EGG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE
|
|
|
- Mary Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EGG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE LABORATORY 8: DC MOTOR CONTROL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS GOAL: This section will introduce DC motors and motor drivers to control the speed and direction of DC motors. OBJECTIVES: Learn the basics of Arduino Programming o Commands: setup() loop() Funtions Interface with the TB6612FNG motor driver Operate a DC motor Control various aspects of DC motor operation OVERVIEW AND REQUIREMENTS: Brushed DC Motors A DC motor is an electric motor that runs on direct current (DC) electricity. DC motors can operate directly from rechargeable batteries, providing the motive power for the first electric vehicles. Today DC motors are still found in applications as small as toys and disk drives, or in large sizes to operate steel rolling mills and paper machines. The brushed DC electric motor generates torque directly from DC power supplied to the motor by using internal commutation, stationary magnets (permanent or electromagnets), and rotating electrical magnets. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 1
2 The inside of a DC Motor When the coil pictured above is powered, a magnetic field is generated around the armature. The left side of the armature is pushed away from the left magnet and drawn toward the right, causing rotation. The armature will then continue to rotate and when the armature becomes horizontally aligned, the commutator reverses the direction of current through the coil, reversing the magnetic field. This process then repeats, causing the motor rotation. Advantages of a brushed DC motor include low initial cost, high reliability, and simple control of motor speed. Disadvantages are high maintenance and low life-span for high intensity uses. Maintenance involves regularly replacing the brushes and springs which carry the electric current, as well as cleaning or replacing the commutator. These components are necessary for transferring electrical power from outside the motor to the spinning wire windings of the rotor inside the motor. The DC motor used for this lab is a 130-size DC motor and has a recommended operation voltage of 3 to 12V. Its approximate specifications at 6V are a free-run speed of 11,500 RPM, free-run current of 70 ma, and stall current of 800 ma. H Bridge An H bridge is an electronic circuit that enables a voltage to be applied across a load in either direction. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards and backwards. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 2
3 An H bridge is built with four switches. When the switches S1 and S4 (in the diagram pictured above) are closed, and S2 and S3 are open, a positive voltage will be applied across the motor. By opening S1 and S4 switches and closing S2 and S3 switches, this voltage is reversed, allowing reverse operation of the motor. The switches S1 and S2 should never be closed at the same time, as this would cause a short circuit on the input voltage source. The same applies to the switches S3 and S4. TB6612FNG Dual Motor Driver Carrier The TB6612FNG motor driver is a dual H Bridge based driver that can control up to two DC motors at a constant current of 1.2A (3.2A peak). Two input signals (IN1 and IN2) can be used to control the motor in one of four function modes - CW, CCW, short-brake, and stop. The two motor outputs (A and B) can be separately controlled, the speed of each motor is controlled via a PWM input signal with a frequency up to 100kHz. The STBY pin should be pulled high to take the motor out of standby mode. Logic supply voltage (VCC) can be in the range of VDC, while the motor supply (VM) is limited to a maximum voltage of 15VDC. The output current is rated up to 1.2A per channel (or up to 3.2A for a short, single pulse). COMPONENTS: Arduino Uno USB A-B Cable TB6612FNG Dual Motor Driver Carrier 6V DC Motor Breadboard Shield Jumper Wire Host PC Installed Arduino Uno drivers and IDE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 3
4 OPERATION: This is the layout for the breakout board of the TB6612FNG. Here is a short guide on how to connect the motor driver. The connection guide is given from the left side down, then the right side down. GND - Connect to the ground terminal on the Arduino board VCC - Connect to the 5V VCC on the Arduino board. AO1 - Connect to the negative lead of motor A. AO2 - Connect to the positive lead of motor A. BO2 - Connect to the positive lead of motor B. BO1 - Connect to the negative lead of motor B. VMOT - Connect to the positive side of the power source you are using to power the motors. GND - Connect to the negative side of the power source you are using to power the motors. PWMA - Connect to PWM pin on the Arduino. [Pins 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11] AIN2 - Connect to a digital pin on the Arduino. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 4
5 AIN1 - Connect to a digital pin on the Arduino. STBY - Connect to a digital pin on the Arduino. BIN1 - Connect to a digital pin on the Arduino. BIN2 - Connect to a digital pin on the Arduino. PWMB - Connect to a PWM pin on the Arduino. [Pins 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11] GND - Connect to the ground of the Arduino. For this exercise the following wiring was used for the Arduino: #define PWMA 3 #define AIN1 2 #define AIN2 1 #define BIN1 4 #define BIN2 5 #define PWMB 6 #define STBY 0 Assembling the circuit: 1. Attach the Breadboard Shield to the Arduino, making sure to properly align the pins. If you are using an R3 revision of the Arduino UNO, there will be 2 pins on each side that will have no corresponding pins on the shield. 2. Wire the circuit as shown in the wiring guide. Your final result should be something similar to the following snapshots. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 5
6 3. Attach the Arduino UNO to the host PC with the use of the USB cable. 4. Connect the VMOT pin and subsequent GND pin to the power source provided for the lab. This is typically a battery pack of 4x AA batteries in series, but if it is not provided then a laboratory power supply can be used to power the motors. Please refer to the power supply tutorial provided in the lab. 5. Use the power supply to provide 6 volts (4x AA = 1.5V x 4 = 6V) in this situation. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 6
7 6. Open the Arduino IDE and create a new sketch titled DCMotor. Verify that the correct COM port is in use. 7. Upload the following sketch to your Arduino UNO: #define PWMA 3 #define AIN1 2 #define AIN2 1 #define BIN1 4 #define BIN2 5 #define PWMB 6 #define STBY 0 #define motor_a 0 #define motor_b 1 #define FORWARD 1 #define REVERSE 0 #define RIGHT 1 #define LEFT 0 void setup() pinmode(pwma,output); pinmode(ain1,output); pinmode(ain2,output); pinmode(pwmb,output); pinmode(bin1,output); pinmode(bin2,output); pinmode(stby,output); motor_standby(false); move //Must set STBY pin to HIGH in order to void loop() motor_drive(forward, 255); delay(1000); motor_stop(); delay(1000); motor_drive(reverse, 255); delay(1000); motor_stop(); delay(1000); //Turns off the outputs of the Motor Driver when true void motor_standby(char standby) if (standby == true) digitalwrite(stby,low); else digitalwrite(stby,high); DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 7
