ENGINEERING STUDIES. ATAR course examination, Question/Answer booklet. Time allowed for this paper Reading time before commencing work:
|
|
|
- Laura Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATAR course examination, 2017 Question/Answer booklet ENGINEERING STUDIES Please place your student identification label in this box Student number: In figures In words Time allowed for this paper Reading time before commencing work: Working time: ten minutes three hours Materials required/recommended for this paper To be provided by the supervisor This Question/Answer booklet Multiple-choice answer sheet Data book Place a tick ( ) in one of the following boxes to indicate your specialist field. Mechanical Mechatronics Number of additional answer booklets used (if applicable): To be provided by the candidate Standard items: pens (blue/black preferred), pencils (including coloured), sharpener, correction fluid/tape, eraser, ruler, highlighters Special items: non-programmable calculators approved for use in this examination Important note to candidates No other items may be taken into the examination room. It is your responsibility to ensure that you do not have any unauthorised material. If you have any unauthorised material with you, hand it to the supervisor before reading any further. 2018/1389 Web version of 2017/62104 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority 2017 Ref:
2 ENGINEERING STUDIES 2 CORE CONTENT Structure of this paper Section Section One Core content Part A: Multiple-choice Part B: Extended answer Section Two Mechanical Part A: Multiple-choice Part B: Extended answer Section Two Mechatronics Part A: Multiple-choice Part B: Extended answer Number of questions available Number of questions to be answered Suggested working time (minutes) Marks available Percentage of examination Total 100 Instructions to candidates 1. The rules for the conduct of the Western Australian external examinations are detailed in the Year 12 Information Handbook Sitting this examination implies that you agree to abide by these rules. 2. Section One: You must answer all questions. Section Two: You must choose to answer only one of the specialist fields. In the specialist field you have chosen, answer all questions. In both Section One and Section Two, answer the questions according to the following instructions. Part A: Multiple-choice Answer all questions on the separate Multiple-choice answer sheet provided. For each question, shade the box to indicate your answer. Use only a blue or black pen to shade the boxes. If you make a mistake, place a cross through that square, then shade your new answer. Do not erase or use correction fluid/tape. Marks will not be deducted for incorrect answers. No marks will be given if more than one answer is completed for any question. Part B: Extended answer Answer all questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided in this Question/Answer booklet. When calculating answers, show all your working clearly. Your working should be in sufficient detail to allow your answers to be checked readily and for marks to be awarded for reasoning. In final answers, include appropriate units where applicable. 3. You must be careful to confine your answers to the specific questions asked and to follow any instructions that are specific to a particular question. 4. Supplementary pages for the use of planning/continuing your answer to a question have been provided at the end of this Question/Answer booklet. If you use these pages to continue an answer, indicate at the original answer where the answer is continued, i.e. give the page number. 5. The Data book is not to be handed in with your Question/Answer booklet.
3 CORE CONTENT 3 ENGINEERING STUDIES Section One: Core content 40% (70 Marks) This section has two (2) parts. Part A: Multiple-choice Answer all questions Part B: Extended answer Answer all questions Suggested working time: 70 minutes. Part A: Multiple-choice 10% (10 Marks) This part has 10 questions. Answer all questions on the separate Multiple-choice answer sheet provided. For each question, shade the box to indicate your answer. Use only a blue or black pen to shade the boxes. If you make a mistake, place a cross through that square, then shade your new answer. Do not erase or use correction fluid/tape. Marks will not be deducted for incorrect answers. No marks will be given if more than one answer is completed for any question. 1. The power developed by an electric pump can be measured in joules per hour. joules. watts per second. newtons per second. 2. Used vehicle batteries can present a serious waste problem. The separation of these batteries into their components (lead, acid and plastic) is a practical example of regeneration. waste reduction. designed obsolescence. recycling. 3. The Water Corporation wishes to lay a new section of above-ground pipe in a region east of Perth. Which of the following would be the engineering consultant s first step in this work? test different types of pipeline systems construct detailed drawings of the pipeline undertake an environmental impact study prepare a planning application 4. An electronics company is obtaining anthropometric data for the design of a new model mobile phone. Which of the following is the most important human dimension the designers need to consider? the average width of the hand the average length of the index finger the average distance from ear to mouth the average width of the ear
4 ENGINEERING STUDIES 4 CORE CONTENT 5. A design brief is intended to specify the requirements of the client. specify the materials to be used in manufacture. set the production timeline. achieve all of the above. 6. Which of the following formulae would be correct for the total surface area of a cylindrical rod of height h and radius r? 2πr(r + h) πr(2r + h) πr(r + 2h) 2πr 2 (1 + h) 7. An advantage of a solar panel compared to a wind generator is that it requires less maintenance. This is because wind generators are in harsh environments. solar panels have no moving parts. wind generators are designed to have a short life span. solar panels produce lower voltage. 8. Which of the following would best allow an energy source to be referred to as renewable? No energy is lost in its production. It can be produced at a zero cost. The energy source can be naturally replenished. The energy is produced from biological sources. 9. Copper wire is used to make electrical cable because it is a very good conductor. Another of its properties that makes it suitable for this purpose is that it is elastic. malleable. plastic. ductile. 10. The diagram on the right is of a letterbox with a length b and a cross section that is a semicircle on top of a square with a base of length 2a. Which of the following would be the correct formula for the total volume of the letter box? 4b(a 2 + πa 2 ) 0.5a 2 b(8 + π) a 2 b(4 + π) 0.5a 2 b(4 + π)
5 CORE CONTENT 5 ENGINEERING STUDIES Section One: Core content Part B: Extended answer 30% (60 Marks) This section has three (3) questions. Answer all questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided. When calculating answers, show all your working clearly. Your working should be in sufficient detail to allow your answers to be checked readily and for marks to be awarded for reasoning. In final answers, include appropriate units where applicable. Supplementary pages for the use of planning/continuing your answer to a question have been provided at the end of this Question/Answer booklet. If you use these pages to continue an answer, indicate at the original answer where the answer is continued, i.e. give the page number. Question 11 (24 marks) Storage tank Blackened panels Metal edges A typical solar hot water system mounted on the roof of a house has two blackened panels with a total area of 4 m 2 positioned side by side, with a cylindrical 360 litre storage tank connected horizontally above them, as shown in the photograph above. The length of the storage tank is 1.6 m, the same as the width of the two panels. The water is carried to and from the storage tank by copper pipes attached to the surface of the panels. Calculate the internal radius of the tank, given that one litre is the same as m 3. (4 marks)
