Evaluating Generation Considering All Plant Losses and Efficiencies Duane H. Morris, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority
|
|
|
- Marylou Candice Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluating Generation Considering All Plant Losses and Efficiencies Duane H. Morris, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority James W. Brower Scientech a business unit of Curtiss-Wright Flow Control Company
2 Evaluating Generation Considering All Plant Losses and Efficiencies Duane H. Morris, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority James W. Brower Scientech a business unit of Curtiss-Wright Flow Control Company Abstract In June 2007, TVA restarted Unit 1 at the Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant (BFNP) after the unit had sat idle for more than 20 years. Prior to restart, the unit s steam path was modified to take advantage of a 20% extended power uprate (EPU). However, because of delays in licensing approval for EPU, the unit has been operated at only 105% of the original licensed thermal power (OLTP). Based on the expected performance at 105% power, the unit has seemingly under produced electrical generation. This paper discusses the methods used to evaluate the generation anomaly for the unit. This evaluation included using thermal performance software to calculate plant performance parameters and efficiencies in order to validate the generation and try to identify the sources of the lost generation. The conclusion of this study was that turbine efficiency and throttle loss were the main culprits to lost generation EPRI Plant Performance Enhancement Program Annual Meeting & Vendor Exposition,
3 Introduction In June 2007, TVA restarted Unit 1 at the Browns Ferry Nuclear Plant (BFNP) after the unit had sat idle for more than 20 years. Prior to restart, the unit s steam path was modified to take advantage of a 20% extended power uprate (EPU). However, because of delays in licensing approval for EPU, the unit has been operated at only 105% of the original licensed thermal power (OLTP). Based on the expected performance at 105% power, the unit has seemingly under produced electrical generation. A few theories for this under production were discussed, but no evidence could support them. One theory was that the feedwater flowrate was reading a flow that was higher than reality. Another was that since the HP turbine was sized for 120% of the OLTP flow rate and was only operating at 105%, it was less efficient. Yet another theory was that excessive throttling of the throttle valves was causing the loss of generation. In addition to these theories, any other possible plant losses had to be examined and/or determined. This paper discusses the methods used to evaluate the generation anomaly for BFNP Unit 1. This evaluation included using plant data and thermal performance software to calculate plant performance parameters including turbine efficiencies and entering this information into heat balance software in order to validate the generation and try to identify the sources of the lost generation. Through this process, the theories discussed above were tested for validity. The conclusion of this study was that BFNP Unit 1 does not perform at its design turbine efficiencies nor does its throttle valve behave as heat balances indicate. These factors cause the generation to be lower than expected. There is some room for possible additional losses including additional HP turbine efficiency loss, feedwater flow measurement error, and others (i.e. valve leaks, instrument error, etc.). However, as will be shown, most of the generation anomaly can be attributed to turbine inefficiencies and throttling losses. 1
4 Problem Based on a comparison of actual plant data and the cycle computer model, BFNP Unit 1 has been generating approximately 14 MWe less than the predicted electrical output since restart in June The upgraded steam path was optimized in support of a 20% EPU; however, because of delays in licensing approval for EPU, the unit currently operates at only 105% OLTP. TVA initially thought that the MWe difference could all be attributed to excessive turbine flow margin either designed in by the vendor or as a result of lax manufacturing tolerances; and since the unit was expected to only operate at the lower thermal power level for a short period of time, a minimal effort was made to resolve the difference. Further delays in achieving EPU operation has, however, compelled TVA to make a full accounting of the discrepancy. Background Information BFNP Unit 1 was first put into commercial operation in The unit is an 1800-RPM tandemcompound design consisting of a double-flow HP section with six (6) stages and a six-flow LP section with eight (8) stages and 43inch last stage buckets. The turbine is a non-reheat N1 code type and is supplied with saturated steam from a boiling water reactor (BWR). The turbine generator was originally rated for a turbine cycle thermal power of 3298 MWt, and was originally designed with 5% flow margin. In 2007, the unit was restarted with anticipation of a 20% EPU; therefore the unit was equipped with a new steam path. The unit currently operates with four (4) control valves in single (full arc) admission mode. Since there was no guarantee language associated with the steam path replacement, management decided that precision testing of the turbine would not be performed following restart. As a result of that decision, test point taps were not installed to aid in the verification of parameters such as the turbine first stage bowl pressure. No vendor heat balances were prepared for the new steam path at 105% OLTP. The Unit 1 steam path modifications also resulted in an apparent loss of approximately 24 MWe when compared with BFNP Unit 2 and Unit 3 s generation. Both Units 2 and 3 are similarly operated at 105% OLTP; however, their HP turbines were optimized for the uprate conditions. After more than two years of delays in obtaining EPU approval, TVA started exploring steam path modifications to reclaim all or some portion of the accumulative loss of 38 MWe. The turbine vendor performed an evaluation of the existing steam turbine. The analysis showed that the existing unit had approximately 22% flow margin at 105% OLTP. This high level of margin resulted in significant performance losses due to control valve throttling. Several options were evaluated and the best option, when considering performance and flow capacity predictability, was to replace the first four (4) HP stages, including both diaphragms and buckets. The performance of the HP turbine section was primarily affected by the steam path design and throttling loss. In the case of BFNP Unit 1, the proposed changes to the HP steam path would result in an efficiency penalty due to the re-designed stages, which would no longer be optimum with the retained stages. However, the recovery in throttling loss due to a smaller flow capacity was greater and the vendor predicted a net expected output gain of 27.5 MWe. 2
5 Evaluation Procedure To evaluate the generation at BFNP Unit 1, on-line and predictive, heat balance thermal performance software was employed. The on-line monitoring software supplied a historian of real-time plant performance data that could be entered into the predictive software to determine if the generation was justified. Available performance data points were collected using the displays from the on-line thermal performance system. Some of these displays are illustrated in Figures 1 through 4. All the displays and calculations used from this system can be seen in Appendix A. Data was then retrieved from this system s historian. Data for 3/24/2010 from 15:00:00 to 16:00:00 was retrieved into Excel and averaged. This hour of data was used simply because the condenser shells were operating at an average backpressure around 2 inhga. The averaged values were then plugged into the predictive, heat balance model. The averaged data used is shown in Table 1. Figure 1: On-line Performance System - HP Turbine Display 3
6 Figure 2: On-line Performance System - LP Turbine Display 4
7 Figure 3: On-line Performance System - Condenser Display 5
8 Figure 4: On-line Performance System - MW Effect Advisor Table 1: 1 Hour Average of Plant performance Data PARAMETER DESCRIPTION MEASURED CALCULATED ADDITIONAL VALUE VALUE CALCULATION U1 REACTOR POWER; NSSS CALCULATED U1 RECIRC PUMP POWER INPUT TO REACTOR U1 RWCU THERMAL LOSS Throttle Valve U1 OTHER REACTOR LOSS Outlet Press U1 MN STM EQUALIZING HEADER PRESS U1 MAIN STEAM ENTHALPY With New Throttle U1 CONTROL ROD DRIVE FLOW Valve Press Drop U1 HP TURBINE GOV SIDE Stage Efficiency (GS) U1 HP TURBINE GEN SIDE Stage Efficiency (GS) U1 HP TURBINE GOV SIDE Stage Efficiency stage U1 HP TURBINE GEN SIDE Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage
9 PARAMETER DESCRIPTION MEASURED CALCULATED ADDITIONAL U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE A Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE B Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage U1 LP TURBINE C Stage Efficiency stage VALUE VALUE CALCULATION U1 FIRST STAGE PRESSURE GEN END U1 FIRST STAGE PRESSURE GOV END U1 GEN HP TURB EXHAUST PRESSURE U1 GOV HP TURB EXHAUST PRESSURE U1 LPA-1 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPA-2 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPA-3 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPA-4 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPA-5 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPA-6 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPA-7 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-1 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-2 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-3 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-4 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-5 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-6 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPB-7 EXTRACTION PRESSURE
10 PARAMETER DESCRIPTION MEASURED CALCULATED ADDITIONAL U1 LPC-1 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPC-2 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPC-3 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPC-4 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPC-5 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPC-6 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 LPC-7 EXTRACTION PRESSURE U1 FWH A2 SHELL RELIEF VALVE FLW U1 FWH C1 SHELL RELIEF VALVE FLW U1 FWH A1 TTD U1 FWH A1 DCA U1 FWH B1 TTD U1 FWH B1 DCA U1 FWH C1 TTD U1 FWH C1 DCA U1 FWH A2 TTD U1 FWH A2 DCA U1 FWH B2 TTD U1 FWH B2 DCA U1 FWH C2 TTD U1 FWH C2 DCA U1 FWH A3 TTD U1 FWH A3 DCA U1 FWH B3 TTD U1 FWH B3 DCA U1 FWH C3 TTD U1 FWH C3 DCA U1 FWH A4 TTD U1 FWH A4 DCA U1 FWH B4 TTD U1 FWH B4 DCA U1 FWH C4 TTD U1 FWH C4 DCA U1 FWH A5 TTD U1 FWH A5 DCA U1 FWH B5 TTD U1 FWH B5 DCA U1 FWH C5 TTD U1 FWH C5 DCA VALUE VALUE CALCULATION 8
11 PARAMETER DESCRIPTION MEASURED CALCULATED ADDITIONAL VALUE VALUE CALCULATION U1 CONDENSER A BACK PRESSURE U1 CONDENSER B BACK PRESSURE U1 CONDENSER C BACK PRESSURE U1 REACTOR FEED PUMP A EFFICIENCY U1 REACTOR FEED PUMP B EFFICIENCY U1 REACTOR FEED PUMP C EFFICIENCY U1 RFP A HEAD U1 RFP B HEAD U1 RFP C HEAD U1 AVERAGE HOTWELL TEMP U1 MAIN GENERATOR POWER (FILTERED) U1 UNACCOUNTED FOR MW EFFECTS U1 RFP A DISCHARGE PRESSURE U1 RFP B DISCHARGE PRESSURE U1 RFP C DISCHARGE PRESSURE U1 FINAL FEED WATER TEMPERATURE U1 THROTTLE STEAM SUPPLY PRESSURE U1 HTR A1 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR B1 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR C1 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR A2 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR B2 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR C2 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR A3 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR B3 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR C3 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR A4 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR B4 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR C4 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR A5 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR B5 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 HTR C5 SHELL STEAM PRESSURE U1 LP TURB A EXTR PRESS TO HTR5-GEN U1 LP TURB A EXTR PRESS TO HTR5-GOV Moisture Separator U1 LP TURB A EXTR PRESS TO HTR5-GEN Inlet Pressure U1 LP TURB INLET PRESSURE U1 RFPT STEAM FLOW FROM MS B U1 RFPT STEAM FLOW FROM MS C
12 Nine case studies were completed in the predictive, heat balance software. The first case demonstrated the unit with design components and 2.0 inhga of condenser back pressure at 105% OLTP and design main steam conditions. The second case demonstrated design components with the plant s actual thermal power (accounting for recirc pump heat addition, RWCU, and reactor losses), main steam pressure, condenser back pressure and sub-cooling, and control rod drive (CRD) flow. The third case imported the boundary conditions from case 2 but also included all the other performance parameters except turbine efficiencies. These parameters included feedwater heater terminal temperature difference (TTD) and drain cooler approach (DCA) temperatures, turbine stage pressures, and pump efficiencies and discharge pressures. Two known feedwater heater relief valve leaks, FWH A2, 70,000 lb/hr & FWH C1, 19,858 lb/hr, as well as 0.5% heater shell operating vent flows were also included in case 3. Finally, the fourth case ran everything from case 3 but also included LP turbine efficiencies. The following 5 cases were set up to study the HP turbine. The fifth case study included everything from the previous case with the addition of a throttle valve pressure drop based on the saturation pressure which was determined from local temperature indication after the throttle valve. The HP bowl pressure was figured to be psia. This new throttle valve pressure drop changed the HP governing stage efficiencies. These changes are shown in Table 2. Table 2: HP Turbine Corrected Efficiencies HP TURBINE STAGE MEASURED AVERAGE VALUE PSIA U1 HP TURBINE GOV SIDE Stage Efficiency (GS) U1 HP TURBINE GEN SIDE Stage Efficiency (GS) U1 HP TURBINE GOV SIDE Stage Efficiency stage U1 HP TURBINE GEN SIDE Stage Efficiency stage The sixth case included the new bowl pressure (704.5 psia) and the actual HP turbine efficiencies adjusted for it. The seventh case further degraded the HP turbine to match generation. In the eighth case, performance data predicted for the modified HP turbine and its design throttle valve pressure loss was inserted into the model. Finally, in the ninth case, the new turbine was run with a corrected new throttle valve pressure loss based on the percent error experienced in case 5. These case studies showed how the different plant conditions were affecting the generation. The generation results for the nine case studies are shown in Table 3. Case 6 would ideally match the actual plant output of MWe, however, it is MWe, which is MWe higher than actual. This difference could be considered reasonable, although a little on the high side given instrument error. In fact, the HP exhaust pressure instrument that was used reads about 11 psia lower than design, which is worth about 3 MWe. It is also very possible that there are some other unknown losses or a slight feed flow problem. Yet, another alternative will be discussed later. 10
13 Table 3: Predictive, Heat Balance Case Study Results CASE DESCRIPTION GENERATION (MW) 1 BASE MODEL /24/2010 ACTUAL PLANT DATA BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ALL ACTUAL CONDITIONS W/O TURBINE EFFICIENCIES LP TURBINE EFFICIENCIES INCLUDED ACTUAL THROTTLE VALVE OUTLET PRESSURE INCLUDED HP TURBINE EFFICIENCIES INCLUDED HP TURBINE DEGRADED TO MATCH GENERATION NEW HP TURBINE & THROTTLING CONDITIONS INCLUDED NEW HP TURBINE WITH 4.15% THROTTLED PRESS DIFF In case 1 with all 100% design conditions and a back pressure of 2 inhga, the output was MWe. When considering actual plant boundary conditions in case 2 (main steam pressure, condenser back pressure and sub-cooling, and Control Rod Drive (CRD) flow), only MWe was lost. When considering all other actual performance parameters besides turbine efficiencies (case 3), we actually gained MWe. This gain was attributed to an 11 psia lower HP turbine exhaust pressure compared to design. The main contributors to lost generation were turbine efficiencies and throttling losses. In case 4, the LP turbine efficiencies were incorporated to give a loss of MWe. This is a 1.15% loss in generation. In the next five cases, the HP turbine was examined. In case 5, actual throttle valve pressure drop was considered. This pressure drop was calculated based on the saturation pressure which was determined from a local temperature indication downstream of the control valves. This reduced the HP turbine inlet pressure from about psia (pressure drop curve based on heat balances) to psia. This was a pressure difference of 4.15% and was worth MWe. Next, in case 6 the actual HP turbine efficiencies were entered for an additional loss of MWe. These efficiencies came from the on-line thermal performance system and are calculated based on the design expansion line. The design expansion line is shaped from the vendor heat balances and is the best available representation of expected steam expansion through the turbine. In case 7 the HP turbine was further degraded until the generation was matched. This illustrated what the efficiencies would be if all of the loss was due to throttle pressure drop and poor HP turbine efficiencies caused by the steam expansion not following the design expansion line. Table 4 shows the efficiency differences between case 3 and case 6; and case 3 and case 7. 11
