ABB machinery drives. Hardware manual ACS drive modules (55 to 200 kw, 60 to 200 hp)
|
|
|
- Dylan Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ABB machinery drives Hardware manual ACS drive modules (55 to 200 kw, 60 to 200 hp)
2 List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides Code (English) ACS drive modules (0.37 to 45 kw) hardware manual 3AUA ACS drive modules (55 to 200 kw, 60 to 200 hp) hardware manual 3AUA ACS drive modules (200 to 500 kw, 250 to 600 hp) hardware manual 3AUA ACS drive modules (160 to 560 kw, 200 to 700 hp) hardware manual 3AUA ACS drive modules (0.37 to 45 kw) quick installation guide 3AUA ACS drive modules (55 to 160 kw, 75 to 200 hp) quick installation guide 3AUA Drive firmware manuals and guides ACS850 standard control program quick start-up guide ACS850 standard control program firmware manual ACS850 crane control program supplement (to std ctrl prg) ACS drives with SynRM motors (option +N7502) supplement 3AUA AUA AUA AUA Option manuals and guides ACS850 Common DC configuration for ACS drives application guide ATEX-certified Safe disconnection function for ACS850 drives (+Q971) application guide Safe torque off function for ACS850 and ACQ810 drives application guide Application programming for ACS850 and ACQ810 drives application guide 3AUA AUA AFE AUA Manuals and quick guides for I/O extension modules, fieldbus adapters, etc. You can find manuals and other product documents in PDF format on the Internet. See section Document library on the Internet on the inside of the back cover. For manuals not available in the Document library, contact your local ABB representative.
3 ACS drive modules (55 to 200 kw, 60 to 200 hp) Hardware manual 3AUA Rev C EN EFFECTIVE: ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved.
4
5 5 Safety instructions What this chapter contains This chapter contains the safety instructions which you must follow when installing, operating and servicing the drive. If ignored, physical injury or death may follow, or damage may occur to the drive, the motor, or driven equipment. Read the safety instructions before you work on the unit. Use of warnings and notes There are four types of safety instructions used in this manual: Dangerous voltage warning warns of high voltage which can cause physical injury and/or damage to the equipment. General warning warns about conditions, other than those caused by electricity, which can result in physical injury and/or damage to the equipment. Electrostatic discharge warning warns of electrostatic discharge which can damage the equipment. Hot surface warning warns of component surfaces that may become hot enough to cause burns if touched. Safety instructions
6 6 Installation and maintenance work These warnings are intended for all who work on the drive, motor cable or motor. WARNING! Ignoring the following instructions can cause physical injury or death, or damage to the equipment. Only qualified electricians are allowed to install and maintain the drive. Never work on the drive, the motor cable or the motor when input power is applied. After disconnecting the input power, always wait for 5 minutes to let the intermediate circuit capacitors discharge before you start working on the drive, the motor or the motor cable. Always ensure by measuring with a multimeter (impedance at least 1 Mohm) that: 1. There is no voltage between the drive input phases U1, V1 and W1 and the ground. 2. There is no voltage between terminals UDC+ and UDC and the ground. 3. There is no voltage between terminals R+ and R and the ground. Drives controlling a permanent magnet motor: A rotating permanent magnet motor feeds power to the drive causing the drive to become live even when it is stopped and the supply power switched off. Before maintenance work on the drive, disconnect the motor from the drive by using a safety switch prevent the start-up of any other motors in the same mechanical system lock the motor shaft measure that the motor is in fact de-energised, then connect the U2, V2 and W2 terminals of the drive to each other and to the PE. Do not work on the control cables when power is applied to the drive or to the external control circuits. Externally supplied control circuits may carry dangerous voltages even when the input power of the drive is switched off. Do not make any insulation or voltage withstand tests on the drive. Disconnect the internal EMC filter of the drive (for directions, see page 52) if the drive is to be installed on an IT power system (an ungrounded power system or a high resistance grounded [over 30 ohms] power system) or a cornergrounded power system. Notes: Even when the motor is stopped, dangerous voltages are present at the power circuit terminals U1, V1, W1 and U2, V2, W2, and UDC+, UDC, R+, R. Depending on the external wiring, dangerous voltages (115 V, 220 V or 230 V) may be present on the terminals of the relay output(s) of the drive. The drive supports the Safe torque off function. See page 43. Safety instructions
