The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
|
|
|
- Alison Knight
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function
2 The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l V6 TDI engine has been developed by Audi and is equipped with a piezo-controlled common rail fuel injection system. This unifies power and smoothness in a compact engine. The engine is combined with a diesel particulate filter and meets the EU 4 exhaust emission standard. S350_001 NEW Attention Note The self-study programme portrays the design and function of new developments! The contents will not be updated. For current testing, adjustment and repair instructions, please refer to the customer service literature intended for this purpose. 2
3 At a glance In brief Engine mechanical system Engine management system Service Test your knowledge
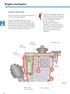
4 In brief The 3.0l V6 TDI engine The 3.0l V6 TDI engine is a new diesel engine developed from the Audi V engine family. This engine family's special characteristic is its extremely short and compact design, which is achieved by means of a chain drive. The engine additionally combines high output and ample torque with smooth running characteristics and low exhaust emissions. A piezo-controlled common rail fuel injection system ensures high injection pressure and a flexible injection process. The engine is installed in the Volkswagen Phaeton and Touareg. (View of the Phaeton engine) S350_003 Technical engine features: High-strength, compacted graphite iron cylinder block 4-valve technology Intake manifolds with swirl flaps Chain drive for valve control system, balancer shaft and oil pump Common rail fuel injection system Piezo-controlled injectors (piezo injectors) Diesel particulate filter 4
5 Technical data Engine code BMK (Phaeton) BKS (Touareg) Design type 6-cylinder V engine (90 V angle) Displacement 2967 cm 3 Bore Stroke 83 mm 91.4 mm Compression ratio 17 : 1 Valves per cylinder 4 Firing sequence Max. output 165 kw at 4000 rpm Max. torque 450 Nm at 1400 to 3250 rpm 500 Nm at 1750 to 2750 rpm Engine management system Fuel Exhaust gas cleaning Bosch EDC 16 C common rail fuel injection system Diesel, at least 51 CN Oxidising catalytic converter, exhaust gas recirculation, diesel particulate filter Exhaust emission standard EU 4 Torque and output graph Torque (Nm) Output (kw) In the Phaeton, the 3.0l V6 TDI engine achieves its maximum torque of 450 Nm as of an engine speed of 1600 rpm; this is available over a wide speed range, up to 3250 rpm. In the Touareg, the engine offers maximum torque of 500 Nm in the engine speed range from 1750 to 2750 rpm. Its maximum output of 165 kw is achieved at 4000 rpm in both vehicles. Phaeton Touareg Engine speed (rpm) S350_040 5
6 Engine mechanical system Cylinder block The cylinder block has a 90 V angle and is manufactured from compacted graphite iron (CGI-450). The cylinder liners are finished using the new UV photon honing process. This reduces friction and improves running-in behaviour. S350_006 Compacted graphite iron Cast iron with vermicular graphite is commonly named as such due to its worm-like graphite structure (worm-shaped = vermicular, Latin). In professional circles, this material is called compacted graphite iron (CGI). Compacted graphite iron is a high-strength material which enables a thin-walled, cast iron construction. This results in a weight saving of 5 10 % in comparison with a grey cast iron design. S350_002 Cast iron with vermicular graphite Cast iron with nodular graphite UV photon honing With UV photon honing The cylinder contact surface is honed in the conventional manner and is then processed using UV photon honing. During this process, a laser beam melts the surface of the cylinder contact surface, and nitrogen penetrates it. This smoothes and hardens the cylinder surface. S350_056 Without UV photon honing 6
7 Bearing frame A grey cast iron bearing frame is bolted into the crankcase. This contains the support for the crankshaft and additionally stiffens the cylinder block. S350_007 Crankshaft and balancer shaft The crankshaft, which is forged from tempered steel, is supported at four points in the bearing frame. Due to the 90 V angle, the crank pins are offset by 30. This is necessary to achieve an even firing interval. To ensure low-vibration engine operation, a balancer shaft is located in the V of the cylinder block to compensate the moments of inertia which occur. The balancer shaft is driven by the crankshaft via a chain. This rotates at engine speed counter to the direction in which the engine is running. S350_008 Pistons The aluminium pistons are designed without valve pockets. The swirl is influenced by the ports in the cylinder head and the position of the swirl flaps in the intake module, and ensures optimum mixture formation. To cool the piston ring zone, the pistons are equipped with an annular cooling duct, into which oil is sprayed via piston spray nozzles. S350_009 7
8 Engine mechanical system Cylinder head The 3.0l V6 TDI engine has two cylinder heads manufactured from aluminium alloy. Two intake and two exhaust valves per cylinder are arranged according to the principle of cross-flow. Injectors Bearing frame Each cylinder head is fitted with one camshaft for the intake valves and one camshaft for the exhaust valves. The intake and exhaust camshafts are linked via spur gear toothing with integrated backlash compansation. The bearing frame for the camshafts is bolted to the cylinder head. The valves are actuated via low-friction roller rocker fingers with hydraulic valve clearance compensation elements. Intake camshaft S350_010 For the structure and function of the hydraulic valve clearance compensation elements, refer to self-study programme No. 183 "The 2.5l V6 TDI 4V engine". Exhaust camshaft Hydraulic valve clearance compensation Injector The injectors are secured in the cylinder head with the aid of clamping pieces. They can be removed via small covers in the cylinder head cover. Clamping piece S350_ 027 8
