1/3/2018 Kuala Lumpur Structure Plan 2020 : Transportation. [ English ] [ Malay ] 10.1 Introduction. Kuala Lumpur Structure Plan 2020
|
|
|
- Deborah McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [ English ] [ Malay ] 10.1 Introduction Kuala Lumpur Structure Plan 2020 Preface Acknowledgement 1 Introduction 2 International and National Context of Growth 3 Vision and Goals of Kuala Lumpur 4 Economic Base and Population 5 Income and Quality of Life 6 Land Use and Development Strategy 7 Commerce 8 Tourism 382. Comprehensive and efficient transportation system networks with good inter and intra city linkages are essential enabling factors to ensure Kuala Lumpur s position as an international commercial and financial centre For the residents of Kuala Lumpur, the City must be able to provide an efficient and equitable city structure that, as far as possible, allows all members of the community equal accessibility to all areas and facilities so that everyone may enjoy the maximum benefits of city living The basic structure is now in place with a comprehensive road and rail network that has been built up since 1984, and the programme now for Kuala Lumpur will be to develop, refine and integrate this transportation system to serve the City and its population until In this respect, CHKL shall assist in the implementation of a fully integrated transportation system Existing situation and issue General a) Transport modal share 9 Industry 10 Transportation 10.1 Introduction 10.2 Existing situation and issue General Public transport Private transportation Road infrastructure Non-motorised transport Freight transport 10.3 Objective 10.4 and proposal General Public transport Private transportation Road infrastructure Non-motorised transport Freight transport 10.5 Future requirement Integrated public transportation system 385. Between 1985 and 1997, the modal share of public transport decreased from 34.3 percent to 19.7 percent. This represents a major shift away from public transport and in particular bus transport, which is partly attributable to higher personal affluence leading to an increase in car ownership and also to deficiencies in the bus services. The increasing reliance on private transportation, in particular private cars, has created considerable pressure on the road network which has contributed to the problems of traffic congestion. ii. Issue Low public transport modal share resulting in high demand on road infrastructure and traffic congestion. b) Travel demand 386. Increased affluence and out migration from Kuala Lumpur have both contributed to the present traffic congestion 1/25
2 Road system 11 Infrastructure and Utilities 12 Housing 13 Community Facilities 14 Urban Design and Landscape 15 Environment 16 Special Areas problems in the City Centre. Between 1980 and 1997, the population of Kuala Lumpur maintained an annual growth rate of 1.1 percent while from 1985 to 1997 person trips by cars increased at an average annual growth rate of 4.2 percent in the Klang Valley Region It is also significant that, although the population of the City Centre accounts for only 3.3 percent of total population of the Klang Valley Region, approximately 19 percent of the 8.3 million person trips made daily within the Klang Valley Region are trips generated in the City Centre The high travel demand has been met in large part by private transportation in particular, private cars. As a consequence, there has been congestion and a serious deterioration of travel speed on major roads in many parts of Kuala Lumpur, especially in the City Centre as well as in the east and south, due to major traffic routes operating at or above capacity during peak hours. Low vehicle occupancy has further aggravated the problem. 17 Strategic Zone 18 Implementation Abbreviations Glossary FAQ ii. Issue High travel demand to and from the City Centre during peak hours. c) Traffic management 389. Traffic management measures are aimed at optimizing the existing infrastructure to improve flow capacities and to be more responsive to traffic demand at different times of the day Various measures have been successfully implemented in Kuala Lumpur. The principal means of traffic control in the City presently comprises a computer based area traffic signal coordination system (SCATS/ITACA) that operates 130 intersections, supplemented by the traffic police during peak hours. Extension of the existing traffic control system, together with an upgrading of the system s capability, is currently being implemented in phases Other traffic control measures which contribute to traffic management in Kuala Lumpur include the one-way street system, reversible lanes to increase lane capacity during morning peak hours, exclusive bus/taxi lanes, penalties for illegal on-street parking and regulations controlling heavy vehicle entry into the City Centre during peak hours Additional measures that relate to road safety are through the use of traffic signage, barriers, pavement line marking and pedestrian bridges. Driver awareness campaigns and strict provisions for the issuance of driving licenses are also relevant contributions to effective traffic management. ii. Issue 393. Although traffic management measures have done much to ease traffic flows particularly in the City Centre, they cannot continue to do so indefinitely if traffic demand on the roads continues to grow. Traffic management measures alone cannot effectively increase existing road capacity levels. 2/25
3 d) Transportation institutional framework 394. The institutional structure responsible for urban transportation within Malaysia and, more specifically, Kuala Lumpur is divided between federal departments and City Hall Kuala Lumpur (CHKL) (refer to Table 10.1) The CHKL Urban Transport Department is entrusted with wide ranging coordination and administrative functions for the planning of urban transport in an effective manner. The Federal Government deals more with nationwide transportation plans, policy guidelines and matters concerning overall transport administration and planning Private sector involvement in the provision of transport infrastructure has expanded from the original role of bus and taxi transport operations to toll road construction and the implementation, operation and maintenance of the commuter, light rapid transit (LRT) and people mover rapid transit (PRT) systems. Table 10.1: Urban Transportation Responsibilities - Federal and Local Government Departments ii. Issue 397. There is a degree of overlap and duplication in the functions of the various agencies responsible for Kuala Lumpur s transportation network which has led, in some instances, to conflicting policies or programmes. This has made it more difficult to formulate policies for public and private transportation which are consistent. Inadequate coordination of policies concerning public transport and public/ private transport modes Public transport a) Rail - Based public transport 3/25
4 398. Rail services have become a significant factor in public transport in Kuala Lumpur since the opening of the Light Rail Transit (LRT) System 1, Sistem Transit Aliran Ringan Sdn Bhd (STAR) in 1996 and subsequently the LRT System II or Projek Usaha Sama Transit Ringan Automatik (PUTRA) in Together they provide approximately 50 kilometres of rail network with 40 stations. In addition to the LRT, the People Mover Rapid Transit (PRT), a monorail system recently completed, serves major office and other commercial developments within the City Centre. The monorail s 10-kilometre route with 10 stations act as a downtown people mover operating on an elevated track The Express Rail Link (ERL), a dedicated high-speed rail system, connects KL Sentral and Kuala Lumpur International Airport (KLIA). The ERL terminus at KL Sentral functions as a city airport terminal for KLIA. At KL Sentral station, an intermodal facility is being provided with KTM Commuter, PRT and LRT System II, where users can transfer between the various modes to their desired destinations The upgrading of KTMB rail services and the operation of the KTM commuter added about 137 kilometres of rail services between Rawang - Seremban and between Sentul - Port Klang passing through 39 stations and halts. This service allows commuters to capture a significant portion of the long distance daily travel needs between Kuala Lumpur and the suburbs. Photo 10.1: Rail services have become a significant factor in public transport in Kuala Lumpur... ii. Issue 4/25
5 401. LRT and commuter rail usage has been encouraging. However, optimal usage has still to be achieved due to: inadequate interchange facilities at stations including car and motor cycle parking and pedestrian linkages; lack of integration between rail-based stations; and poor support services including inadequate feeder bus frequency and service coverage Figure 10.1 indicates the relative accessibility of bus and rail-based public transport. It is clear that rail-based public transport services are far less accessible than bus services and, consequently, their ability to service patrons in a single trip from origin to destination is very limited. The 2-kilometre radius coverage of the feeder buses that operate from stations is not enough to ensure sufficient accessibility. Poor accessibility to rail-based public transport. Figure 10.1: Rail and Bus Accessibility b) Bus services 403. At present there are four major private companies operating about 15,000 bus trips per day. Each company operates about 30 routes, most of which are radial in nature, terminating at the City Centre Improvements to the bus network are being facilitated by CHKL providing exclusive bus and taxi lanes in the City Centre and comfortable stop facilities. Together these improvements are intended to offer passengers a quick, comfortable and convenient transport option. ii. Issue 405. Despite the improvements to the bus system and road infrastructure, bus utilisation is low, primarily as a consequence of route duplication, unreliable service frequency, overcrowding during peak hours and the poor 5/25
6 condition of buses. Under utilisation of bus services; and Unreliable and poor quality of services. Photo 10.2: Improvements to the bus network are being facilitated by CHKL providing exclusive bus/taxi lanes in the City Centre and comfortable shelter/stop facilities The existing main bus terminal is at Puduraya in the City Centre. The majority of inter city buses and coaches terminate there, thus adding to traffic congestion and consequently, longer journey times for passengers. Central location of main bus terminal contributing to traffic congestion. c) Taxis 407. Taxis are an important element of the public transport system offering a convenient form of alternative transport particularly outside peak hours. There are approximately 24,721 taxicabs licensed in Kuala Lumpur, run by 4,183 operators. A traffic classification survey carried out by Japan International Coorperation Agency (JICA) in 1997 indicated that taxis constituted 4 to 6 percent of the total number of vehicles passing through the City Centre. ii. Issue 408. There is no shortage of taxis but availability is frequently a problem at peak periods and during bad weather. Unreliable taxi services Private Transportation a) Cars and car parking 6/25
