|
|
|
- Sheena Chapman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Generator, Unit Hydrogen, Seal Oil, Stator Coolant, Demin Water Plant Operations Training Huntly Power Station: Units 1-4 Assessment ID: 8014, 8012, 8009, 8015, 8016 NZQA Unit Standard: Assessment Marking Schedule /107 marks
2 Questions 1. List 4 possible causes of heat generation within the generator. (4 marks) Friction bearings, seals etc Windage air circulation due to rotating components Copper losses resistance in the windings Iron losses eddy currents, hysteresis 2. Explain the terms hot and cold gas temperature. (2 marks) The hot gas temperature is the temperature of the hydrogen gas in the generator before it is cooled by the hydrogen coolers. The cold gas temperature is the temperature of the hydrogen gas in the generator after it is cooled by the hydrogen coolers. 3. What is the normal operating pressure of hydrogen in the generator? (1 mark) a) 3.5 bar b) 3.0 bar c) 2.5 bar d) 4.0 bar 4. What is the normal operating pressure at the seals of the seal oil? (1 mark) a) 3.5 bar b) 3.0 bar c) 2.5 bar d) 4.0 bar 5. What system directly cools the hydrogen in the generator? (1 mark) a) Auxiliary cooling water b) Demin water c) Stator coolant d) Cooling water 6. What is the explosive range for hydrogen? (1 mark) a) 20% - 75% b) 4% - 95% c) 20% - 95% d) 4% - 75% 8014 Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 2
3 7. Seal Oil / Hydrogen differential pressure is normally? (1 mark) a) 1.0 bar b) 0.6 bar c) 0.5 bar d) 1.5 bar 8. What are the advantages of using hydrogen as the cooling medium in a generator? (5 marks) Low windage losses. Improved heat transfer coefficient. Hydrogen has excellent thermal conductivity. Using hydrogen as the coolant also reduces the possibility that corrosive acids will form due to corona in the generator. With the use of air, and so oxygen, nitric acid can form which will attack the insulation. With no oxygen being present the fire risk is eliminated. Gas tight enclosure ensures the no dust or air can get in. Quieter running Please assign 1 mark for each correct answer above up to a maximum of 5 marks 9. What are the disadvantages of using hydrogen? (3 marks) Risk of explosion. A CO2 system has to be installed so that it can be used to displace the hydrogen in the casing before the casing is opened for inspection or for maintenance. Additional plant is necessary. Seal oil to maintain a gas tight enclosure, hydrogen coolers, cooling water pump, alarms and instrumentation Stator frame built to withstand pressure and possible explosion Please assign 1 mark for each correct answer above up to a maximum of 3 marks 10. When purging the generator from hydrogen to CO 2, where is the CO 2 admitted and why? (2 marks) CO2 is admitted in the bottom of the alternator because it is heavier than the H 2 and will push the H 2 up and out of the alternator 11. What pressure is the generator depressurised to during a de-gas, before purging to CO 2 commences. Why is this pressure maintained during the purge process? (2 marks) The generator is depressurized to 0.5 Bar for a degass. This pressure is maintained during the purge process to ensure positive pressure is maintained in the generator hence not allowing any air from outside to mix with the gas in the generator. 12. What is the function of the electric generator heaters, and when are they turned on? (1 mark) 8014 Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 3
4 The function of the generator electric heaters is to stop the formation of moisture in the generator when the unit is shutdown. 13. Why is it important to maintain hydrogen purity? (1 mark) It is important to maintain hydrogen purity so that the hydrogen in the generator has no change of entering its explosive range. 14. What is the function of the hydrogen dryer? (1 mark) The function of the hydrogen drier is to keep the hydrogen in the generator moisture free. The reason for this is that if moisture is present in the hydrogen then insulation and corrosion problems will occur in the generator windings. 15. What is the purpose of the lute on the side of the hydrogen dryer? (1 mark) The purpose of the lute on the side of the hydrogen dryer control cabinet is that it acts as a water seal for the cabinet which is pressurised with air to stop the ingress of any flammable gas. 16. Why is the auto hydrogen make-up system not normally used? (1 mark) The auto hydrogen system is not used because if the unit develops a leak the amount of H2 being made up to the unit is not known and could go unnoticed Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 4
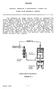
5 17. Referring to the diagram of the seal oil system (Figure 1); (15 marks) a) Discuss overall system function and operation. b) Name all key components (Use the encircled alphabetic reference callouts in your answer to refer to system features) A B C D E F G H J K L M Figure 1 A.C. Seal Oil pump A.C. Seal Oil pump Pressure Control valve D.C. Seal Oil pump Seal Oil Loop Seal Backup supply from Lub Oil system Seal Oil Cooler Filters Bearing 7 hydrogen seal Bearing 8 hydrogen seal Generator Detraining Chamber Gas Trap Oil is drawn from the seal tank by the A.C. seal oil pump (A) and passed into the system through non-return valve SO6. Pressure control valve SO52 (B) on the outlet side of the pump maintains the discharge pressure at approx. 8.6 bar. The oil then flows through isolating valve SO8, differential pressure throttle control valve SO9, isolating valve SO14, the seal oil cooler (F) and is discharged through valve 8014 Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 5
6 SO15 into one of the two filters 'A' or 'B' (G), (service and standby), which are situated downstream of the cooler. A relief valve SO27 operates as a bypass should the pressure drop across the cooler and filter become excessive. From here the oil is passed to the hydrogen seals (H, J). After passing through the hydrogen seals most of the oil discharges outwards from the seals into separation chambers. This oil then flows through sight glasses and is returned to the seal oil tank via a loop seal chamber (D) which is provided with a vapour extractor that evacuates any gas entrained in the oil. Oil which discharges inwards towards the hydrogen side of the seals is led through sight flow glasses into the hydrogen detraining chambers (L). Hydrogen released from the oil in the detraining chambers is returned to the stator casing. An internal drain line is led from the bottom of each detraining chamber through float operated valves into the hydrogen gas trap (M) where any hydrogen left in the oil vents to atmosphere. The oil then flows through the loop seal chamber (D) into the seal oil tank Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 6
7 18. Referring to the diagram of the Seal Oil Gas detraining chambers (Figure 2), briefly describe its operation. (5 marks) Figure 2 A chamber is provided for each hydrogen seal. This serves as a vessel where any hydrogen entrained in the oil, which has drained from the seal, is released and returned to the generator stator casing. The oil level in this tank is normally controlled by the float. The pressure inside the chamber (frame pressure) forces oil out to the gas trap as the level in the chamber rises due to the continual drainage from the gas side returns of the hydrogen seal. There is a back up to this float valve in the form of an air operated, solenoid controlled by-pass valve which opens if the high level mobrey switch is operated and will close when the low level mobrey switch is operated. This prevents oil backing up into the frame in the event that the float valve jams shut. The high and low mobrey switches also initiate high and low level alarms when they are operated Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 7
8 19. What is the purpose of the seal oil system? (1 mark) The purpose of the seal oil system is to provide oil to the generator hydrogen seals in order to prevent any hydrogen escaping from the generator at a controlled pressure and temperature under all operating conditions. 20. What does the oil flow from the seal sides tell you and why is it important. State the implications of too little or too much flow in this sight glass. (4 marks) The flow of oil from the seal sides tells you how much seal oil is passing through the seal to the hydrogen side of the generator. It is essential that the correct amount (3mm diameter trickle max) does flow past the sight glass so that you can be sure the seal is operating correctly and that there is also sufficient lubrication. If there is too little or no flow past the sight glass hydrogen may leak out and the seal may begin to overheat. If this occurs first check that the seal oil to hydrogen diff pressure is not low as this will put more hydrogen pressure on the seal and reduce the flow of seal oil back into the hydrogen side of the seal. If there is too much seal oil flow past the sight glass the seals may be starting to fail or have failed. Also an increase in the seal oil to hydrogen diff pressure will cause more seal oil to pass to the hydrogen side of the seal. 21. Explain the seal oil back-up Oil supply and how it works. (2 marks) The seal oil back up supply is taken from the lubricating oil discharge of the shaft driven oil pump. If the discharge pressure from the AC seal oil pump goes low (6.5 Bar) the back up supply control valve (SO28) opens supplying seal oil to the system. 22. When does the D.C. seal pump cut-in? (1 mark) The Seal Oil DC pump cuts in when selected to remote on the switch gear and auto on the CCR panel, if the seal oil / H2 diff drops below 0.34 Bar 23. What are the implications of the D.C. seal oil pump running for an extended time? (2 marks) The implications of the DC seal oil pump running for an extended time are that when the DC pump is running the seal oil is supplied directly from the pump to the seals by passing the cooler and filters, this means the oil is not cooled or filtered which could in turn overheat the seal or allow impurities to come in contact with the seal faces. 24. Explain the importance of the differential between seal oil pressure and hydrogen pressure. (1 mark) The important of the differential between the seal oil pressure and the hydrogen pressure is that the seal oil pressure needs to be higher to stop any hydrogen escaping from the generator Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 8
