Optimizing Blendstock Composition and Ethanol Feedstock to Reduce Gasoline Well-to-Pump CO 2 Emission
|
|
|
- Gary Dennis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 105 (2017 ) The 8 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2016 Optimizing Blendstock Composition and Ethanol Feedstock to Reduce Gasoline Well-to-Pump CO 2 Emission Bo Zhang a,b*, S. Mani Sarathy a, Amir F.N. Abdul-Manan c a King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Clean Combustion Research Center, Thuwal, , Saudi Arabia b University of Oxford, Chemical Engineering, Engineering Science, Oxford, OX1 3PJ, United Kingdom c Strategic Transport Analysis Team, Fuel Technology R&D, Research & Development Center (R&DC), Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, 31311, Saudi Arabia. Abstract Lifecycle CO2 emission of ethanol blended gasoline was simulated to investigate how fuel properties and composition affect overall emission. Fuel research octane number (RON), octane sensitivity and ethanol content (derived from sugarcane and corn) were varied in the simulations to formulate blended fuels that economically achieve target specifications. The well-to-pump (WTP) simulation results were then analyzed to understand the effects of fuel composition on emission. Elevated ethanol content displaces aromatics and olefins required in gasoline blendstock to reach a target fuel specification. The addition of greater sugarcane-based ethanol percentage in constant aromatics and olefins fuel reduces its WTP CO2 emission. Corn-based ethanol blending does not offer CO2 emission offset due to its high production emissions. The mixing of sugarcane-based with corn-based ethanol is shown to be a potentially effective method for achieving a blended fuel with a lower lifecycle CO2 emission. Besides CO2 emission, the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emission from land-use conversions (LUC), CH4, and N2O are also significant in determining the optimal fuel blend. Herein, we present preliminary results showing that total GHG emissions significantly increase when either corn or sugarcane ethanol is blended at even small percentages; detailed results will be addressed in future communications The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. ( Selection and/or peer-review under responsibility of ICAE Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 8th International Conference on Applied Energy. Keywords: Corn-based ethanol; lifecycle analysis; ethanol blended gasoline; CO 2 emission; well-to-wheel emission Nomenclature E Ethanol content/percentage GHG Greenhouse gas LUC Land-use conversions PTW Pump-to-wheel RON Research octane number The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license ( Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 8th International Conference on Applied Energy. doi: /j.egypro
2 Bo Zhang et al. / Energy Procedia 105 ( 2017 ) S WTP WTW Octane Sensitivity Well-to-pump Well-to-wheel * Corresponding author. Tel.: address: bo.zhang@eng.ox.ac.uk. 1. Introduction A simulation was recently performed to quantitatively assess the change in lifecycle emission of ethanolblended gasoline, and some of the results have been analysed and discussed elsewhere [1]. Various combinations of gasoline research octane number (RON), octane sensitivity (S) and ethanol content (E) were investigated for their well-to-wheel (WTW) CO 2 emission. Ethanol addition to gasoline blendstock was shown to boost fuel anti-knock quality and result in higher fuel efficiency when operating at elevated engine compression ratios. The biogenic credit associated with bio-ethanol production also reduces the WTW emission of ethanol-blended fuel. An optimal blended fuel (lowest CO 2 emission) was identified from the simulations, with RON 105, S 15.5 and 32% ethanol [1]. The possibility of engine downsizing was shown to further improve efficiency and reduce emission. Corn-based ethanol was identified to offer little emission reductions, even when blended at high percentages (30%). The high emissions associated with production and conversion limits the applicability of corn-based ethanol in reducing the emission of blended fuel. Sugarcane-based ethanol, a less emission-intensive biofuel, was shown to reduce fuel WTW CO 2 emission. A refinery linear programming optimization was run to produce the specified product quality and quantity while minimizing the cost of production. Fuel RON, S and E were the set target values that needed to be met through the blending of different refinery streams, along with other gasoline properties (vapour pressure, benzene%, etc.). Default refinery setup and product constraints were applied; the processing capacity and conditions of each refinery units were varied to meet the required quality of its output stream. The final gasoline blendstock composition was shown to vary with target RON, S and ethanol content. A range of gasoline properties have been simulated (RON, ; S, ; E, 0-40%) and shown in Table 2. With the variation in ethanol percentage, the aromatic and olefin contents of the gasoline blendstock must be adjusted to meet the final fuel specification. These components are typical octane boosters for gasoline, but their productions involve complex and costly upgrading in a refinery. Given the increasing interest in high octane fuels as enablers for more efficient engines, we investigate the feasibility of increasing ethanol blends in gasoline as means to boost the octane level and assess their implications on WTW CO2 emissions. This study utilizes the simulation data to investigate the means to mitigate the high WTP CO 2 emission from corn-based ethanol. The effects of ethanol content on gasoline aromatic and olefin content and fuel WTP emission are studied. The mixing of sugarcane-based with corn-based ethanol is also investigated as a means to reduce the overall fuel WTP CO 2 emission. This paper primarily discusses the CO 2 emissions of the simulated fuels; however preliminary results on the impact of land-use conversions (LUC) and two other primary greenhouse gases (GHGs) are also briefly presented. 2. Results and Discussion 2.1. The effect of ethanol blending on blendstock composition
3 3644 Bo Zhang et al. / Energy Procedia 105 ( 2017 ) The emissions of five simulated fuels with RON97 and S12 are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1. With increasing sugarcane-based ethanol, the amount of aromatics and olefins needed to meet anti-knock requirement are reduced. A lower aromatic content reduces the toxicity and carcinogenicity of the fuel [2]. A reduced olefin amount improves oxidative stability and minimizes engine deposit formation [3, 4]. The blending with sugarcane-based ethanol yields slight WTP emission reduction when comparing E28 to E2 fuel. The reduction is largely due to the lower emissions intensity associated with the production of ethanol from sugarcane. The increased knock resistance of the high ethanol fuel enables further emissions reduction through improved vehicle efficiency leading to larger overall WTW CO 2 emissions benefits. On the other hand, the blending of corn-based ethanol significantly increases WTP emission given that production of corn ethanol is highly energy and emissions intensive The enhanced fuel economy enabled by E28 fuel is insufficient to make up for the high WTP emission of corn-based ethanol. WTP CO 2 Emission (g/km) 45 35% 60% 35% % 50% 30% 30 25% 40% 25% 25 20% 20% 20 15% 30% 15% 15 10% 20% 10 10% 5 5% 10% 5% 0 0% 0% 0% 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% WTP (Corn-EtOH) Ethanol % WTP (SC-EtOH) EtOH% Volume % Aromatics% Olefin% Sum ARO OLF Volume % Volume % Figure 1: WTP CO 2 emission, aromatic and olefin content of RON97, S12 fuels with different ethanol content. Aromatics, olefin and ethanol content are presented as a volume percentage of fuel. Aromatic and olefin content corresponds to the secondary axis. Corn-based (Corn) and sugarcane-based (SC) ethanol WTP CO 2 emissions are shown for the each fuel specification. Figure 2: The blending volume percentage of aromatics, olefins and ethanol for the 27 simulated fuels. The combined percentage of aromatics and olefins is shown as the Sum corresponds to the primary axis. Aromatics and Olefins correspond to the secondary axis. Table 1: Comparison of CO 2 Emission, Olefins and Aromatics for RON97, S12 Simulated Gasoline Fuel No EtOH % 28% 18% 13% 12% 2% Aromatics% 17.0% 15.0% 19.3% 19.5% 30.0% Olefins% 9.5% 18.5% 19.2% 20.4% 20.5% WTP (w. corn-etoh) (g/km) WTW (w. corn-etoh) (g/km) WTP (w. SC-EtOH) (g/km) WTW (w. SC-EtOH) (g/km) A set of simulated fuels with approximately 20% aromatics and 20% olefin, but different ethanol content, is compared for their WTP and WTW CO 2 emissions in Figure 3. The blending of sugarcane-based (Fig. 3A) and corn-based (Fig. 3B) ethanol are shown separately. The WTP emission with both types of ethanol appear to have a sharp increase at greater than 22%. This may suggest that, for the shown fuels, a significant change in blending composition is needed to maintain all gasoline properties (e.g., vapor pressure, %evaporation at 200 o F, sulfur content, etc.) within required limits. The remaining trends in WTP emission is consistent with previous identifications. The WTW CO 2 emission with sugarcane-based ethanol is reduced with increasing ethanol content. The large growth margin in WTP emission with increasing cornbased ethanol perturbs the trend in reducing WTW emission. It seems that an optimal mixing ratio between