14 Table 4: Turbine Efficiency Comparison TURBINE STAGE CASE 3 CASE 6 DELTA CASE 3 CASE 7 DELTA DELTA C3 C6 C3 - C6 C3 C7 C3 - C7 C6 - C7 HP GOV EFFICIENCY 87.87% 85.10% 2.77% 87.87% 84.41% 3.46% 0.69% HP 1ST STAGE EFFICIENCY 84.06% 82.20% 1.86% 84.06% 80.30% 3.75% 1.90% LPA 1ST STAGE EFFICIENCY 92.75% 86.75% 6.00% 92.75% 86.75% 6.00% 0.00% LPA 2ND STAGE EFFICIENCY 89.49% 89.69% -0.20% 89.49% 89.69% -0.20% 0.00% LPA 3RD STAGE EFFICIENCY 87.06% 86.66% 0.40% 87.06% 86.66% 0.40% 0.00% LPA 4TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 84.93% 84.87% 0.06% 84.93% 84.87% 0.06% 0.00% LPA 5TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 83.34% 83.80% -0.46% 83.34% 83.80% -0.46% 0.00% LPA 6TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 82.21% 82.04% 0.18% 82.21% 82.04% 0.18% 0.00% LPA 7TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 82.75% 82.65% 0.10% 82.75% 82.65% 0.10% 0.00% LPA 8TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 68.01% 65.91% 2.09% 68.01% 65.91% 2.09% 0.00% LPB 1ST STAGE EFFICIENCY 92.75% 86.74% 6.00% 92.75% 86.74% 6.00% 0.00% LPB 2ND STAGE EFFICIENCY 89.49% 89.69% -0.20% 89.49% 89.69% -0.20% 0.00% LPB 3RD STAGE EFFICIENCY 87.06% 86.66% 0.40% 87.06% 86.66% 0.40% 0.00% LPB 4TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 85.02% 84.83% 0.19% 85.02% 84.83% 0.19% 0.00% LPB 5TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 83.52% 84.02% -0.50% 83.52% 84.02% -0.50% 0.00% LPB 6TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 82.21% 82.32% -0.11% 82.21% 82.32% -0.11% 0.00% LPB 7TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 82.64% 82.53% 0.12% 82.64% 82.53% 0.12% 0.00% LPB 8TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 67.18% 64.99% 2.19% 67.18% 64.99% 2.19% 0.00% LPC 1ST STAGE EFFICIENCY 92.75% 86.74% 6.00% 92.75% 86.74% 6.00% 0.00% LPC 2ND STAGE EFFICIENCY 89.49% 89.69% -0.20% 89.49% 89.69% -0.20% 0.00% LPC 3RD STAGE EFFICIENCY 87.06% 86.66% 0.40% 87.06% 86.66% 0.40% 0.00% LPC 4TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 84.98% 84.85% 0.13% 84.98% 84.85% 0.13% 0.00% LPC 5TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 83.45% 83.93% -0.48% 83.45% 83.93% -0.48% 0.00% LPC 6TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 82.20% 82.23% -0.04% 82.20% 82.23% -0.04% 0.00% LPC 7TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 82.67% 82.54% 0.13% 82.67% 82.54% 0.13% 0.00% LPC 8TH STAGE EFFICIENCY 63.24% 60.45% 2.79% 63.24% 60.45% 2.79% 0.00% Finally, generation returns were studied for inserting the proposed modified HP turbine into the model. These turbine modifications are planned for implementation in the fall of At that point, plant data will again be examined to determine the actual MWe gain (i.e., pre and post test are to be conducted). In case 8, the turbine and throttle valve tuned data from the new turbine heat balances were applied to the model along with the plant conditions from case 4. This resulted in a generation of MWe. This was mostly a result of a lower pressure drop across the throttle valve. In case 4 the throttled pressure was psia, and in this case, it was psia. In fact, the efficiencies of this new turbine are very similar to the design efficiencies of the current turbine as shown in Table 5. 12
15 Table 5: HP Turbine Efficiency Comparison CASE 4 CASE 8 DELTA C4 C8 C4 - C8 HP GOV EFFICIENCY 86.72% 86.76% -0.04% HP 1ST STAGE EFFICIENCY 83.20% 82.73% 0.47% Finally in case 9, the 4.15% throttle valve pressure difference from case 5 was used with the modified HP turbine. This study showed how the generation would be impacted if the new design misses the throttle valve outlet pressure by the same percentage that the original did. The result was a turbine inlet pressure reduction from psia to psia and an output of MWe. This output is MWe less than what the design would produce. These results show how important this pressure can be to generation. A pressure indication after the throttle valve is going to be added during the turbine replacement, so a better analysis of throttle effects can then be performed. From the last two studies, it was shown that generation could increase MWe to MWe if the new turbine allows the plant to operate similar to the vendor s heat balances. This also assumes that the MWe unaccounted loss is due to the HP turbine. However, if this loss is due to some other problem (leaks, feedwater flow, etc.), these gains would only be MWe to MWe. Conclusion This study has shown that BFNP Unit 1 does not perform at its design turbine efficiencies or at its design throttle valve pressure drop, and that these issues cause the generation to pale in comparison to Units 2 & 3. During this study the measured generation was almost matched considering actual plant conditions. The unaccounted losses could be due to instrument error, other losses such as valve leaks, and/or a feedwater flow problem. It could also be a result of the HP turbine steam not expanding as the design expansion line predicts. It was shown that efficiencies based on design expansion lines can account for MWe of HP turbine loss and MWe of LP turbine loss totaling MWe. The other large contributor was the throttled pressure which was worth MWe bringing the total to MWe. This would correct the actual output to MWe, which is close to the MWe expected. This would bring generation in line with Units 2 & 3; however, it is still almost 5 MWe short. This 5 MWe could be the result of several issues. Plant instrument errors, other unknown losses, feedwater flow error, or the HP turbine not behaving as designed could make-up the 5 MWe. If the steam expansion through the HP turbine is the culprit then the total loss to HP turbine efficiency is brought up to 8.56 MWe. HP turbine efficiency and throttling have been suspects in loss generation since it was replaced and turbine flowrates have been at 105% OLTP instead of the 120% OLTP as the turbine was designed. As stated above, the HP turbine is going to be modified for 105% OLTP conditions in 13
16 the fall of 2010 in an attempt to reclaim all or some portion of the losses. The throttle valves are expected to be opened to 54% (similar to Units 2 & 3) from the current 47%. After this occurs, we will have another data point to consider for this study, but some additional analyses were performed based on this upcoming replacement s heat balances. These analyses showed that if the throttle valve and HP turbine behave as indicated by the new heat balances, around 50 MWe of generation could be regained. This number takes into account the 1.15% loss attributed to the LP turbines as well as all other known and about 5 MWe of unknown losses during the data acquisition period on 3/24/2010. The turbine vendor is suggesting a 27.5 MWe gain, so it will be interesting to see just what generation is obtained. 14
17 APPENDIX A A-1
18 APPENDIX A A-2
19 APPENDIX A A-3
20 APPENDIX A A-4
21 APPENDIX A A-5
22 APPENDIX A A-6
23 APPENDIX A A-7
24 APPENDIX A A-8
25 APPENDIX A A-9
26 APPENDIX A A-10
PLANT HATCH FEEDWATER SYSTEM OPERATING EXPERIENCE. Significant events from 2015
 PLANT HATCH FEEDWATER SYSTEM OPERATING EXPERIENCE Significant events from 2015 ICES Report #315779 Hatch Unit 2 March 10, 2015 Startup from 2R23 refueling outage Feedwater Control System (RWL Control)
PLANT HATCH FEEDWATER SYSTEM OPERATING EXPERIENCE Significant events from 2015 ICES Report #315779 Hatch Unit 2 March 10, 2015 Startup from 2R23 refueling outage Feedwater Control System (RWL Control)
External Hard Drive: A DFMA Redesign
 University of New Mexico External Hard Drive: A DFMA Redesign ME586: Design for Manufacturability Solomon Ezeiruaku 4-23-2013 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The following document serves to illustrate the effects
University of New Mexico External Hard Drive: A DFMA Redesign ME586: Design for Manufacturability Solomon Ezeiruaku 4-23-2013 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The following document serves to illustrate the effects
Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance MP-SEE-THRU-01 Rev. 018
 Student Operating Procedure Millstone Station Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance Approval Date: 01/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/12/2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE...3
Student Operating Procedure Millstone Station Startup and Operation of SEE-THRU Nuclear Power Plant for Student Performance Approval Date: 01/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/12/2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE...3
ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSITUTE (EPRI) 2011 CONDENSER TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE AUGUST 3-4, 2011, CHICAGO, ILLINOIS
 ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSITUTE (EPRI) 2011 CONDENSER TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE AUGUST 3-4, 2011, CHICAGO, ILLINOIS IMPORTANCE OF TEMPERATURE OF BYPASS STEAM ADMITTED INTO A STEAM SURFACE CONDENSER IN A COMBINED
ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSITUTE (EPRI) 2011 CONDENSER TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE AUGUST 3-4, 2011, CHICAGO, ILLINOIS IMPORTANCE OF TEMPERATURE OF BYPASS STEAM ADMITTED INTO A STEAM SURFACE CONDENSER IN A COMBINED
Analysis of Gas Turbine Heat Integration in Combined Cycle Power Plants. Milton Venetos, Wyatt Enterprises LLC, USA
 Analysis of Gas Turbine Heat Integration in Combined Cycle Power Plants Milton Venetos, Wyatt Enterprises LLC, USA (milt@wyattllc.com) Marco Dieleman M&N Power Solutions Ltd., Thailand (marco@mandnpower.com)
Analysis of Gas Turbine Heat Integration in Combined Cycle Power Plants Milton Venetos, Wyatt Enterprises LLC, USA (milt@wyattllc.com) Marco Dieleman M&N Power Solutions Ltd., Thailand (marco@mandnpower.com)
Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton Cycle
