Service. Self-Study Programme 218. The Lupo 3L. Design and Function
|
|
|
- Coral Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service. Self-Study Programme 218 The Lupo 3L Design and Function
2 Volkswagen developed the world's first 3-litre car on the basis of the Lupo. This car is now in series production. The development goal was to design a fully fledged vehicle that achieves a fuel consumption of 3 litres per 100 km. The Lupo 3L still meets the Volkswagen Group's requirements relating to environmental compatibility, safety and comfort. This task could only be fulfilled by using the latest technologies and production processes. That is why roughly 80% of all parts used in the standard Lupo have been redesigned. This Self-Study Programme gives you a general insight into the 3-litre car. The following Self-Study Programmes relating to the Lupo 3L are also available: SSP 209 SSP 216 SSP 221 SSP 223 SSP l TDI Engine with Pump Injection System LUPO 3L Body The DS085 Electronic Manual Gearbox The 1. 2 l TDI Engine Electro-mechanical Power Steering Gear New Important Note The Self-Study Programme is not a Workshop Manual. Please always refer to the relevant Service Literature for all inspection, adjustment and repair instructions. 2
3 Table of contents The trendsetter Specifications The 1.2 l TDI engine Electronic manual gearbox The running gear The electrical system Heating and air conditioning Service
4 The trendsetter Towards a new understanding of the motor vehicle The mass mobilisation of mankind has had a profound effect on the environment. The issues central to the debate on the environment are: - economical use of raw materials and energy, - air and water pollution control - potential climatic changes. 218_112 The 3-litre car has become a buzzword. The 3-litre car is an eco-friendly concept embracing all the stages in the life-cycle of a product from manufacturing and utilisation through to recycling. Volkswagen has responded to this challenge by developing the Lupo 3L. The resulting vehicle reflects a new trend towards ultra-low fuel consumption without doing without mobility, comfort and safety. 218_111 The Lupo 3L as a technological pathfinder for future vehicles The Lupo will also become the trendsetter for other vehicles: The lightweight design concept and drivetrain technology, for example, will in future not only be reflected in the Lupo 3L. 4
5 The 3-litre concept The demand for a fuel consumption of 3-litres per 100 km sets high design standards. How can these standards be met? 1. By systematically saving weight throughout the vehicle 2. By improving the drivetrain technology 3. By reducing aerodynamic drag 4. By reducing rolling resistance Only small improvements are achievable with regard to rolling resistance and aerodynamic drag. Weight savings and drivetrain technology are therefore the key factors from a design viewpoint. There is a conflict between saving weight another aims: - to maximise safety - to offer a high level of comfort - to provide room for four persons - to keep environmental pollution down to a minimum by selecting appropriate materials and manufacturing processes, and - to be able to recycle materials sorted into clean material streams Volkswagen had set itself the goal of designing a vehicle which fulfills all of these conflicting requirements. It was therefore necessary to find the best possible compromise for each of these requirements. DIESEL 3-litre 218_093 5
6 The trendsetter What has weight saving got to do with the energy balance? The energy balance of the Lupo 3L In an energy balance, two energy amounts are compared with one another. Energy consumption during manufacture and recycling Energy consumption during use 218_090 Energy required for manufacturing: - Extraction of materials, e.g. aluminium and magnesium - The energy consumed in the production process Energy consumption during use of the vehicle: - Consumption of fuels and lubricants - Energy consumption during care and maintenance Product recycling: - Recycling of materials - Disposal of materials What is the Lupo 3L all about? A major development goal was to reduce fuel consumption to a low level as part of an eco-friendly integrated concept. This concept also involved utilising available technology to the full in order to minimise environmental pollution. In other words, if a vehicle consumes less fuel in operation but a lot more energy during its manufacture, then the environment has effectively gained nothing. The balance shown above would tip to the left in this case. During the production of the Lupo 3L, available technology was utilised to manufacture and recycle materials in an ecologically compatible manner. The result is that the energy balance of the Lupo 3L is positive. The total energy input is much lower than that of other vehicles. 6
7 The light-weight design concept In comparison with the Lupo SDI, weight has been saved in the following areas: Body: Systematic light-weight construction through the use of light alloys, high-strength sheet-metal panels and window panes of thin-glass construction. Engine/gearbox unit: Installation of a 3-cylinder engine with an aluminium cylinder block and a lighter gearbox (e.g. hollow shafts). Running gear: Use of aluminium (e.g. on the front axle) and magnesium (e.g. for the steering wheel) as a substitute for steel. Equipment (trim): Lightweight design modifications down to the smallest detail (e.g. seats with aluminium frame), as well as weight-saving insulating materials. As a result, the Lupo 3L now weighs only 830 kg. That's 150 kg less than the Lupo SDI. 218_110 7
8 The trendsetter Light-weight body design The doors, wings and bonnets are made of aluminium Windows (thin glass) Tailgate of aluminium/ magnesium composite construction 218_083 Insulating-materials made of lightweight materials Seats with aluminium frame The following measures were also taken: State-of-the-art production and joining systems were used to build the lightweight body. These include: - The fasteners (bolts, etc.) have coatings which prevent them from coming directly into contact with aluminium and magnesium - The joints on the bonnet and doors are roll-and-pierce riveted as on the Audi A8 - Clinching is used on the doors - Laser welding was used to produce high-quality joints, e.g. between the body side panels and the sills, or between the roof outer skin and the upper ends of the A and B pillars. Please refer to Self-Study Programme No. 216 "Body of Lupo 3L. 8
9 Aerodynamics Aerodynamic vehicle contours reduce fuel consumption. For this reason the body of the Lupo 3L has been redesigned to improve: - Closed radiator grille: the cooling air flow enters the engine from below - Spoiler on front bumper - The shape of the tailgate - Rear bumper with integral diffusor 218_095 Body contour Lupo Rear diffusor 218_160B Lupo 3L 218_160 - Side skirt with special air deflectors Further measures: - The enlarged front track width with front wheels flush with the outer body optimise the air stream from the outer skin via the wheel housing, - The suspension of the Lupo 3L has been lowered by 10 mm to improve air flow on the underside of the vehicle - The joint dimensions have been reduced still further. Thanks to these measures, the Lupo 3L has a drag coefficient of 0.29 compared with 0.32 for the standard Lupo SDI. This is an extremely low cd figure for a vehicle of this size. 9
10 The trendsetter The engine/gearbox unit At the present level of technological development, an extremely low consumption figure of 3-litres per 100 km can only be achieved using diesel technology. The engine and the gearbox have been developed hand in hand with one another. Engine: The result of this development work was a 1.2-litre 3-cylinder diesel engine with an aluminium cylinder block, pump injection system, turbocharger and charge air cooler. Very high injection pressures of up to 2050 bar can be produced by the pump injection system. High fuel combustion efficiency is the result. This in turn means lower fuel consumption and cleaner exhaust emissions. Gearbox: The Lupo 3L has an electronic manual gearbox. It is derived from manual gearbox 085, and gearshifts are performed automatically. Engine and gearbox management system of the Lupo 3L: To achieve a consumption figure of 3 litres per 100 km, the Lupo 3L has an Economy mode in which the engine and gearbox management systems interact closely. Driving in Economy mode means: - the gearbox is operated automatically and the shift points are selected for optimal consumption - engine power is reduced in order to optimise consumption - a stop/start function shuts down the engine while the vehicle is stationary, e.g. at traffic lights A performance-based sport mode and a manually operated Tiptronic function are also available. 218_061 You will find more detailed information under "1.2 l TDI engine and "The DS085 Electronic Manual Gearbox, as well as in Self-Study Programmes No. 209 and No
11 The outstanding feature of the Lupo 3L is its low fuel consumption, hence the name '3L'. Fuel consumption in accordance with the MVEG standard Fuel consumption is tested in accordance with the MVEG (Engine Vehicle Emission Group) standard applicable throughout the EU. This test incorporates a variety of vehicle states which simulate both the urban cycle and the extraurban cycle. The MVEG test serves to determine the consumption of a vehicle. The test figures are applicable throughout the European Union. This is the part of the MVEG cycle which is used to calculate the vehicle's fuel consumption. The MVEG consumption figure for the Lupo 3L is 2.99 litres per 100 kilometres. It it therefore the first production 3-litre car in the world. Consumption curve: The diagram shows the momentary consumption of the vehicle at a constant speed as a function of the gear engaged. The diagram clearly shows that, in addition to road speed, the choice of gear is a key factor in fuel economy. This is how the Economy mode works: when driving at a constant speed (e.g. 50 kph), upshifts are executed early; to accelerate, the gearbox shifts down again. 218_113 Further information on fuel consumption - You ll find information on how to drive economically in the Owner's Manual for the Lupo 3L. - Optional extras such as air conditioning or power steering increase fuel consump tion. The diagram cannot show the many factors which influence fuel consumption in real life. These include: - accelerating or coasting, - headwind or tailwind, - uphill gradient or downhill gradient, - tyre pressure (is it correct or too low?) 11