7 7 WARNING! Ignoring the following instructions can cause physical injury or death, or damage to the equipment. Never attempt to repair a malfunctioning drive; contact your local ABB representative or Authorized Service Center. Make sure that dust from drilling does not enter the drive during the installation. Electrically conductive dust inside the drive may cause damage or lead to malfunction. Ensure sufficient cooling. WARNING! The printed circuit boards contain components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Wear a grounding wrist band when handling the boards. Do not touch the boards unnecessarily. Safety instructions
8 8 Start-up and operation These warnings are intended for all who plan the operation of the drive, start up or operate the drive. WARNING! Ignoring the following instructions can cause physical injury or death, or damage to the equipment. Before adjusting the drive and putting it into service, make sure that the motor and all driven equipment are suitable for operation throughout the speed range provided by the drive. The drive can be adjusted to operate the motor at speeds above and below the speed provided by connecting the motor directly to the power line. Do not activate automatic fault reset functions if dangerous situations can occur. When activated, these functions will reset the drive and resume operation after a fault. Do not control the motor with an AC contactor or disconnecting device (disconnecting means); instead, use the control panel or external commands via the I/O board of the drive or a fieldbus adapter. The maximum allowed number of charging cycles of the DC capacitors (i.e. power-ups by applying power) is one per two minutes. Drives controlling a permanent magnet motor: Do not run the motor over the rated speed. Motor overspeed leads to overvoltage which may permanently damage the drive. Notes: If an external source for start command is selected and it is ON, the drive will start immediately after an input voltage break or a fault reset unless the drive is configured for 3-wire (pulse) start/stop. When the control location is not set to local, the stop key on the control panel will not stop the drive. WARNING! The surfaces of drive system components (such as the braking resistor, if present) may become hot when the system is in use. Safety instructions
9 9 Table of contents Safety instructions What this chapter contains Use of warnings and notes Installation and maintenance work Start-up and operation Table of contents Introduction to this manual What this chapter contains Compatibility Intended audience Categorization according to the frame size Categorization according to the + code Contents Installation and commissioning flowchart Terms and abbreviations Operation principle and hardware description What this chapter contains Product overview Layout Power connections and control interfaces Main circuit and operation Type designation key Planning the cabinet assembly What this chapter contains Cabinet construction Disposition of the devices Grounding of mounting structures Free space requirements Cooling and degrees of protection Preventing the recirculation of hot air Outside the cabinet Inside the cabinet Cabinet heaters EMC requirements Table of contents
10 10 Mechanical installation Contents of the package Moving, unpacking and checking the delivery Before installation Requirements for the installation site Connection to an IT (ungrounded) or a corner-grounded power system Installation procedure Direct surface mounting Braking resistor installation Planning the electrical installation What this chapter contains Protecting the motor insulation and bearings Checking the compatibility of the motor and drive ABB SynRM motors AC induction and permanent magnet synchronous motors Requirements table Additional requirements for explosion-safe (EX) motors Additional requirements for ABB motors of types other than M2_, M3_, M4_, HX_ and AM_ Additional requirements for the braking applications Additional requirements for ABB high-output and IP23 motors Additional requirements for non-abb high-output and IP23 motors Additional data for calculating the rise time and the peak line-to-line voltage Additional note for sine filters Supply connection Supply disconnecting device Europe Other regions Thermal overload and short circuit protection Thermal overload protection Protection against short-circuit in motor cable Protection against short-circuit in the supply cable or the drive Operating time of the fuses and circuit breakers Circuit breakers Motor thermal protection Ground fault protection Emergency stop devices Safe torque off Selecting the power cables General rules Alternative power cable types Motor cable shield Protecting the relay output contacts and attenuating disturbances in case of inductive loads Selecting the control cables Relay cable Control panel cable Connection of a motor temperature sensor to the drive I/O Table of contents
