Service Training. Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 365
|
|
|
- Clifford Warren
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service Training Audi 4.2 l V8 TDI with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 365
2 In 1999, the 3.3 l A8 (1994) was installed for the first time with a V8 TDI engine, followed in the new A8 by an improved 4.0 l chain-driven engine. With the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine, the vee engine family with its 90 cylinder angle, 90 mm cylinder spacing and outputend chain drive has undergone a complete overhaul. The 4.2 l powerplant represents a logical evolution of the V8 TDI with 240 kw of power and 650 Nm of torque. 365_001
3 Table of contents 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Differences between the 4.0 l and 4.2 l V8 TDI engines Performance features Cranktrain Cylinder head and valve gear Chain drive Oil circulation system Crankcase breather system Cooling system Air intake Exhaust gas recirculation system Fuel system System overview CAN data bus interfaces Exhaust system with diesel particulate filter Special tools The Self-Study Programme contains information on the design and function of new models, new automotive components or new technologies. The self-study programme is not intended as a workshop manual! All values given are only intended to help explain the subject matter and relate to the software version applicable when the SSP was compiled. Use should always be made of the latest technical literature when performing maintenance and repair work. Reference Note
4 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Differences between the 4.0 l and 4.2 l V8 TDI engines Switchable, exhaust gas recirculation cooler with water through-flow Common rail injection system With third-generation piezoelectric injectors Exhaust gas recirculation system with electrical actuators Cast exhaust manifold Adoption of cylinder head concept from the 3.0 l V6 TDI Crankcase with 90 mm cylinder spacing and 83 mm cylinder bore Belt drive with torsion vibration damper, freewheel and additional stabilising roller Optimised exhaust turbocharger 365_001 4
5 Performance features Engine code, torque and power output The engine number is located on the end face of cylinder bank II, left. 365_012 Torque/power curve Max. torque in Nm Max. power output in kw kw 160 Nm Engine speed in RPM Specifications Engine code Type of engine BVN V8 diesel engine 90 vee angle Displacement in cm Max. power output in kw (bhp) 240 (326) Max. torque in Nm 650 at 1600 to 3500 RPM Bore in mm 83 Stroke in mm 95.5 Compression ratio 16,4 : 1 Cylinder spacing in mm 90 Firing order Engine weight in kg 255 Engine management Exhaust gas recirculation system Exhaust emission control Exhaust emission standard Bosch EDC-16CP+ common rail injection system up to 1600 bar with 8-port piezoelectric injectors Water-cooled EGR Two oxidising catalytic converters, Two maintenance-free diesel particulate filters EU IV 5
6 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Crankshaft drive The crankcase with 90 mm cylinder spacing is made of vernicular graphite (GJV 450) and, like the 4.0 l V8 TDI engine, is split at the centre of the crankshaft and bolted to a sturdy crankshaft bearing frame. The weight of the engine block was reduced by approximately 10 kg by utilising the material's special properties. The forged steel crankshaft is made of 42 Cr Mo S4 and cranked in such a way that free first and second order moments are avoided. The crankshaft is runs in five bearings in the crankcase, and the radii of the con-rod bearing journals are rolled for strength reasons. By using a compact design it was possible to achieve torque-free balancing of the cranktrain using the crankshaft's counterweights alone. An optimum balance was achieved with the help of additional weights, which are attached to the vibration damper and the driver plate. The deep aluminium oil pan is to a great extent isolated from crankshaft drive vibration, which has a positive effect on acoustic quality. The main bearing frame contour serves an additional function. It acts as a "baffle plate" in the crankshaft counterweight and con-rod areas. Thus, draining oil is not distributed throughout the engine block, but is collected directly and drained off. Crankcase Main oil port Bearing frame Crankshaft Aluminium oil pan These edges function as baffle plates 365_003 Oil return channels 6
7 The UV laser imaging honing process used to manufacture the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine has also been used for this engine. This process helps to reduce oil consumption. The antifriction properties of the cylinder liners were significantly improved in this way. without laser imaging 365_011a with laser imaging 365_011b Piston Designed as a recessed-head type piston, the piston has a higher recessed head with a larger diameter which reduces the engine's compression ratio from 17.3 : 1 to 16.4 : 1. The piston has an annular cooling duct to reduce the temperature of the piston ring zone and the recess rim. An oil spray nozzle continuously sprays the oil into the annular oil cooling duct in order to cool the piston crown. Comparison of piston crowns new Annular oil cooling duct 365_016 old Oil spray nozzle 365_025 7
8 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Crankshaft vibration damper The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine is equipped with a torsion vibration damper (old version with a belt vibration damper with isolation of the poly vee belt track). To dampen oly vee belt vibrations, which occur at the different rates of acceleration of the piston during the combustion process, a freewheel was installed in the alternator and an additional stabilising roller was fitted. The torsion vibration damper was designed to reduce the torsional moments which occur in the medium engine speed range by approximately 13 % compared to a belt vibration damper. The result is less load on the crankshaft and improved engine acoustics. The new belt drive drives the alternator and the air conditioner compressor. Belt vibration damper Torsion vibration damper Torsional moment, amplitude in Nm 365_035 Engine speed in rpm Additional stabilising rollers Crankshaft counterweight Freewheel on the alternator 365_017 Rubber track Belt track 8
9 Cylinder head and valve gear Derived from the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine, the cylinder head is installed in combination with the following components: four valves per cylinder, assembled camshafts, hydraulic valve lifters, roller cam followers and straight-cut/tensioned gears The camshafts are held in place in the cylinder head by a ladder frame with a flat sealing face. An acoustically isolated plastic cylinder head cover seals the cylinder head off from the exterior. Cylinder head cover Ladder frame Injectors arranged in the centre of the combustion chamber 365_004 Rigid spur gear Design The spur gear of the exhaust camshaft is split into two pieces in the cylinder head, left. The spur gear of the intake camshaft gear is split into two pieces in the cylinder head, right. Non-rigid spur gear The wider part of the spur gear (rigid spur gear) is attached securely to the camshaft. There are six ramps on the front side of the spur gear. The narrower part of the spur gear (moving spur gear) moves in radial and axial directions. Recesses for the six ramps are located on the back of the spur gear. 365_023 Six ramps 9
