The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
|
|
|
- Mark McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function
2 For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important contribution towards environmental protection. The frugal, environmentally-friendly and powerful FSI engines are offered in four derivatives for the following vehicles: ltr./63 kw FSI engine in the Polo ltr./77 kw FSI engine in the Lupo ltr./81 kw FSI engine in the Golf/Bora ltr./85 kw FSI engine in the Touran S296_008 In this self-study programme you will be shown the design and function of the new engine mechanical and management systems. Further information about engine management can be found in self-study programme 253 "The petrol direct injection system with Bosch Motronic MED 7". NEW Important Note The self-study programme shows the design and function of new developments! The contents will not be updated. For current testing, adjustment and repair instructions, refer to the relevant service literature. 2
3 Contents Introduction Technical properties Technical data Engine mechanics Engine cover Intake manifold upper part Control housing seal Electrical exhaust gas recirculation valve Cooling system Regulated Duocentric oil pump Variable valve timing Engine management System overview Engine control unit Operating types Intake system Supply on demand fuel system Fuel pump control unit Fuel pressure sender High pressure fuel pump Functional diagram Service Self-diagnosis Special tools Test yourself
4 Introduction Both engines are basically the same, in that they consist of cylinder block and cylinder head, camshaft drive, control housing, oil pump and ancillaries. The significant differences of the 1.6 ltr. FSI engine are the greater stroke, variable valve timing and further developed operating condition "double injection". S296_011 S296_051 Technical properties Engine mechanics - Engine cover with air cleaner and hot air control - Intake manifold upper part made of plastic - Camshaft driven by chain - Continually variable valve timing *) - Oil cooler *) - Regulated Duocentric oil pump - Dual circuit cooling system - Cross flow cooling in cylinder head - Crankcase breather system Engine management - Petrol direct injection with double injection - Engine control unit with integrated ambient air pressure sender - Intake air temperature sender in engine cover - Supply on demand fuel system - Single spark ignition coil - Exhaust gas treatment with NO x storage catalyst and NO x sender - Integrated radiator and fan control *) 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine only The regulated Duocentric oil pump, the dual circuit cooling system and the supply on demand fuel system are new technologies that will also be used in other vehicles in the future. 4
5 Technical data 1.4 ltr./63 kw FSI engine 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine Performance [kw] Torque [Nm] Performance [kw] Torque [Nm] S296_ Speed [rpm] Speed [rpm] S296_050 Engine codes AUX BAG Displacement Type 4-cylinder in-line engine 4-cylinder in-line engine Valves per cylinder 4 4 Bore 76.5 mm 76.5 mm Stroke 75.6 mm 86.9 mm Compression ratio 12:1 12:1 Maximum output 63 kw at 5000 rpm 85 kw at 5800 rpm Maximum torque 130 Nm at 3500 rpm 155 Nm at 4000 rpm Engine management Bosch Motronic MED Bosch Motronic MED Fuel Super unleaded at RON 98 (unleaded at RON 95 with reduction in performance) Exhaust gas treatment Emissions standard Three-way catalyst with Lambda control, NOx storage catalytic converter EU4 5
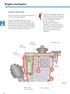
6 Engine mechanics Engine cover Integrated in the engine cover: - Air guide to throttle valve control unit - Hot air regulator - Intake noise insulation - Air cleaner - Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 Engine cover, underside Air outlet to throttle valve control unit J338 Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 Air cleaner to crankcase breather on camshaft housing Intake noise insulation Air inlet Cold air S296_009 Air inlet Hot air Thermostat Hot air regulator 6
7 Intake manifold upper part The intake manifold upper part is made of plastic. This has the following advantages: - Reduction in weight - Air flow improvement thanks to smoother intake walls In the intake manifold upper part there is a vacuum unit that assures actuation of the intake manifold flaps even when vacuum pressure is low. Throttle valve control unit J338 To vacuum positioner element for intake manifold To EGR valve N18 Plastic intake manifold with vacuum unit Intake manifold flap air flow control valve N316 From diaphragm valve for crankcase breather To pressure sensor for brake servo G294 S296_018 Intake manifold pressure sender G71 and air intake temperature sender G42 Solenoid valve 1 for activated charcoal filter system N80 To activated charcoal filter 7
8 Engine mechanics Control housing seal The control housing is sealed to the cylinder head and the cylinder block by a bonded rubber gasket. Between the control housing and the oil sump there is a fluid gasket. Oil filter housing The oil filter housing is integrated in the control housing. This means that there is no requirement for a sealing surface between the cylinder block and the oil filter housing. Cross section of bonded rubber gasket S296_003 S296_017 S296_016 Holes for the fluid gasket Engine oil cross-over area For transference of engine oil from the cylinder block into the control housing, there is an oil pressure of approx. 3.5 bar. Therefore, a bonded rubber gasket is used. Fluid gasket The seal between the control housing and the oil sump is made by a fluid gasket. This is pressed between the sealing surfaces by means of a special drilling in the control housing. 8
9 Electric exhaust gas recirculation valve The electric exhaust gas recirculation valve with EGR valve N18 and the potentiometer for exhaust gas recirculation G212 are bolted to the cylinder head. The valve is designed for treatment of high levels of exhaust gas and draws the exhaust gas directly from the 4th cylinder of the cylinder head. Withdrawal at cylinder no. 4 Potentiometer for exhaust gas recirculation G212 S296_036 Exhaust gas recirculation valve N18 Electric exhaust gas recirculation valve in the coolant circuit Due to the vicinity of the exhaust gas withdrawal point, the exhaust gas recirculation valve is integrated in the coolant circuit of the engine. This allows the exhaust gas recirculation valve to be cooled and protected from excessively high temperatures. Expansion tank S296_037 To coolant pump From radiator Exhaust gas recirculation valve 9