8 //============================================= //FUNCTIONS //============================================= //Stops the motors from spinning and locks the wheels void motor_stop() digitalwrite(ain1,1); digitalwrite(ain2,1); digitalwrite(pwma,low); //Controls the direction the motors turn, speed from 0(off) to 255(full speed) void motor_drive(char direction, unsigned char speed) if (direction == FORWARD) motor_control(motor_a, FORWARD, speed); //Control motor B Forward here else motor_control(motor_a, REVERSE, speed); //Control motor B Reverse here void motor_control(char motor, char direction, unsigned char speed) if (motor == motor_a) if (direction == FORWARD) digitalwrite(ain1,high); digitalwrite(ain2,low); else digitalwrite(ain1,low); digitalwrite(ain2,high); analogwrite(pwma,speed); //Write Motor B code here. 8. Verify your results by checking to see that the motor rotates in one direction, then in reverse. When facing the motor, it should rotate counter clockwise, then clockwise. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 8
9 DEMO AND SCREENSHOTS: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 9
10 PRELAB: 1. What is an H Bridge and why is it used? 2. Why do we have to use an external power supply to power the motors? EXPERIMENTS: Experiment 1 1. Wire the circuit and motor as mentioned in Operation section 2. Verify the operation of the motor 3. Demonstrate the results to the TA Experiment 2 1. Extend the circuit: a. Modify the code so that the motor operates based on PWMB and rotates clockwise at the full speed, and then counter clockwise at half the speed. 2. Demonstrate the results to the TA Experiment 3 3. Extend the circuit: a. Modify the design so that the DC motors is connected to BO1 and BO2. b. Make motors to spin in different directions at the same time 4. Demonstrate the results to the TA POSTLAB REPORT DELIVERIES Include the following elements in your postlab report: 1. Theory of operation a. List 3 types of electrical motors, with few sentences of explanation how each one works b. Provide a circuit that allows to change the direction of DC motor operation without rewiring and changing the direction of source current. 2. Results of the experiments For each experiment, include: a. The code that you developed for the experiment. Each line that was added must be highlighted and commented with the explanation of what is its meaning. b. Brief explanation how the goal of the experiment was reached c. Screenshots of the serial monitor with the values, presenting the operation of your code 3. Answer the questions: a. What are some advantages and disadvantages of brushed DC motors? b. Why DC motor cannot be connected directly to the analog pin of the Arduino? c. This lab uses functions in order to interface with the driver and DC motors. Research and write a short explanation what are the functions in programming. 4. Conclusions DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 10
11 a. Write down your conclusions, things learned, problems encountered during the lab and how they were solved, etc. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 11
EGG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE
 EGG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE LABORATORY 11: AUTOMATED CAR PROJECT DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS GOAL: This section combines the motor
EGG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE LABORATORY 11: AUTOMATED CAR PROJECT DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS GOAL: This section combines the motor
8 Channel 5V Optical Isolated Relay Module
 Handson Technology Data Specification 8 Channel 5V Optical Isolated Relay Module This is a LOW Level 5V 8-channel relay interface board, and each channel needs a 15-20mA driver current. It can be used
Handson Technology Data Specification 8 Channel 5V Optical Isolated Relay Module This is a LOW Level 5V 8-channel relay interface board, and each channel needs a 15-20mA driver current. It can be used
TB6612FNG Hookup Guide
 Page 1 of 10 TB6612FNG Hookup Guide Introduction The TB6612FNG is an easy and affordable way to control motors. The TB6612FNG is capable of driving two motors at up to 1.2A of constant current. Inside
Page 1 of 10 TB6612FNG Hookup Guide Introduction The TB6612FNG is an easy and affordable way to control motors. The TB6612FNG is capable of driving two motors at up to 1.2A of constant current. Inside
The Fleming s Left Hand Rule shows what happens when electrons in a current enter a magnetic field.
 M4: Electrical Actuators M4.1 Fleming s Left Hand Rule The Fleming s Left Hand Rule shows what happens when electrons in a current enter a magnetic field. According to this rule if the index finger is
M4: Electrical Actuators M4.1 Fleming s Left Hand Rule The Fleming s Left Hand Rule shows what happens when electrons in a current enter a magnetic field. According to this rule if the index finger is
ENGR1202 Computer Engineering Assignment Robotics and Control Fall Assignment 2 Motor Control/Power Lab Exercise
 ENGR1202 Computer Engineering Assignment Robotics and Control Fall 2013 Assignment 2 Motor Control/Power Lab Exercise You will follow the Motor control/power lab exercise procedure below. Once you have
ENGR1202 Computer Engineering Assignment Robotics and Control Fall 2013 Assignment 2 Motor Control/Power Lab Exercise You will follow the Motor control/power lab exercise procedure below. Once you have
FireBeetle Covers-DC Motor & Stepper Driver SKU:DFR0508
 FireBeetle Covers-DC Motor & Stepper Driver SKU:DFR0508 Introduction DFRobot FireBeetle series are low power consumption microcontrollers designed for Internet of Things (IoT) development. FireBeetle Covers-DC
FireBeetle Covers-DC Motor & Stepper Driver SKU:DFR0508 Introduction DFRobot FireBeetle series are low power consumption microcontrollers designed for Internet of Things (IoT) development. FireBeetle Covers-DC
Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator
 Exercise 2 Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator EXERCIE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the construction of permanent magnet dc motors as well as
Exercise 2 Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator EXERCIE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the construction of permanent magnet dc motors as well as
The Easy Driver gives you the capability to drive bipolar stepper motors between 150mA to 700mA per phase.
 Introduction The Easy Driver gives you the capability to drive bipolar stepper motors between 150mA to 700mA per phase. Hardware Overview The Easy Driver is designed by Brian Schmalz, and is designed around
Introduction The Easy Driver gives you the capability to drive bipolar stepper motors between 150mA to 700mA per phase. Hardware Overview The Easy Driver is designed by Brian Schmalz, and is designed around
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
 Renewable Energy Permanent Magnet DC Motor Courseware Sample 86357-F0 A RENEWABLE ENERGY PERMANENT MAGNET DC MOTOR Courseware Sample by the staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2011 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights
Renewable Energy Permanent Magnet DC Motor Courseware Sample 86357-F0 A RENEWABLE ENERGY PERMANENT MAGNET DC MOTOR Courseware Sample by the staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2011 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights
PARTS LIST. Beams: 72x. 16x. 64x. 16x. 12x. 2x Breadboards CYB x TotemDuino 1x LabBoard 1x 30cm 34way Flat Cable 1x Power Supply 12v 1,5A
 Totem Mini Lab is a great platform to experiment, learn basics of electronics and Arduino coding. We have made an all-in-one breadboarding and testing unit, that gives you several useful features: Different
Totem Mini Lab is a great platform to experiment, learn basics of electronics and Arduino coding. We have made an all-in-one breadboarding and testing unit, that gives you several useful features: Different
Driver Board User Manual
 Personal Mechatronics Lab Driver Board User Manual 2012 by M.R. Emami Table of Contents General Notes... 3 1 Modular Arrangement of the Driver Board... 4 2 Powering the Board... 5 3 Computer Interface...