 The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Thermodynamics II MIDTERM MECH 351/2 Fall 06 CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 Thermodynamics II MIDTERM MEH 35/ Fall 06 ONORDIA UNIVERSITY FAULTY OF ENGINEERING AND OMPUTER SIENE DEPARTMENT OF MEHANIAL ENGINEERING Student s Name: I.D.: I. [50 points] A steam power plant operates
Thermodynamics II MIDTERM MEH 35/ Fall 06 ONORDIA UNIVERSITY FAULTY OF ENGINEERING AND OMPUTER SIENE DEPARTMENT OF MEHANIAL ENGINEERING Student s Name: I.D.: I. [50 points] A steam power plant operates
Streamlined RI-ISI. Patrick O Regan EPRI
 Streamlined RI-ISI Patrick O Regan EPRI poregan@epri.com Introduction Background Streamlined RI-ISI Methodology Results Discussion, Lessons Learned, Improvements Summary Background GOAL: Based upon the
Streamlined RI-ISI Patrick O Regan EPRI poregan@epri.com Introduction Background Streamlined RI-ISI Methodology Results Discussion, Lessons Learned, Improvements Summary Background GOAL: Based upon the
Primary Heat Transport (PHT) Motor Rotor Retaining Ring Failure
 1 Primary Heat Transport (PHT) Motor Rotor Retaining Ring Failure Ali Malik Components & Equipment Eng. Ontario Power Generation - Darlington Nuclear 2 Ontario Power Generation Darlington Darlington Nuclear
1 Primary Heat Transport (PHT) Motor Rotor Retaining Ring Failure Ali Malik Components & Equipment Eng. Ontario Power Generation - Darlington Nuclear 2 Ontario Power Generation Darlington Darlington Nuclear
A Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Schemes and Ground Grid Design
 A Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Schemes and Ground Grid Design Presented at the 2018 Transmission and Substation Design and Operation Symposium Revision presented at the
A Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Schemes and Ground Grid Design Presented at the 2018 Transmission and Substation Design and Operation Symposium Revision presented at the
STEALTH INTERNATIONAL INC. DESIGN REPORT #1001 IBC ENERGY DISSIPATING VALVE FLOW TESTING OF 12 VALVE
 STEALTH INTERNATIONAL INC. DESIGN REPORT #1001 IBC ENERGY DISSIPATING VALVE FLOW TESTING OF 12 VALVE 2 This report will discuss the results obtained from flow testing of a 12 IBC valve at Alden Research
STEALTH INTERNATIONAL INC. DESIGN REPORT #1001 IBC ENERGY DISSIPATING VALVE FLOW TESTING OF 12 VALVE 2 This report will discuss the results obtained from flow testing of a 12 IBC valve at Alden Research
Evaluation of a Gearbox s High-Temperature Trip
 42-46 tlt case study 2-04 1/13/04 4:09 PM Page 42 Case Study Evaluation of a Gearbox s High-Temperature Trip By Vinod Munshi, John Bietola, Ken Lavigne, Malcolm Towrie and George Staniewski (Member, STLE)
42-46 tlt case study 2-04 1/13/04 4:09 PM Page 42 Case Study Evaluation of a Gearbox s High-Temperature Trip By Vinod Munshi, John Bietola, Ken Lavigne, Malcolm Towrie and George Staniewski (Member, STLE)
AP1000 European 5. Reactor Coolant System and Connected Systems Design Control Document
 CHAPTER 5 REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM AND CONNECTED SYSTEMS 5.1 Summary Description This section describes the reactor coolant system (RCS) and includes a schematic flow diagram of the reactor coolant system
CHAPTER 5 REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM AND CONNECTED SYSTEMS 5.1 Summary Description This section describes the reactor coolant system (RCS) and includes a schematic flow diagram of the reactor coolant system
Appendix G Examples and Recommended Methods
 Reporting Outages to the Generating Availability Data System (GADS) Introduction The examples in this appendix illustrate the reporting of outages and deratings to GADS. They are based on a fictional 600
Reporting Outages to the Generating Availability Data System (GADS) Introduction The examples in this appendix illustrate the reporting of outages and deratings to GADS. They are based on a fictional 600
MHI Integrally Geared Type Compressor for Large Capacity Application and Process Gas Application
 MHI Integrally Geared Type for Large Capacity Application and Process Gas Application NAOTO YONEMURA* 1 YUJI FUTAGAMI* 1 SEIICHI IBARAKI* 2 This paper introduces an outline of the structures, features,
MHI Integrally Geared Type for Large Capacity Application and Process Gas Application NAOTO YONEMURA* 1 YUJI FUTAGAMI* 1 SEIICHI IBARAKI* 2 This paper introduces an outline of the structures, features,
Synthesis of Optimal Batch Distillation Sequences
 Presented at the World Batch Forum North American Conference Woodcliff Lake, NJ April 7-10, 2002 107 S. Southgate Drive Chandler, Arizona 85226-3222 480-893-8803 Fax 480-893-7775 E-mail: info@wbf.org www.wbf.org
Presented at the World Batch Forum North American Conference Woodcliff Lake, NJ April 7-10, 2002 107 S. Southgate Drive Chandler, Arizona 85226-3222 480-893-8803 Fax 480-893-7775 E-mail: info@wbf.org www.wbf.org
WET COMPRESSION. What it Is Not. What it Is. Is not traditional inlet air cooling, like a fogger or a chiller
 IGTI 2011 June 8 th, 2011 What it Is 8 to 25% (~12% 7EA) Power Augmentation at any wet bulb temperature above 45 F Complimentary Technology -used in series w/ inlet cooling & other GT upgrades Technology
IGTI 2011 June 8 th, 2011 What it Is 8 to 25% (~12% 7EA) Power Augmentation at any wet bulb temperature above 45 F Complimentary Technology -used in series w/ inlet cooling & other GT upgrades Technology
PVP Field Calibration and Accuracy of Torque Wrenches. Proceedings of ASME PVP ASME Pressure Vessel and Piping Conference PVP2011-
 Proceedings of ASME PVP2011 2011 ASME Pressure Vessel and Piping Conference Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pressure Vessels July 17-21, & Piping 2011, Division Baltimore, Conference Maryland PVP2011 July
Proceedings of ASME PVP2011 2011 ASME Pressure Vessel and Piping Conference Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pressure Vessels July 17-21, & Piping 2011, Division Baltimore, Conference Maryland PVP2011 July
Technologies & Economics
 Panos Konstantin Power and Energy Systems Technologies & Economics Case Study Cycle Simulation CCT Notes: 1. Cells with black characters include inputs 2. Cells with red characters include formulas 3.
Panos Konstantin Power and Energy Systems Technologies & Economics Case Study Cycle Simulation CCT Notes: 1. Cells with black characters include inputs 2. Cells with red characters include formulas 3.
Substation Equipment (Bushings)
 Substation Equipment (Bushings) Mark B. Goff, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority ABSTRACT Bushings provide a point of interface such that electrical current can pass to and from an electrical apparatus. Much
Substation Equipment (Bushings) Mark B. Goff, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority ABSTRACT Bushings provide a point of interface such that electrical current can pass to and from an electrical apparatus. Much
Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Systems
 Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Systems Presented at the 71st Annual Conference for Protective Engineers Brian Ehsani, Black & Veatch Jason Hulme, Black & Veatch Abstract
Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Systems Presented at the 71st Annual Conference for Protective Engineers Brian Ehsani, Black & Veatch Jason Hulme, Black & Veatch Abstract
GENERATOR SEAL OIL SYSTEM
 GENERATOR SEAL OIL SYSTEM Eskom power utility utilized Flownex SE simulation capabilities to mitigate system shutdowns caused by generator hydrogen (H 2 ) seal ring failures. Engineers modelled the hydrogen
GENERATOR SEAL OIL SYSTEM Eskom power utility utilized Flownex SE simulation capabilities to mitigate system shutdowns caused by generator hydrogen (H 2 ) seal ring failures. Engineers modelled the hydrogen
Is Throttle Pressure Control a Self- Regulating or an Integrating Process?
 Output Is Control a Self- Regulating or an Integrating Process? By Jacques F. Smuts, Ph.D., P.E. Self-regulating and integrating processes respond differently and require the use of different tuning methods.
Output Is Control a Self- Regulating or an Integrating Process? By Jacques F. Smuts, Ph.D., P.E. Self-regulating and integrating processes respond differently and require the use of different tuning methods.
VISBREAKER MONITORING FOR MAXIMUM CONVERSION
 Petrocontrol Advanced Control & Optimization VISBREAKER MONITORING FOR MAXIMUM CONVERSION Z. Friedman, Petrocontrol W. A. Kuijl, RUHR-OL K. Wolfsgruber, Maraven S.A. Paper presented at the PDVSA Deep Conversion
Petrocontrol Advanced Control & Optimization VISBREAKER MONITORING FOR MAXIMUM CONVERSION Z. Friedman, Petrocontrol W. A. Kuijl, RUHR-OL K. Wolfsgruber, Maraven S.A. Paper presented at the PDVSA Deep Conversion
Forsmark 12. S3K Applications. Thomas Smed US User Group Meeting Arizona, October 2008
 Forsmark 12 S3K Applications Thomas Smed US User Group Meeting Arizona, October 2008 Introduction It is well-known that we have vast experience in providing S3R (and RAMONA) to training simulators It may
Forsmark 12 S3K Applications Thomas Smed US User Group Meeting Arizona, October 2008 Introduction It is well-known that we have vast experience in providing S3R (and RAMONA) to training simulators It may
MISHIMOTO ENGINEERING REPORT
 RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT MISHIMOTO ENGINEERING REPORT Testing the Mishimoto BMW E46 M3 Performance Aluminum Radiator Figure 1: Test vehicle: Notice the additional heat exchangers in front of radiator. Test
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT MISHIMOTO ENGINEERING REPORT Testing the Mishimoto BMW E46 M3 Performance Aluminum Radiator Figure 1: Test vehicle: Notice the additional heat exchangers in front of radiator. Test
Hybrid Electric Vehicle End-of-Life Testing On Honda Insights, Honda Gen I Civics and Toyota Gen I Priuses
 INL/EXT-06-01262 U.S. Department of Energy FreedomCAR & Vehicle Technologies Program Hybrid Electric Vehicle End-of-Life Testing On Honda Insights, Honda Gen I Civics and Toyota Gen I Priuses TECHNICAL
INL/EXT-06-01262 U.S. Department of Energy FreedomCAR & Vehicle Technologies Program Hybrid Electric Vehicle End-of-Life Testing On Honda Insights, Honda Gen I Civics and Toyota Gen I Priuses TECHNICAL
USO4CICV01/US04CICH02:
 Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure & Applied Sciences S. Y. B.Sc. Semester-4 Industrial chemistry/ IC (Vocational) USO4CICV0/US04CICH02: Chemical Plant Utilities UNIT 5 Internal combustion engine In an
Investigate Your Options
 Page 1 of 5 Investigate Your Options Kim Covington and Gavin McIntyre, Bryan Research & Engineering, Inc., Bryan, Texas ABSTRACT This paper will investigate how computer aided simulation tools may be used
Page 1 of 5 Investigate Your Options Kim Covington and Gavin McIntyre, Bryan Research & Engineering, Inc., Bryan, Texas ABSTRACT This paper will investigate how computer aided simulation tools may be used
Atmospheric Crude Tower with Aspen HYSYS V8.0
 Atmospheric Crude Tower with Aspen HYSYS V8.0 1. Lesson Objectives Assign petroleum assay to stream Configure column pre-heater Configure crude tower 2. Prerequisites Aspen HYSYS V8.0 Introduction to distillation
Atmospheric Crude Tower with Aspen HYSYS V8.0 1. Lesson Objectives Assign petroleum assay to stream Configure column pre-heater Configure crude tower 2. Prerequisites Aspen HYSYS V8.0 Introduction to distillation
National Board Update
 National Board Update Presentation to the Valve Repair Council June 2, 2016 Prepared by: Joseph F. Ball, P.E. National Board Update National Board activities Who we are and what we do National Board Inspection
National Board Update Presentation to the Valve Repair Council June 2, 2016 Prepared by: Joseph F. Ball, P.E. National Board Update National Board activities Who we are and what we do National Board Inspection
Enhancement of Transient Stability Using Fault Current Limiter and Thyristor Controlled Braking Resistor
 > 57 < 1 Enhancement of Transient Stability Using Fault Current Limiter and Thyristor Controlled Braking Resistor Masaki Yagami, Non Member, IEEE, Junji Tamura, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract This paper
> 57 < 1 Enhancement of Transient Stability Using Fault Current Limiter and Thyristor Controlled Braking Resistor Masaki Yagami, Non Member, IEEE, Junji Tamura, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract This paper
Proposed Solution to Mitigate Concerns Regarding AC Power Flow under Convergence Bidding. September 25, 2009
 Proposed Solution to Mitigate Concerns Regarding AC Power Flow under Convergence Bidding September 25, 2009 Proposed Solution to Mitigate Concerns Regarding AC Power Flow under Convergence Bidding Background
Proposed Solution to Mitigate Concerns Regarding AC Power Flow under Convergence Bidding September 25, 2009 Proposed Solution to Mitigate Concerns Regarding AC Power Flow under Convergence Bidding Background
Here s the smokin sendoff
 Smokin Barracuda Barracuda in Action Schumacher B/RB Headers are designed for excellent street performance. But recently we ran some track tests, using Steve Charette s (of Imperial Services) 68 Barracuda,
Smokin Barracuda Barracuda in Action Schumacher B/RB Headers are designed for excellent street performance. But recently we ran some track tests, using Steve Charette s (of Imperial Services) 68 Barracuda,
Effect Of Main Steam Temperature At Inlet On Turbine Shaft Vibration
 ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect Of Main Steam Temperature At Inlet On Turbine Shaft Vibration Rajeev Rajora Department of Mechanical Engineering UCE, Rajasthan Technical University, Kota, Rajasthan, India
ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect Of Main Steam Temperature At Inlet On Turbine Shaft Vibration Rajeev Rajora Department of Mechanical Engineering UCE, Rajasthan Technical University, Kota, Rajasthan, India
The Establishment and Application of TRACE/FRAPTRAN Model for Kuosheng Nuclear Power Plant
 The Establishment and Application of /FRAPTRAN Model for Kuosheng Nuclear Power Plant S. W. Chen, W. K. Lin, J. R. Wang, C. Shih, H. T. Lin, H. C. Chang, W. Y. Li Abstract Kuosheng nuclear power plant
The Establishment and Application of /FRAPTRAN Model for Kuosheng Nuclear Power Plant S. W. Chen, W. K. Lin, J. R. Wang, C. Shih, H. T. Lin, H. C. Chang, W. Y. Li Abstract Kuosheng nuclear power plant
BLAST CAPACITY ASSESSMENT AND TESTING A-60 OFFSHORE FIRE DOOR
 BLAST CAPACITY ASSESSMENT AND TESTING Final Report December 11, 2008 A-60 OFFSHORE FIRE DOOR Prepared for: JRJ Alum Fab, Inc. Prepared by: Travis J. Holland Michael J. Lowak John R. Montoya BakerRisk Project
BLAST CAPACITY ASSESSMENT AND TESTING Final Report December 11, 2008 A-60 OFFSHORE FIRE DOOR Prepared for: JRJ Alum Fab, Inc. Prepared by: Travis J. Holland Michael J. Lowak John R. Montoya BakerRisk Project
Mohammad Faisal Haider. Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology
 Mohammad Faisal Haider Lecturer Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Steam Turbine 2 Vapor Power Cycle 4 5 Steam Turbine A steam turbine is prime mover
Mohammad Faisal Haider Lecturer Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Steam Turbine 2 Vapor Power Cycle 4 5 Steam Turbine A steam turbine is prime mover
The Practical Uses of Computational Fluid Dynamics Not Just a Pretty Picture
 The Practical Uses of Computational Fluid Dynamics Not Just a Pretty Picture Presenter: William Osley Company: CALGAVIN Ltd Email: william.osley@calgavin.com Page 1 Contents: Introduction Case Study 1:
The Practical Uses of Computational Fluid Dynamics Not Just a Pretty Picture Presenter: William Osley Company: CALGAVIN Ltd Email: william.osley@calgavin.com Page 1 Contents: Introduction Case Study 1:
Feedwater Reg Valve Internal Erosion OR17 Fall 2015
 Seabrook Station Feedwater Reg Valve Internal Erosion OR17 Fall 2015 Jim Johnson Feedwater System Engineer 2 Seabrook FRV Setup Seabrook Station FRV History Started Commercial Operation in 1990 Feedwater
Seabrook Station Feedwater Reg Valve Internal Erosion OR17 Fall 2015 Jim Johnson Feedwater System Engineer 2 Seabrook FRV Setup Seabrook Station FRV History Started Commercial Operation in 1990 Feedwater
Transient Analysis for Simulator Validation. Jeffrey A. Borkowski 2008 US Users Group Meeting Tempe, Arizona October
 Transient Analysis for Simulator Validation Jeffrey A. Borkowski 2008 US Users Group Meeting Tempe, Arizona October 22-24 2008 Advanced Training Simulator Models Engineering-grade model core model S3R
Transient Analysis for Simulator Validation Jeffrey A. Borkowski 2008 US Users Group Meeting Tempe, Arizona October 22-24 2008 Advanced Training Simulator Models Engineering-grade model core model S3R
Analysis and Correlation for Body Attachment Stiffness in BIW
 Analysis and Correlation for Body Attachment Stiffness in BIW Jiwoo Yoo, J.K.Suh, S.H.Lim, J.U.Lee, M.K.Seo Hyundai Motor Company, S. Korea ABSTRACT It is known that automotive body structure must have
Analysis and Correlation for Body Attachment Stiffness in BIW Jiwoo Yoo, J.K.Suh, S.H.Lim, J.U.Lee, M.K.Seo Hyundai Motor Company, S. Korea ABSTRACT It is known that automotive body structure must have
Components of Hydronic Systems
 Valve and Actuator Manual 977 Hydronic System Basics Section Engineering Bulletin H111 Issue Date 0789 Components of Hydronic Systems The performance of a hydronic system depends upon many factors. Because
Valve and Actuator Manual 977 Hydronic System Basics Section Engineering Bulletin H111 Issue Date 0789 Components of Hydronic Systems The performance of a hydronic system depends upon many factors. Because
Complicated Minimal Piping Authors: Presenters: Shelley
 Pipeline Station Pulsati ion Case Study: Minimal Piping Change Creates Complicated Problems Authors: Noah Dixon, Sr. Technical Specialist, Williams Gas Pipeline Carol Palynchuk, Design Project Manager,
Pipeline Station Pulsati ion Case Study: Minimal Piping Change Creates Complicated Problems Authors: Noah Dixon, Sr. Technical Specialist, Williams Gas Pipeline Carol Palynchuk, Design Project Manager,
ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL USER MANUAL
 DRAG-SPORTSMAN N2O For ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL USER MANUAL TELEPHONE 828.645.1505 FAX 828.645.1525 WWW.MORETRACTION.COM US PATENT 6,577,944 Disclaimer...2 Introduction... 3 How Does It Work. 4 Installation...
DRAG-SPORTSMAN N2O For ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL USER MANUAL TELEPHONE 828.645.1505 FAX 828.645.1525 WWW.MORETRACTION.COM US PATENT 6,577,944 Disclaimer...2 Introduction... 3 How Does It Work. 4 Installation...
