Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
|
|
|
- Veronica Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function
2 Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved measuring accuracy are constantly needed. Therefore a new generation of hot-film air-mass meters are now being used for engine management. Simply converting the exhaust gases after combustion is not enough to meet these laws and standards, instead they have to be kept as low as possible by means of efficient combustion. Furthermore modern engines deliver an increasing amount of power with the same or lower fuel consumption. In addition to other measures, the exact measurement of the intake air by the air-mass meter also helps meet all of these requirements. This self-study programme explains the basics of measuring intake air mass, familiarises you with the hot-film air-mass meter HFM 6 and helps you understand how it works. S358_019 NEW Warning Note The self-study programme shows the design and function of new developments. The contents will not be updated. For current testing, adjustment and repair instructions, refer to the relevant service literature. 2
3 Contents Basics of air-mass measurement Temperature and air pressure Effect of temperature and air pressure on the air mass Basics of combustion Air-fuel ratio Emissions guidelines Hot-film air-mass meter HFM Task Location Design Sensor element Design Bypass channel Measuring method Return flow detection Transfer of air-mass signal to the engine control unit Intake air temperature sensor Service Diagnosis Test Yourself
4 Basics of Air-mass Measurement Temperature and air pressure Many people immediately think about the medium around us when they hear the word air. That is air under normal atmospheric pressure and at comfortable temperatures. But as we know, the temperatures and also the air pressure change constantly. Temperatures and air pressure vary extremely across the world depending on the location. (Temperature and air pressure decrease as the altitude rises.) Influence of altitude on air temperature and pressure For example: Altitude: 1000 metres Air pressure: 898 hpa (0.898 bar) Temperature: 13.5 C Altitude: 500 metres Air pressure: 954 hpa (0.954 bar) Temperature: C Altitude: 100 metres Air pressure: 1001 hpa (1.001 bar) Temperature: C Altitude: 0 metres Air pressure: 1013 hpa (1.013 bar) Temperature: 20 C S358_002 4
5 Effect of temperature and air pressure on the air mass At the same volume, the air mass changes with the temperature and the air pressure. Low air pressure, high temperature A cylindrical container with an area of 1 m 2 and a height of 1m contains 1 m 3 air. The air pressure is low and the temperature of the air is high. The air density is low due to the low pressure and the high temperature. (There is a low air mass in the container.) The air mass in the container is low. S358_003 High air pressure, low temperature In the same-sized container, the air is at a high pressure and low temperature. The air density is considerably higher due to the high pressure and the low temperature. (There is a considerably higher air mass in the container.) The air mass in the container is considerably higher. S358_004 5
6 Basics of Combustion Air-fuel ratio Path of air Air filter before Exhaust gases after Catalytic converter Air-mass meter 14.7 kg air CO NO x HC CO 2 N H 2 O Fuel tank 1 kg fuel Catalytic converter Path of fuel S358_005 Combustion engines require 14.7 kg of air for the ideal combustion of 1 kg fuel. In engineering, this ratio of fuel to air is called the stoichiometric ratio. The engine control unit requires exact information on the intake air mass in all operating situations so it can set the correct ratio of fuel to air. Rich air-fuel ratio When there is a rich air-fuel ratio (Lambda < 1), the exhaust gas will contain too much carbon monoxide (CO) and too many unburned hydrocarbons (HC). For example: 1.2 kg fuel 14.7 kg air In stoichiometric operation, the air-fuel ratio has the Lambda value 1. It is only in stoichiometric operation that harmful substances can be almost completely removed from the exhaust gas by the catalytic converter. Lean air-fuel ratio When there is a lean air-fuel ratio (Lambda >1), the exhaust gas will contain too much nitrogen oxide (NO X ). For example: 0.8 kg fuel 14.7 kg air The exact measurement of the intake air mass thus contributes to the air-fuel ratio being kept in the Lambda 1 range and to reducing or preventing harmful substances in the exhaust gas. 6