9 4-valve technology Two intake and two exhaust valves per cylinder are arranged vertically in the cylinder head. The vertically positioned, centrally located injection valve is positioned directly over the central piston recess. This design leads to good mixture formation, resulting in low fuel consumption and low exhaust emissions. Intake camshaft Exhaust camshaft Injector Intake valves Exhaust valves Piston recess S350_044 The shape, size and layout of the intake and exhaust ports ensure good volumetric efficiency and a favourable gas cycle in the combustion chamber. Spiral port The intake ports are designed as spiral and tangential ports. Thanks to the tangential port, the inflowing air generates the desired, high degree of in-cylinder flow. Particularly at high speeds, the spiral port leads to good combustion chamber filling. Tangential port Exhaust port S350_015 9
10 Engine mechanical system Air intake system Intake manifolds with swirl flaps The intake manifolds of both cylinder banks are fitted with continuously variable swirl flaps. Due to the position of the swirl flaps, the intaken air's swirl is adjusted depending on the engine speed and load. Intake manifold top section Intake manifold bottom section Intake manifold flap motor V157, V275 Intaken air Swirl flaps S350_016 Intake manifold flap motor V157, V275 The swirl flaps are moved by the intake manifold flap motor via a push rod. To do this, the positioning motor is actuated by the engine control unit. An integrated sensor serves to feed back the current position of the swirl flaps. The intake manifold flap motors must only be renewed completely together with the intake manifold lower section. Please observe the notes in the workshop manual! Swirl flap Push rod S350_049 10
11 Function of the swirl flaps Swirl flap closed Low engine speeds The swirl flaps are closed when the engine is idling and at low engine speeds. This causes a high level of swirling, which leads to good mixture formation. The swirl flaps are open when the engine is started, in limp-home mode and at full throttle. S350_017 Swirl flap open High engine speeds As of an engine speed of approx rpm, the swirl flaps are open continuously. Good combustion chamber filling is achieved thanks to the increased air throughput. As of an engine speed of approx rpm, the swirl flaps are opened completely. S350_018 11
12 Engine mechanical system Backlash compensation The intake and exhaust camshafts are linked via spur gear toothing with integrated backlash compansation. In this case, the exhaust camshaft's spur gear is driven by the intake camshaft's spur gear. Backlash compensation ensures that the camshafts are driven with little noise. Left cylinder head Spur gears Intake camshaft Intermediate disk S350_012 S350_011 Retaining ring Diaphragm spring Camshaft Exhaust camshaft Fixed spur gear Structure The exhaust camshaft spur gear is split into two parts in the left-hand cylinder head. (The intake camshaft spur gear is split into two parts in the right-hand cylinder head.) Moveable spur gear The broader part of the spur gear (fixed spur gear) is positively connected to the camshaft. Three lugs are located on the front face. The narrower part of the spur gear (moveable spur gear) can be moved radially and axially. Recesses for the three lugs are located on its rear side. Lugs S350_019 12
13 How it works: Both spur gear parts are pushed axially together via the force exerted by a diaphragm spring. Whilst this occurs, they are simultaneously caused to rotate via the lugs. S350_020 Diaphragm spring Backlash compensation This rotational movement offsets the teeth of both spur gear parts and therefore leads to backlash compensation between the intake and exhaust camshafts' gear wheels. Tooth offset S350_021 13
14 Engine mechanical system Chain drive The camshafts, the balancer shaft and the oil pump are driven by the crankshaft via a chain drive. This is located on the engine's gearbox side. The chain drive makes the engine's compact design possible. Camshaft drive bank 2 drive B Camshaft drive bank 1 drive C Central chain drive drive A Intermediate gear Intermediate gear Balancer shaft drive S350_013 Oil pump drive Crankshaft Second chain drive drive D 14
15 The chain drive is comprised of: A central chain from the crankshaft to the intermediate gears (drive A), A chain from each of the intermediate gears to the intake camshafts (drives B and C), The camshaft chain sprockets have the same diameter as the crankshaft sprocket. The necessary camshaft: crankshaft ratio of 2 : 1 is achieved by means of the intermediate gears. The chains are tensioned by sprung, hydraulic chain tensioners; this system is maintenance-free. A chain from the crankshaft to the oil pump drive and to the balancershaft. Ancillary component drive The coolant pump, the power steering pump, the air conditioner compressor and the alternator are driven by the crankshaft via a poly V-belt. Coolant pump Power steering pump Alternator Poly V-belt Hydraulic tensioner S350_022 Air conditioner compressor 15
16 Engine mechanical system Lubrication system Overview of the system Oil filter module Vacuum pump Turbocharger Oil cooler Oil return S350_023 Oil spray nozzles (piston cooling) Pressure relief valve Oil pan Oil pump Oil pressure regulating valve Oil level and oil temperature sender G266 Oil without pressure Oil under pressure 16
17 Oil filter module The oil filter module contains an oil non-return valve and the short-circuit valve. The oil non-return valve prevents oil from flowing back into the oil pan from the oil filter housing when the engine is switched off. The short-circuit valve is a bypass valve, which opens when the oil filter or oil cooler is blocked and thereby ensures that the engine is supplied with oil. It opens at 2.5 bar. Oil pressure regulating valve Oil spray nozzles Oil is sprayed into the pistons' cooling ducts via the oil spray nozzles. This cools the pistons. Pressure relief valve This is a safety valve in the oil pump. It protects the lubrication system from excessive pressure on coldstarting. It opens at 11 bar. The oil pressure regulating valve is integrated into the oil pump and regulates the engine's oil pressure. 17