10 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Breather duct in the cylinder head If a leak occurs in the area of the copper injector ring seal, the air is able to escape from the combustion chamber through a duct due to the combustion pressure of 165 bar. The breather duct is located above the exhaust manifold in the cylinder head. It prevents the excess pressure from travelling from the combustion chamber via the crankcase breather to the compressor side of the exhaust turbocharger and possibly causing malfunctioning or damaging the ring seals. Piezoelectric injector The crankcase breather can be accessed through the oil chamber in the cylinder head Ring seal Glow plug channel 365_022 Ring seal to combustion chamber Breather duct 365_030 10
11 Chain drive The chain drive adopted from the 4.0 l V8 TDI engine has been optimised with regard to friction and rotary oscillation. Part of the sliding rails in chain drive D has been replaced by a new chain tensioner, allowing the chain to be routed directly around the intermediate shaft, thus shortening the length of the chain. Chain drive B has also been optimised, whereby the number of teeth and the belt gear contact angle has been increased and the chain guide has been tapered. Ancillary units such as the oil pump, hydraulic pump and coolant pump are driven by chain drive D via a gear module. Chain drive B Chain drive D 365_038 Chain drive C "New" chain drive B Chain drive A Coolant pump "New" Chain drive D Chain tensioner for chain drive D Oil pump 365_002 Reference For further information, please refer to SSP Audi A6 05 Engines and Transmissions. 11
12 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Oil circulation system The oil circulation system, which is initially filled with 11.5 l oil, begins in the gear oil pump. The oil pressure relief valve is integrated in the oil pump. From here, the oil flows to the water-oil cooler installed in the engine's inner vee. The oil flows to the oil filter along internal ducts in the oil filter module. The oil filter module has a replaceable paper filter for ease of servicing. When the paper filter is removed, the oil remaining in the housing flows back into the oil pan through a drain valve. After leaving the oil cleaner, the pressurised oil is channelled into the main oil duct located in the inner vee of the engine block. Here, the lubrication points of the crankshaft, the crankshaft bearings and the oil spray nozzle are supplied with oil pressure. Both turbochargers are supplied with pressurised oil through additional outer oil lines from the main oilway. The oil pressure flows into the cylinder heads through risers with integrated restrictors, and from here to the camshafts, the cam followers and the hydraulic valve lifters. A special feature is the vacuum pump lubrication system, which is driven and supplied with oil by the intake camshaft in the cylinder head, right. The lubrication system is also supplied with pressurised oil via its own oilway from the main oil duct. Rear view Additional oil line from the oil gallery to the vacuum pump via the camshaft bearing Oil filter module with integrated crankcase breather Water-oil cooler Oil return from the cylinder heads Main oil duct Oil supply for turbocharger Oil pan Turbocharger return line Pressurised oil course Oil return line Oil return pipe from the inner vee and the crankcase breather Oil pump 365_043 12
13 Oil pump The gear oil pump is driven by a hexagonal shaft connected to chain drive D via a gear module. The oil pressure relief valve which the re-routes the excess oil pressure (exceeding approx. 5.1 bar) to the suction side of the oil pump. An additional gear module on the oil pump drives the coolant pump and the oil pump. 365_046 Water pump drive gear Drive gear from chain drive D Oil pump drive gear Coolant pump drive shaft output Oil pump gears Oil intake from the oil pan via an oil intake pipe Overpressure regulator control valve piston Compression spring 365_045 Oil pump cover, high pressure side 365_047 Pressure side to oil-water oil cooler Intake side of oil pan 13
14 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Crankcase breather system An oil filter module in the inner vee of the engine block accommodates the oil filter cartridge, the oilwater heat exchanger and the oil separator of the crankcase breather. The oil-water heat exchanger is designed in such a way that the maximum oil temperature remains well below the 150 C max. limit even in extreme conditions. Almost all oil-free blow-by gases flow through the pressure control valve to the intake side of both turbochargers. The separated oil is channelled into an oilway in the crankcase and an oil drain pipe with integrated non-return valve below the oil level. On the chain and belt sides of the engine, the incoming blow-by gases flow through the settling chamber in the inner vee to the three-cyclone oil mist separator. The blow-by gases flow through the settling chamber into the three-cyclone oil mist separator in which the existing fine oil particles are separated. Three-cyclone oil mist separator Pressure control valve for crankcase breather To intake side of turbocharger Intake manifold outlet Settling chamber Oil return channel with engine-internal oil pipe 365_031 14
15 Cooling system The coolant pump and the thermostat are housed in a shared pump housing outside the engine. The water pump is driven the oil pump gear module which is attached to the chain drive D via two stub shafts. The coolant which is channelled through the engine collects in the inner vee of the crankcase, from where it flows to the cooler or back into the engine via the water pump depending on the thermostat setting. The pump housing has two outputs to the pressure side, each of which is routed to the outer side of the crankcase. On both sides of the crankcase are located press-fitted coolant distributor rails, each of which has four inlets from where the coolant flows into the water jackets between the cylinders. The crankcase coolant chamber is split in two longitudinally according to the cross-flow principle. As a result, the coolant flows upwards from the crankcase into the cylinder head, transversely through the cylinder head and back to the crankcase on the inside of the cylinder banks. A portion of the coolant flows directly from the pressure side to the intake side through small holes in the cylinder webs in order to ensure rapid heat dissipation from the cylinder. Return line from the engine to the coolant pump to the cooler Crankcase, two-piece Inlet to engine Coolant distributor rail Right cylinder bank Coolant distributor rail Left cylinder bank Coolant pump 365_027 Thermostat from cooler 15