7 Emissions guidelines The hot-film air-mass meter helps meet the increasingly stricter emissions guidelines in Europe and the United States thanks to its reduced measuring tolerances compared with the previous models. By measuring the exact air mass taken in, the mixture formation is optimised and the treatment of the exhaust gases by catalytic converters is enhanced. Development of emissions values using Europe as an example Petrol engines Standard Euro 1 Euro 2 Euro 3 Euro 4 Euro 5** Valid 1/7/92 1/1/96 1/1/00 1/1/05 1/9/09 from CO HC NOx NOx HC PM 5* 5* mg/km S358_010 * Vehicles with direct injection ** Values according to previous information See page 19 for explanation of chemical symbols Diesel engines Standard Euro 1 Euro 2 Euro 3 Euro 4 Euro 5** Valid 1/7/92 1/1/96 1/1/00 1/1/05 1/9/09 from CO HC / NOx 900* NOx PM /100* mg/km Legend S358_011 * Vehicles with direct injection ** Values according to previous information See page 19 for explanation of chemical symbols From 1992 also EEC stage 1 (European EconomicCommunity) From 1996 also EEC stage 2 (European EconomicCommunity) from 2000 from 2005 from
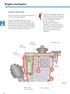
8 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Task The hot-film air-mass meter HFM 6 is used to measure the intake air mass. The engine control unit calculates the exact intake air mass from its signal. With petrol engines, the signals for calculating all load-dependent functions are used. The load-dependent functions are: - the ignition time, - the injection time, - the injection amount and - the activated charcoal filter system. With diesel engines, the signals are used to control: - the exhaust gas recirculation quantity and - the injection time. The following engines are already equipped with this: - 3.2l V6 FSI engine - 3.6l V6 FSI engine - 2.5l R5 TDI engine Location The hot-film air-mass meter is fitted between the air filter and the throttle valve in the engine air intake system. Air intake system Air-mass meter Air filter S358_016 8
9 Design The hot-film air-mass meter HFM 6 consists of: l l the measuring tube and the sensor electronics with sensor element. The air mass is measured in a partial flow (bypass). Thanks to its special design, the air-mass meter can measure the intake and recirculated air mass. Sensor electronics Partial flow Sensor element Protective screen Measuring tube Intake air S358_006 If dirt particles, engine oil vapour and humidity reach the sensor element, the measuring result will be incorrect. For this reason, particular attention was paid to ways of stopping these impurities reaching the sensor electronics when the measuring tube and the protective screen were designed. 9
10 Sensor Element Design The new air-mass meter uses a thermal measuring system like its predecessor. It is made up of the following main components: - the micromechanical sensor element with return flow detection and an intake air temperature sensor, - a sensor system that includes digital signal processing - and a digital interface. Compared with previous air-mass meters, the evaluation of the signal in the engine control unit is more precise and stable in the new generation thanks to the digital interface. Sensor electronics Digital interface Sensor element S358_001 Digital signal processing In contrast to the previous models, the air-mass meter HFM 6 transmits a digital signal to the engine control unit. Up to now the engine control unit received an analogue signal in which the signal became innacurate as the components aged due to the transfer resistance. 10
11 Bypass channel The bypass channel is flow-optimised compared with the previous model HFM 5. The partial flow required for air-mass measurement is drawn into the bypass channel behind the deflector lip. Sensor element Seal Sensor electronics S358_013 Sensor stability The bypass channel is separated completely from the sensor electronics by adhesives and seals for the sensor element. Furthermore the sensor element material has been reinforced. This modification increases the robustness of the sensor. Bypass channel Deflector lip S358_008 How it works: Outlet hole The design of the deflector lip causes a vacuum to form behind it. This vacuum causes the partial air flow required to measure the air mass to be drawn into the bypass channel. The slow dirt particles cannot follow this fast movement and are fed back to the intake air via the outlet hole. The dirt particles can therefore not falsify measurements and cannot damage the sensor element. Deflector lip S358_012 11
12 Sensor Element Measuring procedure The sensor element is next to the sensor electronics. The sensor element protrudes into the partial air flow to measure the air mass. The sensor element consists of: - a heating resistor, - two thermistors R1 and R2 and - an intake air temperature sensor. How it works: The sensor element is heated in the middle to 120 Celsius above the intake air temperature by the heating resistor. Functional example: Intake air temperature 30 C Heating resistor is heated to 120 C Measured temperature 120 C + 30 C = 150 C Due to the distance from the heating resistor, the temperature of the sensor element decreases towards the edge. Measuring example: Intake air temperature: 30 C Temperature at sensor element edge: 30 C Heating resistor: 150 C Temperature at R1 and R2 without intake air flow: 90 C Temperature at R1 with intake air flow: 50 C Temperature at R2 with intake air flow: stays at approx. 90 C Due to the temperature difference at R1 and R2, the electronic module recognises the intake air mass and the flow direction of the air. Heating resistor Intake air temperature sensor Sensor element Thermistor R2 Thermistor R1 Intake air Sensor element S358_007 12