Personal Mechatronics Lab Driver Board User Manual 2012 by M.R. Emami Table of Contents General Notes... 3 1 Modular Arrangement of the Driver Board... 4 2 Powering the Board... 5 3 Computer Interface...
(for example A0) on the Arduino you can expect to read a value of 0 (0V) when in its upright position and 1023 (5V) when it is tilted.
 Tilt Sensor Module Tilt sensors are essential components in security alarm systems today. Standalone tilt sensors sense tilt angle or movement. Tilt sensors can be implemented using mercury and roller
Tilt Sensor Module Tilt sensors are essential components in security alarm systems today. Standalone tilt sensors sense tilt angle or movement. Tilt sensors can be implemented using mercury and roller
Lab 4.4 Arduino Microcontroller, Resistors, and Simple Circuits
 Lab 4.4 Arduino Microcontroller, Resistors, and Simple Circuits A microcontroller is a "brain" of a mechatronic system that interfaces sensors with a computer. Microcontrollers can perform math operations,
Lab 4.4 Arduino Microcontroller, Resistors, and Simple Circuits A microcontroller is a "brain" of a mechatronic system that interfaces sensors with a computer. Microcontrollers can perform math operations,
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
Product Manual L293D BREAKOUT Updated on 24 June 2017
 Product Manual L293D BREAKOUT Updated on 24 June 2017 Index Index 1 Introduction 2 Specification 2 Variants 2 Supported cables: 3 Details 3 How to interface? 4 Example Codes 8 Arduino 8 Contributors 10
Product Manual L293D BREAKOUT Updated on 24 June 2017 Index Index 1 Introduction 2 Specification 2 Variants 2 Supported cables: 3 Details 3 How to interface? 4 Example Codes 8 Arduino 8 Contributors 10
DC motor theory. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 DC motor theory This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
DC motor theory This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Lesson 1 - Make The Car Move Points of this section
 Lesson 1 - Make The Car Move Points of this section Learning part: Learn how to use Arduino IDE Make the car move by uploading program Preparations: One car (with a battery) One USB cable Ⅰ. Introduction
Lesson 1 - Make The Car Move Points of this section Learning part: Learn how to use Arduino IDE Make the car move by uploading program Preparations: One car (with a battery) One USB cable Ⅰ. Introduction
Kelly HPM High Power Full Bridge Permanent Magnet DC Motor Controller User s Manual
 Kelly HPM High Power Full Bridge Permanent Magnet DC Motor Controller User s Manual HPM72601 HPM72801 HPM12401 HPM12601 HPM12801 HPM14301 HPM14501 HPM14701 Rev.3.4 Dec. 2016 Contents Chapter1 Introduction...
Kelly HPM High Power Full Bridge Permanent Magnet DC Motor Controller User s Manual HPM72601 HPM72801 HPM12401 HPM12601 HPM12801 HPM14301 HPM14501 HPM14701 Rev.3.4 Dec. 2016 Contents Chapter1 Introduction...
Week 11. Module 5: EE100 Course Project Making your first robot
 Week 11 Module 5: EE100 Course Project Making your first robot Dr. Ing. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Office Hours: Room 9-245A Tuesday (1000-1100) Wednesday (1500-1600) Course Project: Wall-Follower Robot Week 1
Week 11 Module 5: EE100 Course Project Making your first robot Dr. Ing. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Office Hours: Room 9-245A Tuesday (1000-1100) Wednesday (1500-1600) Course Project: Wall-Follower Robot Week 1
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science
 Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science ENGR 1040 Mechanisms & Electric Circuits Prof. Nicholas Krouglicof Prof. Dennis Fifield Laboratory Exercise ML3: Assembly
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science ENGR 1040 Mechanisms & Electric Circuits Prof. Nicholas Krouglicof Prof. Dennis Fifield Laboratory Exercise ML3: Assembly
Please Handle Carefully!
 ELEC 3004/7312: Digital Linear Systems: Signals & Control! Prac/Lab 3 LeviLab: Part I: System Modelling May 11, 2015 (by C. Reiger & S. Singh) Pre-Lab This laboratory considers system modelling and control
ELEC 3004/7312: Digital Linear Systems: Signals & Control! Prac/Lab 3 LeviLab: Part I: System Modelling May 11, 2015 (by C. Reiger & S. Singh) Pre-Lab This laboratory considers system modelling and control
Load Cell Amplifier HX711 Breakout Hookup Guide
 Load Cell Amplifier HX711 Breakout Hookup Guide CONTRIBUTORS: SARAH AL-MUTLAQ, ALEX THE GIANT FAVORITE 0 Getting Started The HX711 load cell amplifier is used to get measurable data out from a load cell
Load Cell Amplifier HX711 Breakout Hookup Guide CONTRIBUTORS: SARAH AL-MUTLAQ, ALEX THE GIANT FAVORITE 0 Getting Started The HX711 load cell amplifier is used to get measurable data out from a load cell
Mens et Manus. Controlling a Brushless Motor
 Mens et Manus Controlling a Brushless Motor ovember 19, 2018 Parts: Layout and Fabrication Finish your design and fabrication of parts this week: a base plate that supports a motor shaft, 1+ electromagnets
Mens et Manus Controlling a Brushless Motor ovember 19, 2018 Parts: Layout and Fabrication Finish your design and fabrication of parts this week: a base plate that supports a motor shaft, 1+ electromagnets
Getting Started with the Digilent Electronics Explorer Board
 Getting Started with the Digilent Electronics Explorer Board This tutorial provides a very basic overview of the Digilent Electronics Explorer (EE) Board. 1. EE Board Physical Description A top view of
Getting Started with the Digilent Electronics Explorer Board This tutorial provides a very basic overview of the Digilent Electronics Explorer (EE) Board. 1. EE Board Physical Description A top view of
Lab 6: Wind Turbine Generators
 Lab 6: Wind Turbine Generators Name: Pre Lab Tip speed ratio: Tip speed ratio (TSR) is defined as: Ω, where Ω=angular velocity of wind, and R=radius of rotor (blade length). If the rotational speed of
Lab 6: Wind Turbine Generators Name: Pre Lab Tip speed ratio: Tip speed ratio (TSR) is defined as: Ω, where Ω=angular velocity of wind, and R=radius of rotor (blade length). If the rotational speed of
Full Bridge Permanent Magnet DC Motor Controller User's Manual
 www.igreatway.com Email:info@igreatway.com V 3.3 Full Bridge Permanent Magnet DC Motor Controller User's Manual PM24101 PM24201 PM24301 PM36101 PM36201 PM48101 PM48201 PM48301 PM48401B PM48501B PM72101
www.igreatway.com Email:info@igreatway.com V 3.3 Full Bridge Permanent Magnet DC Motor Controller User's Manual PM24101 PM24201 PM24301 PM36101 PM36201 PM48101 PM48201 PM48301 PM48401B PM48501B PM72101
A Practical Exercise Name: Section:
 Introduction to s Updated 7 AUG 06 A Practical Exercise Name: Section: I. Purpose.. Introduce the Hampden DC machine. Introduce the Hampden laboratory bench electrical power supplies 3. Introduce basic
Introduction to s Updated 7 AUG 06 A Practical Exercise Name: Section: I. Purpose.. Introduce the Hampden DC machine. Introduce the Hampden laboratory bench electrical power supplies 3. Introduce basic
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name:
 Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
MANTECH ELECTRONICS. Stepper Motors. Basics on Stepper Motors I. STEPPER MOTOR SYSTEMS OVERVIEW 2. STEPPING MOTORS
 MANTECH ELECTRONICS Stepper Motors Basics on Stepper Motors I. STEPPER MOTOR SYSTEMS OVERVIEW 2. STEPPING MOTORS TYPES OF STEPPING MOTORS 1. VARIABLE RELUCTANCE 2. PERMANENT MAGNET 3. HYBRID MOTOR WINDINGS
MANTECH ELECTRONICS Stepper Motors Basics on Stepper Motors I. STEPPER MOTOR SYSTEMS OVERVIEW 2. STEPPING MOTORS TYPES OF STEPPING MOTORS 1. VARIABLE RELUCTANCE 2. PERMANENT MAGNET 3. HYBRID MOTOR WINDINGS
Kelly HSR Series Motor Controller with Regen User s Manual V 3.3. Kelly HSR Opto-Isolated Series Motor Controller with Regen.