18 Engine mechanical system Oil pan The oil pan is comprised of two components; a cast aluminium upper oil pan section and a sheet steel lower oil pan section. The design of the oil pan differs in the Phaeton and the Touareg. This is the result of installation space conditions and off-road capability requirements. The oil pump's oil intake system has accordingly been adapted to the different design forms. Oil pan top section Phaeton oil pan Due to the limited installation space, the oil pan fitted in the Phaeton flattens and broadens at the bottom. Oil pan lower section S350_014 Oil pan top section Touareg oil pan The design of the oil pan fitted in the Touareg is narrow and deep. Due to the low oil intake point and, in comparison with the Phaeton, lower oil level, guaranteed oil intake with little oil foaming is achieved on gradients. S350_026 Oil pan lower section 18
19 Oil pump The oil pump is a crescent pump. It operates according to the duocentric principle and is driven by chain drive D via a stub shaft. The length of the intake fitting has been adapted to the different oil pan designs. Phaeton Touareg Intake fitting S350_024 Oil filter module The oil filter module is located in the V of the engine. The oil filter, the oil cooler and the cyclonic oil separator with pressure control valve for the crankcase breather system are integrated into the oil filter module. Oil filter Cyclonic oil separator with pressure control valve The oil cooler is connected to the engine's coolant circuit. S350_025 Oil cooler 19
20 Engine mechanical system Crankcase breather system In combustion engines, pressure differences between the combustion chamber and crankcase lead to air flows between the piston rings and cylinder contact surface; these are called blow-by gases. To prevent environmental pollution, these gases, which contain oil, are fed back to the intake area via the crankcase breather system. A cyclonic oil separator separates the oil contained in the gases from the air. This oil is returned to the oil pan via a port in the crankcase. Pressure control valve Cyclonic oil separator Functional principle Turbocharger S350_029 Charge air cooler Pressure control valve Blow-by gases Cyclonic oil separator S350_066 20
21 Function of the cyclonic oil separator The blow-by gases are fed to the cyclonic oil separator via a port inside the engine. To the intake port Pressure control valve Cyclonic oil separator The cyclonic oil separator causes the air to rotate. Due to the centrifugal force which occurs, the oil spray is spun onto the wall of the separator. Oil droplets form there, and these flow off into the oil pan via a port in the crankcase. The air, from which the oil spray has been removed, is fed back into the intake port via the pressure control valve. From the crankcase S350_030 Pressure control valve open Function of the pressure control valve The pressure control valve is located in the cover of the cyclonic oil separator. It is comprised of a membrane and a pressure spring, and regulates the pressure for venting the crankcase. To the intake port Diaphragms Compression spring When the blow-by gases are introduced, the pressure control valve limits the vacuum in the crankcase, as engine gaskets may become damaged if there is an excessive vacuum. If the vacuum in the intake port is high, the pressure control valve closes. In the case of a low vacuum in the intake port, it opens by means of the pressure spring's force. From the crankcase Pressure control valve closed S350_050 S350_034 21
22 Engine mechanical system Coolant circuit Overview of the system Engine coolant circuit Coolant circuit for fuel cooling (Touareg only) Hot Hot Cold Cold Cooler for engine coolant circuit Gearbox oil cooler Alternator Continued coolant circulation pump V51 (with towing attachment only) Air reservoir Heat exchanger Expansion tank Additional heater Choke Oil cooler Cooler for exhaust gas recirculation Exhaust gas recirculation flap Thermostat (opens as of a coolant temperature of 87 C) 22
23 Coolant circuit for fuel cooling (Touareg only) 5 6 In the Touareg, the 3.0l V6 TDI engine is equipped with a separate coolant circuit for the fuel cooler. This is necessary because the temperature of the coolant is too high, when the engine is at operating temperature, to cool the returning fuel. Water pump V36 (Touareg only) 21 The water pump V36 is an electric circulation pump. It is initialised as required by the engine control unit, and ensures that the coolant is circulated in the coolant circuit in order to cool the fuel. Continued coolant circulation pump V51 (vehicles with towing attachment only) 6 The continued coolant circulation pump V51 is an electrically driven pump. It is initialised according to a performance map by the engine control unit, and therefore ensures that the coolant is circulated for cooling purposes when the engine is "off". S350_ Coolant pump Coolant temperature sender G62 Radiator outlet coolant temperature sender G83 Water pump V36 Cooler for fuel cooling Fuel cooler Non-return valve Heating 23
24 Engine mechanical system Common rail fuel injection system The common rail fuel injection system is a highpressure accumulator fuel injection system for diesel engines. The term "common rail" means that all of one cylinder bank's injectors have a common, high-pressure fuel accumulator. In this system, pressure generation and fuel injection are separate. The high pressure required for injection is generated by a separate high-pressure pump. This fuel pressure is stored in a high-pressure accumulator (rail) and is made available to the injectors via short injector pipes. The main features of this fuel injection system are: The injection pressure can be selected almost infinitely within the performance map. The availability of high injection pressure enables optimal mixture formation. A flexible pilot, primary and secondary injection process is achieved. High-pressure accumulator (rail), cylinder bank 1 with injectors N30, N31, N32 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Distributor between the rails High-pressure accumulator (rail), cylinder bank 2 Fuel pressure sender G247 High-pressure pump S350_031 A detailed description of the common rail fuel injection system can be found in selfstudy programme No. 351 "The common rail fuel injection system". Piezo injectors N33, N83, N84 24