13 Return flow detection When the inlet valves are closed, the intake air bounces off them and flows back to the air-mass meter. If this is not recognised as return flow, the measured result will be incorrect. How it works: The return flow air reaches the sensor element and first flows via thermistor R2, then via the heating resistor and via thermistor R1. For example: Intake air temperature: 30 C Heating resistor: 150 C Temperature at R2: 50 C Temperature at R1: 90 C Due to the temperature difference at R1 and R2, the electronic module recognises the air-mass return flow and the flow direction of the air. Heating resistor Thermistor R2 Return flow of hot air Thermistor R1 Sensor element S358_017 13
14 Sensor Element Transfer of air-mass signal to the engine control unit The air-mass meter transmits a digital signal for the measured air mass to the engine control unit in the form of a frequency. The engine control unit can recognise the measured air mass from the period length. Frequency signal Voltage Short period: Large air mass Advantage: The digital messages are less susceptible to interference than analogue wire connections. Long period: Small air mass Time S358_018 Signal use Petrol engine The intake air mass is required by the engine control unit for exact calculation of the load-dependent functions. Effects of signal failure Petrol engine and diesel engine If the air-mass meter fails, the engine control unit will use a substitute air-mass model that is stored in the engine control unit for this case. Diesel engine The measured values are required by the engine control unit to calculate the exhaust gas recirculation quantity and the injection quantity. 14
15 Intake air temperature sensor for sensor element The intake air temperature sensor is on the sensor element. It measures the current intake air temperature. Intake air temperature sensor Signal use The intake air temperature sensor is used to evaluate the temperature inside the air-mass meter. Notes: S358_009 The engine management system has its own separate sensor to recognise the intake air temperature. The 3.2l V6 FSI engine and the 3.6l V6 FSI engine use the intake air temperature sensor G42 to recognise the intake air temperature. The 2.5l R5 TDI engine uses the intake air temperature sensor G42 to recognise the intake air temperature. It is in one component together with the charge air pressure sensor G31. 15
16 Service Diagnosis Fault memory The function of the air-mass meter is monitored by a fault memory in the engine control unit J623. If a fault occurs during operation, an entry will be made in the fault memory. Guided Fault Finding Fault memory content 01 - Motronic injection and ignition system 1 Fault / notice recognised P Air-mass meter G70 Signal too low Ambient Conditions Sort Method Standard Kilometres Static/ sporadic Time Mode Go to Print S358_014 16
17 Test plan A system test plan is called up depending on the entry in the fault memory. The individual steps for diagnosis are described in this test plan. Guided Fault Finding Test plan Engine electronics - (16486) air-mass meter G70 Signal too low - G70 air-mass meter Mode Go to Print S358_015 The air-mass meter is maintenance-free. The necessary repair measures for faults are listed in the Guided Fault Finding. 17
18 Test Yourself 1. Which statement about air density is correct? a) A low air density corresponds with a low air mass. b) A high air density corresponds with a high air mass. c) A low air density corresponds with a high air mass. d) The air density and air mass are not related to each other. 2. Which statement is correct? A combustion engine requires the following for the optimum combustion of 1kg fuel: a) 1 kg air b) 7.4 kg air c) 14.7 kg air d) 17.4 kg air 3. Name the components. b) c) d) a) S358_006 18
19 4. Name the components. c) b) d) a) e) S358_ Which components does the air-mass meter use to detect a return flow of air? a) Thermistor R2 b) The heating resistor c) The intake air temperature sensor G42 d) Thermistor R1 Glossary Explanation of chemical abbreviations - CO carbon monoxide - HC hydrocarbons - NOx nitrogen oxide - PM particles Answers: 1 a, b; 2 c; 3 a: Sensor element, b: Partial air flow c: Measuring tube d: Intake air; 4 a: Thermistor R2, b: Sensor element, c: Thermistor R1, d: Heating resistor, e: Intake air temperature sensor; 5 a, d 19
20 358 VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights and rights to make technical alterations reserved Technical status Volkswagen AG Service Training VSQ-1 Brieffach Wolfsburg ` This paper was manufactured from pulp that was bleached without the use of chlorine.