7 409. Based on the Road Transport Department report, the ratio of registered cars and motorcycles in Kuala Lumpur was per 1,000 population in However, based on the Home Interview Survey carried out by JICA in 1998 the estimated possession ratio in vehicles represents approximately 211 cars per 1,000 population and 164 motorcycles per 1,000 population. Private cars account for 56.6 percent of all motorised trips in Kuala Lumpur CHKL through the town planning approval process controls the number of car and motorcycle parking spaces to be provided for new development. However, at present parking charges are subjected to market forces and are not regulated In order to alleviate traffic congestion, CHKL has successfully implemented roadside parking restrictions on all major arterial roads in the builtup areas There are approximately 65,206 car parking spaces in the City Centre (refer to Figure 10.2). Office buildings record the highest utilisation of spaces averaging 71.0 percent, followed by retail premises (49.0 percent average) and mixed-use (47.0 percent average). Generally, car-parking provision in the City Centre is more than adequate. ii. Issue 413. Parking charges in the City Centre favour regular long-term parking with many car park operators offering cheap seasonal parking tickets. This, together with the flexibility afforded by private transport, encourages commuters to continue to use private transport into the City Centre. The low cost of long-term parking in the City Centre together with the abundance of parking spaces and the flexibility of movement associated with car transport, has made car transport the preferred means of travel in the City Outside the City Centre there is a shortage of car parking spaces in areas close to public transport and also in shop lot development where there are no multi-storey or underground car parks. Shortages of parking spaces outside the City Centre in locations which have reasonable access to public transport and in shop lot development. b) Motorcycles 415. Motorcycles account for approximately 23 percent of all road users in Kuala Lumpur. Principally used by the young and lower income groups, they provide a fast, flexible and economical means of transportation around the City About 52 percent of the total numbers of fatal and serious accidents in Kuala Lumpur involve motorcycles. Motorcycles are the major source of urban air and noise pollution. Noise emission from motorcycles in the City Centre exceeds permissible noise limits (Malaysia Environmental Quality Report 1996, DOE). 7/25
8 ii. Issue The accident rate involving motorcycles is higher than for all other forms of transport; and Motorcycles contribute significantly to noise and air pollution Road infrastructure 417. Under the privatization policy, the road building programme for the Klang Valley set out in the KLSP 1984, which comprised 23 new roads and 21 major road improvement projects, has mostly been completed together with some additional toll highways. The road network now in place has succeeded in its primary purposes of eliminating through traffic from the City Centre, reducing congestion on minor roads and efficiently dispersing traffic from the City Centre In addition, there are a number of road building projects already under way, and some for which a concession agreement has already been signed, or for which approval in principle has been given (refer to Table 10.2). ii. Issue 419. Discontinuities in the old city street layout have resulted in a lack of direct routes being available for traffic entering or leaving the City Centre, specifically from the south along Jalan Syed Putra and from the east along Jalan Kuching. Access to Bukit Bintang from these directions require through traffic to pass along narrow streets within the old city precinct. Constraints in expanding existing routes for traffic entering or leaving the City Centre. Photo 10.3: The road network now in place has succeeded in its primary purposes of eliminating through traffic from the City Centre. 8/25
9 Figure 10.2 : Location of major car parking stations in the city centre, /25
10 Table 10.2: Highway and Road Building Projects, Although the road-building programme is, to all intents and purposes, complete, there remain instances where connections between major roads or major and minor roads are incomplete. In addition, in some instances there is traffic back up at atgrade junctions which are unable to cope with the traffic flow. These factors cause traffic bottlenecks that lead to traffic congestion particularly at peak hours. Discontinuities in the road network; and Traffic back up at at-grade junctions Because no requirement has been made in privatization agreements, major toll highways have been built without any specific provision for public transport or freight vehicles. The potential for maximising the utilisation of these highway routes for high-speed public transport connections to outlying areas has not been exploited. Lack of specific provision in toll highways for public transport or freight vehicles The development of major roads in Kuala Lumpur has not always fully observed road classification requirements. In addition, some roads have assumed functions for which they were not originally designed such as residential roads that have become trunk roads due to ill-considered road connections. These anomalies have presented difficulties in the design and management of the overall road network. Existing designation of major roads does not reflect actual usage Plot ratios for commercial spaces within the City Centre have progressively increased over the years and created increased pressure on the road network. Large-scale projects planned and committed will increase private vehicle travel demand even further. 10/25
11 Increased pressure on the road network due to intensive and large-scale commercial development Non-motorised transport a) Pedestrian 424. A pedestrian network is progressively being implemented in the City Centre. This will facilitate pedestrian and nonmotorised vehicle movement at activity centres, connect transit stations and terminals for convenient inter-modal transfer, provide pedestrian malls and act as traffic restraint measures. The network will also help increase the utilisation of public transportation and reduce short vehicle trips The existing situation and issues relating to pedestrian movement are outlined in Chapter 14: Urban Design and Landscape. b) Bicycles 426. Cycle ways have, for some time, been incorporated into new housing estates and recreational areas. Despite the relatively flat terrain of Kuala Lumpur, cycling as a convenient means of transport is under utilised partly due to local climatic conditions. There are also, however, some shortcomings in the existing cycle way network which contribute to the under utilisation of bicycles. Photo 10.4:...pedestrian and non-motorised vehicle movement at activity centres, connect transit stations and terminals for convenient inter-modal transfer... ii. Issue 427. Opportunities exist for bicycle transport in providing connections to public transport services and short distance local travel. Other cities have utilised their roads, rail and open space corridors to create a comprehensive local area cycle way network. 11/25
12 Cycle ways in housing estates suffer from under usage, misuse (illegal parking) and poor maintenance; and Lack of continuity in the cycle way networks Freight Transport 428. Lorry vehicular trip production is mainly focused in the industrial areas peripheral to the City Centre. Heavy lorry flows are concentrated more in external zones to the south and passing through the region on a north-south axis Within Kuala Lumpur there is some heavy goods vehicle (HGV) movement although this is prohibited during the morning and evening peak hours. ii. Issue 430. There are areas in the north and south of the City where the illegal parking of HGVs, construction vehicles and coaches in residential areas causes inconvenience to the residents. Illegal parking of heavy goods vehicles and construction vehicles in residential and commercial areas due to the lack of proper parking facilities and consequent enforcement difficulties Objective 431. To create an efficient and equitable city structure for Kuala Lumpur, CHKL aims to: provide a comprehensive and integrated transportation system that caters for the needs of inter and intra city travel; reverse the decline in public transport usage and to achieve a targeted public: private transport modal split of 60:40 by the year 2020; optimise the road and rail transportation infrastructure so that it operates at its full capacity and maximum efficiency; ensure that the overall configuration of land use is integrated with road and public transportation networks to optimise the development of land; and ensure that all areas within the City enjoy the same high quality and standard of provision of public transport services To enhance the city living environment, CHKL aims to: create a city that is highly accessible for all its occupants and users, in particular, one that is pedestrian and handicapped friendly. 12/25
13 10.4 and proposal General a) Travel demand management 433. If current trends continue, motorised trips by car in 2020 are expected to be almost double those of Increasing road capacity by constructing new roads and widening existing roads do not, in the long run, resolve the situation but simply postpone the problem until more roads need to be built. Most areas in the City, especially the City Centre, are now built up and land acquisition for road development is becoming increasingly difficult and expensive CHKL is, therefore, moving towards a Travel Demand Management strategy that aims to redirect movement patterns from private to public transport by integrating transport modes, extending and promoting public transport and discouraging the use of private transport. The public transport system in the City must be competitive, convenient, userfriendly and accessible to all income groups. TI 1: TI 2: CHKL shall determine Travel Demand Management measures to increase public transport usage and liase with the relevant authorities to ensure that these measures are implemented. CHKL shall implement a private vehicle restraint programme to improve traffic circulation in the City Centre by discouraging car travel to and from the City Centre during peak hours and enforcing measures to limit access to certain parts of the City. b) Traffic management system 435. In order to optimise the traffic management system now in place, the system needs to be upgraded to one that can monitor and control all aspects of traffic movement in the City. TI 3: CHKL shall enhance the traffic management system. c) Transit oriented development 436. A principal objective of the transportation sector is the integration of land use with transportation and the development of a Transit Oriented Development Strategy. This strategy, which is detailed in Chapter 6: Land Use and Development Strategies, will promote intensified development along the rail network. Any planned extension to 13/25
14 the rail network must, therefore, complement this policy by ensuring that rail stations serve designated urban centres. TI 4: CHKL shall establish a Transit Planning Zone to facilitate intensification of transit oriented residential, commercial and mixeduse development around rail stations. Photo 10.5:...will promote intensified development along the rail network Public transport a) Public transport administration 437. The increased emphasis and capital expenditure on public transport requires complementary coordination between government departments and other related agencies. CHKL shall take pro-active measures in ensuring the implementation of government policy in relation to the public transport administration. TI 5: CHKL shall assist to coordinate the planning, development and operation of public transport and related private transport matters. b) Public transport integration 438. Consistent with the government s policy, emphasis will be on providing an integrated, flexible, wide ranging and efficient public transport system orientated towards passenger accessibility and convenience. Central to this approach is the integration of public transport modes with each other and with private transport so that, with streamlined inter-modal transfer facilities and integrated ticketing, passenger trips become as convenient and seamless as possible In order to avoid traffic congestion occurring on local streets, major bus and rail park-and-ride interchange facilities 14/25