4 Bo Zhang et al. / Energy Procedia 105 ( 2017 ) corn-based ethanol, olefins and aromatics may exist to reach a lowest WTW emission. Future work should further investigate this possibility. Figure 2 plots the percentage of aromatics and olefins in the 27 simulated fuels against their ethanol content. A reduction of aromatics and olefins can be observed with increasing ethanol blending. The effect is more pronounced with the combined blending percentage of aromatics and olefins. WTW CO 2 Emission (g/km) % 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% WTW (SC-EtOH) EtOH% A) B) 40 WTP (SC-EtOH) WTP CO 2 Emission (g/km) WTW CO 2 Emission (g/km) % 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% WTW (Corn-EtOH) EtOH% WTP (Corn-EtOH) WTP CO 2 Emission (g/km) Figure 3: WTW and WTP CO 2 emission of fuels with 20% aromatics and 20% olefin but different ethanol content. WTW emission corresponds to the primary axis and WTP emission is to the secondary axis. A) With sugarcane-based ethanol blended in gasoline. B) With corn-based ethanol blended in gasoline Corn-based and sugarcane-based ethanol mixing Our simulation results have shown the exacerbating WTW CO 2 emission with corn-based ethanol blended fuel, even when blended at more than 30% [1]. Ethanol blending was found to reduce fuel CO 2 emission in pump-to-wheel (PTW) cycle and WTP cycle, only when sugarcane-based ethanol was used. If the high emission of corn-based ethanol can be partially offset, the increase in ethanol blending percentage could still yield beneficial emission result. Extracted results from GREET showed that corn is amongst the most emission-intensive source for bioethanol; sugarcane has the lowest emissions intensity amongst conventional first generation bioethanol [5]. The lower emitting bioethanol offers greater emission offset and thus less WTP emission. Advance generation bioethanols, such as cellulosic ethanol, may offer larger emissions reduction potentials in the future. However, today more research and development is still required before it can be commercialized. The co-mixing of sugarcane-based and corn-based ethanol is able to reduce the overall ethanol production CO 2 emission in high ethanol content fuel. A mixing breakeven percentage (B%) has been calculated to indicate the percentage of sugarcane-based ethanol required to achieve the same WTW emission as the reference fuel. Further sugarcane-based ethanol mixing would yield a reduced emission compared to the business-as-usual case. The fuel with RON 95, S 10 and E10 is selected as the reference fuel, with similar properties as the U.S. premium grade gasoline. The B% is reported in Table 2. A greater than 100% value indicates the impossibility of reaching the target emission. A negative percentage indicates the nonessentiality of mixing sugarcane-based ethanol with corn-based ethanol, i.e., the utilization of 100% cornbased ethanol would still have a better fuel emission. For the low knock resistant E10 fuels, sugarcanebased ethanol alone is insufficient to achieve lower fuel emission; less energy intensive biomass-based ethanol is needed to make this a feasible option. For greater knock resistant E10 fuels, the higher engine efficiency can reduce the PTW emission and allow corn-based ethanol to be mixed in the blend. With E20-
5 3646 Bo Zhang et al. / Energy Procedia 105 ( 2017 ) E40 fuels, the emission gains from operating under higher engine compression ratio is much greater and allows the majority of ethanol to be corn-based. The result from Table 2 indicates that corn-based ethanol can be blended into future high ethanol fuels to reduce overall emission, given that it is supplemented by some sugarcane-based ethanol. Table 2: Selected Simulation Fuel, Ethanol Content, RON, Octane Sensitivity, Sugarcane-Based Ethanol Breakeven Percentage and WTW CO 2 Emission with Corn-Based or Sugarcane-Based Ethanol (g/km). ETOH% RON S B% WTW (W. CORN-ETOH) WTW (W.SC-ETOH) E10 8% % % % % % % % % % % % % (REF) % % % % % % % E20 18% % % % % % % % % % % % % % E30/E40 28% % % % % % % % % % This results here show that with the presently used technology and CO 2 emission models, utilizing cornbased ethanol to reduce WTW CO 2 emission in higher ethanol blended fuels is possible. Technological improvements in corn farming, processing and conversion may reduce the emission footprint of corn-based ethanol. 3. Conclusion Higher ethanol blended fuel can yield fuels with lower WTW CO 2 emission. Corn-based ethanol blended gasoline does not yield better CO 2 emission with existing farming and ethanol production practices. However, mixing of corn-based ethanol with less CO 2 emission-intensive source (i.e., sugarcane-based) can potentially realize greater emissions reductions. The correct mixing strategy would determine if corn ethanol can be utilized as a major ethanol source in gasoline blending as means for producing high octane fuels in order to enable more efficient engines. This paper has only presented the initial WTW CO 2 emissions results of the simulated fuels. In order to evaluate the full lifecycle GHG emissions, it is critical to incorporate the emissions of non-co 2 GHGs, such as CH 4 and N 2O, both of which are potent global warming gasses. An extended study was conducted to incorporate these emissions, detailed results and analysis will be addressed in future communications. Also equally important is to include the emissions due to land use changes associated with biofuels. LUC has received a lot of research and policy interests since Searchinger et al. [6] published their landmark paper in 2008, and policymakers worldwide have responded in different ways to deal with LUC within existing
6 Bo Zhang et al. / Energy Procedia 105 ( 2017 ) biofuels programs [7, 8]. We believe it is prudent to incorporate the effects of LUC to properly account for the WTW GHG emissions savings potential of future SI engines that are enabled by bio-based high octane fuels. Therefore, in our updated study, we adopted the most recent LUC factors that were developed for the California Air Resource Board (ARB) for their Low Carbon Fuels Standard (LCFS). In the latest update to the LCFS, corn ethanol and sugarcane ethanol were assigned LUC factors of 19.8 gco 2eq/MJ and 11.8 gco 2eq/MJ respectively, based on the average of 30 different scenarios that were evaluated [8]. The emissions of CH 4 and N 2O during ethanol production and refinery operations are also shown to be significant in affecting WTP, but not PTW, GHG emissions of simulated fuels. The WTP GHG emissions showed that higher blending percentages of corn-based ethanol exacerbates GHG emission, agreeing with the trend for CO 2 emission. But for sugarcane-based ethanol, it is interesting to note that when we included the non-co 2 GHGs and the effects of LUC, the CO 2 benefits reported earlier for higher blends of sugarcanebased ethanol was found to diminish substantially; the new optimal fuel consists of only 4% ethanol and the top three lowest emitting fuels contain ethanol content less than 10%. The additional emissions from the combustion cycle was found to be negligible. The total GHG emissions increased by 40-95% with the accounting of LUC, CH 4 and N 2O. These initial results suggest that increasing ethanol content in gasoline beyond existing levels in order to increase gasoline octane as means to reduce transport GHG emissions may not be justifiable. Certain refinery units are intensive in GHG emissions. The increased production of certain blendstocks in order to meet fuel standard, may significantly raise refinery emissions under its default setting. Future work would investigate possible means to modify refinery setup in reducing production emission for each simulated fuels. A less emission-intensive biomass will also be examined as potential replacement for corn and sugarcane. References [1] Zhang, B., & Sarathy, S. M. (2016). Lifecycle optimized ethanol-gasoline blends for turbocharged engines. Applied Energy, 181, [2] Yao, Y. C., Tsai, J. H., Chang, A. L., & Jeng, F. T. (2008). Effects of sulfur and aromatic contents in gasoline on motorcycle emissions. Atmospheric Environment, 42(26), [3] Pfaendtner, J., & Broadbelt, L. J. (2008). Mechanistic modeling of lubricant degradation. 1. Structure-reactivity relationships for free-radical oxidation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 47(9), [4] Kalghatgi, G. T. (2014). Fuel/engine interactions. Training, 1998, [5] GREET. Argonne National Laboratory. Energy Systems. Accessed: July 20,2016. Available from: [6] Searchinger, T., Heimlich, R., Houghton, R. A., Dong, F., Elobeid, A., Fabiosa, J.,... & Yu, T. H. (2008). Use of US croplands for biofuels increases greenhouse gases through emissions from land-use change. Science, 319(5867), [7] European Council. (2015). DIRECTIVE (EU) 2015/1513 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 9 September 2015 amending Directive 98/70/EC relating to the quality of petrol and diesel fuels and amending Directive 2009/28/EC on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable. Official Journal of the European Union. [8] Air Resources Board. (2015). Low Carbon Fuels Standard. Retrieved September 6, 2016, from: Biography Bo Zhang The author is a D.Phil. student at the University of Oxford Engineering Science department. He graduated with degrees of Master of Engineering (Cornell University) and Bachelor of Applied Science (University of Toronto) in chemical engineering.
