Chapter 3 Actuators and output devices Festo Didactic TP101 156 An actuator is an output device for the conversion of supply energy into useful work. The output signal is controlled by the control
155 Chapter 3 Actuators and output devices Festo Didactic TP101 156 An actuator is an output device for the conversion of supply energy into useful work. The output signal is controlled by the control
Rotary-Linear Actuator HSE4 Hydraulic / 100 Bar
 Rotary-Linear Actuator HSE4 Hydraulic / 100 Bar 4 Function and features K A1 G1 B1 G2 KM Y B2 RE A2 Z S2 A S1 W B KS [ Operation ] [ Operating pressure ] The Eckart rotary-linear actuator HSE4 is a combination
Rotary-Linear Actuator HSE4 Hydraulic / 100 Bar 4 Function and features K A1 G1 B1 G2 KM Y B2 RE A2 Z S2 A S1 W B KS [ Operation ] [ Operating pressure ] The Eckart rotary-linear actuator HSE4 is a combination
Selection Tool. on the Internet at in the section MÄDLER -Tools. Other sizes and designs on request. Connecting Shafts Page 766
 Couplings Overview Friction Clutches Friction Clutches Type B Axial Arrangement Friction Clutches Type C Transversal Flexibility Sliding Hubs with Torsionally-Flexible Coupling Multi-Disk Friction Clutches
Couplings Overview Friction Clutches Friction Clutches Type B Axial Arrangement Friction Clutches Type C Transversal Flexibility Sliding Hubs with Torsionally-Flexible Coupling Multi-Disk Friction Clutches
Valve lash adjustment elements. Product Information
 Valve lash adjustment elements Product Information Valve lash adjustment elements Foreword Modern engines nowadays have to satisfy far greater demands than even just 10 years ago. One of the main reasons
Valve lash adjustment elements Product Information Valve lash adjustment elements Foreword Modern engines nowadays have to satisfy far greater demands than even just 10 years ago. One of the main reasons
RA / Internal Gear Pump Model GP3, Series 3X Fixed Displacement. Typical application:
 Sizes 20 to 32 Internal Gear Pump Model GP3, Series 3X Fixed Displacement up to 5076 PSI 1.25 to 1.98 in 3 (350 bar) (20.6 to 32.5 cm 3 ) RA 10 234/07.97 Characteristics: Peak pressure of up to 5.076 PSI
Sizes 20 to 32 Internal Gear Pump Model GP3, Series 3X Fixed Displacement up to 5076 PSI 1.25 to 1.98 in 3 (350 bar) (20.6 to 32.5 cm 3 ) RA 10 234/07.97 Characteristics: Peak pressure of up to 5.076 PSI
Formulas and units
 Formulas and units Hydraulic system and circuit design is limited only by the creativity of the application engineer. All basic circuit design begins with the ultimate actuator functions in mind however.
Formulas and units Hydraulic system and circuit design is limited only by the creativity of the application engineer. All basic circuit design begins with the ultimate actuator functions in mind however.
Features of the LM Guide
 Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Project Manual Industrial Hydraulics
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Project Manual Industrial Hydraulics RE 00845/04.07 Trainer s manual Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Project Manual Industrial Hydraulics RE 00845/04.07 Trainer s manual Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics
Vane pumps, direct controlled Type PV7...A
 Vane pumps, direct controlled Type PV7...A Nominal sizes 1 to 25 eries 1X Maximum operating pressure 1 bar Displacements from 1 to 25 cm 3 H/A 617/95 Type PV7-1X/..RA1MA-... H/A/D 56/97 Typ MPU1-V71-9L/...
Vane pumps, direct controlled Type PV7...A Nominal sizes 1 to 25 eries 1X Maximum operating pressure 1 bar Displacements from 1 to 25 cm 3 H/A 617/95 Type PV7-1X/..RA1MA-... H/A/D 56/97 Typ MPU1-V71-9L/...
ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L
 ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L Very long lifetime and lowest leakage A NEW Modular Linear Drive System With this second generation linear drive Parker Origa offers design engineers complete flexibility.
ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L Very long lifetime and lowest leakage A NEW Modular Linear Drive System With this second generation linear drive Parker Origa offers design engineers complete flexibility.