 Kelly HSR Opto-Isolated Series Motor Controller with Regen User s Manual HSR72601 HSR72801 HSR12401 HSR12601 HSR12901 HSR14301 HSR14501 HSR14701 Rev.3.3 Dec. 2011 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 2 1.1
Kelly HSR Opto-Isolated Series Motor Controller with Regen User s Manual HSR72601 HSR72801 HSR12401 HSR12601 HSR12901 HSR14301 HSR14501 HSR14701 Rev.3.3 Dec. 2011 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 2 1.1
1.0 Features and Description
 1.0 Features and Description The is an intelligent actuator designed for precise control of quarter turn valves and dampers. Using stepper motor technology, the SmartStep proportionally positions valves
1.0 Features and Description The is an intelligent actuator designed for precise control of quarter turn valves and dampers. Using stepper motor technology, the SmartStep proportionally positions valves
Kelly KDHA High Voltage Series/PM Motor Controller User s Manual
 Kelly KDHA High Voltage Series/PM Motor Controller User s Manual KDH07500A KDH07501A KDH07700A KDH07701A KDH09400A KDH09401A KDH09500A KDH09501A KDH12400A KDH12401A KDH12500A KDH12501A KDH14300A KDH14301A
Kelly KDHA High Voltage Series/PM Motor Controller User s Manual KDH07500A KDH07501A KDH07700A KDH07701A KDH09400A KDH09401A KDH09500A KDH09501A KDH12400A KDH12401A KDH12500A KDH12501A KDH14300A KDH14301A
Lab 1: DC Motors Tuesday, Feb 8 / Wednesday, Feb 9
 Introduction MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Do the pre-lab before you come
Introduction MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Do the pre-lab before you come
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 1020 HIGH EFFICIENCY USB POWER MANAGER + TRIPLE STEP-DOWN DC/DC LTC3555
 DESCRIPTION Demonstration Circuit 1020 is a High Efficiency USB Power Manager + Three Step-Down DC/DC Converters featuring the LTC 3555. The LTC 3555 is a highly integrated power management and battery
DESCRIPTION Demonstration Circuit 1020 is a High Efficiency USB Power Manager + Three Step-Down DC/DC Converters featuring the LTC 3555. The LTC 3555 is a highly integrated power management and battery
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes)
 Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism (~100 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally related. 2. Just as electric charge produced an electric field, electric current produces a
Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses. Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current
 Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current Section 1: Magnetism Standard 6: Demonstrate an understanding of the nature,
Chapter 8 Magnetism and Its Uses Section 1: Magnetism Section 2: Electricity and Magnetism Section 3: Producing Electric Current Section 1: Magnetism Standard 6: Demonstrate an understanding of the nature,
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1001 SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1001 SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES YEAR / SEM : IV / VII UNIT I SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1001 SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES YEAR / SEM : IV / VII UNIT I SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE
CENTROIDTM. AC Brushless Drive. Product Spec Sheet
 4 Axis, up to 2 KW motors Brake Output for each axis Overtemp and Overcurrent Protection All-software Configuration Self-cooled Fiber Optic Control CENTROIDTM AC Brushless Drive Product Spec Sheet AC Brushless
4 Axis, up to 2 KW motors Brake Output for each axis Overtemp and Overcurrent Protection All-software Configuration Self-cooled Fiber Optic Control CENTROIDTM AC Brushless Drive Product Spec Sheet AC Brushless
DR8010 tm. Hardware Reference Manual. Document Revision B4 May 15, 2018
 tm Hardware Reference Manual Document Revision B4 May 15, 2018 3380 Town Point Drive Suite 330 Kennesaw, GA 30144 Tel: (770) 422-7845 Fax: (770) 422-7854 www.microkinetics.com Table of Contents 1 The Driver
tm Hardware Reference Manual Document Revision B4 May 15, 2018 3380 Town Point Drive Suite 330 Kennesaw, GA 30144 Tel: (770) 422-7845 Fax: (770) 422-7854 www.microkinetics.com Table of Contents 1 The Driver
CS/ECE 5780/6780: Embedded System Design
 CS/ECE 5780/6780: Embedded System Design John Regehr Lecture 17: Relays and Motors Introduction to Relays A relay is a device that responds to a small current or voltage change by activating a switches
CS/ECE 5780/6780: Embedded System Design John Regehr Lecture 17: Relays and Motors Introduction to Relays A relay is a device that responds to a small current or voltage change by activating a switches
Armature Reaction and Saturation Effect
 Exercise 3-1 Armature Reaction and Saturation Effect EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate some of the effects of armature reaction and saturation in
Exercise 3-1 Armature Reaction and Saturation Effect EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate some of the effects of armature reaction and saturation in
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy
 Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism. If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0.
 SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism GALVAOMETERS If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0. otice how the current runs in the opposite directions on opposite
SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism GALVAOMETERS If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0. otice how the current runs in the opposite directions on opposite
Installation Instructions
 Quick-Mount Visual Instructions for Mechanical Installation Quick-Mount Visual Instructions 1. Rotate the damper to its failsafe position. If the shaft rotates counterclockwise, mount the CCW side of the
Quick-Mount Visual Instructions for Mechanical Installation Quick-Mount Visual Instructions 1. Rotate the damper to its failsafe position. If the shaft rotates counterclockwise, mount the CCW side of the
Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary
 Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary Term Definition Coil Solenoid Electric Motor Parts of an electric motor: Rotor commutator armature brushes Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law of Induction Generator
Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary Term Definition Coil Solenoid Electric Motor Parts of an electric motor: Rotor commutator armature brushes Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law of Induction Generator
Small Full Bridge Permanent Magnet Motor DC Controller User Manual
 Small Full Bridge Permanent Magnet Motor DC Controller User Manual SPM24051X SPM24101X SPM24121X SPM48051X SPM48101X SPM48121X SPM72051X SPM72101X SPM72121X SPM48151E SPM48181E SPM48221E SPM72151E SPM72181E
Small Full Bridge Permanent Magnet Motor DC Controller User Manual SPM24051X SPM24101X SPM24121X SPM48051X SPM48101X SPM48121X SPM72051X SPM72101X SPM72121X SPM48151E SPM48181E SPM48221E SPM72151E SPM72181E
Brushed. Brushed. Brushed Motor
 Kelly Kelly Kelly Kelly KD KD KD KD Series Series Series Series DC DC DC DC Motor Motor Motor Motor Controller Controller Controller Controller User User User User s Manual Manual Manual Manual V 2.5 2.5
Kelly Kelly Kelly Kelly KD KD KD KD Series Series Series Series DC DC DC DC Motor Motor Motor Motor Controller Controller Controller Controller User User User User s Manual Manual Manual Manual V 2.5 2.5
QUESTION BANK SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES
 SEVENTH SEMESTER EEE QUESTION BANK SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES TWO MARK QUESTIONS 1. What is a synchronous reluctance 2. What are the types of rotor in synchronous reluctance 3. Mention some applications
SEVENTH SEMESTER EEE QUESTION BANK SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES TWO MARK QUESTIONS 1. What is a synchronous reluctance 2. What are the types of rotor in synchronous reluctance 3. Mention some applications
Lab 9 AC & Stepper Motors
 Lab 9 - AC & Stepper Motors Lab 9-1 Format Lab 9 AC & Stepper Motors This lab will be conducted during your regularly scheduled lab time in a group format. There are three lab stations with a different
Lab 9 - AC & Stepper Motors Lab 9-1 Format Lab 9 AC & Stepper Motors This lab will be conducted during your regularly scheduled lab time in a group format. There are three lab stations with a different
IT 318 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CHAPTER 4
 IT 318 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CHAPTER 4 Electric Motors V. 2013 BARRY M. LUNT Brigham Young University Table of Contents Chapter 4: Electric Motors... 2 Overview... 2 4-1 Commutation... 2 4-2 Stepper Motors...
IT 318 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CHAPTER 4 Electric Motors V. 2013 BARRY M. LUNT Brigham Young University Table of Contents Chapter 4: Electric Motors... 2 Overview... 2 4-1 Commutation... 2 4-2 Stepper Motors...
MODEL MAS BAR TO BAR TESTER INSTRUCTIONS
 INDEX: Mainframe Controls 1 Armature Head (Model H12) Operating Instructions 1 Diagnostics and Self Test Procedure 3 Interpretation of Bar to Bar Readings 4 Induction Rotor Testing (theory of operation)
INDEX: Mainframe Controls 1 Armature Head (Model H12) Operating Instructions 1 Diagnostics and Self Test Procedure 3 Interpretation of Bar to Bar Readings 4 Induction Rotor Testing (theory of operation)
SERIES PR90H PROGRAMMABLE INCREMENTAL HOLLOW SHAFT ENCODER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS REFERENCE PR90H - C C - C. External diameter 58 mm
 PROGRAMMABLE INCREMENTAL HOLLOW SHAFT ENCODER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS Programmable incremental optical encoder from 1 to 65.536 pulses per rotation Programmable via USB, without an additional programming
PROGRAMMABLE INCREMENTAL HOLLOW SHAFT ENCODER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS Programmable incremental optical encoder from 1 to 65.536 pulses per rotation Programmable via USB, without an additional programming
Selected excerpts from the book: Lab Scopes: Introductory & Advanced. Steven McAfee
 Selected excerpts from the book: Lab Scopes: Introductory & Advanced Steven McAfee 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Excerpt from Chapter 1 Lab Scopes How do they work? (page 6) Excerpt from Chapter 3 Pattern Recognition
Selected excerpts from the book: Lab Scopes: Introductory & Advanced Steven McAfee 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Excerpt from Chapter 1 Lab Scopes How do they work? (page 6) Excerpt from Chapter 3 Pattern Recognition
Installation Instructions
 Quick-Mount Visual Instructions for Quick-Mount Visual Instructions 1. Rotate the damper to its failsafe position. If the shaft rotates counterclockwise, mount the CCW side of the actuator out. If it rotates
Quick-Mount Visual Instructions for Quick-Mount Visual Instructions 1. Rotate the damper to its failsafe position. If the shaft rotates counterclockwise, mount the CCW side of the actuator out. If it rotates
Instructor Guide. 215: Elevator: Mechanical Drive Systems Module 3: Gearless Drive Systems
 PR EV IE W O N LY Instructor Guide 215: Elevator: Mechanical Drive Systems Module 3: Gearless Drive Systems Table of Contents Overview.......4 Gearless Drive Operation...8 Geared Vs. Gearless. 22 Summary..29
PR EV IE W O N LY Instructor Guide 215: Elevator: Mechanical Drive Systems Module 3: Gearless Drive Systems Table of Contents Overview.......4 Gearless Drive Operation...8 Geared Vs. Gearless. 22 Summary..29
Attitude Control. Actuators and Attitude Control
 Attitude Control Actuators and Attitude Control Attitude Control Brushless motors Brushless controllers EMQ Framework Safety Instructions Control Theory Exercises & Hints Time scope: 2-4h Emqopter GmbH
Attitude Control Actuators and Attitude Control Attitude Control Brushless motors Brushless controllers EMQ Framework Safety Instructions Control Theory Exercises & Hints Time scope: 2-4h Emqopter GmbH
L, LTC, LTM, LT, Burst Mode, are registered trademarks of Linear Technology Corporation.