16 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Air intake The design of the double-chambered air intake system, with two air filters, two air mass meters and two air-air charge-air intercoolers, was adopted from the 4.0 l V8 TDI engine. Air is drawn in through the two electrically adjustable throttle valves. A connection between the two cylinder banks in the charge air tube, the so-called pressure equaliser tube, provides an even air distribution and equalises the pressure between the cylinder banks and the exhaust-gas return line. The intake plenum, which is designed as a pressure equaliser tube, is subjected to higher temperatures due to the inflow of exhaust gases, and, therefore, is made of aluminium. The actual intake manifold is made of plastic and accommodates the intake manifold flaps. These flaps control the flow rate in the spiral duct and are used for adjusting the swirl depending on thermodynamic requirements. Each cylinder bank has a bidirectional electric motor which actuates the flaps by means of a linkage. Depending on operating state, there are open, closed and intermediate positions. Throttle valve positioner Right cylinder bank Throttle valve positioner Left cylinder bank from turbocharger Connecting duct as pressure equaliser tube from turbocharger Charge air tube Swirl flaps Inflow of the recirculated exhaust gases 365_036 Swirl flap adjuster 16
17 Combustion process The main factors influencing the combustion process in charged diesel engines are: Combustion chamber shape Compression ratio Injection hydraulics Swirl formation Turbocharging They are in mutual interaction with one another. The process was, therefore, optimised in iterative steps by utilising, in particular, the flexibility provided by the common rail system. To achieve these ambitious development goals, the combustion system with the new four-valve concept used successfully in the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine was taken as the basis and adapted for the eight cylinder. The duct geometry in combination with variably activated swirl flaps allows a broad propagation of the cylinder swirl. The switchable EGR cooling system significantly reduces untreated emissions, since hot or cooled exhaust gas can be added depending on the operating point and engine temperature. Four-valve concept Piezoelectric injector Charging duct Swirl duct Exhaust valves Exhaust port in the form of a Y-branch pipe Intake valves Recessed-head type piston 365_041 17
18 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Swirl flaps Swirl flap open: The intake air can flow in large volumes through the open intake ports and into the combustion chamber, thereby ensuring optimal charging. 365_015 Variable swirl flap: To minimise untreated emissions, it is necessary to precisely adapt the cylinder swirl and hence the combustion process in dependence on the operating point. Requirement: continuous swirl flap adjustment rpm NO x emissions (g/kwh) Particulate emissions (g/kwh) 365_034 NO x Particulates Swirl flap position 365_018 Swirl flap closed: The strong swirl effect at low engine load optimises the combustion process within the combustion chamber and therefore results in fewer emissions. 365_014 18
19 Exhaust gas recirculation system The exhaust gas flows from the exhaust manifolds through ducts cast into the cylinder heads to the EGR valves in the inner vee of the engine block. The exhaust gas is precooled via the auxiliary exhaustgas recirculation duct by the cylinder head water cooling system. The EGR valves were modified for electrical - rather than pneumatic - actuation, including position feedback, and protected against excessively high temperatures by means of a water cooling system. The precooled exhaust gases are subsequently cooled by a pneumatically operated exhaust gas recirculation cooler which enables cooling of the exhaust gases to be adapted depending on the operating point. After passing through the exhaust gas recirculation cooler, the exhaust gases flow up into a branching duct within the pressure equalizer tube and mix with the induced air flow directly downstream of the throttle valves. When designing the ducts and inlet points, special attention was paid to optimal mixing of the dual gas flows. Exhaust port from four-cylinder exhaust manifold through the cylinder head to the EGR valve Exhaust-gas recirculation ducts in the pressure equalizer tube 365_037 EGR valve, left bank EGR valve, right bank Transverse duct in the cylinder head 365_020 Exhaust gas recirculation cooler with Bypass flap 19
20 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Exhaust manifold The short gas paths between the cylinder head and the turbocharger made it possible to change over from an air-gap insulated exhaust manifold to a pure cast manifold. This did not result in any additional heat loss for the oxidising catalytic converter. Due to the higher rigidity of the cast manifold (reduced oscillation), the design of the turbocharger support has been simplified, thus influencing positively the natural oscillation of the components. Exhaust gas tap for exhaust gas recirculation Coolant feed for turbocharger Turbocharger 365_006 Support Oil return pipe, turbocharger 20
21 Turbocharger Two Garrett GT17 chargers of the latest generation with electrical actuators are used for charging. The compressor wheel and the guide vanes were optimised and the turbine-side fan was decoupled from the turbine in order to increase turbocharger speed (up to 226,000 rpm), exhaust gas temperature (approx. 860 C) and charge pressure (approx. 2.5 bar absolute) in order to enhance engine performance. The turbine side is now sealed by a double ring seal instead of a single ring seal. This ensures a good level of gas tightness, even at temporarily elevated exhaust back pressures due to loaded particulate filters. The engine management system has dual air mass meters which ensure that both chargers run at the same speed, and therefore have the same delivery rate. Oil inlet Air guide vanes Decoupling of the fan and double ring seal Charge pressure control motor Coolant inlet Exhaust-gas temperature sensor 365_019 21
22 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Fuel system bar from bar max. permissible pressure 1.8 bar Mechanical fuel pump bar Fuel metering valve N290 (fuel metering unit fuel metering unit) High-pressure pump CP bar pressure retention valve Permeability in opposite direction at bar for charging the injectors after repair work. Fuel temperature sender G81 Temperature-dependent switchover Fuel filter with water separator High-pressure bar Return pressure from injector bar Supply pressure max. 1.8 bar Return pressure max. 1.8 bar 22
23 Fuel pressure sender G247 Rail element, cylinder bank II to injectors 5-8 N83, N84. N85, N86 Rail element, cylinder bank I Fuel pressure control valve N bar Injectors 1-4 N30, N31, N32, N33 Fuel cooler (air) on vehicle underbody Check valve Fuel tank module with suction jet pump, non-return valve and prefilter fuel pump (pre-supply pump) Tank 365_021 G6 G23 23