9 25. What is the Stator Coolant normal flow? (1 mark) a) 16.5 litre/minute b) 18.6 lites/minute c) 20 gallons/minute d) 5 gallons/minute 26. What is the Stator Coolant flow value that will generate the alarm Stator Coolant Flow Low? (1 mark) a) 14.2 litres/minute b) 14.2 gallons/minute c) 16.1 litres/minute d) 20 litres/minute 27. What is the Stator Coolant flow value that will start the standby pump? (1 mark) a) 14.2 litres/minute b) 14.2 gallons/minute c) 16.1 litres/minute d) 20 litres/minute 28. What is the trip associated with Stator Coolant flow? (1 mark) a) 5.2 litres/minute b) 16.2 gallons/minute c) 8.1 litres/minute d) 14.0 litres/minute 8014 Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 9
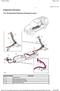
10 29. Referring to the diagram of the stator coolant system (Figure 3). (14 marks) e) Discuss overall system function and operation f) Name all key components g) Describe in detail the function and purpose of all labeled equipment items. (Use the encircled alphabetic reference callouts in your answer to refer to system features) A B C D E F G H Figure 3 Coarse strainer Fine strainer Demineralisation plant Flow measurement Stator Coolant Head tank Supply from WTP Gas Alarm and Automatic release chamber Gas Detraining chamber 8014 Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 10
11 The system is a closed circuit maintained under a constant static pressure by a make-up header tank with an internal float operated valve. The header tank (E) is supplied from the demineralised water system (F) through a strainer at the tank inlet. Two 100% duty a.c. motor driven pumps service and standby are provided to circulate the coolant around the system, via the stator coolant coolers and coolant strainers, through the resistance columns at the exciter end of the casing to the generator stator windings. Having passed through the stator windings the coolant is discharged through the resistance columns at the turbine end of the casing to the suction side of the pump via the gas detraining chamber. A branch pipe is provided in the line between the stator coolant coolers and the coolant strainers to enable approximately 3% of the flow to be passed through the demineralisation plant (C), which maintains purity of the coolant. Equipment is provided to indicate the presence of gas in the system and to allow it to be released via the gas alarm and automatic release chamber (G). Gas release pipes are run from various parts of the system to the connecting pipe between the gas detraining chamber and the gas alarm and automatic release chamber. Any gas entrained in the coolant which passes through the gas detraining chamber (H) is released into the gas alarm and automatic release chamber. The gas is then automatically discharged from the release chamber through a solenoid operated valve and an orifice into a hydrogen trap. From the hydrogen trap the gas is vented to atmosphere. Three flow transmitters are fitted in the outlet pipework at the turbine end of the stator winding. These transmitters are set to sequentially start the stator coolant pumps. Further contacts are provided to initiate a unit trip on coolant flow failure and a 'Coolant Flow Failure' alarm. To prevent the flow transmitters causing a unit trip in the event of one becoming unserviceable, two out of the three transmitters must register low flow before the tripping sequence is initiated. 30. What types of coolers are used on the stator coolant? (1 mark) The types of cooler used on the stator system are 100% capacity plate type heat exchangers. 31. Identify which strainers can be bypassed and for what reason. (1 mark) The strainer that can be bypassed is the fine strainer so that it can be cleaned with the plant in service. 32. Explain why the stator coolant system operates at a slightly lower pressure than the hydrogen system. (1 mark) The Stator coolant system operates at a slightly lower pressure than the hydrogen system so that in the event of a leak in the system the hydrogen would leak into the stator coolant Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 11
12 33. Referring to the diagram of the Stator Coolant gas release chamber (Figure 4), describe operation including alarms and operating timers by completing the sentences provided. (6 marks) Figure 4 The Gas Release Chamber has three mobrey float switches which are operated as the stator coolant level lowers (due to gas collecting). The mobreys control the automatic gas release and initiate alarms as follows. When the top level switch is operated a 20 minute timer is started. As level continues to drop due to the gas leak, one of two situations will occur. Either a) The timer times out before middle float switch is reached in which case the gas will be released and a gas in coolant alarm initiated b) Or if middle float is reached within the timer period and gas in coolant and gas in coolant excessive alarms will be initiated and gas will be released. (If the "gas in coolant excessive" alarm is initiated it means that more than 50m³/24 hours is leaking and an inspection should be carried out). If the bottom Mobrey switch is operated then the Gas in coolant alarm inoperative will be initiated which means either:- a) The solenoid valve has not opened. b) Or the gas leakage is too much for the solenoid valve to cope with. The solenoid valve shuts when the level rises above the top Mobrey switch Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 12
13 34. Explain the implications of the following alarms:- a) Stator coolant conductivity High (1 mark) Because the stator coolant comes in contact with the electrical connects in the generator the water must be pure so that it dos not conduct electricity. Alarm 600 µs/m and generator unloaded if 1000 µs/m b) Gas in coolant (1 mark) Means the system has a small leak and should be monitored c) Gas in coolant excessive (1 mark) Means the system has a leak of 50 cubic metres / 24 hours and inspection should be carried out. d) Gas in coolant alarm inoperative (1 mark) Leak is too much for the gas release chamber to cope with. e) Stator coolant make-up tank level low. (1 mark) The tank has a low level and if not topped up the system will not maintain its head causing loss of coolant to the system (system has a leak.) 35. What unit trip is associated with the stator coolant make-up tank? (1 mark) The unit trip associated with the stator coolant make up tank is a high level trip on the tank Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 13
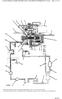
14 36. Referring to the diagram of the Generator Demin system (Figure 5); (13 marks) a) Discuss overall system function and operation b) Name all key components c) Describe the function and purpose of all labeled equipment items. (Use the encircled alphabetic reference callouts in your answer to refer to system features) A B C D E F G H J Figure 5 Demineralised Water Pumps Demineralised Water cooler Seal Oil Cooler Stator Coolant coolers Hydrogen dryer reactivation cooler Inlet manifold or waterbox Outlet manifold or waterbox Demin head tank Makeup from WTP 8014 Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 14
15 The Demin water system is a closed circuit cooling water circuit which operates under a static head pressure provided by the demin water make-up/head tank (H). Demineralised water from the water treatment plant (J) and 1000ton tank common discharge supplies the make-up water to the demin make-up tank. The outlet from the make-up tank connects to the system at the demin pumps inlet. Water is discharged from the i/s pump through a NRV and discharge valve to the i/s cooler (B). From the cooler s common discharge pipe the demin water travels in parallel paths; through the seal oil cooler (C), through the i/s stator coolant cooler (D), through the hydrogen dryer reactivation cooler (E), and through the four hydrogen coolers via the hydrogen coolers inlet (F) and outlet (G) manifolds. The seal oil cooler, the stator coolant coolers and the demin coolers all have a bypass control valve for their systems temperature control. The four parallel paths meet back up at the demin pump s suction pipe. 37. Where does the make-up to demin system come from? (1 mark) The make up for the demin system comes from the RFW (WTP) system 38. Explain how the make-up tank level is controlled (1 mark) The level in the make up tank is controlled by a ball cock on the tank inlet Written Assessment Marking Schedule.doc Genesis Energy 15
(770) Turning Parts Changers Into TROUBLESHOOTERS!