 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuits 1376A-A and 1376A-B are High Efficiency USB Power Manager + Triple Step Down DC/DC featuring the LTC3555-1 and LTC3555-3 respectively. The LTC 3555-1/LTC3555-3 are highly
DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuits 1376A-A and 1376A-B are High Efficiency USB Power Manager + Triple Step Down DC/DC featuring the LTC3555-1 and LTC3555-3 respectively. The LTC 3555-1/LTC3555-3 are highly
STR3. Step Motor Drive. User Manual
 STR3 Step Motor Drive User Manual Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Features... 3 1.3 Block Diagram... 4 1.4 Safety Instructions... 5 2 Getting Started... 6 2.1 Mounting Hardware... 6
STR3 Step Motor Drive User Manual Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Features... 3 1.3 Block Diagram... 4 1.4 Safety Instructions... 5 2 Getting Started... 6 2.1 Mounting Hardware... 6
Basic Electronics Course Part 1
 Basic Electronics Course Part 1 Simple Projects using basic components Following are instructions to complete several basic electronic projects Identify each component in your kit Image 1. [There are other
Basic Electronics Course Part 1 Simple Projects using basic components Following are instructions to complete several basic electronic projects Identify each component in your kit Image 1. [There are other
Session #18 Motors. R w+ - T, ω. Dan Frey. Figure by MIT OCW.
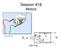 Session #18 Motors Figure by MIT OCW T, ω R w - E i V Dan Frey - Current versus Externally Applied Load I used a NiCd battery pack I discharged it across a (physically) big variable resistance i meas i
Session #18 Motors Figure by MIT OCW T, ω R w - E i V Dan Frey - Current versus Externally Applied Load I used a NiCd battery pack I discharged it across a (physically) big variable resistance i meas i
User s Manual. For DM860T. Fully Digital Stepper Drive. Version 1.0 Designed by StepperOnline All Rights Reserved
 User s Manual For DM860T Fully Digital Stepper Drive Version 1.0 Designed by StepperOnline 2017 All Rights Reserved Web site: www.omc-stepperonline.com E-Mail: sales@stepperonline.com Table of Contents
User s Manual For DM860T Fully Digital Stepper Drive Version 1.0 Designed by StepperOnline 2017 All Rights Reserved Web site: www.omc-stepperonline.com E-Mail: sales@stepperonline.com Table of Contents
Exercise 2: Series-Opposing DC Sources
 Exercise 2: Series-Opposing DC Sources EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to determine voltage by using series-opposing power connections. You will verify your results
Exercise 2: Series-Opposing DC Sources EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to determine voltage by using series-opposing power connections. You will verify your results
ECE 271 Microcomputer Architecture and Applications University of Maine. Lab 3: Stepper Motor Control Instructor: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Spring 2017
 ECE 271 Microcomputer rchitecture and pplications University of Maine Lab 3: Stepper Motor Control Instructor: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Spring 2017 Goals 1. Understand the limitation of GPIO output current 2.
ECE 271 Microcomputer rchitecture and pplications University of Maine Lab 3: Stepper Motor Control Instructor: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Spring 2017 Goals 1. Understand the limitation of GPIO output current 2.
User's Manual O
 11/3/99 3535.ai User's Manual 3535 3535 O Step Motor Drivers Copyright 1998 Applied Motion Products, Inc. 404 Westridge Drive Watsonville, CA 95076 Tel (831) 761-6555 (800) 525-1609 Fax (831) 761-6544
11/3/99 3535.ai User's Manual 3535 3535 O Step Motor Drivers Copyright 1998 Applied Motion Products, Inc. 404 Westridge Drive Watsonville, CA 95076 Tel (831) 761-6555 (800) 525-1609 Fax (831) 761-6544
About the moto:bit Board
 About the moto:bit Board The moto:bit is a carrier board for the micro:bit. Similar to an Arudino shield, it is designed to add functionality to the micro:bit without the hassle of a number of other boards,
About the moto:bit Board The moto:bit is a carrier board for the micro:bit. Similar to an Arudino shield, it is designed to add functionality to the micro:bit without the hassle of a number of other boards,
Hello and welcome to training on general purpose motor drivers in the 3 to 15 volt range. I m Paul Dieffenderfer & I will be your host for this
 Hello and welcome to training on general purpose motor drivers in the 3 to 15 volt range. I m Paul Dieffenderfer & I will be your host for this presentation prepared by H. Tanaka of the LSI Division. 1
Hello and welcome to training on general purpose motor drivers in the 3 to 15 volt range. I m Paul Dieffenderfer & I will be your host for this presentation prepared by H. Tanaka of the LSI Division. 1
The Starter motor. Student booklet
 The Starter motor Student booklet The Starter motor - INDEX - 2006-04-07-13:20 The Starter motor The starter motor is an electrical motor and the electric motor is all about magnets and magnetism: A motor
The Starter motor Student booklet The Starter motor - INDEX - 2006-04-07-13:20 The Starter motor The starter motor is an electrical motor and the electric motor is all about magnets and magnetism: A motor
GE Sensing & Inspection Technologies
 GE Sensing & Inspection Technologies Modus Model RPM-1 Room Pressure Monitor Installation and Setup Guide 1. GENERAL The RPM-1 monitors either positive or negative room pressures (see the Datasheet for
GE Sensing & Inspection Technologies Modus Model RPM-1 Room Pressure Monitor Installation and Setup Guide 1. GENERAL The RPM-1 monitors either positive or negative room pressures (see the Datasheet for
Filtered PWM Speed Control for Permanent Magnet DC Motors
 Instructions for Installation and Operation Filtered PWM Speed Control for Permanent Magnet DC Motors Model 0794 Speed and Direction Control up to 5/8 HP NEMA-1/IP-20 Specifications Product Type:... WPM-2148E1
Instructions for Installation and Operation Filtered PWM Speed Control for Permanent Magnet DC Motors Model 0794 Speed and Direction Control up to 5/8 HP NEMA-1/IP-20 Specifications Product Type:... WPM-2148E1
Exercise 3-3. Basic Operations of GTO Thyristors EXERCISE OBJECTIVES
 Exercise 3-3 Basic Operations of GTO Thyristors EXERCISE OBJECTIVES At the completion of this exercise, you will be able to switch on and off the power GTO thyristor using the 0 to 10 V positive power
Exercise 3-3 Basic Operations of GTO Thyristors EXERCISE OBJECTIVES At the completion of this exercise, you will be able to switch on and off the power GTO thyristor using the 0 to 10 V positive power
Series and Parallel Networks
 Series and Parallel Networks Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 17, 2014 1 Introduction In this experiment you will examine the brightness of light bulbs
