There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
|
|
|
- Eugene Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. The fuel pressure should be tested using an accurate pressure testing kit and the results compared against the manufacturer's specification. The system pressure on the majority of multi-point injection systems is usually around 2.0 bar, increasing to 2.5 bar under acceleration conditions. The fuel pressure regulator (Figure 1.0) is separated into two halves by a diaphragm. Figure 1.0 The lower part has an internal spring and a vacuum take off point; the upper half receives the fuel from the fuel rail. When the fuel pressure overcomes the spring tension, the diaphragm is depressed and the excess pressure escapes back to the fuel tank via the return pipe. If the spring inside the pressure regulator becomes weakened, the pressure reduces accordingly. The vacuum hose that is connected to the lower chamber allows the effective pressure exerted onto the diaphragm to change with different engine loads. Excessive fuelling will occur if the rubber diaphragm inside the pressure regulator is perforated as this will allow fuel to pass into the inlet manifold via the vacuum pipe. The emissions produced by the combustion process have never before been under more scrutiny from both ecological movements and government legislation; it is therefore important that the vehicle runs efficiently, helping to minimise harmful emissions from the exhaust tail pipe. An engine can, in theory, run at such a point where the emissions produced will be no more than harmless oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water. The theory may be correct, but with the combination of moving parts, varying engine speed, changing temperature, and different timing and fuel mapping, the final output is often less than perfect. At a certain Air / Fuel Ratio (AFR) the emissions from the exhaust are minimised and, with the introduction of the catalytic converter and lambda sensor, the outputs can be reduced to satisfy the current construction and use regulations. If the engine should suffer from an ignition misfire or an electronic component failure the combustion
2 process will be greatly compromised, causing both an unacceptable increase in exhaust emissions and the possibility of damage to the catalytic converter. Most vehicles registered after 1992 are equipped with a three way catalytic converter and, more often than not, have 'closed loop' control. 'Closed loop' means that when the expended exhaust gases pass through the exhaust pipe, the lambda (or oxygen) sensor reports the condition of the mixture to the Electronic Control Module (ECM) which can adjust the fuelling accordingly. A sensor that is switching correctly will alter the fuelling about once per second and the speed of this switching can be seen on an oscilloscope. An ideal air/fuel ratio from complete combustion allows the lambda sensor to 'fine tune' the fuelling. Assuming that the fuel pressure is correct, the excess fuel must therefore be due to an increase in injector duration. This can be caused by any of the following sensors and actuators. Coolant temperature sensor Mass airflow meter MAP sensor Throttle position sensor Weak or dribbling injector Air temperature sensor Lambda sensor ECM fault Coolant Temperature Sensor The sensor alters its resistance with engine temperature change. The majority of sensors have a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) which results in the resistance of the component decreasing as the temperature increases. The resistance change therefore alters the voltage seen at the sensor and can be monitored for any discrepancies across its operational range. Select a time scale of 500 seconds, then connect the oscilloscope to the sensor and observe the output voltage. Start the engine and in the majority of cases the voltage will start in the region of 3 to 4 volts; however, this voltage will depend on the temperature of the engine as the temperature increases the resistance decreases and the voltage will also drop. If the resistance of the sensor is higher than anticipated this will fool the ECM into thinking that the engine is colder than it actually is, thus giving additional fuelling. The same effect will be seen if there is a poor conductivity at either the sensor's two pin connector or at the ECM. This will give the equivalent of another resistance in series, increasing the overall resistance. Mass Airflow Meter (Air Vane) The voltage output from the internal track of the Air Flow Meter (AFM) should be proportional to flap movement; this can be measured on an oscilloscope and should look similar to the example shown in Figure 1.1. The waveform should show approximately 1.0 volt when the engine is at idle; this voltage will rise as the engine is accelerated and produces an initial peak. This peak is due to the inertia of the air vane and drops momentarily before the voltage rises again to a peak of approximately 4.0 to 4.5 volts. The initial voltage seen at idle will vary between motor manufacturers and should therefore be compared against the relevant data.