The California Low Carbon Fuel Standard. John D. Courtis August 10-12, 2009
 The California Low Carbon Fuel Standard John D. Courtis August 10-12, 2009 Why LCFS GHG Emissions (MMTCO2e) Large GHG Reductions Required to Meet 2020 Target and 2050 Goal 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0-169
The California Low Carbon Fuel Standard John D. Courtis August 10-12, 2009 Why LCFS GHG Emissions (MMTCO2e) Large GHG Reductions Required to Meet 2020 Target and 2050 Goal 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0-169
Reducing the Green House Gas Emissions from the Transportation Sector
 Reducing the Green House Gas Emissions from the Transportation Sector Oyewande Akinnikawe Department of Petroleum Engineering, Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843 and Christine Ehlig-Economides
Reducing the Green House Gas Emissions from the Transportation Sector Oyewande Akinnikawe Department of Petroleum Engineering, Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843 and Christine Ehlig-Economides
California Environmental Protection Agency. Air Resources Board. Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) Update 2015 CRC LCA of Transportation Fuels Workshop
 California Environmental Protection Agency Air Resources Board Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) Update 2015 CRC LCA of Transportation Fuels Workshop Anil Prabhu October 27-28, 2015 Overview of Presentation
California Environmental Protection Agency Air Resources Board Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) Update 2015 CRC LCA of Transportation Fuels Workshop Anil Prabhu October 27-28, 2015 Overview of Presentation
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 137 (2016 ) GITSS2015
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 137 (2016 ) 244 251 GITSS2015 Simulation Analysis of Double Road Train Adaptability of Highway in China Hao Zhang a,b,*, Hong-wei
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 137 (2016 ) 244 251 GITSS2015 Simulation Analysis of Double Road Train Adaptability of Highway in China Hao Zhang a,b,*, Hong-wei
Ethanol, DME and Renewable Diesel for large scale displacement of fossil diesel in HD applications
 Ethanol, DME and Renewable Diesel for large scale displacement of fossil diesel in HD applications Patric Ouellette, Lew Fulton STEPS Presentation May 24, 2017 Intro and Question Large content of biofuel
Ethanol, DME and Renewable Diesel for large scale displacement of fossil diesel in HD applications Patric Ouellette, Lew Fulton STEPS Presentation May 24, 2017 Intro and Question Large content of biofuel
INDIRECT LAND USE CHANGE, LOW CARBON FUEL STANDARDS, & CAP AND TRADE: The Role of Biofuels in Greenhouse Gas Regulation
 INDIRECT LAND USE CHANGE, LOW CARBON FUEL STANDARDS, & CAP AND TRADE: The Role of Biofuels in Greenhouse Gas Regulation Matthew Carr Policy Director, Industrial & Environmental Section Biotechnology Industry
INDIRECT LAND USE CHANGE, LOW CARBON FUEL STANDARDS, & CAP AND TRADE: The Role of Biofuels in Greenhouse Gas Regulation Matthew Carr Policy Director, Industrial & Environmental Section Biotechnology Industry
Model Differences and Variability CRC E-102. Don O Connor 2013 CRC Life Cycle Analysis of Transportation Fuels Workshop October 16, 2013
 Model Differences and Variability CRC E-102 Don O Connor 2013 CRC Life Cycle Analysis of Transportation Fuels Workshop October 16, 2013 Introduction The goal of CRC Project E-102 was to better quantify
Model Differences and Variability CRC E-102 Don O Connor 2013 CRC Life Cycle Analysis of Transportation Fuels Workshop October 16, 2013 Introduction The goal of CRC Project E-102 was to better quantify
California Greenhouse Gas Vehicle and Fuel Programs
 NCSL Advisory Council on Energy California Greenhouse Gas Vehicle and Fuel Programs Charles M. Shulock California Air Resources Board November 28, 2007 Overview AB 32 basics GHG tailpipe standards Low
NCSL Advisory Council on Energy California Greenhouse Gas Vehicle and Fuel Programs Charles M. Shulock California Air Resources Board November 28, 2007 Overview AB 32 basics GHG tailpipe standards Low
Fuels to Enable More Efficient Engines
 Fuels to Enable More Efficient Engines Robert L. McCormick & Bradley T. Zigler 4 th International Conference on Biofuels Standards: Current Issues, Future Trends Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA November 13,
Fuels to Enable More Efficient Engines Robert L. McCormick & Bradley T. Zigler 4 th International Conference on Biofuels Standards: Current Issues, Future Trends Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA November 13,
Direct Injection Ethanol Boosted Gasoline Engines: Biofuel Leveraging For Cost Effective Reduction of Oil Dependence and CO 2 Emissions
 Direct Injection Ethanol Boosted Gasoline Engines: Biofuel Leveraging For Cost Effective Reduction of Oil Dependence and CO 2 Emissions D.R. Cohn* L. Bromberg* J.B. Heywood Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Direct Injection Ethanol Boosted Gasoline Engines: Biofuel Leveraging For Cost Effective Reduction of Oil Dependence and CO 2 Emissions D.R. Cohn* L. Bromberg* J.B. Heywood Massachusetts Institute of Technology
How Carbon Intense Is Your Fuel?