RA / Internal Gear Pump Model GP2, Series 2X Fixed Displacement. Typical application:
 Sizes 6.3 to 16 Internal Gear Pump Model GP2, Series 2X Fixed Displacement up to 576 PSI.397 to.98 in 3 (35 bar) (6.5 to 16 cm 3 ) RA 1 23/6.97 RA 1 23/6.97 Characteristics: Peak pressure of up to 576
Sizes 6.3 to 16 Internal Gear Pump Model GP2, Series 2X Fixed Displacement up to 576 PSI.397 to.98 in 3 (35 bar) (6.5 to 16 cm 3 ) RA 1 23/6.97 RA 1 23/6.97 Characteristics: Peak pressure of up to 576
Rexroth Hydraulics. Fixed displacement vane pumps Types PVV and PVQ RE /11.97
 RE 1 335/1.97 RE 1 335/11.97 Fixed displacement vane pumps Types and Nominal sizes 18 to 193 Series 1X Maximum operating pressure 21 bar Maximum displacement 18 to 193 cm 3 H/A/D 5769/97 Single pump type
RE 1 335/1.97 RE 1 335/11.97 Fixed displacement vane pumps Types and Nominal sizes 18 to 193 Series 1X Maximum operating pressure 21 bar Maximum displacement 18 to 193 cm 3 H/A/D 5769/97 Single pump type
VARIABLE PUMPS FOR CLOSED LOOP OPERATION type HV-02
 Design characteristics 1-control device modular design, precise and load-independent 2-swash plate hydrostatic bearing 3-piston-slipper assembly 21 swash angle 4-housing monoshell for high rigidity 5-valve
Design characteristics 1-control device modular design, precise and load-independent 2-swash plate hydrostatic bearing 3-piston-slipper assembly 21 swash angle 4-housing monoshell for high rigidity 5-valve
Proven to be better. Development trends in industrial rolling bearings
 Proven to be better Development trends in industrial rolling bearings Contents 1. General trends in power transmission and in machine construction and plant engineering Page 3 2. General trends in rolling
Proven to be better Development trends in industrial rolling bearings Contents 1. General trends in power transmission and in machine construction and plant engineering Page 3 2. General trends in rolling
Truck Hydraulics. Serie VP1 Variable Displacement Pumps
 ruck Hydraulics Variable Displacement Pumps aerospace climate control electromechanical filtration fluid & gas handling hydraulics pneumatics process control sealing & shielding Contents Pump and line
ruck Hydraulics Variable Displacement Pumps aerospace climate control electromechanical filtration fluid & gas handling hydraulics pneumatics process control sealing & shielding Contents Pump and line
GSM. Modular Design. Versions of the series. Type GSM. Gripper type P Z W R. Size. {} AS IS without O.D. clamping I.D. clamping
 GSM s Modular Design Versions of the series Type GSM Gripper type P Z W R Size 32 40 50 64 30 38 45 16 20 25 32 40 16 20 25 32 40 Gripping force safety device {} AS IS without O.D. clamping I.D. clamping
GSM s Modular Design Versions of the series Type GSM Gripper type P Z W R Size 32 40 50 64 30 38 45 16 20 25 32 40 16 20 25 32 40 Gripping force safety device {} AS IS without O.D. clamping I.D. clamping
For advanced drive technology CLAMPEX. Shaft-Hub-Connection. KTR Precision Joints CLAMPEX
 technology CLAMPEX Shaft-Hub-Connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision Joints 07 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 09 Selection and calculation -5 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0 10 0
technology CLAMPEX Shaft-Hub-Connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision Joints 07 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 09 Selection and calculation -5 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0 10 0
EMC-HD. C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm
 C Electromechanical 01_1 Headline_36pt/14.4mm Cylinder EMC-HD C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm 2 Elektromechanischer Zylinder EMC-HD Short product name Example: EMC 085 HD 1 System = ElectroMechanical Cylinder
C Electromechanical 01_1 Headline_36pt/14.4mm Cylinder EMC-HD C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm 2 Elektromechanischer Zylinder EMC-HD Short product name Example: EMC 085 HD 1 System = ElectroMechanical Cylinder
Rodless Pneumatic Cylinders Series OSP-P
 Rodless Pneumatic Cylinders Series OSP-P System Concepts & Components... 2-5 Technical Data... 7-9 Dimensions... 10-15 Active rakes... 16-19 Accessories (Mounts & Supports)... 20-29 Ordering Information...30
Rodless Pneumatic Cylinders Series OSP-P System Concepts & Components... 2-5 Technical Data... 7-9 Dimensions... 10-15 Active rakes... 16-19 Accessories (Mounts & Supports)... 20-29 Ordering Information...30
Linear Drive with Ball Screw Drive Series OSP-E..SB
 Linear Drive with Ball Screw Drive Series OSP-E..SB Contents Description Data Sheet No. Page Overview 1.30.001E 47-50 Technical Data 1.30.002E-1 to 5 51-55 Dimensions 1.30.002E-6, -7 56-57 Order instructions