3 Figure 1.1 Mass Airflow Meter (Hot Wire) This form of air flow meter is, in many ways, superior to the conventional air vane meter as it offers very little resistance to the flow of incoming air. The mass air flow is measured by the cooling effect on a heated wire that is suspended in the air passage, and it is the air flow's cooling effect on the wire that signals to the ECM the quantity of incoming air. Inside the component are two wires, one of which is used to convey the temperature of the incoming air, the other heated to a high temperature (approximately 120 C) by passing a small current through it. As the air flows across the heated wire, it has a cooling effect on it causing a temperature change; a small circuit inside the component increases the current passing through the wire to maintain the temperature, and it is this current that signals to the ECM the mass air flow. The current supplied to the heated wire alters proportionally to the air flow. Any wire that is constantly heated will form an oxide coating. To clean the wire after each journey, a current is passed through the wire heating it to approximately 1000 C, burning off any build up, and ensuring a clean wire for the next time the vehicle is started. MAP Sensor (Analogue) This component can be either an integral part of the electronic control unit or an individual component. The output from the analogue version shows a rise and fall voltage depending upon the vacuum seen. When the engine is stationary or the throttle is wide open, zero vacuum is recorded and a voltage approaching 5 volts will be seen, and as a vacuum is applied the voltage will reduce. With this particular form of engine load recognition, the condition of the vacuum pipes and connections is vital as any air leak will fool the ECM into over fuelling. MAP Sensor (Digital) A digital MAP sensor produces a square wave signal to the engine management ECM; this square wave changes frequency with varying engine vacuum readings. This output waveform can also be monitored on an oscilloscope, or the frequency measured on a certain multimeters that have the appropriate setting (Hz). The frequency seen at idle should match the frequency seen in the manufacturer's data. Air leaks also affect this digital form of monitoring the engine's vacuum.
4 With both forms of MAP sensor, the engine's fuelling will increase if the exhaust system has a restriction that impedes the flow of the spent gases. Throttle Position Sensors This throttle potentiometer (Figure 1.2) indicates to the ECM the exact amount of throttle opening. A throttle switch is unable to give precise positions of opening, but a throttle pot can give precise openings due to its linear output. The majority of modern engine management systems employ this particular sensor, and like the throttle position switch it is located on the butterfly spindle. Figure 1.2 This is also a three-wire device employing a 5 volt supply, an earth connection and a variable output from the centre pin. Some TPS's are attached to the throttle body via elongated locating holes; if this is the case, an initial voltage setting must be made as too high an initial voltage will suggest an open throttle and the ECM will over-fuel. Weak or Dribbling Injectors The injector consists of a solenoid-operated valve which is held in the closed position by a spring until the ECM completes the earth circuit. When the electromagnetic field lifts the pintle off its seat, fuel is delivered to the engine. The total lift on the pintle is approximately 0.15 mm (6 thou) and it has a reaction time around 1 millisecond. Any dirt ingress around the pintle seating area will cause the injector to not seat properly, allowing fuel to escape into the inlet manifold. The same consequences will also occur if the internal spring is damaged or broken. Figure 1.3 The injectors can be tested for flow rate, reaction time and leakage in a specialised test unit. The leakage test can however be performed by removing the fuel rail, pressurising the system and observing the injectors for any leakage. Any faulty injector should of course be replaced with another injector with a comparable flow rate. An example injector can be seen in Figure 1.3. Air Temperature Sensor With the air temperature sensor contributing only 20% of the temperature compensation, the sensor would have any discernible effect only if it was open circuit.