 How Carbon Intense Is Your Fuel? Featured speaker: Dr. Anil Prabhu, California Air Resources Board March 8, 2017 www.wwcleancities.org Robin Gold Coordinator Alternative Fuels & Technology Kimberley Cline
How Carbon Intense Is Your Fuel? Featured speaker: Dr. Anil Prabhu, California Air Resources Board March 8, 2017 www.wwcleancities.org Robin Gold Coordinator Alternative Fuels & Technology Kimberley Cline
Reducing GHG Emissions Through National Renewable Fuel Standards
 Reducing GHG Emissions Through National Renewable Fuel Standards Transportation Research Board 2010 Environment and Energy Conference Robert Larson, USEPA First Renewable Fuel Standards Established by
Reducing GHG Emissions Through National Renewable Fuel Standards Transportation Research Board 2010 Environment and Energy Conference Robert Larson, USEPA First Renewable Fuel Standards Established by
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia CIRP 33 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 33 (2015 ) 581 586 9th CIRP Conference on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering - CIRP ICME '14 Magnetic fluid seal
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 33 (2015 ) 581 586 9th CIRP Conference on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering - CIRP ICME '14 Magnetic fluid seal
Overview Air Qualit ir Qualit Impacts of
 Air Quality Impacts of Expanded Use of Ethanol National Association of Clean Air Agencies Fall Membership Meeting October 28, 2007 Bob Fletcher, Chief Stationary Source Division California Environmental
Air Quality Impacts of Expanded Use of Ethanol National Association of Clean Air Agencies Fall Membership Meeting October 28, 2007 Bob Fletcher, Chief Stationary Source Division California Environmental
California Low Carbon Fuel Standard Status Report. John D. Courtis October 17, 2011
 California Low Carbon Fuel Standard Status Report John D. Courtis October 17, 2011 Background CA legislature adopts Global Warming Solutions Act (AB 32) in 2006 Board passes LCFS April 2009 Title 17, CCR,
California Low Carbon Fuel Standard Status Report John D. Courtis October 17, 2011 Background CA legislature adopts Global Warming Solutions Act (AB 32) in 2006 Board passes LCFS April 2009 Title 17, CCR,
Propane Education and Research Council LCA C.2011, 16 Nov REVIEW OF LIFE CYCLE GHG EMISSIONS FROM LPG RIDING MOWERS
 REVIEW OF LIFE CYCLE GHG EMISSIONS FROM LPG RIDING MOWERS Stefan Unnasch and Larry Waterland, Life Cycle Associates, LLC 1. Summary This paper examines the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from liquefied
REVIEW OF LIFE CYCLE GHG EMISSIONS FROM LPG RIDING MOWERS Stefan Unnasch and Larry Waterland, Life Cycle Associates, LLC 1. Summary This paper examines the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from liquefied
Potential Environmental and Economic Benefit s of Higher-Oct ane Gasoline
 Potential Environmental and Economic Benefit s of Higher-Oct ane Gasoline Raymond Speth, Eric Chow, Robert Malina, Steven Barrett, J ohn Heywood, W illiam Green CRC W orkshop, Argonne National Laboratory
Potential Environmental and Economic Benefit s of Higher-Oct ane Gasoline Raymond Speth, Eric Chow, Robert Malina, Steven Barrett, J ohn Heywood, W illiam Green CRC W orkshop, Argonne National Laboratory
AN INVESTIGATION INTO HOW DIFFERENT BLENDS OF BIO-DIESEL AT A RANGE OF TEMPERATURES AFFECT ENGINE HORSEPOWER, TORQUE AND EMISSIONS
 Scientific Papers, USAMV Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LII, 2009, ISSN 1222-5359 AN INVESTIGATION INTO HOW DIFFERENT BLENDS OF BIO-DIESEL AT A RANGE OF TEMPERATURES AFFECT ENGINE HORSEPOWER, TORQUE AND EMISSIONS
Scientific Papers, USAMV Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LII, 2009, ISSN 1222-5359 AN INVESTIGATION INTO HOW DIFFERENT BLENDS OF BIO-DIESEL AT A RANGE OF TEMPERATURES AFFECT ENGINE HORSEPOWER, TORQUE AND EMISSIONS
Strategy for Biomass and Biofuels
 Strategy for Biomass and Biofuels Peter Tjan Secretary General European Petroleum Industry Association (EUROPIA) Biomass is a limited resource for which there are competing demands Peter Tjan Secretary
Strategy for Biomass and Biofuels Peter Tjan Secretary General European Petroleum Industry Association (EUROPIA) Biomass is a limited resource for which there are competing demands Peter Tjan Secretary
Improved PV Module Performance Under Partial Shading Conditions
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 33 (2013 ) 248 255 PV Asia Pacific Conference 2012 Improved PV Module Performance Under Partial Shading Conditions Fei Lu a,*, Siyu Guo a, Timothy
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 33 (2013 ) 248 255 PV Asia Pacific Conference 2012 Improved PV Module Performance Under Partial Shading Conditions Fei Lu a,*, Siyu Guo a, Timothy
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 150 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 150 (2016 ) 1291 1296 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, ICIE 2016 Energy Datum of the Flow of Exhaust Gases
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 150 (2016 ) 1291 1296 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, ICIE 2016 Energy Datum of the Flow of Exhaust Gases
The Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA): Proposed Changes to the Renewable Fuel Standard Program (RFS2)
 The Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA): Proposed Changes to the Renewable Fuel Standard Program (RFS2) Presentation to the NAS Biofuels Workshop Madison, WI. June 23-24, 2009 1 Agenda Background
The Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA): Proposed Changes to the Renewable Fuel Standard Program (RFS2) Presentation to the NAS Biofuels Workshop Madison, WI. June 23-24, 2009 1 Agenda Background
Creating a Large, Guaranteed Market for Advanced Biofuels Through a Low Carbon Fuel Standard
 www.e2.org Creating a Large, Guaranteed Market for Advanced Biofuels Through a Low Carbon Fuel Standard Adopted in April 2009, California s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) will guarantee a market of up
www.e2.org Creating a Large, Guaranteed Market for Advanced Biofuels Through a Low Carbon Fuel Standard Adopted in April 2009, California s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) will guarantee a market of up
Legislative and Regulatory Developments Likely to Affect the U.S. Refining Sector in the Next Decade
 Legislative and Regulatory Developments Likely to Affect the U.S. Refining Sector in the Next Decade Round Table Discussion on U.S. Refining OPIS 11 th National Supply Summit October 18, 2009 Dave Hirshfeld
Legislative and Regulatory Developments Likely to Affect the U.S. Refining Sector in the Next Decade Round Table Discussion on U.S. Refining OPIS 11 th National Supply Summit October 18, 2009 Dave Hirshfeld
Effects of Ethanol-Gasoline blends on Performance and Emissions of Gasoline Engines
 Effects of Ethanol-Gasoline blends on Performance and Emissions of Gasoline Engines Er. Kapil Karadia 1, Er. Ashish Nayyar 2 1 Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology, Management &Gramothan, Jaipur,Rajasthan
Effects of Ethanol-Gasoline blends on Performance and Emissions of Gasoline Engines Er. Kapil Karadia 1, Er. Ashish Nayyar 2 1 Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology, Management &Gramothan, Jaipur,Rajasthan
Designing a Low-Carbon Fuel Standard for the Northeast
 Designing a Low-Carbon Fuel Standard for the Northeast Matt Solomon msolomon@nescaum.org Northeast LCFS Workshop Yale University October 14, 2008 What s carbon intensity again? A measure of the total CO
Designing a Low-Carbon Fuel Standard for the Northeast Matt Solomon msolomon@nescaum.org Northeast LCFS Workshop Yale University October 14, 2008 What s carbon intensity again? A measure of the total CO
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 129 (2015 ) International Conference on Industrial Engineering
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 129 (2015 ) 166 170 International Conference on Industrial Engineering Refinement of hybrid motor-transmission set using micro
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 129 (2015 ) 166 170 International Conference on Industrial Engineering Refinement of hybrid motor-transmission set using micro
Ethanol Supply Chain and Industry Overview: More Harm Than Good?