11 11 Routing the cables Control cable ducts Electrical installation What this chapter contains Removing the cover assembly Checking the insulation of the assembly Drive Supply cable Motor and motor cable Braking resistor assembly Connection to an IT (ungrounded) power system Frame size E0: Disconnection of internal EMC filtering (option +E202 included) Frame size E: Disconnection of internal EMC filtering (option +E202 included) Power cable connection Power cable connection diagram Procedure Frame size E0: Screw terminal installation Frame size E: Cable lug installation (16 to 70 mm 2 [AWG6 to AWG2/0] cables) Frame size E: Screw terminal installation (95 to 240 mm 2 [AWG3/0 to 400MCM] cables) Grounding the motor cable shield at the motor end DC connection Installation of optional modules Mechanical installation Electrical installation Connecting the control cables Control connections to the JCU control unit Jumpers External power supply for the JCU control unit (XPOW) DI6 (XDI:6) as a thermistor input Drive-to-drive link (XD2D) Safe torque off (XSTO) Grounding and routing the control cables Mounting the clamp plate Routing the control cables Installation checklist What this chapter contains Checklist Maintenance What this chapter contains Safety Maintenance intervals Table of contents
12 12 Heatsink Cooling fan Fan replacement (frame E0) Fan replacement (frame E) Additional cooling fan replacement (frame E0) Capacitors Reforming Changing Other maintenance actions Transferring the memory unit to a new drive module Technical data What this chapter contains Ratings V AC supply V AC supply V AC supply Derating Ambient temperature derating Altitude derating Dimensions, weights, noise Cooling characteristics Supply cable fuses AC input (supply) connection DC connection Motor connection JCU control unit Efficiency Cooling Degree of protection Ambient conditions Materials Applicable standards CE marking Compliance with the European Low Voltage Directive Compliance with the European EMC Directive Definitions Compliance with EN :2004, category C Compliance with EN : 2004, category C Compliance with EN : 2004, category C Compliance with the Machinery Directive C-Tick marking UL marking UL checklist Dimension drawings What this chapter contains Drive module, frame size E Table of contents
13 13 Drive module, frame size E Resistor braking What this chapter contains Braking choppers and resistors with the drive Braking choppers Braking resistor selection Chopper data / Resistor selection table Resistor installation and wiring Contactor protection of drive Braking circuit commissioning du/dt and common mode filtering What this chapter contains When is du/dt or common mode filtering required? Filter types du/dt filters Common mode filters Technical data du/dt filters Dimensions and weights Degree of protection Common mode filters Installation Further information Product and service inquiries Product training Providing feedback on ABB Drives manuals Document library on the Internet Table of contents
14 14 Table of contents
15 15 Introduction to this manual What this chapter contains Compatibility Intended audience This chapter describes the intended audience and contents of this manual. It contains a flowchart of steps in checking the delivery, installing and commissioning the drive. The flowchart refers to chapters/sections in this manual and other manuals. The manual is compatible with ACS drive modules of frame sizes E0 and E. This manual is intended for people who plan the installation, install, commission, use and service the drive. Read the manual before working on the drive. The reader is expected to know the fundamentals of electricity, wiring, electrical components and electrical schematic symbols. This manual is written for readers worldwide. Both SI and imperial units are shown wherever appropriate. Categorization according to the frame size Some instructions, technical data and dimensional drawings which concern only certain frame sizes are marked with the symbol of the frame size E0 or E. The frame size is marked on the drive designation label. The frame size of each drive type is also indicated in the rating tables in chapter Technical data. Categorization according to the + code The instructions, technical data and dimensional drawings which concern only certain optional selections are marked with + codes, e.g. +L500. The options included in the drive can be identified from the + codes visible on the type designation label of the drive. The + code selections are listed in chapter Operation principle and hardware description under Type designation key. Introduction to this manual