5 Lambda Sensor The most popular lambda sensor used on European vehicles is the Zirconia type. This sensor is essentially two porous platinum electrodes. The outer electrode surface is exposed to the exhaust gases and is coated in a porous ceramic with the inner coated surface exposed to fresh air. The sensor then produces a voltage when there is a difference in oxygen content between the two electrodes. This signal is then sent to the ECM which adjusts the mixture accordingly. The voltage range is normally 0.2 volts when lean to 0.8 volts when rich. A constant high voltage output from the sensor shows that the engine is running constantly rich and is outside the ECM's adjusting range. Figure 1.4 Lambda sensors, when working correctly, switch approximately once per second (1 Hz) and only start to switch when at normal operating temperature. This switching can be monitored on an oscilloscope with the waveform looking similar to the one in Figure 1.4. A conventional Zirconia sensor will display a high voltage while the engine is running with an excess of fuel, with a low voltage while running lean. The same principle also applies to the Titania variant but this time at a higher voltage of 0 to 5 volts. ECM Fault The ECM fitted to today's modern engine management system is responsible for the 'mapping' of the ignition timing and the fuel delivery. In order for the ECM to calculate the required ignition and fuelling parameters, it must be fed with input signals from the engine's sensors. The ECM is pre-programmed with data that ensures that the engine's performance and efficiency are maintained throughout the operational rev range and can be trimmed using a knock sensor to finely adjust the ignition timing and a lambda sensor to control the fuelling when in closed loop. The majority of ECM's have a self-diagnosis facility which is able to detect any problems from signals outside their normal operating range. Another facility that the ECM has is its ability to operate in 'limp home' or LOS mode (Limited Operation Strategy). This allows the ECM to operate from preset parameters when the system encounters a failure, often illuminating the engine warning light. If a faulty ECM is suspected, it can be tested to assess its condition before a substitute unit is fitted.
6 Contact >> Mount AutoEquip for all your Pico Scope requirements This Tutorial was first published by The Institute of the Motor Industry Information supplied courtesy of Auto Solve
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
4 Wire Wide Band Oxygen Sensors by Jim Gilmour Blue Print Technical Consultant
 4 Wire Wide Band Oxygen Sensors by Jim Gilmour Blue Print Technical Consultant Blue Print Technical Consultant Jim Gilmour, takes a look at 4 Wire Wide Band Oxygen Sensors, how they work and how to correctly
4 Wire Wide Band Oxygen Sensors by Jim Gilmour Blue Print Technical Consultant Blue Print Technical Consultant Jim Gilmour, takes a look at 4 Wire Wide Band Oxygen Sensors, how they work and how to correctly
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
2. Air Line AIR LINE FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL B: MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR FU(H4DOTC)-3
 W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator
 Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator Introduction Some of the notes here are repetitious in order to review the components
Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator Introduction Some of the notes here are repetitious in order to review the components
51. absolute pressure sensor
 51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
FIGURE 32 3 Most conventional zirconia oxygen sensors and some wide-band oxygen sensors use the cup (finger) type of design.
 FIGURE 32 1 Many oxygen sensors are located in the exhaust manifold near its outlet so that the sensor can detect the presence or absence of oxygen in the exhaust stream for all cylinders that feed into
FIGURE 32 1 Many oxygen sensors are located in the exhaust manifold near its outlet so that the sensor can detect the presence or absence of oxygen in the exhaust stream for all cylinders that feed into
amperometric (currentbased) cell coupled with a potentiometric
 26 July 213 WIDE-RANGE AIR/FUEL SENSORS: FROM THE INSIDE OUT BY BERNIE THOMPSON The construction and operation of the six-wire, wide-range air/fuel ratio (WRAF) sensor are entirely different from a conventional
26 July 213 WIDE-RANGE AIR/FUEL SENSORS: FROM THE INSIDE OUT BY BERNIE THOMPSON The construction and operation of the six-wire, wide-range air/fuel ratio (WRAF) sensor are entirely different from a conventional
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
The Bosch LH 2.4 Jetronic System is used on the models (and later non-turbo/non-odbii models)
 The Bosch LH 2.4 Jetronic System is used on the 89-93 models (and later non-turbo/non-odbii models) 1-1-1 No faults. 1-1-2 Control unit fault. 1-1-3 Fuel injectors - Injector cable break or blocked injector;
The Bosch LH 2.4 Jetronic System is used on the 89-93 models (and later non-turbo/non-odbii models) 1-1-1 No faults. 1-1-2 Control unit fault. 1-1-3 Fuel injectors - Injector cable break or blocked injector;
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
POCKET GUIDE. Lambda Sensors. Never settle for second best, always insist on NTK, the world s No.1OE fitment.