Linear Drive with Ball Screw Drive Series OSP-E..SB Contents Description Data Sheet No. Page Overview 1.30.001E 47-50 Technical Data 1.30.002E-1 to 5 51-55 Dimensions 1.30.002E-6, -7 56-57 Order instructions
Hydraulics. Axial Piston Pumps Series PVP. Introduction. With thru shaft option for multiple pump options Swash plate type for open circuit
 Introduction *not included Pump with standard compensator, code: "omit" With thru shaft option for multiple pump options Swash plate type for open circuit Pump with load sensing, code: "A" Mounting style
Introduction *not included Pump with standard compensator, code: "omit" With thru shaft option for multiple pump options Swash plate type for open circuit Pump with load sensing, code: "A" Mounting style
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS. This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module:
 FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material
SCHMIDT PneumaticPress
 Maximum pressing force from 1.6 kn to 60 kn The SCHMIDT PneumaticPress range consists of a modular system suitable for transforming, joining and assembling operations optimally within the pressing capacities
Maximum pressing force from 1.6 kn to 60 kn The SCHMIDT PneumaticPress range consists of a modular system suitable for transforming, joining and assembling operations optimally within the pressing capacities
Metalworking ETP HYDRO-GRIP. Achieve Excellence through Simplicity. Hydraulic high precision toolholders
 Metalworking ETP HYDRO-GRIP Hydraulic high precision toolholders Achieve Excellence through Simplicity ETP HYDRO-GRIP Hydraulic high precision toolholders HYDRO-GRIP high precision tool holders are your
Metalworking ETP HYDRO-GRIP Hydraulic high precision toolholders Achieve Excellence through Simplicity ETP HYDRO-GRIP Hydraulic high precision toolholders HYDRO-GRIP high precision tool holders are your
Compact Modules. with ball screw drive and toothed belt drive R310EN 2602 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 with ball screw drive and toothed belt drive R310EN 2602 (2007.02) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings
with ball screw drive and toothed belt drive R310EN 2602 (2007.02) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings
Axial piston variable motor A6VM series 71
 xial piston variable motor 6VM series 71 RE 91610 Edition: 06.2014 Replaces: 04.2013 Sizes 60 to 215 Nominal pressure 450 bar Maximum pressure 500 bar Open and closed circuits Features Variable motor with
xial piston variable motor 6VM series 71 RE 91610 Edition: 06.2014 Replaces: 04.2013 Sizes 60 to 215 Nominal pressure 450 bar Maximum pressure 500 bar Open and closed circuits Features Variable motor with
Directional servo-valve in 4-way design
 Directional servo-valve in 4-way design RE 2983/.11 Replaces: 7.3 1/ Type 4WS.2E... Size Component series X Maximum operating pressure 31 bar Maximum flow 1 l/min HD892 Type 4WSE2ED -X/...K31EV HD893 Type
Directional servo-valve in 4-way design RE 2983/.11 Replaces: 7.3 1/ Type 4WS.2E... Size Component series X Maximum operating pressure 31 bar Maximum flow 1 l/min HD892 Type 4WSE2ED -X/...K31EV HD893 Type
Input, Control and Processing elements
 PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS CHAPTER FIVE Input, Control and Processing elements Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Valves The function of valves is to control the fluid path or the pressure or the flow rate. Depending
PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS CHAPTER FIVE Input, Control and Processing elements Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Valves The function of valves is to control the fluid path or the pressure or the flow rate. Depending
Variable Displacement Plug-In Motor A6VE
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly echnologies Pneumatics Service Variable Displacement Plug-In Motor A6VE RE 91 606/06.05 1/16 Replaces: 05.99 echnical data sheet Series
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly echnologies Pneumatics Service Variable Displacement Plug-In Motor A6VE RE 91 606/06.05 1/16 Replaces: 05.99 echnical data sheet Series
Die changing technique
 Die changing Die changing 8 Contents Product group 8 Roller bar, hydraulically lifted for heavy loads (400 bar), lifting of the complete roller bar for medium loads (120 bar), lifting of individual rollers
Die changing Die changing 8 Contents Product group 8 Roller bar, hydraulically lifted for heavy loads (400 bar), lifting of the complete roller bar for medium loads (120 bar), lifting of individual rollers
White Paper. Phone: Fax: Advance Lifts, Inc. All rights reserved.