12 The trendsetter Safety features 218_014 The Lupo 3L has adopted the safety equipment and features of the Lupo SDI. It has inertia-reel seat belts for the driver and front passenger complete with a belt-fastened recognition sensor, belt force limiter and ball-type tensioner. The rear seat bench has inertia-reel seat belts, and there is a lap belt for the middle seating position. The Lupo 3L is fitted with driver's and front passenger's airbags as standard. The airbag module fitted on the driver's and front passenger's sides have volumes of 52 litres and 100 litres respectively. Two side airbags with a volume of 12 litres each are fitted depending on regional market requirements. The fixing of the airbag module had to be modified in order to accommodate the new steering wheel. Please observe the detailed instructions given in the relevant Workshop Manual. 12
13 Specifications Lupo 3L and Lupo SDI The specifications of the Lupo 3L and Lupo SDI in comparison with one another in the table below. 218_054 c 218_084 b 218_053 a Lupo SDI Lupo 3L Engine power [kw] 44 at 4200 rpm 45 at 4000 rpm Torque [Nm] 115 at rpm 140 at rpm Number of cylinders/displacement [cm 3 ] 4/1716 3/1191 Maximum speed [kph] Drag coefficient c d Weight [kg] Dimensions [mm] Length (a) Height (b) Width (c)
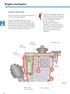
14 The 1.2-litre TDI engine The 1.2 l TDI engine is a 3-cylinder inline engine based on the 4-cylinder in-line engine with no intermediate shaft. This engine was designed specially for the Lupo 3L and is the first diesel engine in the Volkswagen Group to have a diecast aluminium cylinder block. The development goal was to reduce fuel consumption systematically. This goal was achieved by means of: - a pump injection system - weight saving measures, and - friction reduction measures 218_056 You will find more detailed information on 1.2-litre TDI engine in Self-Study Programme No Specifications Engine code Type ANY 3-cylinder in-line engine Displacement 1191 cm 3 Bore / stroke 76.5 mm / 86.7 mm Compression ratio 19.5 : 1 Firing order Engine management system Fuel type Exhaust gas aftertreatment BOSCH EDC 15P Diesel min. 49 CN or biodiesel (RME) Exhaust gas recirculation and oxidation catalytic converter The engine conforms to the D3 exhaust emission standard 14
15 Power output and torque As already mentioned in the chapter entitled "Trendsetter", the Lupo 3L can be operated in Economy mode to optimise fuel economy and, alternatively, in performance-based Sport mode. In Economy mode, the engine control unit reduces engine power output. Comparison of power output curves Comparison of torque curves [kw] [Nm] Sport mode ECO mode Sport mode ECO mode 218_ _ [rpm] [rpm] As the comparison performance curve shows, maximum power output in Sport mode is 45 kw at 4000 rpm. In Economy mode, maximum power output is 33 kw at 3000 rpm. In Sport mode, maximum torque is 140 Nm at an engine speed of 1800 rpm and is available up to an engine speed of 2400 rpm. In Economy mode, the maximum torque of 120 Nm is available at engine speeds ranging from 1600 to 2400 rpm. 15
16 The 1.2-litre TDI engine The pump injection system The 1.2 l TDI engine is fitted with a pump injection system. Complete combustion depends on good mixture formation. To achieve this, the fuel must be injected in the correct quantity and at the correct point in time in a finely atomised form. The pump injection system has a pump injector in the cylinder head for each cylinder. These units are driven by an additional cam on the valve camshaft via a roller-type rocker arm. Roller-type rocker arm Camshaft Pump injector Fuel return line Fuel supply line 209_086 16
17 In the pump injector, the pressurising pump is combined with the injector and the control unit. This compact design results in a low high-pressure volume which makes injection pressures of up to 2050 bar possible. The engine management system controls pressure build-up, the commencement of fuel injection and injection quantity via the solenoid valve. The pump injection system has the following advantages over a distributor injection pump: - low fuel consumption, - lower pollutant emissions, - high efficiency and - low combustion noise. Pressurising pump Control unit (solenoid valve) 209_014 Injector You ll find more information on the design and mode of operation of the pump injection system in Self-Study Programme No
18 The 1.2-litre TDI engine Weight-saving measures The cylinder block is made of aluminium and has cast-in grey cast iron cylinder liners. 218_115 The crankshaft should not be not slackened or removed. Even slackening the bearing cover bolts will cause the aluminium bearing seats to lose shape. If the bearing cover bolts are slackened, the cylinder block must be replaced complete with the crankshaft. The exhaust system comprises two oxidation catalytic converters and a single silencer. To reduce weight, the wall thicknesses of the exhaust pipes have been reduced. The exhaust manifold is a diecasting, but it is manufactured from sheet steel. Only one silencer is needed due to the low engine displacement. The exhaust system is made of stainless steel in order to inhibit corrosion. Oxidation catalytic converter 218_132 Silencer 18
19 Friction-reducing measures Tension bolts Cylinder head nut Cylinder head nut The tension bolts Steel pins are used as tension bolts. They join the cylinder head, the aluminium cylinder block and the crankshaft bearing cover. Aluminium is not as strong as grey cast iron. Due to the high combustion pressures which build up inside this engine, use of a conventional threaded connection for the cylinder head in the cylinder block is risky because the threaded connection may become undone. 218_117 Crankshaft Bearing cover For this reason, the cylinder head and the cylinder block are joined by means of tension bolts. Tension bolts allow a continuous flow of force from the cylinder head to the bearing cover. This ensures a safe threaded connection and reduces stresses in the cylinder block. For installation, the tension bolts are screwed into the cylinder block and fixed in place using "Loctite locking fluid. They cannot be replaced. The engine oil 0W 30 VW50600 The 1.2 l TDI engine is filled with VW engine lube oil. This oil has the specification 0W30, which means it produces less friction than the engine oil used previously. Further advantages of this oil grade are that it can withstand higher thermal stresses and has better cleaning properties. 218_118 The engine oil may not be mixed with other oils so as not to impair its lubricating properties. Please observe the instructions given in the Workshop Manual. 19
20 The 1.2-litre TDI engine Further technical features The balancing shaft has the task of reducing engine vibration. The upwards and downwards movements of the piston and conrod in the engine crank drive produce forces which act upon the crankshaft. The layout of the crank pins in a 3-cylinder inline engine is such that these mass forces are not compensated and cause vibration. To make the engine run smoothly, the balancing shaft rotates in the opposite direction to the engine. The balancing shaft is driven by the crankshaft via a chain and is secured to a ladder-type frame. The chain also drives the oil pump and is tensioned by a hydraulic chain tensioner. Chain tensioner 218_062 Deflection pulley Oil pump drive gear Balancing shaft Crankshaft 218_070 Bearing cover Ladder-type frame Balancing shaft 20
21 The cooler for exhaust gas recirculation The engine has a cooler for exhaust gas recirculation. It is connected to the coolant circuit. Cooling the recirculated exhaust gases allows a higher volume of exhaust gas to enter the combustion chamber. As a result, the combustion temperature drops and fewer nitrogen oxide emissions are produced. 218_148 Variable turbine geometry The variable turbine geometry has quick response at low engine speeds and reduces backpressure in the exhaust in the part-throttle range. The result is improved bottom-end torque and lower fuel consumption. 218_149 The variable turbine geometry is described in Self-Study Programme No Oxidation catalytic converter Primary catalytic converter Main catalytic converter The Lupo 3L has a primary catalytic converter and a main catalytic converter. The primary catalytic converter is positioned close to the engine so that it can heat up quickly and reach its operating temperature early. These measures help to reduce pollutant emissions. 218_132 21
22 Electronic manual gearbox 085 The 085 electronic manual gearbox was developed specially for the Lupo 3L and is operated by means of an electronic gate selector lever. The development goal was to reduce fuel consumption. This gearbox is based on conventional manual gearbox 085 which was revised to incorporate several weight-saving measures. To save weight: - the shafts were drilled hollow - the crown wheel was drilled - the 5th gear is spoked - the cheeks of the gear wheels were recessed to make them lighter - oil capacity was reduced by 0.2 litres while maintaining the same oil level by modifying the housing A manual gearbox with the characteristics of an automatic gearbox There is no clutch pedal. The manual gearbox is operated automatically via a hydraulic selector lever. A control unit decides what gear is to be engaged by means of the selector. As a result, the engine operates in the optimal torque range with regard to fuel economy. Why a manual gearbox? A manual gearbox has the following advantages over an automatic gearbox: - it is lighter, and - it is more efficient Despite having the characteristics of an automatic gearbox, the manual gearbox still provides a choice of automatic or manual gear-changing. The manual gear-changing mechanism is the same as in the Tiptronic. 218_060 22