 Ethanol Supply Chain and Industry Overview: More Harm Than Good? Authors: Sarah L Bruce Advisor: Alexis Hickman Bateman, Edgar Blanco Sponsor: Yossi Sheffi MIT SCM ResearchFest May 23-24, 2012 Ethanol
Ethanol Supply Chain and Industry Overview: More Harm Than Good? Authors: Sarah L Bruce Advisor: Alexis Hickman Bateman, Edgar Blanco Sponsor: Yossi Sheffi MIT SCM ResearchFest May 23-24, 2012 Ethanol
DEVELOPING VEHICLE FUEL ECONOMY STANDARDS FOR SOUTH AFRICAN PASSENGER VEHICLES
 DEVELOPING VEHICLE FUEL ECONOMY STANDARDS FOR SOUTH AFRICAN PASSENGER VEHICLES INTRODUCTION: POLICY DIRECTIVE 2 Developing FES and the linkages with The Green Transport Strategy The Development of the
DEVELOPING VEHICLE FUEL ECONOMY STANDARDS FOR SOUTH AFRICAN PASSENGER VEHICLES INTRODUCTION: POLICY DIRECTIVE 2 Developing FES and the linkages with The Green Transport Strategy The Development of the
Opportunities for Reducing Transportation s Petroleum Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
 Opportunities for Reducing Transportation s Petroleum Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions John B. Heywood Professor of Mechanical Engineering Director, Sloan Automotive Laboratory M.I.T. Transportation @
Opportunities for Reducing Transportation s Petroleum Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions John B. Heywood Professor of Mechanical Engineering Director, Sloan Automotive Laboratory M.I.T. Transportation @
A Global Solution for Sustainable Biofuels
 A Global Solution for Sustainable Biofuels 1 Agrisoma Develops and Sells Carinata Seeds and More Expanding sales of Carinata seeds a non-food, sustainable crop for biofuels and high protein feed Commercial
A Global Solution for Sustainable Biofuels 1 Agrisoma Develops and Sells Carinata Seeds and More Expanding sales of Carinata seeds a non-food, sustainable crop for biofuels and high protein feed Commercial
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROGEN BLENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION OF POLLUTANTS EMITTED FROM A FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROGEN BLENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION OF POLLUTANTS EMITTED FROM A FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE Haroun A. K. Shahad hakshahad@yahoo.com Department of mechanical
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROGEN BLENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION OF POLLUTANTS EMITTED FROM A FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE Haroun A. K. Shahad hakshahad@yahoo.com Department of mechanical
Low Carbon Fuel Standard i LUC Status
 California Environmental Protection Agency Air Resources Board Low Carbon Fuel Standard i LUC Status February 20, 2013 LCFS Requirements Requires a 10 percent reduction in the carbon intensity(ci) by 2020;
California Environmental Protection Agency Air Resources Board Low Carbon Fuel Standard i LUC Status February 20, 2013 LCFS Requirements Requires a 10 percent reduction in the carbon intensity(ci) by 2020;
Fuels Roadmap for 2020 and beyond - implications for future strategy
 Fuels Roadmap for 2020 and beyond - implications for future strategy Celine Cluzel Principal Consultant Element Energy Jonathan Murray Policy and Operations Director Low Carbon Vehicle Partnership LowCVP
Fuels Roadmap for 2020 and beyond - implications for future strategy Celine Cluzel Principal Consultant Element Energy Jonathan Murray Policy and Operations Director Low Carbon Vehicle Partnership LowCVP
Extension of the Lower Load Limit in Dieseline Compression Ignition Mode
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 2363 2370 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Extension of the Lower Load Limit in Dieseline
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 2363 2370 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Extension of the Lower Load Limit in Dieseline
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 67 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 518 523 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 518 523 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Vivek Pandey 1, V.K. Gupta 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Technology, GBPUA&T, Pantnagar, India
 Study of Ethanol Gasoline Blends for Powering Medium Duty Transportation SI Engine Vivek Pandey 1, V.K. Gupta 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Technology, GBPUA&T, Pantnagar, India
Study of Ethanol Gasoline Blends for Powering Medium Duty Transportation SI Engine Vivek Pandey 1, V.K. Gupta 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Technology, GBPUA&T, Pantnagar, India
EU Policy for Biofuels Dr Mairi J Black (Dr Jeremy Woods)
 EU Policy for Biofuels Dr Mairi J Black (Dr Jeremy Woods) Federation of Latin American Chemical Societies Meeting Biofuels and Bio-based Products Chemistry and Environmental Impacts Symposium Puerto Rico
EU Policy for Biofuels Dr Mairi J Black (Dr Jeremy Woods) Federation of Latin American Chemical Societies Meeting Biofuels and Bio-based Products Chemistry and Environmental Impacts Symposium Puerto Rico
Replacing the Volume & Octane Loss of Removing MTBE From Reformulated Gasoline Ethanol RFG vs. All Hydrocarbon RFG. May 2004
 Replacing the Volume & Octane Loss of Removing MTBE From Reformulated Gasoline Ethanol RFG vs. All Hydrocarbon RFG May 2004 Prepared and Submitted by: Robert E. Reynolds President Downstream Alternatives
Replacing the Volume & Octane Loss of Removing MTBE From Reformulated Gasoline Ethanol RFG vs. All Hydrocarbon RFG May 2004 Prepared and Submitted by: Robert E. Reynolds President Downstream Alternatives
ILUC ETHANOL ILUC-FREE ETHANOL FROM EUROPE. Proud member of. JAMES COGAN 7th ISCC Global Sustainability Conference Brussels, February 15, 2017
 ILUC ETHANOL ILUC-FREE ETHANOL FROM EUROPE JAMES COGAN 7th ISCC Global Sustainability Conference Brussels, February 15, 2017 About Ethanol Europe Renewables Ltd Producer of ethanol and feed Thank you ISCC
ILUC ETHANOL ILUC-FREE ETHANOL FROM EUROPE JAMES COGAN 7th ISCC Global Sustainability Conference Brussels, February 15, 2017 About Ethanol Europe Renewables Ltd Producer of ethanol and feed Thank you ISCC
Biodiesel CO2 emissions under Sweden policy scenario and technical constraints
 Biodiesel CO2 emissions under Sweden policy scenario and technical constraints BIOGRACE LABORATORY CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TOOLS MJ2470 Mercè Labordena Mir 20/11/2012 1. Introduction The energy systems
Biodiesel CO2 emissions under Sweden policy scenario and technical constraints BIOGRACE LABORATORY CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TOOLS MJ2470 Mercè Labordena Mir 20/11/2012 1. Introduction The energy systems
Impacts of Options for Modifying the Renewable Fuel Standard. Wallace E. Tyner Farzad Taheripour. Purdue University
 Impacts of Options for Modifying the Renewable Fuel Standard Wallace E. Tyner Farzad Taheripour Purdue University The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) was created in 2005 and modified in 2007 with the objective
Impacts of Options for Modifying the Renewable Fuel Standard Wallace E. Tyner Farzad Taheripour Purdue University The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) was created in 2005 and modified in 2007 with the objective
THE EU AND PALM OIL: WHAT S GOING ON?
 THE EU AND PALM OIL: WHAT S GOING ON? RSPO Roundtable 9 Kota Kinabalu, 24 November 2011 Nina Činkole Delegation of the European Union to Malaysia 1 PRESENTATION OUTLINE EU Context & Policy background Biofuels:
THE EU AND PALM OIL: WHAT S GOING ON? RSPO Roundtable 9 Kota Kinabalu, 24 November 2011 Nina Činkole Delegation of the European Union to Malaysia 1 PRESENTATION OUTLINE EU Context & Policy background Biofuels:
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 36 (2013 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 852 861 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment Introducing a PV Design Program Compatible with Iraq
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 852 861 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment Introducing a PV Design Program Compatible with Iraq
Thank you, Chairman Shimkus and Ranking Member Tonko. I appreciate the opportunity to
 Thank you, Chairman Shimkus and Ranking Member Tonko. I appreciate the opportunity to testify today on behalf of the National Corn Growers Association (NCGA). NCGA represents nearly 40,000 dues-paying
Thank you, Chairman Shimkus and Ranking Member Tonko. I appreciate the opportunity to testify today on behalf of the National Corn Growers Association (NCGA). NCGA represents nearly 40,000 dues-paying
Oil Refining in a CO 2 Constrained World Implications for Gasoline & Diesel Fuels
 Oil Refining in a CO 2 Constrained World Implications for Gasoline & Diesel Fuels Amir F.N. Abdul-Manan & Hassan Babiker Strategic Transport Analysis Team (STAT), Saudi Aramco Agenda 1. Global Mobility
Oil Refining in a CO 2 Constrained World Implications for Gasoline & Diesel Fuels Amir F.N. Abdul-Manan & Hassan Babiker Strategic Transport Analysis Team (STAT), Saudi Aramco Agenda 1. Global Mobility
Emission Factor of Carbon Dioxide from In-Use Vehicles in Thailand
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 6, No. 8; 2012 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Emission Factor of Carbon Dioxide from In-Use Vehicles in Thailand Sutthicha
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 6, No. 8; 2012 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Emission Factor of Carbon Dioxide from In-Use Vehicles in Thailand Sutthicha
Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged, Lean-burn, Hydrogen-fuelled, Direct Injection Engines
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 29 (2012 ) 455 462 World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2012 Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 29 (2012 ) 455 462 World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2012 Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged,
The Future for the Internal Combustion Engine and the Advantages of Octane