 POCKET GUIDE Lambda Sensors Never settle for second best, always insist on NTK, the world s No.1OE fitment. The Key to Effective Catalytic Converter Pollution Control Lambda Sensors What is a sensor? A
POCKET GUIDE Lambda Sensors Never settle for second best, always insist on NTK, the world s No.1OE fitment. The Key to Effective Catalytic Converter Pollution Control Lambda Sensors What is a sensor? A
EMISSION SUB SYSTEMS - Closed Loop Feedback Control System
 Emission Control Sub-Systems Closed Loop Feedback Control System The heart of the emissions control system is the closed loop fuel feedback control system. It is responsible for controlling the content
Emission Control Sub-Systems Closed Loop Feedback Control System The heart of the emissions control system is the closed loop fuel feedback control system. It is responsible for controlling the content
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01
 Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
4. Sensors and Switches
 W1860BE.book Page 17 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions
W1860BE.book Page 17 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions
Evaporative Emissions
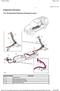 Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ): P Code Charts General Information
 P0133 O2-Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 / Sensor 1) - The linear O2 sensor is mounted on the front side of the Catalytic Converter (warm-up catalytic converter) or in the front exhaust pipe. It detects
P0133 O2-Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 / Sensor 1) - The linear O2 sensor is mounted on the front side of the Catalytic Converter (warm-up catalytic converter) or in the front exhaust pipe. It detects
Catalytic Failures. Engine running too hot.
 Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
SECTION 2.05 FUEL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
 SECTION 2.05 FUEL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS The engine fuel system consists of the following engine mounted components: Carburetors Throttle valves Fuel pressure regulator and balance line(s)
SECTION 2.05 FUEL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS The engine fuel system consists of the following engine mounted components: Carburetors Throttle valves Fuel pressure regulator and balance line(s)
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis
 Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS
 UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS AND EMISSIONS Gas Diagnostic Steps This procedure will help in your efforts to figure out what the five-gas reading are telling you. In order for five gas analyses to be conclusive
UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS AND EMISSIONS Gas Diagnostic Steps This procedure will help in your efforts to figure out what the five-gas reading are telling you. In order for five gas analyses to be conclusive
Fuel control. The fuel injection system tasks. Starting fuel pump (FP)
 1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
Electronics III Sensors
 Electronics III Sensors Matthew Whitten Brookhaven College Sensor Defined. A device that responds to a stimulus, such as heat, light, or pressure, and generates a signal that can be measured or interpreted.
Electronics III Sensors Matthew Whitten Brookhaven College Sensor Defined. A device that responds to a stimulus, such as heat, light, or pressure, and generates a signal that can be measured or interpreted.
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich
 Page 1 of 6 1997 Chevrolet Cavalier Cavalier, Sunfire (VIN J) Service Manual Document ID: 47788 DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich System Description A Closed Loop air/fuel metering system is used to provide
Page 1 of 6 1997 Chevrolet Cavalier Cavalier, Sunfire (VIN J) Service Manual Document ID: 47788 DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich System Description A Closed Loop air/fuel metering system is used to provide
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
4. Sensors and Switches
 FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) SENSORS AND SWITCHES 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions exposed
FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) SENSORS AND SWITCHES 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions exposed
HFM Gasoline Injection and Ignition System
 07.5-0030 HFM Design and Function HFM Gasoline Injection and Ignition System A. General The HFM gasoline injection and ignition system is a further development of the LH and EZL. The basic system of the
07.5-0030 HFM Design and Function HFM Gasoline Injection and Ignition System A. General The HFM gasoline injection and ignition system is a further development of the LH and EZL. The basic system of the
Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6
 Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
Service Training Self-study Programme 358 Hot-film Air-mass Meter HFM 6 Design and Function Due to the further development of standards and laws for exhaust emissions in vehicles, components with improved
9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor
 9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1. Troubles 1. The signal line is short to ground (Abnormally low signal voltage : below 0.5 [volt]) Cause of trouble Counter action Engine state Signal
9. The signal check of Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1. Troubles 1. The signal line is short to ground (Abnormally low signal voltage : below 0.5 [volt]) Cause of trouble Counter action Engine state Signal
Electronics III Sensors
 Electronics III Sensors Matthew Whitten Brookhaven College Sensor Defined. A device that responds to a stimulus, such as heat, light, or pressure, and generates a signal that can be measured or interpreted.