16 16 Contents The chapters of this manual are briefly described below. Safety instructions give safety instructions for the installation, commissioning, operation and maintenance of the drive. Introduction to this manual lists the steps in checking the delivery and installing and commissioning the drive and refers to chapters/sections in this manual and other manuals for particular tasks. Operation principle and hardware description describes the drive module. Planning the cabinet assembly guides in planning the installation of the drive module into a user-defined cabinet. Mechanical installation instructs how to place and mount the drive. Planning the electrical installation instructs on the motor and cable selection, the protections and the cable routing. Electrical installation instructs on how to wire the drive. Installation checklist contains a list for checking the mechanical and electrical installation of the drive. Maintenance lists periodic maintenance actions along with work instructions. Technical data contains the technical specifications of the drive, for example, the ratings, sizes, technical requirements and provisions for fulfilling the requirements for CE and other markings. Dimension drawings contains the dimensional drawings of the drive modules. Resistor braking describes how to select, protect and wire braking resistors. du/dt and common mode filtering lists the du/dt and common mode filtering options available for the drive. Introduction to this manual
17 17 Installation and commissioning flowchart Task Plan the installation. Check the ambient conditions, ratings, required cooling air flow, input power connection, compatibility of the motor, motor connection, and other technical data. Select the cables. See Planning the cabinet assembly (page 27) Planning the electrical installation (page 35) Technical data (page 85) Option manual (if optional equipment is included) Unpack and check the units. Check that all necessary optional modules and equipment are present and correct. Only intact units may be started up. Mechanical installation: Contents of the package (page 33) If the converter has been non-operational for more than one year, the converter DC link capacitors need to be reformed. Ask ABB for more information. Check the installation site. Mechanical installation: Before installation (page 34) Technical data (page 85) If the drive is about to be connected to an IT (ungrounded) or corner-grounded system, check that the internal EMC filtering of the drive has been disconnected. Electrical installation: Connection to an IT (ungrounded) power system (page 52) Install the drive in a cabinet. Mechanical installation: Installation procedure (page 34) Route the cables. Planning the electrical installation: Routing the cables (page 47) Check the insulation of the supply cable, the motor and the motor cable, and the resistor cable (if present). Electrical installation: Checking the insulation of the assembly (page 51) Introduction to this manual
18 18 Task Connect the power cables. Connect the control and the auxiliary control cables. See Electrical installation: Power cable connection: (page 63) and Connecting the control cables: (page 69) For optional equipment: Resistor braking (page 101) Manuals for any optional equipment Check the installation. Installation checklist (page 77) Commission the drive. Appropriate Firmware manual Commission the braking chopper if required. Resistor braking (page 101) Operating of the drive: start, stop, speed control etc. Appropriate Firmware manual Introduction to this manual
19 19 Terms and abbreviations Term/Abbreviation EMC FIO-01 FIO-11 FIO-21 FEN-01 FEN-11 FEN-21 FEN-31 FCAN-01 FDNA-01 FECA-01 FENA-11 FLON-01 FSCA-01 FPBA-01 Frame (size) IGBT I/O JCU JMU PELV RFI STO SynRM Explanation Electromagnetic compatibility Optional digital I/O extension module for the ACS850 Optional analog I/O extension module for the ACS850 Optional analog/digital I/O extension module extension for the ACS850 Optional TTL encoder interface for the ACS850 Optional absolute encoder interface for the ACS850 Optional resolver interface for the ACS850 Optional HTL encoder interface for the ACS850 Optional CANopen fieldbus adapter module for the ACS850 Optional DeviceNet fieldbus adapter module for the ACS850 Optional EtherCAT fieldbus adapter module Optional Ethernet/IP fieldbus adapter module for the ACS850 Optional LONWORKS fieldbus adapter module for the ACS850 Optional Modbus fieldbus adapter module for the ACS850 Optional PROFIBUS DP fieldbus adapter module for the ACS850 Size of the drive module. This manual deals with ACS frames E0 and E. To determine the frame size of a drive module, refer to the drive designation label attached to the drive, or the rating tables in chapter Technical data. Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor; a voltage-controlled semiconductor type widely used in inverters due to their easy controllability and high switching frequency Input/Output The control unit of the drive module. The JCU is installed on top of the power unit. The external I/O control signals are connected to the JCU, or optional I/O extensions mounted on it. The memory unit attached to the control unit of the drive Protective extra low voltage Radio-frequency interference Safe torque off Synchronous reluctance motor Introduction to this manual
