The Golf 2004 Running gear
|
|
|
- Blake Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
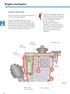
1 Service Training Self-study programme 321 The Golf 2004 Running gear Design and function
2 With the refined safety running gear of the Golf, which is configured for both sporty and comfortable driving, VW has set a further standard in the development of running gear technology. With the aim of developing the best underpinnings in its class, a dynamic running gear system was created that keeps the driver away from unpleasant surprises in any situation. The running gear of the Golf features an optimised suspension strut axle, multi-link rear axle, completely new electronic power steering and the newest generation of ESP and brake assist system to offer a unique synthesis of best-in-class driving comfort and, at the same time, best steering and driving response. S321_179 NEW Important Note This self-study programme shows the design and function of new developments! The contents will not be updated. For current inspection, adjustment and repair instructions, please refer to the relevant service literature. 2
3 Contents Introduction Front axle Rear axle Steering Brake system Wheels and tyres Foot pedal cluster Service Test yourself
4 Introduction The running gear Once again, the running gear of the Golf sets a standard in its class. To achieve this a suspension strut axle, perfectly optimised in many ways, has been installed. With regards to driving dynamics and driving comfort, the new four link rear axle is also ground-breaking. The electromechanical power steering of the Golf supports the vehicle's driving characteristics in a remarkable way. To do this, it transmits a precise steering feeling and adapts the steering forces harmoniously as speed increases. In addition to the Golf, the Touran and Audi A3 also currently use this running gear platform. Floor mounted accelerator pedal with non-contact accelerator pedal position senders Optimised suspension strut axle based on the McPherson principle Direct anti-roll bar connection with ratio of 1:1 Electromechanical power steering Brake servo with dual rate map characteristic Electronic stabilisation program based on MK 60 system from Continental Teves 4
5 The Golf can be equipped with standard, sports or heavy duty running gear. The various running gear systems differ in the spring, damper, anti-roll bar equipment and the mounting elements. The sports running gear is lowered by 15 mm compared with the agile and comfort-orientated standard running gear. The body height of the vehicle with heavy duty running gear is 20 mm higher than on the standard running gear version. Four link rear axle 4motion drive, optional Tyre monitoring system, optional Brake assist system Track and camber on rear axle can be adjusted separately S321_135 Wheel designs in 15", 16" or 17" versions 5
6 Front axle The front axle The Golf has a McPherson front axle with bottom wishbones and wheel locating suspension struts. The front axle offers optimal comfort at a high level of stability. Anti-roll bar Subframe Suspension strut Wishbone suspension Wheel bearing housing Console Coupling rod S321_007 Wheel bearing 6
7 Subframe Console Subframe Console S321_022 The subframe comprises of three parts and is made of aluminium. It is joined to the body at six points. With this type of connection, the body is stiffened in the front area. The optimal layout of the bonded rubber bushes in the wishbones and suspension strut mountings has a positive influence on the driving dynamics and body acoustics. Key: = Bonding point to body Wheel bearing The wheel bearings are of the 3rd generation. This type of component is a compact wheel bearing unit comprised of wheel hub and wheel bearing, which is bolted from the interior to the swivel mounting by four bolts. The advantage of this wheel bearing is that the bearing play no longer has to be adjusted. S321_020 7
8 Front axle Suspension strut The spring used is a combination of cylindrical coil spring and polyurethane auxiliary damper. The coil spring is made from high tensile steel and is drawn in at the ends. The damping characteristic of the coil springs is linear. The polyurethane auxiliary spring has a progressive damping characteristic. Auxiliary damper Coil spring S321_039 Suspension strut mounting The suspension strut mounting is a bonded rubber bush. By decoupling the spring and shock absorber connection to the body, the damping force is absorbed separately by the body. In this way, pretension in the damper mounting is prevented. This positively influences rolling comfort and reduces the transfer of noise from the road surface to the body. The mounting features a soft damping characteristic in the direction of normal travel. In this way, an improvement is achieved in driving comfort and acoustics. In the lateral direction, the mounting is designed to be stiffer. This measure positively influences the driving dynamics and the steering response. S321_041 8
9 Swivel mounting The swivel mounting is joined to the suspension strut by a clamp-type connection. At the lower level it is attached to the wishbone via a guide joint. The wheel bearing unit is bolted to the swivel mounting. Depending on the version, either a bolted or integrated swivel mounting is installed. Integrated swivel mounting Bolted swivel mounting Clamp-type connection Suspension strut Swivel mounting Suspension strut Swivel mounting Brake carrier Clamp-type connection Brake caliper S321_019 S321_043 Wheel bearing unit Guide joint Wheel bearing unit Bolted connection Wishbone suspension Subframe The wishbones form the lower connection between the body and swivel mounting. Depending on the engine, they are made from cast iron or sheet metal and are joined via bonded rubber bushes to the consoles of the subframe. Wishbone suspension S321_021 9
10 Front axle Anti-roll bar The tubular anti-roll bar is joined directly to the suspension strut via a coupling rod in a ratio of 1:1. The advantage compared to the Golf 98 is that a higher degree of anti-roll stabilisation is achieved with the same tube diameter. Suspension strut Bushes Anti-roll bar Coupling rod Subframe S321_045 The anti-roll bar is mounted on the subframe by means of two bushes. The positive connection of the bonded rubber bushes prevents relative movements between anti-roll bar and bonded rubber bush. Anti-roll bar Instead of turning in the rubber bush, the rotational movements of the anti-roll bar are absorbed in the mounting. In this way, a high degree of efficiency is achieved. S321_134 Absorbed relative movement Bonded rubber bush Bearing 10
11 The drive shafts Left-hand drive shaft Right-hand drive shaft S321_046 Intermediate shaft S321_048 Installed in the Golf is the track proven drive shaft concept with short and long drive shafts. The shorter shaft on the left-hand side is solid. The longer shaft on the right, however, is a hollow tubular construction. On higher powered engines, the drive shafts are of the same length. This is made possible by an intermediate shaft, which is mounted additionally on the crankcase. This drive shaft concept is advantageous in that, even during full acceleration, there are no repercussions on the steering and straight running of the vehicle from driving forces. Furthermore, pulling to one side is also avoided. Intermediate shaft S321_049 11
12 Rear axle The front wheel drive rear axle The rear axle of the Golf is of the compact four link design. On each side it has three suspension links (lower link, track rod and upper link) and a trailing arm. This layout means that longitudinal and lateral forces are almost completely separated from each other. In this way, a very high level of driving stability and comfort are achieved. With a predetermined alteration in the wheel position during cornering, a light understeer is achieved due to the natural opposing steering force of the outer wheel (self steering response or toe-in steering). Steel spring Anti-roll bar Upper link Damper Bearing bracket Subframe Track rod Lower link Trailing arm S321_171 12