15 will be located at the points of intersection of the rail stations and major roads. The recommended locations of these interchanges are shown in Figure TI 6: CHKL shall assist in the implementation of a fully integrated transportation system in line with the government s policy. c) Rail-based public transport 440. The rail network is the most efficient means of providing high capacity rapid public transport. Medium and longterm plans for the introduction of different types of rail systems such as tram and the expansion of the rail network to outlying areas should be regularly examined in every 10 years for their feasibility The major growth areas in Kuala Lumpur are now well linked to the City Centre except those on the east-west axis. The feasibility of a new Damansara - Cheras LRT line linking growth areas in the east and west shall be investigated together with new rail links to serve district centres, comprehensive development areas and growth areas. Photo 10.6:...the integration of public transport modes It is also proposed that the STAR LRT line from Sentul Timur station be extended northward towards Taman Wahyu and westward towards Kepong and another line be extended from Sri Petaling station westward to serve the area around Bukit Jalil A further extension to the LRT is proposed from KL Sentral station to the proposed district centre at Bukit Indah. These five future lines will add a further 41.9 kilometres to the existing network. TI 7: CHKL shall assist in the preparation of feasibility studies for future extensions to the rail network and coordinate with the relevant authorities with regard to implementation. 15/25
16 d) Bus services 444. Buses will remain the principal form of public transport especially outside the City Centre for the foreseeable future. In order to encourage greater usage of bus services, it is essential that measures be undertaken to improve their reliability, coverage, comfort and convenience. TI 8: CHKL shall assist in determining measures to improve bus services with maximum penetration into growth areas and all major employment and retail centres and coordinate with the relevant agencies and operators. 16/25
17 Figure 10.3 : Integrated rail based public transport system, CHKL shall also implement measures to create a network of bus terminals on the periphery of Kuala Lumpur for buses and coaches serving separate inter-regional and intra-regional services. These terminals will be integrated with the rail system via multi-modal interchanges to enable easy access to the City Centre and other areas of the City. Inter-regional terminals shall be located at Gombak (to serve the east), Bandar Tasik Selatan (to serve the south), Jalan Ipoh (to serve the north) and the station at CDA Jalan Duta (to serve the west). Hentian Putra, Pasarama Kota and Plaza Rakyat terminals will serve as the intra-regional terminals. Terminals to cater for local services shall be developed at various suitable locations in the City (refer to Figure 10.4). TI 9: CHKL shall implement a bus terminal network for inter-regional, intraregional and local bus services. e) Cars and car parking 446. By controlling the supply and distribution of car parking facilities in Kuala Lumpur, CHKL can help to reinforce public transport and Travel Demand Management objectives by making private transport a less attractive proposition than public transport, especially within the City Centre. This can further be reinforced by controlling the cost of car parking in different parts of the City. Photo 10.7: CHKL shall regulate the supply of parking facilities. TI 10: CHKL shall regulate the supply of parking facilities. 17/25
18 f) Taxis 447. In view of the vital role that taxis play in the business and commercial life of the City, it is important that significant improvements are made to the levels of service and reliability. In achieving better overall public transport services, taxis need to be expanded with innovative services into new markets. TI 11: CHKL shall assist in improving the reliability and availability of taxi services in coordination with the relevant agencies Private transportation a) Motorcycles 448. As Kuala Lumpur looks to a cleaner and safer living environment, the role of the motorcycle in transportation must be examined. A large percentage of motorcycle users are those that would benefit from a more comprehensive public transportation system. In a long term, measures to encourage motorcycle users to make greater use of public transport and limit motorcycle usage in the City Centre to only essential users should be looked into In the short and medium term, measures to improve safety for motorcycle users shall be implemented and more rigorous enforcement of existing regulations shall be exercised. TI 12: CHKL shall assist and coordinate with the relevant authorities in the improvement of road infrastructure to enhance safety measures for motorcycle users. 18/25
19 Figure 10.4 : Location of bus terminals, Road infrastructure a) New roads development 450. The major road systems currently in place together with those which are under construction or committed are considered sufficient to satisfy Kuala Lumpur s needs to the year However, two new roads are proposed that are principally intended to improve traffic flow in and out from the City Centre. In view of the difficulty of increasing existing road capacities in the City Centre and the high cost associated with obtaining new corridors, an underground expressway is proposed beneath Jalan Raja Chulan connecting to the Middle Ring Road in the east. 19/25
20 451. An inner city by-pass road is also proposed, part of which will be underground, to provide a direct link from Jalan Syed Putra in the south of the City Centre to Jalan Dang Wangi (refer to Figure 10.5 and Table 10.3). TI 13: CHKL shall determine a road development programme and coordinate with the relevant authorities regarding implementation In future the requirement, if any, for new roads must be examined in the context of CHKL s general transportation policies. However, any new roads that may be deemed necessary should support CHKL s policies to promote public transportation by making provision for high-occupancy vehicles and/or trunk bus routes. The reserves of these roads should be clearly demarcated to prevent urban encroachment on the right of way Privatization bids on arterial roads must also conform to the network proposed in the structure plan and local plans and not be conceived independently. TI 14: CHKL shall ensure that proposed and committed major roads are considered in the broader context of public transport services, freight movement and impact upon the community and environment. Photo 10.8:... a road network improvement programme must be carried out to upgrade existing roads to arterial roads, build missing linkages and improve interchanges. b) Improvements to the Existing Road Network 454. In order to complete the existing road network, increase its capacity and eradicate bottlenecks, a road network improvement programme must be carried out to upgrade existing roads to arterial roads, build missing linkages and improve interchanges (refer to Figure 10.5 and Table 10.3). 20/25
21 TI 15: CHKL shall determine a road improvement programme and coordinate with the relevant authorities regarding implementation. c) Hierarchy of Roads 455. In order to be able to better monitor and optimise usage of the existing road system, a review of the actual status of all existing roads and the road hierarchy system should be undertaken. 21/25
22 Figure 10.5 : Major road network, 2000 Table 10.3: New Roads Construction and Improvements to Existing Roads 22/25
23 Photo 10.9:...review of the actual status of all existing roads and the road hierarchy system. TI 16: CHKL shall implement an improved road hierarchy classification system Non-motorised transport a) Pedestrian 456. Policies regarding pedestrianisation are covered in Chapter 14: Urban Design and Landscape A pedestrian friendly environment will be created throughout the City with particular emphasis on the City Centre and other urban centres. Pedestrian networks in the City Centre will emphasise on linking public transport facilities and will incorporate urban design elements. A proposed parkland PRT loop passing through the parkland sector in the western part of the City Centre shall connect to the existing PRT line and complement the pedestrian network Special attention is to be given to areas around main transport interchanges to ensure that they incorporate facilities to make them fully accessible to the aged and handicapped. TI 17: CHKL shall develop specific guidelines and standards to provide for the needs of the aged and handicapped to be applied to pedestrian networks, new public transport terminuses and stations as well as multi-modal interchanges. b) Bicycles 459. Bicycles can and should continue to be encouraged as a healthy form of exercise and as an alternative means of private transportation for short journeys in residential and recreational areas. 23/25
24 Photo 10.10: Adequate lorry parks for the benefit of HGV owners residing in the City... TI 18: CHKL shall improve the cycle way network and promote cycling activities in residential and recreational areas Freight Transport 460. Adequate lorry parks for the benefit of HGV owners residing in the City shall be provided so that they do not have to resort to illegally parking in commercial or residential areas. These lorry parks will also include parking facilities for coaches and construction vehicles. TI 19: CHKL shall provide adequate parking and other ancillary facilities for heavy goods vehicles, coaches and construction vehicles in appropriate locations at the City perimeter Future requirement Integrated public transportation system 461. The complete rail network to the year 2020 including integrated park-and-ride stations and multimodal interchanges are indicated in Figure Road network 24/25
25 462. Ultimately, Kuala Lumpur still needs a comprehensive road network in order to provide efficient and convenient road travel. The requirements for new roads and improvement to existing roads are indicated in Figure 10.5 and summarised in Table /25
ASIAN MAYOR S POLICY DIALOGUE FOR THE PROMOTION OF ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORT IN CITIES. 23 rd 24 th APRIL 2007, KYOTO JAPAN
 ASIAN MAYOR S POLICY DIALOGUE FOR THE PROMOTION OF ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORT IN CITIES. 23 rd 24 th APRIL 2007, KYOTO JAPAN Mak See Deputy Director Urban Transportation Department City Hall
ASIAN MAYOR S POLICY DIALOGUE FOR THE PROMOTION OF ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORT IN CITIES. 23 rd 24 th APRIL 2007, KYOTO JAPAN Mak See Deputy Director Urban Transportation Department City Hall
Parking Management Element
 Parking Management Element The State Transportation Planning Rule, adopted in 1991, requires that the Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) area implement, through its member jurisdictions, a parking
Parking Management Element The State Transportation Planning Rule, adopted in 1991, requires that the Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) area implement, through its member jurisdictions, a parking
Transportation Demand Management Element
 Transportation Demand Management Element Over the years, our reliance on the private automobile as our primary mode of transportation has grown substantially. Our dependence on the automobile is evidenced
Transportation Demand Management Element Over the years, our reliance on the private automobile as our primary mode of transportation has grown substantially. Our dependence on the automobile is evidenced
4. Transportation Plan
 The sizes of the most suitable sites are indicated in Table 4.3.6.2. Table 4.3.6.2: Site Sizes and Potential Development Area Potential Development Site Site Size (m 2 ) Area m 2 (3 Floors) D1 29,000 87,000
The sizes of the most suitable sites are indicated in Table 4.3.6.2. Table 4.3.6.2: Site Sizes and Potential Development Area Potential Development Site Site Size (m 2 ) Area m 2 (3 Floors) D1 29,000 87,000
Back ground Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Altitude about 2500 meters above MSL Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa
 Back ground Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Altitude about 2500 meters above MSL Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa Annual growth rate is 3.8% By 2020 population growth would
Back ground Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Altitude about 2500 meters above MSL Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa Annual growth rate is 3.8% By 2020 population growth would
Executive Summary. Treasure Valley High Capacity Transit Study Priority Corridor Phase 1 Alternatives Analysis October 13, 2009.