20 20 Introduction to this manual
21 21 Operation principle and hardware description What this chapter contains Product overview Layout This chapter describes the construction and operating principle of the drive in short. The ACS is an IP20 drive module for controlling AC motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors and ABB synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM motors). It is to be installed into a cabinet by the customer. The ACS is available in several frame sizes depending on output power. All frame sizes use the same control unit (type JCU). This manual only deals with frame sizes E0 and E. Cooling air outlet JCU control unit with cover assembly removed External 24 V power input Relay outputs JCU control unit +24 V output Digital inputs Slots 1 and 2 for optional I/O extensions and encoder/resolver interface Digital inputs/outputs Reference voltage and analog inputs Analog outputs Drive-to-drive link Slot 3 for optional fieldbus adapter Safe torque off connection AC supply, DC, braking resistor and motor connections Cooling air inlet with fan Control panel/pc connection Memory unit (JMU) connection Operation principle and hardware description
22 22 Power connections and control interfaces The diagram shows the power connections and control interfaces of the drive. Slot 1 / Slot 2 FIO-01 (Digital I/O extension) FIO-11 (Analog I/O extension) FIO-21 (Digital/Analog I/O extension) FEN-01 (Incremental [TTL] encoder interface) FEN-11 (Absolute encoder interface) FEN-21 (Resolver interface) FEN-31 (Incremental [HTL] encoder interface) Note: No two encoder/resolver interfaces of the same type can be connected at a time Slot 3 (Fieldbus adapter) FCAN-01 (CANopen) FDNA-01 (DeviceNet ) FECA-01 (EtherCAT ) FENA-11 (Ethernet/IP ) FLON-01 (LONWORKS ) FSCA-01 (Modbus) FPBA-01 (PROFIBUS DP) Fxx Fxx Fxxx Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Control unit (JCU) Memory unit 1) External power input XPOW Relay outputs 2) XRO V output XD24 Digital inputs 2) XDI Digital inputs/outputs 2) XDIO Reference voltage and XAI analog inputs 2) Analog outputs 2) XAO Drive-to-drive link XD2D Safe torque off XSTO Control panel or PC 1) See page 84. For more information on these connections, see page 69. For specifications, see page 88. 2) Programmable 3-phase power supply PE L1 L2 L3 PE U1 V1 W1 Power unit Braking chopper R- UDC+ R+ UDC- U2 V2 W2 M 3 ~ AC motor Braking resistor (optional) t Operation principle and hardware description
23 23 Main circuit and operation AC supply UDC+ UDC- U1 V1 W1 ACS Rectifier Capacitor bank Inverter U2 V2 W2 R- R+ Braking chopper (see chapter Resistor braking on page 101) du/dt filter (see chapter du/dt and common mode filtering on page 105) Motor output Braking resistor (see chapter Resistor braking on page 101) This table describes the operation of the main circuit in short. Component Description Rectifier Converts the three-phase AC voltage to DC voltage. Inverter Converts the DC voltage to AC voltage and vice versa. The motor is controlled by switching the IGBTs of the inverter. Capacitor bank Energy storage which stabilizes the intermediate circuit DC voltage. Braking chopper Conducts the energy generated by a decelerating motor from the DC bus to a braking resistor. The braking chopper is built in the ACS850-04; braking resistors are external options. Braking resistor Dissipates the regenerative energy by converting it to heat. du/dt filter See page 105. Operation principle and hardware description