13 Subframe The subframe is a welded construction made from steel. It is bolted directly to the body. The body mounting points on front wheel drive and 4motion drive systems are identical. S321_027 Wheel carrier The wheel carrier is a forged metal construction made from steel with a moulded stub axle to mount the wheel bearing. Wheel bearing The wheel hub and wheel bearing form one component. The wheel bearing is bolted to the stub axle of the wheel carrier by means of a stretch bolt. In this way, the necessary bearing preload is achieved (2nd generation wheel bearing). Stub axle Wheel bearing Wheel carrier Stretch bolt S321_029 13
14 Rear axle Four link principle On the four link axle of the Golf 2004, longitudinal and lateral connections are separate. The advantage is that no compromise had to made between comfort and driving dynamics. The front mounting (trailing arm) is not subjected to lateral forces and has therefore been made very soft. Cracks and grooves running across the road surface are absorbed easily. Longitudilal Trailing arm Track rod Lateral force Top link Bottom link S321_018 As a comparison, the following illustration shows the force distribution on the double wishbone suspension of the Golf 98. Longitudinal force Trailing arm Upper wishbone Lateral force Lower wishbone S321_190 14
15 The 4motion rear axle The driven rear axle has been modified on the subframe, anti-roll bar, wheel carrier and wheel bearings. The advantage of this axle design is that the floor assembly on vehicles with front wheel and 4motion drive systems is the same with regards to the body mounting points. Subframe Wheel bearing Anti-roll bar Wheel carrier S321_031 15
16 Rear axle Subframe The subframe is a welded construction made from aluminium. It also supports the rear differential. It is bolted to the body by means of oversized bonded rubber bushes. In this way, noise reduction is promoted thanks to isolation of the body. Subframe An additional aluminium cross member, bolted in position, serves as a means of increasing rigidity in the lower area by complementing the subframe. The use of aluminium means that a weight saving of approx. 7 kg has been achieved. Cross member S321_033 Bonded rubber bush Wheel carrier Wheel bearing The wheel carrier was modified geometrically to accommodate the drive from the rear axle (introduction of modified wheel bearing and drive shaft). The wheel bearing installed here is of the 3rd generation (as installed in the front axle). Wheel carrier Wheel bearing S321_035 16
17 Steering The steering The electromechanical power steering supports the driving response of the Golf. To do this, it conveys a precise feel for the vehicle and the road. As speed increases, the steering forces are adapted harmoniously. Disrupting factors from bumps in the road surface are filtered out as far as possible. Overview Steering column Steering wheel S321_053 Universal joint shaft Electromechanical power steering 17
18 Steering The steering wheels Installed as standard is a 4-spoke PU steering wheel. PU (polyurethane) is a very strong synthetic material, which is good to work with and can be recycled. As an alternative, a steering wheel with soft leather covering and one-piece cast magnesium frame is available. During assembly, the airbag module is installed in the steering wheel mechanically and can only be removed if the steering column is disengaged. This is an effective anti-theft measure to prevent unauthorised removal of the driver airbag. S321_124 The steering wheel features a weight-optimised framework cast from magnesium. The design can be seen in the cross sectional diagram of the multi-function steering wheel. Cross-section based on wooden steering wheel Leather covering of left spoke trim Mounting for left multifunction switch Mounting for right multi-function switch Leather covering of right spoke trim Wood veneer shell Leather covering Magnesium frame PU foam covering S321_196 Sheet metal plate 18
19 Various designs of 3-spoke steering wheel will be available as an option. Design 1: The steering wheel is of the 3-spoke design, finished in either leather or a combination of leather and aluminium. S321_012 Design 2: The steering wheel is of the 3-spoke design, finished in wood and leather. The multi-function steering wheel features an audio and telephone function. S321_014 Design 3: The steering wheel is of the 3-spoke design, finished in leather. The multi-function steering wheel features an audio and telephone function and also Tiptronic. S321_010 19
20 Steering The steering column The reach and rake adjustment of the steering column is mechanical. For optimal adaptation to the driver's requirements, it can be adjusted up and down by 50 mm and back and forth by 60 mm. Fixing of the steering wheel in position is by means of a multi-plate bundle with ten steel plates. Five plates in the horizontal plane make reach adjustment possible. The other five plates are installed in the vertical plane and make rake adjustment possible. Multi-plate bundle for reach adjustment Multi-plate bundle for rake adjustment S321_084 Connection of the steering column to the dash module carrier is by means of an assembly bracket pressure cast from aluminium. 20
21 Principle of the clamping function The clamping function is provided by two rollers that are pushed up a ramp to fix the steering wheel in position. In this way, the multi-plate bundle is pressed together via a thrust piece. Due to the fact that no gear teeth are used in the clamping mechanism, adjustment is infinitely variable. Multi-clamp bundle released Thrust piece Plates for rake adjustment Roller Multi-clamp bundle clamped S321_128 Ramp Plates for reach adjustment Thrust piece Plates for rake adjustment Roller S321_126 Ramp Plates for reach adjustment 21
22 Steering Crash concept As part of occupant safety, the steering column and the universal joint shaft are designed to slide into each other. In this way, the steering column and the steering wheel will not be pushed towards the driver if the front end of the vehicle deforms. The steering column tube and universal joint shaft are designed so that the steering column is decoupled from the steering gear in the event of the steering gear being forced inwards in a crash. This prevents the steering wheel from jutting against the driver as a result of further deformation of the front end. S321_130 The cradle and console are joined together by means of a shear plate. In the event of a crash, a defined force is placed against the shear plate by the movement caused from the impact of the driver against the cradle. The geometrical design of the shear plate means that a progressive force/travel characteristic is achieved. Cradle Shear plate S321_173 Console 22
23 The electromechanical power steering S321_137 The Golf is fitted as standard with an electromechanical power steering system. This steering system consists of steering box and an electric motor with control unit. The system is installed on the subframe. The steering assistance from the electric motor, which is flanged in parallel to the toothed rack, is transmitted via a second pinion (drive pinion) to the toothed rack. The electro-mechanical power steering is an active steering system, which is directly dependent on road speed, the steering force and the steering angle. Data is transferred via the drive train CAN data bus. The control unit is flanged to the electric motor. Steering force sender Control unit Electric motor Steering pinion Steering column Toothed rack Drive pinion S321_057 Steering angle sender Further information can be found in SSP 317 "The dual pinion electromechanical power steering". 23
24 Brake system The brake system The basis for good braking properties is provided by a newly designed brake system. The Golf is fitted as standard with the newest generation of ESP and brake assist system. Overview Brake servo ESP unit Rear wheel brake S321_155 Brake cable Handbrake Front wheel brake Brake lines 24
25 The brake equipment Engine 55 kw- 85 kw Front brakes (single piston floating caliper brake) Ø280x22 Rear brakes Ø255x10 Ø260x12 S321_156 Integrated swivel mounting 100 kw- 110 kw and 77 kw TDI with DSG 02E Ø288x25 S321_164 S321_166 S321_158 bolted swivel mounting 147 kw and 118 kw TDI Ø312x25 Ø286x12 / Ø286x12 S321_168 S321_160 bolted swivel mounting 177 kw Ø345x30 Ø310x22 S321_170 S321_162 bolted swivel mounting 25
26 Brake system The dual rate booster brake servo In all left-hand drive vehicles, a 10" brake servo is installed. Right-hand drive vehicles are equipped with a tandem brake servo of 7/8" in dimension. A main new feature is the introduction of the "dual rate characteristic". The inside of the brake servo is modified, which results in a progressive characteristic. In this way, higher brake pressures are available than on conventional brake servos, even at low pedal forces. Braking forces are still imparted softly during normal operation however. S321_078 Standard characteristic Dual rate characteristic Brake pressure Pedal force S321_037 26