 White Paper TURNTABLE AppLicATioN GUidE This section covers the full range of turntables manufactured by Advance Lifts. The basic information necessary to select an appropriate turntable for an application
White Paper TURNTABLE AppLicATioN GUidE This section covers the full range of turntables manufactured by Advance Lifts. The basic information necessary to select an appropriate turntable for an application
For advanced drive technology CLAMPEX. Shaft-hub-connection. KTR Precision joints CLAMPEX
 technology CLAMPEX Shaft-hub-connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision joints 227 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 228 Selection and calculation 25-255 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0
technology CLAMPEX Shaft-hub-connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision joints 227 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 228 Selection and calculation 25-255 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0
Nomenclature... xi Hydraulic Laws, Theorems, and Equations...xii
 Nomenclature... xi Hydraulic Laws, Theorems, and Equations...xii 1 Introduction 1.1 Component Design Perspective...1 1.2 Hydraulic Power Evolution...2 1.3 Hydraulic Applications...6 1.4 Component Design
Nomenclature... xi Hydraulic Laws, Theorems, and Equations...xii 1 Introduction 1.1 Component Design Perspective...1 1.2 Hydraulic Power Evolution...2 1.3 Hydraulic Applications...6 1.4 Component Design
Open center control block in mono block design MO-16, 22, 32
 Open center control block in mono block design MO-,, 3 RE 35 Edition: 0.0 Replaces: 0.003 Sizes,, 3 Series X Maximum working pressure on the pump side 350 bar on the consumer side 0 bar Maximum flow MO-:
Open center control block in mono block design MO-,, 3 RE 35 Edition: 0.0 Replaces: 0.003 Sizes,, 3 Series X Maximum working pressure on the pump side 350 bar on the consumer side 0 bar Maximum flow MO-:
Axial piston variable pump A4VG Series 32. Europe. RE-E Edition: Replaces:
 Axial piston variable pump A4VG Series 32 Europe RE-E 92003 Edition: 04.2016 Replaces: 06.2012 High-pressure pump for applications in a closed circuit Size 28 to 125 Nominal pressure 400 bar Maximum pressure
Axial piston variable pump A4VG Series 32 Europe RE-E 92003 Edition: 04.2016 Replaces: 06.2012 High-pressure pump for applications in a closed circuit Size 28 to 125 Nominal pressure 400 bar Maximum pressure
Slotted nut NMG. Housing nut GWR. Bosch Rexroth AG. for economical constructions. a min. 0,3. M A = tightening torque of slotted nut.
 R310EN 3301 (2009.08) Precision Ball Screw Assemblies Bosch Rexroth AG 113 Slotted nut NMG for economical constructions B D d d1 b M A = tightening torque of slotted nut a min. 0,3 Polyamide insert Designation
R310EN 3301 (2009.08) Precision Ball Screw Assemblies Bosch Rexroth AG 113 Slotted nut NMG for economical constructions B D d d1 b M A = tightening torque of slotted nut a min. 0,3 Polyamide insert Designation
AGN 076 Alternator Bearings
 Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 076 Alternator Bearings BEARING TYPES In the design of STAMFORD and AvK alternators, the expected types of rotor
Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 076 Alternator Bearings BEARING TYPES In the design of STAMFORD and AvK alternators, the expected types of rotor
Vickers 45. VMQ Series 30 Vane Pumps. Fixed Displacement, For Industrial and Mobile Applications (4.188)
 [ (4.188) 49,4 (1.94) /21,8 /.86) 174,7/172,3 (6.88/6.78) 332,9/33,5 (13.11/13.1) "M" is marked if metric port threads No marking if inch port threads AS-568-152 O-ring Vickers 45 65,3 (2.57) 13 (5.1 VMQ
[ (4.188) 49,4 (1.94) /21,8 /.86) 174,7/172,3 (6.88/6.78) 332,9/33,5 (13.11/13.1) "M" is marked if metric port threads No marking if inch port threads AS-568-152 O-ring Vickers 45 65,3 (2.57) 13 (5.1 VMQ
Specifications. Trantorque GT CALL FAX