 Hydraulic Consulting, Inc. Turning Parts Changers Into TROUBLESHOOTERS! This e-book manual is your customized troubleshooting manual in Adobe Acrobat Portable Document File (PDF) format. It requires the
Hydraulic Consulting, Inc. Turning Parts Changers Into TROUBLESHOOTERS! This e-book manual is your customized troubleshooting manual in Adobe Acrobat Portable Document File (PDF) format. It requires the
Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance Fire Pumps NFPA 25, Chapter 8 as amended by CCR, Title 19 Page 1 of 8
 , Chapter 8 as amended by CCR, Title 19 Page 1 of 8 Address: City: Date of Pump Test: Shaft Orientation: Horizontal Vertical Annual Fire Pump Test Results Number of pumps at this location: If multiple
, Chapter 8 as amended by CCR, Title 19 Page 1 of 8 Address: City: Date of Pump Test: Shaft Orientation: Horizontal Vertical Annual Fire Pump Test Results Number of pumps at this location: If multiple
Appendix A. Standard Symbols for Hydraulic Components
 Table B.1 Flow lines Appendix A Standard Symbols for Components Continuous flow E Pilot connection L L>10E E Drain connection L L
Table B.1 Flow lines Appendix A Standard Symbols for Components Continuous flow E Pilot connection L L>10E E Drain connection L L
SEASONAL MAINTENANCE CHECKLISTS Johnson Controls
 SPRING CHECK LIST ABSORPTION CHILLERS Check starter and control panel. Leak test. Check hand valve diaphragms and replace as required. Check operation of purge unit. Change oil in the purge pump. Lubricate
SPRING CHECK LIST ABSORPTION CHILLERS Check starter and control panel. Leak test. Check hand valve diaphragms and replace as required. Check operation of purge unit. Change oil in the purge pump. Lubricate
A system of lubricant dispensing devices (oil or grease) connected by piping to a central pumping unit that is operated automatically or manually.
 Air/Oil Systems: A lubrication system in which small measured quantities of oil are introduced into an air/oil mixing device which is connected to a lube line that terminates at a bearing, or other lubrication
Air/Oil Systems: A lubrication system in which small measured quantities of oil are introduced into an air/oil mixing device which is connected to a lube line that terminates at a bearing, or other lubrication
6. Document tasks performed during visit and report any observations to the appropriate
 Chiller Annual Maintenance RFP Attachment B Services Required Tasking: Vibration Analysis 1. All work shall be performed in accordance with safety policies 2. Check with appropriate customer representative
Chiller Annual Maintenance RFP Attachment B Services Required Tasking: Vibration Analysis 1. All work shall be performed in accordance with safety policies 2. Check with appropriate customer representative
Secondary Coolant 301
 Secondary Coolant 301 Instructor Rusty Walker Hill PHOENIX Learning Center Secondary Coolant 301 Start-Up Procedures Secondary Coolant 301 Objectives Describe the initial startup procedures for a medium
Secondary Coolant 301 Instructor Rusty Walker Hill PHOENIX Learning Center Secondary Coolant 301 Start-Up Procedures Secondary Coolant 301 Objectives Describe the initial startup procedures for a medium
LACT MEASUREMENT. Total Head = Or PSI = S.G. 2.31
 LACT MEASUREMENT Prepared By: Ken A. Steward. P.E. Linco-Electromatic, Inc. 4580 West Wall Street Midland, Texas 79703 The Operation of L.A.C.T. Units The simplest approach to the understanding of the
LACT MEASUREMENT Prepared By: Ken A. Steward. P.E. Linco-Electromatic, Inc. 4580 West Wall Street Midland, Texas 79703 The Operation of L.A.C.T. Units The simplest approach to the understanding of the
OPERATOR S MANUAL AND PARTS LIST
 Portable Air Compressor 300HH, 375, 375H a n d 425 Ex p o r t Caterpillar Standard and Aftercooled and Filtered Part Number: 02250169-733 keep for future reference Sullair corporation The information in
Portable Air Compressor 300HH, 375, 375H a n d 425 Ex p o r t Caterpillar Standard and Aftercooled and Filtered Part Number: 02250169-733 keep for future reference Sullair corporation The information in
Copeland Screw Compressors Semi-Hermetic Compact Operating Instructions
 Copeland Screw Compressors Semi-Hermetic Compact Operating Instructions SCH2 & SCA2 High Temperature Compressors 35-240 Horsepower 1. Introduction This series of semi-hermetic compact screw compressors
Copeland Screw Compressors Semi-Hermetic Compact Operating Instructions SCH2 & SCA2 High Temperature Compressors 35-240 Horsepower 1. Introduction This series of semi-hermetic compact screw compressors
Check Valves Check Valves are the simplest form of directional control valves, but they can also be used as pressure controls.
 Check Valves Check Valves are the simplest form of directional control valves, but they can also be used as pressure controls. Standard Check Valve The standard check valve permits free flow in one direction
Check Valves Check Valves are the simplest form of directional control valves, but they can also be used as pressure controls. Standard Check Valve The standard check valve permits free flow in one direction
Installation, Operating, Maintenance and Safety Instructions for CW332 Pressurised water system for boats 24 volt d.c.
 24V DC-CW332 DOC531/11 Installation, Operating, Maintenance and Safety Instructions for CW332 Pressurised water system for boats 24 volt d.c. To obtain the best performance from your Pressurised water
24V DC-CW332 DOC531/11 Installation, Operating, Maintenance and Safety Instructions for CW332 Pressurised water system for boats 24 volt d.c. To obtain the best performance from your Pressurised water
Section 3 Technical Information
 Section 3 Technical Information In this Module: Engine identification Modes of operation Battery charging and heat manage operation Service and repair procedures Maintenance requirements Engine Identification
Section 3 Technical Information In this Module: Engine identification Modes of operation Battery charging and heat manage operation Service and repair procedures Maintenance requirements Engine Identification
Pressure Reducing Valve Type 2114/2415
 Pressure Reducing Valve Type 2114/2415 Fig. 1 Type 2114/2415 1. Design and principle of operation The Type 2114/2415 Pressure Reducing Valve consists of the Type 2114 Valve and the Type 2415 Actuator.
Pressure Reducing Valve Type 2114/2415 Fig. 1 Type 2114/2415 1. Design and principle of operation The Type 2114/2415 Pressure Reducing Valve consists of the Type 2114 Valve and the Type 2415 Actuator.