27 The anti-lock braking system ABS/ESP Continental/Teves MK 60 A new ESP unit of the product family MK 60 is installed. The main new features are: Active wheel speed sender without forwards and reverse travel recognition. Combined yaw rate/lateral acceleration sensor. This sensor is compatible with the CAN system. Installed in the ESP unit is the brake pressure sender. The brake pressure sender was installed until now on the tandem brake master cylinder. New ESP warning lamp. S321_192 Hydraulic unit with brake pressure sender (G201) Sender spring contacts Brake pressure sender S321_060 Installed as an exclusive ABS system is the MK 70. As this component only features the ABS function (4 inlet and 4 outlet valves), it is smaller and lighter than the MK 60 system. 27
28 Brake system The brake pressure sender (G201) It measures the pressure applied at the brake pedal by the driver. To ensure a higher level of safety, the sensor supplies two pressure signals independently of each other. These are sent at the same time as two opposing voltages. The control unit constantly compares these with each other. S321_176 S321_178 S321_ Measuring chamber 2. Piezo resistive thick film sensor element 3. Sensor electronics and signal amplifier 4. Contact springs to control unit J Piezo resistive measuring bridge 6. Flexible thick film membrane 7. Piezo bridge elements within measuring bridge Electric switching The sensor is joined via 4 contact springs to control unit J104 (4). Two contacts serve as a means of supplying power, the other two provide two independent pressure signals. 28
29 Construction The sensor works on the principle of piezo resistance. To do this, use is made of the change in conductivity of the materials from structural deformation. Four piezo resistive measuring elements, which are switched together to form a bridge (5), are installed on a membrane (6). Piezo resistive measuring elements are resistors made from semi-conductor material. The function is similar to that of bi-metallic strips. Function As pressure increases, the length of the membrane (6) changes and also the piezo resistive measuring bridge (5) connected to it. This change in length imparts force on the piezo bridge elements in the measuring bridge (7), which alters the charge distribution within the piezo elements. With a change in the charge distribution, the electrical properties of the piezo bridge elements also change. These are proportional to the pressure and are transmitted as an amplified sensor signal to control unit J104. Self-diagnosis The pressure sensor is monitored by the electronic control unit via both output signals. If both signals deviate from each other within the tolerance level, a fault is diagnosed by the control unit. Effects of failure In the event of pressure sensor failure, the ESP function is reduced to ABS and EBD (electronic brake pressure distribution). 29
30 Brake system The optimised hydraulic brake servo (OHBS) The most effective way to supply vacuum pressure to the brake servo is to utilise the vacuum from the intake manifold on the engine. On petrol engines with automatic gearboxes, the vacuum pressure available at the intake manifold can drop significantly in certain operating conditions (cold start phase). This can have a negative impact on the comfort of brake actuation. The cause of this is the opening of the throttle valve under load, which drastically reduces the vacuum in the intake manifold. Until now, the necessary vacuum for such situations was provided by an auxiliary unit (e.g. electric vacuum pump). In the Golf 2004, a new path has been found. Point of brake servo actuation Map characteristic at 800 mbar vacuum Brake pressure Lower vacuum level (e.g. cold start) Braking assistance by means of OHBS function Foot pressure S321_062 30
31 Function The loss of braking assistance, as a result of insufficient vacuum pressure, is balanced out with an active and controlled build-up of brake pressure from the ESP hydraulics. To enable this control, measurement of the pneumatic forces in both chambers of the brake servo (BS) is necessary. The pressure difference is a direct benchmark for the maximum amount of braking assistance available. If the pressure in both chambers is equai, the point of brake servo actuation is reached. Thereafter, a further increase in braking force is only possible, without additional braking assistance, by an increase in foot pressure on the brake pedal. Stored in the ESP control unit J104 is the specified map characteristic for the build-up of brake pressure, depending on the pressure difference in both servo chambers. If the intake manifold vacuum is insufficient, the point of actuation is reached even at brake pressure levels below the specified amount. If this is the case, a controlled build-up of brake pressure is initiated by the ESP hydraulics. Compared to conventional braking assistance, the driver will notice no difference here with regards to the force required at the brake pedal and braking comfort. To enable the controlled build-up of brake pressure, the use of new solenoid valves is made to switch to ESP regulated mode. The degree to which these valves is opened can be controlled on a time basis. In this way, the pressure patterns can be adapted to each situation. 31
32 Brake system Differential pressure sensor The sensor measures the pneumatic pressures in both chambers of the brake servo. S321_064 Installation position of differential pressure sensor shown as cross-sectional diagram Differential pressure sensor Vacuum pressure chamber Working pressure chamber Brake servo S321_066 Signal application The differential pressure sensor calculates the difference in brake servo pressure conditions to atmospheric pressure. For OHBS regulation, however, only the pressure in the vacuum pressure chamber is used. Effects of failure If the signal from the working pressure chamber should fail, an entry is made in the fault memory. The OHBS function remains intact. In the event of signal failure in the vacuum pressure chamber, an entry is made in the fault memory and the brake system warning lamp K118 will light up. 32
33 The exchange of ESP and CAN data The ESP control unit exchanges data with other control units of the onboard electrical system. J104 ESP control unit J220 Motronic control unit J217 Automatic gearbox control unit J533 Data bus diagnostic interface J492 Four-wheel drive control unit J527 Steering column electronics control unit G85 Steering angle sender Diagnosis connection J500 Electromechanical power steering control unit J285 Control unit with display in dash panel insert S321_180 Drivetrain CAN data bus Diagnostic CAN data bus Dash panel CAN data bus Data bus wiring 33
34 Brake system The handbrake The new design means that the amount of space required in the centre console has been minimised. In this way, additional stowage facilities have been created behind the handle. The lever is pressure cast from magnesium. This resulted in a weight saving of more than half that of the steel version. S321_073 The toothed segment is joined positively to the bearing bracket. In the neutral position, the pawl is engaged with the toothed segment and the brake lever is locked. When the release button is pressed, the pawl is pulled away from the toothed segment and the brake lever is free to move. S321_201 S321_203 34
35 Wheels and tyres The wheels and tyres Equipment overview Tyre size Profile Rim size Rim type 195/65/ R T Summer 6 J x 15 offset 47 Steel 195/65/ R T/H Summer 6.5 J x 15 offset 50 Alloy 195/65/ R T/H Winter 6 J x 15 offset 47 Steel 205/60/ R H Summer 6 J x 15 offset 47 Alloy 205/55/ R H/V/W Summer 6.5 J x 16 offset 50 Alloy 205/55/ R Q Winter 6 J x 16 offset 50 Alloy 205/45/ R H/V Summer 7 J x 17 offset 54 Alloy Spare wheel of emergency type T125/70/ R 18 Spare wheel of conventional type or Tirefit J x 18 - Tyre monitoring system The tyre monitoring system is a software module in the ABS control unit. It detects slow punctures and gradual tyre pressure loss at the wheel. More detailed information can be found in self-study programme SSP 319 "The Golf 2004 Electrical system". 35