25 Injectors (piezo injectors) The 3.0l V6 TDI engine is fitted with piezo-controlled injectors. In comparison with solenoid valve-controlled injectors, piezo technology has approximately 75 % less moved mass at the injector needle. This weight reduction offers the following advantages: Very short switching times Several injections per working cycle are possible Precisely apportionable injection quantities The injection process, with a total of up to five partial injections per working cycle, has up to two pilot injections in the lower engine speed range and two secondary injections. This enables low emissions and smooth combustion. Piezo effect (Piezo [Greek] = pressure) The piezo-electric effect was discovered by Pierre Curie in If a crystalline lattice (turmaline, quartz) comprised of ions is deformed under pressure, electrical voltage is generated. The piezo-electric effect can also be reversed by applying an electric voltage. In this case, the crystal expands. This effect is used to control the injectors. Piezo actuator Connecting piston Valve piston Caution! The piezo-controlled injectors are actuated with a voltage of V. Observe the safety instructions in the workshop manual! Switching valve Injector needle S350_032 25
26 Engine mechanical system Fuel system Overview of the system The fuel system is sub-divided into three pressure ranges: Supply and return pressure Return pressure between the injectors and pressure retention valve High pressure In the fuel supply system, the fuel is delivered to the high-pressure pump from the fuel tank via the fuel filter by the pressurisation pump and the mechanical gear pump. The high fuel pressure required for injection is generated in the high-pressure pump and is fed into the high-pressure accumulator (rail). High-pressure pump Mechanical gear pump Fuel metering valve N290 Pressure retention valve Fuel temperature sender G81 High pressure bar Return pressure between injectors and pressure retention valve 10 bar Fuel filter Supply pressure Return pressure Pre-heater valve (expansion element) 26
27 From the high-pressure accumulator, the fuel is forwarded to the injectors, which inject it into the combustion chambers. The pressure retention valve maintains the injectors' return pressure of 10 bar. This pressure is required for the piezo injectors' function. Fuel pressure sender G247 High-pressure accumulator (rail), cylinder bank Choke High-pressure accumulator (rail), cylinder bank Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Piezo injectors 1 3 N30, N31, N32 In the Phaeton, the fuel is cooled by means of a fuel-air cooler on the vehicle floor. Fuel-coolant cooler (Touareg) Fuel tank Fuel system pressurisation pump G6 S350_033 27
28 Engine mechanical system Exhaust system The 3.0l V6 TDI engine's exhaust system is comprised of an electrically adjustable turbocharger, an oxidising catalytic converter located beneath the bonnet, a diesel particulate filter, two rear silencers and an exhaust gas recirculation system with switchable exhaust gas recirculation cooler. The Figure shows the exhaust system fitted in the Phaeton. Adjustable turbocharger Exhaust gas recirculation valve with exhaust gas recirculation cooler Oxidising catalytic converter Diesel particulate filter S350_047 Rear silencers 28
29 Turbocharger In the 3.0l V6 TDI engine, the charge pressure is generated by an adjustable turbocharger. This is equipped with adjustable guide vanes, which enable the flow of exhaust gas onto the turbine impeller to be influenced. The advantage of this is that optimal charge pressure and therefore good combustion are achieved throughout the entire engine speed range. In the lower engine speed range, the adjustable guide vanes offer high torque and good starting behaviour; in the upper engine speed range, they enable low fuel consumption and low emission values. The guide vanes are adjusted via an electric positioning motor. Electric initialisation makes fast turbocharger response behaviour and precise regulation possible. An exhaust gas temperature sender is located upstream of the turbocharger. The engine control unit uses the exhaust gas temperature sender's signal to protect the turbocharger from impermissibly high exhaust gas temperatures. In the event of excessive exhaust gas temperatures, e.g. during full-throttle operation, the engine output is reduced. Guide vane adjustment Positioning motor Guide vanes Turbocharger 1 control unit J724 Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 G235 S350_043 The principle of the adjustable turbocharger is explained in self-study programme No. 190 "Adjustable turbocharger". 29
30 Engine mechanical system Exhaust gas recirculation Thanks to exhaust gas recirculation, part of the exhaust gases are returned to the combustion process. The reduction in the fuel-air mixture's oxygen concentration which is achieved in this process slows combustion down. This leads to a reduction in the peak combustion temperature and therefore reduces nitrogen oxide emissions. The quantity of exhaust gas which is recirculated is controlled by the exhaust gas recirculation valve according to a performance map in the engine control unit. An exhaust gas recirculation cooler ensures that the combustion temperature is additionally lowered by cooling the recirculated exhaust gases, and that an increased quantity of exhaust gases can be recirculated. Exhaust gas recirculation valve Coolant connections Exhaust gas recirculation cooler Exhaust gas Bypass valve for exhaust gas recirculation cooler Charge air S350_065 Exhaust gas 30