 The Future for the Internal Combustion Engine and the Advantages of Octane DAVE BROOKS Director, Global Propulsion Systems R&D Laboratories GM Research & Development KEY DRIVERS OF THE TRANSFORMATION
The Future for the Internal Combustion Engine and the Advantages of Octane DAVE BROOKS Director, Global Propulsion Systems R&D Laboratories GM Research & Development KEY DRIVERS OF THE TRANSFORMATION
Experimental Study on Inlet Structure of the Rod Pump with Down-hole Oil-water Hydrocyclone
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 18 (2011) 369 374 The Second SREE Conference on Oil and Gas Engineering Experimental Study on Inlet Structure of the Rod Pump with Down-hole
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 18 (2011) 369 374 The Second SREE Conference on Oil and Gas Engineering Experimental Study on Inlet Structure of the Rod Pump with Down-hole
Improving Engine Efficiency and Fuels: An Overview. John B. Heywood. Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Improving Engine Efficiency and Fuels: An Overview John B. Heywood Sun JaeProfessor of Engineering, Emeritus Massachusetts Institute of Technology Presentation at CRC Advanced Fuel and Engine Efficiency
Improving Engine Efficiency and Fuels: An Overview John B. Heywood Sun JaeProfessor of Engineering, Emeritus Massachusetts Institute of Technology Presentation at CRC Advanced Fuel and Engine Efficiency
Experimental Study on Overflow Pipe Structure of the Rod Pump with Down-hole Oil-water Hydrocyclone
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 18 (2011) 387 391 The Second SREE Conference on Oil and Gas Engineering Experimental Study on Overflow Pipe Structure of the Rod Pump with
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 18 (2011) 387 391 The Second SREE Conference on Oil and Gas Engineering Experimental Study on Overflow Pipe Structure of the Rod Pump with
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 110 (2017 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 110 (2017 ) 210 215 1st International Conference on Energy and Power, ICEP2016, 14-16 December 2016, RMIT University, Melbourne,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 110 (2017 ) 210 215 1st International Conference on Energy and Power, ICEP2016, 14-16 December 2016, RMIT University, Melbourne,
CALIFORNIA S LOW CARBON FUEL STANDARD (LCFS) REVIEW OF COMPLIANCE TRENDS
 CALIFORNIA S LOW CARBON FUEL STANDARD (LCFS) REVIEW OF COMPLIANCE TRENDS Julie Witcover Sonia Yeh Institute of Transportation Studies, UC Davis IAEE Meeting, New York, June 2014 LCFS goal: Reduce transport
CALIFORNIA S LOW CARBON FUEL STANDARD (LCFS) REVIEW OF COMPLIANCE TRENDS Julie Witcover Sonia Yeh Institute of Transportation Studies, UC Davis IAEE Meeting, New York, June 2014 LCFS goal: Reduce transport
A roadmap for the adoption of renewable jet fuels (RJF) in Europe. Sierk de Jong Utrecht University and SkyNRG
 Copernicus Institute of Sustainable Development A roadmap for the adoption of renewable jet fuels (RJF) in Europe IEA Bioenergy workshop, 9 November 216 Sierk de Jong Utrecht University and SkyNRG Combustion
Copernicus Institute of Sustainable Development A roadmap for the adoption of renewable jet fuels (RJF) in Europe IEA Bioenergy workshop, 9 November 216 Sierk de Jong Utrecht University and SkyNRG Combustion
Biofuel. academy/index.php
 Biofuel Ahyun Chung, Devin Davis, Jakob Harbers, Cecelia Kaiser, Ava Lyons, Will Medley, Annelise Nauman, Lewis Poggie, Amanthi Ranatuga, Isabel Reynolds, Kevin Wang https://www.purdue.edu/discoverypark/energy/programs/energy
Biofuel Ahyun Chung, Devin Davis, Jakob Harbers, Cecelia Kaiser, Ava Lyons, Will Medley, Annelise Nauman, Lewis Poggie, Amanthi Ranatuga, Isabel Reynolds, Kevin Wang https://www.purdue.edu/discoverypark/energy/programs/energy
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF ETHANOL AND AUTOMOTIVE GASOLINE BLENDS By
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF ETHANOL AND AUTOMOTIVE GASOLINE BLENDS By 1. Department of Mining and Petroleum Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. tarekfetouh@yahoo.com 2. Department of Chemical
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF ETHANOL AND AUTOMOTIVE GASOLINE BLENDS By 1. Department of Mining and Petroleum Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. tarekfetouh@yahoo.com 2. Department of Chemical
An easy and inexpensive way to estimate the trapping efficiency of a two stroke engine
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 82 (2015 ) 17 22 ATI 2015-70th Conference of the ATI Engineering Association An easy and inexpensive way to estimate the trapping
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 82 (2015 ) 17 22 ATI 2015-70th Conference of the ATI Engineering Association An easy and inexpensive way to estimate the trapping
The Role of Bio-ethers in Meeting National Biofuel Targets
 The Role of Bio-ethers in Meeting National Biofuel Targets Graeme Wallace (European Fuel Oxygenates Association, Brussels, Belgium) Introduction The European Union (EU) clean air strategy has consistently
The Role of Bio-ethers in Meeting National Biofuel Targets Graeme Wallace (European Fuel Oxygenates Association, Brussels, Belgium) Introduction The European Union (EU) clean air strategy has consistently
Study of the Effect of CR on the Performance and Emissions of Diesel Engine Using Butanol-diesel Blends
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 77 416, P-ISSN 47 5161 16 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Study of the
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 77 416, P-ISSN 47 5161 16 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Study of the
Fischer-Tropsch Refining
 Fischer-Tropsch Refining by Arno de Klerk A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctor (Chemical Engineering) in the Department of Chemical Engineering
Fischer-Tropsch Refining by Arno de Klerk A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctor (Chemical Engineering) in the Department of Chemical Engineering
The Clean Energy Biofuels Act of 2008: Promoting Advanced Biofuels in Massachusetts
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Conference on Cellulosic Biofuels September 2008 The Clean Energy Biofuels Act of 2008: Promoting Advanced Biofuels in Massachusetts Dwayne
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Conference on Cellulosic Biofuels September 2008 The Clean Energy Biofuels Act of 2008: Promoting Advanced Biofuels in Massachusetts Dwayne
PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM
 PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM Abstract Process Economics Program Report No. 158 SRI INTERNATIONAL Menlo Park, California 94025 OCTANE IMPROVERS FOR GASOLINE (November 1983) There la currently worldwide interest
PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM Abstract Process Economics Program Report No. 158 SRI INTERNATIONAL Menlo Park, California 94025 OCTANE IMPROVERS FOR GASOLINE (November 1983) There la currently worldwide interest
The Implementation of RenovaBio: National Biofuel Policy. Pietro A. S. Mendes, DSc Advisor of General Director
 The Implementation of RenovaBio: National Biofuel Policy Pietro A. S. Mendes, DSc Advisor of General Director Brazilian energy system structure Policymaking PRESIDENT OF REPUBLIC National Energy Policy
The Implementation of RenovaBio: National Biofuel Policy Pietro A. S. Mendes, DSc Advisor of General Director Brazilian energy system structure Policymaking PRESIDENT OF REPUBLIC National Energy Policy
Department of Energy Analyses in Support of the EPA Evaluation of Waivers of the Renewable Fuel Standard November 2012
 Department of Energy Analyses in Support of the EPA Evaluation of Waivers of the Renewable Fuel Standard November 2012 Ethanol Demand Curve for 2012 and 2013 In support of EPA analyses of the 2012 RFS
Department of Energy Analyses in Support of the EPA Evaluation of Waivers of the Renewable Fuel Standard November 2012 Ethanol Demand Curve for 2012 and 2013 In support of EPA analyses of the 2012 RFS
LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF A DIESEL AND A COMPRESSED NATURAL GAS MEDIUM-DUTY TRUCK. THE CASE OF TORONTO
 48 96 144 192 24 288 336 384 432 48 528 576 624 672 72 768 816 864 912 96 18 156 114 1152 12 1248 1296 1344 1392 144 1488 1536 1584 1632 168 1728 1776 Speed (Km/h) LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF A DIESEL AND
48 96 144 192 24 288 336 384 432 48 528 576 624 672 72 768 816 864 912 96 18 156 114 1152 12 1248 1296 1344 1392 144 1488 1536 1584 1632 168 1728 1776 Speed (Km/h) LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF A DIESEL AND
LOW CARBON FUELS IN BRITISH COLUMBIA
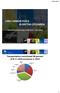 LOW CARBON FUELS IN BRITISH COLUMBIA International Bioenergy Conference June 2016 Transportation contributed 38 percent of B.C. s GHG emissions in 2012 Agriculture 3% Waste 6% Buildings 12% Other Industry
LOW CARBON FUELS IN BRITISH COLUMBIA International Bioenergy Conference June 2016 Transportation contributed 38 percent of B.C. s GHG emissions in 2012 Agriculture 3% Waste 6% Buildings 12% Other Industry
A Balanced Approach to Octane Replacement
 A Balanced Approach to Octane Replacement Policy Development Meeting on Clean Fuels and Vehicles for the Middle East and North Africa 24 May 2006 Cairo, Egypt Lee Chook Khean Communications Director http://www.acfa.org.sg
A Balanced Approach to Octane Replacement Policy Development Meeting on Clean Fuels and Vehicles for the Middle East and North Africa 24 May 2006 Cairo, Egypt Lee Chook Khean Communications Director http://www.acfa.org.sg
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 129 (2015 ) International Conference on Industrial Engineering
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 129 (2015 ) 201 206 International Conference on Industrial Engineering Simulation of lithium battery operation under severe
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 129 (2015 ) 201 206 International Conference on Industrial Engineering Simulation of lithium battery operation under severe
(i) Place a cross in the box next to a pair of greenhouse gases.