23 The gear change system The driver can move the electronic gate selector lever into two selector gates. The Stop position is not equivalent to the Park position in an automatic gearbox. It is also necessary to apply the handbrake. If the handbrake is not applied, a warning lamp on the dash panel will flash for up to 5 minutes. 218_120 The engine is shut down automatically when the vehicle is stationary and first gear is selected. The can be started as soon as the driver's door is closed and the brake pedal is pressed. Manual gearshifts Automatic gearshifts In Tiptronic mode, each gear is engaged individually. To put the vehicle in reverse, press the Lock button at the head of the gate selector lever and the brake. Upshifts In the neutral position, it is possible to start the engine when the driver's door is closed and the brake is pressed at the same time. Middle position In this position, gears are engaged automatically. In Economy mode, the stop/start function is deactivated and the vehicle runs very economically. Downshifts Even in Economy mode, the driver can still utilise the engine's full power by means of a kickdown function. 218_119 23
24 The electronic manual gearbox 085 System overview Switch for electronic manual gearbox E262 Potentiometer for selector lever forwards/backwards G272 Switch for gate recognition, selector lever F257 Switch for N-recognition, selector lever F258 Switch for stop recognition F259 Electronic manual gearbox control unit J514 Potentiometer -2- for gear recognition G240 Potentiometer -1- for gear recognition G239 Clutch movement sender G162 Sender for hydraulic pressure G270 Gearbox speed sender G38 Coolant temperature sender G62 Brake pressure switch F270 Door contact switch, driver's side F2 Bonnet switch F207 Diagnostic connection 24
25 CAN databus Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Handbrake warning lamp K14 e.g. coolant temperature signal accelerator pedal position signal Selector lever lock solenoid N110 Control unit for display unit in dash panel insert J285 Valves for selector lever N286, N287 Valves 3+ 4 for selector lever N284, N285 ECO Hydraulic pump Warning lamp for Economy mode Gearshift indicator Clutch positioner valve N255 ABS control unit 218_131 25
26 Electronic manual gearbox 085 System design The electronic manual gearbox comprises three main elements: the electrics the hydraulics, and the mechanicals The electrics comprise sensors, actuators and the gearbox control unit. The control unit can recognise the actual state of the system, e.g. what gear is currently engaged, from the signals which the sensors generate. The input signals are processed in the gearbox control unit. The output signals for activating the actuators are then calculated, e.g. for a gearshift operation. The components the electrical system are: - The electronic gate selector lever A single potentiometer and three micro-switches on the gate selector lever determine the position of the selector lever and transmit this information to the gearbox control unit. - The electronic accelerator pedal transmits the current position of the accelerator pedal to the engine control unit. The engine control unit then transmits a corresponding signal along the CAN databus to the gearbox control unit. - Potentiometer on selector and clutch actuator One potentiometer recognises the selector gate position. The second potentiometer recognises the gear row, e.g. 3rd or 4th gear. The potentiometer on the clutch actuator recognises the current clutch position. - The gearbox control unit calculates the optimal gear position on the basis of this information and activates the gearshift operation. - An electro-hydraulic valve for the clutch actuator is activated when the clutch is activated via the hydraulics. - Four electro-hydraulic valves on the selector lever admit the system pressure to the hydraulic piston in the gear selector depending on requirements and activate a gear operation. 26
27 The hydraulics The system utilises the hydraulics to execute the necessary movements, e.g. clutch engagement/ disengagement or gearshift operations The components the hydraulics are: - A hydraulic pump and pressure accumulator generates the system pressure which is required in order to be able to perform gearshifts and operate the clutch. The pressure accumulator keeps sufficient oil and pressure in reserve to allow a quick response. The mechanicals are the same as in manual gearbox 085 The individual gears are engaged via the selector shaft: - The selector gate is selected through rotation of the selector shaft - A gear is selected through backwards and forwards movements of the selector shaft. - A clutch actuator engages and disengages the clutch during gearshift operations. - A selector lever moves the selector shaft via hydraulic pistons. 218_104 Selector shaft 218_154 27
28 Electronic manual gearbox 085 CAN databus CAN means: Controller Area Network. The gearbox control unit connected to the diesel direct injection control unit, the ABS control unit and the dash panel insert via the CAN databus. The control units exchange information along the CAN databus. As a result, multiple control units can process the information generated by a sensor and activate their actuators accordingly. Then gearbox control unit controls the gearshift operations depending on the data acquired, e.g. engine speed, wheel speed, engine load, brake activation etc. CAN databus gearbox control unit: - Glow plug data (diesel engine) - Engine speed - Engine torque - Accelerator pedal position - Engine run mode - Brake pedal signal CAN databus engine control unit: - Engine torque control - Engine shut-off Electronic manual gearbox control unit Diesel direct injection system control unit 28
29 For example, the gearbox control unit informs the engine control unit that engine torque has been reduced when the clutch is engaged/disengaged. The control unit for the dash panel insert obtains the position of the gate selector lever and whether the vehicle is currently being driven in Economy mode from the gearbox control unit via the CAN databus. This is indicated by warning lamps in the dash panel insert. CAN databus control unit for display unit in the dash panel insert: - Signal switch for electronic manual gearbox - ECO mode indicator, fuel consumption indicator, shift indicator, etc. CAN databus ABS control unit: - Wheel speed sensor signal 218_ _101 Control unit with display unit in dash panel insert ABS control unit 29
30 Electronic manual gearbox 085 The stop/start function The Lupo 3L has a stop/start function in Economy mode. What does this mean? In stationary phases, the engine is shut down in order to avoid unnecessary fuel consumption. This happens when the foot brake is kept pressed down for longer than three seconds. What conditions must be met before the engine is shut down automatically? 1. The gate selector lever is in position E. 6a. The coolant temperature must be higher than 17 C. 2. Economy mode is active. 6b. The intake air temperature must be higher than 0 C. 3. The brake must be kept pressed down for at least three seconds. 6c. The auxiliary heater must not be switched on. 4. The brake pressure switch indicates that a certain brake pressure is being applied to the brakes. 6d. The headlights must be switched off. 5. The ABS wheel speed sensor, as well as the gearbox speed sender and the speedometer sender signal to the system that the vehicle is stationary. 6e. The alternator load factor must not exceed 55%. 30
31 How does the vehicle resume operation? 1. The driver releases the brake pedal. 4. The gearbox control unit activates the clutch and engages first gear. 2. The gearbox control unit starts the engine. 5. The driver presses the accelerator pedal. The vehicle accelerates. 218_ The gearbox control unit ends the starting cycle and allows the starter to disengage. ECO 218_147B The switch for electronic manual gearbox E262 is integrated in the dash panel. The ECO mode can be activated and de-activated with this switch. ECO _147A 31
32 The running gear The running gear is also a factor contributing to the Lupo 3L's consumption of 3 litres per 100 km. Weight was saved by using light alloys e.g. for the subframe. The running gear also influences the vehicle's aerodynamic characteristics. The running gear was improved compared to the Lupo SDI by - lowering the vehicle 10 mm, and - streamlining the outer contour of the rims The following features are presented next pages: - the lightweight front axle - the wheel bearing - the rear axle - the steering - the electro-mechanical power steering - the brakes - the active wheel sensor, and - the puncture repair set The wheel bearings, the brake system and the low-friction tyres developed by Bridgestone specially for the Lupo 3L also affect fuel consumption. 218_040 32
33 The lightweight front axle The Lupo 3L has a front axle with McPherson suspension struts. They comprise aluminium dampers and coil springs made of high-tensile steel. The following are also new developments: - the subframe - the brackets - the axle guide with integrated guide links 218_015 Steering gear Brackets Subframe Axle guide with rubber mounting and ball joint 218_057 The subframe and the axle guide are made of aluminium. The brackets are diecastings. As a result, the axle on the Lupo 3L weighs 25% less than the standard Lupo axle. Four bolts join the brackets and the steering gear to the subframe. The track width of the front axle was enlarged by 33 mm compared to the Lupo SDI. As a result, the wheels are flush with the outer body. This flushness with the outer body improves the vehicle's aerodynamics. The larger track width improves the vehicle's cornering ability. 33