31 Exhaust gas cooling switched off Up to a coolant temperature of 60 C, the bypass valve remains open and the exhaust gas is conducted past the cooler. As a result of this, the engine and catalytic converter reach their relevant operating temperature within a short time. Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Exhaust gas recirculation valve N18 Exhaust gas recirculation valve Cooler Vacuum unit Bypass valve S350_045 Exhaust gas cooling switched on As of a coolant temperature of 60 C, the bypass valve is closed by the change-over valve. Cooler The recirculated exhaust gas is thereby conducted to the exhaust gas recirculation valve via the cooler. Exhaust gas recirculation cooler change-over valve N345 Vacuum unit Bypass valve S350_046 In the following cases, the bypass valve is also switched when the engine is at operating temperature: The bypass valve is opened during idling to maintain the oxidising catalytic converter's operating temperature. During deceleration, the bypass valve is switched back and forth once to guarantee unimpeded valve movement. 31
32 Engine mechanical system Diesel particulate filter In the 3.0l V6 TDI engine, carbon particulate emissions are additionally reduced by means of a diesel particulate filter in addition to measures implemented inside the engine. This diesel particulate filter is located in the exhaust system downstream of the oxidising catalytic converter which is positioned under the bonnet. Oxidising catalytic converter Catalytically coated particulate filter S350_035 Overview of the system S350_ Control unit with display in dash panel insert J285 Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Air mass meter G70 Diesel engine Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 G235 Turbocharger Lambda probe G39 Oxidising catalytic converter Catalytic converter temperature sensor 1 G20 (Phaeton only) Bank 1 exhaust gas temperature sender 2 G448 Particulate filter Exhaust gas pressure sensor 1 G450 32
33 Structure The diesel particulate filter is comprised of a honeycombshaped ceramic body manufactured from silicon carbide, which is contained in a metal housing. The ceramic body is sub-divided into a multitude of small channels, which are sealed on alternating sides. This results in intake and exhaust channels which are separated by filter walls. The silicon carbide filter walls are porous and are coated with a substrate comprised of aluminium oxide and cerium oxide. The precious metal platinum, which serves as the catalyst, is vapour-deposited onto this substrate. The cerium oxide coating in the particulate filter lowers the carbon's ignition temperature and accelerates the thermal reaction with oxygen. Connections for exhaust gas pressure sensor 1 G450 Bank 1 exhaust gas temperature sender 2 G448 S350_062 Metal housing Ceramic body Function The exhaust gas, which contains carbon, flows through the intake channels' filter walls. Unlike the gaseous components of the exhaust gas, the carbon particles are retained in the intake channels. S350_036 33
34 Engine mechanical system Regeneration To prevent the particulate filter from becoming blocked with carbon particles, thereby impeding its function, it must be regularly regenerated. During the regeneration process, the carbon particles which have collected in the particulate filter are burned (oxidised). During regeneration of the catalytically coated particulate filter, a distinction is made between passive and active regeneration. This process is imperceptible to the driver. Passive regeneration During passive regeneration, the carbon particles are continuously combusted without engine management system intervention. This is primarily carried out at high engine loads, e.g. motorway driving, at exhaust gas temperatures of C. In this case, the carbon particles are converted to carbon dioxide via a reaction with nitrogen dioxide. Active regeneration In urban traffic, i.e. low engine load, the exhaust gas temperatures are too low for passive regeneration. As no further carbon particles can be degraded, the carbon accumulates in the filter. As soon as a specific level of carbon has been reached in the filter, active regeneration is introduced by the engine management system. This process takes approximately minutes. The carbon particles are combusted together with oxygen at an exhaust gas temperature of C to form carbon dioxide. 34
35 Active regeneration function The particulate filter's carbon level is calculated by two pre-programmed level models in the engine control unit. One carbon level model is determined from the user's driving style and the exhaust gas temperature sensor and lambda probe signals. The other carbon level model is the diesel particulate filter's flow resistance, which is calculated from the signals output by exhaust gas pressure sensor 1, bank 1 exhaust gas temperature sender 2 and the air mass meter. Air mass meter G70 Exhaust gas pressure sensor 1 G450 Bank 1 exhaust gas temperature sender 2 G448 Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Diesel particulate filter S350_037 As soon as the carbon level limit value has been reached in the particulate filter, active regeneration is introduced by the engine management system. The following measures lead to a specific, temporary increase in exhaust gas temperature to approximately C. In this temperature range, the carbon collected in the particulate filter oxidises to form carbon dioxide. The intake air supply is regulated via the electric throttle valve. S350_041 Exhaust gas recirculation is switched off to increase the combustion temperature and the oxygen content in the combustion chamber. S350_038 35