Series and Parallel Networks Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 17, 2014 1 Introduction In this experiment you will examine the brightness of light bulbs
715B CONTROL SERIES. Instruction Manual Line Voltage DC Brushless Motor Control CONTROLS. Phone (317) Fax (317)
 715B CONTROL SERIES CONTROLS Instruction Manual Line Voltage DC Brushless Motor Control LT715B (IM-715B-0100) P.O. Box 10 5000 W. 106th Street Zionsville, Indiana 46077 Phone (317) 873-5211 Fax (317) 873-1105
715B CONTROL SERIES CONTROLS Instruction Manual Line Voltage DC Brushless Motor Control LT715B (IM-715B-0100) P.O. Box 10 5000 W. 106th Street Zionsville, Indiana 46077 Phone (317) 873-5211 Fax (317) 873-1105
Historical Development
 TOPIC 3 DC MACHINES DC Machines 2 Historical Development Direct current (DC) motor is one of the first machines devised to convert electrical power into mechanical power. Its origin can be traced to the
TOPIC 3 DC MACHINES DC Machines 2 Historical Development Direct current (DC) motor is one of the first machines devised to convert electrical power into mechanical power. Its origin can be traced to the
Exercise 2-1. The Separately-Excited DC Motor N S EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Simplified equivalent circuit of a dc motor
 Exercise 2-1 The Separately-Excited DC Motor EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate the main operating characteristics of a separately-excited dc motor
Exercise 2-1 The Separately-Excited DC Motor EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate the main operating characteristics of a separately-excited dc motor
Weatherproof Tubular Slip Ring Assembly
 Weatherproof Tubular Slip Ring Assembly Model B8-4.3W 8 circuit weatherproof slip ring Compact design Mounts on shafts up to 4.3 [109.2 mm] in diameter Permanently lubricated bearings Rugged stainless
Weatherproof Tubular Slip Ring Assembly Model B8-4.3W 8 circuit weatherproof slip ring Compact design Mounts on shafts up to 4.3 [109.2 mm] in diameter Permanently lubricated bearings Rugged stainless
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 M68HC08 Microcontrollers 8-Bit Software Development Kit for Motor Control Targeting the MC68HC908MR32 SDKMR32UG/D Rev. 1, 11/2002 MOTOROLA.COM/SEMICONDUCTORS 8-Bit Software Development Kit for Motor Control
M68HC08 Microcontrollers 8-Bit Software Development Kit for Motor Control Targeting the MC68HC908MR32 SDKMR32UG/D Rev. 1, 11/2002 MOTOROLA.COM/SEMICONDUCTORS 8-Bit Software Development Kit for Motor Control
Note 8. Electric Actuators
 Note 8 Electric Actuators Department of Mechanical Engineering, University Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drive, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada 1 1. Introduction In a typical closed-loop, or feedback, control
Note 8 Electric Actuators Department of Mechanical Engineering, University Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drive, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada 1 1. Introduction In a typical closed-loop, or feedback, control
Fall 1997 EE361: MIDTERM EXAM 2. This exam is open book and closed notes. Be sure to show all work clearly.
 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Fall 1997 EE361: MIDTERM EXAM 2 This exam is open book and closed notes. Be sure to show all work clearly. 1. 10 points - Mechanical and Electrical Energy Relationships: A dc motor
NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Fall 1997 EE361: MIDTERM EXAM 2 This exam is open book and closed notes. Be sure to show all work clearly. 1. 10 points - Mechanical and Electrical Energy Relationships: A dc motor
Autonomously Controlled Front Loader Senior Project Proposal
 Autonomously Controlled Front Loader Senior Project Proposal by Steven Koopman and Jerred Peterson Submitted to: Dr. Schertz, Dr. Anakwa EE 451 Senior Capstone Project December 13, 2007 Project Summary:
Autonomously Controlled Front Loader Senior Project Proposal by Steven Koopman and Jerred Peterson Submitted to: Dr. Schertz, Dr. Anakwa EE 451 Senior Capstone Project December 13, 2007 Project Summary:
Chapter 3. ECE Tools and Concepts
 Chapter 3 ECE Tools and Concepts 31 CHAPTER 3. ECE TOOLS AND CONCEPTS 3.1 Section Overview This section has four exercises. Each exercise uses a prototyping board for building the circuits. Understanding
Chapter 3 ECE Tools and Concepts 31 CHAPTER 3. ECE TOOLS AND CONCEPTS 3.1 Section Overview This section has four exercises. Each exercise uses a prototyping board for building the circuits. Understanding
Blancett Flow Meters A Division of Racine Federated Inc. 100 East Felix Street South, Suite 190 Fort Worth, Texas FAX:
 Active Sensor Installation and Operation Manual - Preliminary Frequency-to-Current/ Frequency-to-Voltage Converter For use with Blancett Model 1100 Series Turbine Flow Meters Introduction The Active Sensor
Active Sensor Installation and Operation Manual - Preliminary Frequency-to-Current/ Frequency-to-Voltage Converter For use with Blancett Model 1100 Series Turbine Flow Meters Introduction The Active Sensor
Application Information
 Moog Components Group manufactures a comprehensive line of brush-type and brushless motors, as well as brushless controllers. The purpose of this document is to provide a guide for the selection and application
Moog Components Group manufactures a comprehensive line of brush-type and brushless motors, as well as brushless controllers. The purpose of this document is to provide a guide for the selection and application
Experiment 6: Induction
 Experiment 6: Induction Part 1. Faraday s Law. You will send a current which changes at a known rate through a solenoid. From this and the solenoid s dimensions you can determine the rate the flux through
Experiment 6: Induction Part 1. Faraday s Law. You will send a current which changes at a known rate through a solenoid. From this and the solenoid s dimensions you can determine the rate the flux through
BLDC SPEED CONTROL INSTRUCTION MANUAL Line voltage Brushless DC control
 BLDC SPEED CONTROL INSTRUCTION MANUAL Line voltage Brushless DC control Phone 712.722.4135 groschopp.com 420 15th St NE, Sioux Center, IA 51250 Toll-Free 800.829.4135 Email sales@groschopp.com FAX 712.722.1445
BLDC SPEED CONTROL INSTRUCTION MANUAL Line voltage Brushless DC control Phone 712.722.4135 groschopp.com 420 15th St NE, Sioux Center, IA 51250 Toll-Free 800.829.4135 Email sales@groschopp.com FAX 712.722.1445
MondoStep 7.8. High Performance Microstepping Driver. User s Manual. Version PROBOTIX All Rights Reserved
 MondoStep 7.8 High Performance Microstepping Driver User s Manual Version 1.0 2010 PROBOTIX All Rights Reserved Attention: Please read this manual carefully before using the driver! Table of Contents 1.
MondoStep 7.8 High Performance Microstepping Driver User s Manual Version 1.0 2010 PROBOTIX All Rights Reserved Attention: Please read this manual carefully before using the driver! Table of Contents 1.