34 The running gear The wheel bearing The wheel bearing is a two-row angular continuous ball bearing with integrated wheel hub. The pretension on the wheel bearing is provided by flanging the bearing inner race with the wheel hub. A ring with 10 retaining lugs is fitted on the wheel bearing. These lugs lock into a groove on the wheel bearing housing when pressed in and hold the wheel bearing in position. Bearing inner race Wheel hub Movement when removing the bearing Retaining lug 218_035A When removing the wheel bearings, the the retaining lug will break off and a new wheel bearing has to be fitted. 218_035B You require special tool T in order to install the wheel bearing. Also refer to page 52 in the chapter entitled "Service". 34
35 The rear axle The rear axle has the same design as the rear axle of the Lupo SDI. As with all suspension parts, the rear axle has been adapted to meet the weight-oriented requirements of the Lupo 3L. 218_016 The coil springs and the shock absorbers are laid out separately in order to maximise the loading width. The suspension springs are made of high-tensile steel and are shorter than the springs used in the Lupo SDI. The twin-sleeve shock absorbers are made of aluminium. The steering The steering column is the safety steering column. It prevents upward intrusion of the steering wheel into the occupant cell during a crash and optimise the position of the airbag relative to the occupants. 218_018 The steering wheel is made of magnesium. The steering wheel rim is padded and the spokes are painted. The paintwork reduces the temperature of the steering wheel spokes when exposed to direct sunlight. 35
36 The running gear The electro-mechanical power steering The Lupo 3L can be equipped with power steering. As power steering increases fuel consumption, Volkswagen has developed a new electro-mechanical power steering system in association with Delphi. With this system, the vehicle consumes less fuel than a vehicle with hydraulic power steering. The Lupo 3L has an electronic power-assisted steering system based on the steering system used in the Lupo SDI. Its advantage over a hydraulic power steering system lies in the fact that it is lighter and only operates when required by the driver. The steering system is made up of the following component parts: - steering column switch and steering-wheel lock - steering column - electric motor - worm gear with torque and wheel angle sensors - control unit, and - universal joint shaft A description of the electro-mechanical power steering can be found SSP 225. Electric motor Control unit Steering column switch and steering-wheel lock Worm gear Universal joint shaft 218_096 Vehicles with electronic power steering do not have a stop/start function. 36
37 The brake system Front brakes (239 mm x 15 mm) The front wheel brakes are ventilated and 4 kg lighter than the brakes in the Lupo SDI. The brake caliper is made of aluminium. The brake disc is made of gray cast iron and is coated with a zink-aluminium alloy. This material is known by the name 'Geomet' and has excellent corrosion inhibiting properties. 218_042 Rear brakes (180 mm x 30 mm) The brake drums used in the Lupo 3L are made of a special aluminium alloy. As a result, they are the lightest brake drums in the world. 218_ _101 The brake system has ABS as standard. The hydraulic unit and the control unit are combined in the ABS unit. The brake system has the designation Teves Mark 30 and is largely identical to the Teves 20IE system. The difference between the two systems is that rear axle valves in the Teves Mark 30 are smaller and do not have a switching orifice function. The hydraulic pump motor and the control unit are identical to those used in the Mark 20 system. The system includes EBD, ESBS and EBC functions. 218_100 The 9-inch brake servo with aluminium housing operates according to the proven vacuum booster principle. 37
38 The running gear The active wheel sensors A sensor is referred to as being 'active' if it requires an external voltage supply. If it did not have this voltage supply, the sensor would not be able to supply signals. To measure the engine speed, the active ABS sensor mounted securely in the wheel bearing housing requires counterpart which rotates with the wheel hub. This counterpart is known as the 'signal sender disc'. The resistance of a magnetoresistive element varies depending on the magnetic field lines. A signal sender disc with a reader track is used in the Lupo 3L. It is an integral part of the wheel bearing seal and is press-fitted in the wheel bearing. The advantages of this technology are: - speeds upwards of 0 kph can be measured - little installation space is required - it is highly corrosion resistant, and - there is little interference since the air gap remains almost constant The active sensor is installed in the wheel bearing housing Sensor element The structure of the signal sender disc can be portrayed in simplified terms by imagining that small areas adjacent on the read track are magnetised differently according to north pole and south pole. When the wheel bearing rotates, these areas run closely past the active sensor. Sensor electronics Read track 218_043 38
39 Functional principle of the active sensor Read track Sensor element Sensor electronics Ω The magnetic field lines on the read track are arranged vertically in the immediate vicinity of the magnetised areas. Depending on polarity, these lines run either away from the track or towards it. Since the read track runs very closely past the sensor, the field lines also penetrate the sensor and affect its resistance. An electronic amplifier/trigger circuit integrated in the sensor transduces the change of resistance to two different current levels. If the resistance of the sensor element increases due to the direction of the magnetic field lines passing through it, the current will drop. Field lines 218_045 Ω If the resistance of the sensor element decreases due to a reversal in the direction of the field lines, the current will rise. 218_044 Ω This alternation of north and south poles on the read track results in a square-wave pulse whose frequency is a measure of engine rpm. 218_046 39
40 The running gear The puncture repair set To save weight, the spare wheel has been replaced by a puncture repair set. It comprises a pressure unit with a tyre sealant and a compressor which receives its power via the cigarette lighter. In the event of minor damage, the tyre can be made serviceable using the puncture repair set to the extent that the vehicle can reach next workshop. In the event of a breakdown, the sealant is pressed out of the pressure unit and through the tyre valve into the tyre. The tyre is then reinflated using the compressor. The rolling motion of the tyres allows an even distribution of sealant inside the tyre. The heat which is generated while driving is sufficient to galvanise the sealant and the tyre. Pressure unit with the sealant Compressor 218_134 The puncture repair set is not in available in every country. Vehicles can also be equipped with space-saver spare or a fully fledged spare instead of the puncture repair set depending on national legal requirements. 40
41 The electrical system The control units The fitting locations of the individual control units are the same as in the Lupo. However, two new control units have been added: - The electronic manual gearbox control unit and - an electrical powersteering control unit with the power steering option The layout the control units: Diagnosis plug Airbag control unit behind central console on tunnel Diesel direct injection system control unit in plenum chamber 218_124 Electronic manual gearbox control unit in the plenum chamber Immobiliser control unit above fuse box Control unit for electrical power steering on steering column ABS control unit in engine compartment on hydraulic unit Radiator fan control unit in engine compartment, front left 41
42 The electrical system The vehicle electrical system The vehicle electrical system has a decentralised configuration like in the Lupo. The main components are: Connector station on A pillar, front passenger's side Potential distributor behind dash panel Potential distributor in engine compartment. The alternator current is conducted via the main fuse box to the potential distributor where it is distributed to the starter and to the battery as charging current. Battery in spare-wheel well in luggage compartment 218_125 Voltage stabiliser behind side trim Main fuse box in engine compartment Relay holder behind dash panel Connector station behind dash panel Fuse box behind dash panel Connector station on A pillar, driver's side The battery is fitted in the engine compartment when the Lupo 3L starts production. The battery will be fitted exclusively in the spare-wheel well in the luggage compartment at a later date. 42
43 The dash panel insert The dash panel insert of the Lupo 3L has newer displays and warning lamps than the Lupo SDI. The control unit in the dash panel insert also communicates with the diesel direct injection system control unit, the electronic manual gearbox and ABS along the CAN databus. The following displays have been added: The average consumption indicator in the rev counter shows the average fuel consumption in litres per 100 km. It is an LC display. The current consumption indicator in the rev counter shows the momentary fuel consumption. For this purpose, the control unit in the dash panel insert receives a consumption signal from the engine control unit. 218_126A, G-K 218_ _025 The Reset button on the steering column switch zeroes the average fuel consumption indicator. The shift indicator in the speedometer shows the position of the gate selector lever and the selected gear. This information is supplied by the electronic manual gearbox control unit. It is also an LC display. 43