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Lecture 14:Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions
 Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions
 Service. Self-Study Programme 230 Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions Composition, emission control, standards, etc. Basics The exhaust emissions of various engines, systems and vehicles are mentioned and
Service. Self-Study Programme 230 Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions Composition, emission control, standards, etc. Basics The exhaust emissions of various engines, systems and vehicles are mentioned and
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 3: Introduction to Pollutant Formation POLLUTANT FORMATION
 Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Module 5: Emission Control for SI Engines Lecture20:ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS
 ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS The Lecture Contains: Crankcase Emission Control (PCV System) Evaporative Emission Control Exhaust Gas Recirculation Water Injection file:///c /...%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture20/20_1.htm[6/15/2012
ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS The Lecture Contains: Crankcase Emission Control (PCV System) Evaporative Emission Control Exhaust Gas Recirculation Water Injection file:///c /...%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture20/20_1.htm[6/15/2012
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01
 Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Internal Combustion Engines
 Emissions & Air Pollution Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss emission control strategies: Fuel modifications Engine technology Exhaust gas aftertreatment We will become particularly familiar
Emissions & Air Pollution Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss emission control strategies: Fuel modifications Engine technology Exhaust gas aftertreatment We will become particularly familiar
Technical Support Note
 Title: Measuring Emissions from Diesel-Fueled Equipment TSN Number: 09 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\Technical_Support_Notes\ 09_Measuring_Emissions_from_Diesel_Fuel_Equipment.docx
Title: Measuring Emissions from Diesel-Fueled Equipment TSN Number: 09 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\Technical_Support_Notes\ 09_Measuring_Emissions_from_Diesel_Fuel_Equipment.docx
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 GENERAL Diesel engines are the primary power source of vehicles used in heavy duty applications. The heavy duty engine includes buses, large trucks, and off-highway construction
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 GENERAL Diesel engines are the primary power source of vehicles used in heavy duty applications. The heavy duty engine includes buses, large trucks, and off-highway construction
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
Chapter 4 ANALYTICAL WORK: COMBUSTION MODELING
 a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
ENGINE TECHNOLOGY. Bobcat Engine_B _ _EN_reworked.indd 1
 ENGINE TECHNOLOGY Bobcat Engine_B4459500_01-2015_EN_reworked.indd 1 1/30/2015 10:07:51 AM A COMPANY THAT S GROWING WITH SOCIETY Bobcat prides itself on innovations that shape the future. For decades, we
ENGINE TECHNOLOGY Bobcat Engine_B4459500_01-2015_EN_reworked.indd 1 1/30/2015 10:07:51 AM A COMPANY THAT S GROWING WITH SOCIETY Bobcat prides itself on innovations that shape the future. For decades, we
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
Testing of particulate emissions from positive ignition vehicles with direct fuel injection system. Technical Report
 Testing of particulate emissions from positive ignition vehicles with direct fuel injection system -09-26 by Felix Köhler Institut für Fahrzeugtechnik und Mobilität Antrieb/Emissionen PKW/Kraftrad On behalf
Testing of particulate emissions from positive ignition vehicles with direct fuel injection system -09-26 by Felix Köhler Institut für Fahrzeugtechnik und Mobilität Antrieb/Emissionen PKW/Kraftrad On behalf
Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive
 Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Fuel control. The fuel injection system tasks. Starting fuel pump (FP)
 1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
Exhaust Gas CO vs A/F Ratio
 Title: Tuning an LPG Engine using 2-gas and 4-gas analyzers CO for Air/Fuel Ratio, and HC for Combustion Efficiency- Comparison to Lambda & Combustion Efficiency Number: 18 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\18_CO
Title: Tuning an LPG Engine using 2-gas and 4-gas analyzers CO for Air/Fuel Ratio, and HC for Combustion Efficiency- Comparison to Lambda & Combustion Efficiency Number: 18 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\18_CO
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 9:Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd.
 Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd. The Lecture Contains: HC from Lubricating Oil Film Combustion Chamber Deposits HC Mixture Quality and In-Cylinder Liquid Fuel HC from Misfired Combustion
Mechanisms of HC Formation in SI Engines... contd. The Lecture Contains: HC from Lubricating Oil Film Combustion Chamber Deposits HC Mixture Quality and In-Cylinder Liquid Fuel HC from Misfired Combustion
Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB)
 Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB) 04-01-01 1 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials,
Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB) 04-01-01 1 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials,
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Full list of fault codes and events
 Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Evaporative Emissions
 Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table
 Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
How does Exhaust Gas Recirculation work?