 Treasure Valley High Capacity Transit Study Priority Corridor Phase 1 Alternatives Analysis October 13, 2009 Background As the Treasure Valley continues to grow, high-quality transportation connections
Treasure Valley High Capacity Transit Study Priority Corridor Phase 1 Alternatives Analysis October 13, 2009 Background As the Treasure Valley continues to grow, high-quality transportation connections
Draft Marrickville Car Share Policy 2014
 Draft Marrickville Car Share Policy 2014 1. Background 1.1. Marrickville Council has supported car sharing in the LGA since 2007 as part of a holistic approach to encouraging more sustainable modes of
Draft Marrickville Car Share Policy 2014 1. Background 1.1. Marrickville Council has supported car sharing in the LGA since 2007 as part of a holistic approach to encouraging more sustainable modes of
Strategic Plan
 2005-2015 Strategic Plan SUMMARY OF THE REVISED PLAN IN 2011 A decade focused on developing mass transit in the Outaouais A updated vision of mass transit in the region The STO is embracing the future
2005-2015 Strategic Plan SUMMARY OF THE REVISED PLAN IN 2011 A decade focused on developing mass transit in the Outaouais A updated vision of mass transit in the region The STO is embracing the future
Submission to Greater Cambridge City Deal
 What Transport for Cambridge? 2 1 Submission to Greater Cambridge City Deal By Professor Marcial Echenique OBE ScD RIBA RTPI and Jonathan Barker Introduction Cambridge Futures was founded in 1997 as a
What Transport for Cambridge? 2 1 Submission to Greater Cambridge City Deal By Professor Marcial Echenique OBE ScD RIBA RTPI and Jonathan Barker Introduction Cambridge Futures was founded in 1997 as a
KUALA LUMPUR URBAN RAIL DEVELOPMENT: MALAYSIA EXPERIENCE
 KUALA LUMPUR URBAN RAIL DEVELOPMENT: MALAYSIA EXPERIENCE CAPACITY BUILDING WORKSHOP ON SUSTAINABLE URBAN TRANSPORT INDEX 30-31 OCTOBER 2017 COLOMBO, SRI LANKA Content The Intent Rail Services in Kuala
KUALA LUMPUR URBAN RAIL DEVELOPMENT: MALAYSIA EXPERIENCE CAPACITY BUILDING WORKSHOP ON SUSTAINABLE URBAN TRANSPORT INDEX 30-31 OCTOBER 2017 COLOMBO, SRI LANKA Content The Intent Rail Services in Kuala
CORE AREA SPECIFIC PLAN
 only four (A, B, D, and F) extend past Eighth Street to the north, and only Richards Boulevard leaves the Core Area to the south. This street pattern, compounded by the fact that Richards Boulevard is
only four (A, B, D, and F) extend past Eighth Street to the north, and only Richards Boulevard leaves the Core Area to the south. This street pattern, compounded by the fact that Richards Boulevard is
2.4 TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION. Support the revitalization of urban cores STRATEGIC DIRECTION
 TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION TRANSIT VISION 2040 defines a future in which public transit maximizes its contribution to quality of life with benefits that support a vibrant and equitable society,
TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION TRANSIT VISION 2040 defines a future in which public transit maximizes its contribution to quality of life with benefits that support a vibrant and equitable society,
Amman Green Policies Projects and Challenges. Prepared by: Eng. Sajeda Alnsour Project coordinator Sept. 20, 2017
 Amman Green Policies Projects and Challenges Prepared by: Eng. Sajeda Alnsour Project coordinator Sept. 20, 2017 Amman: Demographics Greater AMMAN Municipality GAM Amman is the capital of Jordan with a
Amman Green Policies Projects and Challenges Prepared by: Eng. Sajeda Alnsour Project coordinator Sept. 20, 2017 Amman: Demographics Greater AMMAN Municipality GAM Amman is the capital of Jordan with a
Section 9 Residual Impacts
 Section 9 Residual Impacts 9. 9.1 INTRODUCTION The residual impacts of the Project are those impacts that could potentially persist in the long-term even after all practicable mitigation measures have
Section 9 Residual Impacts 9. 9.1 INTRODUCTION The residual impacts of the Project are those impacts that could potentially persist in the long-term even after all practicable mitigation measures have
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Introduction
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The purpose of this study is to ensure that the Village, in cooperation and coordination with the Downtown Management Corporation (DMC), is using best practices as they plan
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The purpose of this study is to ensure that the Village, in cooperation and coordination with the Downtown Management Corporation (DMC), is using best practices as they plan
Transport systems integration into urban development planning processes
 Transport systems integration into urban development planning processes Phd. Vytautas Palevičius 2014-03-28 Klaipėda Šiauliai Panevėžys Kaunas Vilnius At the beginning of year 2013, Lithuania was populated
Transport systems integration into urban development planning processes Phd. Vytautas Palevičius 2014-03-28 Klaipėda Šiauliai Panevėžys Kaunas Vilnius At the beginning of year 2013, Lithuania was populated
Executive Summary. Draft Environmental Impact Statement/Environmental Impact Report ES-1
 Executive Summary Introduction The Eastside Transit Corridor Phase 2 Project is a vital public transit infrastructure investment that would provide a transit connection to the existing Metro Gold Line
Executive Summary Introduction The Eastside Transit Corridor Phase 2 Project is a vital public transit infrastructure investment that would provide a transit connection to the existing Metro Gold Line
The Engineering Department recommends Council receive this report for information.
 CORPORATE REPORT NO: R161 COUNCIL DATE: July 23, 2018 REGULAR COUNCIL TO: Mayor & Council DATE: July 19, 2018 FROM: General Manager, Engineering FILE: 8740-01 SUBJECT: Surrey Long-Range Rapid Transit Vision
CORPORATE REPORT NO: R161 COUNCIL DATE: July 23, 2018 REGULAR COUNCIL TO: Mayor & Council DATE: July 19, 2018 FROM: General Manager, Engineering FILE: 8740-01 SUBJECT: Surrey Long-Range Rapid Transit Vision
Executive Summary EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Parking Issues Trenton Downtown Parking Policy and Sidewalk Design Standards E.S. Page 1 Final Report 2008
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY A walkable environment that accommodates market demand while minimizing the negative impacts of growth is an important element in promoting the City s downtown revitalization. There are
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY A walkable environment that accommodates market demand while minimizing the negative impacts of growth is an important element in promoting the City s downtown revitalization. There are
Seoul. (Area=605, 10mill. 23.5%) Capital Region (Area=11,730, 25mill. 49.4%)
 Seoul (Area=605, 10mill. 23.5%) Capital Region (Area=11,730, 25mill. 49.4%) . Major changes of recent decades in Korea Korea s Pathways at a glance 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Economic Development
Seoul (Area=605, 10mill. 23.5%) Capital Region (Area=11,730, 25mill. 49.4%) . Major changes of recent decades in Korea Korea s Pathways at a glance 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Economic Development
Findings from the Limassol SUMP study
 5 th European Conference on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans 14-15 May 2018 Nicosia, Cyprus Findings from the Limassol SUMP study Apostolos Bizakis Deputy PM General Information The largest city in the
5 th European Conference on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans 14-15 May 2018 Nicosia, Cyprus Findings from the Limassol SUMP study Apostolos Bizakis Deputy PM General Information The largest city in the
Implementing Transport Demand Management Measures
 Implementing Transport Demand Management Measures Dominik Schmid, GIZ Transport Policy Advisory Services Urban Mobility India Conference, Delhi, December 2013 Page 1 Agenda Context: Why Transport Demand
Implementing Transport Demand Management Measures Dominik Schmid, GIZ Transport Policy Advisory Services Urban Mobility India Conference, Delhi, December 2013 Page 1 Agenda Context: Why Transport Demand
Brainstormed Solutions - Passenger