44 The electrical system The following warning lamps have been added: The "tailgate opened warning lamp is lit when the tailgate is open. This information is supplied by a microswitch integrated in the tailgate lock. When the tailgate is open, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the vehicle interior. The ECO warning lamp indicates whether the vehicle is driving in Economy mode or not. If the ECO warning lamp is lit, the Economy mode is active. In ECO mode, - the vehicle is operated in the optimal rev range with regard to fuel economy and - when the foot brake is pressed while the vehicle is stationary, the engine is shut down after three seconds (stop/start function). The control unit in the dash panel insert receives this information from the electronic manual gearbox control unit. ECO 218_126B-F 218_025 The "coolant temperature warning lamp is lit (blue LED) during the engine warm-up period and goes off when the engine reaches its operating temperature. If the coolant temperature is too high, the red LED of the warning lamp is lit. The "selector lever lock warning lamp indicates that the gate selector lever is inhibited in its current position. To engage another selector lever position, the foot brake must be pressed. This information is supplied by the electronic manual gearbox control unit. 44
45 Voltage stabiliser J532 is fitted behind the left side trim next to the rear seats. It provides: - the radio - the dash panel insert, and - the airbag control unit with a stable voltage supply while the engine is being restarted in Economy mode. This is necessary because the items of electrical equipment specified above are not switched off via the X contact. Electrical equipment If the voltage stabiliser is not installed, Battery Voltage response the electrical equipment would be subject to excessive voltage fluctuations which would cause the equipment to malfunction. In this case, the fault memory of the electrical equipment would register a malfunction such as "Vehicle power supply, signal too low. 218_155 If the voltage stabiliser is installed, Voltage stabiliser the voltage is stabilised for the electrical equipment during the restart. 218_156 As soon as the voltage drops during the restart due to the high starter current, the voltage dip is equalised for the electrical equipment. The voltage is kept at a constant approx volts. This way malfunctions are avoided. 45
46 Heating and air conditioning Two equipment variants are available for heater and air conditioner operation in the Lupo 3L: - Heating + fresh air/air recirculation mode - Manual air conditioning The design and function of both variants are identical to those of the systems fitted in the Golf 98 and Lupo. Also, the heater and air conditioner have been combined with an heater element for additional heater. The heating The heater element for additional heater is in the air stream behind the heat exchanger. Powered by the vehicle electrical system, it heats up the air fed into the vehicle interior. The 1.2-litre TDI engine does not supply enough waste heat during the warm-up period and at low ambient temperatures to heat up the vehicle interior. This is why the heat exchanger is combined with an heater element for additional heater. Heat exchanger Heater element for additional heater 218_094 Air stream Heat exchanger Heater element for additional heater The manual air conditioning system 218_167 The liquid tank with drier is installed horizontally in front of the condenser due to the constraints on space. Its dimensions and drier volume have also been reduced. The amount of refrigerant has been adapted accordingly. Cooler Dyier Capacitor 218_169 46
47 Heater element for additional heater Z35 heats up the passenger cabin quickly. When the heater element for additional heater is connected, an electrical current flows through ceramic PTC resistors.these resistors can reach a temperature of up to 160 C in the process. PTC resistors have a self-regulating property. As the temperature rises, the resistance increases, thereby reducing the current flow. The PTC resistor is prevented from overheating in this way. The design Corrugated aluminium contact plates, silicon sections and ceramic PTC thermistors are the main components of the heater element for additional heater. All in all, the heater element for additional heater is subdivided into three heating elements with a total of fifteen PTC resistors. There is one silicon section holding five PTC resistors per heating element. The section also functions as an electrical Isolator between the contact plates. The contact plates heated by the PTC resistors conduct their heat to the corrugations. PTC thermistor Silicon section Corrugated aluminium contact plates The electrical terminals are brazed to the additional heating element. 218_128 47
48 Heating and air conditioning The heating output control About 10 seconds after starting the engine, the diesel direct injection system control unit enables the heater element for additional heater for heating. This ensures that the engine runs properly straight away. If the rotary push-button for interior temperature is in the position for 80% heating output and higher, the heater element for additional heater will now be switched on under certain conditions. Switch-on conditions Rotary push-button for interior temperature Position of the rotary push-button: between 80% - 100% heating output Contact switch F268 for heating element Z35 Contact switch opened 80% heating output and higher Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Intake air temperature less than 19 C Coolant temperature less than 80 C The control unit tests the following signals as switch-on conditions Battery voltage higher than 11V 3-phase AC alternator load factor not higher than 50% (terminal DF) Heater element for additional heater Z35 Engine speed higher than 450 rpm _135 If all these switch-on conditions are met, the heater element for additional heater is switched on.
49 The engine control unit switches the three heating elements on and off in steps via relays. The relays for low and high heating output are located behind the relay carrier. If the switch-on conditions are met, the relays are activated in the following order: Low heat output relay First, the low heat output relay is activated. It switches on a heating element with five PTC resistors. High heat output relay Heating element If the load factor of the 3-phase AC alternator is subsequently below approx. 50%, the high heating output relay will be activated and two heating elements will be switched on. The low heating output relay cuts out at the same time. If the load factor of the 3-phase AC alternator now remains below approx. 50%, the low heating output relay cuts in again and all heating elements are switched off. The heating elements are switched off step-by-step in the reverse order when the load factor of the 3-phase AC alternator is permanently above 95%. 218_
50 Heating and air conditioning Contact switch F268 for heating element Z35 The contact switch is located on the housing of the heater or air conditioner. The rotary push-button for interior temperature moves the lever of the temperature flap by means of of a Bowden cable. A cam on the lever activates the contact switch. 218_094 Contact switch Lever 218_127 Bowden cable Contact switch closed The contact switch closed in the operating range Cooling and up to 80% heating output. When the contact switch is closed state, signal earth is present at the engine control unit. The heater element for additional heater does not cut in in this operating range. 218_122 Contact switch F _139 Contact switch open If the position of rotary switch is for between 80%-100% heating output, the lever is moved until the cam opens the contact switch. This breaks the signal earth contact to the engine control unit. If all switch-on conditions are met, the heater element for additional heater cuts in. 218_ _138 50
51 Function diagram J248 S J317 S J359 J360 F268 G62 S S S S A +/- Z35 Components 218_168 A+/- Battery J317 J248 J359 J360 Voltage supply relay, terminal 30 Diesel direct injection system control unit Low heat output relay High heat output relay F268 Contact switch for heater Z35 G62 Coolant temperature sender S Z35 Fuse Heater element for additional heater Input signal Output signal Positive Earth 51
52 Service Special tools T Drift For arresting the tensioning device for the ribbed V-belt. It replaces special tool T Socket insert For undoing and tighten the cylinder head nuts, as well as the fastening bolts for the balancing weight. T Centring tool For centring the clutch disc. T Fitting tool For fitting the wheel bearing 3282/28 Adjustment plate For adjusting the gearbox mount /29 Bolt Accessories for adjustment plate 3282/28 Engine oil Please note that the 1.2 l. TDI engine may only be filled with engine oil VW with the specification 0W30. General body repairs When working on the light-alloy body parts, it is absolutely necessary to use tool set V.A.G. 2010/2, since corrosion damage can occur when work is performed incorrectly. To avoid mixing up the aluminium tools with the conventional steel tools, the aluminium tools are colour-coded red. 52
53 Notes 53
54 54 Notes
55 55
56 218 For internal use only VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights reserved. Technical specifications subject to change without notice Technical status: 5/9 This paper is produced from non-chlorine-bleached pulp.