10 Engine mechanics Cooling system The cooling system is of a dual circuit design. This system features a separate coolant path, with different temperatures, through the cylinder block and the cylinder head. The coolant flow is controlled by two thermostats in the coolant distribution housing. One for the cylinder block and one for the cylinder head. Furthermore, both engines feature cross flow cooling of the cylinder head. Expansion tank Exhaust gas recirculation valve Coolant pump Coolant circuit of cylinder block Coolant circuit of cylinder head Oil cooler (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine only) Radiator 10
11 The dual circuit cooling system has the following advantages: - The cylinder block is heated up faster because the coolant stays in the cylinder block until it reaches 105 C. - There is less friction in the crankcase drive system due to higher temperatures in the cylinder block. - There is improved cooling in the combustion chambers thanks to lower temperatures in the cylinder head. This leads to improved filling with less risk of knocking. Heating system heat exchanger Thermostat 1 from cylinder head (opens at 87 C) Coolant distribution housing Thermostat 2 from cylinder block (opens at 105 C) S296_020 11
12 Engine mechanics Dual circuit cooling system The cooling system is split into two circuits in the engine. A third of the coolant in the engine flows to the cylinders and two thirds to the combustion chambers in the cylinder head. From cylinder head From cylinder block To radiator From radiator Coolant distribution housing Coolant temperature 87 C Coolant temperature 105 C S296_055 Position of thermostats up to 87 C: Both thermostats are closed, which means the engine is heated up faster. Thermostat 1 The coolant flows through the following components: - Coolant pump - Cylinder head - Coolant distribution housing - Heating system heat exchanger - Oil cooler (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine only) - Exhaust gas recirculation valve - Expansion tank Thermostat 2 S296_038 12
13 Position of thermostats from 87 C to 105 C: Thermostat 1 is open and thermostat 2 is closed. This regulates the temperature in the cylinder head to 87 C and increases the temperature in the cylinder block further. Thermostat 1 The coolant flows through the following components: - Coolant pump - Cylinder head - Coolant distribution housing - Heating system heat exchanger - Oil cooler (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine only) - Exhaust gas recirculation valve - Expansion tank - Radiator S296_039 Thermostat 2 Position of thermostats above 105 C: Both thermostats are open. This regulates the temperature in the cylinder head to 87 C and in the cylinder block to 105 C. Thermostat 1 The coolant flows through the following components: - Coolant pump - Cylinder head - Coolant distributor - Heating system heat exchanger - Oil cooler (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine only) - Exhaust gas recirculation valve - Expansion tank - Radiator - Cylinder block S296_040 Thermostat 2 13
14 Engine mechanics Regulated Duocentric oil pump A regulated Duocentric oil pump is installed for the first time. Thanks to this equipment, oil pressure is regulated to approx. 3.5 bar across almost the entire rev range. Regulation is by means of a control ring and control spring. This provides the following advantages: - The drive performance of the oil pump is reduced by up to 30 %. - Wear in the oil is reduced because less oil is being circulated. - The build up of oil foam in the oil pump is minimised as oil pressure remains constant across almost the entire rev range. Pressure limiter valve Housing Chain sprocket In the adjacent diagram you can see the individual parts of the regulated oil pump. Outer rotor Control ring Control spring Drive shaft with inner rotor Oil suction pump Housing cover S296_023 Drive of regulated oil pump Crankshaft The oil pump is bolted to the underside of the cylinder block and is chain driven from the crankshaft. The chain is maintenance-free. The chain is tensioned by means of a steel spring on the chain tensioner. Spring Roller chain Chain sprocket oil pump S296_013 Spring-loaded chain tensioner 14
15 Principle of oil delivery The inner rotor sits on the drive shaft and drives the outer rotor. Due to the different rotating axes of the inner and outer rotors, a larger space is created on the suction side due to the rotating motion. The oil is drawn in and transported to the pressure side. On the pressure side, the space between the teeth becomes smaller again and oil is forced into the oil circuit. Regulation of oil pressure On the regulated Duocentric oil pump, oil pressure is regulated at 3.5 bar in the amount of oil delivered. Oil pressure below 3.5 bar In Pressure side Suction side Outer rotor The control spring forces the control ring against the oil pressure (arrows). The control ring also causes the outer rotor to turn and an increase in space between inner and outer rotors is the result. This means that more oil is transported from the suction side to the pressure side and forced into the oil circuit. With a greater amount of oil, there is also greater oil pressure. oil circuit Control ring Inner rotor Control spring From S296_014 oil sump Oil pressure above 3.5 bar Into Pressure side Suction side Outer rotor The oil pressure (arrows) forces the control ring against the control spring. The outer rotor is also turned in the direction of the arrow and a decrease in space between the inner and outer rotors is the result. This means that less oil is transported from the suction side to the pressure side and forced into the oil circuit. With a reduced amount of oil, there is less oil pressure. oil circuit Control ring Inner rotor Control spring From S296_015 oil sump 15