24 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system High-pressure fuel circuit The three-piston high-pressure pump is located in the inner vee of the engine, and is driven by the intake camshaft of cylinder bank II via a toothed belt. The high-pressure circuit consists of the following components: High-pressure pump with fuel metering valve (fuel metering unit) N290. Rail element I with fuel pressure regulating valve N276 and Rail element II with rail pressure sensor G247 and 8-port piezoelectric injectors. Reference It was possible to dispense with the distributor block in the CR system, as used in the 4.0 l V8 TDI engine. This fuel pressure regulator and the fuel pressure sensor were distributed along both rails. The rails themselves are now of welded construction, and no longer of forged construction. The rails are based on a seamlessly extruded steel tube, the open ends of which are sealed with threaded plugs. The connecting fittings for the high-pressure line and the rail pressure sensor were attached by capacitor discharge welding*. *Notes on capacitor discharge welding: The advantage of this method lies in the very limited heat affected zone around the weld seam. Thus, the basic structure of the raw material remains unaltered. For further information on design and function, please refer to SSP Audi A6 05 Engines and Transmissions. Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Fuel pressure sender G247 Rail I Fuel metering valve N290 Rail II Injector 365_032 24
25 Restrictors in the rail When the injector closes and during subsequent injection cycles, a pressure wave forms at the injector outlet. This pressure wave propagates to the rail, wher it is reflected. To dampen the pressure waves, flow restrictors are integrated in the rail in the supply line, in the highpressure pump rail, in the left and right rails and upstream of each injector. These restrictors are produced by machining the outer surface of the rail. Note Make sure that the injector fuel line and the connecting line between the rails is tightened to the correct torque. Deformed or damaged high-pressure lines must not be reused, and must be replaced. High-pressure line Cap nut Restrictor Rail 365_040 25
26 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 A new fuel pressure regulating valve is used for the common rail system of the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine. When the valve is in a deenergised state, it ensures a "short circuit between the high-pressure end and the low-pressure end. Reference For further information on design and function, please refer to SSP l V8 TDI Common Rail Injection System. Function: When the engine is running, the poppet valve is in force equilibrium with the spring and the magnetic circuit. The valve is open in the deenergised state whereby the spring relieves the load on the ball in the seat. Unlike the previous version (which had a short-time retention pressure of approx. 100 bar), the pressure in the rail is reduced immediately, thus preventing the fuel from draining into the cylinder if an injector is open. Previous version 365_033 Note In the event of a faulty fuel pressure regulating valve, the complete rail must be replaced. Iron plate Armature Valve seat ball 365_029 Applied rail pressure Compression spring Dual-regulator concept The 3.0 l V6 TDI engine with common rail used a dual-regulator concept which activated the fuel pressure regulating valve N276 or the fuel metering valve (fuel metering unit) N290. With this concept, the pressure can be controlled simultaneously via the fuel pressure regulating valve and the fuel metering unit. Injection rate Pressure regulating valve control at engine start and for fuel heatin Fuel metering unit control at high injection rates and high rail pressures Dual-regulator operation at idle, when coasting and at low injection rates Speed 365_028 26
27 Piezoelectric injectors By using piezoelectric injectors, it is possible to achieve: multiple electrical activation periods per working cycle, very short switching times for up to five injection cycles, large forces counter to the current rail pressure, high stroke precision for rapid rail pressure reduction Depending on the rail pressure, piezoelectric injectors require a drive voltage of between 110 and 148 V through capacitors in the control unit. Note When an injector is replaced, the adaptation value for the new injector must be written to the engine control unit. When the engine control unit is replaced, the injector rate matching values and the injector voltage matching valve must be transferred to the new engine control unit. Reference For further information, please refer to SSP Audi A6 05 Engines and Transmissions. 0-ring Connector overmoulding Electrical connection (blade terminal) Rod filter Body Return connection 0-ring Actuator foot Actuator module Actuator Actuator sleeve Actuator head Membrane Adjusting disc Coupler body Adjusting piece Low-pressure ring seal Coupler piston Valve piston Coupler module Valve plate Tubular spring Switch valve Valve pin Valve spring Valve piston spring Nozzle body Restrictor plate Spring retainer Nozzle clamping nut Sealing disc Injector spring Adjusting disc Nozzle module Nozzle ports modified from 7 to 8-port Injector pintle 365_039 27
28 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system System overview Sensors Air mass meter G70 Charge pressure sender G31 Intake air temperature sensor G42 Engine speed sender G28 Coolant temperature sender G62 Oil temperature sender G8 Fuel temperature sender G81 Fuel pressure sender G247 Coolant temperature sender at radiator outlet G83 Altitude sender CAN-Low CAN-High Powertrain CAN data bus Hall sender G40 Engine control unit J623 (master) Accelerator pedal position sender G79 Accelerator pedal position sender -2- G185 Exhaust gas pressure sensor 1 G450 Exhaust gas temperature sender -1- G235 Engine control unit 2 J624 (slave) Lambda probe 1 G39 Catalytic converter temperature sensor I G20 Exhaust gas temperature sender 2 for bank 1 G448 Auxiliary signals: P/N signal Term. 50 at starter Start relay, term. 50 stage 1/2 Request start Cruise control system Auxiliary water pump (relay to control) 28
29 Actuators Automatic glow period control unit 1 J179 Injectors for cylinders 1, 4, 6, 7 N30, N33, N84, N85 Glow plugs for cylinders 1, 4, 6, 7 Q10, Q13, Q15, Q16 Fuel pressure regulating valve N276 Throttle valve module J338 Intake manifold flap motor V157 Exhaust gas recirculation actuator V338 Fuel metering valve N290 Exhaust gas recirculation cooler change-over valve N345 Fuel pump relay J17 and fuel pump G6 and G23 Electro-hydraulic engine mounting solenoid valve, right N145 Engine component current supply relay J757 Lambda probe heater Z19 Diagnostic connection Auxiliary signals: Radiator fan control unit PWM 1/2 Engine speed Turbocharger 1 control unit J724 Turbocharger 2 control unit J725 Injectors for cylinders 2, 3, 5, 8 N31, N32, N83, N86 Exhaust gas temperature sender -1-, bank 2 G236 Lambda probe 2 heater Z28 Air mass meter 2 G246 Exhaust gas temperature sender 2 for bank 2 G449 Glow time control unit 2 J703 Intake manifold flap motor 2 V275 Glow plugs for cylinders 2, 3, 5, 8 Q11, Q12, Q14. Q17 Catalytic converter check temperature sensor II G29 Exhaust gas recirculation actuator 2 V339 Lambda probe 2 G108 Electro/hydraulic engine mounting solenoid valve, left N144 Exhaust gas pressure sensor 2 G451 Throttle valve module 2 J _042 29