36 Pedal cluster The pedal cluster The foot pedal cluster was adapted to the Golf. Accelerator pedal, clutch and brake actuation are of a modular design. To remove the accelerator pedal module, please use special tool T10238 or T S321_087 The clutch position sender G476 Fitting location The clutch position sender is clipped onto the master cylinder. This sender detects when the clutch pedal is actuated. Signal application With the clutch pedal actuated, the cruise control system is switched off and the amount of fuel injected is reduced briefly to prevent gear change jolts. Clutch pedal with clutch position sender S321_195 36
37 How it works The master cylinder is attached to the bearing bracket via a bayonet connection. When the clutch pedal is actuated, the plunger moves the piston in the master cylinder. Clutch master cylinder Bearing bracket Plunger Clutch position sender Piston with permanent magnet Pedal travel S321_204 Clutch pedal not pressed When the clutch pedal is not pressed, the plunger and piston are in the rest position. The electronic evaluation feature of the clutch position sender sends a voltage signal to the engine control unit, which is 2 volts under the supply voltage (battery voltage). The engine control unit thereby detects that the clutch pedal is not pressed. Piston with Plunger permanent magnet Switch point (Hall sender) Clutch position Voltage signal to engine sender control unit S321_224 Clutch pedal pressed When the clutch pedal is pressed, the plunger is pushed together with the piston in the direction of the clutch position sender. At the front end of the piston is a permanent magnet. As soon as the permanent magnet passes over the switch point of the Hall sender, the electronic evaluation feature now only sends a voltage signal of 0 to 2 volts to the engine control unit. In this way, it detects that the clutch pedal is pressed. Piston with Plunger permanent magnet S321_226 Switch point (Hall sender) Clutch position Voltage signal to engine sender control unit 37
38 Pedal cluster The accelerator pedal position senders G79 and G185 Both accelerator pedal position senders are part of the accelerator pedal module and operate without contact as inductive senders. Advantages - No wear as senders operate without contact - No basic setting for kick-down necessary as sender is part of accelerator pedal module, which therefore does not result in tolerances between accelerator pedal and vehicle body Signal application The engine control unit uses the accelerator pedal position sender signals to calculate the amount injected. S321_217 Accelerator pedal with accelerator pedal position senders Effects of signal failure In the event of failure in one or both senders, an entry is made in the fault memory and the electronic power control (EPC) warning lamp will be activated. The convenience features, such as cruise control or engine braking control will be deactivated. If one sender fails the system will adopt the idle position. If the second sender is detected at idle within a defined test period, normal driving mode will be authorised again. If both senders fail the engine will only run at increased idling speed (max rpm) and will no longer respond to input from the accelerator pedal. If a full throttle input is made, speed will increase only slowly. 38
39 Construction The accelerator pedal module comprises of an accelerator pedal, the pedal end stop, the mechanical components to convert rotational motion and both accelerator pedal position senders G79 and G185. The senders are joined to a circuit board and each consist of an exciter coil, three receiver coils and electronics for control and evaluation. For reasons of safety, both senders operate independently of each other. Accelerator pedal Mechanical components Small metal plate S321_219 Cover Circuit board The mechanical components of the accelerator pedal module convert leverage movement of the accelerator pedal into straight line motion. A small metal plate is attached so that when the accelerator pedal is actuated, it is brought in line just short of the circuit board. Accelerator pedal not pressed Accelerator pedal pressed Mechanical Mechanical components Small metal plate S321_222 Circuit board Area of receiver coils Exciter coils components Small metal plate Circuit board S321_220 39
40 Pedal cluster How it works Supplied with 5V of power, the pedal electronics generate a high frequency alternating voltage, which results in the build-up of an electromagnetic alternating field. This electro-magnetic alternating field affects one moving small metal plate. As this happens, a further electromagnetic alternating field is generated around the small metal plate. Exciter coils Small metal plate J248 Diesel direct injection system control unit Electronics for evaluation S321_228 This location-dependent alternating field influences the receiver coils, inducing a relevant alternating signal there. The strength of the induced alternating voltage depends largely on the position of the small metal plate. Each position results in a different coverage of the small metal plate to the receiver coils. In the idle position, the coverage is at its lowest and, therefore, so is the induced alternating voltage. Electro-magnetic alternating field of small metal plate Receiver coils Electro-magnetic alternating field of exciter coil S321_230 In the full throttle, i.e. kick-down position on automatic gearboxes, coverage is at its greatest and, therefore, so is the alternating voltage. Small metal plate in idle position Small metal plate in full throttle position Kickdown area Accelerator pedal position travel Evaluation The electronics for evaluation set the alternating voltages of the three receiver coils at a common value, they amplify them and bring the output voltages of the three receiver coils together into the equation. Following voltage evaluation, the result is converted into a linear voltage signal and sent on to the engine control unit. Signal voltage in volts S321_232 Driver input percentage Full throttle stop Accelerator pedal end stop 40
41 Service The axle geometry Installed in the Golf is an adjustable rear axle, e.g. track and camber can be changed independently of each other. The track is adjusted via an eccentric bolt between lower link and subframe. S321_116 S321_120 The camber is adjusted via an eccentric bolt. This eccentric bolt joins the link to the subframe. To adjust the camber, special tools S321_118 shock absorber set T10001 and ring spanner T10179 are required. 41
42 Service Special tools Designation Tool Application T10179 Ring spanner For adjusting camber on rear axle in conjunction with shock absorber set T10001 S321_114 T10219 (1) Sleeve T10219 (2) Drift (1) (2) For renewing bonded rubber bush on wishbone of front axle S321_112 T10149 Support For adjusting unladen weight position of bonded rubber bushes on front and rear axle S321_194 T10238 (1) T10240 (2) (1) (2) Release tool for accelerator pedal module, LHD (1) and RHD (2) S321_200 42
43 Test yourself 1. What is so special about the four link rear axle? a) Oversteer is achieved by means of a predefined change in the wheel position during cornering. b) Separation of longitudinal and lateral connection. c) Cracks and grooves running across the road surface are absorbed easily. 2. Of which components is the electro-mechanical power steering comprised? a) Steering column, mechanical steering gear and hydraulic pump. b) Steering angle sender, steering column, steering force sender, control unit, electric motor and steering gear. c) Steering angle sender, steering column, steering force sender, yaw rate sender and swivel mounting. 3. What is the role of OHB-V? a) OHB-V measures the brake pressure applied by the driver via the brake pedal. b) The loss of braking assistance, as a result of insufficient vacuum pressure, is balanced out with an active and controlled build-up of brake pressure from the ESP hydraulics. c) Due to modifications to the interior of the brake servo, it makes high braking pressures available even at low pedal forces. Answers 1.) b, c; 2.) b; 3.) b 43
44 321 VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg, VK-36 Service Training All rights and the right to make technical alterations reserved Technical status 09/03 This paper was manufactured from pulp that was bleached without the use of chlorine.