 1-1a Air / Exand: Expand capacity (runway lengths) at BG airport (LOW) find solution! 1-1b Air / fuel: Improve fuel availabilty and reduce cost (LOW) Sound Walls X X X Reduce scatter lighting - more focused
1-1a Air / Exand: Expand capacity (runway lengths) at BG airport (LOW) find solution! 1-1b Air / fuel: Improve fuel availabilty and reduce cost (LOW) Sound Walls X X X Reduce scatter lighting - more focused
The City of Toronto s Transportation Strategy July 2007
 The City of Toronto s Transportation Strategy July 2007 Presentation Outline Transportation Statistics Transportation Building Blocks Toronto s Official Plan Transportation and City Building Vision Projects
The City of Toronto s Transportation Strategy July 2007 Presentation Outline Transportation Statistics Transportation Building Blocks Toronto s Official Plan Transportation and City Building Vision Projects
CITY OF LONDON STRATEGIC MULTI-YEAR BUDGET ADDITIONAL INVESTMENTS BUSINESS CASE # 6
 2016 2019 CITY OF LONDON STRATEGIC MULTI-YEAR BUDGET ADDITIONAL INVESTMENTS BUSINESS CASE # 6 STRATEGIC AREA OF FOCUS: SUB-PRIORITY: STRATEGY: INITIATIVE: INITIATIVE LEAD(S): BUILDING A SUSTAINABLE CITY
2016 2019 CITY OF LONDON STRATEGIC MULTI-YEAR BUDGET ADDITIONAL INVESTMENTS BUSINESS CASE # 6 STRATEGIC AREA OF FOCUS: SUB-PRIORITY: STRATEGY: INITIATIVE: INITIATIVE LEAD(S): BUILDING A SUSTAINABLE CITY
EUGENE-SPRINGFIELD, OREGON EAST WEST PILOT BRT LANE TRANSIT DISTRICT
 EUGENE-SPRINGFIELD, OREGON EAST WEST PILOT BRT LANE TRANSIT DISTRICT (BRIEF) Table of Contents EUGENE-SPRINGFIELD, OREGON (USA)... 1 COUNTY CONTEXT AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION... 1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW... 1 PLANNING
EUGENE-SPRINGFIELD, OREGON EAST WEST PILOT BRT LANE TRANSIT DISTRICT (BRIEF) Table of Contents EUGENE-SPRINGFIELD, OREGON (USA)... 1 COUNTY CONTEXT AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION... 1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW... 1 PLANNING
Mobility of Gurugram & NCR-
 Mobility of Gurugram & NCR- Vision for Efficient Transport Systems By Sujata Savant Additional General Manger Urbanization and Mobility Urbanization & Mobility Magnitude 31% Indians live in urban areas
Mobility of Gurugram & NCR- Vision for Efficient Transport Systems By Sujata Savant Additional General Manger Urbanization and Mobility Urbanization & Mobility Magnitude 31% Indians live in urban areas
The Motorcycle Industry in Europe. Powered Two-Wheelers the SMART Choice for Urban Mobility
 The Motorcycle Industry in Europe Powered Two-Wheelers the SMART Choice for Urban Mobility PTWs: the SMART Choice For Urban Mobility Europe s cities are main engines of economic growth, but today s urbanisation
The Motorcycle Industry in Europe Powered Two-Wheelers the SMART Choice for Urban Mobility PTWs: the SMART Choice For Urban Mobility Europe s cities are main engines of economic growth, but today s urbanisation
Chapter 4. Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus. October 2016
 Chapter 4 Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus October 2016 This chapter should be cited as ERIA (2016), Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus, in Kutani, I. and Y. Sado (eds.), Addressing Energy Efficiency
Chapter 4 Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus October 2016 This chapter should be cited as ERIA (2016), Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus, in Kutani, I. and Y. Sado (eds.), Addressing Energy Efficiency
Johannesburg Inner City Traffic & Transportation Study
 Johannesburg Inner City Traffic & Transportation Study Executive Summary Final March 2010 March 2010 JICTTS Executive Summary - Final 1 Contents Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Purpose of Report 1.2. Terms
Johannesburg Inner City Traffic & Transportation Study Executive Summary Final March 2010 March 2010 JICTTS Executive Summary - Final 1 Contents Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Purpose of Report 1.2. Terms
Energy Technical Memorandum
 Southeast Extension Project Lincoln Station to RidgeGate Parkway Prepared for: Federal Transit Administration Prepared by: Denver Regional Transportation District May 2014 Table of Contents Page No. Chapter
Southeast Extension Project Lincoln Station to RidgeGate Parkway Prepared for: Federal Transit Administration Prepared by: Denver Regional Transportation District May 2014 Table of Contents Page No. Chapter
5. OPPORTUNITIES AND NEXT STEPS
 5. OPPORTUNITIES AND NEXT STEPS When the METRO Green Line LRT begins operating in mid-2014, a strong emphasis will be placed on providing frequent connecting bus service with Green Line trains. Bus hours
5. OPPORTUNITIES AND NEXT STEPS When the METRO Green Line LRT begins operating in mid-2014, a strong emphasis will be placed on providing frequent connecting bus service with Green Line trains. Bus hours
Light rail, Is New Zealand Ready for Light Rail? What is Needed in Terms of Patronage, Density and Urban Form.
 Light rail, Is New Zealand Ready for Light Rail? What is Needed in Terms of Patronage, Density and Urban Form. THE PROBLEM LIGHT RAIL THE SOLUTION? INTRODUCTION Light rail transit (LRT) provides the opportunity
Light rail, Is New Zealand Ready for Light Rail? What is Needed in Terms of Patronage, Density and Urban Form. THE PROBLEM LIGHT RAIL THE SOLUTION? INTRODUCTION Light rail transit (LRT) provides the opportunity
Seoul Transportation
 Seoul Transportation September 2014 Joonho Ko, Ph.D. Director, Megacity Research Center The Seoul Institute Contents Ⅰ. Past & Now 3 Ⅱ. Vision 1 5 Ⅲ. Implementation 1 9 Ⅰ. Past & Now 1. Past & Now Seoul
Seoul Transportation September 2014 Joonho Ko, Ph.D. Director, Megacity Research Center The Seoul Institute Contents Ⅰ. Past & Now 3 Ⅱ. Vision 1 5 Ⅲ. Implementation 1 9 Ⅰ. Past & Now 1. Past & Now Seoul
Public Transportation Problems and Solutions in the Historical Center of Quito
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1266 205 Public Transportation Problems and Solutions in the Historical Center of Quito JACOB GREENSTEIN, Lours BERGER, AND AMIRAM STRULOV Quito, the capital of Ecuador,
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1266 205 Public Transportation Problems and Solutions in the Historical Center of Quito JACOB GREENSTEIN, Lours BERGER, AND AMIRAM STRULOV Quito, the capital of Ecuador,
Structure. Transport and Sustainability. Lessons from Past. The Way Forward
 1 Structure Transport and Sustainability Lessons from Past The Way Forward 2 Transport and Sustainability Consequences for fuel demand By 2025 more than half of the population in SSA will be living in
1 Structure Transport and Sustainability Lessons from Past The Way Forward 2 Transport and Sustainability Consequences for fuel demand By 2025 more than half of the population in SSA will be living in
Doubling the Market Share of Public Transport Worldwide by 2025: A Smart Future for Cities
 Doubling the Market Share of Public Transport Worldwide by 2025: A Smart Future for Cities Dawn CHUI International Association of Public Transport (UITP) Contents 1. What would happen in 2025 if current
Doubling the Market Share of Public Transport Worldwide by 2025: A Smart Future for Cities Dawn CHUI International Association of Public Transport (UITP) Contents 1. What would happen in 2025 if current
Transport Sector Performance Indicators: Sri Lanka Existing Situation
 Transport Sector Performance Indicators: Sri Lanka Existing Situation Amal S. Kumarage Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Moratuwa Chairman, National Transport Commission kumarage@sltnet.lk
Transport Sector Performance Indicators: Sri Lanka Existing Situation Amal S. Kumarage Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Moratuwa Chairman, National Transport Commission kumarage@sltnet.lk
Office of Transportation Bureau of Traffic Management Downtown Parking Meter District Rate Report
 Office of Transportation Bureau of Traffic Management 1997 Downtown Parking Meter District Rate Report Introduction The City operates approximately 5,600 parking meters in the core area of downtown. 1
Office of Transportation Bureau of Traffic Management 1997 Downtown Parking Meter District Rate Report Introduction The City operates approximately 5,600 parking meters in the core area of downtown. 1