6 ENGINEERING STUDIES 6 CORE CONTENT Question 11 (continued) The water can be heated in two ways. When the sun is shining, the radiation from it is absorbed by the panels and transferred to the water. If there is insufficient radiation from the sun, the water in the storage tank can be heated by an electric or gas heater backup. It requires 4180 joules of energy to raise the temperature of 1 L of water by each degree Celsius. The water in the hot water system is initially at 22 C and is to be heated to 76 C. Show that the energy needed to heat a full tank (360 L) of water from 22 C to 76 C is 81.2 MJ. (4 marks) If the efficiency of such a hot water system using solar energy is 60%, how much solar energy must fall on the panels to heat a full tank of water from 22 C to 76 C? (2 marks) The average effective solar irradiance in Perth on a given day in June on these panels is 2.96 kw m -2. How many minutes would it take to heat a full tank of water from 22 C to 76 C? Assume 100% efficiency. (4 marks)
7 CORE CONTENT 7 ENGINEERING STUDIES (e) On a very cloudy and cold day, the electric heater backup used 84.4 MJ of energy to bring the temperature of a full tank of water to the maximum 76 C. How many kilowatt hours of electricity does this represent? (2 marks) (f) The average solar irradiance on a horizontal surface in Perth in June is 2.62 kwh m -2. The panels are not, however, horizontal but generally fixed at an angle of 58 to the horizontal. If they could be moved, the best angles to the horizontal are 43 in winter and 73 in summer. (i) Why are the panels placed at this set angle of 58 to the horizontal and not horizontally? (1 mark) (ii) Why are the pipes and panel surfaces painted black? (1 mark) (g) Is a solar hot water system a renewable or non-renewable energy system? Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
8 ENGINEERING STUDIES 8 CORE CONTENT Question 11 (continued) (h) The government is encouraging more people to install solar hot water systems. State a positive environmental impact that this would have. (1 mark) (i) Suggest a metal most suited to being used for the edges and supports of the panels. (1 mark) (j) Give two reasons why you chose your answer to part (i) above. (2 marks) One: Two:
9 CORE CONTENT 9 ENGINEERING STUDIES Question 12 (23 marks) Gatepost 11 horizontal steel ribs 50 mm wide Hinges 160 mm x 40 mm steel tube Hydraulic ram The picture above is of an electrically-operated and electronically-controlled gate. Its external dimensions are 3 m wide and 1.8 m high and it is constructed from structural steel. The frame of the gate is fabricated from rectangular structural tube steel with a thickness of 4 mm. The external dimensions of the top and sides of the frame are 80 mm wide 40 mm deep and the steel tube at the bottom is 160 mm high 40 mm deep. The bottom tube goes all the way across the base and the sides are welded on top of it. It has a plastic plug at each end to keep water out. The 11 horizontal ribs are solid steel plate of width 50 mm and thickness 7 mm and the vertical ribs are 15 mm square steel bar. Both of these are fitted within the frame. Calculate the total mass of the horizontal steel ribs. (5 marks)
10 ENGINEERING STUDIES 10 CORE CONTENT Question 12 (continued) What is the function of the vertical and horizontal ribs welded inside the frame? (1 mark) Calculate the volume of steel in the bottom beam of the gate frame. (4 marks) The gatepost on the right of the gate is 12 cm square tube, with a height of 2.2 m above the ground. It has a square cover on its top. The post is bolted to the brick pillar at several places along its height. The gap between the gate and the post is 6 cm. The gate swings from the post on two hinges bolted to the gatepost. Give a structural reason why the hinges are bolted to a steel post and not directly to the brick pillar. Justify your answer. (2 marks)
11 CORE CONTENT 11 ENGINEERING STUDIES The gate is opened and closed by a horizontal hydraulic ram driven by an electric motor. This ram is connected to the gatepost at one end and 1.4 m along the bottom of the gate frame at the other and the gate has no contact with the brick pillar on its left-hand side. When this gate was originally fitted, it had a steel mesh grid covering the area within the tube steel frame and there was a resistance to it opening. It was found when the mesh was removed that this problem disappeared. (e) Give a possible problem caused by this mesh that made the gate difficult to open and a reason why the removal of the mesh solved this problem. (2 marks) The process for the manufacture of this gate would have started with a design brief and finished with selection of the final design solution. (f) In the table below, list four other steps in the design process between the design brief and the final design and provide a short description of each. (8 marks) Step in design process Design brief Description not required Description of each design step Final design solution Description not required (g) At what stage in the design process should any problem with the mesh have been realised? (1 mark)
12 ENGINEERING STUDIES 12 CORE CONTENT Question 13 (13 marks) Below is a dimensioned isometric drawing of a machined fitting made from brass. SCSA On the grid provided on page 13, draw a scaled, labelled and dimensioned orthographic projection of this fitting, showing all three views. (11 marks) This fitting was manufactured from a solid block of brass with original external dimensions of 250 mm 100 mm 125 mm. The circular hole was placed in the original block before any machining commenced. What volume of metal, in cubic millimetres, was removed from the original block by the drill used to make the holes? (2 marks)
13 CORE CONTENT 13 ENGINEERING STUDIES TOP VIEW FRONT VIEW SCALE: END VIEW A spare grid is provided at the end of this Question/Answer booklet. If you need to use it, cross out this attempt. End of Section One
14 ENGINEERING STUDIES 14 Section Two: Specialist fields 60% (110 Marks) Candidates are required to choose one of the following options, according to which specialist field they studied in Tick one of the boxes below to indicate your choice of option. Specialist field P Question numbers Pages Mechanical Mechatronics Now turn to the relevant pages and answer the questions for the specialist field you have selected.
15 MECHANICAL 15 ENGINEERING STUDIES Section Two: Specialist field Mechanical 60% (110 Marks) This section has two (2) parts. Part A: Multiple-choice Answer all questions Part B: Extended answer Answer all questions Suggested working time: 110 minutes. Part A: Multiple-choice 10% (10 Marks) This part has 10 questions. Answer all questions on the separate Multiple-choice answer sheet provided. For each question, shade the box to indicate your answer. Use only a blue or black pen to shade the boxes. If you make a mistake, place a cross through that square, then shade your new answer. Do not erase or use correction fluid/tape. Marks will not be deducted for incorrect answers. No marks will be given if more than one answer is completed for any question. 14. Toughness is best defined as the energy absorbed by a material without fracturing. energy absorbed by a material without yielding. area under the stress-strain graph up to the point of yielding. ability of a material to resist deformation. 15. Which of the following measurements is equivalent to 10 megapascals (MPa)? 10 N mm kn m N mm kpa
16 ENGINEERING STUDIES 16 MECHANICAL 16. The figure below shows the stress/strain graph for a ductile material. Which of the labelled points on the graph represents the elastic limit of the material? i ii iii iv 17. The formal definition of work is that work is done when the potential energy of an object in motion increases. an object moves in the direction of an applied force. the kinetic energy of an object in motion increases. the total potential energy of a system increases. The following information applies to Questions 18 and 19 and requires information from the Data book. A load of 1 kn is applied to four different material samples. Each sample has a length of 10 cm and diameter of 1 cm. 18. Which material would extend the most? brass cast iron copper zinc 19. If the diameter of a sample was halved, the stress in the sample would a) double. remain unchanged. quadruple. halve.
17 MECHANICAL 17 ENGINEERING STUDIES 20. A ball is thrown vertically into the air. Which one of the following statements describes its trajectory correctly? You can ignore air resistance. The acceleration of the ball decreases as the height of the ball increases. The acceleration of the ball is constant. The acceleration of the ball increases as the height of the ball increases. The acceleration of the ball is greater on the way down than on the way up. 21. Which one of the following is a unit for work? joules/second watts/second newton second watt second 22. The wrench shown below is being used to tighten a nut. A force F is applied at an angle of 45 to the wrench at a distance L from the centre of the nut. F 45 L The moment applied to the wrench under these conditions is closest to 1.2 FL. 1.4 FL. 1.0 FL FL. 23. The coat hook shown is made from metal. Which of the processes below would be the best to use to manufacture it? pressing cold drawing casting forging
18 ENGINEERING STUDIES 18 MECHANICAL Part B: Extended answer 50% (100 Marks) This part has six (6) questions. Answer all questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided. When calculating answers, show all your working clearly. Your working should be in sufficient detail to allow your answers to be checked readily and for marks to be awarded for reasoning. In final answers, include appropriate units where applicable. Supplementary pages for the use of planning/continuing your answer to a question have been provided at the end of this Question/Answer booklet. If you use these pages to continue an answer, indicate at the original answer where the answer is continued, i.e. give the page number. Question 24 (12 marks) A 60 kg person walks across a simply-supported timber balance beam. The supports are 1.5 m apart. The beam has a width of 70 mm and a height of 30 mm as shown. Consider the weight of the person as a point source in your answers. SCSA Complete the following by circling the correct answer. (2 marks) The top surface of the beam is under: tension compression The bottom surface of the beam is under: tension compression Calculate the second moment of area of the beam about its horizontal centroidal axis. (2 marks)
19 MECHANICAL 19 ENGINEERING STUDIES Calculate the maximum deflection in millimetres of the beam when the person stands at its centre. Convert your maximum deflection to metres. (You can ignore the mass of the timber beam in your calculations.) (5 marks) Beams 1 and 2 shown in the diagram are identical; however, Beam 1 is rotated 90 along its longitudinal axis relative to Beam 2, as shown in the diagram. SCSA If two people with the same mass stand in the middle of each of the beams as shown, which beam will have the greater maximum deflection? Circle your answer and provide an explanation. (3 marks) Beam 1 Beam 2 Explanation:
20 ENGINEERING STUDIES 20 MECHANICAL Question 25 (26 marks) The diagram below is of a tower crane used to lift construction materials. The materials are lifted vertically by a winch at A which is 5 m from the centreline of the tower. A steel cable with a 15 mm diameter connects the load to the winch. The mass of the boom is 1500 kg and its centre of mass is 1 m to the right of the centreline of the tower. The tower has a mass of 1000 kg and its centre of mass is 3.5 m above support B. The counterweight has a mass of kg and is its centre of mass is 4 m from the centreline of the tower. The weight of the load is 70 kn. 4 m 1 m 5 m Calculate the vertical reaction force at B. (3 marks)
21 MECHANICAL 21 ENGINEERING STUDIES Calculate the reaction moment at B. State whether the moment is clockwise or anticlockwise. (4 marks) The winch now lifts the 70 kn load 2 m above the position shown in a time of 20 seconds. (i) Calculate the change in potential energy of the load. (2 marks)
22 ENGINEERING STUDIES 22 MECHANICAL Question 25 (continued) (ii) Calculate the efficiency of the winch if it consumes 10 kw of electrical power while lifting the load. (4 marks) Calculate the tensile force in the cable if it accelerates 1000 kg vertically upward at 1.5 m s -2. (4 marks) (e) Applying a load to the cable causes it to increase in length from 4000 mm to 4008 mm. Calculate the strain in the cable. (3 marks)
23 MECHANICAL 23 ENGINEERING STUDIES (f) Calculate the safe working stress of the cable if its ultimate tensile stress is 1000 MPa and the factor of safety is 2.5. (2 marks) (g) Name and justify two physical properties of steel that make it a suitable material for use in the manufacture of the cable. (4 marks) Property one: Property two:
24 ENGINEERING STUDIES 24 MECHANICAL Question 26 (16 marks) The truss shown is used as a road bridge to span a small creek. Members AB, BC and CD support a road deck which acts as a 1 kn m -1 uniformly distributed load. At the instant shown, a car applies a point load of 12 kn vertically downward at Point B. Assume that the weight of all members can be ignored in your calculations. Show that the vertical reaction force at A is N. (4 marks) Determine the size of angle BAE. (1 mark)
25 MECHANICAL 25 ENGINEERING STUDIES Calculate the force in Member AE. (4 marks) Is Member AE under compression or tension? Circle your answer below and provide an explanation. (3 marks) tension compression Explanation: Member CF is a 150 mm 150 mm 8 mm square hollow section as shown in the diagram below. (e) If the tension force in CF is 12 kn, calculate the stress in Member CF. (4 marks)
26 ENGINEERING STUDIES 26 MECHANICAL Question 27 (16 marks) The diagram below shows a 2 m long cantilevered beam that supports a road sign (not shown). The beam is a circular tube section made from structural steel. The circular tube section has an outside diameter of 150 mm and an inside diameter of 145 mm. The weight of the road sign is 500 N and it acts as shown 0.5 m from the right end of the beam. 500 N 0.5 m 2 m SCSA Show that the total weight of the beam is 713 N. (5 marks)
27 MECHANICAL 27 ENGINEERING STUDIES Calculate the reaction force and moment at the fixed end A. (i) Force (2 marks) (ii) Moment (3 marks)
28 ENGINEERING STUDIES 28 MECHANICAL Question 27 (continued) Using the grid below, and taking into account all relevant forces, construct a shear force diagram and a bending moment diagram for the beam. (6 marks) A spare grid is provided at the end of this Question/Answer booklet. If you need to use it, cross out this attempt.
29 MECHANICAL 29 ENGINEERING STUDIES Question 28 (17 marks) A shot tower is a tower designed for the production of small-diameter lead balls for muzzle-loading rifles. In a shot tower, lead is heated until it is molten and then dropped in predetermined masses through a copper sieve high in the tower and allowed to fall freely. The surface tension in the liquid lead causes it to form tiny spherical balls which partially cool and solidify as they fall. These partially-cooled balls are caught at the floor of the tower in a water-filled basin. e available. For each of the following question parts, assume that the molten lead masses are dropped from 25 m above the base of the tower and ignore air resistance. Calculate the mass of a spherical lead shot if it has a radius of 3 mm. Assume that the density of lead is kg m -3. (4 marks)
30 ENGINEERING STUDIES 30 MECHANICAL Question 28 (continued) Calculate the time that a lead shot takes to drop to the bottom of the tower. (3 marks) Calculate the speed of a falling lead shot when it is at a height of 10 m above the base of the tower. (4 marks)
31 MECHANICAL 31 ENGINEERING STUDIES A lead shot with a mass of 3 g is now dropped from the top of the tower. Calculate its height above the base of the tower when its kinetic energy is 0.59 J. (3 marks) (e) This 3 g lead shot and another lead shot with a mass of 5 g were dropped from the tower at the same time. Did the 3 g lead shot or the 5 g lead shot hit the bottom of the tower first or did they hit at the same time? You can ignore the effects of air resistance. Circle your answer and provide an explanation. (3 marks) 3 g lead shot first 5 g lead shot first same time Explanation:
32 ENGINEERING STUDIES 32 MECHANICAL Question 29 (13 marks) During a tensile test, a sample is subjected to a tension force until it fails. The results from the tensile test are used to define the stress/strain curve for the material. SCSA A cylindrical brass sample with an initial length of 5 cm and diameter of 3 mm is subjected to a tensile test. Calculate the force required to break the sample. (4 marks) Calculate the length of the sample when a 300 N force is applied, given it is still in the elastic region. (5 marks)
33 MECHANICAL 33 ENGINEERING STUDIES As the sample is stretched it begins to plastically deform. Define what is meant by plastic deformation in the context of material testing. (2 marks) The stress/strain graph of a different material sample is shown in the graph below. Explain what happens to the material between Point A and Point B on the graph. (2 marks) End of Mechanical Section
34 ENGINEERING STUDIES 34 MECHATRONICS Section Two: Specialist field Mechatronics 60% (110 Marks) This section has two (2) parts. Part A: Multiple-choice Answer all questions Part B: Extended answer Answer all questions Suggested working time: 110 minutes. Part A: Multiple-choice 10% (10 Marks) This part has 10 questions. Answer all questions on the separate Multiple-choice answer sheet provided. For each question, shade the box to indicate your answer. Use only a blue or black pen to shade the boxes. If you make a mistake, place a cross through that square, then shade your new answer. Do not erase or use correction fluid/tape. Marks will not be deducted for incorrect answers. No marks will be given if more than one answer is completed for any question. 30. The purpose of an idler gear placed between two gears is to enable gear ratios to be changed. enable the two gears to rotate in the same direction. reduce friction in a gear train by improved meshing. prevent rotation when the second gear needs to idle. 31. A DPDT relay has the ability to control back emf. smooth the voltage in a circuit. double the current in a circuit. switch two different voltages in a circuit. 32. A microcontroller requires an analogue input voltage of 4.2 V. For testing purposes, which one of the following components could provide this voltage? a 7805 regulator three 1.5 V batteries and a silicon diode a 6 V battery and three silicon diodes a 3.7 V phone battery and a silicon diode 33. If the mechanical advantage of a pulley system is 3.5 and the diameter of the input pulley is 150 mm, what is the diameter of the output pulley? 525 mm 85.7 mm mm mm
35 MECHATRONICS 35 ENGINEERING STUDIES 34. Two resistors are connected in parallel. The first has a value of 1.2 kω. The combined value of the two resistors is 300 Ω. The value of the other resistor is 900 Ω. 400 Ω. 1.5 kω. 350 Ω. 35. An NPN transistor is controlled by its collector-emitter voltage. base-collector voltage. base current. collector current. 36. A windscreen wiper on a car uses rotary to linear transformation. oscillating transformation. reciprocating transformation. circular transformation. 37. Which one of the following statements is true? A stepper motor gives feedback to the control circuit. Stepper motors need replacing when their brushes wear out. A stepper motor continues to use power after reaching its rotational position. A unipolar stepper motor has only four wires. 38. Which one of the following statements about a worm and worm wheel is correct? In operation, the worm and worm wheel are self-locking. You can rotate the worm by rotating the worm wheel. The number of teeth on the worm is usually higher than the number of teeth on the worm wheel. Only small speed reductions are possible. 39. A super blue LED has a 3.6 V operating voltage and a current draw of 20 ma. When operating from a 5 V supply, the best series resistor should be coloured red, violet, black and gold. green, blue, brown and gold. red, violet, brown and gold. blue, grey, black and gold.
36 ENGINEERING STUDIES 36 MECHATRONICS Part B: Extended answer 50% (100 Marks) This part has six (6) questions. Answer all questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided. When calculating answers, show all your working clearly. Your working should be in sufficient detail to allow your answers to be checked readily and for marks to be awarded for reasoning. In final answers, include appropriate units where applicable. Supplementary pages for the use of planning/continuing your answer to a question have been provided at the end of this Question/Answer booklet. If you use these pages to continue an answer, indicate at the original answer where the answer is continued, i.e. give the page number. Question 40 (17 marks) A 24 V battery is connected to the circuit shown below. The current flowing from the battery is 3 A and the current flowing through R1 is 1.8 A. V R2 1.8 A R1 What is the current through the 5 Ω resistor? Give a reason why. (2 marks) Calculate the current through the 12 Ω resistor. (2 marks)
37 MECHATRONICS 37 ENGINEERING STUDIES Show by calculation the potential difference displayed on the voltmeter. (2 marks) Calculate the power dissipated in the 5 Ω resistor. (2 marks) (e) Calculate the value of Resistor R1. (3 marks) (f) Calculate the value of Resistor R2. (3 marks) (g) If the voltage of the 24 V battery was to drop to 19.6 V, calculate the new reading on the voltmeter. (3 marks)
38 ENGINEERING STUDIES 38 MECHATRONICS Question 41 (8 marks) A windmill that pumps water operates by means of blades moving in the wind which turn a wheel shaft connected to a small pinion drive gear. The pinion gear turns a larger bull (driven) gear that is connected to a Pitman arm. The Pitman arm pushes a sliding yoke up and down in a pump rod guide. This lifts a pump rod up and down to a pump that is located in water below. For copyright reasons this image cannot be reproduced in the online version of this document, but may be viewed at pumping-water-wind?v=print
39 MECHATRONICS 39 ENGINEERING STUDIES Name the type of motion transformation that occurs between the driven gear and the pump rod. (1 mark) In the windmill diagram shown, the pinion gear has 14 teeth and the driven gear has 56 teeth. If the wind wheel shaft is turning at 146 rpm, calculate the velocity of the bull (driven) gear. (3 marks) If the pump rod has 165 upstrokes in one minute, calculate the velocity of the wind wheel shaft. (4 marks)
40 ENGINEERING STUDIES 40 MECHATRONICS Question 42 (10 marks) The circuit below is used to control a DC motor by pulse width modulation (PWM) on the DC supply to the motor. SCSA State two advantages of using PWM in this circuit rather than lowering the voltage by resistance to control the motor speed. (2 marks) One: Two: What is the design purpose of Resistor R1? (1 mark) What is the design purpose of Transistor Q1? (1 mark)
41 MECHATRONICS 41 ENGINEERING STUDIES What is the design purpose of Diode D3? (1 mark) (e) What is the reason for including Switch S1? (1 mark) (f) A switch could be placed at the +12 V input. Explain the advantage of such a switch. (2 marks) (g) Complete the table below if R2 is a 5% tolerance carbon resistor. (2 marks) Resistor Colour code Maximum value R2
42 ENGINEERING STUDIES 42 MECHATRONICS Question 43 (25 marks) An elevator is installed in a four-storey building. It has the usual UP/DOWN request buttons on the wall near the entrance and the usual destination control panel inside. For safety, the elevator always checks the total weight of occupants and flashes a warning light if a mass of greater than 630 kg is detected. The door then opens and remains open until the weight of passengers is below 630 kg. When no request has been made from the UP/DOWN buttons located on the upper floors for two minutes, the elevator always returns to the ground floor. The sequence required for the elevator to operate correctly is shown without the weight detection stage included. 1. IDLE AT GROUND FLOOR 2. REQUEST TO MOVE UP OR DOWN 3. DOOR OPENS 4. DOOR CLOSES 5. ELEVATOR MOVES TO REQUESTED FLOOR 6. DOOR OPENS 7. DOOR CLOSES 8. CHECK FOR NEW REQUEST 9. ELEVATOR MOVES TO REQUESTED FLOOR 10. IF NO NEW REQUEST, TWO MINUTE TIMER STARTS 11. ELEVATOR MOVES TO GROUND FLOOR AND REMAINS IDLE In the sequence above circle each numbered stage that the elevator is almost certain to be unoccupied? (3 marks) In the space below, draw a flow chart to show the operation of the elevator. Include the 630 kg weight check and the flashing warning light. (9 marks)
43 MECHATRONICS 43 ENGINEERING STUDIES Below is a diagrammatic representation of a simple drive system for an elevator. The elevator moves vertically at 1.2 m s -1 and there is no slip between the cable and the drive pulley. The table refers to the specifications of an elevator using this design. Maximum empty load Passenger load Drive pulley RPM Motor RPM Motor voltage Motor current Gearbox output power 1600 kg 630 kg VDC 14 A kw SCSA (i) Calculate the ratio of the gearbox. (2 marks)
44 ENGINEERING STUDIES 44 MECHATRONICS Question 43 (continued) (ii) Suggest a type of gearbox that would be best suited to this application. (1 mark) (iii) Calculate the input power to the motor. (2 marks) (iv) Calculate the efficiency of the motor and gearbox. (2 marks) (v) Name the type of motion transformation between the drive pulley and the elevator. (1 mark) (vi) The counterweight is approximately 2000 kg. Justify this mass. (2 marks) In the last 20 years, new designs for elevator motors have appeared. Most are gearless and the motor RPM has been controlled by microprocessors using pulse width modulation (PWM). Besides the increased safety of these large PWM motors, list three other advantages over the high-voltage DC motors they have replaced. (3 marks) One: Two: Three:
45 MECHATRONICS 45 ENGINEERING STUDIES Question 44 (19 marks) A shop door alarm that was designed to use a microcontroller is shown in the circuit below. A high-power white LED illuminates an LDR on the input and the output is a red LED and a piezoelectric speaker. When the LDR is darkened by a person interrupting the light from the white LED, the speaker sounds and the red LED flashes the total count of entries and exits through the door. SCSA State the purpose of the DB9 connector. (1 mark) State the specific type of input for pin 6 on the IC. (1 mark) The white LED draws 24 ma in this circuit. Calculate its operating voltage. (2 marks)
46 ENGINEERING STUDIES 46 MECHATRONICS Question 44 (continued) The shop owner tried to use a 5 V relay in place of the red LED and the 330 Ω resistor but it destroyed the IC because the relay was rated at 50 ma. Complete the circuit below using additional components to show how a 5 V relay can be used. Values of the components do not have to be shown. (6 marks) SCSA (e) The power supply needed to operate the shop door alarm is missing some components in the schematic. It requires an input 9 VDC voltage and the 5 V output should have a fuse. Label the voltage input, showing polarity and draw in the labelled components required to make a working circuit. (5 marks) SCSA (f) Capacitor C3 has three numbers marked on it to indicate its capacitance. What are the numbers? (1 mark)
47 MECHATRONICS 47 ENGINEERING STUDIES The circuit is now to be operated from a 12 V battery instead of 9 V. (g) What would the output voltage be? (1 mark) (h) What would be a suitable voltage rating for C1? (1 mark) (i) Draw in a switch to the schematic in part (e) to turn the shop door alarm off. (1 mark)
48 ENGINEERING STUDIES 48 MECHATRONICS Question 45 (21 marks) In designing a small robot car a student considers a number of possibilities for propulsion and steering. The student decides on the differential drive method in which two rear wheels are powered to provide forward motion, backward motion and direction. Complete the table below to show the direction in which the vehicle will travel. (4 marks) Left motor motion Right motor motion Direction that the vehicle will travel Forward Forward Forward Backward Backward Backward Forward Backward To control the vehicle, the student decides to use a circuit similar to that shown below. Name the components A, B and C1/C2 in the circuit shown. (3 marks) A: B: C1/C2:
49 MECHATRONICS 49 ENGINEERING STUDIES The following diagram shows an arrangement of gears that convert a rotational motion of the circular gear into a linear motion of the flat gear. The pitch of the gear teeth is 3 mm. SCSA State the common name given to this gear arrangement. On the basis of this name, label the parts on the diagram above. (2 marks) Name: Calculate the translation distance of the flat gear for one revolution of the circular gear. (2 marks) (e) If the circular gear was twice the diameter with the same gear pitch, what would be the translation distance for two revolutions of the circular gear? (2 marks)
50 ENGINEERING STUDIES 50 MECHATRONICS Question 45 (continued) (f) By changing the diameter of the circular gear as described in part (e), would the mechanical advantage be greater or smaller? Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks) (g) Refer to the diagram shown on page 49. How many rotations of the circular gear would be required to provide a translation of 960 mm? (2 marks) (h) Complete the table below for a suitable mechanical drive system for each of the applications given. (4 marks) Application Drive system Car alternator and water pump Car steering Bicycle propulsion Car gearbox End of Mechatronics Section End See of next questions page
51 51 ENGINEERING STUDIES Supplementary page Question number:
52 ENGINEERING STUDIES 52 Supplementary page Question number:
53 53 ENGINEERING STUDIES Supplementary page Question number:
54 ENGINEERING STUDIES 54 Supplementary page Question number:
55 55 ENGINEERING STUDIES Supplementary page Question number:
56 ENGINEERING STUDIES 56 Supplementary page Question number:
57 57 ENGINEERING STUDIES Supplementary page Question number:
58 ENGINEERING STUDIES 58 Spare grid TOP VIEW FRONT VIEW SCALE: END VIEW
59 Spare grid 59 ENGINEERING STUDIES
60 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Question 11 Question 12 Question 22 Question 23 Question 28 Question 41 Question 45 Photograph of solar system tank by courtesy of the examining panel. Photograph of automatic gate by courtesy of the examining panel. Photograph of wrench by courtesy of the examining panel. Photograph of coat hook by courtesy of the examining panel. Image: Matnkat. (2006, August 12). Clifton Hill shot tower, Melbourne, Australia. Retrieved April, 2017, from Used under a Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic licence. Diagram adapted from: Ironman Windmill Co. (1977). Gear box: Up stroke; Pump: Up stroke. Retrieved May, 2017, from (see Gearbox and windmill overview schematic under Inside this article ) Circuit diagram adapted from: Gadgetronicx. (n.d.) Wiring diagram robot car. Retrieved May, 2017, from This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that it is not changed and that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with prior written permission of the School Curriculum and Standards Authority. Copying or communication of any third party copyright material can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with permission of the copyright owners. Any content in this document that has been derived from the Australian Curriculum may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY) licence. Published by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority of Western Australia 303 Sevenoaks Street CANNINGTON WA 6107
Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 20 November 2017
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Victorian Certificate of Education 2017 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 20 November 2017 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Friday 12 November 2010
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2010 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Friday 12 November 2010 Reading time: 11.45
Victorian Certificate of Education 2010 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Friday 12 November 2010 Reading time: 11.45
Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 16 November 2015
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2015 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 16 November 2015 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Victorian Certificate of Education 2015 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 16 November 2015 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am
Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 18 November 2013
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2013 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 18 November 2013 Reading time: 9.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2013 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 18 November 2013 Reading time: 9.00
Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING. Written examination. Monday 19 November 2012
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2012 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 19 November 2012 Reading time: 9.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2012 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Written examination Monday 19 November 2012 Reading time: 9.00
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7100832055* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/41 Paper 4 Systems and Control October/November 2017 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7100832055* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/41 Paper 4 Systems and Control October/November 2017 1 hour
To be taken together with Paper 1 in one session of 2 hours 45 minutes.
 Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/04 Paper 4 Technology May/June
Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/04 Paper 4 Technology May/June
Design and Technology: Systems and Control Technology
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2015 Design and Technology: 45651
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2015 Design and Technology: 45651
DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 Candidate Name Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 142/02 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 FOCUS AREA: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL TECHNOLOGY Foundation Tier A.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2008 1 1 2 hours Leave Blank Question
Candidate Name Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 142/02 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 FOCUS AREA: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL TECHNOLOGY Foundation Tier A.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2008 1 1 2 hours Leave Blank Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8019038925* PHYSICS 0625/03 Paper 3 Extended October/November 2007 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8019038925* PHYSICS 0625/03 Paper 3 Extended October/November 2007 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certifi cate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certifi cate of Secondary Education *7007622549* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/43 Paper 4 Systems and Control
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certifi cate of Secondary Education *7007622549* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/43 Paper 4 Systems and Control
DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 Candidate Name Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 142/04 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 FOCUS AREA: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL TECHNOLOGY Higher Tier A.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2008 1 1 2 hours Leave Blank Question
Candidate Name Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 142/04 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 FOCUS AREA: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL TECHNOLOGY Higher Tier A.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2008 1 1 2 hours Leave Blank Question
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2641043214* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/43 Paper 4 Systems and Control October/November
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2641043214* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/43 Paper 4 Systems and Control October/November
PHA3/W PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 3 Current Electricity and Elastic Properties of Solids
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA3/W Unit 3 Current
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA3/W Unit 3 Current
PHYA5/2C. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June Section B. Monday 18 June am to am (JUN12PHYA52C01)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name:
 Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8545487682* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/42 Paper 4 Systems and Control May/June 2016 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8545487682* DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/42 Paper 4 Systems and Control May/June 2016 1 hour Candidates
SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGY
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2006 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGY Written examination Friday 10 November 2006 Reading time: 9.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2006 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGY Written examination Friday 10 November 2006 Reading time: 9.00
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT Department of Physics Class:XII Physics Worksheet-3 (2018-2019) Chapter 3: Current Electricity Section A Conceptual and Application type Questions 1 Two wires of equal length, one
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT Department of Physics Class:XII Physics Worksheet-3 (2018-2019) Chapter 3: Current Electricity Section A Conceptual and Application type Questions 1 Two wires of equal length, one
Moments. It doesn t fall because of the presence of a counter balance weight on the right-hand side. The boom is therefore balanced.
 Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
2013 Systems Engineering GA 3: Examination
 2013 Systems Engineering GA 3: GENERAL COMMENTS In the 2013 Systems Engineering examination a number of students completed all of the questions involving formulas well, but had trouble with the design
2013 Systems Engineering GA 3: GENERAL COMMENTS In the 2013 Systems Engineering examination a number of students completed all of the questions involving formulas well, but had trouble with the design
MS.RAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3
 MSRAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3 1- In Fig 91, A and B are two conductors on insulating stands Both A and B were initially uncharged X Y A B Fig 91 (a) Conductor A is given the positive charge shown
MSRAJA ELGADFY/ELECTROMAGENETIC PAPER3 1- In Fig 91, A and B are two conductors on insulating stands Both A and B were initially uncharged X Y A B Fig 91 (a) Conductor A is given the positive charge shown
DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS - I
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS - I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS - I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions
GCSE Design & Technology Systems and Control Technology
 GCSE Design & Technology Systems and Control Technology 45651 Unit 1 Written Paper Mark scheme 4565 June 2016 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered,
GCSE Design & Technology Systems and Control Technology 45651 Unit 1 Written Paper Mark scheme 4565 June 2016 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered,
SUPER CAPACITOR CHARGE CONTROLLER KIT
 TEACHING RESOURCES ABOUT THE CIRCUIT COMPONENT FACTSHEETS HOW TO SOLDER GUIDE POWER YOUR PROJECT WITH THIS SUPER CAPACITOR CHARGE CONTROLLER KIT Version 2.0 Teaching Resources Index of Sheets TEACHING
TEACHING RESOURCES ABOUT THE CIRCUIT COMPONENT FACTSHEETS HOW TO SOLDER GUIDE POWER YOUR PROJECT WITH THIS SUPER CAPACITOR CHARGE CONTROLLER KIT Version 2.0 Teaching Resources Index of Sheets TEACHING
UNIT IV DESIGN OF ENERGY STORING ELEMENTS. Prepared by R. Sendil kumar
 UNIT IV DESIGN OF ENERGY STORING ELEMENTS Prepared by R. Sendil kumar SPRINGS: INTRODUCTION Spring is an elastic body whose function is to distort when loaded and to recover its original shape when the
UNIT IV DESIGN OF ENERGY STORING ELEMENTS Prepared by R. Sendil kumar SPRINGS: INTRODUCTION Spring is an elastic body whose function is to distort when loaded and to recover its original shape when the
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A
 KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
Simple Gears and Transmission
 Simple Gears and Transmission Simple Gears and Transmission page: of 4 How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be?
Simple Gears and Transmission Simple Gears and Transmission page: of 4 How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be?
CDI Revision Notes Term 1 ( ) Grade 12 General Unit 1 Materials & Unit 2 Fundamentals of Electronics
 CDI Revision Notes Term 1 (2017 2018) Grade 12 General Unit 1 Materials & Unit 2 Fundamentals of Electronics STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Student must attempt all questions. For this examination, you must have:
CDI Revision Notes Term 1 (2017 2018) Grade 12 General Unit 1 Materials & Unit 2 Fundamentals of Electronics STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Student must attempt all questions. For this examination, you must have:
MECHANISMS. AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX
 MECHANISMS AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION 2 LEVER 3 PULLEYS 4 BELT AND PULLEY SYSTEM 5 GEARS 6 GEARS WITH CHAIN 7 WORM GEAR 8 RACK AND PINION 9 SCREW AND NUT 10 CAM 11 ECCENTRIC
MECHANISMS AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION 2 LEVER 3 PULLEYS 4 BELT AND PULLEY SYSTEM 5 GEARS 6 GEARS WITH CHAIN 7 WORM GEAR 8 RACK AND PINION 9 SCREW AND NUT 10 CAM 11 ECCENTRIC
Question 2: Around the bar magnet draw its magnetic fields. Answer:
 Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER. Mr. Hussam Samir
 CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
CLASSIFIED 5 MAGNETISM ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION GENERATOR MOTOR - TRANSFORMER Mr. Hussam Samir EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (5) 1. A wire perpendicular to the page carries an electric current in a direction
Work done and Moment. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift.
 Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
Yr 11 Physics worksheet Paper 2 Work done and Moment Q1) The diagram shows weightlifting equipment found in most gyms. When using the equipment, John wants to do 300J of work in each lift. He can vary
A-level PHYSICS A PHYA5/2C. Unit 5C Applied Physics. Section B. Tuesday 28 June 2016
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature A-level PHYSICS A Unit 5C Applied Physics Section B Tuesday 28 June 2016 Materials For this
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature A-level PHYSICS A Unit 5C Applied Physics Section B Tuesday 28 June 2016 Materials For this
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 22.
 Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
BURGLAR ALARM KIT MODEL K-23. Assembly and Instruction Manual ELENCO
 BURGLAR ALARM KIT MODEL K-23 Assembly and Instruction Manual ELENCO Copyright 2017, 1989 ELENCO Electronics, Inc. Revised 2017 REV-R- 753223 No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic,
BURGLAR ALARM KIT MODEL K-23 Assembly and Instruction Manual ELENCO Copyright 2017, 1989 ELENCO Electronics, Inc. Revised 2017 REV-R- 753223 No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic,
P5 STOPPING DISTANCES
 P5 STOPPING DISTANCES Practice Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 84 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 28 The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and
P5 STOPPING DISTANCES Practice Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 84 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 28 The stopping distance of a car is the sum of the thinking distance and
Additional Science. Physics Unit Physics P2 PHY2H. (Jun11PHY2H01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2011.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 Written Paper General Certificate
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Additional Science Unit Physics P2 Physics Unit Physics P2 Written Paper General Certificate
1. What type of material can be induced to become a temporary magnet? A) diamagnetic B) ferromagnetic C) monomagnetic D) paramagnetic
 Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Driver Driven. InputSpeed. Gears
 Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
Gears Gears are toothed wheels designed to transmit rotary motion and power from one part of a mechanism to another. They are fitted to shafts with special devices called keys (or splines) that ensure
Theory of Machines. CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms
 CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms 1. Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. 2. Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one. 3. Define (1) Mechanism (2) Inversion
CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms 1. Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. 2. Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one. 3. Define (1) Mechanism (2) Inversion
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT OUTLINE AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT OUTLINE AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT OUTLINE AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained
B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY
 1 B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
1 B.TECH III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations November 2012 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
LEVEL 1/2 CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL AWARD/CERTIFICATE IN PRINCIPLES IN ENGINEERING AND ENGINEERING BUSINESS. Candidate Surname
 SPECIMEN LEVEL 1/2 CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL AWARD/CERTIFICATE IN PRINCIPLES IN ENGINEERING AND ENGINEERING BUSINESS R101: Engineering Principles Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials:
SPECIMEN LEVEL 1/2 CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL AWARD/CERTIFICATE IN PRINCIPLES IN ENGINEERING AND ENGINEERING BUSINESS R101: Engineering Principles Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials:
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT EDULABZ. the mere presence of magnet, is called...
 Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack
 Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack Name: Class: Date: Time: 63 minutes Marks: 63 marks Comments: Page of 49 The graphs in List A show how the velocities of three vehicles change with time. The statements
Chapter 9 Motion Exam Question Pack Name: Class: Date: Time: 63 minutes Marks: 63 marks Comments: Page of 49 The graphs in List A show how the velocities of three vehicles change with time. The statements
Level 1 Physics, 2018
 90937 909370 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Physics, 2018 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 2.00 p.m. Friday 23 November 2018 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit
90937 909370 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Physics, 2018 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 2.00 p.m. Friday 23 November 2018 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit
CDI Revision Notes Term 1 ( ) Grade 11 Advanced Unit 1 Materials and Unit 2 Fundamentals of Electronics
 CDI Revision Notes Term 1 (2017 2018) Grade 11 Advanced Unit 1 Materials and Unit 2 Fundamentals of Electronics STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Student must attempt all questions. For this examination, you must have:
CDI Revision Notes Term 1 (2017 2018) Grade 11 Advanced Unit 1 Materials and Unit 2 Fundamentals of Electronics STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Student must attempt all questions. For this examination, you must have:
NME-501 : MACHINE DESIGN-I
 Syllabus NME-501 : MACHINE DESIGN-I UNIT I Introduction Definition, Design requirements of machine elements, Design procedure, Standards in design, Selection of preferred sizes, Indian Standards designation
Syllabus NME-501 : MACHINE DESIGN-I UNIT I Introduction Definition, Design requirements of machine elements, Design procedure, Standards in design, Selection of preferred sizes, Indian Standards designation
AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552
 AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552 Mechanical devices Unit 2 Energy, materials, systems and devices 8 Objectives Be able to recognise and identify a range of movements Understand the functions of mechanical
AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552 Mechanical devices Unit 2 Energy, materials, systems and devices 8 Objectives Be able to recognise and identify a range of movements Understand the functions of mechanical
Quali cations. Forename(s) Surname Number of seat
 FOR OFFICIAL USE Quali cations N5National 205 X723/75/0 Mark Engineering Science TUESDAY, 2 MAY :00 PM 2:30 PM *X723750* Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
FOR OFFICIAL USE Quali cations N5National 205 X723/75/0 Mark Engineering Science TUESDAY, 2 MAY :00 PM 2:30 PM *X723750* Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
2.007 Design and Manufacturing I, Spring 2013 EXAM #2
 1 of 7 2.007 Design and Manufacturing I, Spring 2013 EXAM #2 NAME: Date: Tuesday 30 April, 11AM Please answer the following 9 questions showing your work to the extent possible within the allotted time.
1 of 7 2.007 Design and Manufacturing I, Spring 2013 EXAM #2 NAME: Date: Tuesday 30 April, 11AM Please answer the following 9 questions showing your work to the extent possible within the allotted time.
DARSHAN INSTITUTE OF ENGG. & TECH.
 DARSHAN INSTITUTE OF ENGG. & TECH. B.E. Semester V Design of Machine Elements (2151907) Batch: Roll No.: List of Assignments Sr. No. Title Start Date End Date Sign Remark 1. Introduction 2. Design against
DARSHAN INSTITUTE OF ENGG. & TECH. B.E. Semester V Design of Machine Elements (2151907) Batch: Roll No.: List of Assignments Sr. No. Title Start Date End Date Sign Remark 1. Introduction 2. Design against
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
kwh. 6 February
 14 10 The Robinson family have an electricity meter. The diagram shows their meter on two different dates. 28182 kwh 6 January 2 9 030 kwh 6 February (a) Use the meters to find the number of kilowatt hours
14 10 The Robinson family have an electricity meter. The diagram shows their meter on two different dates. 28182 kwh 6 January 2 9 030 kwh 6 February (a) Use the meters to find the number of kilowatt hours
Electromagnetic Induction
 Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper Level ubject Exam oard Unit Topic ooklet O Level Physics ambridge International Examinations Electricity and Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper
Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper Level ubject Exam oard Unit Topic ooklet O Level Physics ambridge International Examinations Electricity and Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Question Paper
Class X Chapter 09 Electrical Power and Household circuits Physics
 EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
EXERCISE- 9 (A) Question 1: Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of current, resistance and time. Solution 1: Electrical energy,
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Code No: R05310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Mechatronics
 9210-223 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Mechatronics 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book calculator (programmable calculators are not allowed) pen pencil
9210-223 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Mechatronics 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book calculator (programmable calculators are not allowed) pen pencil
If the windlass has a diameter of 300mm, calculate the torque produced by the load. (Show all working and units.)
 8. A winch system used to raise a 5N load is shown. (a) If the windlass has a diameter of mm, calculate the torque produced by the load. (Show all working and units.) T = r = 5 5 = 875Nmm = 8. 75Nm substitution
8. A winch system used to raise a 5N load is shown. (a) If the windlass has a diameter of mm, calculate the torque produced by the load. (Show all working and units.) T = r = 5 5 = 875Nmm = 8. 75Nm substitution
0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 204 series 0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/42 Paper 4 (Systems and Control), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 204 series 0445 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 0445/42 Paper 4 (Systems and Control), maximum
Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above?
 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
UNIT 2. INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES. General Objective
 DC GENERATOR (Part 1) E2063/ Unit 2/ 1 UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES General Objective : To apply the basic principle of DC generator, construction principle and types of DC generator.
DC GENERATOR (Part 1) E2063/ Unit 2/ 1 UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES General Objective : To apply the basic principle of DC generator, construction principle and types of DC generator.
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race.
 Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Q1. The graph shows the speed of a runner during an indoor 60 metres race. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the runner during the first four seconds. (Show your working.) (b) How far does the runner travel
Graphical representation of a gear
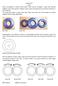 Homework 4 Gears Gears are designed to transmit rotary motion. Often they are arranged in a gear train (meshed together). Gear trains provide a change in speed, torque (turning force) and direction (clockwise
Homework 4 Gears Gears are designed to transmit rotary motion. Often they are arranged in a gear train (meshed together). Gear trains provide a change in speed, torque (turning force) and direction (clockwise
1. (a) Discuss various types of Kinematic links with examples. (b) Explain different types of constrained motions with examples.
 Code No: RR310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3
Code No: RR310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3
2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (Com. to ECE, EIE, BME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (Com. to ECE, EIE, BME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Design and Technology: Electronic Products
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GSE entre Number Design and Technology: Electronic Products Paper 2: Knowledge and Understanding of Electronic Products Tuesday 19 May 2015 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GSE entre Number Design and Technology: Electronic Products Paper 2: Knowledge and Understanding of Electronic Products Tuesday 19 May 2015 Morning
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
ELECTRICITY: INDUCTORS QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS QUESTION TWO (2017;2) In a car engine, an induction coil is used to produce a very high voltage spark. An induction coil acts in a similar way
Mechanisms and Structures. Mechanical Systems. Levers. Basic Forces
 Mechanisms and Structures Mechanical Systems Levers Basic Forces Pupil Name Teacher Class Page 1 MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Our every day lives are made much easier by a variety of mechanical systems that help
Mechanisms and Structures Mechanical Systems Levers Basic Forces Pupil Name Teacher Class Page 1 MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Our every day lives are made much easier by a variety of mechanical systems that help
R10 Set No: 1 ''' ' '' '' '' Code No: R31033
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
*N25842RA0116* N25842RA W850/R1974/ /5/3/3. Turn over
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 9 7 4 3 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 1974/3H Edexcel GCSE Design and Technology: Systems & Control Technology (Mechanisms) (Full Course 1974) Paper
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 9 7 4 3 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 1974/3H Edexcel GCSE Design and Technology: Systems & Control Technology (Mechanisms) (Full Course 1974) Paper
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
James wore a blindfold and ear defenders. He rested his head on a wooden stick pushed into the ground so that he could feel vibrations.
 Level 7 Physics Questions 1. Three pupils took part in an investigation into the speed of sound. All three pupils stood 1020 m from an explosion. Sylvia wore a blindfold. Paul wore ear defenders. James
Level 7 Physics Questions 1. Three pupils took part in an investigation into the speed of sound. All three pupils stood 1020 m from an explosion. Sylvia wore a blindfold. Paul wore ear defenders. James
Unit P.3, P3.2. Using physics to make things work. 1. (a) Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the centre of mass?
 Using physics to make things work 1. Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the centre of mass? The drawing shows a thin sheet of plastic. The sheet is 250 mm wide. Two holes, each with a
Using physics to make things work 1. Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the centre of mass? The drawing shows a thin sheet of plastic. The sheet is 250 mm wide. Two holes, each with a
7.9.1 Circuits. 123 minutes. 170 marks. Page 1 of 56
 7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
Contacts The moveable contact, which is the one affected by the armature is sometimes referred to as the hinge contact.
 Relays & Wiring 101 Basically, a relay is an electrically operated, remotely controlled switch. A simple electromagnetic relay is an adaptation of an electromagnet. It consists of a coil of wire surrounding
Relays & Wiring 101 Basically, a relay is an electrically operated, remotely controlled switch. A simple electromagnetic relay is an adaptation of an electromagnet. It consists of a coil of wire surrounding
V=I R P=V I P=I 2 R. E=P t V 2 R
 Circuit Concepts Learners should be able to: (a) draw, communicate and analyse circuits using standard circuit symbols using standard convention (b) apply current and voltage rules in series and parallel
Circuit Concepts Learners should be able to: (a) draw, communicate and analyse circuits using standard circuit symbols using standard convention (b) apply current and voltage rules in series and parallel
Unit P.2, P2.3. Currents in electric circuits E ½. F Fuel gauge indicator. Fuel tank. Ammeter. Float. Battery. Sliding contact. Pivot 12V.
 Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
FLYWHEEL POWER GENERATION AND MULTIPLICATION
 FLYWHEEL POWER GENERATION AND MULTIPLICATION Chaganti Srinivas Bhaskar 1, Chaganti Bala 2 1,2Cow and Calf Dairy Farms Limited (Research Institute), Hyderabad, Telangana State, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
FLYWHEEL POWER GENERATION AND MULTIPLICATION Chaganti Srinivas Bhaskar 1, Chaganti Bala 2 1,2Cow and Calf Dairy Farms Limited (Research Institute), Hyderabad, Telangana State, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4)
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
Simple Gears and Transmission
 Simple Gears and Transmission Contents How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be? Initial Problem Statement 2 Narrative
Simple Gears and Transmission Contents How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be? Initial Problem Statement 2 Narrative
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
Technical Math 2 Lab 3: Garage Door Spring 2018
 Name: Name: Name: Name: As you may have determined the problem is a broken spring (clearly shown on the left in the picture below) which needs to be replaced. I. Garage Door Basics: Common residential
Name: Name: Name: Name: As you may have determined the problem is a broken spring (clearly shown on the left in the picture below) which needs to be replaced. I. Garage Door Basics: Common residential
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A.
 High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
High Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) Teresa set up the circuit shown in the diagram. The ammeter reading was 0.4 A. A 4 Ω (i) What is the value of the current through the 4Ω resistor? (ii) What is
CODE 10 OECD STANDARD CODE FOR THE OFFICIAL TESTING OF FALLING OBJECT PROTECTIVE STRUCTURES ON AGRICULTURAL AND FORESTRY TRACTORS
 CODE 10 OECD STANDARD CODE FOR THE OFFICIAL TESTING OF FALLING OBJECT PROTECTIVE STRUCTURES ON AGRICULTURAL AND FORESTRY TRACTORS 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 1. DEFINITIONS... 3 1.1 Agricultural
CODE 10 OECD STANDARD CODE FOR THE OFFICIAL TESTING OF FALLING OBJECT PROTECTIVE STRUCTURES ON AGRICULTURAL AND FORESTRY TRACTORS 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 1. DEFINITIONS... 3 1.1 Agricultural
ELECTRICAL SERVICE TECHNICIAN EXAMINATION 16 September 2017 QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOKLET
 Candidate Code No. EST 2074 For Board Use Only Result Date Int Result Date Int ELECTRICAL SERVICE TECHNICIAN EXAMINATION 16 September 2017 QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOKLET INSTRUCTIONS READ CAREFULLY Time Allowed:
Candidate Code No. EST 2074 For Board Use Only Result Date Int Result Date Int ELECTRICAL SERVICE TECHNICIAN EXAMINATION 16 September 2017 QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOKLET INSTRUCTIONS READ CAREFULLY Time Allowed:
(1) 17 km (2) 23 km (3) 16 km (4) 7 km (5) 30 km
 Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Exam 1 September 18, 2017 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Exam 1 September 18, 2017 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17610 16172 4 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17610 16172 4 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
Eastside Invitational Jan 28, 2017 Wind Power Div C - Part 2
 Eastside Invitational Jan 28, 2017 Wind Power Div C - Part 2 Team Information Team Name and number: Name of Students: and Instructions Wind Power is a combination of hands on activities and written test
Eastside Invitational Jan 28, 2017 Wind Power Div C - Part 2 Team Information Team Name and number: Name of Students: and Instructions Wind Power is a combination of hands on activities and written test
Coleman Air C440-HVM 440 Amp Diversion Controller Version 3.2
 Coleman Air C440-HVM 440 Amp Diversion Controller Version 3.2 With Extended Diversion Mode Page 1 Page 2 Introduction This diversion controller is the result of our many attempts to use the controllers
Coleman Air C440-HVM 440 Amp Diversion Controller Version 3.2 With Extended Diversion Mode Page 1 Page 2 Introduction This diversion controller is the result of our many attempts to use the controllers
Technology Exploration_II
 Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion
Technology Exploration_II Module 1 Electrical Machines PREPARED BY Academic Services Sep 2011 Institute of Applied Technology, 2011 Module Objectives Module 1: Electrical Machines After the completion
Pre-lab Questions: Please review chapters 19 and 20 of your textbook
 Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
How to Build with the Mindstorm Kit
 How to Build with the Mindstorm Kit There are many resources available Constructopedias Example Robots YouTube Etc. The best way to learn, is to do Remember rule #1: don't be afraid to fail New Rule: don't
How to Build with the Mindstorm Kit There are many resources available Constructopedias Example Robots YouTube Etc. The best way to learn, is to do Remember rule #1: don't be afraid to fail New Rule: don't
AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the north poles of
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the north poles of
7.9.2 Potential Difference
 7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
Electronics Questions NAT 5
 Electronics Questions NAT 5 1) A radio and a computer mouse are examples of electronic systems. a) An electronic system can be represented by a block diagram as shown. Complete the block diagram by filling
Electronics Questions NAT 5 1) A radio and a computer mouse are examples of electronic systems. a) An electronic system can be represented by a block diagram as shown. Complete the block diagram by filling