By: Eugenijus Uspuras Algirdas Kaliatka Sigitas Rimkevicius ASME 2012 Verification & Validation Symposium May 2-4, 2012, Las Vegas, NV
 Computer codes validation for transient analysis at nuclear power plants with RBMK-1500 reactor By: Eugenijus Uspuras Algirdas Kaliatka Sigitas Rimkevicius ASME 2012 Verification & Validation Symposium
Computer codes validation for transient analysis at nuclear power plants with RBMK-1500 reactor By: Eugenijus Uspuras Algirdas Kaliatka Sigitas Rimkevicius ASME 2012 Verification & Validation Symposium
AP Plant Operational Transient Analysis
 www.ijnese.org International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering Volume 3 Issue 2, June 2013 AP1000 1 Plant Operational Transient Analysis LIU Lixin 1, ZHENG Limin 2 Shanghai Nuclear Engineering
www.ijnese.org International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering Volume 3 Issue 2, June 2013 AP1000 1 Plant Operational Transient Analysis LIU Lixin 1, ZHENG Limin 2 Shanghai Nuclear Engineering
HIGH VOLTAGE vs. LOW VOLTAGE: POTENTIAL IN MILITARY SYSTEMS
 2013 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM POWER AND MOBILITY (P&M) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 21-22, 2013 TROY, MICHIGAN HIGH VOLTAGE vs. LOW VOLTAGE: POTENTIAL IN MILITARY SYSTEMS
2013 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM POWER AND MOBILITY (P&M) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 21-22, 2013 TROY, MICHIGAN HIGH VOLTAGE vs. LOW VOLTAGE: POTENTIAL IN MILITARY SYSTEMS
The Enhanced Platform
 Power Generation The Enhanced Platform The Next Generation of Industrial Steam Turbines www.siemens.com / energy / steamturbines Advanced Steam Turbine Design Figure 1: Enhanced Platform Design The Enhanced
Power Generation The Enhanced Platform The Next Generation of Industrial Steam Turbines www.siemens.com / energy / steamturbines Advanced Steam Turbine Design Figure 1: Enhanced Platform Design The Enhanced
IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RCP SHIELD MECHANICAL SEAL MODEL IN THE COMANCHE PEAK PRA
 IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RCP SHIELD MECHANICAL SEAL MODEL IN THE COMANCHE PEAK PRA Nathan Larson Principal Engineer Daniel Tirsun Fellow Engineer Aaron Moreno Senior Engineer Glen Rose, TX SHIELD is a trademark
IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RCP SHIELD MECHANICAL SEAL MODEL IN THE COMANCHE PEAK PRA Nathan Larson Principal Engineer Daniel Tirsun Fellow Engineer Aaron Moreno Senior Engineer Glen Rose, TX SHIELD is a trademark
EE 456 Design Project
 F-2014 EE 456 Design Project PROJECT REPORT MALUWELMENG, CONNIE SHARP, MEGAN Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Assignment I... 2 Setup... 2 Simulation... 2 Assignment II... 3 Problems... 3 Solution...
F-2014 EE 456 Design Project PROJECT REPORT MALUWELMENG, CONNIE SHARP, MEGAN Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Assignment I... 2 Setup... 2 Simulation... 2 Assignment II... 3 Problems... 3 Solution...
R35 GTR VR38 ALPHA DAMPER
 R35 GTR VR38 ALPHA DAMPER a single piece damper moving the overhung weight of the rubber absorber behind and inside the OEM sized belt ribs. The Fluidampr design is approximately 9.75lbs., The OEM part
R35 GTR VR38 ALPHA DAMPER a single piece damper moving the overhung weight of the rubber absorber behind and inside the OEM sized belt ribs. The Fluidampr design is approximately 9.75lbs., The OEM part
Unitil Energy Demand Response Demonstration Project Proposal October 12, 2016
 Unitil Energy Demand Response Demonstration Project Proposal October 12, 2016 Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company d/b/a Unitil ( Unitil or the Company ) indicated in the 2016-2018 Energy Efficiency
Unitil Energy Demand Response Demonstration Project Proposal October 12, 2016 Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company d/b/a Unitil ( Unitil or the Company ) indicated in the 2016-2018 Energy Efficiency
Design and Fabrication of Shell and Tube Type Heat Exchanger and Performance Analysis
 Design and Fabrication of Shell and Tube Type Heat Exchanger and Performance Analysis Tanveer Raza 1, Marooph Patel 2. 1 Student, Mechanical Engineering Department, SKN, tanveer.raza23@gmail.com 2 Student,
Design and Fabrication of Shell and Tube Type Heat Exchanger and Performance Analysis Tanveer Raza 1, Marooph Patel 2. 1 Student, Mechanical Engineering Department, SKN, tanveer.raza23@gmail.com 2 Student,
Supervised Learning to Predict Human Driver Merging Behavior
 Supervised Learning to Predict Human Driver Merging Behavior Derek Phillips, Alexander Lin {djp42, alin719}@stanford.edu June 7, 2016 Abstract This paper uses the supervised learning techniques of linear
Supervised Learning to Predict Human Driver Merging Behavior Derek Phillips, Alexander Lin {djp42, alin719}@stanford.edu June 7, 2016 Abstract This paper uses the supervised learning techniques of linear
Sohn Suk-Whun
 Application of the Performance Validation Tool for the Evaluation of NSSS Control System Performance Sohn Suk-Whun 29. 1. 29 1 Pre-Op Dynamic Test 2 Test Results 3 Pre-PAT Dynamic Test 4 Conclusion 2 29
Application of the Performance Validation Tool for the Evaluation of NSSS Control System Performance Sohn Suk-Whun 29. 1. 29 1 Pre-Op Dynamic Test 2 Test Results 3 Pre-PAT Dynamic Test 4 Conclusion 2 29
When should an Electric Adjustable Speed Drive be used instead of a Gas or Steam Turbine? Paul Blaiklock, Manish Verma, Stephan Bondy
 When should an Electric Adjustable Speed Drive be used instead of a Gas or Steam Turbine? Paul Blaiklock, Manish Verma, Stephan Bondy TMEIC Corporation Roanoke, VA, and Houston, TX 2/8/2013 When should
When should an Electric Adjustable Speed Drive be used instead of a Gas or Steam Turbine? Paul Blaiklock, Manish Verma, Stephan Bondy TMEIC Corporation Roanoke, VA, and Houston, TX 2/8/2013 When should
Product Loss During Retail Motor Fuel Dispenser Inspection
 Product Loss During Retail Motor Fuel Dispenser Inspection By: Christian Lachance, P. Eng. Senior Engineer - ment Engineering and Laboratory Services ment Canada Date: Product Loss During Retail Motor
Product Loss During Retail Motor Fuel Dispenser Inspection By: Christian Lachance, P. Eng. Senior Engineer - ment Engineering and Laboratory Services ment Canada Date: Product Loss During Retail Motor
Comparison of Bruce A, Bruce Band Darlington
 CompariSOIl ofbmce and Darling/oil A-I Appendix 1 Comparison of Bruce A, Bruce Band Darlington 1.1 Introduction An over'iiew of the differences between Bruce A, Bruce B and Darlington A has been made,
CompariSOIl ofbmce and Darling/oil A-I Appendix 1 Comparison of Bruce A, Bruce Band Darlington 1.1 Introduction An over'iiew of the differences between Bruce A, Bruce B and Darlington A has been made,
CONTROLS UPGRADE CASE STUDY FOR A COAL-FIRED BOILER
 CONTROLS UPGRADE CASE STUDY FOR A COAL-FIRED BOILER ABSTRACT This paper discusses the measures taken to upgrade controls for a coal-fired boiler which was experiencing problems with primary air flow, furnace
CONTROLS UPGRADE CASE STUDY FOR A COAL-FIRED BOILER ABSTRACT This paper discusses the measures taken to upgrade controls for a coal-fired boiler which was experiencing problems with primary air flow, furnace
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report R0. By Kimbal A.