Public Meeting. City of Chicago Department of Transportation & Department of Housing and Economic Development
 Public Meeting City of Chicago Department of Transportation & Department of Housing and Economic Development Funded by Regional Transportation Authority September 12, 2011 In partnership with Presentation
Public Meeting City of Chicago Department of Transportation & Department of Housing and Economic Development Funded by Regional Transportation Authority September 12, 2011 In partnership with Presentation
The project faces a number of challenges:
 On-Track Light Rail Project The Ministry of Transport of the city of Gotham is proposing to construct an elevated 20- kilometer light rail transit (LRT) with 5 passenger stations, connecting several nearby
On-Track Light Rail Project The Ministry of Transport of the city of Gotham is proposing to construct an elevated 20- kilometer light rail transit (LRT) with 5 passenger stations, connecting several nearby
Smart Green Transportation of LG CNS. Seoul Case
 Smart Green Transportation of LG CNS Seoul Case about Seoul Seoul Was about Seoul about Seoul - 1/22 Economic Growth of Korea Item 1970 2004 Differences Population 5,433,198 10,297,004 2 times Vehicles
Smart Green Transportation of LG CNS Seoul Case about Seoul Seoul Was about Seoul about Seoul - 1/22 Economic Growth of Korea Item 1970 2004 Differences Population 5,433,198 10,297,004 2 times Vehicles
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): TRANSPORT AND INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
 Urban Transport Development Investment Program (RRP MON 39256) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): TRANSPORT AND INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY A. Urban Development in Ulaanbaatar 1. Population. Ulaanbaatar
Urban Transport Development Investment Program (RRP MON 39256) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): TRANSPORT AND INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY A. Urban Development in Ulaanbaatar 1. Population. Ulaanbaatar
residents of data near walking. related to bicycling and Safety According available. available. 2.2 Land adopted by
 2. Assessment of Current Conditions and Needs In order to prepare a plan to reach the vision desired by the residents of Texarkana, it is first necessary to ascertain the current situation. Since there
2. Assessment of Current Conditions and Needs In order to prepare a plan to reach the vision desired by the residents of Texarkana, it is first necessary to ascertain the current situation. Since there
Calgary Transit and the Calgary Transportation Plan Chris Jordan, M.Sc., P.Eng. Coordinator, Strategic Transit Planning, Calgary Transit
 Calgary Transit and the Calgary Transportation Plan Chris Jordan, M.Sc., P.Eng. Coordinator, Strategic Transit Planning, Calgary Transit 1. Plan It Calgary the new Municipal Development Plan and Calgary
Calgary Transit and the Calgary Transportation Plan Chris Jordan, M.Sc., P.Eng. Coordinator, Strategic Transit Planning, Calgary Transit 1. Plan It Calgary the new Municipal Development Plan and Calgary
Policy Options to Decarbonise Urban Passenger Transport
 Policy Options to Decarbonise Urban Passenger Transport Results of expert opinion survey Guineng Chen, ITF/OECD 19 April 2018 2 INTRODUCTION The expert survey is part of the ITF Decarbonising Transport
Policy Options to Decarbonise Urban Passenger Transport Results of expert opinion survey Guineng Chen, ITF/OECD 19 April 2018 2 INTRODUCTION The expert survey is part of the ITF Decarbonising Transport
APPENDIX VMT Evaluation
 APPENDIX 2.7-2 VMT Evaluation MEMORANDUM To: From: Mr. Jonathan Frankel New Urban West, Incorporated Chris Mendiara LLG, Engineers Date: May 19, 2017 LLG Ref: 3-16-2614 Subject: Villages VMT Evaluation
APPENDIX 2.7-2 VMT Evaluation MEMORANDUM To: From: Mr. Jonathan Frankel New Urban West, Incorporated Chris Mendiara LLG, Engineers Date: May 19, 2017 LLG Ref: 3-16-2614 Subject: Villages VMT Evaluation
GO Transit s deliverable: the 2020 Service Plan
 GO Transit s deliverable: the 2020 Service Plan GO Transit s 2020 Service Plan describes GO s commitment to customers, existing and new, to provide a dramatically expanded interregional transit option
GO Transit s deliverable: the 2020 Service Plan GO Transit s 2020 Service Plan describes GO s commitment to customers, existing and new, to provide a dramatically expanded interregional transit option
Chapter 4 : THEME 2. Transportation
 Chapter 4 : THEME 2 Strengthen connections to keep the Central Area easy to reach and get around 55 Figure 4.2.1 Promote region-wide transit investments. Metra commuter rail provides service to the east,
Chapter 4 : THEME 2 Strengthen connections to keep the Central Area easy to reach and get around 55 Figure 4.2.1 Promote region-wide transit investments. Metra commuter rail provides service to the east,
Click to edit Master title style
 Nelson/Nygaard Consulting Associates SERVICE IMPROVEMENT STRATEGIES September 22, 2015 1 PROJECT OVERVIEW & WORK TO DATE 1. Extensive stakeholder involvement Throughout 2. System and market assessment
Nelson/Nygaard Consulting Associates SERVICE IMPROVEMENT STRATEGIES September 22, 2015 1 PROJECT OVERVIEW & WORK TO DATE 1. Extensive stakeholder involvement Throughout 2. System and market assessment
Recommended Vision for the Downtown Rapid Transit Network
 Recommended Vision for the Downtown Rapid Transit Network April 2008 Presentation Overview Context Transit options Assessment of options Recommended network Building the network 2 1 Rapid Our Vision Reliable
Recommended Vision for the Downtown Rapid Transit Network April 2008 Presentation Overview Context Transit options Assessment of options Recommended network Building the network 2 1 Rapid Our Vision Reliable
Error! Reference source not found.
 shown in Error! Reference source not found..5. Four scenarios are shown representing the AM and PM peak periods for the current status quo of traffic and the 2011 projected traffic with all of the public
shown in Error! Reference source not found..5. Four scenarios are shown representing the AM and PM peak periods for the current status quo of traffic and the 2011 projected traffic with all of the public
Sustainable Mobility Project 2.0 Project Overview. Sustainable Mobility Project 2.0 Mobilitätsbeirat Hamburg 01. July 2015
 Sustainable Mobility Project 2.0 Project Overview Sustainable Mobility Project 2.0 Mobilitätsbeirat Hamburg 01. July 2015 Agenda Goals of the meeting Who We Are World Business Council for Sustainable Development
Sustainable Mobility Project 2.0 Project Overview Sustainable Mobility Project 2.0 Mobilitätsbeirat Hamburg 01. July 2015 Agenda Goals of the meeting Who We Are World Business Council for Sustainable Development
Urban traffic situation and possible solutions for HANOI
 Alumnitalk 2013 Urban traffic situation and possible solutions for HANOI Hanoi, 6.2013 Dr.-Ing. Khuat Viet Hung 1 Contents Overview of Urban Transportation in Hanoi Hanoi Traffic: Problems and Causes Possible
Alumnitalk 2013 Urban traffic situation and possible solutions for HANOI Hanoi, 6.2013 Dr.-Ing. Khuat Viet Hung 1 Contents Overview of Urban Transportation in Hanoi Hanoi Traffic: Problems and Causes Possible
2 EXISTING ROUTE STRUCTURE AND SERVICE LEVELS
 2 EXISTING ROUTE STRUCTURE AND SERVICE LEVELS In the Study Area, as in most of the Metro Transit network, there are two distinct route structures. The base service structure operates all day and the peak
2 EXISTING ROUTE STRUCTURE AND SERVICE LEVELS In the Study Area, as in most of the Metro Transit network, there are two distinct route structures. The base service structure operates all day and the peak
Energy Efficiency Transport Sector
 Energy Efficiency Transport Sector Danida Fellowship Course 2015 Xianli Zhu Copenhagen Centre on Energy Efficiency (C2E2) UNEP DTU Partnership 18 August 2015 Outline Status & trends of energy use in the
Energy Efficiency Transport Sector Danida Fellowship Course 2015 Xianli Zhu Copenhagen Centre on Energy Efficiency (C2E2) UNEP DTU Partnership 18 August 2015 Outline Status & trends of energy use in the
Transportation: On the Road to Cleaner Air Did you know?