16 Engine mechanics Variable valve timing (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine) The 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine has variable inlet valve timing. Adjustment of the camshaft is load and speed dependent and comes from a vane cell adjuster attached directly to the inlet camshaft. Inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve N205 Variable valve timing leads to: - very effective inner exhaust gas recirculation, whereby combustion temperature and nitrogen oxides are reduced, and - also improved torque development. Vane cell adjuster S296_068 The central securing bolt of the vane cell adjuster has a left-handed thread. Vane cell adjuster The vane cell adjuster is bolted to the timing control side of the inlet camshaft. Adjustment range camshaft 20 The adjustment range covers a maximum 40 crankshaft angle and a 20 camshaft angle, starting from the basic position towards "advanced". The advantages of the vane cell adjuster as opposed to the camshaft adjuster of the 1.4 ltr./77 kw FSI are: - Adjustment is possible even at low oil pressures - It is easier - It is cheaper Housing Inner rotor S296_069 Further information about this principle of variable valve timing can be found in self-study programme number 246 "Variable valve timing with the vane cell adjuster". 16
17 Inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve N205 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in oil being fed to one or both oil channels. Depending on which oil channel is accessible, the inner rotor is adjusted in the direction of "advanced" or "retarded", or held in its position. As the inner rotor is bolted to the inlet camshaft, the camshaft is adjusted in the same way. Retarded adjustment Advanced adjustment Inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve N205 Oil supply Effects of failure If the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve N205 fails in its function, there is no variable timing adjustment. Oil return S296_067 Oil cooler Due to the higher rev range of the 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine, the engine oil is subjected to greater heat. To guarantee precise adjustment of the inlet camshaft across the entire rev range, an oil cooler is installed. Oil cooler S296_057 17
18 Engine management System overview Inlet manifold pressure sender G71 Intake air temperature sender G42 Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 Engine speed sender G28 Hall sender G40 Throttle valve control unit J338 Throttle valve drive angle sender 1+2 G187 and G188 Accelerator pedal position sender G79 and G185 Clutch pedal switch F36 Diagnosis connection Brake light switch F and brake pedal switch F47 Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G247 Fuel pressure sender, vacuum pressure G410 Knock sensor G61 Coolant temperature sender G62 Coolant temperature sender - radiator outlet G83 Potentiometer for intake manifold flap G336 Communications line CAN drive Potentiometer for exhaust gas recirculation G212 Lambda probe G39 Exhaust gas temperature sender G235 NOx* sender G295, NOx sensor* control unit J583 Onboard power supply control unit J519 Diagnosis interface for databus J533 Brake servo pressure sensor G294 Temperature selection potentiometer G Additional input signals
19 Fuel pump control unit J538 Fuel pump G6 Motronic control unit J220 with ambient air pressure sender Injectors, cylinders 1-4 N30-33 Ignition coils 1-4 with output stages N70, N127, N291, N292 Throttle valve control unit J338 Throttle valve drive G186 Motronic current supply relay J271 ABS/EDL control unit J104 Airbag control unit J234 Power steering control unit J500 Steering angle sender G85 Fuel pressure control valve N276 Solenoid valve for activated charcoal filter system N80 Intake manifold flap air flow control valve N316 Exhaust gas recirculation valve N18 EPC Lambda probe heating Z19 Control unit with display unit in dash panel insert J285 NOx sender heater* Z44 Inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve N205 (1.6 lt r. FSI e ngine only) Additional output signals S296_022 *(One component on 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine) 19
20 Engine management Engine control unit J220 (1.4 ltr./63 kw FSI engine) The engine control unit on the Polo can be found on the bulkhead in the engine compartment and has 121 pins. The installation location was carefully selected to allow easy access but also to protect against dampness. The torque-based engine management system is Bosch Motronic MED In the housing of the control unit there is also an ambient air pressure sender. The engine control unit calculates and controls the optimum fuel and air mixture for the following modes of operation. Stratified injection Homogeneous-lean Homogeneous Double injection, catalyst warm-up Engine control unit with ambient air pressure sender J220 The designation MED stands for: S296_025 M E D =Motronic =Electric throttle operation =Direct injection 7. =Version 5.11 =Development stage 20
21 Engine control unit J220 (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine) The engine control unit on the Touran can be found in the plenum chamber and has 154 pins. The torque-based engine management system is Bosch Motronic MED The engine control unit calculates and controls the optimum fuel and air mixture for the following modes of operation. Stratified injection Homogeneous-lean Homogeneous Double injection, catalyst warm-up Double injection, full throttle Engine control unit with ambient air pressure sender J220 The designation MED stands for: S296_056 M E D =Motronic =Electric throttle operation =Direct injection 9. =Version 5.10 =Development stage 21
22 Engine management Operating types In addition to the operating types stratified injection, homogeneous-lean and homogeneous, there are two further operating modes. These are 'double injection, catalyst warm-up' and 'double injection, full throttle'. Thanks to these two modes, firstly, the catalyst is warmed up faster and, secondly, torque is increased in the lower rev range. Double injection, catalyst warm-up In homogeneous catalyst warm-up mode, the catalyst is warmed up faster and it therefore reaches its optimal operating temperature earlier. Furthermore, quieter running is the result and there are fewer HC emissions. All in all, there is a reduction in exhaust emissions and fuel consumption. First injection The first injection is when the crankshaft angle is at approx. 300 before TDC during the intake stroke. This helps to achieve a balanced distribution of the air and fuel mixture. 1st injection S296_059 Second injection During the second injection, a small amount of fuel is injected when the crankshaft angle is at approx. 60 before TDC. This mixture burns very late and exhaust gas temperature increases. 2nd injection The warmer exhaust gas heats up the catalyst, which allows it to reach its optimal operating temperature. S296_060 To catalyst 22 S296_061