30 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system CAN data bus interfaces (powertrain CAN data bus) Engine control unit (master) J623 Idling information (EBC) Kick-down information Clutch pedal switch Engine speed ACTUAL engine torque Coolant temperature Brake light switch information Brake pedal switch CCS switch positions CCS nominal speed NOMINAL/ACTUAL idling speed Preglow signal Throttle-valve angle Intake temperature OBD2 lamp "Hot" coolant warning lamp Fuel consumption Radiator fan activation Air conditioner compressor Power reduction Particulate filter lamp Start module Interlock switch Starter enable Starter de-mesh Load shedding Oil temperature Automatic gearbox control unit J217 Selector mechanism activated/ deactivated Air conditioner compressor OFF Torque converter lock-up clutch state Target gear Selector lever position NOMINAL engine torque Motion resistance index (on downhill gradients) Limp-home program (information on self-diagnosis) OBD2 status Turbine speed Nominal idling speed CAN High Data bus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) ACC information Idle up Mileage Date Time Brake light Trailer detector CAN Low Discrete line CAN 2 Low CAN 2 High Engine control unit 2 (slave) J624 sends all information such as the master control unit via CAN 2 directly to the master control unit. The slave control unit also controls: - charge pressure for both turbochargers The signal from engine speed sender G28 is also transmitted via a discrete line. ABS control unit J104 TCS request ABS request EDL request ESP intervention ESP brake light switch Road speed signal EBC intervention torque Lateral acceleration Wheel speed Steering angle sensor G85 Steering wheel angle (is utilised for pre-control of idling speed and for calculating the engine torque based on the power demand of the power steering system) 30
31 Exhaust system with diesel particulate filter A double-chambered exhaust system with particulate filter is used in combination the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine. Each channel of the exhaust system comprises a close-coupled oxidising catalytic converter and a catalysed soot diesel particulate filter located in the under-body area. To minimise heat loss, the pipes from the turbochargers to the diesel particulate filters are air-gap insulated. As in the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine, a diesel particulate filter consisting of a thin-wall silicon carbite substrate is used. Wall thickness has been reduced by 37 % to increase cellularity and thus enlarge the active surface area between the catalytic coating and the particulate layer. This helps to reduce the exhaust backpressure and ensure faster filter regeneration times. The combination of a thin-wall substrate and a catalytic coating allows controlled filter regeneration at temperatures between 580 and 600 C in addition to low exhaust back-pressures. Reference For further information on filter regeneration, please refer to SSP Audi A6 05 Engines and transmissions. Pressure line tap upstream of diesel particulate filter Temperature sensor upstream of diesel particulate filter Catalysed soot diesel particulate filter Pressure line tap downstream of diesel particulate filter Lambda probes upstream of oxidising catalytic converter Oxidising catalytic converters Temperature sensors downstream of oxidising catalytic converter 365_009 Air-gap insulated pipes Diesel particulate filter 31
32 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail injection system Special tools Here you can see the special tools for the 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail. 365_048 T40069 Locating pin T40094 Camshaft insertion tool 365_ _050 T40062 Adaptor Sprocket wheel 32
33 365_051 T40049 Adaptor 365_052 T40060 Timing pins 365_053 T40061 Adaptor Camshaft 33
34 34 Notes
35 To broaden your knowledge of the common rail injection system, the following self-study programmes and CBTs have been prepared:
36 Vorsprung durch Technik All rights reserved. Technical specifications subject to change without notice. Copyright AUDI AG N/VK-35 Fax / AUDI AG D Neckarsulm Technical status: 10/05 Printed in Germany A05.5S
Service Training. Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System. Self-Study Programme 420
 Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
Service Training Audi 2.0-litre TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Self-Study Programme 420 The 105 kw (143 hp) 2.0-litre TDI engine featuring common rail (CR) injection technology marks the
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
The 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
Service Training Self-study programme 350 The 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and function The range of engines fitted in the Phaeton and Touareg is being extended by a hightech turbodiesel engine. The 3.0l
The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
Service Training Self-study Programme 467 The 4.2 l V8 TDI engine with common rail fuel injection system Design and Function Following the introduction of the 3.0 l V6 TDI engine in the Phaeton and Touareg
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3,
 0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
0#*?36#& 0#(7$8)9-:$;*.!"#$%&'$()*&$+,-$%&.$()*&$/01$#,23,# 43)"$)353,2$6"+3, Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service Training. Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System. Self-Study Programme 412
 Service Training Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System Self-Study Programme 412 In this booklet we explain to you the design and function of the 2.0 l 125 kw four-valve TDI engine, focussing
Service Training Audi 2.0l 125 kw TDI Engine with Pump Injection System Self-Study Programme 412 In this booklet we explain to you the design and function of the 2.0 l 125 kw four-valve TDI engine, focussing
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
Service Training Self-study Programme 388 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI Engine Design and Function 1 The 4.2l V8 4V FSI engine is a further example of direct petrol injection. It replaces the 4.2l V8 5V engine in
The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger
 Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Service Training Self-study programme 337 The 2.0l FSI engine with turbocharger Design and function The new FSI engines from Volkswagen do without stratified injection and place greater emphasis on output
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
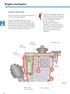 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging
 Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
Service Training Self-study Programme 359 1.4l TSI Engine with Dual-charging Design and Function 1 The 1.4l TSI* engine is the world s first petrol engine with direct petrol injection and dual-charging.