Section 13 - E. 1 of 18. Engine Systems
 Engine Systems 1 of 18 ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM Introduction The fuel system uses electronic, hydraulic and mechanical functions to regulate the power and adapt it to the requirements at any one time. Air pressure
Engine Systems 1 of 18 ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM Introduction The fuel system uses electronic, hydraulic and mechanical functions to regulate the power and adapt it to the requirements at any one time. Air pressure
Schuyler McElrath Gas Turbine Consultant JASC: Jansen s Aircraft Systems Controls, Inc
 Fuel flexibility and reliability in Combined Cycle gas turbine applications Schuyler McElrath Gas Turbine Consultant JASC: Jansen s Aircraft Systems Controls, Inc schuyler@jasc-controls.com www.jasc-controls.com
Fuel flexibility and reliability in Combined Cycle gas turbine applications Schuyler McElrath Gas Turbine Consultant JASC: Jansen s Aircraft Systems Controls, Inc schuyler@jasc-controls.com www.jasc-controls.com
BOILER PM & INSPECTION
 BOILER PM & INSPECTION Record inspection log for Gaming Commission and Safety Department. The following listed maintenance items are not intended to be a complete list. Follow any additional maintenance
BOILER PM & INSPECTION Record inspection log for Gaming Commission and Safety Department. The following listed maintenance items are not intended to be a complete list. Follow any additional maintenance
Pump Acceptance Test Data
 Customer Location: 500 Base Ave East Venice, Fl. 34275 941-485-5402 941-483-3321 Fax Pump Acceptance Test Data Division: Customer Number: Date: City & State Work Order: Technician: PUMP IF VERTICAL TYPE
Customer Location: 500 Base Ave East Venice, Fl. 34275 941-485-5402 941-483-3321 Fax Pump Acceptance Test Data Division: Customer Number: Date: City & State Work Order: Technician: PUMP IF VERTICAL TYPE
Fluid Maintenance. The hydraulic oil performs four functions in the hydraulic system:
 The hydraulic oil performs four functions in the hydraulic system: Transmits Energy Coolant Lubricant Sealant Viscosity Viscosity is the rating of the oil thickness or resistance to flow. Viscosity is
The hydraulic oil performs four functions in the hydraulic system: Transmits Energy Coolant Lubricant Sealant Viscosity Viscosity is the rating of the oil thickness or resistance to flow. Viscosity is
Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234
 Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234 STEAM VALVE HYDRAULIC CONTROL The movement of large control valves to regulate the steam supply to modern steam turbines, requires amplification of the control
Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234 STEAM VALVE HYDRAULIC CONTROL The movement of large control valves to regulate the steam supply to modern steam turbines, requires amplification of the control
LECTURE 30 to 31 ACCESSORIES USED IN FLUID POWER SYSTEMS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 LECTURE 30 to 31 ACCESSORIES USED IN FLUID POWER SYSTEMS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Explain the two types of the leakages in hydraulic system. In what way do they affect the performance of a fluid system?
LECTURE 30 to 31 ACCESSORIES USED IN FLUID POWER SYSTEMS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Explain the two types of the leakages in hydraulic system. In what way do they affect the performance of a fluid system?
ROGERS MACHINERY COMPANY, INC
 KOBELCO KNW SERIES Sample Specifications AIR-COOLED, OIL-FREE AIR COMPRESSOR Frame 0, 1, 2 50 500 HP ROGERS 2110_KA.doc Effective: 03-24-17 Supersedes: 04-06-15 Page 1 of 9 1. SPECIFICATIONS SCOPE 1.1
KOBELCO KNW SERIES Sample Specifications AIR-COOLED, OIL-FREE AIR COMPRESSOR Frame 0, 1, 2 50 500 HP ROGERS 2110_KA.doc Effective: 03-24-17 Supersedes: 04-06-15 Page 1 of 9 1. SPECIFICATIONS SCOPE 1.1
PACKAGED LIQUID CHILLER 6. HUMIDIFIER SECTIONS. C Member. Liquid Chiller. nowlc And noalc Series
 6. HUMIDIFIER SECTIONS Liquid Chiller nowlc And noalc Series C Member 1 Features and Benefits OMRAN cold generator reciprocating Liquid chiller are designed and built to provide reliable,efficient performance
6. HUMIDIFIER SECTIONS Liquid Chiller nowlc And noalc Series C Member 1 Features and Benefits OMRAN cold generator reciprocating Liquid chiller are designed and built to provide reliable,efficient performance
GENCORE 5 FUEL CELL SYSTEM System Fundamentals
 GENCORE 5 FUEL CELL SYSTEM System Fundamentals GenCore 5T48 GenCore 5B48 GenCore 5U48 GenCore 5T24 GenCore 5U120 Revision 1 December 1, 2004 GENCORE DESCRIPTION GenCore fuel cell systems are direct hydrogen
GENCORE 5 FUEL CELL SYSTEM System Fundamentals GenCore 5T48 GenCore 5B48 GenCore 5U48 GenCore 5T24 GenCore 5U120 Revision 1 December 1, 2004 GENCORE DESCRIPTION GenCore fuel cell systems are direct hydrogen
Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance MP-SEE-THRU-01 Rev. 018
 Student Operating Procedure Millstone Station Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance Approval Date: 01/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/12/2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE...3
Student Operating Procedure Millstone Station Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance Approval Date: 01/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/12/2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE...3
Sample Specifications 2110_KA.DOC KOBELCO KNW SERIES 1 OF 10 AIR-COOLED, OIL FREE AIR COMPRESSOR Frame 0, 1, HP
 KOBELCO KNW SERIES 1 OF 10 1. SPECIFICATIONS SCOPE 1.1 This specification covers the requirement for supply of a packaged oil-free rotary screw air compressor, Kobelco KNW Series model. 1.2 Any and all
KOBELCO KNW SERIES 1 OF 10 1. SPECIFICATIONS SCOPE 1.1 This specification covers the requirement for supply of a packaged oil-free rotary screw air compressor, Kobelco KNW Series model. 1.2 Any and all
Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers
 Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges Pressure gauges Pressure gauges should be installed in at least the following situations: Upstream of a pressure
Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges Pressure gauges Pressure gauges should be installed in at least the following situations: Upstream of a pressure
SECTION 3.00 WARNING WARNING ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION
 SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: TF Configuration TB Configurations Implement Control Valve:
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
MONOVAR is the energy dissipating valve.