 How does Exhaust Gas Recirculation work? Words: Dr. Johannes Kech Pictures: MTU Tags/Keywords Nitrogen oxide (NOX) emissions can be reduced using internal engine technology by cooling some of the exhaust
How does Exhaust Gas Recirculation work? Words: Dr. Johannes Kech Pictures: MTU Tags/Keywords Nitrogen oxide (NOX) emissions can be reduced using internal engine technology by cooling some of the exhaust
Emissions Theory and Diagnostics
 SECTION 1 Introduction 5-Gas Theory Emissions History OBD II SECTION 2 PCV System Function Failure Diagnosis Emissions Theory and Diagnostics SECTION 3 EGR EGR Theory Vacuum Systems Backpressure Systems
SECTION 1 Introduction 5-Gas Theory Emissions History OBD II SECTION 2 PCV System Function Failure Diagnosis Emissions Theory and Diagnostics SECTION 3 EGR EGR Theory Vacuum Systems Backpressure Systems
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
After Treatment System to meet BS-6 Emission Norms for Two Wheelers
 After Treatment System to meet BS-6 Emission Norms for Two Wheelers Dinesh K Gogia Air Purification-Automotive Page 1 BS-6 Norms for 2W Vehicle Class CO mg/k m THC mg/ km NOx mg/ km NMHC mg/ km All Classes
After Treatment System to meet BS-6 Emission Norms for Two Wheelers Dinesh K Gogia Air Purification-Automotive Page 1 BS-6 Norms for 2W Vehicle Class CO mg/k m THC mg/ km NOx mg/ km NMHC mg/ km All Classes
EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
 Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET
 Page 1 of 18 31592 WYNN S DPF Cleaner & Regenerator WYNN S Diesel Particulate Filter Cleaner & Regenerator Product Number: 31592 12 x 325ml New technologies to reduce emissions with diesel engines The
Page 1 of 18 31592 WYNN S DPF Cleaner & Regenerator WYNN S Diesel Particulate Filter Cleaner & Regenerator Product Number: 31592 12 x 325ml New technologies to reduce emissions with diesel engines The
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel
 Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry. Topic 8: Fuels and Earth science. Fuels. Notes.
 Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 8: Fuels and Earth science Fuels Notes 8.1 Recall that Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only 8.2 Describe crude oil as: A complex mixture of hydrocarbons
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 8: Fuels and Earth science Fuels Notes 8.1 Recall that Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only 8.2 Describe crude oil as: A complex mixture of hydrocarbons
Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry. 1 Introduction Preface Model-Building Simulation... 5 References...
 Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Catalytic Converter Testing
 Catalytic Converter Testing The first catalytic converter was created before the use of onboard computer systems its job was to oxidize HC and CO into CO2 and H2O. The term oxidizes means to add O2 to
Catalytic Converter Testing The first catalytic converter was created before the use of onboard computer systems its job was to oxidize HC and CO into CO2 and H2O. The term oxidizes means to add O2 to
Chapter 4 Part D: Exhaust and emission control systems
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Exhaust and emission control systems Contents Air inlet heating system components - removal and refitting...... 4 Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Exhaust and emission control systems Contents Air inlet heating system components - removal and refitting...... 4 Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Diesel Particulate Filter: Exhaust aftertreatment for the reduction of soot emissions
 Engine technology Diesel Particulate Filter: Exhaust aftertreatment for the reduction of soot emissions Authors: Guido Schäffner Design Exhaust Aftertreatment Klaus Rusch Design Exhaust Aftertreatment
Engine technology Diesel Particulate Filter: Exhaust aftertreatment for the reduction of soot emissions Authors: Guido Schäffner Design Exhaust Aftertreatment Klaus Rusch Design Exhaust Aftertreatment
1. CAUTIONS. 1) Standard pattern of soot accumulation Normal Soot Combustion. Abnormal Soot Accumulation
 241202 143 1. CAUTIONS 1) Standard pattern of soot accumulation Abnormal Soot Accumulation Normal Soot Combustion Cautions to protect the catalyst filter Use the designated fuel only. Observe the recommended
241202 143 1. CAUTIONS 1) Standard pattern of soot accumulation Abnormal Soot Accumulation Normal Soot Combustion Cautions to protect the catalyst filter Use the designated fuel only. Observe the recommended
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
This engine is certified to operate on regular 87 octane unleaded fuel (R+M)/2 Idle Speed (in gear): 650 RPM. Timing: Idle: 4-8 ATDC WOT:28 BTDC
 FUEL SYSTEMS 3 E Emission Control Information This engine conforms to 1998 Model Year U.S. EPA regulations for marine SI engines. Refer to Owners Manual for required maintenance. Exhaust Emission Control
FUEL SYSTEMS 3 E Emission Control Information This engine conforms to 1998 Model Year U.S. EPA regulations for marine SI engines. Refer to Owners Manual for required maintenance. Exhaust Emission Control