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator
 Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B
 Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
6-speed manual gearbox 02M
 Service. Self-Study Programme 205 6-speed manual gearbox 02M Design and Function Adapting modern automobiles to meet the rapidly growing demands on driving comfort, environmental compatibility and driving
Service. Self-Study Programme 205 6-speed manual gearbox 02M Design and Function Adapting modern automobiles to meet the rapidly growing demands on driving comfort, environmental compatibility and driving
Polo Sedan Specifications
 Polo Sedan Specifications 1.4 Trendline 1.4 Comfortline 1.6 Trendline Engine Cylinders 4 4 4 4 4 4 Capacity (cm 3 ) 1.398 1.398 1.598 1.598 1.598 1.498 Valves (per cylinder) 4 4 4 4 4 4 Compression Ratio
Polo Sedan Specifications 1.4 Trendline 1.4 Comfortline 1.6 Trendline Engine Cylinders 4 4 4 4 4 4 Capacity (cm 3 ) 1.398 1.398 1.598 1.598 1.598 1.498 Valves (per cylinder) 4 4 4 4 4 4 Compression Ratio
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service. Self-Study Programme No The New Beetle. Design and Function
 Service Self-Study Programme No. 211 The New Beetle Design and Function The New Beetle has caused a sensation and aroused instant enthusiasm throughout the world. The Concept 1 study in the mantle of the
Service Self-Study Programme No. 211 The New Beetle Design and Function The New Beetle has caused a sensation and aroused instant enthusiasm throughout the world. The Concept 1 study in the mantle of the
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Hexhead Torque Values
 Contents: 11: Engine 12: Engine Electrical 13: Fuel Preparation 16: Fuel Supply 17: Cooling 18: Exhaust 21: Clutch 23: Gearbox 31: Front Axle, Front Wheel Steering 32: Steering 33: Rear axle, rear-wheel
Contents: 11: Engine 12: Engine Electrical 13: Fuel Preparation 16: Fuel Supply 17: Cooling 18: Exhaust 21: Clutch 23: Gearbox 31: Front Axle, Front Wheel Steering 32: Steering 33: Rear axle, rear-wheel
Supercharged MK1 MR2 Part Diagrams
 Supercharged MK1 MR2 Part Diagrams Created by: Charles K. (ckowalc) 1 Table of Contents PART DIAGRAM PAGE ACCELERATOR LINK 9 AIR CLEANER 10 AIR CLEANER 4AGZE 11 ALTERNATOR 4AGZE 12 ANTENNA 13 ARMREST &
Supercharged MK1 MR2 Part Diagrams Created by: Charles K. (ckowalc) 1 Table of Contents PART DIAGRAM PAGE ACCELERATOR LINK 9 AIR CLEANER 10 AIR CLEANER 4AGZE 11 ALTERNATOR 4AGZE 12 ANTENNA 13 ARMREST &
Convenience CAN databus
 Convenience CAN databus The convenience CAN databus operates with a transmission rate of 100 kbit/s. Onboard power supply control unit J519 with databus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) CLIMAtronic
Convenience CAN databus The convenience CAN databus operates with a transmission rate of 100 kbit/s. Onboard power supply control unit J519 with databus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) CLIMAtronic
Vibration damper control
 Vibration damper control The damper control system registers the condition of the road surface and the movements of the vehicle via four wheel acceleration sensors and three body acceleration sensors.
Vibration damper control The damper control system registers the condition of the road surface and the movements of the vehicle via four wheel acceleration sensors and three body acceleration sensors.
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (040) 09/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
Service. Self-Study Programme 248. The W Engine Concept. Design and Function
 Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
MACK SERVICE AGREEMENTS.
 MACK SERVICE AGREEMENTS. SMOOTH RUNNING, OUT ON THE ROAD AND BACK IN THE OFFICE. THREE LEVELS OF AGREEMENT, ONE HIGH STANDARD When it comes to servicing, every business has different needs. With a choice
MACK SERVICE AGREEMENTS. SMOOTH RUNNING, OUT ON THE ROAD AND BACK IN THE OFFICE. THREE LEVELS OF AGREEMENT, ONE HIGH STANDARD When it comes to servicing, every business has different needs. With a choice
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
PRODUCT INFORMATION. VZ Light Commercial Vehicles Ute, Crewman and One Tonner
 23 August 2004 PRODUCT INFORMATION VZ Light Commercial Vehicles Ute, Crewman and One Tonner Development Cost $11 million. Quality Validation 1.6 million durability and test kilometres (VZ sedans) 113,000
23 August 2004 PRODUCT INFORMATION VZ Light Commercial Vehicles Ute, Crewman and One Tonner Development Cost $11 million. Quality Validation 1.6 million durability and test kilometres (VZ sedans) 113,000
FORD ECOSPORT SPECIFICATIONS
 FORD ECOSPORT SPECIFICATIONS PERFORMANCE AND ECONOMY 1.0-litre EcoBoost (5-speed manual) 1.5-litre Duratec Ti-VCT (6-speed automatic) 1.5-litre Duratorq TDCi (5-speed manual) Power (PS) CO 2 (g/km) Urban
FORD ECOSPORT SPECIFICATIONS PERFORMANCE AND ECONOMY 1.0-litre EcoBoost (5-speed manual) 1.5-litre Duratec Ti-VCT (6-speed automatic) 1.5-litre Duratorq TDCi (5-speed manual) Power (PS) CO 2 (g/km) Urban
3/22 Switch for rear power window lifts 3/23 Switch for power door mirror, driver's side 3/24 Switch for power door mirror, passenger's side 3/25
 List of Components 1/1 Battery 2/2 Relay, front foglights USA/CDN 2/3 Regulator DIM-DIP 2/4 Intermittent relay, windshield wipers 2/5 Relay, seat belt reminder/ignition key warning 2/6 Bypass relay 151
List of Components 1/1 Battery 2/2 Relay, front foglights USA/CDN 2/3 Regulator DIM-DIP 2/4 Intermittent relay, windshield wipers 2/5 Relay, seat belt reminder/ignition key warning 2/6 Bypass relay 151
Onboard power supply management
 Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
The Golf 2004 Running gear
 Service Training Self-study programme 321 The Golf 2004 Running gear Design and function With the refined safety running gear of the Golf, which is configured for both sporty and comfortable driving, VW
Service Training Self-study programme 321 The Golf 2004 Running gear Design and function With the refined safety running gear of the Golf, which is configured for both sporty and comfortable driving, VW
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
 Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Self-Adjusting Clutch (SAC) Technology Special tools / User instructions
 Self-Adjusting Clutch (SAC) Technology Special tools / User instructions The content of this brochure shall not be legally binding and is for information purposes only. To the extent legally permissible,
Self-Adjusting Clutch (SAC) Technology Special tools / User instructions The content of this brochure shall not be legally binding and is for information purposes only. To the extent legally permissible,
Hybrid Architectures for Automated Transmission Systems
 1 / 5 Hybrid Architectures for Automated Transmission Systems - add-on and integrated solutions - Dierk REITZ, Uwe WAGNER, Reinhard BERGER LuK GmbH & Co. ohg Bussmatten 2, 77815 Bühl, Germany (E-Mail:
1 / 5 Hybrid Architectures for Automated Transmission Systems - add-on and integrated solutions - Dierk REITZ, Uwe WAGNER, Reinhard BERGER LuK GmbH & Co. ohg Bussmatten 2, 77815 Bühl, Germany (E-Mail:
POWER DAILY MINIBUS A EURO 3
 POWER DAILY MINIBUS A 50.13 EURO 3 TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION 1 Power Daily MINIBUS A50.13 Euro 3 Dimensions (mm) A Maximum Length 7.133 H Overall Height 2.875 B Overall Withdraw 2.000 Weights (kg) G.V.M
POWER DAILY MINIBUS A 50.13 EURO 3 TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION 1 Power Daily MINIBUS A50.13 Euro 3 Dimensions (mm) A Maximum Length 7.133 H Overall Height 2.875 B Overall Withdraw 2.000 Weights (kg) G.V.M
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive
 Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA
 Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMS
 GROUP 80 CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMS CONTENTS OVERALL CONFIGURATION DIAGRAM...................... 80-2......... 80-3 .. 80-3 .. 80-5 ...... 80-7 INSTRUMENT PANEL............ 80-9 FLOOR
GROUP 80 CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMS CONTENTS OVERALL CONFIGURATION DIAGRAM...................... 80-2......... 80-3 .. 80-3 .. 80-5 ...... 80-7 INSTRUMENT PANEL............ 80-9 FLOOR
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition
 Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Layout Diagrams. Section CONTENTS. General Layout Diagram Floor / Roof Engine Compartment Door
 1-1 Section 1 Layout Diagrams CONTENTS General Layout Diagram...1-3 Engine Compartment...1-4 Engine / Transmission...1-6 Floor / Roof...1-16 Door...1-18 Boot Compartment...1-20 Instrument Panel...1-10
1-1 Section 1 Layout Diagrams CONTENTS General Layout Diagram...1-3 Engine Compartment...1-4 Engine / Transmission...1-6 Floor / Roof...1-16 Door...1-18 Boot Compartment...1-20 Instrument Panel...1-10
MODEL RANGE X5 M HIGHLIGHTS.