 MONOVAR is the energy dissipating valve. Features Extremely simple design (patented) Excellent cavitation characteristics Very accurate flow or pressure control Manual or automatic control Suitable for
MONOVAR is the energy dissipating valve. Features Extremely simple design (patented) Excellent cavitation characteristics Very accurate flow or pressure control Manual or automatic control Suitable for
XCITE Owner s Manual. Reso-not TM Damping System XCITE 1502C HYDRAULIC POWER SUPPLY
 Reso-not TM Damping System XCITE Owner s Manual 1502C HYDRAULIC POWER SUPPLY Xcite Systems Corporation 675 Cincinnati RDS Batavia - 1 Pike Cincinnati, Ohio 45245 Tel: (239) 980-9093 Fax: (239) 985-0074
Reso-not TM Damping System XCITE Owner s Manual 1502C HYDRAULIC POWER SUPPLY Xcite Systems Corporation 675 Cincinnati RDS Batavia - 1 Pike Cincinnati, Ohio 45245 Tel: (239) 980-9093 Fax: (239) 985-0074
DESIGN, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE OF L.A.C.T. UNITS
 DESIGN, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE OF L.A.C.T. UNITS INTRODUCTION The two most common methods of measuring the volume of petroleum liquids are tank gauging and liquid metering. The problems associated with
DESIGN, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE OF L.A.C.T. UNITS INTRODUCTION The two most common methods of measuring the volume of petroleum liquids are tank gauging and liquid metering. The problems associated with
4.2 Component Identification
 Digital Control Panels Deep Sea Electronics 5220 4.1 General 4.2 Component Identification 4.3 The YML5220 Controller 4.4 Description of Controls 4.5 Navigation 4.5.1 General Navigation 4.5.2 The Event
Digital Control Panels Deep Sea Electronics 5220 4.1 General 4.2 Component Identification 4.3 The YML5220 Controller 4.4 Description of Controls 4.5 Navigation 4.5.1 General Navigation 4.5.2 The Event
Heating and Gas Installations - December 2014
 This is an example of good practice maintenance specifications. It is not exhaustive and should only be used to assist with facilities management or specification of a maintenance contract. Emergency Gas
This is an example of good practice maintenance specifications. It is not exhaustive and should only be used to assist with facilities management or specification of a maintenance contract. Emergency Gas
SUB-CHAPTER E.4 DESIGN OF COMPONENTS AND SUB-SYSTEMS
 PAGE : 1 / 11 SUB-CHAPTER E.4 DESIGN OF COMPONENTS AND SUB-SYSTEMS 1. REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS 1.1. DESCRIPTION OF REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS The reactor coolant pumps (GMPP) [RCP] are assigned at RCC-M level
PAGE : 1 / 11 SUB-CHAPTER E.4 DESIGN OF COMPONENTS AND SUB-SYSTEMS 1. REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS 1.1. DESCRIPTION OF REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS The reactor coolant pumps (GMPP) [RCP] are assigned at RCC-M level
Starting up hydraulic systems
 General / Installation A hydraulic system that operates economically, safely, and trouble-free requires careful planning, as well as proper installation and start-up. Conscientious maintenance has a considerable
General / Installation A hydraulic system that operates economically, safely, and trouble-free requires careful planning, as well as proper installation and start-up. Conscientious maintenance has a considerable
7. Evaporative Emission Control System
 W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
Sealless Magnetic Coupled Hot Oil Circulation Pumps acc. to DIN EN / ISO 2858 Type NMWR / NMWB / NMW. our. contribution for
 Sealless Magnetic Coupled Hot Oil Circulation Pumps acc. to DIN EN 22858 / ISO 2858 Type NMWR / NMWB / NMW our contribution for environmental protection General DICKOW pumps of series NMWR / NMWB / NMW
Sealless Magnetic Coupled Hot Oil Circulation Pumps acc. to DIN EN 22858 / ISO 2858 Type NMWR / NMWB / NMW our contribution for environmental protection General DICKOW pumps of series NMWR / NMWB / NMW
MANIFOLDS & WATER TEMPERATURE CONTROL
 MANIFOLDS & WATER TEMPERATURE CONTROL Overview Water based underfloor heating (UFH) systems work by turning the entire floor into one large low temperature radiator which is heated via a network of pipes
MANIFOLDS & WATER TEMPERATURE CONTROL Overview Water based underfloor heating (UFH) systems work by turning the entire floor into one large low temperature radiator which is heated via a network of pipes
MOBILE FIRE - RESCUE DEPARTMENT FIRE CODE ADMINISTRATION
 MOBILE FIRE - RESCUE DEPARTMENT FIRE CODE ADMINISTRATION Fire Pump Acceptance Inspection Date of Review / / BLD20 - Project Address: Project Name: Numbers following worksheet comments represent an NFPA
MOBILE FIRE - RESCUE DEPARTMENT FIRE CODE ADMINISTRATION Fire Pump Acceptance Inspection Date of Review / / BLD20 - Project Address: Project Name: Numbers following worksheet comments represent an NFPA
NECO Pumping Systems
 INSTALLATION OPERATION & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS For Your NECO Pumping Systems PACKAGED CIRCULATING SYSTEM THIS COMPLETELY ASSEMBLED, TESTED, PACKAGED CIRCULATING SYSTEM IS OF THE HIGHEST QUALITY AND
INSTALLATION OPERATION & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS For Your NECO Pumping Systems PACKAGED CIRCULATING SYSTEM THIS COMPLETELY ASSEMBLED, TESTED, PACKAGED CIRCULATING SYSTEM IS OF THE HIGHEST QUALITY AND
AIR COOLED CHILLERS WATER COOLED CHILLERS
 AIR COOLED CHILLERS WATER COOLED CHILLERS STANDARD UNIT SPECIFICATIONS OF COMMERCIAL AIR COOLED CHILLERS General Description & Assembly Air Cooled Chillers are commercial packaged systems complete with
AIR COOLED CHILLERS WATER COOLED CHILLERS STANDARD UNIT SPECIFICATIONS OF COMMERCIAL AIR COOLED CHILLERS General Description & Assembly Air Cooled Chillers are commercial packaged systems complete with
IS7.6 INSTALLATION MANUAL
 IS7.6 INSTALLATION MANUAL #12501 MIN. 13.5" 1" 1" 29-7/8" 3" 14-7/8" 3" 20-7/8" 29-7/8" 24-5/8" Fig. 1 1 2 Fig. 2 Fig. 3 MAX. 80" MIN. 12" IS7.6 MIN. 8" Fig. 4 2 MIN. 6" MIN. 13.5" MIN. 12" MIN. 6" MIN.
IS7.6 INSTALLATION MANUAL #12501 MIN. 13.5" 1" 1" 29-7/8" 3" 14-7/8" 3" 20-7/8" 29-7/8" 24-5/8" Fig. 1 1 2 Fig. 2 Fig. 3 MAX. 80" MIN. 12" IS7.6 MIN. 8" Fig. 4 2 MIN. 6" MIN. 13.5" MIN. 12" MIN. 6" MIN.
M3770: SOLENOID CONTROLLED / ELECTRICALLY POSITIONED VALVE - STEP BY STEP VALVE
 ST M3770 ENG STA R1 04/17 M3770: SOLENOID CONTROLLED / ELECTRICALLY POSITIONED VALVE - STEP BY STEP VALVE DN300 to DN1000 OPERATING PRINCIPLE The valve is equipped with two solenoids, both configured standard
ST M3770 ENG STA R1 04/17 M3770: SOLENOID CONTROLLED / ELECTRICALLY POSITIONED VALVE - STEP BY STEP VALVE DN300 to DN1000 OPERATING PRINCIPLE The valve is equipped with two solenoids, both configured standard
TECHNICAL PAPER 1002 FT. WORTH, TEXAS REPORT X ORDER
 I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
RELIABLE AND EFFICIENT SYSTEMS
 RELIABLE AND EFFICIENT SYSTEMS Systems must be leak-free as possible All systems leak Piping materials are slightly porous Very small leaks are not detectable and do not affect system efficiency Some systems
RELIABLE AND EFFICIENT SYSTEMS Systems must be leak-free as possible All systems leak Piping materials are slightly porous Very small leaks are not detectable and do not affect system efficiency Some systems
Section 7.1. Wheel Drive Circuit - General System
 Section 7.1 Wheel Drive Circuit - General System Simplified Travel Circuit Diagrams: Neutral Controls... 7.1.2 Forward Travel... 7.1.4 Reverse Travel... 7.1.5 General... 7.1.3 Wheel Drive Circuit: General...
Section 7.1 Wheel Drive Circuit - General System Simplified Travel Circuit Diagrams: Neutral Controls... 7.1.2 Forward Travel... 7.1.4 Reverse Travel... 7.1.5 General... 7.1.3 Wheel Drive Circuit: General...
3. Fuel System FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-7
 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
Installation, Operation & Service Manual. PPL Bag Filter Housings. Table of Contents Page No. Eaton Filtration, LLC
 Installation, Operation & Service Manual PPL Bag Filter Housings Eaton Filtration, LLC 900 Fairmount Avenue, Elizabeth, NJ 07207 Read all instructions before installation or operation of equipment. Failure
Installation, Operation & Service Manual PPL Bag Filter Housings Eaton Filtration, LLC 900 Fairmount Avenue, Elizabeth, NJ 07207 Read all instructions before installation or operation of equipment. Failure
Model DE-3 Air Release Heads Parts List
 Issue/Rev. 0.0 (1/14) Smith Meter Air Eliminator Model DE-3 Air Release Heads Parts List Bulletin MN03021 Contents Section 1 Introduction... Page 2 Principle of Operation... Page 2 Section 2 Installation...