Electronics III Sensors Matthew Whitten Brookhaven College Sensor Defined. A device that responds to a stimulus, such as heat, light, or pressure, and generates a signal that can be measured or interpreted.
General information - Various makes and models Technical Information : 01
 General information - Various makes and models Technical Information : 01 System: Engine management Lambda sensor general Tec info General System Information: Figure 1 - Lambda sensors The lambda sensor
General information - Various makes and models Technical Information : 01 System: Engine management Lambda sensor general Tec info General System Information: Figure 1 - Lambda sensors The lambda sensor
Catalytic Converter Testing
 Catalytic Converter Testing The first catalytic converter was created before the use of onboard computer systems its job was to oxidize HC and CO into CO2 and H2O. The term oxidizes means to add O2 to
Catalytic Converter Testing The first catalytic converter was created before the use of onboard computer systems its job was to oxidize HC and CO into CO2 and H2O. The term oxidizes means to add O2 to
SPN 3227 or Suspect Parameter Number (SPN) and Failure Mode Indicator (FMI) Description
 SPN 3227 or 3266 Suspect Parameter Number (SPN) and Failure Mode Indicator (FMI) Description SPN FMI Description Possible Causes 3227 4 EGO Bank A Sensor 2 Open or short to ground on Voltage Low signal
SPN 3227 or 3266 Suspect Parameter Number (SPN) and Failure Mode Indicator (FMI) Description SPN FMI Description Possible Causes 3227 4 EGO Bank A Sensor 2 Open or short to ground on Voltage Low signal
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
DTC P0420. Circuit Description. Conditions for Running the DTC.
 Page 1 of 5 DTC P0420 2003 Buick LeSabre LeSabre (VIN H) Service Manual Document ID: 792202 Circuit Description In order to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen
Page 1 of 5 DTC P0420 2003 Buick LeSabre LeSabre (VIN H) Service Manual Document ID: 792202 Circuit Description In order to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components
 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
DTC P0125 Insufficient Coolant Temp. for Closed Loop Fuel Control
 DI4 DIAGSTICS EINE DI38404 DTC P05 Insufficient Coolant Temp. for Closed Loop Fuel Control CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and x components of the exhaust gas, a threeway
DI4 DIAGSTICS EINE DI38404 DTC P05 Insufficient Coolant Temp. for Closed Loop Fuel Control CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and x components of the exhaust gas, a threeway
G - TESTS W/CODES Volvo 960 INTRODUCTION SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics
 G - TESTS W/CODES 1994 Volvo 960 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics 960 INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES, proceed with SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.
G - TESTS W/CODES 1994 Volvo 960 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics 960 INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES, proceed with SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control
 The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
DESCRIPTION Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20. Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI
 Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Lotus Service Notes Section EMR
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. Self-Diagnostics - RAV4. Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs).
 2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Honda Accord/Prelude
 Honda Accord/Prelude 1984-1995 In Tank Fuel Pumps TEST 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. On the Accord, remove the screws securing the underdash fuse box to its mount. Remove the fuel cut off relay from the
Honda Accord/Prelude 1984-1995 In Tank Fuel Pumps TEST 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. On the Accord, remove the screws securing the underdash fuse box to its mount. Remove the fuel cut off relay from the
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review
 Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS
 2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
2005 Jaguar S-Type (X200) V8-4.2L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Computers and Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS Electronic Engine Controls Vehicles
LAMBDA SENSORS EXPLAINED
 LAMBDA SENSORS EXPLAINED The exhaust gas oxygen sensor (EGO or O2), or lambda sensor, is the key sensor in the engine fuel control feedback loop. The computer uses the O2 sensor s input to balance the