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
Service. Self-Study Programme 248. The W Engine Concept. Design and Function
 Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Service. Self-Study Programme 248 The W Engine Concept Design and Function Introduction The constantly rising demands regarding performance, running comfort and fuel economy have led to the advancement
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Service Training. Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine. Self-Study Programme 377
 Service Training Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine Self-Study Programme 377 Special features of the current Audi vee engine family are the 90-degree included angle between the cylinder banks and the spacing
Service Training Audi 4.2-litre V8 FSI engine Self-Study Programme 377 Special features of the current Audi vee engine family are the 90-degree included angle between the cylinder banks and the spacing
Technical platform. Engines. Running gear. Braking system. Electrical system. Heating/ air-conditioning system
 Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Technical platform Like the Audi A3 and the Skoda Octavia, the new Golf is based on the A-platform. The platform components are therefore almost identical from a technical aspect. Engines Running gear
Workshop Manual. System Description & Operation
 Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
Workshop Manual System Description & Operation ENGINE DESCRIPTION Td6 AND OPERATION Description General Td 6 External View M12 7758 The Td6 diesel engine is a 3.0 litre, 6 cylinder, in-line direct injection
VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine
 Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 823603 VW 3.2 and 3.6 liter FSI Engine Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 10/2006 Course Number 823603 2006 Volkswagen of America,
The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
Service Training Self-study programme 316 The 2.0 ltr. TDI engine Design and function The days of sluggish and noisy diesel engines that, when started, startled the whole neighbourhood out of bed and left
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Product Information. N57 Engine.
 Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
Product Information. N57. Rear-mounted chain drive system Vacuum pump in sump Complies with EURO 5 and EURO Notes on this Product Information Symbols used The following symbols are used in this Product
ENGINE GENERAL ENGINE GENERAL GENERAL OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. STRUCTURE...
 GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment kw at 2100 rpm
 2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT
 A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
A N AV I S TA R C O M PA N Y MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update Study Guide TMT-120710 Study Guide MaxxForce TM 5 Engine Update TMT-120710 2007 International Truck and Engine Corporation 4201 Winfield Road,
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual
 Instant Manual Download CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual Download Here CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 Service Workshop Repair Shop Manual PLEASE NOTE: YOU NEED TO BE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET
Instant Manual Download CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual Download Here CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 Service Workshop Repair Shop Manual PLEASE NOTE: YOU NEED TO BE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Engine. External View GENERAL TECHNICAL FEATURES. file://c:\users\duncan Capewell\Documents\Data Files - DCapewell\Mydocs\Disco3...
 Page 1 of 32 Published : May 7, 2004 Engine External View GENERAL The TdV6 engine is a 2.7 litre, direct injection, six-cylinder diesel engine having two banks of three cylinders, arranged at 60 degrees
Page 1 of 32 Published : May 7, 2004 Engine External View GENERAL The TdV6 engine is a 2.7 litre, direct injection, six-cylinder diesel engine having two banks of three cylinders, arranged at 60 degrees
AD07.61-P-4000AC ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory Possible cause Note Fault code description
 Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B
 Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
Service. Self-Study Programme 232 5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi
ENGINE <4G6> 1-1 CONTENTS OVERVIEW... 2 COOLING SYSTEM... 4 MAIN UNIT... 2 INTAKE AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS... 4 LUBRICATION SYSTEM... 2 FUEL SYSTEM...
 1-1 ENGINE CONTENTS OVERVIEW.............................. 2 MAIN UNIT.............................. 2 Pistons.................................... 2 LUBRICATION SYSTEM.................. 2 Oil Pan....................................
1-1 ENGINE CONTENTS OVERVIEW.............................. 2 MAIN UNIT.............................. 2 Pistons.................................... 2 LUBRICATION SYSTEM.................. 2 Oil Pan....................................
1012. The engine for construction equipment kw at min -1
 1012. The engine for construction equipment. 41-123 kw at 1500-2500 min -1... Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1012: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1012. The engine for construction equipment. 41-123 kw at 1500-2500 min -1... Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1012: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
gas passes through baffle plates in cylinder oil separator inlet port. Separated oil returns The first separation will happen when blowby
 2 05 LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW Lubrication System PCV Oil Separator Cylinder head cover (oil + gas) Blow-by gas (air duct hose) Inlet port Oil (oil gauge pipe) The first separation will happen when blowby gas
2 05 LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW Lubrication System PCV Oil Separator Cylinder head cover (oil + gas) Blow-by gas (air duct hose) Inlet port Oil (oil gauge pipe) The first separation will happen when blowby gas
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies. Turbochargers
 Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
1013. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED
 SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
SECTION 6A1-2 - ENGINE MECHANICAL - V6 SUPERCHARGED CAUTION: This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS will consist of either seat belt pre-tensioners and a driver
DIESEL ENGINE MECHANICAL
 SECTION 1B3 DIESEL ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
SECTION 1B3 DIESEL ENGINE MECHANICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator
 Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Fuel filter with fuel pressure regulator Securing clip for pressure regulator The fuel filter is located on the right-hand side of the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator is connected to the fuel filter
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual
 Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual DOWNLOAD HERE "Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual Signature
Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual DOWNLOAD HERE "Cummins engine Signature ISX QSX15 Service Workshop Shop Repair Manual - PDF Service Manual Signature
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456. This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine.