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 299 The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D Design and Function The Touareg is an exclusive cross country vehicle with the driving properties and driving comfort of a sporty luxury
Service. Self-Study Programme 299 The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D Design and Function The Touareg is an exclusive cross country vehicle with the driving properties and driving comfort of a sporty luxury
Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive
 Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator
 Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
DRIVE-CONTROL COMPONENTS
 3-1 DRIVE-CONTROL COMPONENTS CONTENTS FRONT SUSPENSION................... 2 Lower Arms............................... 5 Strut Assemblies........................... 6 REAR SUSPENSION.....................
3-1 DRIVE-CONTROL COMPONENTS CONTENTS FRONT SUSPENSION................... 2 Lower Arms............................... 5 Strut Assemblies........................... 6 REAR SUSPENSION.....................
Performance concept: Chassis
 Chassis Performance concept: Chassis Total vehicle concept Chassis mechanics Mechatronic chassis systems Systematic attention to driving dynamic requirements in total vehicle concept Driver-oriented operating
Chassis Performance concept: Chassis Total vehicle concept Chassis mechanics Mechatronic chassis systems Systematic attention to driving dynamic requirements in total vehicle concept Driver-oriented operating
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Onboard power supply management
 Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
6-speed automatic transmission 09D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service Training. Audi Q7 - Running Gear. Self-Study Programme 362
 Service Training Audi Q7 - Running Gear Self-Study Programme 362 With the Q7 Audi offers a vehicle that marks a superlative new development in the sport utility vehicle (SUV) segment. The Audi Q7 ingeniously
Service Training Audi Q7 - Running Gear Self-Study Programme 362 With the Q7 Audi offers a vehicle that marks a superlative new development in the sport utility vehicle (SUV) segment. The Audi Q7 ingeniously
Rear Drive Axle and Differential
 Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
Page 1 of 13 Rear Drive Axle and Differential GENERAL Item Part Number Description A - Electronic rear differential B - Open rear differential 1 - Rear driveshaft 2 - Electronic rear differential 3 - RH
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
The Brake Assist System
 Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Suspension and Steering Objectives of the Module...2 Purpose of the System...3
 Table of Contents Subject Page Suspension and Steering Objectives of the Module.....................................2 Purpose of the System.......................................3 Front Axle System Components........................................
Table of Contents Subject Page Suspension and Steering Objectives of the Module.....................................2 Purpose of the System.......................................3 Front Axle System Components........................................
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Vibration damper control
 Vibration damper control The damper control system registers the condition of the road surface and the movements of the vehicle via four wheel acceleration sensors and three body acceleration sensors.
Vibration damper control The damper control system registers the condition of the road surface and the movements of the vehicle via four wheel acceleration sensors and three body acceleration sensors.
Engine Exhaust system. Engine
 Engine Engine 272 - Exhaust system The engine of the 6-cylinder version satisfies the US exhaust emissions limits. To meet these limits the monolith coating of the catalytic converters has been modified
Engine Engine 272 - Exhaust system The engine of the 6-cylinder version satisfies the US exhaust emissions limits. To meet these limits the monolith coating of the catalytic converters has been modified
Service Training Edition Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B. Trainer Information (GB)
 7.02 Edition 09.2000 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Trainer Information (GB) Contents Section Page General Information 2 Input and output signals 7 Control System Details 9 ATF Pressure Control 16 Lock-up
7.02 Edition 09.2000 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Trainer Information (GB) Contents Section Page General Information 2 Input and output signals 7 Control System Details 9 ATF Pressure Control 16 Lock-up
6-speed manual gearbox 02M
 Service. Self-Study Programme 205 6-speed manual gearbox 02M Design and Function Adapting modern automobiles to meet the rapidly growing demands on driving comfort, environmental compatibility and driving
Service. Self-Study Programme 205 6-speed manual gearbox 02M Design and Function Adapting modern automobiles to meet the rapidly growing demands on driving comfort, environmental compatibility and driving
Table of Contents. Introduction to DSC
 Table of Contents Subject Page Module Objectives...2 Overview of DSC Systems...3 Puspose of the System...4 DSC Components...9 Control Module/Hydraulic Unit... 10 Wheel Speed Sensors... 11 Hydraulic Pressure
Table of Contents Subject Page Module Objectives...2 Overview of DSC Systems...3 Puspose of the System...4 DSC Components...9 Control Module/Hydraulic Unit... 10 Wheel Speed Sensors... 11 Hydraulic Pressure
Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics
 Service. Self-Study Programme 273 Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics Design and Function Open sesame - thanks to a new system for entry and start authorisation, the Phaeton can be accessed without
Service. Self-Study Programme 273 Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics Design and Function Open sesame - thanks to a new system for entry and start authorisation, the Phaeton can be accessed without
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
6-speed Automatic Gearbox 09G/09K/09M
 Service Training Self-study Programme 309 6-speed Automatic Gearbox 09G/09K/09M The 6-speed automatic gearbox from the Japanese manufacturer AISIN is used in the following Volkswagen vehicles: Code Maximum
Service Training Self-study Programme 309 6-speed Automatic Gearbox 09G/09K/09M The 6-speed automatic gearbox from the Japanese manufacturer AISIN is used in the following Volkswagen vehicles: Code Maximum
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B
 Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
Mercedes Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I
 Mercedes 722.9 Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I Features Electronically Controlled Automatic Gearbox 7 Forward and 2 Reverse Gears Transmission Control Module is : Integrated into the
Mercedes 722.9 Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I Features Electronically Controlled Automatic Gearbox 7 Forward and 2 Reverse Gears Transmission Control Module is : Integrated into the
Service Training. Audi A5 - Networking. Self-Study Programme 395
 Service Training Audi A5 - Networking Self-Study Programme 395 Innovations in the electrical system and electronics on the Audi A5 The number of s in motor vehicles continues to increase, and the Audi
Service Training Audi A5 - Networking Self-Study Programme 395 Innovations in the electrical system and electronics on the Audi A5 The number of s in motor vehicles continues to increase, and the Audi
Service. Self-Study Programme No The New Beetle. Design and Function
 Service Self-Study Programme No. 211 The New Beetle Design and Function The New Beetle has caused a sensation and aroused instant enthusiasm throughout the world. The Concept 1 study in the mantle of the
Service Self-Study Programme No. 211 The New Beetle Design and Function The New Beetle has caused a sensation and aroused instant enthusiasm throughout the world. The Concept 1 study in the mantle of the
STEERING SYSTEM Introduction
 STEERING SYSTEM Introduction The steering makes it possible to change direction. The steering must be reliable and safe; there must not be too much play in the steering. It must be possible to steer accurately.