LAMBDA SENSORS EXPLAINED The exhaust gas oxygen sensor (EGO or O2), or lambda sensor, is the key sensor in the engine fuel control feedback loop. The computer uses the O2 sensor s input to balance the
Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors
 Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors 8183 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 6 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in
Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors 8183 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 6 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in
4.0L CEC SYSTEM Jeep Cherokee DESCRIPTION OPERATION FUEL CONTROL DATA SENSORS & SWITCHES
 4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins
 Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins Introduction The bi-fuel system modifies standard heavy-duty diesel engines to operate on diesel and gas simultaneously. The gas is used as main fuel and
Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins Introduction The bi-fuel system modifies standard heavy-duty diesel engines to operate on diesel and gas simultaneously. The gas is used as main fuel and
D. Functions in the KE control unit. a) General
 D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
ARTICLE BEGINNING INTRODUCTION SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM RETRIEVING DTCS ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline Cabrio, Golf III, GTI, Jetta III, Passat INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing preliminary
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline Cabrio, Golf III, GTI, Jetta III, Passat INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing preliminary
Exhaust Gas CO vs A/F Ratio
 Title: Tuning an LPG Engine using 2-gas and 4-gas analyzers CO for Air/Fuel Ratio, and HC for Combustion Efficiency- Comparison to Lambda & Combustion Efficiency Number: 18 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\18_CO
Title: Tuning an LPG Engine using 2-gas and 4-gas analyzers CO for Air/Fuel Ratio, and HC for Combustion Efficiency- Comparison to Lambda & Combustion Efficiency Number: 18 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\18_CO
Stop Lamp Switch. STP or BRK. Stop Lamps
 WORKSHEET 2 1 Position/Mode Switches and Circuits (Instructor Copy) Vehicle Year/Prod. Date Engine Transmission Technician Objectives With this worksheet, you will learn to test position/mode circuits
WORKSHEET 2 1 Position/Mode Switches and Circuits (Instructor Copy) Vehicle Year/Prod. Date Engine Transmission Technician Objectives With this worksheet, you will learn to test position/mode circuits
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 -1 ENGINE CONTROL.......... GENERAL INFORMATION...... SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE......... ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT.................... ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL......................
-1 ENGINE CONTROL.......... GENERAL INFORMATION...... SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE......... ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT.................... ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL......................
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. System Sensors
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
11. Diagnostics Chart with Trouble Code
 DTC No. Abbreviation (Subaru select monitor) ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM 11. Diagnostics Chart with Trouble Code A: DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) LIST P0100 QA Mass air flow sensor circuit malfunction
DTC No. Abbreviation (Subaru select monitor) ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM 11. Diagnostics Chart with Trouble Code A: DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) LIST P0100 QA Mass air flow sensor circuit malfunction
NZQA Expiring unit standard 3400 version 4 Page 1 of 6. Check a four stroke petrol engine for condition using hand held test equipment
 Page 1 of 6 Title Check a four stroke petrol engine for condition using hand held test equipment Level 3 Credits 4 Purpose This unit standard is for people in the automotive repair industry. People credited
Page 1 of 6 Title Check a four stroke petrol engine for condition using hand held test equipment Level 3 Credits 4 Purpose This unit standard is for people in the automotive repair industry. People credited
DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2)
 05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
COBB TUNING. AccessTUNER. USDM Mitsubishi Table Descriptions and Tuning Tips. Copyright 2008 Cobb Tuning Products, LLC. All Rights Reserved. P.