36 Engine mechanical system Shortly after "retarded" main injection, the first secondary injection is introduced to increase the combustion temperature. S350_039 Further secondary injection is introduced long after main injection. This fuel does not combust in the cylinder, but evaporates in the combustion chamber. The uncombusted hydrocarbons contained in this fuel vapour are oxidised in the oxidising catalytic converter. The heat which is generated during this process increases the exhaust gas temperature upstream of the particulate filter to approximately 620 C. The engine control unit uses the signals transmitted by the bank 1 exhaust gas temperature sender 2 (Touareg) or catalytic converter temperature sensor 1 (Phaeton) to calculate the injection quantity for retarded secondary injection. S350_069 The charge pressure is adapted to prevent the driver from noticing a perceptible change in torque during the regeneration process. S350_042 36
37 Diesel particulate filter warning lamp K231 In the event of extreme, short-distance operation, regeneration of the diesel particulate filter may be impeded, because the exhaust gas temperature fails to achieve the required temperature value. As regeneration is unable to take place, filter damage or blockage due to carbon overloading is possible. To avoid cases such as these, the diesel particulate filter warning lamp in the dash panel insert lights up if the carbon level has reached a certain limit value. S350_070 Via this signal, the driver is requested to drive at increased speed for a short period of time. The warning lamp must go out following this measure. If the diesel particulate filter warning lamp does not go out despite this measure, the glow period warning lamp lights up. The text "Engine malfunction - workshop" appears in the dash panel insert display. The driver is thereby requested to seek the next workshop. For detailed information on driving behaviour when the diesel particulate filter warning lamp lights up, please refer to the owner's manual. A detailed description of the diesel particulate filter system can be found in self-study programme No. 336 "The catalytically coated diesel particulate filter". 37
38 Engine management system Overview of the system Sensors Air mass meter G70 Engine speed sender G28 Hall sender G40 Coolant temperature sender G62 Radiator outlet coolant temperature sender G83 Fuel temperature sender G81 Fuel pressure sender G247 CAN data bus Accelerator position sender G79 Accelerator position sender 2 G185 Lambda probe G39 Brake light switch F Brake pedal switch F47 Clutch pedal switch F36 Diesel direct injection system control unit J248 Catalytic converter temperature sensor 1 G20 (Phaeton only) Exhaust gas temperature sender 1 G235 Diagnostic connection Bank 1 exhaust gas temperature sender 2 G448 Exhaust gas pressure sensor 1 G450 Intake air temperature sender G42 Charge air pressure sender G31 38
39 Actuators Intake manifold flap motor V157 Intake manifold flap 2 motor V275 Automatic glow period control unit J179 Injectors for cylinders 1 6 N30, N31, N32, N33, N83 and N84 Glow plugs 1 6 Q10, Q11, Q12, Q13, Q14 and Q15 Throttle valve module J338 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Exhaust gas recirculation valve N18 Exhaust gas recirculation cooler changeover valve N345 Radiator fan control unit J293 Radiator fan control unit 2 J671 Radiator fan V7 Radiator fan 2 V177 Left electrohydraulic engine mounting solenoid valve N144 (Phaeton only) Lambda probe heater Z19 Fuel pump relay J17 for fuel pumps G6 and G23 Turbocharger 1 control unit J724 Fuel metering valve N290 S350_048 39
40 Service Special tools Designation Tool Use T40049 Adapter For turning the crankshaft over. S350_059 T40055 Socket For loosening and tightening the union nut connection on high-pressure pipes in the common rail fuel injection system. S350_051 T40058 Adapter For turning the crankshaft over. S350_058 T40060 Adjustment pin For securing the camshafts when adjusting valve timing. S350_060 T40061 Adapter For correcting the position of the camshafts when adjusting the valve timing. S350_061 40
41 Designation Tool Use T40062 Adapter For tensioning the chain sprocket when adjusting valve timing. S350_057 T40094 Camshaft insert tool For installing the camshafts. S350_052 T40094/1 and T40094/2 Support For installing the camshafts. S350_055 T40095 Bracket For installing the camshafts. S350_054 T40096 Tensioner For installing the camshafts. S350_053 41
42 Test your knowledge Which are the correct answers? One, several or all answers may be correct. 1. What is the task of camshaft spur gear backlash compensation? a) Backlash compensation ensures that the camshafts are driven with little noise. b) Backlash compensation ensures that the intake camshaft is adjusted at high engine speeds. c) Backlash compensation ensures rigid engine speed compensation between the gears on the intake and exhaust camshaft. 2. What do the swirl flaps in the intake manifold do? a) The swirl flaps interrupt the supply of air in the intake port. Due to this, less air is intaken and compressed, as a result of which engine coasting is gentle. b) Due to the position of the swirl flaps, air movement in the intake swirl port is adapted to the engine speed. c) In certain engine operating states, the swirl flaps generate a difference between the intake manifold pressure and exhaust gas pressure. This guarantees effective exhaust gas recirculation. 3. In the timing chain drive, how is the necessary camshaft : crankshaft ratio of 2 : 1 achieved? a) Via hydraulic chain tensioners. b) Via intermediate gears. c) Via the length of the timing chains. 4. Which statement regarding the diesel particulate filter system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg is correct? a) An oxidising catalytic converter and a catalytically coated diesel particulate filter are combined in one component and located beneath the bonnet. b) A catalytically coated diesel particulate filter is located in the exhaust system below the vehicle floor. c) The 3.0l V6 TDI engine has a diesel particulate filter system which is supported by an additive. 42
43 Solutions: 1. a; 2. b; 3. b; 4. b 43
44 350 VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights and technical changes reserved Technical status Volkswagen AG Service Training VK-21 Brieffach 1995 D Wolfsburg This paper has been manufactured from cellulose bleached without the use of chlorine.