 GT Specifications The following pages contain engineering data and product specifications for GT. For CAD drawings of GT, please click on the part number to download the drawing. All drawings are in AutoCAD
GT Specifications The following pages contain engineering data and product specifications for GT. For CAD drawings of GT, please click on the part number to download the drawing. All drawings are in AutoCAD
Hydraulic Jacks & Tools Valves
 Hydraulic Jacks & Tools Valves VH-4/3-1 with VSM-21 VH-4/3-1 VH-3/3-1 VH-4/3-2 VHH-4/3 This port can easily be used to connect a pressure gauge and a pressure relief valve (e.g. VR-1). The oil port T shall
Hydraulic Jacks & Tools Valves VH-4/3-1 with VSM-21 VH-4/3-1 VH-3/3-1 VH-4/3-2 VHH-4/3 This port can easily be used to connect a pressure gauge and a pressure relief valve (e.g. VR-1). The oil port T shall
GSM. Modular Design. Versions of the series. Type GSM. Gripper type P Z W R. Size. {} AS IS without O.D. clamping I.D. clamping
 GSM Pneumatic Gripper-Swivel System Modular Design Versions of the series Type GSM Gripper type P Z W R Size 32 40 50 64 30 38 45 16 20 25 32 40 16 20 25 32 40 Gripping force safety device {} AS IS without
GSM Pneumatic Gripper-Swivel System Modular Design Versions of the series Type GSM Gripper type P Z W R Size 32 40 50 64 30 38 45 16 20 25 32 40 16 20 25 32 40 Gripping force safety device {} AS IS without
SPRING HANGERS, SPRING SUPPORTS PRODUCT GROUP
 SPRING HANGERS, SPRING SUPPORTS PRODUCT GROUP VARIABLE SPRING ELEMENTS CONTENTS PAGE 0 Spring hangers, spring supports, sway braces.1 Load table for spring hangers, spring supports and other spring elements.3
SPRING HANGERS, SPRING SUPPORTS PRODUCT GROUP VARIABLE SPRING ELEMENTS CONTENTS PAGE 0 Spring hangers, spring supports, sway braces.1 Load table for spring hangers, spring supports and other spring elements.3
...our linkages, your solution. Rod Ends
 ...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
Precision Modules PSK
 Precision Modules PSK 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Precision Modules PSK R999000500 (2015-12) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example:: P S K - 050 - N N - 1 System = Precision Module
Precision Modules PSK 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Precision Modules PSK R999000500 (2015-12) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example:: P S K - 050 - N N - 1 System = Precision Module
LOCKED SERIES. Machine Failures. General Information. set up. maintenance. reconditioning. repair 30.4%
 General Information LOCKED SERIES 2 Lowering machinery process costs is key in today s world. According to a recent study approximately a third of all machine stoppages result in unexpected damage and
General Information LOCKED SERIES 2 Lowering machinery process costs is key in today s world. According to a recent study approximately a third of all machine stoppages result in unexpected damage and
Radial piston pump PR4 Series 1X
 Radial piston pump R4 eries 1X RE 1160 Edition: 07.015 Replaces: 08.005 Fixed displacement izes 0,40 to,00 Maximum working pressure 700 bar Maximum displacement cm 3 R4-1X/1,00-450WA01M01 Features elf-priming,
Radial piston pump R4 eries 1X RE 1160 Edition: 07.015 Replaces: 08.005 Fixed displacement izes 0,40 to,00 Maximum working pressure 700 bar Maximum displacement cm 3 R4-1X/1,00-450WA01M01 Features elf-priming,
SCM M2. Other advantages:
 Sunfab s SCM 025-108 M2 is a range of robust axial piston motors with cartridge flange especially suitable for winch-, slewing-, wheel- and track drives. SCM 025-108 M2 is of the bent-axis type with spherical
Sunfab s SCM 025-108 M2 is a range of robust axial piston motors with cartridge flange especially suitable for winch-, slewing-, wheel- and track drives. SCM 025-108 M2 is of the bent-axis type with spherical
Servo solenoid valves with positive overlap and on-board electronics (OBE)
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Servo solenoid valves with positive overlap and on-board electronics (OBE) RA 2989/1.5 1/24 Model 4WRLE