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report 412509-1R0 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY May 2012 ALDEN RESEARCH
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report 412509-1R0 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY May 2012 ALDEN RESEARCH
Design and Fabrication of Simple Turbo Alternator
 Design and Fabrication of Simple Turbo Alternator S.Arunkumar, A.Sridhar, S.Praveen vaitheeswaran, S.Sasikumar, Sefin Jose Department of mechanical engineering, Nandha College of technology, Erode. Abstract
Design and Fabrication of Simple Turbo Alternator S.Arunkumar, A.Sridhar, S.Praveen vaitheeswaran, S.Sasikumar, Sefin Jose Department of mechanical engineering, Nandha College of technology, Erode. Abstract
How to Design an Electric Motor Regreasing Program
 How to Design an Electric Motor Regreasing Program Jerry S. Honeycutt, Tennessee Valley Authority and Wayne Johnson, Electric Power Research Institute Rolling element bearings used in electric motors have
How to Design an Electric Motor Regreasing Program Jerry S. Honeycutt, Tennessee Valley Authority and Wayne Johnson, Electric Power Research Institute Rolling element bearings used in electric motors have
SAM-e. Engineering Manual
 Your guide to selecting and specifying Nortec SAM-e Short Absorption Manifolds! SAM-e Engineering Manual Includes technical specifications, guidelines, and options for selection and application of SAM-e
Your guide to selecting and specifying Nortec SAM-e Short Absorption Manifolds! SAM-e Engineering Manual Includes technical specifications, guidelines, and options for selection and application of SAM-e
REMOTE SENSING DEVICE HIGH EMITTER IDENTIFICATION WITH CONFIRMATORY ROADSIDE INSPECTION
 Final Report 2001-06 August 30, 2001 REMOTE SENSING DEVICE HIGH EMITTER IDENTIFICATION WITH CONFIRMATORY ROADSIDE INSPECTION Bureau of Automotive Repair Engineering and Research Branch INTRODUCTION Several
Final Report 2001-06 August 30, 2001 REMOTE SENSING DEVICE HIGH EMITTER IDENTIFICATION WITH CONFIRMATORY ROADSIDE INSPECTION Bureau of Automotive Repair Engineering and Research Branch INTRODUCTION Several
Technical & Commercial Evaluation Of Steam Tracing System V/s SECT Skin Effect Heating System Electric Heat Tracing System
 Technical & Commercial Evaluation Of Steam Tracing System V/s SECT Skin Effect Heating System Electric Heat Tracing System For SUITED COSTAL / EXPORT REFINERY PROJECTS 5-Km 450 NB (18 Dia.) Long Pipe Line
Technical & Commercial Evaluation Of Steam Tracing System V/s SECT Skin Effect Heating System Electric Heat Tracing System For SUITED COSTAL / EXPORT REFINERY PROJECTS 5-Km 450 NB (18 Dia.) Long Pipe Line
Paper No: 05-IAGT-1.1 INDUSTRIAL APPLICATION OF GAS TURBINES COMMITTEE
 Paper No: 05-IAGT-1.1 INDUSTRIAL APPLICATION OF GAS TURBINES COMMITTEE Mercury 50 Field Evaluation and Product Introduction by David Teraji of Solar Turbines Incorporated San Diego, California, USA 1 AUTHORS
Paper No: 05-IAGT-1.1 INDUSTRIAL APPLICATION OF GAS TURBINES COMMITTEE Mercury 50 Field Evaluation and Product Introduction by David Teraji of Solar Turbines Incorporated San Diego, California, USA 1 AUTHORS
ECE 480 Design Team 3: Designing Low Voltage, Low Current Battery Chargers
 Michigan State University Electrical Engineering Department ECE 480 Design Team 3: Designing Low Voltage, Low Current Battery Chargers Application Note Created by: James McCormick 11/8/2015 Abstract: The
Michigan State University Electrical Engineering Department ECE 480 Design Team 3: Designing Low Voltage, Low Current Battery Chargers Application Note Created by: James McCormick 11/8/2015 Abstract: The
Increasing competitiveness of CCGT plants in a dynamic market: An owner s approach
 Increasing competitiveness of CCGT plants in a dynamic market: An owner s approach Dr. Artur Ulbrich, Andy Jones, Christian Schäferkordt, Stuart Simpson 8th International Gas Turbine Conference, Brussels
Increasing competitiveness of CCGT plants in a dynamic market: An owner s approach Dr. Artur Ulbrich, Andy Jones, Christian Schäferkordt, Stuart Simpson 8th International Gas Turbine Conference, Brussels
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP: Parallel and Series Operation 11/11/02
 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP: Parallel and Series Operation 11/11/02 1 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP Location Sub-basement SB-92. (Manual is available) Introduction This experiment illustrates the basic operation and characteristics
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP: Parallel and Series Operation 11/11/02 1 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP Location Sub-basement SB-92. (Manual is available) Introduction This experiment illustrates the basic operation and characteristics
Operation Results of a Closed Supercritical CO2 Simple Brayton Cycle
 Operation Results of a Closed Supercritical CO2 Simple Brayton Cycle JaeEun Cha*, Seong Won Bae*, Jekyoung Lee**, Song Kuk Cho**, JeongIk Lee**, Joo Hyun Park*** * Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute
Operation Results of a Closed Supercritical CO2 Simple Brayton Cycle JaeEun Cha*, Seong Won Bae*, Jekyoung Lee**, Song Kuk Cho**, JeongIk Lee**, Joo Hyun Park*** * Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute
APPENDIX C ROADWAY BEFORE-AND-AFTER STUDY
 APPENDIX C ROADWAY BEFORE-AND-AFTER STUDY The benefits to pedestrians and bus patrons are numerous when a bus bay is replaced with a bus bulb. Buses should operate more efficiently at the stop when not
APPENDIX C ROADWAY BEFORE-AND-AFTER STUDY The benefits to pedestrians and bus patrons are numerous when a bus bay is replaced with a bus bulb. Buses should operate more efficiently at the stop when not
Table of Contents Introduction 3 Chapter 2: Operation 4 Chapter 3: Components 5 Chapter 4: Specifications 8
 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Application 3 Chapter 2: Operation 4 Manifold Function 4 Chapter 3: Components 5 Required Parts 5 Manifold without Actuators without Pressure Bypass Kit 5 Pump Kit (QHMPK_)
Table of Contents Introduction 3 Application 3 Chapter 2: Operation 4 Manifold Function 4 Chapter 3: Components 5 Required Parts 5 Manifold without Actuators without Pressure Bypass Kit 5 Pump Kit (QHMPK_)
Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234
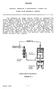 Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234 STEAM VALVE HYDRAULIC CONTROL The movement of large control valves to regulate the steam supply to modern steam turbines, requires amplification of the control
Turbine, Generator & Auxiliaries - Course 234 STEAM VALVE HYDRAULIC CONTROL The movement of large control valves to regulate the steam supply to modern steam turbines, requires amplification of the control
B. HOLMQVIST Nuclear Fuel Division, ABB Atom AB, Vasteras, Sweden
 I Iflllll IPIBM1I IHtl!!!! Blini Vllll! «! all REDUCTION OF COST OF POOR QUALITY IN NUCLEAR FUEL MANUFACTURING XA0055764 B. HOLMQVIST Nuclear Fuel Division, ABB Atom AB, Vasteras, Sweden Abstract Within
I Iflllll IPIBM1I IHtl!!!! Blini Vllll! «! all REDUCTION OF COST OF POOR QUALITY IN NUCLEAR FUEL MANUFACTURING XA0055764 B. HOLMQVIST Nuclear Fuel Division, ABB Atom AB, Vasteras, Sweden Abstract Within
Electromagnetic Fully Flexible Valve Actuator
 Electromagnetic Fully Flexible Valve Actuator A traditional cam drive train, shown in Figure 1, acts on the valve stems to open and close the valves. As the crankshaft drives the camshaft through gears
Electromagnetic Fully Flexible Valve Actuator A traditional cam drive train, shown in Figure 1, acts on the valve stems to open and close the valves. As the crankshaft drives the camshaft through gears
Steam Turbine 34.5-Inch Low-Pressure Section Upgrade
 GE Energy Steam Turbine 34.5-Inch Low-Pressure Section Upgrade Kim Kavney Joe Lesiuk Jim Wright GE Energy Atlanta, GA Contents Introduction...1 Fleet Demographics...1 Reasons for Low-Pressure Section
GE Energy Steam Turbine 34.5-Inch Low-Pressure Section Upgrade Kim Kavney Joe Lesiuk Jim Wright GE Energy Atlanta, GA Contents Introduction...1 Fleet Demographics...1 Reasons for Low-Pressure Section
Substation inspection guidelines Mark B. Goff, P.E.
 Substation inspection guidelines Mark B. Goff, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority, Chattanooga, Tennessee ABSTRACT We need to better understand what our infrared camera is really showing us. Without guidelines,
Substation inspection guidelines Mark B. Goff, P.E. Tennessee Valley Authority, Chattanooga, Tennessee ABSTRACT We need to better understand what our infrared camera is really showing us. Without guidelines,
OPTIMAL BATCH DISTILLATION SEQUENCES USING ASPEN PLUS
 OPTIMAL BATCH DISTILLATION SEQUENCES USING ASPEN PLUS Bradley H. Cook, Matthew J. Engel, and Anthony J. Zehnder Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. 7201 Hamilton Blvd. Allentown, PA 18195-1501 Craig S. Landis
OPTIMAL BATCH DISTILLATION SEQUENCES USING ASPEN PLUS Bradley H. Cook, Matthew J. Engel, and Anthony J. Zehnder Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. 7201 Hamilton Blvd. Allentown, PA 18195-1501 Craig S. Landis
Design and Performance Study of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger with Single Segmental Baffle Having Perpendicular & Parallel-Cut Orientation.