STEERING SYSTEM Introduction The steering makes it possible to change direction. The steering must be reliable and safe; there must not be too much play in the steering. It must be possible to steer accurately.
DRIVETRAIN 7.0 Introduction 7.1 Drivetrain configurations 7.2 Drivetrain elements 7.3 Clutch Operation
 DRIVETRAIN 7.0 Introduction Drivetrain is the assembly of all the components that are involved in the transmission of the power from the engine of the vehicle to its wheels. 7.1 Drivetrain configurations
DRIVETRAIN 7.0 Introduction Drivetrain is the assembly of all the components that are involved in the transmission of the power from the engine of the vehicle to its wheels. 7.1 Drivetrain configurations
A double-wishbone type suspension is used in the front. A multi-link type suspension is used in the rear. Tread* mm (in.) 1560 (61.
 CHASSIS SUSPENSION AND AXLE CH-69 SUSPENSION AND AXLE SUSPENSION 1. General A double-wishbone type suspension is used in the front. A multi-link type suspension is used in the rear. 08D0CH111Z Specifications
CHASSIS SUSPENSION AND AXLE CH-69 SUSPENSION AND AXLE SUSPENSION 1. General A double-wishbone type suspension is used in the front. A multi-link type suspension is used in the rear. 08D0CH111Z Specifications
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg
 Service Training Self-Study Programme 331 Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg Design and Function The running gear is a key component of the entire vehicle. It transmits all the forces acting between
Service Training Self-Study Programme 331 Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg Design and Function The running gear is a key component of the entire vehicle. It transmits all the forces acting between
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
The Audi S5 Cabriolet
 The Audi S5 Cabriolet Audi S5 Cabriolet Athletic dynamism The Audi S5 Cabriolet is a remarkable blend of progressive sports car technology and an authentic convertible experience. An athletic profile with
The Audi S5 Cabriolet Audi S5 Cabriolet Athletic dynamism The Audi S5 Cabriolet is a remarkable blend of progressive sports car technology and an authentic convertible experience. An athletic profile with
EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
 Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Chassis development at Porsche
 Chassis development at Porsche Determining factors Challenges automotive industry Challenges chassis development e-mobility product differentiation customization driving resistance vehicle mass resource
Chassis development at Porsche Determining factors Challenges automotive industry Challenges chassis development e-mobility product differentiation customization driving resistance vehicle mass resource
6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (040) 09/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
Three variants will be available in Australia, details on the Goldwing Tour are as follows:
 The 2018 Goldwing The next generation of Goldwing. The new Gold Wing series offers a completely revised package, promising to be more exciting and offer a more fulfilling, superb riding experience to riders
The 2018 Goldwing The next generation of Goldwing. The new Gold Wing series offers a completely revised package, promising to be more exciting and offer a more fulfilling, superb riding experience to riders
Product information on Audi Genuine Accessories
 Audi Genuine Accessories Product information on Audi Genuine Accessories Audi A5 Coupé 27.02.2008 Information subject to change Page 1 Contents page Sport and design...3 Front spoiler with blade...3 Rear
Audi Genuine Accessories Product information on Audi Genuine Accessories Audi A5 Coupé 27.02.2008 Information subject to change Page 1 Contents page Sport and design...3 Front spoiler with blade...3 Rear
FRONT GENERAL A X L E
 GENERAL General diagram of braking circuits 30 FRONT AXLE GENERAL Tightening torques (in dan.m) 30 FRONT AXLE GENERAL Tightening torques (in dan.m) 30 REAR AXLE GENERAL Tightening torques (in dan.m) 30
GENERAL General diagram of braking circuits 30 FRONT AXLE GENERAL Tightening torques (in dan.m) 30 FRONT AXLE GENERAL Tightening torques (in dan.m) 30 REAR AXLE GENERAL Tightening torques (in dan.m) 30
SUBJECT: Electronic Damping Control (EDC III)
 Group 37 37 01 90 (2107) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Integrated Suspension Systems Service Engineering --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Group 37 37 01 90 (2107) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Integrated Suspension Systems Service Engineering --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER TRAIN 2-1 CONTENTS AYC SYSTEM... 9 CLUTCH... 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS... 4 FRONT AXLE... 5 REAR AXLE... 6
 2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
. Control unit (N53) The roll-over bar control unit is located on the tunnel below the rear seat.
 A. Roll-over bar The roll-over bar (1) consists of high tensile strength tubular steel bent in a U-shape integrated into the head restraints (8) on both sides and recessed behind the rear seats. The roll-over
A. Roll-over bar The roll-over bar (1) consists of high tensile strength tubular steel bent in a U-shape integrated into the head restraints (8) on both sides and recessed behind the rear seats. The roll-over
Performance Benefits. 4.2-Liter V8 Engine. Just what you didn t expect from the Beetle company a really fearless SUV.
 Just what you didn t expect from the Beetle company a really fearless SUV. Car and Driver, September 2002 Performance Benefits 4.2-Liter V8 Engine The 4.2-liter V8 engine available in the Touareg is a
Just what you didn t expect from the Beetle company a really fearless SUV. Car and Driver, September 2002 Performance Benefits 4.2-Liter V8 Engine The 4.2-liter V8 engine available in the Touareg is a
Unit HV04K Knowledge of Heavy Vehicle Chassis Units and Components
 Assessment Requirements Unit HV04K Knowledge of Heavy Vehicle Chassis Units and Components Content: Chassis layouts i. types of chassis ii. axle configurations iii. rear steered axles iv. self-steered
Assessment Requirements Unit HV04K Knowledge of Heavy Vehicle Chassis Units and Components Content: Chassis layouts i. types of chassis ii. axle configurations iii. rear steered axles iv. self-steered
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Steering Column. Steering Column Component Layout.