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Servo solenoid valves with positive overlap and on-board electronics (OBE) RA 2989/1.5 1/24 Model 4WRLE
TPV Variable Displacement Closed Loop System Axial Piston Pump THE PRODUCTION LINE OF HANSA-TMP HT 16 / M / 851 / 0813 / E
 HYDRAULIC COMPONENTS HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSIONS GEARBOXES - ACCESSORIES THE PRODUCTION LINE OF HANSA-TMP Variable Displacement Closed Loop System CONTENTS General Information... Order Code... Manual Control
HYDRAULIC COMPONENTS HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSIONS GEARBOXES - ACCESSORIES THE PRODUCTION LINE OF HANSA-TMP Variable Displacement Closed Loop System CONTENTS General Information... Order Code... Manual Control
MOTOR SCM ISO
 MOTOR SCM 012-130 ISO SCM 012-130 ISO is a range of robust axial piston motors especially suitable for mobile hydraulics. SCM 012-130 ISO is of the bent-axis type with spherical pistons. The design results
MOTOR SCM 012-130 ISO SCM 012-130 ISO is a range of robust axial piston motors especially suitable for mobile hydraulics. SCM 012-130 ISO is of the bent-axis type with spherical pistons. The design results
SIT-LOCK self locking elements
 self locking elements Advantages of on the shaft-hub connection compared with traditional systems Easy assembly and disassembly Both actions take place by locking and unlocking the clamping screws with
self locking elements Advantages of on the shaft-hub connection compared with traditional systems Easy assembly and disassembly Both actions take place by locking and unlocking the clamping screws with
Flow sharing control block in mono block / sandwich plate design M6-22
 Flow sharing control block in mono block / sandwich plate design M6-22 RE 64322 Edition: 01.2015 Replaces: 05.2012 Size 22 Series 3X Maximum operating pressure on pump side 350 bar on consumer side 420
Flow sharing control block in mono block / sandwich plate design M6-22 RE 64322 Edition: 01.2015 Replaces: 05.2012 Size 22 Series 3X Maximum operating pressure on pump side 350 bar on consumer side 420
Axial piston fixed motor A2FM series 70. Americas. RE-A Edition:
 Axial piston fixed motor A2FM series 70 Americas RE-A 91071 Edition: 05.2015 A2FMN (Sizes 90 and 107): Nominal pressure 300 bar Maximum pressure 350 bar A2FMM (Sizes 80 and 90): Nominal pressure 400 bar
Axial piston fixed motor A2FM series 70 Americas RE-A 91071 Edition: 05.2015 A2FMN (Sizes 90 and 107): Nominal pressure 300 bar Maximum pressure 350 bar A2FMM (Sizes 80 and 90): Nominal pressure 400 bar
Radial piston pump PR4 series 1X
 Radial piston pump R4 series 1X RA 1160 Edition: 07.015 Replaces: 08.005 Fixed displacement izes 0,40 to,00 Maximum working pressure 700 bar (10150 psi) Maximum displacement cm 3 (0.1 in 3 ) R4-1X/1,00-450WA01M01
Radial piston pump R4 series 1X RA 1160 Edition: 07.015 Replaces: 08.005 Fixed displacement izes 0,40 to,00 Maximum working pressure 700 bar (10150 psi) Maximum displacement cm 3 (0.1 in 3 ) R4-1X/1,00-450WA01M01
All Greenerd Presses are designed and built to ANSI B (R-2000) compliance. 4-POST HYDRAULIC DEEP DRAW PRESS
 All Greenerd Presses are designed and built to ANSI B-11.2 1995 (R-2000) compliance. 4-POST HYDRAULIC DEEP DRAW PRESS Model Number... 4D-562-36 x 36-48/48/33/45 Force of Main Ram... Adjustable 112 to 562
All Greenerd Presses are designed and built to ANSI B-11.2 1995 (R-2000) compliance. 4-POST HYDRAULIC DEEP DRAW PRESS Model Number... 4D-562-36 x 36-48/48/33/45 Force of Main Ram... Adjustable 112 to 562
/2015. Roller and ball bars for easy and safe die change
 Roller and ball bars for easy and safe die change T-slot tolerances acc. to DIN 650 h h n a b c min. max. max. 18 H8 30 +2 12 +2 30 36 1,6 22 H8 37 +3 16 +2 38 45 1,6 28 H8 46 +4 20 +2 48 56 1,6 36 H8