23 Double injection, fullthrottle (1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine) On petrol direct injection systems, there are times when the fuel and air mixture is unfavourable at engine speeds up to 3000 rpm and at full throttle. Thanks to double injection, this is avoided and torque is increased by 1-3 Nm. The first injection The first injection happens when the crankshaft angle is at approx. 300 before TDC during the intake stroke. Here, approx. two thirds of the total amount is injected. 1st injection The second injection S296_062 The remaining amount of fuel, approx. one third, is injected at about the start of the compression stroke. In this way, less fuel is built up on the cylinder wall. The fuel evaporates almost completely and mixture distribution is improved. Furthermore, there is also a richer mixture in the area of the spark plug compared to the rest of the combustion chamber. This improves combustion and reduces the risk of knocking. 2nd injection S296_065 23
24 Engine management Intake system The intake system has been changed, compared to the Bosch Motronic MED system, as far as engine load detection is concerned. The hot film air mass meter G70 has been discontinued. For calculation of the engine load, use is made of intake air temperature sender 2 G299 in the engine cover and the ambient air pressure sender in the engine control unit. Activated charcoal filter Solenoid valve for activated charcoal filter system N80 Engine cover and air cleaner Throttle valve control unit J338 Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 EGR valve with potentiometer for exhaust gas recirculation G212 - Exhaust gas recirculation valve N18 Engine control unit with ambient air pressure sender J220 24
25 Intake manifold flap air flow control valve N316 Intake manifold flap vacuum unit Intake manifold flap potentiometer G336 Brake servo pressure sensor G294 Intake manifold pressure sender G71 with intake air temperature sender G42 S296_029 25
26 Engine management Engine load detection On FSI engines, engine load was previously measured using a hot film air mass meter. It is now calculated by the engine control unit as the hot film air mass meter has been discontinued. In place of this component, there is now an air intake temperature sender and an ambient air pressure sender. Engine load is calculated from the following signals: - Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 - Ambient air pressure sender (in engine control unit) J220 - Intake manifold pressure sender G71 - Intake air temperature sender G42 - Engine speed sender G28 - Throttle valve drive angle sender 1+2 G187 and G188 - Intake manifold flap air flow control potentiometer G336 - Hall sender G40 (for position of inlet camshaft on 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine) Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 The sender is installed in the engine cover in front of the throttle valve control unit. S296_010 Signal application It detects the temperature of the fresh air drawn in and passes on this information to the engine control unit. This then calculates the density of the fresh air. Ambient air pressure sender The sender is part of the engine control unit. Signal application Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 Air outlet to throttle valve control unit It measures ambient air pressure and passes on a relevant signal to the engine control unit. This then detects the pressure at the throttle valve control unit. S296_026 Effects of signal failure If one or both of the senders fail in their function, emergency running mode is selected, engine load is calculated by the engine control unit using stored values. Ambient pressure sender 26
27 Amount of exhaust gas recirculation On FSI engines, a high amount of exhaust gas recirculation is necessary to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions. In order that the amount of exhaust gas can be pushed up to its limit, it has to be calculated precisely. The following information is required for calculation of the amount of recirculated exhaust gas: - Intake manifold pressure sender G71 - Intake air temperature sender G42 - Ambient air pressure sender (in engine control unit) J220 (to calculate counter pressure of exhaust gas) - Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 G235 - The calculated engine load This is how it works: If exhaust gas is recirculated, intake manifold volume is increased by the recirculated exhaust gas and intake manifold pressure increases. The intake manifold pressure sender detects this pressure increase and sends a relevant voltage signal to the engine control unit. From this signal, the total amount is calculated (fresh air + exhaust gas). It deducts this total amount from the mass of fresh air from the calculated engine load and is thus left with the amount of exhaust gas. Intake manifold pressure sender G71, intake air temperature sender G42 This combined sender is attached on the right (from seated driver's perspective) of the plastic intake manifold. S296_021 Signal application It calculates the pressure and the temperature in the intake manifold and passes on a relevant signal to the engine control unit that, in turn, calculates the intake manifold volume. Effects of signal failure If one of the senders should fail in its function, the amount of exhaust gas is calculated by the engine control unit and the amount of recirculated exhaust gas is reduced based on the map. Intake manifold pressure sender G71 Intake air temperature sender G42 27