 COBB TUNING AccessTUNER TM USDM Mitsubishi Table Descriptions and P.1 Note: This is a list of tables available on all Mitsubishi AccessTUNER products. Not all tables are available in your software. Boost
COBB TUNING AccessTUNER TM USDM Mitsubishi Table Descriptions and P.1 Note: This is a list of tables available on all Mitsubishi AccessTUNER products. Not all tables are available in your software. Boost
DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175
 Page 1 of 6 2009 Pontiac G8 G8 Service Manual Document ID: 2076050 DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic
Page 1 of 6 2009 Pontiac G8 G8 Service Manual Document ID: 2076050 DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic
Lotus Service Notes Section EMD
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
Adaptive Fuel DTC Diagnostic Techniques
 2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 2: Diagnostic Methods Procedure revision date: 03/29/2006 Adaptive Fuel DTC Diagnostic Techniques The Adaptive Fuel Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) Diagnostic Techniques
2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 2: Diagnostic Methods Procedure revision date: 03/29/2006 Adaptive Fuel DTC Diagnostic Techniques The Adaptive Fuel Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) Diagnostic Techniques
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (continued) SAE Defined Codes
 78 SAE Defined Codes P01XX Fuel and Air Metering P0100 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Problem P0101 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Range or Performance Problem P0102 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Low
78 SAE Defined Codes P01XX Fuel and Air Metering P0100 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Problem P0101 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Range or Performance Problem P0102 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Low
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
Module 5: Emission Control for SI Engines Lecture20:ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS
 ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS The Lecture Contains: Crankcase Emission Control (PCV System) Evaporative Emission Control Exhaust Gas Recirculation Water Injection file:///c /...%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture20/20_1.htm[6/15/2012
ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS The Lecture Contains: Crankcase Emission Control (PCV System) Evaporative Emission Control Exhaust Gas Recirculation Water Injection file:///c /...%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture20/20_1.htm[6/15/2012
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
E - THEORY/OPERATION ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L
 E - THEORY/OPERATION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and
E - THEORY/OPERATION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and
Oregon Fuel Injection
 2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT
 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS
 1F-44 G32D TROUBL COD DIAGNOSIS CLARING TROUBL CODS Notice To prevent ngine Control Module (CM) dam-age, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting the power to the CM (for example battery
1F-44 G32D TROUBL COD DIAGNOSIS CLARING TROUBL CODS Notice To prevent ngine Control Module (CM) dam-age, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting the power to the CM (for example battery
Part 1. Reduced fuel flow due to a restricted inlet screen. Sluggish plunger movement due to contamination.
 http://www.datec.us/instructor/ More about the author http://www.datec.us /instructor SCREEN Part 1 There is not a good way to check the fuel distribution per cylinder. The intention of this session is
http://www.datec.us/instructor/ More about the author http://www.datec.us /instructor SCREEN Part 1 There is not a good way to check the fuel distribution per cylinder. The intention of this session is
NGK Guide to Spark Plugs
 Spark plug gap Always check that the spark plug gap is compatible with the engine manufacturer s specification. A gap that is too small means that the spark duration will be very quick and the spark will
Spark plug gap Always check that the spark plug gap is compatible with the engine manufacturer s specification. A gap that is too small means that the spark duration will be very quick and the spark will
STAFOR HHO MAF/MAP fully digital and automatic enhancer (corrector). Installation manual. Version
 STAFOR HHO MAF/MAP fully digital and automatic enhancer (corrector). Installation manual. Version 05.14. HHO hydrogen on demand dual fuel systems Introduction The present MAF/MAP Sensor Enhancer is fully
STAFOR HHO MAF/MAP fully digital and automatic enhancer (corrector). Installation manual. Version 05.14. HHO hydrogen on demand dual fuel systems Introduction The present MAF/MAP Sensor Enhancer is fully
DTC P20EE, P249D, P249E, or P2BAD
 Page 1 of 7 Document ID: 2614257 DTC P20EE, P249D, P249E, or P2BAD Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. Review Strategy Based
Page 1 of 7 Document ID: 2614257 DTC P20EE, P249D, P249E, or P2BAD Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. Review Strategy Based
Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel
 Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Page 1 of 9 Published: Mar 8, 2007 Exhaust System - 2.2L Diesel COMPONENT LOCATION - WITH DIESEL PARTICULATE FILTER Item Part Number Description 1 Exhaust manifold (ref only) 2 Pressure differential sensor
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 3: Introduction to Pollutant Formation POLLUTANT FORMATION
 Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Application Note Original Instructions Development of Gas Fuel Control Systems for Dry Low NOx (DLN) Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines
 Application Note 83404 Original Instructions Development of Gas Fuel Control Systems for Dry Low NOx (DLN) Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines Woodward reserves the right to update any portion of this publication
Application Note 83404 Original Instructions Development of Gas Fuel Control Systems for Dry Low NOx (DLN) Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines Woodward reserves the right to update any portion of this publication
L (LU4, LJ3, L88) used in Saab 9-5 ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC PARAMETERS
 Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Front vs. Rear O2 sensor signal Evaluated data 1,75 times FTP std 80 (unitless) Coolant temp Throttle Delta load, positive Delta load, negative Engine speed, man. trans
Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Front vs. Rear O2 sensor signal Evaluated data 1,75 times FTP std 80 (unitless) Coolant temp Throttle Delta load, positive Delta load, negative Engine speed, man. trans