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training. Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System. Self-Study Programme 412
 Service Training Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System Self-Study Programme 412 In this booklet we explain to you the design and function of the 2.0 l 125 kw four-valve TDI engine, focussing
Service Training Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System Self-Study Programme 412 In this booklet we explain to you the design and function of the 2.0 l 125 kw four-valve TDI engine, focussing
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service Training. Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 365
 Service Training Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 365 In 1999, the 3.3 l A8 (1994) was installed for the first time with a V8 TDI engine, followed in the new A8
Service Training Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 365 In 1999, the 3.3 l A8 (1994) was installed for the first time with a V8 TDI engine, followed in the new A8
Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel
 Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 248. The W Engine Concept. Design and Function
 Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Exhaust After-Treatment System. This information covers design and function of the Exhaust After-Treatment System (EATS) on the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 1.2007 258 44 1(6) Exhaust After-Treatment System Design and Function D16F Exhaust After-Treatment System W2005772
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 1.2007 258 44 1(6) Exhaust After-Treatment System Design and Function D16F Exhaust After-Treatment System W2005772
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
1013. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment kw at 2100 rpm
 2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Workshop Manual. System Description & Operation
 Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
1012. The engine for construction equipment kw at min -1
 1012. The engine for construction equipment. 41-123 kw at 1500-2500 min -1... Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1012: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1012. The engine for construction equipment. 41-123 kw at 1500-2500 min -1... Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1012: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Product Information. N57 Engine.
 Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
16A. STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting REFITTING 16A-11 K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION
 STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting 16A K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION JR5 a Clip: -the gearbox control cable sleeve stops on the gearbox, - the control cables onto the gearbox.
STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting 16A K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION JR5 a Clip: -the gearbox control cable sleeve stops on the gearbox, - the control cables onto the gearbox.
Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT
 A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine
 Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED
 SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry. 1 Introduction Preface Model-Building Simulation... 5 References...
 Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Service Training. Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine. Self-Study Programme 377
 Service Training Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine Self-Study Programme 377 Special features of the current Audi vee engine family are the 90-degree included angle between the cylinder banks and the spacing
Service Training Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine Self-Study Programme 377 Special features of the current Audi vee engine family are the 90-degree included angle between the cylinder banks and the spacing
ENGINE GENERAL ENGINE GENERAL GENERAL OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. STRUCTURE...
 GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Training Service. Self-Study Programme 522. The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw. Design and function
 Training Service Self-Study Programme 522 The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw Design and function We would like, in this self-study program, introduced the 2.0 TSI engine the 162 kw / 169 kilowatts
Training Service Self-Study Programme 522 The 2.0 TSI engine from the 162/169 kw Design and function We would like, in this self-study program, introduced the 2.0 TSI engine the 162 kw / 169 kilowatts
GAS/PETROL THE ALTERNATIVE: ENGINES LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER AND MORE COMPACT ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY 22,0 6,6 431,1
 THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual
 Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual DOWNLOAD HERE "Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual Signature
Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual DOWNLOAD HERE "Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual Signature
Automotive Fuel and Emissions Control Systems 4/E
 Automotive Fuel and Emissions Control Systems 4/E Opening Your Class KEY ELEMENT Introduce Content Motivate Learners State the learning objectives for the chapter or course you are about to cover and explain
Automotive Fuel and Emissions Control Systems 4/E Opening Your Class KEY ELEMENT Introduce Content Motivate Learners State the learning objectives for the chapter or course you are about to cover and explain
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
6-speed automatic transmission 09D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2. Self-study programme 268. For internal use only
 268 Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2 Self-study programme 268 For internal use only Contents Engine, Mechanics Page Belt drive/ancillaries...................................................