28 Engine management Supply on demand fuel system The supply on demand fuel system is a further development of the 1.4 ltr./77 kw FSI engine. The electric fuel pump supplies only the correct amount of fuel required by the high pressure fuel pump. In this way, power drawn by the pump is reduced and fuel consumption is reduced. Low pressure fuel system In the low pressure fuel system, fuel pressure is at 4 bar during normal operation. For hot and cold starting, the pressure is increased to 5 bar. Door contact switch It consists of the: - Fuel pump control unit J538 - Fuel tank - Electric fuel pump G6 - Fuel filter - Fuel pressure sender, low pressure G410 Battery Fuel pump control unit J538 If the engine control unit or the electric fuel pump are renewed, adaption of the new parts must be carried out. To do this, refer to the notes displayed during "Guided fault finding" on VAS Fuel filter Electric fuel pump G6 Colour codes/key No pressure 4 to 5 bar 50 to 100 bar Fuel tank 28
29 High pressure fuel system In the high pressure fuel system, fuel pressure is between 50 and 100 bar. It consists of the: Onboard electrical supply control unit J519 - High pressure fuel pump - Fuel pressure control valve N276 - High pressure fuel line - Fuel rail - Pressure limiter valve - Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G247 - High pressure injectors N30-N33 Motronic control unit J220 Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G247 High pressure fuel line Fuel return line In the fuel return line to the fuel tank, only a small amount of fuel flows from the high pressure pump and only when the pressure limiter valve is open. High pressure fuel pump To protect components, the pressure limiter valve opens at a fuel pressure of 120 bar. Fuel rail Fuel pressure sender, vacuum pressure G410 Fuel pressure control valve N276 High pressure injectors N30-N33 S296_024 29
30 Engine management Fuel pump control valve J538 The control unit can be found under the rear bench seat in the cover of the electric fuel pump. Task The control unit J538 actuates the electric fuel pump and regulates the pressure in the low pressure fuel system at a constant 4 bar. For hot and cold starting, the pressure is increased to 5 bar. Fuel pump control valve J538 S296_031 Effects of signal failure If the fuel pump control unit should fail in its function, the engine will not run. Terminal diagram J519 G G1 G6 Fuel gauge sender Fuel gauge sender Fuel pump J220 Engine control unit J285 Control unit with display unit in dash panel insert J538 Control unit for fuel pump J519 Onboard electrical system control unit 87 M The fuel gauge sender is supplied with earth from the control unit with display unit in dash panel insert J285. G6 G 31 J285 J538 G1 S296_034 J220 30
31 Fuel pressure sender, vacuum pressure G410 The sender is installed in the presupply line to the high pressure pump. It measures fuel pressure in the low pressure fuel system and sends a signal to the engine control unit. Signal application Use is made of this signal to regulate pressure in the low pressure fuel system. - In normal operation to 4 bar and - during cold and hot starting to 5 bar S296_004 Fuel pressure sender, vacuum pressure G410 Effects of signal failure If the fuel pressure sender should fail in its function, the electric fuel pump will be actuated with a fixed PWM signal and the pressure in the low pressure fuel system is increased. Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G247 The sender can be found on the intake manifold lower part and is screwed on the fuel rail. It measures fuel pressure in the high pressure fuel system and sends the signal to the engine control unit. Signal application The engine control unit evaluates the signals and, via the fuel pressure control valve, regulates the pressure in the fuel rail. Effects of signal failure S296_027 Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G247 If the fuel pressure sender should fail in its function, the control valve is actuated from the engine control unit with a fixed value. 31
32 Engine management High pressure fuel pump It is screwed into the camshaft housing and is operated by a double cam on the inlet camshaft. It has the task of building up fuel pressure in the high pressure fuel system by up to 100 bar. The component consists of a quantity-controlled single cylinder high pressure pump. It pumps just the required amount of fuel to the fuel rail depending on a map, and just the required amount of fuel for injection. In this way, the output of the high pressure pump is reduced, which contributes to a saving in fuel. S296_030 Single cylinder high pressure fuel pump Double cams on the inlet camshaft Suction stroke function: The pump plunger is moved down by means of the plunger spring. In this way, volume is increased in the pump chamber and pressure is decreased. As soon as the pressure in the low pressure fuel system is greater than the pressure in the pump chamber, the inlet valve will open and fuel will begin to flow. The outlet valve is closed because fuel pressure is greater in the fuel rail than in the pump chamber. Fuel supply Inlet valve From low pressure fuel system Pump chamber Outlet valve Pump plunger 32 S296_063 Plunger spring
33 Delivery stroke function: Once the pump plunger begins to rise, pressure increases in the pump chamber and the inlet valve closes. If pressure in the pump chamber is greater than pressure in the fuel rail, the outlet valve will open and fuel will be pumped to the fuel rail. Inlet valve Pump chamber To fuel rail Outlet valve S296_064 Pump plunger Fuel pressure regulation: Once the required fuel pressure has built up, the fuel pressure control valve is charged and the valve needle is actuated electro-magnetically. This frees the way for fuel supply, high fuel pressure in the pump chamber is reduced and the outlet valve closes. The pressure damper serves as a means of rapidly breaking down peaks in pressure when the control valve is opened and it prevents surges in pressure in the low pressure fuel system. Pressure damper Spring and spring plate Fuel supply Outlet valve Membrane Fuel pressure control valve Fuel return line When the valve needle opens, a small amount of fuel flows to the pump plunger for the purposes of lubrication and back to the fuel tank via the fuel return line. S296_066 Valve needle 33