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems
 Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy : Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy : Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
REVIEW ON GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION
 International Journal of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering REVIEW ON GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION Jayant Kathuria B.Tech Automotive Design Engineering jkathuria97@gmail.com ABSTRACT Gasoline direct-injection
International Journal of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering REVIEW ON GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION Jayant Kathuria B.Tech Automotive Design Engineering jkathuria97@gmail.com ABSTRACT Gasoline direct-injection
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS EC1 EC2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) System Purpose System SYSTEM PURPOSE Abbreviation Purpose Positive crankcase ventilation Fuel evaporative
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS EC1 EC2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) System Purpose System SYSTEM PURPOSE Abbreviation Purpose Positive crankcase ventilation Fuel evaporative
ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS
 2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor
 9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1. Troubles 1. The signal line is short to ground (Abnormally low signal voltage : below 0.5 [volt]) Cause of trouble Counter action Engine state Signal
9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1. Troubles 1. The signal line is short to ground (Abnormally low signal voltage : below 0.5 [volt]) Cause of trouble Counter action Engine state Signal
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
EGR System, Design and Function. This information covers design and function of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system on a Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 254 59 1(6) EGR System Design and Function D16F EGR System, Design and Function W2005836 This information
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 254 59 1(6) EGR System Design and Function D16F EGR System, Design and Function W2005836 This information
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
VDA AdBlue Containers up to 5 Litres for Passenger Cars
 VDA Recommendation 267 dated May 2014 Page 1 of 7 VDA AdBlue Containers up to 5 Litres for Passenger Cars The following objective is associated with these VDA guidelines: Definition of standards for AdBlue
VDA Recommendation 267 dated May 2014 Page 1 of 7 VDA AdBlue Containers up to 5 Litres for Passenger Cars The following objective is associated with these VDA guidelines: Definition of standards for AdBlue
A REVIEW ON EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM IN IC ENGINES
 A REVIEW ON EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM IN IC ENGINES Jitender Singh 1, Vikas Bansal 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University College of Engineering, Rajasthan Technical University,
A REVIEW ON EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM IN IC ENGINES Jitender Singh 1, Vikas Bansal 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University College of Engineering, Rajasthan Technical University,
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
amperometric (currentbased) cell coupled with a potentiometric
 26 July 213 WIDE-RANGE AIR/FUEL SENSORS: FROM THE INSIDE OUT BY BERNIE THOMPSON The construction and operation of the six-wire, wide-range air/fuel ratio (WRAF) sensor are entirely different from a conventional
26 July 213 WIDE-RANGE AIR/FUEL SENSORS: FROM THE INSIDE OUT BY BERNIE THOMPSON The construction and operation of the six-wire, wide-range air/fuel ratio (WRAF) sensor are entirely different from a conventional
VS403 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION & CONTENTS. fig.1
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
THE INFLUENCE OF THE EGR RATE ON A HCCI ENGINE MODEL CALCULATED WITH THE SINGLE ZONE HCCI METHOD
 CONAT243 THE INFLUENCE OF THE EGR RATE ON A HCCI ENGINE MODEL CALCULATED WITH THE SINGLE ZONE HCCI METHOD KEYWORDS HCCI, EGR, heat release rate Radu Cosgarea *, Corneliu Cofaru, Mihai Aleonte Transilvania
CONAT243 THE INFLUENCE OF THE EGR RATE ON A HCCI ENGINE MODEL CALCULATED WITH THE SINGLE ZONE HCCI METHOD KEYWORDS HCCI, EGR, heat release rate Radu Cosgarea *, Corneliu Cofaru, Mihai Aleonte Transilvania
Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors
 Light Vehicle Diesel Engines First Edition Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors LEARNING OBJECTIVES (1 of 2) 20.1 Prepare for the Light Vehicle Diesel Engine (A9) ASE certification fuel system diagnosis and
Light Vehicle Diesel Engines First Edition Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors LEARNING OBJECTIVES (1 of 2) 20.1 Prepare for the Light Vehicle Diesel Engine (A9) ASE certification fuel system diagnosis and
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Chapter 4 Part C: Emissions control systems