Issue/Rev. 0.0 (1/14) Smith Meter Air Eliminator Model DE-3 Air Release Heads Parts List Bulletin MN03021 Contents Section 1 Introduction... Page 2 Principle of Operation... Page 2 Section 2 Installation...
Page 1 of 5. Project : CATERPILLAR CM GENSETS PROJECT (RADIATOR COOLING) 2 x 16CM32, 6.3 kv, 50 Hz. TUS(S)PL Supply. Customer Supply DESCRIPTION
 2 x 16CM32, 6.3 kv, 50 Hz GENSET PORTION 1.1 DIESEL ENGINE - CATERPILLAR 16CM32 2 1.2 Additional engine components (mounted on the engine) Electric turning devices 2 Gauge panels 2 Governors 2 Electric
2 x 16CM32, 6.3 kv, 50 Hz GENSET PORTION 1.1 DIESEL ENGINE - CATERPILLAR 16CM32 2 1.2 Additional engine components (mounted on the engine) Electric turning devices 2 Gauge panels 2 Governors 2 Electric
Tests & Adjustments - General Machine. General Safety Hydraulic Tank Turbo Boost Regulator
 Section 8.1 Tests & Adjustments - General Machine General Safety......................................... 8.1.2 Hydraulic Tank Turbo Boost Regulator........................ 8.1.2 Hydraulic Tank Safety
Section 8.1 Tests & Adjustments - General Machine General Safety......................................... 8.1.2 Hydraulic Tank Turbo Boost Regulator........................ 8.1.2 Hydraulic Tank Safety
abc CPD7948/075 Rotors, rotor shafts and rotor casings are coated with an anti-corrosive and anti wear coating to prolong element life and efficiency.
 CPD7948/075 Specification Oil-Free, Air Cooled, Rotary Screw Compressors - Dryclon Range Models D75, D90, D110, D132, D150 (50Hz) D55, D75, D90, D110, D150 (60Hz) COMPRESSOR PACKAGE An enclosed two stage
CPD7948/075 Specification Oil-Free, Air Cooled, Rotary Screw Compressors - Dryclon Range Models D75, D90, D110, D132, D150 (50Hz) D55, D75, D90, D110, D150 (60Hz) COMPRESSOR PACKAGE An enclosed two stage
Operation of the FFBH is enabled and disabled by the Automatic Temperature Control Module (ATCM).
 Page 1 of 8 Published : Apr 22, 2004 Auxiliary Heater COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 - Fuel line connection with fuel tank 2 - Auxiliary fuel pump 3 - Fuel fired booster heater GENERAL
Page 1 of 8 Published : Apr 22, 2004 Auxiliary Heater COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 - Fuel line connection with fuel tank 2 - Auxiliary fuel pump 3 - Fuel fired booster heater GENERAL
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Name Date. True-False. Multiple Choice
 Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Routine Compressor Maintenance
 Establishing a regular, well-organized maintenance program and strictly following it is critical to maintaining the performance of a compressed air system. One person should be given the responsibility
Establishing a regular, well-organized maintenance program and strictly following it is critical to maintaining the performance of a compressed air system. One person should be given the responsibility
Medium and high pressure pumps
 Screw pumps Medium and high pressure pumps Installation and Start-up Instruction This instruction is valid for all standard high pressure pumps: E4, D4 and D6 Contents Page Pump identification 2 Installation
Screw pumps Medium and high pressure pumps Installation and Start-up Instruction This instruction is valid for all standard high pressure pumps: E4, D4 and D6 Contents Page Pump identification 2 Installation
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
AUTOGAS 150 SERIES PUMPS INSTALLATION GUIDELINES FOR UNDERGROUND TANK APPLICATIONS
 Application Bulletin A Unit of IDEX Corporation No. 13 June 21 AUTOGAS 1 SERIES PUMPS INSTALLATION GUIDELINES FOR UNDERGROUND TANK APPLICATIONS CORKEN, INC. A Unit of IDEX Corporation P.O. Box 12338, Oklahoma
Application Bulletin A Unit of IDEX Corporation No. 13 June 21 AUTOGAS 1 SERIES PUMPS INSTALLATION GUIDELINES FOR UNDERGROUND TANK APPLICATIONS CORKEN, INC. A Unit of IDEX Corporation P.O. Box 12338, Oklahoma
ROGERS MACHINERY COMPANY, INC
 KOBELCO KNW SERIES Sample Specifications ROGERS MACHINERY COMPANY, INC WATER-COOLED, OIL-FREE AIR COMPRESSOR Frame 00 20-50 HP 2110_00.doc Effective: 03/24/17 Supersedes: 10-11-13 Page 1 of 8 1. SPECIFICATION
KOBELCO KNW SERIES Sample Specifications ROGERS MACHINERY COMPANY, INC WATER-COOLED, OIL-FREE AIR COMPRESSOR Frame 00 20-50 HP 2110_00.doc Effective: 03/24/17 Supersedes: 10-11-13 Page 1 of 8 1. SPECIFICATION
ALTERNATOR STARTUP Turning gear to full operation. Procedure initiated by:. 7/03 Before starting procedure, remove all check marks.
 ALTERNATOR STARTUP Turning gear to full operation. Procedure initiated by:. 7/03 Before starting procedure, remove all check marks. 1. Check log book for incomplete compliance for further operation. 2.
ALTERNATOR STARTUP Turning gear to full operation. Procedure initiated by:. 7/03 Before starting procedure, remove all check marks. 1. Check log book for incomplete compliance for further operation. 2.
Input, Control and Processing elements
 PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS CHAPTER FIVE Input, Control and Processing elements Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Valves The function of valves is to control the fluid path or the pressure or the flow rate. Depending
PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS CHAPTER FIVE Input, Control and Processing elements Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Valves The function of valves is to control the fluid path or the pressure or the flow rate. Depending
Lease Automatic Custody Transfer
 Lease Automatic Custody Transfer Angus Manufactured LACT Units Updated 19-Dec-01, Slide 2 LACT Unit Requirements Are used for the automatic unattended measurement of crude oil. Accurately measure the quantity
Lease Automatic Custody Transfer Angus Manufactured LACT Units Updated 19-Dec-01, Slide 2 LACT Unit Requirements Are used for the automatic unattended measurement of crude oil. Accurately measure the quantity
CENTRIFUGAL CHILLER. Lubrication System Pull oil sample for spectroscopic analysis.