34 Engine management Functional diagram (1.4 ltr./63 kw FSI engine) J M ϑ ϑ N30 N31 N32 N33 G6 G F36 F47 F 31 J538 G1 G294 G235 G83 J285 J220 N70 N127 N291 N292 G79 G185 G28 G40 G P Q P Q P Q P Q S296_ F Brake light switch G185 Accelerator position sender 2 F36 Clutch pedal switch G186 Throttle valve drive F47 Brake pedal switch for CCS G187 Throttle valve drive angle sender 1 G Fuel gauge sender G188 Throttle valve drive angle sender 2 G1 Fuel gauge G212 Potentiometer for exhaust gas recirculation G6 Fuel pump G235 Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 G28 Engine speed sender G336 Intake manifold flap potentiometer G39 Lambda probe G247 Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G40 Hall sender G294 Brake servo pressure sensor G42 Air intake temperature sender G295 NOx sender G61 Knock sensor 1 G299 Air intake temperature sender 2 G62 Coolant temperature sender G410 Fuel pressure sender, vacuum pressure G71 Intake manifold pressure sender J220 Motronic control unit G79 Accelerator pedal position sender J285 Control unit with display unit in dash panel insert G83 Coolant temperature sender - radiator outlet J338 Throttle valve control unit
35 J ϑ Z44 λ J583 G39 G295 N80 Z19 N316 ϑg299 N276 J271 ϑ M M G188 J338 G187 G186 Positive G42 G71 N18 G212 G247 G410 G62 G61 Earth Input signal Output signal Bi-directional line CAN drive train databus 31 J271 Motronic current supply relay P Spark plug connector J519 Onboard electrical supply control unit Q Spark plugs J533 Diagnosis interface for databus Z19 Lambda probe heating J538 Fuel pump control unit Z44 NOx sender heater J583 NOx sensor control unit N18 Exhaust gas recirculation valve 1 K/W lead N30- Injectors Heater actuation N33 3 CCS switch N70 Ignition coil 1 with final output stages 4 Alternator terminal DFM N80 Solenoid valve 1 for activated charcoal filter system 5 Radiator control 1 N127 Ignition coil 2 with final output stages 6 Radiator control 2 N276 Fuel pressure control valve N291 Ignition coil 3 with final output stages N292 Ignition coil 4 with final output stages N316 Intake manifold flap air flow control valve 35
36 Service Self-diagnosis Diagnosis On vehicle diagnosis, testing and information system VAS 5051 or vehicle diagnosis and service information system VAS 5052, the following modes of operation are available to you: - Guided fault finding (VAS 5051 only) - Vehicle self-diagnosis "Guided fault finding" checks, specific to the vehicle, all installed control units for fault entries and automatically creates an individual test chart. This guides you to the cause of the fault with the help of ELSA information, such as current flow diagrams or workshop manuals. As an alternative, you also have the opportunity of creating your own test chart. Via the function and component selection, the tests chosen by you will be included in the test chart and can be run through the diagnosis in any order. S296_042 "Vehicle self-diagnosis" can still be used in the normal way, but more detailed information via ELSA is not available. S296_043 Further information regarding "Guided fault finding" can be found in the VAS 5051 instruction manual. 36
37 Special tools Designation Tool Application T 10133/1 Puller T 10133/3 Slide hammer S296_044 Together with the slide hammer, the puller serves as a means of removing the injectors. T 10133/4 Nylon cylinder brush S296_046 For cleaning cylinder head drilling. T 10133/5 Taper tool S296_048 For fitting new seals on injectors. S296_045 T 10133/6 Assembly sleeve T 10133/7 Calibration sleeve S296_047 The assembly sleeve is used to fit the seal over the taper tool onto the injector. For adapting the seal to the injector. T 10133/8 Calibration sleeve S296_053 For adapting the seal to the injector. S296_054 37
38 Test yourself 1. Which components are integrated in the engine cover? A. Hot film air mass meter G70 B. Intake air temperature sender 2 G299 C. Ambient air pressure sender in engine control unit J220 D. Intake manifold pressure sender G71 2. Name the advantages of a dual circuit cooling system? 3. How many thermostats are installed in the coolant distribution housing and what are their function? A. One. Once the operating temperature has been reached, coolant flows through the radiator. B. Two. For separated flow of coolant, two thermostats are required, one for the cylinder block and one for the cylinder head. C. Three. In addition to the thermostats for the cylinder block and cylinder head, another thermostat is required for cooling of the electric exhaust gas recirculation valve. 4. What are the advantages of the regulated Duocentric oil pump? A. The output of the oil pump is reduced by up to 30 %. B. Wear in the oil is reduced as less oil is circulated. C. Build up of oil foam in the oil pump is minimised as oil pressure remains constant across the entire engine speed range. 38
39 5. Which additional operating mode is there when the 1.6 ltr./85 kw FSI engine is compared with the 1.4 ltr./63 kw FSI engine? A. Stratified injection B. Homogeneous-lean C. Homogeneous D. Double injection, catalyst warm-up E. Double injection, full throttle 6. Which component is not part of the high fuel pressure system? A. High pressure fuel pump B. Fuel pressure control valve N276 C. High pressure fuel line D. Fuel pump control unit J538 E. Fuel rail F. Pressure limiter valve G. Fuel pressure sender, high pressure G247 H. High pressure injectors N30-N33 7. Which components belong to the low fuel pressure system? A. Fuel pump control unit J538 B. Fuel tank C. Pressure limiter valve D. Electric fuel pump G6 E. Fuel filter F. Fuel pressure sender, low pressure G Which statement is true? A. The fuel pressure control valve N276 is screwed into the plastic fuel rail and regulates fuel pressure in the high fuel pressure system. B. The fuel pressure control valve N276 is screwed into the plastic fuel rail and regulates fuel pressure in the low fuel pressure system. C. The fuel pressure control valve N276 is screwed into the single cylinder high pressure fuel pump and regulates fuel pressure in the high pressure fuel system. Answers 1. B.; 3. B.; 4. A., B., C.; 5. E.; 6. D.; 7. A., B., D., E., F.; 8. C. Answers to question 2: The cylinder block is warmed up faster. There is less friction in the crankshaft drive. Cooling in the combustion chambers is better. 39
40 296 For internal use only VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights and the right to make technical alterations reserved Technical status 02/03 This paper was manufactured from pulp that was bleached without the use of chlorine.
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65).
 DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA
 Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition
 Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Swirl Flaps. A = Non swirl not active. B = Swirl active
 Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator
 Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Full list of fault codes and events
 Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE
 16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
4.0L CEC SYSTEM Jeep Cherokee DESCRIPTION OPERATION FUEL CONTROL DATA SENSORS & SWITCHES
 4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
2005 Escape Workshop Manual Cylinder block
 22 6010 Cylinder block Cylinder Head Item Part Number Description 1 12A366 Coil-on-plug assembly (4 req'd) 2 6M293 Valve cover 3 12K073 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor 4 6766 Oil filler cap 5 6M293 Valve
22 6010 Cylinder block Cylinder Head Item Part Number Description 1 12A366 Coil-on-plug assembly (4 req'd) 2 6M293 Valve cover 3 12K073 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor 4 6766 Oil filler cap 5 6M293 Valve
Motronic September 1998
 The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited
 Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
PARTIAL ENGINE ASSY (2ZZ GE)
 COMPONENTS 14189 140R701 7.0 (71, 62 in. lbf) Cylinder Head Cover No. 2 19 (194, 14) Radiator Support Upper 19 (194, 14) Radiator Hose Inlet Cruise Control Actuator Assy 6.0 (61, 53 in. lbf) Radiator Assy
COMPONENTS 14189 140R701 7.0 (71, 62 in. lbf) Cylinder Head Cover No. 2 19 (194, 14) Radiator Support Upper 19 (194, 14) Radiator Hose Inlet Cruise Control Actuator Assy 6.0 (61, 53 in. lbf) Radiator Assy
Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (-40 )
 149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
1992 Toyota Cressida
 Monday, May 16, 2016 5:32:47 PM Page 13 2005 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. Fig. 7: Exploded View Of Typical Cylinder Head & Components Fig. 8: Cylinder Head Bolt Removal Sequence Monday, May
Monday, May 16, 2016 5:32:47 PM Page 13 2005 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. Fig. 7: Exploded View Of Typical Cylinder Head & Components Fig. 8: Cylinder Head Bolt Removal Sequence Monday, May
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
Timing Chain Renew ( ) Renew. Section Title. Special Tools. Proprietary Tools Scraper Engine support bar
 Timing Chain Renew ( 34 0) Special Tools 40 400 40 Engine support bar 40 0 Adaptor for -40 40 03 Adaptor for -40 Proprietary Tools Scraper Workshop Equipment Transmission jack Materials Cable ties Sealer
Timing Chain Renew ( 34 0) Special Tools 40 400 40 Engine support bar 40 0 Adaptor for -40 40 03 Adaptor for -40 Proprietary Tools Scraper Workshop Equipment Transmission jack Materials Cable ties Sealer
Removing and installing timing case cover. A. Engine
 01-2100 Removing and installing timing case cover Operation no. of operation texts and work units or standard texts and flat rates 01-0080, 8009 A. Engine 119.960 Viscous fan clutch remove, install (20-3120).
01-2100 Removing and installing timing case cover Operation no. of operation texts and work units or standard texts and flat rates 01-0080, 8009 A. Engine 119.960 Viscous fan clutch remove, install (20-3120).
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service. Self-Study Programme 248. The W Engine Concept. Design and Function
 Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
PARTIAL ENGINE ASSY COMPONENTS. Clip. Radiator Grille. Clip. Front Bumper Cover. Engine Under Cover LH. N m (kgf cm, ft lbf) : Specified torque
 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1417 COMPONENTS 141FP01 Radiator Grille Front Bumper Cover Engine Under Cover RH Engine Under Cover LH A79361 962 1418 ENGINE MECHANICAL Heater Outlet Water Hose 7.0 (71, 62 in. lbf)
ENGINE MECHANICAL 1417 COMPONENTS 141FP01 Radiator Grille Front Bumper Cover Engine Under Cover RH Engine Under Cover LH A79361 962 1418 ENGINE MECHANICAL Heater Outlet Water Hose 7.0 (71, 62 in. lbf)
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Timing Chain - Renew ( )
 «Scorpio '95 Table of Contents» «Section 21: Engine» «Subsection 21-05: 2,9 V6 24V Cosworth Engine» «REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION» Timing Chain - Renew (21 314 0) Special Tools 21-140-01Adaptor for 21-140
«Scorpio '95 Table of Contents» «Section 21: Engine» «Subsection 21-05: 2,9 V6 24V Cosworth Engine» «REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION» Timing Chain - Renew (21 314 0) Special Tools 21-140-01Adaptor for 21-140
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review
 Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
Service Training. Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine. Self-Study Programme 377
 Service Training Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine Self-Study Programme 377 Special features of the current Audi vee engine family are the 90-degree included angle between the cylinder banks and the spacing
Service Training Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine Self-Study Programme 377 Special features of the current Audi vee engine family are the 90-degree included angle between the cylinder banks and the spacing
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2. Self-study programme 268. For internal use only
 268 Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2 Self-study programme 268 For internal use only Contents Engine, Mechanics Page Belt drive/ancillaries...................................................
268 Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2 Self-study programme 268 For internal use only Contents Engine, Mechanics Page Belt drive/ancillaries...................................................