 !"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
!"#$%&'()*+(,%&%-)-".&(/01*%)$"%&2(#2$&3456 This can be found in the camshaft housing and is included in the oil circuit of the engine. Actuation of the inlet camshaft timing adjustment valve results in
955L Traxcavator S/n 64J, 71J & 85J Volume 1 of 2
 Caterpillar Service Manual 955L Traxcavator S/n 64J, 71J & 85J Volume 1 of 2 Service Manual THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF CATERPILLAR OR IT S SUCCESSORS. CATERPILLAR
Caterpillar Service Manual 955L Traxcavator S/n 64J, 71J & 85J Volume 1 of 2 Service Manual THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF CATERPILLAR OR IT S SUCCESSORS. CATERPILLAR
HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE
 16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA
 Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Strona 1 z 10 Audi A3 Current Flow Diagram No. 75 / 1 Edition 09.1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic, 4-cylinder) engine codes AQA From model year 1999 Audi A3 (1,8 l litre
Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2. Self-study programme 268. For internal use only
 268 Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2 Self-study programme 268 For internal use only Contents Engine, Mechanics Page Belt drive/ancillaries...................................................
268 Service. The 6.0 l W12 engine in the Audi A8 - Part 2 Self-study programme 268 For internal use only Contents Engine, Mechanics Page Belt drive/ancillaries...................................................
Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (-40 )
 149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
CREATING POWER SOLUTIONS. 4H50TIC The new generation. Hatz Diesel Engines Made in Germany.
 CREATING POWER SOLUTIONS. 4H50TIC The new generation Hatz Diesel Engines Made in Germany EN www.hatz-diesel.com The new generation of water-cooled Hatz diesel engines From 2014 a new engine family will
CREATING POWER SOLUTIONS. 4H50TIC The new generation Hatz Diesel Engines Made in Germany EN www.hatz-diesel.com The new generation of water-cooled Hatz diesel engines From 2014 a new engine family will
The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
Service Training Self-study Programme 452 The 3.0 l V6 245kW TSI engine with supercharger in the Touareg Hybrid Design and Function The 3.0 l V6 engine with supercharger and hybrid drive sees Volkswagen
PARTIAL ENGINE ASSY (2ZZ GE)
 COMPONENTS 14189 140R701 7.0 (71, 62 in. lbf) Cylinder Head Cover No. 2 19 (194, 14) Radiator Support Upper 19 (194, 14) Radiator Hose Inlet Cruise Control Actuator Assy 6.0 (61, 53 in. lbf) Radiator Assy
COMPONENTS 14189 140R701 7.0 (71, 62 in. lbf) Cylinder Head Cover No. 2 19 (194, 14) Radiator Support Upper 19 (194, 14) Radiator Hose Inlet Cruise Control Actuator Assy 6.0 (61, 53 in. lbf) Radiator Assy
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
MAN Energy Solutions
 ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied; however, all
ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied; however, all
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine. Month XX, 20XX
 EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine Month XX, 20XX EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine PRESENTER S NAME PRESENTER S POSITION TRADITION OF ENGINE INNOVATION MX, EU PX DD575 PR MX, NA MX 11, EU 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine Month XX, 20XX EPA 2016 PACCAR MX-11 Engine PRESENTER S NAME PRESENTER S POSITION TRADITION OF ENGINE INNOVATION MX, EU PX DD575 PR MX, NA MX 11, EU 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
This information covers the design and function of the intake and exhaust systems for the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR S, UNIT, INTERMEDIATE (DS) AND INTERMEDIATE (GS) MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR
 TM 5-2815-232-14 TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR S, UNIT, INTERMEDIATE (DS) AND INTERMEDIATE (GS) MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR ENGINE, DIESEL, CATERPILLAR, MODEL 3508 NSN 2815-01-216-0938 HEADQUARTERS, DEPARTMENT
TM 5-2815-232-14 TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR S, UNIT, INTERMEDIATE (DS) AND INTERMEDIATE (GS) MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR ENGINE, DIESEL, CATERPILLAR, MODEL 3508 NSN 2815-01-216-0938 HEADQUARTERS, DEPARTMENT
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment ,9 kw hp at rpm
 The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
PID Code/Condition: Description: Mack MP8-455M US17 Date: March 1, 2017
 PID Code/Condition: 100-1770 Description: Mack MP8-455M US17 Date: March 1, 2017 High Torque MAXIDYNE Diesel Engine Maximum Horsepower 455 BHP [339 kw] Electronic Common Rail Fuel Injection V-MAC IV Total
PID Code/Condition: 100-1770 Description: Mack MP8-455M US17 Date: March 1, 2017 High Torque MAXIDYNE Diesel Engine Maximum Horsepower 455 BHP [339 kw] Electronic Common Rail Fuel Injection V-MAC IV Total
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE
 EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system, the DIS (Direct Ignition System), and a plastic intake manifold have been used on the
EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system, the DIS (Direct Ignition System), and a plastic intake manifold have been used on the
GAS/PETROL THE ALTERNATIVE: ENGINES LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER AND MORE COMPACT ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY 22,0 6,6 431,1
 THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry. 1 Introduction Preface Model-Building Simulation... 5 References...
 Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Contents Part I Foundations of Thermodynamics and Chemistry 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Preface.... 3 1.2 Model-Building... 3 1.3 Simulation... 5 References..... 8 2 Reciprocating Engines... 9 2.1 Energy Conversion...