 Design and Performance Study of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger with Single Segmental Baffle Having Perpendicular & Parallel-Cut Orientation. Swarup S Deshpande Mechanical Engineering Intern Excel Plants
Design and Performance Study of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger with Single Segmental Baffle Having Perpendicular & Parallel-Cut Orientation. Swarup S Deshpande Mechanical Engineering Intern Excel Plants
EXAMINATION OF NOZZLE INNER RADIUS AND PIPING FROM THE OUTER SURFACE
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18560 ABSTRACT NEW DEVELOPMENTS FOR AUTOMATED NOZZLE INNER RADIUS AND PIPING INSPECTIONS D. Eargle,WesDyne International, USA WesDyne has recently engaged
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18560 ABSTRACT NEW DEVELOPMENTS FOR AUTOMATED NOZZLE INNER RADIUS AND PIPING INSPECTIONS D. Eargle,WesDyne International, USA WesDyne has recently engaged
SpiritPFC Torque/Horsepower Comparison Dynamometer Test Date: 5/7/2006
 SpiritPFC / Comparison Dynamometer Test Date: 5/7/2006 Dynamometer Test Outline: Contained within this document you will find data collected using a Dyno Datamite engine dynamometer hardware and software
SpiritPFC / Comparison Dynamometer Test Date: 5/7/2006 Dynamometer Test Outline: Contained within this document you will find data collected using a Dyno Datamite engine dynamometer hardware and software
Presented at the 2012 Aerospace Space Power Workshop Manhattan Beach, CA April 16-20, 2012
 Complex Modeling of LiIon Cells in Series and Batteries in Parallel within Satellite EPS Time Dependent Simulations Presented at the 2012 Aerospace Space Power Workshop Manhattan Beach, CA April 16-20,
Complex Modeling of LiIon Cells in Series and Batteries in Parallel within Satellite EPS Time Dependent Simulations Presented at the 2012 Aerospace Space Power Workshop Manhattan Beach, CA April 16-20,
Investigation of Radiators Size, Orientation of Sub Cooled Section and Fan Position on Twin Fan Cooling Packby 1D Simulation
 Investigation of Radiators Size, Orientation of Sub Cooled Section and Fan Position on Twin Fan Cooling Packby 1D Simulation Neelakandan K¹, Goutham Sagar M², Ajay Virmalwar³ Abstract: A study plan to
Investigation of Radiators Size, Orientation of Sub Cooled Section and Fan Position on Twin Fan Cooling Packby 1D Simulation Neelakandan K¹, Goutham Sagar M², Ajay Virmalwar³ Abstract: A study plan to
Sport Shieldz Skull Cap Evaluation EBB 4/22/2016
 Summary A single sample of the Sport Shieldz Skull Cap was tested to determine what additional protective benefit might result from wearing it under a current motorcycle helmet. A series of impacts were
Summary A single sample of the Sport Shieldz Skull Cap was tested to determine what additional protective benefit might result from wearing it under a current motorcycle helmet. A series of impacts were
Advantages of a Magnetically Driven Gear Pump By Steven E. Owen, P.E.
 Advantages of a Magnetically Driven Gear Pump By Steven E. Owen, P.E. Introduction Before considering a magnetically driven pump for use in a fluid system, it is best to know something about the technology
Advantages of a Magnetically Driven Gear Pump By Steven E. Owen, P.E. Introduction Before considering a magnetically driven pump for use in a fluid system, it is best to know something about the technology
Supplemental Report on the NCTPC Collaborative Transmission Plan
 Supplemental Report on the NCTPC 2007-2017 Collaborative Transmission Plan May 16, 2008 1 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary...1 II. Richmond-Fort Bragg Woodruff Street 230 kv Line...2 II.A. Need for
Supplemental Report on the NCTPC 2007-2017 Collaborative Transmission Plan May 16, 2008 1 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary...1 II. Richmond-Fort Bragg Woodruff Street 230 kv Line...2 II.A. Need for
Asia Pacific Research Initiative for Sustainable Energy Systems 2011 (APRISES11)
 Asia Pacific Research Initiative for Sustainable Energy Systems 2011 (APRISES11) Office of Naval Research Grant Award Number N0014-12-1-0496 Hydrogen Energy System Simulation Model for Grid Management
Asia Pacific Research Initiative for Sustainable Energy Systems 2011 (APRISES11) Office of Naval Research Grant Award Number N0014-12-1-0496 Hydrogen Energy System Simulation Model for Grid Management
Less Emissions Through Waste Heat Recovery
 Summary Less Emissions Through Waste Heat Recovery Heinrich Schmid Manager, Application Technology, Ship Power Wärtsilä Switzerland Ltd, Winterthur Current interest in reducing emissions and reducing engine
Summary Less Emissions Through Waste Heat Recovery Heinrich Schmid Manager, Application Technology, Ship Power Wärtsilä Switzerland Ltd, Winterthur Current interest in reducing emissions and reducing engine
Weir Valves & Controls USA Inc. World Leader in Design, Manufacture and Service Support for BWR and PWR MSIV s
 Atwood & Morrill Main Steam Isolation Valves Weir Valves & Controls USA Inc. 1 World Leader in Design, Manufacture and Service Support for BWR and PWR MSIV s 2 Capabilities in Nuclear Power Generation
Atwood & Morrill Main Steam Isolation Valves Weir Valves & Controls USA Inc. 1 World Leader in Design, Manufacture and Service Support for BWR and PWR MSIV s 2 Capabilities in Nuclear Power Generation
STEAM TURBINE MODERNIZATION SOLUTIONS PROVIDE A WIDE SPECTRUM OF OPTIONS TO IMPROVE PERFORMANCE
 STEAM TURBINE MODERNIZATION SOLUTIONS PROVIDE A WIDE SPECTRUM OF OPTIONS TO IMPROVE PERFORMANCE Michael W. Smiarowski, Rainer Leo, Christof Scholten, Siemens Power Generation (PG), Germany John Blake,
STEAM TURBINE MODERNIZATION SOLUTIONS PROVIDE A WIDE SPECTRUM OF OPTIONS TO IMPROVE PERFORMANCE Michael W. Smiarowski, Rainer Leo, Christof Scholten, Siemens Power Generation (PG), Germany John Blake,
An Evaluation of Active Knee Bolsters
 8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (1) An Evaluation of Active Knee Bolsters Zane Z. Yang Delphi Corporation Abstract In the present paper, the impact between an active knee bolster
8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (1) An Evaluation of Active Knee Bolsters Zane Z. Yang Delphi Corporation Abstract In the present paper, the impact between an active knee bolster
Locomotive Allocation for Toll NZ
 Locomotive Allocation for Toll NZ Sanjay Patel Department of Engineering Science University of Auckland, New Zealand spat075@ec.auckland.ac.nz Abstract A Locomotive is defined as a self-propelled vehicle
Locomotive Allocation for Toll NZ Sanjay Patel Department of Engineering Science University of Auckland, New Zealand spat075@ec.auckland.ac.nz Abstract A Locomotive is defined as a self-propelled vehicle
VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT OIL PUMP IMPROVES TRACKED VEHICLE TRANSMISSION EFFICIENCY
 2018 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM POWER & MOBILITY (P&M) TECHNICAL SESSION AUGUST 7-9, 2018 NOVI, MICHIGAN VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT OIL PUMP IMPROVES TRACKED VEHICLE TRANSMISSION
2018 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM POWER & MOBILITY (P&M) TECHNICAL SESSION AUGUST 7-9, 2018 NOVI, MICHIGAN VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT OIL PUMP IMPROVES TRACKED VEHICLE TRANSMISSION
Design and Installation of a Compressed Hydrogen Fueling System in a 2009 Chevrolet Colorado
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 12-2010 Design and Installation
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 12-2010 Design and Installation
Test Plans & Test Results
 P10227 Variable Intake System for FSAE Race Car Test Plans & Test Results By: Dave Donohue, Dan Swank, Matt Smith, Kursten O'Neill, Tom Giuffre Table of contents 1. MSD I: WKS 8-10 PRELIMINARY TEST PLAN...
P10227 Variable Intake System for FSAE Race Car Test Plans & Test Results By: Dave Donohue, Dan Swank, Matt Smith, Kursten O'Neill, Tom Giuffre Table of contents 1. MSD I: WKS 8-10 PRELIMINARY TEST PLAN...
8.2 ROUTE CHOICE BEHAVIOUR:
 8.2 ROUTE CHOICE BEHAVIOUR: The most fundamental element of any traffic assignment is to select a criterion which explains the choice by driver of one route between an origin-destination pair from among
8.2 ROUTE CHOICE BEHAVIOUR: The most fundamental element of any traffic assignment is to select a criterion which explains the choice by driver of one route between an origin-destination pair from among
Driver Instructions. Hydraulic Launch Assist (HLA ) TRDR1200
 Driver Instructions Hydraulic Launch Assist (HLA ) TRDR1200 September 2011 Table of Contents Warnings and Cautions Definitions... 1 Driver Display Module... 7 Operation... 9 Service and Maintenance...
Driver Instructions Hydraulic Launch Assist (HLA ) TRDR1200 September 2011 Table of Contents Warnings and Cautions Definitions... 1 Driver Display Module... 7 Operation... 9 Service and Maintenance...
Eastman Chemical Company Motor Analysis Stepping out of the Box
 Eastman Chemical Company Motor Analysis Stepping out of the Box By: Tom Whittemore, Jr., P.E.; Paul Aesque; and Danny Hawkins, Eastman Chemical Company Eastman Chemical Company started its Motor Analysis
Eastman Chemical Company Motor Analysis Stepping out of the Box By: Tom Whittemore, Jr., P.E.; Paul Aesque; and Danny Hawkins, Eastman Chemical Company Eastman Chemical Company started its Motor Analysis
Technical Service Bulletin IOX/DCX Transmitter Maintenance Schedule
 Technical Service Bulletin 140610 IOX/DCX Transmitter Maintenance Schedule Service Bulletin 140610 applies to Comark IOX, DCX and Paragon transmitters. This bulletin contains important maintenance schedule
Technical Service Bulletin 140610 IOX/DCX Transmitter Maintenance Schedule Service Bulletin 140610 applies to Comark IOX, DCX and Paragon transmitters. This bulletin contains important maintenance schedule