 CENTRIFUGAL CHILLER Annual Inspection Refrigerant Circuit Check and record refrigerant level Inspect for leak results Calculate refrigerant lass and report to the customer. Repair minor leaks as required
CENTRIFUGAL CHILLER Annual Inspection Refrigerant Circuit Check and record refrigerant level Inspect for leak results Calculate refrigerant lass and report to the customer. Repair minor leaks as required
A E R Z E N S C R E W C O M P R E S S O R S
 A E R Z E N S C R E W C O M P R E S S O R S AERZEN - DELTA TWIN - Two Stage Screw Compressors Oil free compressed air technology A E R Z E N E R M A S C H I N E N F A B R I K G M B H V1-016 01 EN 2000
A E R Z E N S C R E W C O M P R E S S O R S AERZEN - DELTA TWIN - Two Stage Screw Compressors Oil free compressed air technology A E R Z E N E R M A S C H I N E N F A B R I K G M B H V1-016 01 EN 2000
Case Study Balancing a System
 Case Study Balancing a System Piping systems providing heat transfer fluid to a variety of loads can present their own special problems. Since there are multiple paths for the fluid to travel, the system
Case Study Balancing a System Piping systems providing heat transfer fluid to a variety of loads can present their own special problems. Since there are multiple paths for the fluid to travel, the system
Single Stage Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump Installation and Operation Manual RX-10 RX-21 RX-25
 V acuum Pumps Single Stage Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump Installation and Operation Manual RX-10 RX-21 RX-25 www.republicsales.com Revised 10.14 2014 Republic Sales & Manufacturing Single Stage Rotary Vane Vacuum
V acuum Pumps Single Stage Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump Installation and Operation Manual RX-10 RX-21 RX-25 www.republicsales.com Revised 10.14 2014 Republic Sales & Manufacturing Single Stage Rotary Vane Vacuum
Table Summary of Sprinkler System Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance. Reference. Inspection , ,
 Table 5.1.1.2 Summary of Sprinkler System Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance Item Frequency Reference Inspection Gauges (dry, preaction, and deluge systems) Quarterly 5.2.4.2, 5.2.4.3, 5.2.4.4 Control
Table 5.1.1.2 Summary of Sprinkler System Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance Item Frequency Reference Inspection Gauges (dry, preaction, and deluge systems) Quarterly 5.2.4.2, 5.2.4.3, 5.2.4.4 Control
Evaporative Emissions
 Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Hand Expansion Valves Built Stronger to Last Longer Sizes: 6mm (¼ ) to 305mm (4 )
 Hand Expansion Valves Built Stronger to Last Longer Sizes: 6mm (¼ ) to 305mm (4 ) Bulletin No. 82-00A Suitable For: Ammonia, Fluorocarbons, Nitrogen and Carbon Dioxide Features ASTM 352 LCB Cast Steel
Hand Expansion Valves Built Stronger to Last Longer Sizes: 6mm (¼ ) to 305mm (4 ) Bulletin No. 82-00A Suitable For: Ammonia, Fluorocarbons, Nitrogen and Carbon Dioxide Features ASTM 352 LCB Cast Steel
Fuel Cell Lab Manual. Non Conventional Energy Systems Facility. Non Conventional Energy Systems Facility. Boiler House
 Fuel Cell Lab Manual Non Conventional Energy Systems Facility Boiler House Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur System Description The Nexa system provides up to 1200 watts of unregulated DC
Fuel Cell Lab Manual Non Conventional Energy Systems Facility Boiler House Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur System Description The Nexa system provides up to 1200 watts of unregulated DC
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: Implement Control Valve: Implement Circuit
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: Implement Circuit... 6.1.3 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.4 Operational Description: General... 6.1.5 Compensator Control... 6.1.6 Standby Condition...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: Implement Circuit... 6.1.3 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.4 Operational Description: General... 6.1.5 Compensator Control... 6.1.6 Standby Condition...
Flow Computer Installation
 Flow Computer Installation WARNING: Only personnel who are experienced with field wiring should perform these procedures. All field wiring must conform to the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70, Article
Flow Computer Installation WARNING: Only personnel who are experienced with field wiring should perform these procedures. All field wiring must conform to the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70, Article
Single-Valve Powerstation
 Single-Valve Powerstation Description Powerstation is a complete, fully assembled water tempering system, designed to provide safe water throughout commercial and institutional facilities. Powerstation
Single-Valve Powerstation Description Powerstation is a complete, fully assembled water tempering system, designed to provide safe water throughout commercial and institutional facilities. Powerstation
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS Contents Section 1. General Observations... 2 2. Operation... 4 3. Control During Operation... 5 4. Trouble Shooting... 6 5. Maintenance... 7 Please
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS Contents Section 1. General Observations... 2 2. Operation... 4 3. Control During Operation... 5 4. Trouble Shooting... 6 5. Maintenance... 7 Please
The Filling Procedure
 The Filling Procedure Model(s): ECO Series What is needed! 1. Pump 2. 3 water hoses with metric adapters (found on the chiller pump) 3. Glycol (Premixed 37% of KKT Protect) 4. Hand tools 5. Pressure gauge
The Filling Procedure Model(s): ECO Series What is needed! 1. Pump 2. 3 water hoses with metric adapters (found on the chiller pump) 3. Glycol (Premixed 37% of KKT Protect) 4. Hand tools 5. Pressure gauge
Sample Specifications 2111_A00.doc 01/18/06 KOBELCO KNWA00 SERIES 1 of 8 AIR-COOLED, OIL FREE AIR COMPRESSOR Frame HP
 KOBELCO KNWA00 SERIES 1 of 8 1. SPECIFICATION SCOPE 1.1 This specification covers the requirement for supply of a packaged oil-free rotary screw air compressor, Kobelco KNW Series model. 1.2 Any and all
KOBELCO KNWA00 SERIES 1 of 8 1. SPECIFICATION SCOPE 1.1 This specification covers the requirement for supply of a packaged oil-free rotary screw air compressor, Kobelco KNW Series model. 1.2 Any and all
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
MSC Manifolds - DIN for Steam Distribution and Condensate Collection Installation and Maintenance Instructions
 1170650/3 IM-P117-17 ST Issue 3 MSC Manifolds - DIN for Steam Distribution and Condensate Collection Installation and Maintenance Instructions 1 General safety information 2 General product information
1170650/3 IM-P117-17 ST Issue 3 MSC Manifolds - DIN for Steam Distribution and Condensate Collection Installation and Maintenance Instructions 1 General safety information 2 General product information
Torque Converter, Transmission Pump, Screen And Filter
 Page 13 of 27 Transmission Hydraulic System In Forward (Engine Running - Type 2 & 3 Control Valve Shown) (4) Transmission control valve. (5) Neutralizer valve. (6) Neutralizer solenoid. (7) Flow control
Page 13 of 27 Transmission Hydraulic System In Forward (Engine Running - Type 2 & 3 Control Valve Shown) (4) Transmission control valve. (5) Neutralizer valve. (6) Neutralizer solenoid. (7) Flow control
SINGLE-STAGE INJECTOR MODELS 200-3C, 200C, 201C, 202C, 203C, 204C, 206C, 208C
 D E M A SINGLE-STAGE MODELS SINGLE-STAGE MODELS 1. PARTS A. Injector B. Backup washer (Models 204C & smaller). C. Ceramic Weight. D. Tubing 8 long w/ foot strainer. E. Three brass nozzle bushings Metering
D E M A SINGLE-STAGE MODELS SINGLE-STAGE MODELS 1. PARTS A. Injector B. Backup washer (Models 204C & smaller). C. Ceramic Weight. D. Tubing 8 long w/ foot strainer. E. Three brass nozzle bushings Metering
ECTOS Deliverable 4. European Commission. Fifth Framework For Research And Development
 The Hydrogen Fuelling Station ECTOS Deliverable 4 Ecological City Transport System. Demonstration, Evaluation And Research Project Of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Bus Transportation System Of The Future. Contract:
The Hydrogen Fuelling Station ECTOS Deliverable 4 Ecological City Transport System. Demonstration, Evaluation And Research Project Of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Bus Transportation System Of The Future. Contract:
Mitsubishi Diesel Engine Generators (Year 2008) Model: S12R-PTA (1250 kva, 3300V, 50Hz)
 Mitsubishi Diesel Engine Generators (Year 2008) Model: S12R-PTA (1250 kva, 3300V, 50Hz) 1. Condition Engine starts within 40 seconds after Automatic Start ordered. Lubricating Oil must be Operating Condition:
Mitsubishi Diesel Engine Generators (Year 2008) Model: S12R-PTA (1250 kva, 3300V, 50Hz) 1. Condition Engine starts within 40 seconds after Automatic Start ordered. Lubricating Oil must be Operating Condition:
LESSON 2 BASIC CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF HYDRAULIC ACTUATING DEVICES, FLOW CONTROL, AND DIRECTIONAL DEVICES. STP Tasks:
 LESSON 2 BASIC CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF HYDRAULIC ACTUATING DEVICES, FLOW CONTROL, AND DIRECTIONAL DEVICES STP Tasks: 552-758-1003 552-758-1071 OVERVIEW LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this lesson you will
LESSON 2 BASIC CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF HYDRAULIC ACTUATING DEVICES, FLOW CONTROL, AND DIRECTIONAL DEVICES STP Tasks: 552-758-1003 552-758-1071 OVERVIEW LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this lesson you will
POWER GENERATION SYSTEMS
 POWER GENERATION SYSTEMS The Power Generation Systems on HI 595 CF&D consist of three Waukesha 7042 gas driven generators and two diesel driven generators. Two of the three Gas Generators must run to provide
POWER GENERATION SYSTEMS The Power Generation Systems on HI 595 CF&D consist of three Waukesha 7042 gas driven generators and two diesel driven generators. Two of the three Gas Generators must run to provide
INSTRUCTIONS. Fc. -1,<" SERIES ST-261 REGULATING UNLOADER VALVE
 INSTRUCTIONS Fc. -1,
INSTRUCTIONS Fc. -1,
Exercise 4-1. Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Rotameters. How do rotameter tubes work?