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine
 Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
GF07.16-P-9997OGG Overview of system components for common rail diesel injection (CDI)
 GF07.16-P-9997OGG Overview of system components for common rail diesel injection (CDI) 19.12.2016 Engine 642.8 in model 164.1 Engine 642.8 in model 164.8 Engine 642.8 in model 251.0 Engine 642.8 in model
GF07.16-P-9997OGG Overview of system components for common rail diesel injection (CDI) 19.12.2016 Engine 642.8 in model 164.1 Engine 642.8 in model 164.8 Engine 642.8 in model 251.0 Engine 642.8 in model
ENGINE MECHANICAL <134>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
TM &P TECHNICAL MANUAL
 TM 5-3895-355-14&P TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR'S, ORGANIZATIONAL, DIRECT SUPPORT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL (INCLUDING REPAIR PARTS INFORMATION AND SUPPLEMENTAL MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PARTS INSTRUCTIONS)
TM 5-3895-355-14&P TECHNICAL MANUAL OPERATOR'S, ORGANIZATIONAL, DIRECT SUPPORT AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL (INCLUDING REPAIR PARTS INFORMATION AND SUPPLEMENTAL MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PARTS INSTRUCTIONS)
MAN B&W ME Engine Description. Page 1 of 6. Frame Box
 ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with MAN Diesel & Turbo drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied;
ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with MAN Diesel & Turbo drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied;
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
Disconnect the APP sensor harness connector. See Fig. 4. Remove the accelerator pedal mounting nuts. Remove the APP assembly.
 ENGINE CONTROLS - REMOVAL, OVERHAUL & INSTALLATION - 6.6L DIESEL... Page 1 of 41 FUEL SYSTEMS ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR Removal & Installation Disconnect the APP sensor harness connector. See Fig.
ENGINE CONTROLS - REMOVAL, OVERHAUL & INSTALLATION - 6.6L DIESEL... Page 1 of 41 FUEL SYSTEMS ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR Removal & Installation Disconnect the APP sensor harness connector. See Fig.
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
Vibration damper control
 Vibration damper control The damper control system registers the condition of the road surface and the movements of the vehicle via four wheel acceleration sensors and three body acceleration sensors.
Vibration damper control The damper control system registers the condition of the road surface and the movements of the vehicle via four wheel acceleration sensors and three body acceleration sensors.
6-speed automatic transmission 09D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
2012 BMW 135i. ENGINE N55 - Service Information. N55 - Service Information
 ENGINE N55 - Service Information INTRODUCTION The N55 engine is the successor to the N54, Re-engineering and modifications have made it possible to now use only one exhaust turbocharger. Against the backdrop
ENGINE N55 - Service Information INTRODUCTION The N55 engine is the successor to the N54, Re-engineering and modifications have made it possible to now use only one exhaust turbocharger. Against the backdrop
Engine Dismantle and Assemble ( )
 Engine Dismantle and Assemble ( 34 8) Special Tools 5 053 Slide hammer 47 Vibration damper remover 47 5053 00 Splined head socket, cylinder head bolts 87 Mounting stand with geared drive 00 059C Installer
Engine Dismantle and Assemble ( 34 8) Special Tools 5 053 Slide hammer 47 Vibration damper remover 47 5053 00 Splined head socket, cylinder head bolts 87 Mounting stand with geared drive 00 059C Installer
Section 10 Chapter 7
 Section 10 Chapter 7 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Troubleshooting Symptoms Identification Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have
Section 10 Chapter 7 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Troubleshooting Symptoms Identification Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have
Oil Module in the Inner V
 Oil Module in the Inner V There are numerous oil supply passages under a cover in the V of the engine. The cover is bolted directly to the cylinder block, with a metal gasket positioned between them. Oil
Oil Module in the Inner V There are numerous oil supply passages under a cover in the V of the engine. The cover is bolted directly to the cylinder block, with a metal gasket positioned between them. Oil
COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS)
 MITSUBISHI 4N13, 4N14 ENGINES COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) Issued : November 2010 Applicable Vehicle : Vehicle Manufacturer MITSUBISHI Vehicle Name LANCER ASX OUTLANDER 50000023E 2010 DENSO CORPORATION All
MITSUBISHI 4N13, 4N14 ENGINES COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) Issued : November 2010 Applicable Vehicle : Vehicle Manufacturer MITSUBISHI Vehicle Name LANCER ASX OUTLANDER 50000023E 2010 DENSO CORPORATION All
Diesel Technology: Engines
 Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Workshop Manual. F-Super Duty : Powertrain. 03: Engine
 Workshop Manual 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 3: Powertrain 03: Engine 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 Contents/Index GROUP 03: Engine SECTION 303-00: Engine System General Information SECTION 303-01A: Engine 5.4L
Workshop Manual 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 3: Powertrain 03: Engine 1999 F-Super Duty 250-550 Contents/Index GROUP 03: Engine SECTION 303-00: Engine System General Information SECTION 303-01A: Engine 5.4L
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
AfterSales Training. Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C
 AfterSales Training Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C Porsche AfterSales Training Student Name: Training Center Location: Instructor Name: Date: Important Notice: Some of the contents of this AfterSales
AfterSales Training Cayenne Engine Repair V8 and V6 P10C Porsche AfterSales Training Student Name: Training Center Location: Instructor Name: Date: Important Notice: Some of the contents of this AfterSales
Coolant Temperature Switch; Black with Round Top and 4 Pin Connector $ $ Fuel Injector Insulator; O-Ring; Green
 AC & Heater Control Valve; Mono Valve Solenoid Repair Kit 3065 1 $ 40.24 $ 40.24 Distributor Cap 03227 1 $ 88.73 $ 88.73 Distributor Rotor 04177 1 $ 19.86 $ 19.86 Vacuum Line, Transparent/Yellow, 1.0 X
AC & Heater Control Valve; Mono Valve Solenoid Repair Kit 3065 1 $ 40.24 $ 40.24 Distributor Cap 03227 1 $ 88.73 $ 88.73 Distributor Rotor 04177 1 $ 19.86 $ 19.86 Vacuum Line, Transparent/Yellow, 1.0 X
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER
 A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
ENGINE MECHANICAL <2.0L ENIGNE>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 This model is equipped with a newly developed 4B11 engine. It is a 4-cylinder,
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 This model is equipped with a newly developed 4B11 engine. It is a 4-cylinder,