Roller and ball bars for easy and safe die change T-slot tolerances acc. to DIN 650 h h n a b c min. max. max. 18 H8 30 +2 12 +2 30 36 1,6 22 H8 37 +3 16 +2 38 45 1,6 28 H8 46 +4 20 +2 48 56 1,6 36 H8
Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FNM for Fan Drives and Flywheel Mass
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and ssembly Technologies Pneumatics Service xial Piston Fixed Motor 2FNM for Fan Drives and Flywheel Mass RE 91007/02.11 1/16 Data sheet Series 61
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and ssembly Technologies Pneumatics Service xial Piston Fixed Motor 2FNM for Fan Drives and Flywheel Mass RE 91007/02.11 1/16 Data sheet Series 61
Starting up hydraulic systems
 General / Installation A hydraulic system that operates economically, safely, and trouble-free requires careful planning, as well as proper installation and start-up. Conscientious maintenance has a considerable
General / Installation A hydraulic system that operates economically, safely, and trouble-free requires careful planning, as well as proper installation and start-up. Conscientious maintenance has a considerable
Internal Gear Unit. for motor/pump function Series QXM. Reference: 100-P US-10 1/18. Issue:
 Internal Gear Unit for motor/pump function Series QXM Reference: 1-P-63-US-1 Issue: 1.218 1/18 2/18 1-P-63-US-1/1.218 Contents Page 1 General... 5 1.1 Product description... 5 1.2 Advantages... 5 1.3 Application...
Internal Gear Unit for motor/pump function Series QXM Reference: 1-P-63-US-1 Issue: 1.218 1/18 2/18 1-P-63-US-1/1.218 Contents Page 1 General... 5 1.1 Product description... 5 1.2 Advantages... 5 1.3 Application...
Fixed Displacement Plug-In Motor A2FE
 Industrial Hydraulics Electric Drives and Controls Linear Motion and ssembly echnologies Pneumatics Service utomation Mobile Hydraulics Fixed Displacement Plug-In Motor 2FE RE 9008/03.97 replaces 04.96
Industrial Hydraulics Electric Drives and Controls Linear Motion and ssembly echnologies Pneumatics Service utomation Mobile Hydraulics Fixed Displacement Plug-In Motor 2FE RE 9008/03.97 replaces 04.96
Steering unit LAGU. Data sheet
 Steering unit LAGU Data sheet Nominal sizes Nominal pressure Maximum flow HE 11867/09.2017 125 320 175 bar 50 l / min 2 LAGU HE 11867 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering
Steering unit LAGU Data sheet Nominal sizes Nominal pressure Maximum flow HE 11867/09.2017 125 320 175 bar 50 l / min 2 LAGU HE 11867 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering
SCM SAE. Other advantages: Sunfab s SCM SAE is a range of robust axial piston motors especially suitable for mobile hydraulics.
 Sunfab s SCM 010-130 SAE is a range of robust axial piston motors especially suitable for mobile hydraulics. SCM 010-130 SAE is of the bent-axis type with spherical pistons. The design results in a compact
Sunfab s SCM 010-130 SAE is a range of robust axial piston motors especially suitable for mobile hydraulics. SCM 010-130 SAE is of the bent-axis type with spherical pistons. The design results in a compact
ENGEL e-motion TL. All-electric, tie-bar-less. be the first.
 ENGEL e-motion TL All-electric, tie-bar-less be the first. ENGEL e-motion TL generously dimensioned, barrier-free mould mounting surface excellent platen parallelism encapsulated toggle levers perfect
ENGEL e-motion TL All-electric, tie-bar-less be the first. ENGEL e-motion TL generously dimensioned, barrier-free mould mounting surface excellent platen parallelism encapsulated toggle levers perfect
Proportional directional control valve, pilot operated with on-board electronics (OBE) and inductive position transducer
 Proportional directional control valve, pilot operated with on-board electronics (OBE) and inductive position transducer RE 29076/12.05 1/24 Type 4WRBKE Nominal size (NG) 10, 16, 27, 35 Unit series 1X
Proportional directional control valve, pilot operated with on-board electronics (OBE) and inductive position transducer RE 29076/12.05 1/24 Type 4WRBKE Nominal size (NG) 10, 16, 27, 35 Unit series 1X