 1 First generation biofuels are made from sugars and vegetable oils found in food crops. (a) Some countries are replacing small percentages of petrol and diesel with first generation biofuels to reduce
1 First generation biofuels are made from sugars and vegetable oils found in food crops. (a) Some countries are replacing small percentages of petrol and diesel with first generation biofuels to reduce
Evaluating opportunities for soot-free, low-carbon bus fleets in Brazil: São Paulo case study
 Evaluating opportunities for soot-free, low-carbon bus fleets in Brazil: São Paulo case study Tim Dallmann International seminar Electric mobility in public bus transport: Challenges, benefits, and opportunities
Evaluating opportunities for soot-free, low-carbon bus fleets in Brazil: São Paulo case study Tim Dallmann International seminar Electric mobility in public bus transport: Challenges, benefits, and opportunities
EPA MANDATE WAIVERS CREATE NEW UNCERTAINTIES IN BIODIESEL MARKETS
 2nd Quarter 2011 26(2) EPA MANDATE WAIVERS CREATE NEW UNCERTAINTIES IN BIODIESEL MARKETS Wyatt Thompson and Seth Meyer JEL Classifications: Q11, Q16, Q42, Q48 Keywords: Biodiesel, Biofuel Mandate, Waivers
2nd Quarter 2011 26(2) EPA MANDATE WAIVERS CREATE NEW UNCERTAINTIES IN BIODIESEL MARKETS Wyatt Thompson and Seth Meyer JEL Classifications: Q11, Q16, Q42, Q48 Keywords: Biodiesel, Biofuel Mandate, Waivers
Electric vehicles a one-size-fits-all solution for emission reduction from transportation?
 EVS27 Barcelona, Spain, November 17-20, 2013 Electric vehicles a one-size-fits-all solution for emission reduction from transportation? Hajo Ribberink 1, Evgueniy Entchev 1 (corresponding author) Natural
EVS27 Barcelona, Spain, November 17-20, 2013 Electric vehicles a one-size-fits-all solution for emission reduction from transportation? Hajo Ribberink 1, Evgueniy Entchev 1 (corresponding author) Natural
Academia, Industry and Government: together for automotive engineering development
 Academia, Industry and Government: together for automotive engineering development code: EAEC- 15 009B-FEP Paper title: CO2 EMISSION DETERMINATION IN ACCORD WITH EUROPEAN REGULATION FOR OLD AND TODAY CARS
Academia, Industry and Government: together for automotive engineering development code: EAEC- 15 009B-FEP Paper title: CO2 EMISSION DETERMINATION IN ACCORD WITH EUROPEAN REGULATION FOR OLD AND TODAY CARS
14009/14 ADD 2 MS/am DG E 1B
 Council of the European Union Brussels, 7 October 2014 (OR. en) 14009/14 ADD 2 COVER NOTE From: date of receipt: 7 October 2014 To: No. Cion doc.: Subject: CLIMA 90 ENV 814 ENER 424 TRANS 465 ENT 218 IA
Council of the European Union Brussels, 7 October 2014 (OR. en) 14009/14 ADD 2 COVER NOTE From: date of receipt: 7 October 2014 To: No. Cion doc.: Subject: CLIMA 90 ENV 814 ENER 424 TRANS 465 ENT 218 IA
Sensing of Diesel Vehicle Exhaust Gases under Vibration Condition
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences () 7 Sensing of Diesel Vehicle Exhaust Gases under Vibration Condition Chuliang Wei and Zhemin Zhuang, Qin Xin, A.I. Al-Shamma
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences () 7 Sensing of Diesel Vehicle Exhaust Gases under Vibration Condition Chuliang Wei and Zhemin Zhuang, Qin Xin, A.I. Al-Shamma
Promising Alternative Fuels for Improving Emissions from Future Vehicles
 Promising Alternative Fuels for Improving Emissions from Future Vehicles Research Seminar: CTS Environment and Energy in Transportation Council Will Northrop 12/17/2014 Outline 1. Alternative Fuels Overview
Promising Alternative Fuels for Improving Emissions from Future Vehicles Research Seminar: CTS Environment and Energy in Transportation Council Will Northrop 12/17/2014 Outline 1. Alternative Fuels Overview
GHG Mitigation Potential of Biofuels in Canada
 GHG Mitigation Potential of Biofuels in Canada Stephanie Bailey Stamler Resource Efficient Agricultural Production (REAP)-Canada Toronto, Ontario sbailey@ GHG s-why They re Important Include water vapour,
GHG Mitigation Potential of Biofuels in Canada Stephanie Bailey Stamler Resource Efficient Agricultural Production (REAP)-Canada Toronto, Ontario sbailey@ GHG s-why They re Important Include water vapour,
Addressing Indirect Land Use Change in the NEMA LCFS
 Addressing Indirect Land Use Change in the NEMA LCFS Options for Discussion with Stakeholders September 29, 2010 DRAFT Sept. 29, 2010-2 This presentation presents options for consideration and discussion
Addressing Indirect Land Use Change in the NEMA LCFS Options for Discussion with Stakeholders September 29, 2010 DRAFT Sept. 29, 2010-2 This presentation presents options for consideration and discussion
Co-Optimization of Fuels and Engines
 Co-Optimization of Fuels and Engines Michael Berube, Director, DOE Vehicle Technologies Office Petroleum Equipment Institute Convention October 19, 2016 Goal: better fuels and better vehicles sooner Fuel
Co-Optimization of Fuels and Engines Michael Berube, Director, DOE Vehicle Technologies Office Petroleum Equipment Institute Convention October 19, 2016 Goal: better fuels and better vehicles sooner Fuel
Meeting the Time Varying Gasoline Engine s Octane Requirement Through On Board Fuel Blending
 Meeting the Time Varying Gasoline Engine s Octane Requirement Through On Board Fuel Blending John B. Heywood Sun Jae Professor of Engineering, Emeritus Sloan Automotive Laboratory, MIT 2 nd CRC Advanced
Meeting the Time Varying Gasoline Engine s Octane Requirement Through On Board Fuel Blending John B. Heywood Sun Jae Professor of Engineering, Emeritus Sloan Automotive Laboratory, MIT 2 nd CRC Advanced
Renewable and Low Carbon Fuel Requirements Regulation Summary:
 Summary: 2010-2017 British Columbia s (Regulation) resulted in the avoidance of over 1.36 million tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions globally in 2017, and a total of 7.73 million tonnes between 2010 and
Summary: 2010-2017 British Columbia s (Regulation) resulted in the avoidance of over 1.36 million tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions globally in 2017, and a total of 7.73 million tonnes between 2010 and
CITY OF MINNEAPOLIS GREEN FLEET POLICY
 CITY OF MINNEAPOLIS GREEN FLEET POLICY TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction Purpose & Objectives Oversight: The Green Fleet Team II. Establishing a Baseline for Inventory III. Implementation Strategies Optimize
CITY OF MINNEAPOLIS GREEN FLEET POLICY TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction Purpose & Objectives Oversight: The Green Fleet Team II. Establishing a Baseline for Inventory III. Implementation Strategies Optimize
Evaluation of Thailand Existing Motorcycle Fueled with Ethanol Blended Gasoline on Tailpipe Emissions
 The 7 th International Conference on Automotive Engineering (ICAE-7) March 28 April 1, 211, Challenger, Impact, Muang Thong Thani, Bangkok, Thailand Evaluation of Thailand Existing Motorcycle Fueled with
The 7 th International Conference on Automotive Engineering (ICAE-7) March 28 April 1, 211, Challenger, Impact, Muang Thong Thani, Bangkok, Thailand Evaluation of Thailand Existing Motorcycle Fueled with
Biofuel sustainability The issue of indirect land use change (ILUC)
 Biofuel sustainability The issue of indirect land use change () Presentation at the Annual Danish Environmental Economic Conference 27 August 2013 Content Short introduction to biofuel sustainability Issues