 Exercise 4-1 Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the basics of differential pressure flowmeters via the use of a Venturi tube and learn how to safely connect (and disconnect) a differential pressure flowmeter
Exercise 4-1 Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the basics of differential pressure flowmeters via the use of a Venturi tube and learn how to safely connect (and disconnect) a differential pressure flowmeter
GENERATOR SEAL OIL SYSTEM
 GENERATOR SEAL OIL SYSTEM Eskom power utility utilized Flownex SE simulation capabilities to mitigate system shutdowns caused by generator hydrogen (H 2 ) seal ring failures. Engineers modelled the hydrogen
GENERATOR SEAL OIL SYSTEM Eskom power utility utilized Flownex SE simulation capabilities to mitigate system shutdowns caused by generator hydrogen (H 2 ) seal ring failures. Engineers modelled the hydrogen
Electronic Control Valves
 MODEL 131 Series (Full Internal Port) 631 Series (Reduced Internal Port) Electronic Control Valves Model 131-01/631-01 Simple Proven Design Quality Solenoid Pilot Controls Ideal For SCADA Systems Multi-Function
MODEL 131 Series (Full Internal Port) 631 Series (Reduced Internal Port) Electronic Control Valves Model 131-01/631-01 Simple Proven Design Quality Solenoid Pilot Controls Ideal For SCADA Systems Multi-Function
50-01 (Full Internal Port) (Reduced Internal Port) Pressure Relief. & Pressure Sustaining Valve MODEL
 50-01 650-01 & 1 Hytrol (Main ) 2 X42N-2 Strainer & Needle 3 CRL Control Accurate Pressure Control Optional Check Feature Fast Opening to Maintain Line Pressure Slow Closing to Prevents s Completely Automatic
50-01 650-01 & 1 Hytrol (Main ) 2 X42N-2 Strainer & Needle 3 CRL Control Accurate Pressure Control Optional Check Feature Fast Opening to Maintain Line Pressure Slow Closing to Prevents s Completely Automatic
EJECTORS GENERAL OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL
 EJECTORS GENERAL OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL The information contained in this manual was current at the time of printing. The most current versions of all Hydro Instruments manuals can be found on
EJECTORS GENERAL OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL The information contained in this manual was current at the time of printing. The most current versions of all Hydro Instruments manuals can be found on
Underground Tank Applications Installation Guide
 IF Underground Tank Applications Installation Guide Coro-Flo Pumps Background: Because of the environmental problems caused by traditional fuels such as gasoline and diesel, the use of alternative fuels,
IF Underground Tank Applications Installation Guide Coro-Flo Pumps Background: Because of the environmental problems caused by traditional fuels such as gasoline and diesel, the use of alternative fuels,
348002K/348012K Manifold Block Style Service Manual 12/2000
 348002K/348012K Manifold Block Style Service Manual 12/2000 Service Manual 348002K/348012K Manifold Block Style Recovery/Recycling/Recharging Unit For R-12 or R-134a Only TABLE OF CONTENTS: Theory of Operation
348002K/348012K Manifold Block Style Service Manual 12/2000 Service Manual 348002K/348012K Manifold Block Style Recovery/Recycling/Recharging Unit For R-12 or R-134a Only TABLE OF CONTENTS: Theory of Operation
Section 3.2. Machine Maintenance - Hydraulic Oil and Tank Information
 Section 3.2 Machine Maintenance - Hydraulic Oil and Tank Information Hydraulic Oil Tank: Hydraulic Tank Oil Level... 3.2.2 Sight Gauge... 3.2.2 Warning Lights... 3.2.2 Hydraulic Oil Tank Pressurizing System...
Section 3.2 Machine Maintenance - Hydraulic Oil and Tank Information Hydraulic Oil Tank: Hydraulic Tank Oil Level... 3.2.2 Sight Gauge... 3.2.2 Warning Lights... 3.2.2 Hydraulic Oil Tank Pressurizing System...
Series 34. Specifications
 Series Air Release Valves Stainless Steel T Trim Standard Stainless Steel Floats Guaranteed Easily Serviced Without Removal From Pipeline Working Pressures to 800 PSI Engineered For Drip Tight Seal At
Series Air Release Valves Stainless Steel T Trim Standard Stainless Steel Floats Guaranteed Easily Serviced Without Removal From Pipeline Working Pressures to 800 PSI Engineered For Drip Tight Seal At
BERMAD Waterworks. Booster Pump Control Valve Active Check Valve. 700 Series. Model 740. Features and Benefits. Major Additional Features
 Booster Pump Control Valve Active Check Valve Isolates system from the effects of pump starts and stops for: Solitary single speed pumps Battery of single speed pumps (add & switch) Battery of variable
Booster Pump Control Valve Active Check Valve Isolates system from the effects of pump starts and stops for: Solitary single speed pumps Battery of single speed pumps (add & switch) Battery of variable
United States Army Aviation Center of Excellence. Fort Rucker, Alabama JULY 2011 STUDENT HANDOUT
 United States Army Aviation Center of Excellence Fort Rucker, Alabama JULY 2011 STUDENT HANDOUT TITLE: AH-64D INTEGRATED PRESSURIZED AIR SYSTEM (IPAS) FILE NUMBER: 011-0910-1.5 (LOT13) PROPONENT FOR THIS
United States Army Aviation Center of Excellence Fort Rucker, Alabama JULY 2011 STUDENT HANDOUT TITLE: AH-64D INTEGRATED PRESSURIZED AIR SYSTEM (IPAS) FILE NUMBER: 011-0910-1.5 (LOT13) PROPONENT FOR THIS
Exercise 3-1. Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Complete hydraulic circuit
 Exercise 3-1 Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic schematic and components of the nacelle trainer. You will identify
Exercise 3-1 Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic schematic and components of the nacelle trainer. You will identify
DELUGE VALVE MODEL: SD-DVA TECHNICAL DATA : VALVE OPERATION TRIM DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION PRESSURE THREADED OPENING
 DELUGE VALVE MODEL: SD-DVA TECHNICAL DATA : NOMINAL SIZE MATERIAL MAXIMUM SERVICE PRESSURE 200, 150, 100, 80 & 50NB Cast Iron 12 Bar (175 PSI) THREADED OPENING MOUNTING FACTORY HYDROSTATIC TEST PRESSURE
DELUGE VALVE MODEL: SD-DVA TECHNICAL DATA : NOMINAL SIZE MATERIAL MAXIMUM SERVICE PRESSURE 200, 150, 100, 80 & 50NB Cast Iron 12 Bar (175 PSI) THREADED OPENING MOUNTING FACTORY HYDROSTATIC TEST PRESSURE