 Opposite and above State transportation officials are urging commuters to use mass transit, carpool, ride a bike, or to telecommute, in a campaign to help communities get cleaner air. Cities are also turning
Opposite and above State transportation officials are urging commuters to use mass transit, carpool, ride a bike, or to telecommute, in a campaign to help communities get cleaner air. Cities are also turning
Toward the Realization of Sustainable Mobility
 GIES 2008 Toward the Realization of Sustainable Mobility March 13, 2008 Toyota Motor Corporation Senior Technical Executive Hiroyuki Watanabe 1 CO 2 Emission from Transportation Sector Distribution by
GIES 2008 Toward the Realization of Sustainable Mobility March 13, 2008 Toyota Motor Corporation Senior Technical Executive Hiroyuki Watanabe 1 CO 2 Emission from Transportation Sector Distribution by
UTA Transportation Equity Study and Staff Analysis. Board Workshop January 6, 2018
 UTA Transportation Equity Study and Staff Analysis Board Workshop January 6, 2018 1 Executive Summary UTA ranks DART 6 th out of top 20 Transit Agencies in the country for ridership. UTA Study confirms
UTA Transportation Equity Study and Staff Analysis Board Workshop January 6, 2018 1 Executive Summary UTA ranks DART 6 th out of top 20 Transit Agencies in the country for ridership. UTA Study confirms
STRATEGIC PRIORITIES AND POLICY COMMITTEE MAY 5, 2016
 STRATEGIC PRIORITIES AND POLICY COMMITTEE MAY 5, 2016 Shift Rapid Transit Initiative Largest infrastructure project in the city s history. Rapid Transit initiative will transform London s public transit
STRATEGIC PRIORITIES AND POLICY COMMITTEE MAY 5, 2016 Shift Rapid Transit Initiative Largest infrastructure project in the city s history. Rapid Transit initiative will transform London s public transit
Yonge-Eglinton. Mobility Hub Profile. September 19, 2012 YONGE- EGLINTON
 September 19, 2012 PEEL YORK HALTON DURHAM HAMILTON TORONTO YONGE- EGLINTON MOBILITY HUBS: places of connectivity between regional and rapid transit services, where different modes of transportation come
September 19, 2012 PEEL YORK HALTON DURHAM HAMILTON TORONTO YONGE- EGLINTON MOBILITY HUBS: places of connectivity between regional and rapid transit services, where different modes of transportation come
ACT Canada Sustainable Mobility Summit Planning Innovations in Practice Session 6B Tuesday November 23, 2010
 ACT Canada Sustainable Mobility Summit Planning Innovations in Practice Session 6B Tuesday November 23, 2010 Presentation Outline Context t of Mississauga i City Centre Implementing Paid Parking and TDM
ACT Canada Sustainable Mobility Summit Planning Innovations in Practice Session 6B Tuesday November 23, 2010 Presentation Outline Context t of Mississauga i City Centre Implementing Paid Parking and TDM
Three ULTra Case Studies examples of the performance of the system in three different environments
 Three ULTra Case Studies examples of the performance of the system in three different environments airport application: London Heathrow : linking business and staff car parks through the access tunnel
Three ULTra Case Studies examples of the performance of the system in three different environments airport application: London Heathrow : linking business and staff car parks through the access tunnel
CSE CONCLAVE. ENABLING CITY ACTION PLAN FOR CLEAN AIR India Habitat Centre, New Delhi April 19-20,
 CSE CONCLAVE ENABLING CITY ACTION PLAN FOR CLEAN AIR India Habitat Centre, New Delhi April 19-20,2016 --------------------------------- Action on Emission Standards Roadmap and Controls on Vehicular Emissions
CSE CONCLAVE ENABLING CITY ACTION PLAN FOR CLEAN AIR India Habitat Centre, New Delhi April 19-20,2016 --------------------------------- Action on Emission Standards Roadmap and Controls on Vehicular Emissions
August 2, 2010 Public Meeting
 Public Meeting LYMMO Expansion Alternatives Analysis Study Purpose of study is to provide a fresh look at potential LYMMO expansion, following Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Alternatives Analysis
Public Meeting LYMMO Expansion Alternatives Analysis Study Purpose of study is to provide a fresh look at potential LYMMO expansion, following Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Alternatives Analysis
PROMOTING THE UPTAKE OF ELECTRIC AND OTHER LOW EMISSION VEHICLES
 Chair Cabinet Economic Growth and Infrastructure Committee Office of the Minister of Transport Office of the Minister of Energy and Resources PROMOTING THE UPTAKE OF ELECTRIC AND OTHER LOW EMISSION VEHICLES
Chair Cabinet Economic Growth and Infrastructure Committee Office of the Minister of Transport Office of the Minister of Energy and Resources PROMOTING THE UPTAKE OF ELECTRIC AND OTHER LOW EMISSION VEHICLES
Respecting the Rules Better Road Safety Enforcement in the European Union. ACEA s Response
 Respecting the Rules Better Road Safety Enforcement in the European Union Commission s Consultation Paper of 6 November 2006 1 ACEA s Response December 2006 1. Introduction ACEA (European Automobile Manufacturers
Respecting the Rules Better Road Safety Enforcement in the European Union Commission s Consultation Paper of 6 November 2006 1 ACEA s Response December 2006 1. Introduction ACEA (European Automobile Manufacturers
CEDAR AVENUE TRANSITWAY Implementation Plan Update
 CEDAR AVENUE TRANSITWAY Implementation Plan Update EECUTIVE SUMMARY DECEMBER 2015 Executive Summary In 2013, the Twin Cities metropolitan area s first bus rapid transit (BRT) line, the METRO Red Line,
CEDAR AVENUE TRANSITWAY Implementation Plan Update EECUTIVE SUMMARY DECEMBER 2015 Executive Summary In 2013, the Twin Cities metropolitan area s first bus rapid transit (BRT) line, the METRO Red Line,
Policy Coordination in Urban Transport Planning: Some Experience from Asia- Nepal and Japan
 Regional Expert Group Meeting on Policy Options for Sustainable Transport Development 27-29 November 2013, Incheon Policy Coordination in Urban Transport Planning: Some Experience from Asia- Nepal and
Regional Expert Group Meeting on Policy Options for Sustainable Transport Development 27-29 November 2013, Incheon Policy Coordination in Urban Transport Planning: Some Experience from Asia- Nepal and
STH 60 Northern Reliever Route Feasibility Study Report
 #233087 v3 STH 60 Northern Reliever Route Feasibility Study Report Washington County Public Works Committee Meeting September 28, 2016 1 STH 60 Northern Reliever Route Feasibility Study Hartford Area Development
#233087 v3 STH 60 Northern Reliever Route Feasibility Study Report Washington County Public Works Committee Meeting September 28, 2016 1 STH 60 Northern Reliever Route Feasibility Study Hartford Area Development
Develop ground transportation improvements to make the Airport a multi-modal regional
 Project Overview TRANSPORTATION IMPROVEMENTS WHAT ARE THE PROJECT GOALS? Transportation transportation hub. Develop ground transportation improvements to make the Airport a multi-modal regional Land Use
Project Overview TRANSPORTATION IMPROVEMENTS WHAT ARE THE PROJECT GOALS? Transportation transportation hub. Develop ground transportation improvements to make the Airport a multi-modal regional Land Use
Appendix G: Rapid Transit Technology Backgrounder July 2017
 Appendix G: Rapid Transit Technology Backgrounder This appendix provides additional details regarding Bus Rapid Transit and Light Rail Transit technologies, with examples from other systems, including:
Appendix G: Rapid Transit Technology Backgrounder This appendix provides additional details regarding Bus Rapid Transit and Light Rail Transit technologies, with examples from other systems, including:
US 29 Bus Rapid Transit Planning Board Briefing. February 16, 2017
 US 29 Bus Rapid Transit Planning Board Briefing February 16, 2017 Project Goals Improve the quality of transit service Improve mobility opportunities and choices Enhance quality of life Support master
US 29 Bus Rapid Transit Planning Board Briefing February 16, 2017 Project Goals Improve the quality of transit service Improve mobility opportunities and choices Enhance quality of life Support master
building liveable cities
 N 3-2016 building liveable cities + Combatting climate change North american mobility renaissance Holger Mette / El Panecillo hill and bus station, Quito Ecuador Deposit at 1080 Brussels - Price per copy
N 3-2016 building liveable cities + Combatting climate change North american mobility renaissance Holger Mette / El Panecillo hill and bus station, Quito Ecuador Deposit at 1080 Brussels - Price per copy
Metropolitan Council Budget Overview SFY
 Metropolitan Council Budget Overview SFY 2016-2017 H T t ti C itt House Transportation Committee February 4, 2015 Transit connects us to the places that matter Transportation Needs Grow as the Region Grows
Metropolitan Council Budget Overview SFY 2016-2017 H T t ti C itt House Transportation Committee February 4, 2015 Transit connects us to the places that matter Transportation Needs Grow as the Region Grows
IKORODU- CMS BRT EXTENSION PROJECT
 IKORODU- CMS BRT EXTENSION PROJECT A Presentation by SENIOR Environmental Specialist, Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority Mr Omoniyi Isaac, at The Regional consultation on Air Quality, Clean Vehicles
IKORODU- CMS BRT EXTENSION PROJECT A Presentation by SENIOR Environmental Specialist, Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority Mr Omoniyi Isaac, at The Regional consultation on Air Quality, Clean Vehicles
2.1 TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION. Expand regional rapid transit networks STRATEGIC DIRECTION
 TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION TRANSIT VISION 2040 defines a future in which public transit maximizes its contribution to quality of life with benefits that support a vibrant and equitable society,
TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION TRANSIT VISION 2040 defines a future in which public transit maximizes its contribution to quality of life with benefits that support a vibrant and equitable society,
TORONTO TRANSIT COMMISSION REPORT NO.
 Form Revised: February 2005 TORONTO TRANSIT COMMISSION REPORT NO. MEETING DATE: October 24, 2012 SUBJECT: DOWNTOWN RAPID TRANSIT EXPANSION STUDY (DRTES) PHASE 1 STRATEGIC PLAN ACTION ITEM RECOMMENDATIONS
Form Revised: February 2005 TORONTO TRANSIT COMMISSION REPORT NO. MEETING DATE: October 24, 2012 SUBJECT: DOWNTOWN RAPID TRANSIT EXPANSION STUDY (DRTES) PHASE 1 STRATEGIC PLAN ACTION ITEM RECOMMENDATIONS
Country Report 9. Lao PDR Country Report. Leeber Leebouapao National Economic Research Institute. March 2008
 Country Report 9 Lao PDR Country Report Leeber Leebouapao National Economic Research Institute March 2008 This chapter should be cited as Leebouapao, L. (2008), Lao PDR Country Report, in Soesastro, H.
Country Report 9 Lao PDR Country Report Leeber Leebouapao National Economic Research Institute March 2008 This chapter should be cited as Leebouapao, L. (2008), Lao PDR Country Report, in Soesastro, H.