 MODEL RANGE X5 M HIGHLIGHTS. The BMW X5 M is available with a variety of standard equipment; below highlights some of this equipment. Adaptive Dynamic suspension Adaptive M suspension Air Breather, left
MODEL RANGE X5 M HIGHLIGHTS. The BMW X5 M is available with a variety of standard equipment; below highlights some of this equipment. Adaptive Dynamic suspension Adaptive M suspension Air Breather, left
Torque Converter. Lubricant Capacity (L) 2,00 5,7 2,00 2,00 6,1 2,00
 ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) 998 998 998 1 248 1 248 1 248 Bore x Stroke (mm) 71.0 X 84.0 71.0 X 84.0 71.0 X 84.0 71.0 x 78.8 71.0 x 78.8 71.0 x 78.8 Compression Ratio 10.5 : 1 10.5 : 1 10.5 :
ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) 998 998 998 1 248 1 248 1 248 Bore x Stroke (mm) 71.0 X 84.0 71.0 X 84.0 71.0 X 84.0 71.0 x 78.8 71.0 x 78.8 71.0 x 78.8 Compression Ratio 10.5 : 1 10.5 : 1 10.5 :
VOLVO C30, S40 & V50 drive OWNERS MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
 VOLVO C30, S40 & V50 drive OWNERS MANUAL SUPPLEMENT General Quieter and cleaner Environmental care is one of Volvo Car Corporation s core values which guides all our activities. This target-orientation
VOLVO C30, S40 & V50 drive OWNERS MANUAL SUPPLEMENT General Quieter and cleaner Environmental care is one of Volvo Car Corporation s core values which guides all our activities. This target-orientation
Home About Us Products Certificate Contact Us
 Home About Us Products Certificate Contact Us http://www.bksmotors.in/products/skoda/skoda octavia wagon spare parts/ 1/10 Skoda Octavia (Wagon) Spare Parts Home Products Skoda Skoda Octavia (Wagon) Spare
Home About Us Products Certificate Contact Us http://www.bksmotors.in/products/skoda/skoda octavia wagon spare parts/ 1/10 Skoda Octavia (Wagon) Spare Parts Home Products Skoda Skoda Octavia (Wagon) Spare
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine
 Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
3/25 Switch, power sunroof 3/26 Control module, driver's seat 3/27 Control module, passenger's seat 3/28 Switch for heated driver's seat 3/29 Switch
 List of Components 1/1 Battery 2/1 Headlight relay with bulb failure sensor 2/2 Foglight relay 2/3 Regulator DIM-DIP 2/4 Intermittent wiper relay, windshield wipers 2/5 Relay, seat belt reminder/ignition
List of Components 1/1 Battery 2/1 Headlight relay with bulb failure sensor 2/2 Foglight relay 2/3 Regulator DIM-DIP 2/4 Intermittent wiper relay, windshield wipers 2/5 Relay, seat belt reminder/ignition
Polo Vivo Sedan Specifications
 Polo Vivo Sedan Specifications ANYTHING IS POSSIBLE WITH THE POLO VIVO. 1.4 55kW Conceptline 1.4 55kW Blueline 1.4 63kW Trendline 1.4 63kW Trendline Tiptronic 1.6 77kW Trendline 1.6 77kW Comfortline Engine
Polo Vivo Sedan Specifications ANYTHING IS POSSIBLE WITH THE POLO VIVO. 1.4 55kW Conceptline 1.4 55kW Blueline 1.4 63kW Trendline 1.4 63kW Trendline Tiptronic 1.6 77kW Trendline 1.6 77kW Comfortline Engine
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
VOLKSWAGEN COMMERCIAL VEHICLES Specifications / March The Multivan
 VOLKSWAGEN COMMERCIAL VEHICLES Specifications / March 2010 The Multivan 01 Comfortline Highline FEATURES AND OPTIONS S = Standard O = Optional Extra Not Available Safety and Security Driver's and front
VOLKSWAGEN COMMERCIAL VEHICLES Specifications / March 2010 The Multivan 01 Comfortline Highline FEATURES AND OPTIONS S = Standard O = Optional Extra Not Available Safety and Security Driver's and front
Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics
 Service. Self-Study Programme 273 Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics Design and Function Open sesame - thanks to a new system for entry and start authorisation, the Phaeton can be accessed without
Service. Self-Study Programme 273 Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics Design and Function Open sesame - thanks to a new system for entry and start authorisation, the Phaeton can be accessed without
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Scirocco Specifications
 Scirocco Specifications Das Auto. SPECIFICATIONS 1.4 TSI Engine Cylinders 4 4 4 Capacity l/cm 3 1.4/1390 2.0/1984 2.0/1984 Bore / Stroke (mm) 76.5/75.6 82.5/92.8 82.5/92.8 Valves (per cylinder) 4 4 4 Compression
Scirocco Specifications Das Auto. SPECIFICATIONS 1.4 TSI Engine Cylinders 4 4 4 Capacity l/cm 3 1.4/1390 2.0/1984 2.0/1984 Bore / Stroke (mm) 76.5/75.6 82.5/92.8 82.5/92.8 Valves (per cylinder) 4 4 4 Compression
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)
 23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER
 A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
Stage 1 Performance Enhancement Number of Cylinders
 ENGINE General Data Engine Type Kappa 1.2 MPI Kappa 1.2 MPI Kappa 1.4 MPI Kappa 1.4 MPI Kappa 1.4 MPI Displacement (cc) Bore x Stroke (mm) Compression Ratio Max. Power (Kw @ rpm) Max. Torque (Nm @ rpm)
ENGINE General Data Engine Type Kappa 1.2 MPI Kappa 1.2 MPI Kappa 1.4 MPI Kappa 1.4 MPI Kappa 1.4 MPI Displacement (cc) Bore x Stroke (mm) Compression Ratio Max. Power (Kw @ rpm) Max. Torque (Nm @ rpm)
Audi > B4 > Liter V6 2V Engine Mechanical, Engine Code(s): AAH, AFC 10 Engine Assembly
 Audi > B4 > 1993 1995 2.8 Liter V6 2V Engine Mechanical, Engine Code(s): AAH, AFC 10 Engine Assembly Removing The engine is removed from above, after being separated from the transmission. Note: All tie
Audi > B4 > 1993 1995 2.8 Liter V6 2V Engine Mechanical, Engine Code(s): AAH, AFC 10 Engine Assembly Removing The engine is removed from above, after being separated from the transmission. Note: All tie
Service Training Edition Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B. Trainer Information (GB)
 7.02 Edition 09.2000 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Trainer Information (GB) Contents Section Page General Information 2 Input and output signals 7 Control System Details 9 ATF Pressure Control 16 Lock-up
7.02 Edition 09.2000 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Trainer Information (GB) Contents Section Page General Information 2 Input and output signals 7 Control System Details 9 ATF Pressure Control 16 Lock-up
Powertrain Management: Electrical Diagrams Fuel Injection System
 1995 Volvo 940 L4-2.3L SOHC VIN 88 B230F Copyright 2009, ALLDATA 9.70 Page 1 Powertrain Management: Electrical Diagrams Fuel Injection System Wiring Diagram 1995 Volvo 940 L4-2.3L SOHC VIN 88 B230F Copyright
1995 Volvo 940 L4-2.3L SOHC VIN 88 B230F Copyright 2009, ALLDATA 9.70 Page 1 Powertrain Management: Electrical Diagrams Fuel Injection System Wiring Diagram 1995 Volvo 940 L4-2.3L SOHC VIN 88 B230F Copyright
Mercedes Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I
 Mercedes 722.9 Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I Features Electronically Controlled Automatic Gearbox 7 Forward and 2 Reverse Gears Transmission Control Module is : Integrated into the
Mercedes 722.9 Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I Features Electronically Controlled Automatic Gearbox 7 Forward and 2 Reverse Gears Transmission Control Module is : Integrated into the
6-speed automatic transmission 09D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
ALL-NEW FORD FIESTA SPECIFICATIONS
 ALL-NEW FORD FIESTA SPECIFICATIONS PERFORMANCE AND ECONOMY Fiesta 3dr and 5dr Engine* 1.1-litre petrol 5-spd 1.1-litre petrol 5-spd 1.0-litre EcoBoost 6-spd 1.0-litre EcoBoost 6-spd automatic 1.0-litre
ALL-NEW FORD FIESTA SPECIFICATIONS PERFORMANCE AND ECONOMY Fiesta 3dr and 5dr Engine* 1.1-litre petrol 5-spd 1.1-litre petrol 5-spd 1.0-litre EcoBoost 6-spd 1.0-litre EcoBoost 6-spd automatic 1.0-litre
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
SOUL GDI REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE
 SOUL 2013-1.6 GDI REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE (First Numbers are page number within section - Numbers in parenthesis are overall document page) GENERAL INFORMATION (23 PAGES) 01-07 (01-07): Identification Number
SOUL 2013-1.6 GDI REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE (First Numbers are page number within section - Numbers in parenthesis are overall document page) GENERAL INFORMATION (23 PAGES) 01-07 (01-07): Identification Number
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
Gear change & shift cables Gearchange balljoints and bushes. Globes 12 and 24 volt Grilles
 A Accessories Air Bags Air compressor assembly and components Air conditioner idler pulleys and condensers Air dryer assemblies and repair kits Air filter elements Air master assembly and repair kits Air
A Accessories Air Bags Air compressor assembly and components Air conditioner idler pulleys and condensers Air dryer assemblies and repair kits Air filter elements Air master assembly and repair kits Air
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Product Information. N57 Engine.
 Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
16A. STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting REFITTING 16A-11 K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION
 STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting 16A K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION JR5 a Clip: -the gearbox control cable sleeve stops on the gearbox, - the control cables onto the gearbox.
STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting 16A K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION JR5 a Clip: -the gearbox control cable sleeve stops on the gearbox, - the control cables onto the gearbox.
LINCOLN. Continental 1
 3154_U01.qxd 8/1/03 7:28 AM Page 1 Continental 1 BRAKES...1-27 DRIVE TRAIN...1-21 ENGINE REPAIR...1-7 FUEL SYSTEM...1-20 PRECAUTIONS...1-7 SPECIFICATION CHARTS...1-2 STEERING AND SUSPENSION...1-22 A Air
3154_U01.qxd 8/1/03 7:28 AM Page 1 Continental 1 BRAKES...1-27 DRIVE TRAIN...1-21 ENGINE REPAIR...1-7 FUEL SYSTEM...1-20 PRECAUTIONS...1-7 SPECIFICATION CHARTS...1-2 STEERING AND SUSPENSION...1-22 A Air
1.2 TSI Trendline 2.0 TDI Trendline 2.0 TDI Trendline DSG 1.4 TSI Highline
 Das Auto. 1.2 TSI Trendline 2.0 TDI Trendline 2.0 TDI Trendline DSG 1.4 TSI Highline Engine Cylinders 4 4 4 4 Capacity (cm 3 ) 1197 1968 1968 1390 Valves (per cylinder) 4 4 4 4 Power output (kw @ r/min)
Das Auto. 1.2 TSI Trendline 2.0 TDI Trendline 2.0 TDI Trendline DSG 1.4 TSI Highline Engine Cylinders 4 4 4 4 Capacity (cm 3 ) 1197 1968 1968 1390 Valves (per cylinder) 4 4 4 4 Power output (kw @ r/min)
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Number of Cylinders 4 4. Cylinder Block Aluminium Aluminium. Cylinder Head Aluminium Aluminium. Timing Chain Silent Timing Chain Silent Timing Chain
 ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) Bore x Stroke (mm) Compression Ratio Max. Power (Kw @ rpm) Max. Torque (Nm @ rpm) 1 591 1 591 77 x 85.44 77 x 85.44 10.5 : 1 10.5 : 1 96 @ 6300 96 @ 6300 157 @ 4850
ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) Bore x Stroke (mm) Compression Ratio Max. Power (Kw @ rpm) Max. Torque (Nm @ rpm) 1 591 1 591 77 x 85.44 77 x 85.44 10.5 : 1 10.5 : 1 96 @ 6300 96 @ 6300 157 @ 4850
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED
 SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
Onboard power supply management
 Onboard power supply management Switching off convenience electrical equipment With the ignition on or active alternator (engine running), the onboard power supply control is classified by the onboard
Onboard power supply management Switching off convenience electrical equipment With the ignition on or active alternator (engine running), the onboard power supply control is classified by the onboard
In total, there are four different versions of the data bus diagnostic interface: Data bus diagnostic interface J533
 New features The data bus diagnostic interface now also includes a battery power management function. For this purpose, a LIN line is connected to a socalled "battery data module" located directly adjacent
New features The data bus diagnostic interface now also includes a battery power management function. For this purpose, a LIN line is connected to a socalled "battery data module" located directly adjacent
SPÉCIFICATIONS TECHNIQUES
 SPÉCIFICATIONS TECHNIQUES FORD TOURNEO CONNECT/GRAND TOURNEO CONNECT FUEL CONSUMPTION AND PERFORMANCE Engine Power (PS) CO 2 (g/km) Urban Fuel consumption l/100km (mpg) Extra Urban Combined Max Speed (km/h)
SPÉCIFICATIONS TECHNIQUES FORD TOURNEO CONNECT/GRAND TOURNEO CONNECT FUEL CONSUMPTION AND PERFORMANCE Engine Power (PS) CO 2 (g/km) Urban Fuel consumption l/100km (mpg) Extra Urban Combined Max Speed (km/h)
Rear Drive Axle and Differential
 Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty
 PRESS info P07901EN / Per-Erik Nordström 5 September 2007 Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty As the first heavy vehicle manufacturer, Scania achieves Euro
PRESS info P07901EN / Per-Erik Nordström 5 September 2007 Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty As the first heavy vehicle manufacturer, Scania achieves Euro
D. Functions in the KE control unit. a) General
 D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
MODEL RANGE. M Sport Highlights In addition / replacement to SE models
 MODEL RANGE. The BMW 5 Series Touring is available in a variety of engine and model variants, each providing a different level of standard specification. Below highlights some of the equipment differences
MODEL RANGE. The BMW 5 Series Touring is available in a variety of engine and model variants, each providing a different level of standard specification. Below highlights some of the equipment differences
H1 PANEL VAN. H1 2.5 VGTi 3 Seater Panel Van Diesel. 5-spd Automatic ENGINE. General Data. Displacement (cc) Bore x Stroke (mm) 91 x 96
 ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) 2 497 Bore x Stroke (mm) 91 x 96 Compression Ratio 16.4 Max. Power (Kw/rpm) 125 @ 3600 Max. Torque (Nm/rpm) 441 @ 2000~2250 Number of Cylinders 4 Cylinder Block Cylinder
ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) 2 497 Bore x Stroke (mm) 91 x 96 Compression Ratio 16.4 Max. Power (Kw/rpm) 125 @ 3600 Max. Torque (Nm/rpm) 441 @ 2000~2250 Number of Cylinders 4 Cylinder Block Cylinder
The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 299 The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D Design and Function The Touareg is an exclusive cross country vehicle with the driving properties and driving comfort of a sporty luxury
Service. Self-Study Programme 299 The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D Design and Function The Touareg is an exclusive cross country vehicle with the driving properties and driving comfort of a sporty luxury
MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En
 02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
Bore x Stroke (mm) 88.0 x Compression Ratio Max. Power (Kw/rpm) Max. Torque (Nm/rpm) Number of Cylinders 4 4
 ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) 2 359 2 497 Bore x Stroke (mm) 88.0 x 97.0 91 x 96 Compression Ratio 10.5 17.6 Max. Power (Kw/rpm) 126 @ 6000 125 @ 3800 Max. Torque (Nm/rpm) 224 @ 4200 441 @ 2000
ENGINE General Data Displacement (cc) 2 359 2 497 Bore x Stroke (mm) 88.0 x 97.0 91 x 96 Compression Ratio 10.5 17.6 Max. Power (Kw/rpm) 126 @ 6000 125 @ 3800 Max. Torque (Nm/rpm) 224 @ 4200 441 @ 2000
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Service. Variable Automatic Gearbox multitronic 01J Design and Function. Self-Study Programme 228. For internal use only
 228 Service. Variable Automatic Gearbox multitronic 01J Design and Function Self-Study Programme 228 For internal use only multitronic The name multitronic stands for the new variable automatic gearbox
228 Service. Variable Automatic Gearbox multitronic 01J Design and Function Self-Study Programme 228 For internal use only multitronic The name multitronic stands for the new variable automatic gearbox