268 Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2 Self-study programme 268 For internal use only Contents Engine, Mechanics Page Belt drive/ancillaries...................................................
Engine Exhaust system. Engine. AMG exhaust system. The AMG sports exhaust system ends in two chrome-plated twin tailpipes bearing the AMG logo.
 113 - Exhaust system AMG exhaust system The AMG sports exhaust system in the SLK 55 AMG satisfies the US emissions limits and is perfectly tuned in terms of function and sound to the AMG 5.5 l V8 engine.
113 - Exhaust system AMG exhaust system The AMG sports exhaust system in the SLK 55 AMG satisfies the US emissions limits and is perfectly tuned in terms of function and sound to the AMG 5.5 l V8 engine.
EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant. After-Threatment
 EURO4-5 Common Rail EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant After-Threatment 1 Exhaust gas recirculation EGR fundamentals: AFR: Air to Fuel Ratio. This parameter is used to define the ratio between fuel (petrol,
EURO4-5 Common Rail EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant After-Threatment 1 Exhaust gas recirculation EGR fundamentals: AFR: Air to Fuel Ratio. This parameter is used to define the ratio between fuel (petrol,
The Construction Equipment Engine kw hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 The Construction Equipment Engine 50 85 kw 67 114 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes ranging
The Construction Equipment Engine 50 85 kw 67 114 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes ranging
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
CHAPTER 2 : ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE VEHICLE AND ENGINE AND INFORMATION CONCERNING THE CONDUCT OF TESTS
 CHAPTER 2 : ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE VEHICLE AND ENGINE AND INFORMATION CONCERNING THE CONDUCT OF TESTS 1.0 Description of the Vehicle - 1.1 Trade name or mark of the vehicle - 1.2 Vehicle type
CHAPTER 2 : ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE VEHICLE AND ENGINE AND INFORMATION CONCERNING THE CONDUCT OF TESTS 1.0 Description of the Vehicle - 1.1 Trade name or mark of the vehicle - 1.2 Vehicle type
AfterSales Training. Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C
 AfterSales Training Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C Porsche AfterSales Training Student Name: Training Center Location: Instructor Name: Date: Important Notice: Some of the contents of this AfterSales
AfterSales Training Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C Porsche AfterSales Training Student Name: Training Center Location: Instructor Name: Date: Important Notice: Some of the contents of this AfterSales
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
Section 10 Chapter 7
 Section 10 Chapter 7 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Troubleshooting Symptoms Identification Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have
Section 10 Chapter 7 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Troubleshooting Symptoms Identification Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
Internal Combustion Engines
 Emissions & Air Pollution Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss emission control strategies: Fuel modifications Engine technology Exhaust gas aftertreatment We will become particularly familiar
Emissions & Air Pollution Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss emission control strategies: Fuel modifications Engine technology Exhaust gas aftertreatment We will become particularly familiar
CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual
 Instant Manual Download CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual Download Here CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 Service Workshop Repair Shop Manual PLEASE NOTE: YOU NEED TO BE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET
Instant Manual Download CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual Download Here CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 Service Workshop Repair Shop Manual PLEASE NOTE: YOU NEED TO BE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET
Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reduction Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reduction Design and Function In addition to the continuous improvement of internal combustion within the
Service Training Self-study Programme 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reduction Design and Function In addition to the continuous improvement of internal combustion within the
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
Engine for Industrial Applications kw hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 Engine for Industrial Applications 28-55.9 kw 38-75 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim 4 cylinder in-line engines turbocharged, with or without charge air cooler Water-cooled
Engine for Industrial Applications 28-55.9 kw 38-75 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim 4 cylinder in-line engines turbocharged, with or without charge air cooler Water-cooled
(3) (4) (6) (5) (10) (9) (8) (7)
 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies. Turbochargers
 Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
DIESEL ENGINE MECHANICAL
 SECTION 1B3 DIESEL ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
SECTION 1B3 DIESEL ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
Air Filter Element, Replacing and Cleaning Housing
 Air Filter Element, Replacing and Cleaning Housing Note Only use silicone-free lubricant for assembling the intake hoses. Secure all hose connections with hose clamps that match current standard production.
Air Filter Element, Replacing and Cleaning Housing Note Only use silicone-free lubricant for assembling the intake hoses. Secure all hose connections with hose clamps that match current standard production.
Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA
 Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Swirl Flaps. A = Non swirl not active. B = Swirl active
 Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65).
 DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment ,9 kw hp at rpm
 The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
DISASSEMBLED VIEWS. Disassembled Views. Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW or LFX)
 2012 Cadillac CTS Wagon AWD V6-3.0L Vehicle > Engine, Cooling and Exhaust > Engine > Locations > Components DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Disassembled Views Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW
2012 Cadillac CTS Wagon AWD V6-3.0L Vehicle > Engine, Cooling and Exhaust > Engine > Locations > Components DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Disassembled Views Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW
