FIG Top view of the reactor core of the ARE. Hexagonal beryllium oxide blocks serve as the moderator. Inconel tubes pass through the moderator
|
|
|
- Hugo Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 16 AIRCRAFT REACTOR EXPERIMENT* The feasibility of the operation of a molten-salt-fueled reactor at a truly high temperature was demonstrated in 1954 in experiments with a reactor constructed at ORNL. The temperature of the fuel exiting from the core of this reactor was about 1500 F, and the temperature of the fuel at the inlet to the core was about 1200 F. The reactor was constructed before the mechanism and control of corrosion by molten salts had been fully explored, and therefore the experimental operation of the reactor was of short duration. Since the work was supported by the Aircraft Reactors Branch of the Atomic Energy Commission, the reactor was called the Aircraft Reactor Experiment (ARE).t The ARE was a thermal reactor in which moderation was accomplished by BeO blocks through which the fluoride fuel was circulated in Inconel tubes arranged in a symmetrical, heterogeneous matrix. The Inconel vessel containing the core was essentially a right cylinder, approximately 52 in. OD and 44 in. in height, with 2-in.-thick walls. The fuel passages consisted of 1-in.-diameter Inconel tubes arranged in six parallel circuits, and each circuit, by the use of reverse bends at top and bottom of the core, made eleven passes through the core. The fuel passages did not traverse the peripheral BeO blocks which served as a reflector around the core of the reactor. A top view of the BeO blocks and the Inconel tubes is shown in Fig The moderator and reflector blocks were cooled by circulating liquid sodium from the bottom to the top of the pressure vessel. The sodium permeated all interstices of the BeO and flowed rapidly through 1/2-in. vertical holes in the reflector sections of the BeO. An elevation drawing of the reactor which illustrates these features is presented in Fig. 16-2, and a photograph of the reactor vessel that was taken before assembly of the thermal shield is shown in Fig Since the purpose of the operation of this experimental reactor was to study the behavior of the circulating-fluoride-fuel system and to identify the problems associated therewith, the power output of the reactor was not utilized but, rather, was simply dumped as heat. The heat-removal system is shown schematically in Fig The fuel was circulated through a finned-tube radiator type of heat exchanger. This radiator was located within a sheet-metal housing of a toroidal shape. In another part of the toroidal housing there was a second finned-tube radiator through *By E. S. Bettis and A'. K. Ergen. tr. C. Briant et al., 1V uclear Science and Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 6, (1957).
2 FIG Top view of the reactor core of the ARE. Hexagonal beryllium oxide blocks serve as the moderator. Inconel tubes pass through the moderator blocks to carry the molten-salt fuel. which plant water flowed. A large centrifugal blower circulated the coolant gas (helium) in the toroidal loop so that heat was picked up from the fuel radiator and dumped into the water radiator. An identical arrangement of radiators and blower was used for cooling the sodium used as the moderator-reflector coolant. In the interest of safety (for removal of afterheat in the event of a pump failure), the sodium circuit was installed in duplicate so that an entire sodium cooling system was available as a spare. These two sodium loops were operated alternately during the experiment in an effort to keep a check on the operability of each loop. Had one loop failed to operate, the experiment would have been terminated for lack of a spare cooling system. The control system of the reactor was based on conventional practice. The three safety shim rods were actuated by electrically driven lead screws which moved electromagnets in a vertical plane. When these magnets were driven to their lowest extremity, an armature was engaged to which the shim (poison) rods were attached. Loss of current in the electromagnets would allow the rods to fall under the action of gravity into thimbles in the central region of the core. The regulating rod was a simple stainlesssteel pipe which was rigidly attached to a rack driven by a reversible elec-
3 FIG Elevative section of the Aircraft Reactor Experiment. tric motor through a pinion. Fission chambers located in the reflector, as well as ionization chambers located outside the pressure shell of the reactor, furnished the neutron and gamma-ray signals for the control system. The shim and control rods which entered the hot reactor core had to be cooled to prevent overheating from neutron capture and gamma-ray absorption. This cooling was effected by circulating helium in a closed loop that included a water-cooled radiator, as in the case of the fuel and sodium circuits. This helium circuit was integral with a helium-filled monitoring annulus which surrounded all fuel and sodium piping in the system. This annulus was formed by putting a continuous stainless-steel sleeve around all hot piping, and the helium circulated in the annulus performed two functions : (1) it kept the hot lines at essentially an even temperature during the warmup period when the system was heated by means of electrical heating units placed on the outer surface of the annulus, and (2) the helium was monitored to ensure that the fuel and sodium piping was leaktight. Large, heated reservoir tanks were connected to the system through isolation valves so that the sodium and the fused fluoride mixture could
4 FIG View of the ARE Vessel before addition of the thermal shield. The external strip heaters with their electrical leads are shown in place.
5 FIG Schematic diagram of the heat-removal system for the ARE. be pressurized from the tanks into the system and could be drained back into the tanks after the experiment was over. Dry helium was used for operating penumatic instruments and for pressurizing the liquids into the system from the tanks. Pumps for both the sodium and the molten-fluoride mixture consisted of sump-type centrifugal pumps with overhanging shafts. The pumps were mounted vertically, and a gas space was provided between the liquid level and the upper bearings of the pump. The pumps were located so that the free-liquid surface in the sump tank was the high point in both the fuel and the sodium circuits. The sump tank of the pump also served as an expansion tank for the liquid. The isometric drawing of the fuel system presented in Fig indicates the relative levels of the components. Both of the liquid systems, fuel and sodium, were fabricated entirely of Inconel, and all closures were made by inert-gas-shielded electric-arc (Heliarc) welding. The welding procedure was adopted after extensive experimental research and developmental work, and meticulous care was exercised in all welding operations. The entire reactor system, that is, the reactor vessel, heat exchangers, pumps, dump tanks, piping, and auxiliary equipment (with the exception of control rod drives), was located in concrete pits below ground level. After the reactor was brought to criticality by manual fuel injection, concrete blocks were placed on top of the pits to complete the shielding of the system as required during power operation. Fuel was added as a molten mixture of NaF and UF4 (enriched in U235) after the sodium system had been heated and filled with sodium and the fuel system had been heated and filled with fuel carrier a molten mixture of Nat" and ZrF4. The fuel additions were made into the sump of the fuel pump through the use of a temporary enrichment system that was capable of injecting (by manual operation) a few hundred grams of fuel mixture
6 FIG Layout of the fuel system components for the ARE. at a time. This method of fuel addition was laborious and time-consuming, but it effectively and safely enriched the reactor to a critical concentration. The reactor was taken to criticality essentially without incident. The total amount of U235 added to the system to make the reactor critical was approximately 61 kg, but small amounts of fuel were withdrawn from the system for sampling and in trimming the pump level. The uranium concentration at criticality was 384 g/liter of fluoride mixture. The calculated volume of the core was 38.8 liters at 1300 F, and thus the clean critical mass of the reactor was 14.9 kg of U235. It was demonstrated that the reactor had an over-all temperature coefficient of reactivity of -6 X 10-5 (Ak/k)/ F. As was anticipated, the fast negative temperature coefficient of reactivity (associated with the fuel expansion coefficient) served to stabilize the reactor power level. From a power lever of 200 kw upward, the temperature coefficient controlled the system so precisely that the reactor responded to load demands in a thoroughly reliable manner. The response of the reactor was demonstrated in a number of experiments, one of which is described in Fig The abscissa, to be read from right to left, is the time in minutes, and the print-outs from recorders giving the reactor inlet and outlet temperatures are the ordinate. Initially, in this experiment, the reactor was operating at low power. Then the heat
7 FIG Chart of inlet and outlet temperatures for the ARE as influenced by various experimental procedures. extraction from the fuel was slowly increased and there was, first, a resultant decrease in the temperature of the fuel which reached the reactor inlet from the heat exchanger. This increased the reactivity and the reactor power, as indicated by the temperature rise at the reactor outlet. The spread of inlet and outlet temperatures corresponds to a power level of 2.5 '-\Iw. When the heat extraction was reduced, the inlet temperature
8 rose and the outlet temperature fell until the two temperatures became nearly coincident. As may he seen, the control rods (lid not determine the power output ; they only influenced the average temperature. Insertion of the shire rods decreased the temperature. Another rapid increase in the power demand on the fuel system again spread apart the inlet and outlet temperature recordings, and full insertion and full withdrawal of the regulating rod depressed and then raised both temperatures simultaneously. Next, the power extraction was stopped and the regulating rod was inserted to make the reactor subcritical. The third spread of the temperatures in Fig. 1G-6 was a result of a demonstration which showed that the reactor could be brought to criticality, without use of the rods, by the power demand alone. Power extraction from the sodium system cooled the reactor to make it critical, and power extraction from the fuel again caused the spread of inlet and outlet temperatures. The remarkable stability of the system made it unexpectedly possible to demonstrate that no more than 5% of the Xer 35 was retained in the molten fuel. It had been computed that the xenon poisoning after 27 hr of operation at full power would amount to 2 X 10-3 in 0k/k if all the xenon formed stayed in the fuel until it decayed. This level of poisoning was less than would be expected from the usual equations, partly because the fuel spent only one-fourth of the time in the core and was thus effectively only subjected to one-fourth of the flux, and partly because many of the neutrons had energies above the large Xe 135 absorption resonance. As little as 5% of this computed poisoning would have been detectable, but none was found. There was a small leakage from the gas volume above the liquid surface of the fuel pumps which made operation at a high power level somewhat awkward, but danger to operating personnel was circumvented by operating with the reactor pit at a subatmospheric pressure and remotely exhausting the pit gases to the atmosphere at a location where they were adequately dispersed. The entire program of experiments that had been planned for the reactor was completed satisfactorily. The reactor was shut down after a total power production of 96 '-\Iwh, and it was later dismantled. The fuel and sodium systems had been in operation for a total of 462 and 635 hr, respectively, including 221 hr of nuclear operation, with the final 74 hr of operation in the megawatt range.
ANALYSIS OF BREST-OD-300 SAFETY DURING ANTICIPATED OPERATIONAL OCCURRENCES
 ANALYSIS OF BREST-OD-300 SAFETY DURING ANTICIPATED OPERATIONAL OCCURRENCES D.V. Didorin, V.A. Kogut, A.G. Muratov, V.V. Tyukov, A.V. Moiseev (NIKIET, Moscow, Russia) 1. Brief description of the aim and
ANALYSIS OF BREST-OD-300 SAFETY DURING ANTICIPATED OPERATIONAL OCCURRENCES D.V. Didorin, V.A. Kogut, A.G. Muratov, V.V. Tyukov, A.V. Moiseev (NIKIET, Moscow, Russia) 1. Brief description of the aim and
POWER RAMPING AND CYCLING TESTING OF VVER FUEL RODS IN THE MIR REACTOR
 POWER RAMPING AND CYCLING TESTING OF VVER FUEL RODS IN THE MIR REACTOR A.G. Eshcherkin*, V.A. Ovchinnikov, E.E. Shakhmut, E.E. Kuznetsova, A.L. Izhutov, V.V. Kalygin INTRODUCTION A series of experiments
POWER RAMPING AND CYCLING TESTING OF VVER FUEL RODS IN THE MIR REACTOR A.G. Eshcherkin*, V.A. Ovchinnikov, E.E. Shakhmut, E.E. Kuznetsova, A.L. Izhutov, V.V. Kalygin INTRODUCTION A series of experiments
Report No. IDO APPENDIX B ML-1 PLANT CHARACTERISTICS 1. GENERAL Mu to gas; 3.41 Mw total Cycle efficiency. Gross elect. wr. Net elect.
 ... Report No. IDO-28653 APPENDIX B ML-1 PLANT CHARACTERISTICS 0 Design performance at 100 F Gross electrical output Net electrical output 1. GENERAL Reactor thermal power 2.98 Mu to gas; 3.41 Mw total
... Report No. IDO-28653 APPENDIX B ML-1 PLANT CHARACTERISTICS 0 Design performance at 100 F Gross electrical output Net electrical output 1. GENERAL Reactor thermal power 2.98 Mu to gas; 3.41 Mw total
FRM II Converter Facility
 FRM II Converter Facility Volker Zill Heiko Gerstenberg Axel Pichmaier Technical University of Munich Forschungs-Neutronenquelle Heinz Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II) Lichtenbergstrasse 1, 85748 Garching - Federal
FRM II Converter Facility Volker Zill Heiko Gerstenberg Axel Pichmaier Technical University of Munich Forschungs-Neutronenquelle Heinz Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II) Lichtenbergstrasse 1, 85748 Garching - Federal
Re evaluation of Maximum Fuel Temperature
 IAEA Technical Meeting on on Re evaluation of Maximum Operating Temperatures and Accident Conditions for High Temperature Reactor Fuel and Structural Materials, 10 12 July 2012, Vienna, Austria Re evaluation
IAEA Technical Meeting on on Re evaluation of Maximum Operating Temperatures and Accident Conditions for High Temperature Reactor Fuel and Structural Materials, 10 12 July 2012, Vienna, Austria Re evaluation
Single-phase Coolant Flow and Heat Transfer
 22.06 ENGINEERING OF NUCLEAR SYSTEMS - Fall 2010 Problem Set 5 Single-phase Coolant Flow and Heat Transfer 1) Hydraulic Analysis of the Emergency Core Spray System in a BWR The emergency spray system of
22.06 ENGINEERING OF NUCLEAR SYSTEMS - Fall 2010 Problem Set 5 Single-phase Coolant Flow and Heat Transfer 1) Hydraulic Analysis of the Emergency Core Spray System in a BWR The emergency spray system of
Design Study for Passive Shutdown System of the PGSFR
 Design Study for Passive Shutdown System of the PGSFR 2015. 10. 20 Lee, Jae-Han Koo, Gyeong-Hoi 20151021 IAEA TM on passive shutdown system 1 1. Reactor Control and Shutdown Concepts of PGSFR 6 Primary
Design Study for Passive Shutdown System of the PGSFR 2015. 10. 20 Lee, Jae-Han Koo, Gyeong-Hoi 20151021 IAEA TM on passive shutdown system 1 1. Reactor Control and Shutdown Concepts of PGSFR 6 Primary
FUNDAMENTAL SAFETY OVERVIEW VOLUME 2: DESIGN AND SAFETY CHAPTER E: THE REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM AND RELATED SYSTEMS
 PAGE : 1 / 13 4. PRESSURISER 4.1. DESCRIPTION The pressuriser (PZR) is a pressurised vessel forming part of the reactor coolant pressure boundary (CPP) [RCPB]. It comprises a vertical cylindrical shell,
PAGE : 1 / 13 4. PRESSURISER 4.1. DESCRIPTION The pressuriser (PZR) is a pressurised vessel forming part of the reactor coolant pressure boundary (CPP) [RCPB]. It comprises a vertical cylindrical shell,
Finally, the INOR alloys (see Chapter 13) show promise of being as resistant to the beryllium salts as to the zirconium salts, and therefore there is
 CHAPTER 14 NUCLEAR ASPECTS OF MOLTEN-SALT REACTORS* The ability of certain molten salts to dissolve uranium and thorium. salts in quantities of reactor interest made possible the consideration of fluidfueled
CHAPTER 14 NUCLEAR ASPECTS OF MOLTEN-SALT REACTORS* The ability of certain molten salts to dissolve uranium and thorium. salts in quantities of reactor interest made possible the consideration of fluidfueled
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER WITH TRIANGULAR BAFFLES
 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Volume: 3 Issue: 8 Aug-216 www.irjet.net p-issn: 2395-72 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER WITH
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Volume: 3 Issue: 8 Aug-216 www.irjet.net p-issn: 2395-72 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER WITH
1: CANDU Reactor. B. Rouben McMaster University Nuclear Reactor Physics EP 4D03/6D Sept-Dec September 1
 1: CANDU Reactor B. Rouben McMaster University Nuclear Reactor Physics EP 4D03/6D03 2015 Sept-Dec 2015 September 1 Outline A quick look at the design of CANDU Reactors: Reactor Assembly Pressure Tubes
1: CANDU Reactor B. Rouben McMaster University Nuclear Reactor Physics EP 4D03/6D03 2015 Sept-Dec 2015 September 1 Outline A quick look at the design of CANDU Reactors: Reactor Assembly Pressure Tubes
AP1000 European 5. Reactor Coolant System and Connected Systems Design Control Document
 CHAPTER 5 REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM AND CONNECTED SYSTEMS 5.1 Summary Description This section describes the reactor coolant system (RCS) and includes a schematic flow diagram of the reactor coolant system
CHAPTER 5 REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM AND CONNECTED SYSTEMS 5.1 Summary Description This section describes the reactor coolant system (RCS) and includes a schematic flow diagram of the reactor coolant system
Fuel Management in EWN
 Fuel Management in EWN Fuel Management in EWN Dr. Helmut Förtsch, EWN GmbH Eberhard Thurow, EWN GmbH Fuel Management in EWN Part 1: Status in 1990 Part 2: Spent nuclear fuel strategy of EWN Part 3: Technical
Fuel Management in EWN Fuel Management in EWN Dr. Helmut Förtsch, EWN GmbH Eberhard Thurow, EWN GmbH Fuel Management in EWN Part 1: Status in 1990 Part 2: Spent nuclear fuel strategy of EWN Part 3: Technical
AP1000 European 7. Instrumentation and Controls Design Control Document
 7.3 Engineered Safety Features AP1000 provides instrumentation and controls to sense accident situations and initiate engineered safety features (ESF). The occurrence of a limiting fault, such as a loss
7.3 Engineered Safety Features AP1000 provides instrumentation and controls to sense accident situations and initiate engineered safety features (ESF). The occurrence of a limiting fault, such as a loss
DESCRIPTION OF THE DELPHI SUBCRITICAL ASSEMBLY AT DELFT UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 IRI-131-2003-008 DESCRIPTION OF THE DELPHI SUBCRITICAL ASSEMBLY AT DELFT UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY J.L. Kloosterman October, 2003 INTRODUCTION For educational purposes, the Reactor Physics Department of
IRI-131-2003-008 DESCRIPTION OF THE DELPHI SUBCRITICAL ASSEMBLY AT DELFT UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY J.L. Kloosterman October, 2003 INTRODUCTION For educational purposes, the Reactor Physics Department of
CHAPTER-3 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP. The experimental set up is made with necessary. instrumentations to evaluate the performance, emission and
 95 CHAPTER-3 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP The experimental set up is made with necessary instrumentations to evaluate the performance, emission and combustion parameters of the compression ignition engine at different
95 CHAPTER-3 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP The experimental set up is made with necessary instrumentations to evaluate the performance, emission and combustion parameters of the compression ignition engine at different
TREAT Startup Update
 Resumption of Transient Testing Program TREAT Startup Update John D. Bumgardner Director, Resumption of Transient Testing Program December 5 th, 2018 1 Facility Location 2 Nuclear Fuels Development Requires
Resumption of Transient Testing Program TREAT Startup Update John D. Bumgardner Director, Resumption of Transient Testing Program December 5 th, 2018 1 Facility Location 2 Nuclear Fuels Development Requires
AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant Squib Valve Design Challenges & Regulatory Interface. September 2017
 AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant Squib Valve Design Challenges & Regulatory Interface September 2017 Randy C. Ivey Director Supplier Quality Oversight Westinghouse Electric Company AP1000 is a trademark or registered
AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant Squib Valve Design Challenges & Regulatory Interface September 2017 Randy C. Ivey Director Supplier Quality Oversight Westinghouse Electric Company AP1000 is a trademark or registered
Section 3 Technical Information
 Section 3 Technical Information In this Module: Engine identification Modes of operation Battery charging and heat manage operation Service and repair procedures Maintenance requirements Engine Identification
Section 3 Technical Information In this Module: Engine identification Modes of operation Battery charging and heat manage operation Service and repair procedures Maintenance requirements Engine Identification
Module 09 Heavy Water Moderated and Cooled Reactors (CANDU)
 Prof.Dr. Böck Technical University Vienna Atominstitut Stadionallee 2, 1020 Vienna, Austria ph: ++43-1-58801 141368 boeck@ati.ac.at Module 09 Heavy Water Moderated and Cooled Reactors (CANDU) 1.10.2016
Prof.Dr. Böck Technical University Vienna Atominstitut Stadionallee 2, 1020 Vienna, Austria ph: ++43-1-58801 141368 boeck@ati.ac.at Module 09 Heavy Water Moderated and Cooled Reactors (CANDU) 1.10.2016
INTEGRATION OF THE MODULAR DUAL COOLANT PB-17LI BLANKET CONCEPT IN THE ARIES-CS POWER PLANT
 INTEGRATION OF THE MODULAR DUAL COOLANT PB-17LI BLANKET CONCEPT IN THE ARIES-CS POWER PLANT X.R. Wang 1, S. Malang 2, L.A. El-Guebaly 3, A. R. Raffray 1 and the ARIES Team 1 University of California, San
INTEGRATION OF THE MODULAR DUAL COOLANT PB-17LI BLANKET CONCEPT IN THE ARIES-CS POWER PLANT X.R. Wang 1, S. Malang 2, L.A. El-Guebaly 3, A. R. Raffray 1 and the ARIES Team 1 University of California, San
JOYO, THE IRRADIATION AND DEMONSTRATION TEST FACILITY OF FBR DEVELOPMENT
 JOYO, THE IRRADIATION AND DEMONSTRATION TEST FACILITY OF FBR DEVELOPMENT Aoyama T. 1, Sekine T. 1, Nakai S. 1 and Suzuki S. 1 1 O-arai Research and Development Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki,
JOYO, THE IRRADIATION AND DEMONSTRATION TEST FACILITY OF FBR DEVELOPMENT Aoyama T. 1, Sekine T. 1, Nakai S. 1 and Suzuki S. 1 1 O-arai Research and Development Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki,
Profile SFR-2 ESPRESSO CHINA. Energy(CIAE),FangshanDistrict,Beijing,China
 Profile SFR-2 CHINA GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone, email): SODIUM China Institute
Profile SFR-2 CHINA GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone, email): SODIUM China Institute
AIRCRAFT GENERAL KNOWLEDGE (1) AIRFRAME/SYSTEMS/POWERPLANT
 1 In flight, a cantilever wing of an airplane containing fuel undergoes vertical loads which produce a bending moment: A highest at the wing root B equal to the zero -fuel weight multiplied by the span
1 In flight, a cantilever wing of an airplane containing fuel undergoes vertical loads which produce a bending moment: A highest at the wing root B equal to the zero -fuel weight multiplied by the span
CHAPTER 20 Fuel Handling and Storage
 1 CHAPTER 20 Fuel Handling and Storage prepared by Diane Damario P. Eng, Senior Engineer Mechanical, Fuel Handling, Nuclear Power, SNC-Lavalin Nuclear Inc., Candu Energy Inc. Summary: CANDU reactors are
1 CHAPTER 20 Fuel Handling and Storage prepared by Diane Damario P. Eng, Senior Engineer Mechanical, Fuel Handling, Nuclear Power, SNC-Lavalin Nuclear Inc., Candu Energy Inc. Summary: CANDU reactors are
Heat Exchangers (Chapter 5)
 Heat Exchangers (Chapter 5) 2 Learning Outcomes (Chapter 5) Classification of heat exchangers Heat Exchanger Design Methods Overall heat transfer coefficient LMTD method ε-ntu method Heat Exchangers Pressure
Heat Exchangers (Chapter 5) 2 Learning Outcomes (Chapter 5) Classification of heat exchangers Heat Exchanger Design Methods Overall heat transfer coefficient LMTD method ε-ntu method Heat Exchangers Pressure
TerraPower s Molten Chloride Fast Reactor Program. August 7, 2017 ANS Utility Conference
 TerraPower s Molten Chloride Fast Reactor Program August 7, 2017 ANS Utility Conference Molten Salt Reactor Features & Options Key Molten Salt Reactor (MSR) Distinguishing Features Rather than using solid
TerraPower s Molten Chloride Fast Reactor Program August 7, 2017 ANS Utility Conference Molten Salt Reactor Features & Options Key Molten Salt Reactor (MSR) Distinguishing Features Rather than using solid
FUNDAMENTAL SAFETY OVERVIEW VOLUME 2: DESIGN AND SAFETY CHAPTER D: REACTOR AND CORE
 PAGE : 1 / 12 SUB-CHAPTER D.2 FUEL DESIGN This sub-chapter lists the safety requirements related to the fuel assembly design. The main characteristics of the fuel and control rod assemblies which have
PAGE : 1 / 12 SUB-CHAPTER D.2 FUEL DESIGN This sub-chapter lists the safety requirements related to the fuel assembly design. The main characteristics of the fuel and control rod assemblies which have
Back pressure safety valves
 1/12 Back pressure safety valves 1. Introduction 2. Safety valve in the installation 3. Influence of back pressure on functioning behaviour 4. Limits of admissible back pressure (without metal bellow)
1/12 Back pressure safety valves 1. Introduction 2. Safety valve in the installation 3. Influence of back pressure on functioning behaviour 4. Limits of admissible back pressure (without metal bellow)
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING)
 POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) TILT STEERING COLUMN 1. Tilt Steering Column A: TILT MECHANISM The steering wheel vertical position can be adjusted within a 38 mm (1.50 in) range by using the tilt
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) TILT STEERING COLUMN 1. Tilt Steering Column A: TILT MECHANISM The steering wheel vertical position can be adjusted within a 38 mm (1.50 in) range by using the tilt
Types, Problems and Conversion Potential of Reactors Produced in Russia
 Types, Problems and Conversion Potential of Reactors Produced in Russia Moscow, Russian-American symposium on Conversion of the Research Reactors to LEU Fuel, 8-10 June 2011 Director, General Designer
Types, Problems and Conversion Potential of Reactors Produced in Russia Moscow, Russian-American symposium on Conversion of the Research Reactors to LEU Fuel, 8-10 June 2011 Director, General Designer
Current Status of the Melcor Nodalization for Atucha I Nuclear Power Plant. Zárate. S.M. and Valle Cepero, R.
 Current Status of the Melcor Nodalization for Atucha I Nuclear Power Plant Zárate. S.M. and Valle Cepero, R. presentado en USNRC Cooperative Severe Accident Research Program (CSARP), Maryland, EE. UU.,
Current Status of the Melcor Nodalization for Atucha I Nuclear Power Plant Zárate. S.M. and Valle Cepero, R. presentado en USNRC Cooperative Severe Accident Research Program (CSARP), Maryland, EE. UU.,
SECTION 3.00 WARNING WARNING ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION
 SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
NATIONAL NUCLEAR SECURITY ADMINISTRATION GLOBAL THREAT REDUCTION INITIATIVE Core Modifications to address technical challenges of conversion
 NATIONAL NUCLEAR SECURITY ADMINISTRATION GLOBAL THREAT REDUCTION INITIATIVE Core Modifications to address technical challenges of conversion G17 G18 G19 G20 G21 G16 F15 F16 G22 F17 F14 9.76 9.85 9.91 F18
NATIONAL NUCLEAR SECURITY ADMINISTRATION GLOBAL THREAT REDUCTION INITIATIVE Core Modifications to address technical challenges of conversion G17 G18 G19 G20 G21 G16 F15 F16 G22 F17 F14 9.76 9.85 9.91 F18
Fuel cladding stress evaluation for the control rods pattern change at the Shimane Nuclear Power Station Unit No1 and No2
 GENES4/ANP2003, Sep. 15-19, 2003, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 1086 Fuel cladding stress evaluation for the control rods pattern change at the Shimane Nuclear Power Station Unit No1 and No2 Saemi Shimatani 1*, Masayuki
GENES4/ANP2003, Sep. 15-19, 2003, Kyoto, JAPAN Paper 1086 Fuel cladding stress evaluation for the control rods pattern change at the Shimane Nuclear Power Station Unit No1 and No2 Saemi Shimatani 1*, Masayuki
M. A. Green, and S. Yu Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley CA 94720, USA
 LBNL-48445 SCMAG-749 SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FOR INDUCTION LINAC PHASE-ROTATION IN A NEUTRINO FACTORY M. A. Green, and S. Yu Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley CA 94720, USA ABSTRACT The neutrino
LBNL-48445 SCMAG-749 SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FOR INDUCTION LINAC PHASE-ROTATION IN A NEUTRINO FACTORY M. A. Green, and S. Yu Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley CA 94720, USA ABSTRACT The neutrino
Neutronics of Prismatic Fluoride Salt Cooled High Temperature Reactors
 Neutronics of Prismatic Fluoride Salt Cooled High Temperature Reactors Workshop on Advanced Reactors Concepts PHYSOR 2012 Knoxville, TN April 15, 2012 Dan Ilas IlasD@ornl.gov Main Neutronic Design Characteristics
Neutronics of Prismatic Fluoride Salt Cooled High Temperature Reactors Workshop on Advanced Reactors Concepts PHYSOR 2012 Knoxville, TN April 15, 2012 Dan Ilas IlasD@ornl.gov Main Neutronic Design Characteristics
ITER Shield Blanket Design Activities At SWIP
 1 ITER Shield Blanket Design Activities At SWIP F. Zhang 1), W. S. Kang 1), J. H. Wu 1), Y. K. Fu 1), J. M. Chen 1) F. Elio 2) 1) Southwestern Institute of Physics, P. O. Box 432 Chengdu, 610041, China
1 ITER Shield Blanket Design Activities At SWIP F. Zhang 1), W. S. Kang 1), J. H. Wu 1), Y. K. Fu 1), J. M. Chen 1) F. Elio 2) 1) Southwestern Institute of Physics, P. O. Box 432 Chengdu, 610041, China
Improvement of Irradiation Capability in the Experimental Fast Reactor Joyo
 IAEA Technical Meeting November, 2008 Improvement of Irradiation Capability in the Experimental Fast Reactor Joyo Tomonori Soga Fast Reactor Technology Section Experimental Fast Reactor Department O-arai
IAEA Technical Meeting November, 2008 Improvement of Irradiation Capability in the Experimental Fast Reactor Joyo Tomonori Soga Fast Reactor Technology Section Experimental Fast Reactor Department O-arai
Journal of Engineering Sciences and Innovation Volume 2, Issue 4 / 2017, pp
 Journal of Engineering Sciences and Innovation Volume 2, Issue 4 / 2017, pp. 11-19 Technical Sciences Academy of Romania www.jesi.astr.ro A. Mechanics, Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Mechatronics
Journal of Engineering Sciences and Innovation Volume 2, Issue 4 / 2017, pp. 11-19 Technical Sciences Academy of Romania www.jesi.astr.ro A. Mechanics, Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Mechatronics
Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton Cycle
 The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Hydraulic energy control, conductive part
 Chapter 2 2 Hydraulic energy control, conductive part Chapter 2 Hydraulic energy control, conductive part To get the hydraulic energy generated by the hydraulic pump to the actuator, cylinder or hydraulic
Chapter 2 2 Hydraulic energy control, conductive part Chapter 2 Hydraulic energy control, conductive part To get the hydraulic energy generated by the hydraulic pump to the actuator, cylinder or hydraulic
Chemical decontamination in nuclear systems radiation protection issues during planning and realization
 Chemical decontamination in nuclear systems radiation protection issues during planning and realization F. L. Karinda, C. Schauer, R. Scheuer TÜV SÜD Industrie Service GmbH, Westendstrasse 199, 80686 München
Chemical decontamination in nuclear systems radiation protection issues during planning and realization F. L. Karinda, C. Schauer, R. Scheuer TÜV SÜD Industrie Service GmbH, Westendstrasse 199, 80686 München
DEMO FUSION CORE ENGINEERING: Blanket Integration and Maintenance
 DEMO FUSION CORE ENGINEERING: Blanket Integration and Maintenance 1.) Overview on European Blanket Concepts and Integration principles 2.) Large Module Integration 3.) Multi Module Segment (MMS) Integration
DEMO FUSION CORE ENGINEERING: Blanket Integration and Maintenance 1.) Overview on European Blanket Concepts and Integration principles 2.) Large Module Integration 3.) Multi Module Segment (MMS) Integration
IMPROVED BWR CORE DESIGN USING HYDRIDE FUEL
 Joint Reactor Seminar University of Tokyo (GoNERI) and UC Berkeley March 5, 2009 IMPROVED BWR CORE DESIGN USING HYDRIDE FUEL Massimiliano Fratoni, Alessandro Piazza, Ehud Greenspan University of California,
Joint Reactor Seminar University of Tokyo (GoNERI) and UC Berkeley March 5, 2009 IMPROVED BWR CORE DESIGN USING HYDRIDE FUEL Massimiliano Fratoni, Alessandro Piazza, Ehud Greenspan University of California,
Design, Fabrication and Testing of helical tube in tube coil heat exachanger
 Design, Fabrication and Testing of helical tube in tube coil heat exachanger #1 Sachin Meshram, #2 Prof.P.T.Nitnaware, #3 M.R.Jagdale ABSTRACT Helical coil heat exchangers are one of the most common equipment
Design, Fabrication and Testing of helical tube in tube coil heat exachanger #1 Sachin Meshram, #2 Prof.P.T.Nitnaware, #3 M.R.Jagdale ABSTRACT Helical coil heat exchangers are one of the most common equipment
LINE SILENCER. Copyright 2009 by PULSCO Incorporated. All rights reserved. Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
 LINE SILENCER Copyright 2009 by PULSCO Incorporated. All rights reserved. Reproduction without permission is prohibited. PRODUCT GUIDE PULSCO LINE SILENCER TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION PAGE PULSCO LINE
LINE SILENCER Copyright 2009 by PULSCO Incorporated. All rights reserved. Reproduction without permission is prohibited. PRODUCT GUIDE PULSCO LINE SILENCER TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION PAGE PULSCO LINE
Installation manual. Cooling system. Industrial engines DC09, DC13, DC16 OC16. 01:05 Issue 12 en-gb. Scania CV AB 2018, Sweden
 Installation manual Cooling system Industrial engines DC0, DC13, DC OC 333 3 01:05 Issue en-gb Changes from the previous issue...3 Design and dimensioning...3 Expansion tank...4 and earlier emission levels...
Installation manual Cooling system Industrial engines DC0, DC13, DC OC 333 3 01:05 Issue en-gb Changes from the previous issue...3 Design and dimensioning...3 Expansion tank...4 and earlier emission levels...
Chapter 13: Application of Proportional Flow Control
 Chapter 13: Application of Proportional Flow Control Objectives The objectives for this chapter are as follows: Review the benefits of compensation. Learn about the cost to add compensation to a hydraulic
Chapter 13: Application of Proportional Flow Control Objectives The objectives for this chapter are as follows: Review the benefits of compensation. Learn about the cost to add compensation to a hydraulic
OPAL : Commissioning a New Research Reactor. IAEA Conference, Sydney, November 2007
 OPAL : Commissioning a New Research Reactor IAEA Conference, Sydney, November 2007 Project Timeline Government announcement 1997 Design and licence application 2000/2001 Construction Licence April 2002
OPAL : Commissioning a New Research Reactor IAEA Conference, Sydney, November 2007 Project Timeline Government announcement 1997 Design and licence application 2000/2001 Construction Licence April 2002
Multipulse Detonation Initiation by Spark Plugs and Flame Jets
 Multipulse Detonation Initiation by Spark Plugs and Flame Jets S. M. Frolov, V. S. Aksenov N.N. Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia Moscow Physical Engineering
Multipulse Detonation Initiation by Spark Plugs and Flame Jets S. M. Frolov, V. S. Aksenov N.N. Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia Moscow Physical Engineering
1. Review of the Test
 NuMI-B-800 Ionization Chambers used at the Fermilab Booster Test Beam Sacha E. Kopp, Robert M. Zwaska, Marek Proga University of Texas, Austin, TX 1. Review of the Test The Beam Monitoring group wished
NuMI-B-800 Ionization Chambers used at the Fermilab Booster Test Beam Sacha E. Kopp, Robert M. Zwaska, Marek Proga University of Texas, Austin, TX 1. Review of the Test The Beam Monitoring group wished
KSTAR Assembly. National Fusion Research Center, Daejeon, Korea
 1 FT/2-2 KSTAR Assembly H. L. Yang, H. K. Kim, K. M. Kim, J. W. Sa, S. T. Kim, H. T. Kim, K. H. Hong, W. C. Kim, K. H. Kim, Y. S. Kim, J. Y. Kim, C. H. Choi, Y. K. Oh, Y. M. Park, M. Kwon, J. S. Bak, G.
1 FT/2-2 KSTAR Assembly H. L. Yang, H. K. Kim, K. M. Kim, J. W. Sa, S. T. Kim, H. T. Kim, K. H. Hong, W. C. Kim, K. H. Kim, Y. S. Kim, J. Y. Kim, C. H. Choi, Y. K. Oh, Y. M. Park, M. Kwon, J. S. Bak, G.
Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234
 Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234 STEAM VALVE HYDRAULIC CONTROL The movement of large control valves to regulate the steam supply to modern steam turbines, requires amplification of the control
Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234 STEAM VALVE HYDRAULIC CONTROL The movement of large control valves to regulate the steam supply to modern steam turbines, requires amplification of the control
Introduction and Summary
 6 Chapter Core and Fuel Design Introduction and Summary The design of the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) core and fuel is based on the proper combination of many design variables and operating experience.
6 Chapter Core and Fuel Design Introduction and Summary The design of the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) core and fuel is based on the proper combination of many design variables and operating experience.
SMALL-SIZE BETATRONS FOR RADIOGRAPHIC INSPECTION
 SMALL-SIZE BETATRONS FOR RADIOGRAPHIC INSPECTION M. Stein 1, V. A. Kasyanov 1, V. L. Chakhlov 1, J. Macleod 2, P. Marjoribanks 2, and S. Hubbard 2 1 RII at TPU, Tomsk, Russia; 2 JME Ltd., Lowestoft, UK
SMALL-SIZE BETATRONS FOR RADIOGRAPHIC INSPECTION M. Stein 1, V. A. Kasyanov 1, V. L. Chakhlov 1, J. Macleod 2, P. Marjoribanks 2, and S. Hubbard 2 1 RII at TPU, Tomsk, Russia; 2 JME Ltd., Lowestoft, UK
WM2012 Conference, February 26 March 1, 2012, Phoenix, Arizona, USA. Treatment of Uranium Slugs at the CEA Marcoule site 12026
 Treatment of Uranium Slugs at the CEA Marcoule site 12026 Didier Boya, Line Fourquet CEA Marcoule, France ABSTRACT The decladding units on the Marcoule nuclear site in southeast France were commissioned
Treatment of Uranium Slugs at the CEA Marcoule site 12026 Didier Boya, Line Fourquet CEA Marcoule, France ABSTRACT The decladding units on the Marcoule nuclear site in southeast France were commissioned
Installation Procedures
 For the precision ball and roller bearings supplied by MRC Bearings, skill and cleanliness while handling, mounting and dismounting are necessary to ensure satisfactory bearing performance. As precision
For the precision ball and roller bearings supplied by MRC Bearings, skill and cleanliness while handling, mounting and dismounting are necessary to ensure satisfactory bearing performance. As precision
Question 2: Around the bar magnet draw its magnetic fields. Answer:
 Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING THE HORIZONTAL FUEL CHANNELS IN THE CANDU 6 NUCLEAR REACTOR. PART 1 - PRESENTATION OF THE FUEL CHANNEL
 6 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2015 15-16 October 2015, Braşov, Romania CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING THE HORIZONTAL FUEL CHANNELS IN THE CANDU 6 NUCLEAR
6 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2015 15-16 October 2015, Braşov, Romania CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING THE HORIZONTAL FUEL CHANNELS IN THE CANDU 6 NUCLEAR
CFD ANALYSIS ON LOUVERED FIN
 CFD ANALYSIS ON LOUVERED FIN P.Prasad 1, L.S.V Prasad 2 1Student, M. Tech Thermal Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India 2Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam,
CFD ANALYSIS ON LOUVERED FIN P.Prasad 1, L.S.V Prasad 2 1Student, M. Tech Thermal Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India 2Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam,
Bombardier Challenger Auxiliary Power Unit
 GENERAL A Honeywell 36 150(CL) constant-speed gas turbine auxiliary power unit (APU) is installed within a fire-resistant compartment in the aft equipment bay. The APU drives a generator, providing AC
GENERAL A Honeywell 36 150(CL) constant-speed gas turbine auxiliary power unit (APU) is installed within a fire-resistant compartment in the aft equipment bay. The APU drives a generator, providing AC
CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF HELICAL COIL HEAT EXCHANGE USING CFD
 CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF HELICAL COIL HEAT EXCHANGE USING CFD Rudragouda R Patil 1, V Santosh Kumar 2, R Harish 3, Santosh S Ghorpade 4 1,3,4 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Department, Jayamukhi
CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF HELICAL COIL HEAT EXCHANGE USING CFD Rudragouda R Patil 1, V Santosh Kumar 2, R Harish 3, Santosh S Ghorpade 4 1,3,4 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Department, Jayamukhi
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
 Industrial Type Turbine Flowmeter NT Hygienic Type Turbine Flowmeter BNO Low Flow Pelton Wheel Flowmeter NS INSTALLATION AND OPERATION Nixon Flowmeters Ltd. Leckhampton, Cheltenham, Glos UK Tel. 0044 (0)
Industrial Type Turbine Flowmeter NT Hygienic Type Turbine Flowmeter BNO Low Flow Pelton Wheel Flowmeter NS INSTALLATION AND OPERATION Nixon Flowmeters Ltd. Leckhampton, Cheltenham, Glos UK Tel. 0044 (0)
Module 5: Cooling Fundamentals
 Terms and Definitions Major Mechanical Parts of a Four Speed Auto Transmission Parts of a Planetary Gear System Planetary Gear System Operation Speed, Torque, and Directional Function Fluid Pump and Pressure
Terms and Definitions Major Mechanical Parts of a Four Speed Auto Transmission Parts of a Planetary Gear System Planetary Gear System Operation Speed, Torque, and Directional Function Fluid Pump and Pressure
SUB-CHAPTER B.3 COMPARISON TABLE COMPARISON WITH REACTORS OF SIMILAR DESIGN (N4 AND KONVOI)
 CHAPTER B: INTRODUCTION AND GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE SUB-CHAPTER: B.3 SECTION : - PAGE : 1 / 9 SUB-CHAPTER B.3 COMPARISON TABLE COMPARISON WITH REACTORS OF SIMILAR DESIGN (N4 AND KONVOI) A comparison
CHAPTER B: INTRODUCTION AND GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE SUB-CHAPTER: B.3 SECTION : - PAGE : 1 / 9 SUB-CHAPTER B.3 COMPARISON TABLE COMPARISON WITH REACTORS OF SIMILAR DESIGN (N4 AND KONVOI) A comparison
CANDU Fuel Bundle Deformation Model
 CANDU Fuel Bundle Deformation Model L.C. Walters A.F. Williams Atomic Energy of Canada Limited Abstract The CANDU (CANada Deuterium Uranium) nuclear power plant is of the pressure tube type that utilizes
CANDU Fuel Bundle Deformation Model L.C. Walters A.F. Williams Atomic Energy of Canada Limited Abstract The CANDU (CANada Deuterium Uranium) nuclear power plant is of the pressure tube type that utilizes
SLtr ge. r iiisinto operation ' wm. The extent of the movement of the lever C, is controlled CHAPTER VII.
 SLtr ge r iiisinto operation ' wm «* PREECE'S THREE-WIRE SYSTEM. 6? CHAPTER VII. PREECE'S THREE-WIRE SYSTEM. no. MR. PREECE'S three-wire system is a permanent current system only as regards the rendering
SLtr ge r iiisinto operation ' wm «* PREECE'S THREE-WIRE SYSTEM. 6? CHAPTER VII. PREECE'S THREE-WIRE SYSTEM. no. MR. PREECE'S three-wire system is a permanent current system only as regards the rendering
Gearbox, Bearings and Lubrication
 Chapter 4 Gearbox, Bearings and Lubrication Typical small gas turbine reduction gear train Small gas turbine engines spin at very high speed in the order of 25,000-85,000 rpm. A reduction gearbox is normally
Chapter 4 Gearbox, Bearings and Lubrication Typical small gas turbine reduction gear train Small gas turbine engines spin at very high speed in the order of 25,000-85,000 rpm. A reduction gearbox is normally
Profile LFR-67 RUSSIA. Sodium, sodium-potassium.
 GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE FACILITY ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE FACILITY LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone, email): Profile LFR-67 6B RUSSIA
GENERAL INFORMATION NAME OF THE FACILITY ACRONYM COOLANT(S) OF THE FACILITY LOCATION (address): OPERATOR CONTACT PERSON (name, address, institute, function, telephone, email): Profile LFR-67 6B RUSSIA
INTRODUCTION Principle
 DC Generators INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using the principle of magnetic induction. Principle Whenever a conductor is moved within a
DC Generators INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using the principle of magnetic induction. Principle Whenever a conductor is moved within a
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 3: Introduction to Pollutant Formation POLLUTANT FORMATION
 Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
CONFIGURATION DESIGN AND MAINTENANCE APPROACH FOR THE ARIES-CS STELLARATOR POWER PLANT
 CONFIGURATION DESIGN AND MAINTENANCE APPROACH FOR THE ARIES-CS STELLARATOR POWER PLANT X.R. Wang 1, S. Malang 2, A. R. Raffray 1 and The ARIES Team 1 University of California, San Diego, CA, 9500 Gilman
CONFIGURATION DESIGN AND MAINTENANCE APPROACH FOR THE ARIES-CS STELLARATOR POWER PLANT X.R. Wang 1, S. Malang 2, A. R. Raffray 1 and The ARIES Team 1 University of California, San Diego, CA, 9500 Gilman
Overview. Selection of System Components VT BBK/CWH. Chart LNG Vehicle Tank and Fuel System Installation Guidelines
 Overview The information contained in this bulletin is intended to provide general installation guidelines and recommended specifications. It will aid an up-fitter or OEM in system design and/or installation
Overview The information contained in this bulletin is intended to provide general installation guidelines and recommended specifications. It will aid an up-fitter or OEM in system design and/or installation
SD Bendix BP-R1 Bobtail Proportioning Relay Valve DESCRIPTION
 SD-03-1067 Bendix BP-R1 Bobtail Proportioning Relay Valve CONTROL SERVICE SERVICE CONTROL SUPPLY DELIVERY SUPPLY DESCRIPTION The BP-R1 bobtail proportioning relay valve is a combination of two individual
SD-03-1067 Bendix BP-R1 Bobtail Proportioning Relay Valve CONTROL SERVICE SERVICE CONTROL SUPPLY DELIVERY SUPPLY DESCRIPTION The BP-R1 bobtail proportioning relay valve is a combination of two individual
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
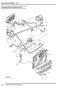 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
2.0 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 3.0 CHARACTERISTICS K. CO (HI-LO) Overcurrent Relay
 41-100K 2.0 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION The type CO relays consist of an overcurrent unit (CO), either an Indicating Switch (ICS) or an ac Auxiliary Switch (ACS) and an Indicating Instantaneous Trip unit
41-100K 2.0 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION The type CO relays consist of an overcurrent unit (CO), either an Indicating Switch (ICS) or an ac Auxiliary Switch (ACS) and an Indicating Instantaneous Trip unit
Conceptual Design Report on JT-60SA Fuelling System Gas Fuelling System
 3.10 Fuelling System 3.10.1 Gas Fuelling System 3.10.1.1 Overview The gas fuelling system is the equipment to inject gas into the vacuum vessel. The equipment consists of injection, delivery, vacuum pumping
3.10 Fuelling System 3.10.1 Gas Fuelling System 3.10.1.1 Overview The gas fuelling system is the equipment to inject gas into the vacuum vessel. The equipment consists of injection, delivery, vacuum pumping
GEOMETRICAL PARAMETERS BASED OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER RATE IN DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER USING TAGUCHI METHOD D.
 ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/March 2018/ Vol-8/Issue-3/18-24 D. Bahar et. al., / International Journal of Engineering & Science Research GEOMETRICAL PARAMETERS BASED OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER RATE IN DOUBLE
ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/March 2018/ Vol-8/Issue-3/18-24 D. Bahar et. al., / International Journal of Engineering & Science Research GEOMETRICAL PARAMETERS BASED OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER RATE IN DOUBLE
CHAPTER 20: Operation and maintenance
 Pressurized Irrigation Techniques 20.1 CHAPTER 20: Operation and maintenance INTRODUCTION The efficient operation of an irrigation system depends mainly on the ability of the farmer to make the best use
Pressurized Irrigation Techniques 20.1 CHAPTER 20: Operation and maintenance INTRODUCTION The efficient operation of an irrigation system depends mainly on the ability of the farmer to make the best use
Antifreeze Type SYC1025 (Long life coolant) Mixing ratio (water:antifreeze) Cooling fan module Type Electric Capacity
 152000 083 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification Cooling system Type Water cooling, forced circulation Coolant Capacity approx. 8.5 L Radiator Core size 555W x 582.4H x 27T (over 326,250mm2)
152000 083 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification Cooling system Type Water cooling, forced circulation Coolant Capacity approx. 8.5 L Radiator Core size 555W x 582.4H x 27T (over 326,250mm2)
WHISPERPOWER GENERATOR SETS
 ADDITIONAL MANUAL FOR KEEL COOLING APPLICATIONS WHISPERPOWER GENERATOR SETS Art.nr. 40200251 WHISPER POWER BV Kelvinlaan 82 9207 JB Drachten Netherlands Tel.: +31-512-571550 Fax.: +31-512-571599 www.whisperpower.eu
ADDITIONAL MANUAL FOR KEEL COOLING APPLICATIONS WHISPERPOWER GENERATOR SETS Art.nr. 40200251 WHISPER POWER BV Kelvinlaan 82 9207 JB Drachten Netherlands Tel.: +31-512-571550 Fax.: +31-512-571599 www.whisperpower.eu
CHAPTER IV EXPERIMENTAL WORK
 78 CHAPTER IV EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4.1 INTRODUCTION The details of the experimental set up are presented in this chapter. The information about the engine, components, instrumentation and controls used in
78 CHAPTER IV EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4.1 INTRODUCTION The details of the experimental set up are presented in this chapter. The information about the engine, components, instrumentation and controls used in
Tips & Technology For Bosch business partners
 Tips & Technology For Bosch business partners Current topics for successful workshops No. 05 Trucks Starters and starter systems Part 2 Moderately heavy commercial vehicles with diesel engines having a
Tips & Technology For Bosch business partners Current topics for successful workshops No. 05 Trucks Starters and starter systems Part 2 Moderately heavy commercial vehicles with diesel engines having a
MHI Integrally Geared Type Compressor for Large Capacity Application and Process Gas Application
 MHI Integrally Geared Type for Large Capacity Application and Process Gas Application NAOTO YONEMURA* 1 YUJI FUTAGAMI* 1 SEIICHI IBARAKI* 2 This paper introduces an outline of the structures, features,
MHI Integrally Geared Type for Large Capacity Application and Process Gas Application NAOTO YONEMURA* 1 YUJI FUTAGAMI* 1 SEIICHI IBARAKI* 2 This paper introduces an outline of the structures, features,
Development of Emission Control Technology to Reduce Levels of NO x and Fuel Consumption in Marine Diesel Engines
 Vol. 44 No. 1 211 Development of Emission Control Technology to Reduce Levels of NO x and Fuel Consumption in Marine Diesel Engines TAGAI Tetsuya : Doctor of Engineering, Research and Development, Engineering
Vol. 44 No. 1 211 Development of Emission Control Technology to Reduce Levels of NO x and Fuel Consumption in Marine Diesel Engines TAGAI Tetsuya : Doctor of Engineering, Research and Development, Engineering
SUB-CHAPTER E.4 DESIGN OF COMPONENTS AND SUB-SYSTEMS
 PAGE : 1 / 11 SUB-CHAPTER E.4 DESIGN OF COMPONENTS AND SUB-SYSTEMS 1. REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS 1.1. DESCRIPTION OF REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS The reactor coolant pumps (GMPP) [RCP] are assigned at RCC-M level
PAGE : 1 / 11 SUB-CHAPTER E.4 DESIGN OF COMPONENTS AND SUB-SYSTEMS 1. REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS 1.1. DESCRIPTION OF REACTOR COOLANT PUMPS The reactor coolant pumps (GMPP) [RCP] are assigned at RCC-M level
By: Eugenijus Uspuras Algirdas Kaliatka Sigitas Rimkevicius ASME 2012 Verification & Validation Symposium May 2-4, 2012, Las Vegas, NV
 Computer codes validation for transient analysis at nuclear power plants with RBMK-1500 reactor By: Eugenijus Uspuras Algirdas Kaliatka Sigitas Rimkevicius ASME 2012 Verification & Validation Symposium
Computer codes validation for transient analysis at nuclear power plants with RBMK-1500 reactor By: Eugenijus Uspuras Algirdas Kaliatka Sigitas Rimkevicius ASME 2012 Verification & Validation Symposium
SD Bendix TC-4 Modulating Control Valve TYPICAL PIPING DIAGRAM EXHAUST PORT DELIVERY PORT DELIVERY PORT FIGURE 1 SUPPLY PORT FIGURE 2
 SD-03-4503 Bendix TC-4 Modulating Control Valve EXHAUST DELIVERY DELIVERY FIGURE 1 SUPPLY TC-2 TP-2 TRAILER SERVICE BRAKE CHAMBERS GAUGE TW-1 MANIFOLD TC-2 SV-1 DS-1 COUPLINGS TRAILER EMERGENCY SPRING
SD-03-4503 Bendix TC-4 Modulating Control Valve EXHAUST DELIVERY DELIVERY FIGURE 1 SUPPLY TC-2 TP-2 TRAILER SERVICE BRAKE CHAMBERS GAUGE TW-1 MANIFOLD TC-2 SV-1 DS-1 COUPLINGS TRAILER EMERGENCY SPRING
HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR REPLACEMENT USING ELECTROMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY
 HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR REPLACEMENT USING ELECTROMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY SCOPE This white paper discusses several issues encountered by Lee Air with past projects that involved the replacement of Hydraulic Actuators
HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR REPLACEMENT USING ELECTROMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY SCOPE This white paper discusses several issues encountered by Lee Air with past projects that involved the replacement of Hydraulic Actuators
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
walton TEMPERATURE CONTROL SYSTEMS Pneumatically Operated (Rotary)
 walton TEMPERATURE CONTROL SYSTEMS Pneumatically Operated (Rotary) WALTON ENGINEERING CO. LTD. 61 London Road St Albans Hertfordshire AL1 1LJ England Telephone +44 (0)1727 855616 Fax +44 (0)1727 841145
walton TEMPERATURE CONTROL SYSTEMS Pneumatically Operated (Rotary) WALTON ENGINEERING CO. LTD. 61 London Road St Albans Hertfordshire AL1 1LJ England Telephone +44 (0)1727 855616 Fax +44 (0)1727 841145
A. IMPROVEMENTS ON A PUNCHED CARD SELECTOR FRAME
 XIX. SHOP NOTES A. IMPROVEMENTS ON A PUNCHED CARD SELECTOR FRAME Hand-sorted punched card systems are commonly used for filing and cross-indexing literature reference material. However, the use of such
XIX. SHOP NOTES A. IMPROVEMENTS ON A PUNCHED CARD SELECTOR FRAME Hand-sorted punched card systems are commonly used for filing and cross-indexing literature reference material. However, the use of such
Computer-Assisted Induction Aluminum
 Home Computer-Assisted Induction Aluminum Brazing November 11, 2003 Coupled electromagnetic and thermal computer simulation provides a sufficient basis for process optimization and quality improvement
Home Computer-Assisted Induction Aluminum Brazing November 11, 2003 Coupled electromagnetic and thermal computer simulation provides a sufficient basis for process optimization and quality improvement
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL. Primary Current Injection Test Set. 750ADM-H mk2
 OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL Product: Type: Primary Current Injection Test Set 750ADM mk2 750ADM-H mk2 DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY: T & R Test Equipment Limited 15-16 Woodbridge Meadows, Guildford,
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL Product: Type: Primary Current Injection Test Set 750ADM mk2 750ADM-H mk2 DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY: T & R Test Equipment Limited 15-16 Woodbridge Meadows, Guildford,
DATA & FACTS Unit Heaters MultiMAXX HB. Quick Selection and Fast Delivery
 DATA & FACTS Unit Heaters MultiMAXX HB Quick Selection and Fast Delivery Table of Contents MultiMAXX HB Unit Type Code... 3 About this Catalogue... 4 Overview of Capacity... 5 Unit Description... 6 Unit
DATA & FACTS Unit Heaters MultiMAXX HB Quick Selection and Fast Delivery Table of Contents MultiMAXX HB Unit Type Code... 3 About this Catalogue... 4 Overview of Capacity... 5 Unit Description... 6 Unit
Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance MP-SEE-THRU-01 Rev. 018
 Student Operating Procedure Millstone Station Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance Approval Date: 01/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/12/2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE...3
Student Operating Procedure Millstone Station Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance Approval Date: 01/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/12/2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE...3
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