Converting BRT to LRT in the Nation s Capital Ottawa, Canada. John Manconi City of Ottawa Ottawa, Canada
 Converting BRT to LRT in the Nation s Capital Ottawa, Canada John Manconi City of Ottawa Ottawa, Canada 1 The Challenge *Mackenzie King Bridge Ottawa, AM peak period 2 The Challenge Ottawa s population
Converting BRT to LRT in the Nation s Capital Ottawa, Canada John Manconi City of Ottawa Ottawa, Canada 1 The Challenge *Mackenzie King Bridge Ottawa, AM peak period 2 The Challenge Ottawa s population
Pedestrians, Cars, Buses and Trains? Considerations for Rapid Transit Service at Western University
 Pedestrians, Cars, Buses and Trains? Considerations for Rapid Transit Service at Western University Shift: The City of London s Rapid Transit Proposal Shift: The City of London s Rapid Transit Proposal
Pedestrians, Cars, Buses and Trains? Considerations for Rapid Transit Service at Western University Shift: The City of London s Rapid Transit Proposal Shift: The City of London s Rapid Transit Proposal
Intermodality - A Solution to the Problems of Large Urban Agglomerations. Author: Eng. Eugenia Alina Roman
 Intermodality - A Solution to the Problems of Large Urban Agglomerations Author: Eng. Eugenia Alina Roman DN1 A3 DN7 DN2 Area: 228 square kilometres A major intersection of Romania s National Road Network:
Intermodality - A Solution to the Problems of Large Urban Agglomerations Author: Eng. Eugenia Alina Roman DN1 A3 DN7 DN2 Area: 228 square kilometres A major intersection of Romania s National Road Network:
CHAPTER 9: VEHICULAR ACCESS CONTROL Introduction and Goals Administration Standards
 9.00 Introduction and Goals 9.01 Administration 9.02 Standards 9.1 9.00 INTRODUCTION AND GOALS City streets serve two purposes that are often in conflict moving traffic and accessing property. The higher
9.00 Introduction and Goals 9.01 Administration 9.02 Standards 9.1 9.00 INTRODUCTION AND GOALS City streets serve two purposes that are often in conflict moving traffic and accessing property. The higher
1 Downtown LRT Connector: Draft Concept
 Downtown LRT Connector: Draft Concept Plan November 2010 We re moving forward. Get involved. On June 21, 2010, City Council approved a street-level downtown LRT route, including a connector for the future
Downtown LRT Connector: Draft Concept Plan November 2010 We re moving forward. Get involved. On June 21, 2010, City Council approved a street-level downtown LRT route, including a connector for the future
Tulsa Transportation Management Area. Urbanized Area Surface Transportation Program
 Tulsa Transportation Management Area Urbanized Area Surface Transportation Program FFY 2022 Application Information Sponsor Location Description STP Request Other Funds Broken Arrow Elm Place: Kenosha
Tulsa Transportation Management Area Urbanized Area Surface Transportation Program FFY 2022 Application Information Sponsor Location Description STP Request Other Funds Broken Arrow Elm Place: Kenosha
Public Meeting. March 21, 2013 Mimosa Elementary School
 Public Meeting March 21, 2013 Mimosa Elementary School Today s Meeting Purpose 2 Where We Are The Process What We ve Heard and Findings Transit Technologies Station Types Break-out Session Where We Are
Public Meeting March 21, 2013 Mimosa Elementary School Today s Meeting Purpose 2 Where We Are The Process What We ve Heard and Findings Transit Technologies Station Types Break-out Session Where We Are
Downtown Transit Connector. Making Transit Work for Rhode Island
 Downtown Transit Connector Making Transit Work for Rhode Island 3.17.17 Project Evolution Transit 2020 (Stakeholders identify need for better transit) Providence Core Connector Study (Streetcar project
Downtown Transit Connector Making Transit Work for Rhode Island 3.17.17 Project Evolution Transit 2020 (Stakeholders identify need for better transit) Providence Core Connector Study (Streetcar project
Appendix C. Parking Strategies
 Appendix C. Parking Strategies Bremerton Parking Study Introduction & Project Scope Community concerns regarding parking impacts in Downtown Bremerton and the surrounding residential areas have existed
Appendix C. Parking Strategies Bremerton Parking Study Introduction & Project Scope Community concerns regarding parking impacts in Downtown Bremerton and the surrounding residential areas have existed
Ministry of Environment and Forests. Ministry of Communication
 Developments in EST in Bangladesh Ministry of Environment and Forests & Ministry of Communication Thailand, 23 25 August 2010 Modes of Transport in Bangladesh Roads -60% Waterways -14% Railways -12% Airways
Developments in EST in Bangladesh Ministry of Environment and Forests & Ministry of Communication Thailand, 23 25 August 2010 Modes of Transport in Bangladesh Roads -60% Waterways -14% Railways -12% Airways
SERVICE DESIGN GUIDELINES
 VTA TRANSIT SUSTAINABILITY POLICY: APPENDIX A SERVICE DESIGN GUIDELINES Adopted February 2007 COMMUNITYBUS LOCALBUS EXPRESSBUS BUSRAPIDTRANSIT LIGHTRAILTRANSIT STATIONAREAS S A N T A C L A R A Valley Transportation
VTA TRANSIT SUSTAINABILITY POLICY: APPENDIX A SERVICE DESIGN GUIDELINES Adopted February 2007 COMMUNITYBUS LOCALBUS EXPRESSBUS BUSRAPIDTRANSIT LIGHTRAILTRANSIT STATIONAREAS S A N T A C L A R A Valley Transportation
LOCAL. Legend. Le Roux Road which provides a link across the N1 will be extended westwards to link with the planned K73.
 N LOCAL K71 Kyalami Main Road (R55) K58 Olifantsfontein Road (R562) K73 New Road M71) Le Roux Lever Road R101 N1 Highway Old Pretoria Main Road K56 Dale Road Olifantsfontein Road (R562) PWV 5 Allan Road
N LOCAL K71 Kyalami Main Road (R55) K58 Olifantsfontein Road (R562) K73 New Road M71) Le Roux Lever Road R101 N1 Highway Old Pretoria Main Road K56 Dale Road Olifantsfontein Road (R562) PWV 5 Allan Road
Needs and Community Characteristics
 Needs and Community Characteristics Anticipate Population and Job Growth in the City Strongest density of population and jobs in Ann Arbor are within the Study Area Population expected to grow 8.4% by
Needs and Community Characteristics Anticipate Population and Job Growth in the City Strongest density of population and jobs in Ann Arbor are within the Study Area Population expected to grow 8.4% by
Location Concept Plan Amendment Recommendation Approved 2011 Concept Plan
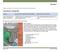 Valley Line West LRT Concept Plan Recommended Amendments Lewis Farms LRT Terminus Site Location Concept Plan Amendment Recommendation Approved 2011 Concept Plan Lewis Farms LRT terminus site, 87 Avenue/West
Valley Line West LRT Concept Plan Recommended Amendments Lewis Farms LRT Terminus Site Location Concept Plan Amendment Recommendation Approved 2011 Concept Plan Lewis Farms LRT terminus site, 87 Avenue/West
actsheet Car-Sharing
 actsheet Car-Sharing This paper was prepared by: SOLUTIONS project This project was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission Solutions project www.uemi.net The graphic
actsheet Car-Sharing This paper was prepared by: SOLUTIONS project This project was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission Solutions project www.uemi.net The graphic
London 2050 Infrastructure Plan
 London 2050 Infrastructure Plan RTPI London Future City Summit Michèle Dix 23 rd October 2014 The background to the 2050 London Infrastructure Plan is the city s expected strong population growth.. By
London 2050 Infrastructure Plan RTPI London Future City Summit Michèle Dix 23 rd October 2014 The background to the 2050 London Infrastructure Plan is the city s expected strong population growth.. By
Cycling to work. Towards a safer, more efficient and sustainable commuting. Madrid, 20 September confederación sindical de comisiones obreras
 Kingdom of the Netherlands Cycling to work Towards a safer, more efficient and sustainable commuting Manel Ferri Mobility dept. Trade Union Confederation CCOO Madrid, 20 September 2012 Current state of
Kingdom of the Netherlands Cycling to work Towards a safer, more efficient and sustainable commuting Manel Ferri Mobility dept. Trade Union Confederation CCOO Madrid, 20 September 2012 Current state of
Proposed Program of Interrelated Projects
 DALLAS AREA RAPID TRANSIT Proposed Program of Interrelated Projects Federal Transit Administration Capital Investment Program Summer 204 INTRODUCTION The current federal transportation bill, Moving Ahead
DALLAS AREA RAPID TRANSIT Proposed Program of Interrelated Projects Federal Transit Administration Capital Investment Program Summer 204 INTRODUCTION The current federal transportation bill, Moving Ahead
Sales and Use Transportation Tax Implementation Plan
 Sales and Use Transportation Tax Implementation Plan Transportation is more than just a way of getting from here to there. Reliable, safe transportation is necessary for commerce, economic development,
Sales and Use Transportation Tax Implementation Plan Transportation is more than just a way of getting from here to there. Reliable, safe transportation is necessary for commerce, economic development,
Attachment 5 Eglinton West LRT Planning and Technical Update
 Eglinton West LRT Planning and Technical Update 1. Introduction In July 2016, City Council approved an Eglinton West LRT with between 8 and 12 stops between Mount Dennis and Renforth Gateway, and up to
Eglinton West LRT Planning and Technical Update 1. Introduction In July 2016, City Council approved an Eglinton West LRT with between 8 and 12 stops between Mount Dennis and Renforth Gateway, and up to
RELEASED UNDER THE OFFICIAL INFORMATION ACT 1982
 Subject MINISTERIAL BRIEFING NOTE Rapid Transit in Auckland Date 1 November 2017 Briefing number BRI-1133 Contact(s) for telephone discussion (if required) Name Position Direct line Cell phone 1 st contact
Subject MINISTERIAL BRIEFING NOTE Rapid Transit in Auckland Date 1 November 2017 Briefing number BRI-1133 Contact(s) for telephone discussion (if required) Name Position Direct line Cell phone 1 st contact