Temperature Sensor. Positive + (to 5 volts.) Ground. To A0 To GND Signal. To 5v
 Temperature Sensor This system measures the change in temperature and converts it to a colorful thermometer using LEDs. The first time you run the sketch, you will use the serial monitor to find the lowest
Temperature Sensor This system measures the change in temperature and converts it to a colorful thermometer using LEDs. The first time you run the sketch, you will use the serial monitor to find the lowest
Kelly KDC Series/PM Motor Controller User s Manual
 Kelly KDC Series/PM Motor Controller User s Manual KDC48600 KDC48601 KDC48602 KDC48603 KDC72600 KDC72601 KDC72602 KDC72603 KDC72800 KDC72801 KDC72802 KDC72803 KDC12602 KDC12603 Rev.3.3 May 2011 Contents
Kelly KDC Series/PM Motor Controller User s Manual KDC48600 KDC48601 KDC48602 KDC48603 KDC72600 KDC72601 KDC72602 KDC72603 KDC72800 KDC72801 KDC72802 KDC72803 KDC12602 KDC12603 Rev.3.3 May 2011 Contents
Glow Plug for E Series Only
 Charging the Battery - Do not charge the battery, with a charger using negative discharge pulses, when connected to the ECU. This will destroy the electronics of the ECU. The only method is to disconnect
Charging the Battery - Do not charge the battery, with a charger using negative discharge pulses, when connected to the ECU. This will destroy the electronics of the ECU. The only method is to disconnect
ENGG1015: lab 5. A Taste of the Project
 ENGG1015: lab 5 A Taste of the Project 1 st Semester 2012-13 The goal of this lab is further understand the relationship between the input and output (driving) stage of a circuit. You will gain hands-on
ENGG1015: lab 5 A Taste of the Project 1 st Semester 2012-13 The goal of this lab is further understand the relationship between the input and output (driving) stage of a circuit. You will gain hands-on
Assembly Instructions: Conventional Motor (Beakman's Motor Kit)
 Assembly Instructions: Conventional Motor (Beakman's Motor Kit) 1. Leave about 3" (7-8cm) and wind the wire 10-35 times around the AA battery. You do not have to be neat as some randomness does not affect
Assembly Instructions: Conventional Motor (Beakman's Motor Kit) 1. Leave about 3" (7-8cm) and wind the wire 10-35 times around the AA battery. You do not have to be neat as some randomness does not affect
Issue 2.0 December EPAS Midi User Manual EPAS35
 Issue 2.0 December 2017 EPAS Midi EPAS35 CONTENTS 1 Introduction 4 1.1 What is EPAS Desktop Pro? 4 1.2 About This Manual 4 1.3 Typographical Conventions 5 1.4 Getting Technical Support 5 2 Getting Started
Issue 2.0 December 2017 EPAS Midi EPAS35 CONTENTS 1 Introduction 4 1.1 What is EPAS Desktop Pro? 4 1.2 About This Manual 4 1.3 Typographical Conventions 5 1.4 Getting Technical Support 5 2 Getting Started
Automated Circuit Breaker Calibration
 Automated Circuit Breaker Calibration Philip Simonin (EE) Kyle Weber (EE) Louis LeBlanc (EE) Tyler Lyon (EE) Advisor: Ali Gokirmak Sponsor: Carling Technologies Carling Contacts: Marek Szafranski, John
Automated Circuit Breaker Calibration Philip Simonin (EE) Kyle Weber (EE) Louis LeBlanc (EE) Tyler Lyon (EE) Advisor: Ali Gokirmak Sponsor: Carling Technologies Carling Contacts: Marek Szafranski, John
DC Motor and Generator Theory By
 DC Principles Study Unit DC Motor and Generator Theory By Robert Cecci iii Preview DC motors and generators are widely used in industrial applications. Both motors and generators are devices that produce
DC Principles Study Unit DC Motor and Generator Theory By Robert Cecci iii Preview DC motors and generators are widely used in industrial applications. Both motors and generators are devices that produce
Question Bank ( ODD)
 Programme : B.E Question Bank (2016-2017ODD) Subject Semester / Branch : EE 6703 SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES : VII-EEE UNIT - 1 PART A 1. List the applications of synchronous reluctance motors. 2. Draw
Programme : B.E Question Bank (2016-2017ODD) Subject Semester / Branch : EE 6703 SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES : VII-EEE UNIT - 1 PART A 1. List the applications of synchronous reluctance motors. 2. Draw
Operating Manual For Stepper Driver
 Contents Table of Contents Operating Manual For Stepper Driver 5042 High Performance Micro stepping Driver Attention: Please read this manual carefully before using the driver! E L E C T R O N I C S 54
Contents Table of Contents Operating Manual For Stepper Driver 5042 High Performance Micro stepping Driver Attention: Please read this manual carefully before using the driver! E L E C T R O N I C S 54
Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270
 Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270 DC Test Equipment Purpose: This lab will introduce many of the fundamental test equipment and procedures used for verifying the operations of electrical circuits.
Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270 DC Test Equipment Purpose: This lab will introduce many of the fundamental test equipment and procedures used for verifying the operations of electrical circuits.
Lab 6: Electrical Motors
 Lab 6: Electrical Motors Members in the group : 1. Nattanit Trakullapphan (Nam) 1101 2. Thaksaporn Sirichanyaphong (May) 1101 3. Paradee Unchaleevilawan (Pop) 1101 4. Punyawee Lertworawut (Earl) 1101 5.
Lab 6: Electrical Motors Members in the group : 1. Nattanit Trakullapphan (Nam) 1101 2. Thaksaporn Sirichanyaphong (May) 1101 3. Paradee Unchaleevilawan (Pop) 1101 4. Punyawee Lertworawut (Earl) 1101 5.
Synchronous Motor Drives
 UNIT V SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVES 5.1 Introduction Synchronous motor is an AC motor which rotates at synchronous speed at all loads. Construction of the stator of synchronous motor is similar to the stator
UNIT V SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVES 5.1 Introduction Synchronous motor is an AC motor which rotates at synchronous speed at all loads. Construction of the stator of synchronous motor is similar to the stator
ATOTH-G Series BLDC Motor Controller. User s Manual
 ATOTH-G Series BLDC Motor Controller User s Manual Contents Chapter One Summary...1 Chapter Two Main Features and Specifications.2 2.1 Basic Functions...2 2.2 Features... 5 2.3 Specifications...6 Chapter
ATOTH-G Series BLDC Motor Controller User s Manual Contents Chapter One Summary...1 Chapter Two Main Features and Specifications.2 2.1 Basic Functions...2 2.2 Features... 5 2.3 Specifications...6 Chapter
Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8. Name:
 Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8 Name: Exploration 1 Rapidly turn the handles clockwise on all three generators at the end of the table, watching the System Voltage panel: 1. Draw the needle when the
Exploring the Energy Grid Grades 6-8 Name: Exploration 1 Rapidly turn the handles clockwise on all three generators at the end of the table, watching the System Voltage panel: 1. Draw the needle when the