 Page 1 of 9 Published : May 5, 2004 Steering Column Steering Column Component Layout Item Part Number Description 1 - Screw (3 off) 2 - Steering angle sensor 3 - Upper steering column assembly 4 - Cowl
Page 1 of 9 Published : May 5, 2004 Steering Column Steering Column Component Layout Item Part Number Description 1 - Screw (3 off) 2 - Steering angle sensor 3 - Upper steering column assembly 4 - Cowl
Sequential manual transmission (SMG) E60. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (044) 10/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 23 23 03 03 (044) Sequential manual transmission (SMG) E60 weltweit Datum/Date: 10/2003 Introduction The sequential manual transmission (SMG) has its origins in motor racing and
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 23 23 03 03 (044) Sequential manual transmission (SMG) E60 weltweit Datum/Date: 10/2003 Introduction The sequential manual transmission (SMG) has its origins in motor racing and
MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En
 02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The Transporter 2004 Electrical system
 Service. Self-study programme 311 The Transporter 2004 Electrical system Design and function The Transporter 2004 has an extensive network of electronic control units. Functions which were controlled in
Service. Self-study programme 311 The Transporter 2004 Electrical system Design and function The Transporter 2004 has an extensive network of electronic control units. Functions which were controlled in
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (5AT)
 (5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
(5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
Service Training. Audi Q7. Self-study programme 361
 Service Training Audi Q7 Self-study programme 361 The Audi Q7 In superior fashion, the Audi Q7 combines sportiness and versatility, advanced technology and premium-class luxury. On the road, it excels
Service Training Audi Q7 Self-study programme 361 The Audi Q7 In superior fashion, the Audi Q7 combines sportiness and versatility, advanced technology and premium-class luxury. On the road, it excels
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
The parking brake is an electrically actuated system that operates drum brakes integrated into the rear brake discs. The
 Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)
 23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function
 GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
4-cylinder, TSI petrol engine with 16 valves, turbocharger. Permanent all-wheel drive (4MOTION)
 Golf R 2.0 TSI Engine Engine type 4-cylinder, TSI petrol engine with 16 valves, turbocharger Capacity L / cc 2.0 / 1,984 Power PS / rpm 290 / 5,400 6,500 Torque Nm / rpm 380 / 1,850 5,300 Emission category
Golf R 2.0 TSI Engine Engine type 4-cylinder, TSI petrol engine with 16 valves, turbocharger Capacity L / cc 2.0 / 1,984 Power PS / rpm 290 / 5,400 6,500 Torque Nm / rpm 380 / 1,850 5,300 Emission category
New Škoda Superb 103TDI
 PRESS RELEASE - AUGUST 2011 PHOTOGRAPHIC PORTFOLIO Škoda Superb_Detail_001 Škoda Superb_Detail_002 Škoda Superb_Ext_001 Škoda Superb_Ext_002 Škoda Superb_Ext_003 Škoda Superb_Ext_004 Škoda Superb_Ext_005
PRESS RELEASE - AUGUST 2011 PHOTOGRAPHIC PORTFOLIO Škoda Superb_Detail_001 Škoda Superb_Detail_002 Škoda Superb_Ext_001 Škoda Superb_Ext_002 Škoda Superb_Ext_003 Škoda Superb_Ext_004 Škoda Superb_Ext_005
TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION CIRCUIT ACTYON
 311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
VOLKSWAGEN COMMERCIAL VEHICLES Specifications / March The Multivan
 VOLKSWAGEN COMMERCIAL VEHICLES Specifications / March 2010 The Multivan 01 Comfortline Highline FEATURES AND OPTIONS S = Standard O = Optional Extra Not Available Safety and Security Driver's and front
VOLKSWAGEN COMMERCIAL VEHICLES Specifications / March 2010 The Multivan 01 Comfortline Highline FEATURES AND OPTIONS S = Standard O = Optional Extra Not Available Safety and Security Driver's and front
Chassis Technology Workshop Cayenne
 Chassis Technology Workshop Cayenne Driving dynamic properties of all Porsche models Optimum driving dynamics and steering precision from high-performance chassis, steering and all-wheel drive systems
Chassis Technology Workshop Cayenne Driving dynamic properties of all Porsche models Optimum driving dynamics and steering precision from high-performance chassis, steering and all-wheel drive systems
Function description of roll-over bar
 91-800 Function description of roll-over bar Roll-over bar system, model 129 (version up to approx. 05/95) P91.50-0203-59 A1e29 Roll-over bar warning lamp (RB) S68/7 Front left seat belt buckle/seat belt
91-800 Function description of roll-over bar Roll-over bar system, model 129 (version up to approx. 05/95) P91.50-0203-59 A1e29 Roll-over bar warning lamp (RB) S68/7 Front left seat belt buckle/seat belt
A 1 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
 A1 A2 Clutch CLUTCH Specifications Pedal height (from asphalt sheet) Release point (from pedal stroke end position) Push rod play at pedal top Pedal freeplay Disc rivet head depth Disc runout Diaphragm
A1 A2 Clutch CLUTCH Specifications Pedal height (from asphalt sheet) Release point (from pedal stroke end position) Push rod play at pedal top Pedal freeplay Disc rivet head depth Disc runout Diaphragm
Volkswagen Golf > VW Rabbit GTI 2006-> (A5)
 Volkswagen Golf 5 2004-> VW Rabbit GTI 2006-> (A5) Allocation of PR. No. for brakes The brake system installed in a vehicle is documented on the vehicle data sticker via the relevant PR number. Example
Volkswagen Golf 5 2004-> VW Rabbit GTI 2006-> (A5) Allocation of PR. No. for brakes The brake system installed in a vehicle is documented on the vehicle data sticker via the relevant PR number. Example
Service. adaptive air suspension in the Audi A8. Home study program 292. For internal company use only
 292 Service adaptive air suspension in the Audi A8 Home study program 292 For internal company use only The development of the running gear is subject to conflicting objectives. For now, besides "classic"
292 Service adaptive air suspension in the Audi A8 Home study program 292 For internal company use only The development of the running gear is subject to conflicting objectives. For now, besides "classic"
SUBJECT: Automatic Stability Control with Traction Control System (ASC+T)
 Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Onboard Power Supply. Relay Carriers and Fuse Boxes. Locations. Relay carrier. Relay carrier on onboard power supply control unit
 Onboard Power Supply Relay Carriers and Fuse Boxes Locations The relay carrier and the onboard power supply control unit are under the left-hand side of the dash panel. Relay carrier The relays connected
Onboard Power Supply Relay Carriers and Fuse Boxes Locations The relay carrier and the onboard power supply control unit are under the left-hand side of the dash panel. Relay carrier The relays connected
PRODUCT INFORMATION. VZ Light Commercial Vehicles Ute, Crewman and One Tonner
 23 August 2004 PRODUCT INFORMATION VZ Light Commercial Vehicles Ute, Crewman and One Tonner Development Cost $11 million. Quality Validation 1.6 million durability and test kilometres (VZ sedans) 113,000
23 August 2004 PRODUCT INFORMATION VZ Light Commercial Vehicles Ute, Crewman and One Tonner Development Cost $11 million. Quality Validation 1.6 million durability and test kilometres (VZ sedans) 113,000
New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment
 New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment Introduction Dr. Ing. Ansgar Damm, Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Gödecke, Dr. Ing. Ralf Wörner, Dipl.-Ing. Gerhard
New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment Introduction Dr. Ing. Ansgar Damm, Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Gödecke, Dr. Ing. Ralf Wörner, Dipl.-Ing. Gerhard
Service Training. Audi A4 Cabriolet convertible top control. Self-Study Programme 314
 Service Training Audi A4 Cabriolet convertible top control Self-Study Programme 314 Introduction The perfectly shaped Audi Cabriolet continues to enjoy undiminished popularity. Innovative technology, sportiness,
Service Training Audi A4 Cabriolet convertible top control Self-Study Programme 314 Introduction The perfectly shaped Audi Cabriolet continues to enjoy undiminished popularity. Innovative technology, sportiness,
Cylinders/Valves 4/4 4/4 4/4 4/4 4/4 V6/4. Capacity (cc) 1,798 1,984 1,968 1,984 1,984 3,189
 The Technical Data Cylinders/Valves 4/4 4/4 4/4 4/4 4/4 V6/4 Capacity (cc) 1,798 1,984 1,968 1,984 1,984 3,189 Power (kw/rpm) 118 / 4,500-6,200 147 / 5,100-6,000 125 / 4200 147 / 5,100-6,000 147 / 5,100-6,000
The Technical Data Cylinders/Valves 4/4 4/4 4/4 4/4 4/4 V6/4 Capacity (cc) 1,798 1,984 1,968 1,984 1,984 3,189 Power (kw/rpm) 118 / 4,500-6,200 147 / 5,100-6,000 125 / 4200 147 / 5,100-6,000 147 / 5,100-6,000
Participant's Manual Vehicle Chassis, Suspension and Dynamic Driving Systems E87
 Participant's Manual Vehicle Chassis, Suspension and Dynamic Driving Systems E87 BMW Service Aftersales Training The information contained in this Participant's Manual is intended solely for the participants
Participant's Manual Vehicle Chassis, Suspension and Dynamic Driving Systems E87 BMW Service Aftersales Training The information contained in this Participant's Manual is intended solely for the participants
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Marine and Outdoor Power Equipment Technician Level 2
 Level 2 Unit: B2 Trade Mathematics II Level: Two Duration: 16 hours Theory: Practical: 16 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge and ability to apply
Level 2 Unit: B2 Trade Mathematics II Level: Two Duration: 16 hours Theory: Practical: 16 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge and ability to apply
Hexhead Torque Values
 Contents: 11: Engine 12: Engine Electrical 13: Fuel Preparation 16: Fuel Supply 17: Cooling 18: Exhaust 21: Clutch 23: Gearbox 31: Front Axle, Front Wheel Steering 32: Steering 33: Rear axle, rear-wheel
Contents: 11: Engine 12: Engine Electrical 13: Fuel Preparation 16: Fuel Supply 17: Cooling 18: Exhaust 21: Clutch 23: Gearbox 31: Front Axle, Front Wheel Steering 32: Steering 33: Rear axle, rear-wheel
Function Description Of Roll-over Bar
 Function Description Of Roll-over Bar General The U-shaped roll-over bar is mounted on two main bearings on the left and right center pillars. In the retracted state the roll-over bar is positioned in
Function Description Of Roll-over Bar General The U-shaped roll-over bar is mounted on two main bearings on the left and right center pillars. In the retracted state the roll-over bar is positioned in
11.AWD Transfer System
 W1860BE.book Page 54 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 11.AWD Transfer System A: MPT MODELS 1. GENERAL This all-wheel-drive (AWD) transfer system uses an electronically controlled multi-plate type transfer
W1860BE.book Page 54 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 11.AWD Transfer System A: MPT MODELS 1. GENERAL This all-wheel-drive (AWD) transfer system uses an electronically controlled multi-plate type transfer
Transmission Description
 Page 1 of 23 Published: Feb 1, 2007 Transmission Description COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Transmission selector lever assembly 2 Cable bracket 3 Automatic transmission 4 Transmission
Page 1 of 23 Published: Feb 1, 2007 Transmission Description COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Transmission selector lever assembly 2 Cable bracket 3 Automatic transmission 4 Transmission
Convenience CAN databus
 Convenience CAN databus The convenience CAN databus operates with a transmission rate of 100 kbit/s. Onboard power supply control unit J519 with databus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) CLIMAtronic
Convenience CAN databus The convenience CAN databus operates with a transmission rate of 100 kbit/s. Onboard power supply control unit J519 with databus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) CLIMAtronic
Service Training. Audi A6 05 Electrics. Self-Study Programme 326
 Service Training Audi A6 05 Electrics Self-Study Programme 326 The Audi A6 the most progressive vehicle takes the lead The new Audi A6 the most progressive vehicle takes the lead. The new Audi A6 consistently
Service Training Audi A6 05 Electrics Self-Study Programme 326 The Audi A6 the most progressive vehicle takes the lead The new Audi A6 the most progressive vehicle takes the lead. The new Audi A6 consistently
Torque steer effects resulting from tyre aligning torque Effect of kinematics and elastokinematics
 P refa c e Tyres of suspension and drive 1.1 General characteristics of wheel suspensions 1.2 Independent wheel suspensions- general 1.2.1 Requirements 1.2.2 Double wishbone suspensions 1.2.3 McPherson
P refa c e Tyres of suspension and drive 1.1 General characteristics of wheel suspensions 1.2 Independent wheel suspensions- general 1.2.1 Requirements 1.2.2 Double wishbone suspensions 1.2.3 McPherson
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Chapter B-3. Chapter 3. Actuators and output devices. Festo Didactic TP101
 155 Chapter 3 Actuators and output devices Festo Didactic TP101 156 An actuator is an output device for the conversion of supply energy into useful work. The output signal is controlled by the control
155 Chapter 3 Actuators and output devices Festo Didactic TP101 156 An actuator is an output device for the conversion of supply energy into useful work. The output signal is controlled by the control