Biofuel sustainability The issue of indirect land use change () Presentation at the Annual Danish Environmental Economic Conference 27 August 2013 Content Short introduction to biofuel sustainability Issues
Update: Estimated GHG Increase from Obama Administration Inaction on the 2014 RFS
 Update: Estimated GHG Increase from Obama Administration Inaction on the 2014 The blend wall should not be a consideration for setting the, because the United States is using more transportation fuel in
Update: Estimated GHG Increase from Obama Administration Inaction on the 2014 The blend wall should not be a consideration for setting the, because the United States is using more transportation fuel in
Light-Duty SI Engine Technologies and the Impact of Higher Carbon Alcohol Fuels
 1 Sustainable Fuels and Clean Vehicles Light-Duty SI Engine Technologies and the Impact of Higher Carbon Alcohol Fuels Jeffrey D. Naber APSRC Center Director Ronald and Elaine Starr Professor of Energy
1 Sustainable Fuels and Clean Vehicles Light-Duty SI Engine Technologies and the Impact of Higher Carbon Alcohol Fuels Jeffrey D. Naber APSRC Center Director Ronald and Elaine Starr Professor of Energy
Well-to-wheel efficiency for fuels from natural gas and biomass. Meeting in Stockholm Peter Ahlvik, Ecotraffic ERD 3
 Well-to-wheel efficiency for fuels from natural gas and biomass Meeting in Stockholm 2003-06-17 Peter Ahlvik, Ecotraffic ERD 3 Outline Introduction and background Methodology Assumptions and conditions
Well-to-wheel efficiency for fuels from natural gas and biomass Meeting in Stockholm 2003-06-17 Peter Ahlvik, Ecotraffic ERD 3 Outline Introduction and background Methodology Assumptions and conditions
Performance Enhancement & Emission Reduction of Single Cylinder S.I. Engine using Tri Fuels -An Experimental Investigation
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Performance Enhancement & Emission Reduction of Single Cylinder S.I. Engine using Tri
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 11 May 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Performance Enhancement & Emission Reduction of Single Cylinder S.I. Engine using Tri
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF PETROL ENGINE USING FUEL CATALYST
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF PETROL ENGINE USING FUEL CATALYST Sagar.A.Patil 1, Priyanka.V.Kadam 2, Mangesh.S.Yeolekar 3, Sandip.B.Sonawane 4 1 Student (Final Year), Department
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF PETROL ENGINE USING FUEL CATALYST Sagar.A.Patil 1, Priyanka.V.Kadam 2, Mangesh.S.Yeolekar 3, Sandip.B.Sonawane 4 1 Student (Final Year), Department
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition combustion and fuel composition
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition combustion and fuel composition This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition combustion and fuel composition This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by
Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone Springs and Dynamic Absorber
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011 ) 431 435 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology 2011 Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011 ) 431 435 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology 2011 Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone
SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF GASOLINE BLENDING IN A NIGERIAN PETROLEUM REFINING COMPANY.
 GSJ: VOLUME 6, ISSUE 3, MARCH 2018 7 GSJ: Volume 6, Issue 3, March 2018, Online: ISSN 2320-9186 SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF GASOLINE BLENDING IN A NIGERIAN PETROLEUM REFINING COMPANY. JOHN T. IMINABO,
GSJ: VOLUME 6, ISSUE 3, MARCH 2018 7 GSJ: Volume 6, Issue 3, March 2018, Online: ISSN 2320-9186 SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF GASOLINE BLENDING IN A NIGERIAN PETROLEUM REFINING COMPANY. JOHN T. IMINABO,
GLOBAL AUTOMOTIVE SEMINAR. Potential and Challenges of Biofuels for Sustainable Mobility Over the Next 30 Years
 GLOBAL AUTOMOTIVE SEMINAR 16 NOVEMBER 2007 SHANGHAI AUTOMOBILE EXHIBITION CENTRE ANTING Potential and Challenges of Biofuels for Sustainable Mobility Over the Next 30 Years Simon Wardell Director, Global
GLOBAL AUTOMOTIVE SEMINAR 16 NOVEMBER 2007 SHANGHAI AUTOMOBILE EXHIBITION CENTRE ANTING Potential and Challenges of Biofuels for Sustainable Mobility Over the Next 30 Years Simon Wardell Director, Global
BOLK: Impact of biofuels on engine technology and emissions
 BOLK: Impact of biofuels on engine technology and emissions 17 April 2008 VROM, Den Haag Ruud Verbeek / Richard Smokers Contents Objectives / introduction Engine development & compatibility with renewable
BOLK: Impact of biofuels on engine technology and emissions 17 April 2008 VROM, Den Haag Ruud Verbeek / Richard Smokers Contents Objectives / introduction Engine development & compatibility with renewable
Life Cycle Assessment on the Energy Consumption and Emissions of Alternative Fuels of Automobile
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 276 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2015, 8, 276-280 Open Access Life Cycle Assessment on the Energy Consumption and Emissions of Alternative
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 276 The Open Fuels & Energy Science Journal, 2015, 8, 276-280 Open Access Life Cycle Assessment on the Energy Consumption and Emissions of Alternative
Method of Aircraft Fuel Tank System Ignition Source Fail- Safe Feature Analysis
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 17 (2011 ) 638 644 The 2nd International Symposium on Aircraft Airworthiness (ISAA 2011) Method of Aircraft Fuel Tank System Ignition Source
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 17 (2011 ) 638 644 The 2nd International Symposium on Aircraft Airworthiness (ISAA 2011) Method of Aircraft Fuel Tank System Ignition Source
Effect of Biodiesel Production on Life-Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Energy Use for Canada
 Effect of Biodiesel Production on Life-Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Energy Use for Canada Brian G. McConkey 1, Stephen Smith 2, James Dyer 3, Ravinderpal Gil 2, Suren Kulshreshtha 4, Cecil Nagy 4,
Effect of Biodiesel Production on Life-Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Energy Use for Canada Brian G. McConkey 1, Stephen Smith 2, James Dyer 3, Ravinderpal Gil 2, Suren Kulshreshtha 4, Cecil Nagy 4,
The influence of fuel injection pump malfunctions of a marine 4-stroke Diesel engine on composition of exhaust gases
 Article citation info: LEWIŃSKA, J. The influence of fuel injection pump malfunctions of a marine 4-stroke Diesel engine on composition of exhaust gases. Combustion Engines. 2016, 167(4), 53-57. doi:10.19206/ce-2016-405
Article citation info: LEWIŃSKA, J. The influence of fuel injection pump malfunctions of a marine 4-stroke Diesel engine on composition of exhaust gases. Combustion Engines. 2016, 167(4), 53-57. doi:10.19206/ce-2016-405
Optimum Matching of Electric Vehicle Powertrain
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 88 (2016 ) 894 900 CUE2015-Applied Energy Symposium and Summit 2015: Low carbon cities and urban energy systems Optimum Matching
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 88 (2016 ) 894 900 CUE2015-Applied Energy Symposium and Summit 2015: Low carbon cities and urban energy systems Optimum Matching