 Chapter 4 Part C: Emissions control systems Contents Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........ 9 Crankcase emissions control system - testing and renewal....... 2 Exhaust emissions
Chapter 4 Part C: Emissions control systems Contents Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........ 9 Crankcase emissions control system - testing and renewal....... 2 Exhaust emissions
5 Further systems and diagnosis
 5.3 Ignition misfires (uneven running detection) Jerking or a reduced performance is the noticeable result of malfunctions in the engine running. These malfunctions are caused by errors in the ignition
5.3 Ignition misfires (uneven running detection) Jerking or a reduced performance is the noticeable result of malfunctions in the engine running. These malfunctions are caused by errors in the ignition
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF
 PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1036 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDES : KS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1036 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDES : KS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE
Strategy for calibration of On-board Diagnostics to meet future Indian Emission Regulations
 Speakers Information- Controls, Measurement & Calibration Congress Strategy for calibration of On-board Diagnostics to meet future Indian Emission Regulations Rohit Arora, Amit Kumar, Ajay Kumar Vashisth
Speakers Information- Controls, Measurement & Calibration Congress Strategy for calibration of On-board Diagnostics to meet future Indian Emission Regulations Rohit Arora, Amit Kumar, Ajay Kumar Vashisth
Checking lambda control Checking lambda probe and lambda control upstream of catalytic converter
 Стр. 1 из 9 Checking lambda control Checking lambda probe and lambda control upstream of catalytic converter Special tools and workshop equipment required V.A.G 1526 A V.A.G 1594 A V.A.G 1598/31 VAS 5051
Стр. 1 из 9 Checking lambda control Checking lambda probe and lambda control upstream of catalytic converter Special tools and workshop equipment required V.A.G 1526 A V.A.G 1594 A V.A.G 1598/31 VAS 5051
NZQA Expiring unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 5. Perform minor servicing tasks on a petrol fuel system
 Page 1 of 5 Title Perform minor servicing tasks on a petrol fuel system Level 2 Credits 2 Purpose This unit standard is for people who wish to enter or are employed in the automotive repair industry. People
Page 1 of 5 Title Perform minor servicing tasks on a petrol fuel system Level 2 Credits 2 Purpose This unit standard is for people who wish to enter or are employed in the automotive repair industry. People
Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors
 Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors 8183 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 6 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in
Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors 8183 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 6 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in
Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reduction Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reduction Design and Function In addition to the continuous improvement of internal combustion within the
Service Training Self-study Programme 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reduction Design and Function In addition to the continuous improvement of internal combustion within the
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Ignition control. The ignition system tasks. How is the ignition coil charge time and the ignition setting regulated?
 1 Ignition control The ignition system tasks To transform the system voltage (approximately 14 V) to a sufficiently high ignition voltage. In electronic systems this is normally above 30 kv (30 000 V).
1 Ignition control The ignition system tasks To transform the system voltage (approximately 14 V) to a sufficiently high ignition voltage. In electronic systems this is normally above 30 kv (30 000 V).
TG 150 G8V TX 86 (Dwg. No /xx)
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION ENGINE TYPE TG 150 G8V TX 86 1/7 Description: Engine type TG 150 G8V TX 86 (Dwg. No. 7000 850/xx) Fuel natural gas (according to TEDOM: 61 0 0282.1 regulation) Engine design stationary
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION ENGINE TYPE TG 150 G8V TX 86 1/7 Description: Engine type TG 150 G8V TX 86 (Dwg. No. 7000 850/xx) Fuel natural gas (according to TEDOM: 61 0 0282.1 regulation) Engine design stationary
EFFECT OF EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
 EFFECT OF EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 1 Ajinkya B. Amritkar, 2 Nilesh Badge 1ajinkyaamritkar333@gmail.com, 2 badgenilesh6@gmail.com 1,2B.E.Student, Department of Mechanical
EFFECT OF EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 1 Ajinkya B. Amritkar, 2 Nilesh Badge 1ajinkyaamritkar333@gmail.com, 2 badgenilesh6@gmail.com 1,2B.E.Student, Department of Mechanical