1983 BMW 320i. 1.8L 4-CYL 1983 Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder
 ENGINE IDENTIFICATION 1.8L 4-CYL 1983 Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder For engine repair procedures not covered in this article, see ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION article in the GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION 1.8L 4-CYL 1983 Engines - 1.8L 4-Cylinder For engine repair procedures not covered in this article, see ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION article in the GENERAL INFORMATION
PIERBURG. Carburetor: 2E3
 PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
51. absolute pressure sensor
 51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
3.0 litre fuel injection engine (162 kw - Motronic - 6-cylinder), engine code AVK
 No. 66/.0 litre fuel injection engine (6 kw - Motnic - 6-cylinder), engine code AVK Fm model year 00 Main fuse On battery A97 00 Edition 08.0 No. 66/ Fuse box 7 6 5 0 9 8 5 9 8 7 6 0 Dash panel, driver
No. 66/.0 litre fuel injection engine (6 kw - Motnic - 6-cylinder), engine code AVK Fm model year 00 Main fuse On battery A97 00 Edition 08.0 No. 66/ Fuse box 7 6 5 0 9 8 5 9 8 7 6 0 Dash panel, driver
Heat Transfer in Engines. Internal Combustion Engines
 Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Heat Transfer in Engines Internal Combustion Engines Energy Distribution Removing heat is critical in keeping an engine and lubricant from thermal failure Amount of energy available for use: Brake thermal
Chapter 4 Part C: Fuel and exhaust systems - multi-point fuel injection models
 4C 1 Chapter 4 Part C: Fuel and exhaust systems - multi-point fuel injection models Contents ACAV intake system (1998 cc 16-valve models) - general information, 19 Accelerator cable - removal, refitting
4C 1 Chapter 4 Part C: Fuel and exhaust systems - multi-point fuel injection models Contents ACAV intake system (1998 cc 16-valve models) - general information, 19 Accelerator cable - removal, refitting
T erm STI2D. The process by which a car works is a lot simpler than you may think. When a driver turns a key in the ignition:
 1. How a car engine Works The process by which a car works is a lot simpler than you may think. When a driver turns a key in the ignition: The car battery powers up sending Power to the starter motor,
1. How a car engine Works The process by which a car works is a lot simpler than you may think. When a driver turns a key in the ignition: The car battery powers up sending Power to the starter motor,
GAS/PETROL THE ALTERNATIVE: ENGINES LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER AND MORE COMPACT ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY 22,0 6,6 431,1
 THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Federal and California Emissions Warranties Parts List
 Emissions warranties are state specific. Refer to the years/miles 1 columns below as follows: A Minimum coverage for all vehicles in all states. B Vehicles registered and normally operated in California,
Emissions warranties are state specific. Refer to the years/miles 1 columns below as follows: A Minimum coverage for all vehicles in all states. B Vehicles registered and normally operated in California,
Coolant Temperature Switch; Black with Round Top and 4 Pin Connector $ $ Fuel Injector Insulator; O-Ring; Green
 AC & Heater Control Valve; Mono Valve Solenoid Repair Kit 3065 1 $ 40.24 $ 40.24 Distributor Cap 03227 1 $ 88.73 $ 88.73 Distributor Rotor 04177 1 $ 19.86 $ 19.86 Vacuum Line, Transparent/Yellow, 1.0 X
AC & Heater Control Valve; Mono Valve Solenoid Repair Kit 3065 1 $ 40.24 $ 40.24 Distributor Cap 03227 1 $ 88.73 $ 88.73 Distributor Rotor 04177 1 $ 19.86 $ 19.86 Vacuum Line, Transparent/Yellow, 1.0 X
Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system - transistorised type
 5B 1 Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system - transistorised type Contents Coil - testing........................................... 9 Distributor - overhaul..................................... 7 Distributor
5B 1 Chapter 5 Part B: Ignition system - transistorised type Contents Coil - testing........................................... 9 Distributor - overhaul..................................... 7 Distributor
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Torque Guidelines (Z 22 SE)
 Page 1 of 14 Torque Guidelines (Z 22 SE) No. Designation Nm 1 Retaining bolts, coolant pump sprocket to coolant pump 2 Retaining bolts, balancer shaft timing chain guide rail to 3 Retaining bolts, balancer
Page 1 of 14 Torque Guidelines (Z 22 SE) No. Designation Nm 1 Retaining bolts, coolant pump sprocket to coolant pump 2 Retaining bolts, balancer shaft timing chain guide rail to 3 Retaining bolts, balancer
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
PARTIAL ENGINE ASSY (2TR FE)
 COMPONENTS 147 1421Z01 Clip Hood Subassy x9 Radiator Support to Frame Seal LH 30 (306, 22) 30 (306, 22) Fan and Generator V Belt 5.0 (51, 44 in. lbf) Fan Shroud Fan Pulley Fan w/ Fluid Coupling PRE RUNNER
COMPONENTS 147 1421Z01 Clip Hood Subassy x9 Radiator Support to Frame Seal LH 30 (306, 22) 30 (306, 22) Fan and Generator V Belt 5.0 (51, 44 in. lbf) Fan Shroud Fan Pulley Fan w/ Fluid Coupling PRE RUNNER
General Specifications
 General Specifications Engine Data Description Litres Engine management EEC V/SFI Emission standard 96 EEC Engine code NSD Firing order 1-3 - 4-2 Bore mm 86,0 Stroke mm 86,0 Cubic capacity cm 3 1998 Compression
General Specifications Engine Data Description Litres Engine management EEC V/SFI Emission standard 96 EEC Engine code NSD Firing order 1-3 - 4-2 Bore mm 86,0 Stroke mm 86,0 Cubic capacity cm 3 1998 Compression
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL
 17 ENGINE & EMISSION CONTROL 1996 Engine Control System ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Post-installation Operation (Refer to Adjusting the Accelerator Cable.)
17 ENGINE & EMISSION CONTROL 1996 Engine Control System ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Post-installation Operation (Refer to Adjusting the Accelerator Cable.)
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 PE07.61-P-2001-60DB Legend of block diagram of ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system ENGINE 271 in MODEL 211 Code Designation Coordinate A1 Instrument cluster 43E A1p13 Multifunction display 42F A7/3
PE07.61-P-2001-60DB Legend of block diagram of ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system ENGINE 271 in MODEL 211 Code Designation Coordinate A1 Instrument cluster 43E A1p13 Multifunction display 42F A7/3