24 24 Type designation key The type designation key contains information on the specifications and configuration of the drive. The first digits from left express the basic configuration (for example, ACS A-5). The optional selections are given thereafter, preceded by + signs (for example, +L501). The main selections are described below. Not all selections are necessarily available for all types; refer to ACS Ordering Information, available on request. See also section Moving, unpacking and checking the delivery on page 33. Selection Alternatives Product series ACS850 product series Type 04 Drive module. When no options are selected: IP20 (UL Open type), plain front cover, no control panel, no EMC filter, boards with coating, Safe torque off, ACS850 standard control program, Quick installation guide (multilingual), Quick start-up guide (multilingual) and CD containing all manuals Size Refer to Technical data: Ratings. Voltage range V AC + options Resistor braking D +D150: Braking chopper Filters E +E210: EMC/RFI-filter, C3, 2nd Environment, Unrestricted (Earthed & Unearthed Networks) +E202: EMC/RFI-filter, C2, 1st Environment, Restricted (Earthed Network) Control panel and control unit mechanics J +0C168: No control unit cover, no control panel +J400: Control panel mounted on drive module front cover +J410: Control panel with door mounting platform kit including 3 m cable +J414: Control panel mounting platform on drive module (no control panel included) Fieldbus K... +K451: FDNA-01 DeviceNet fieldbus adapter module +K454: FPBA-01 PROFIBUS DP fieldbus adapter module +K457: FCAN-01 CANopen fieldbus adapter module +K473: FENA-11 Ethernet/IP fieldbus adapter module +K458: FSCA-01 Modbus fieldbus adapter module +K452: FLON-01 LONWORKS fieldbus adapter module +K469: FECA-01 EtherCAT fieldbus adapter module I/O extensions and feedback interfaces L... +L500: FIO-11 analog I/O extension module +L501: FIO-01 digital I/O extension module +L519: FIO-21 analog/digital I/O extension module +L502: FEN-31 HTL encoder interface module +L516: FEN-21 resolver interface module +L517: FEN-01 TTL encoder interface module +L518: FEN-11 absolute encoder interface module Programs N... +N5050, +N3050: Crane control program. See ACS850 crane control program supplement (to std ctrl prg) (3AUA [English]). +N7502: SynRM control program Specialities P +P904: Extended warranty +Q971: ATEX certified safe disconnection Operation principle and hardware description
25 25 Selection Printed hardware and firmware manuals in specified language (English manuals will be delivered despite of the selection if no manuals in selected language exist) Alternatives R +R700: English +R701: German +R702: Italian +R703: Dutch +R704: Danish +R705: Swedish +R706: Finnish +R707: French +R708: Spanish +R709: Portuguese +R710: Portuguese spoken in Brazil +R711: Russian +R712: Chinese +R714: Turkish Operation principle and hardware description
26 26 Operation principle and hardware description
27 27 Planning the cabinet assembly What this chapter contains This chapter guides in planning the installation of a drive module into a user-defined cabinet. The issues discussed are essential for safe and trouble-free use of the drive system. Note: Please note that the installation must always be designed and made according to applicable local laws and regulations. ABB does not assume any liability whatsoever for any installation which breaches the local laws and/or other regulations. Cabinet construction The cabinet frame must be sturdy enough to carry the weight of the drive components, control circuitry and other equipment installed in it. The cabinet must protect the drive module against contact and meet the requirements for dust and humidity (see chapter Technical data). Disposition of the devices For easy installation and maintenance, a spacious layout is recommended. Sufficient cooling air flow, obligatory clearances, cables and cable support structures all require space. For layout examples, see section Cooling and degrees of protection below. Grounding of mounting structures Make sure all cross-members or shelves on which drive system components are mounted are properly grounded and the connecting surfaces left unpainted. Note: Ensure that the components are properly grounded through their fastening points to the installation base. Planning the cabinet assembly
28 28 Free space requirements The modules can be installed side by side. The dimensions of the drive modules are presented in chapter Dimension drawings. The free space requirements (valid for both frame sizes) are shown below. Free space above the module: 200 mm (7.9 ) Free space in front of the module: 50 mm (2.0 ) Free space below the module: 300 mm (12 ) The temperature of the cooling air entering the unit must not exceed the maximum allowed ambient temperature (see Ambient conditions in chapter Technical data). Consider this when installing heat-generating components (such as other drives, mains chokes and braking resistors) nearby. Planning the cabinet assembly
29 29 Cooling and degrees of protection The cabinet must have enough free space for the components to ensure sufficient cooling. Observe the minimum clearances given for each component. The air inlets and outlets must be equipped with gratings that guide the air flow protect against contact prevent water splashes from entering the cabinet. The drawing below shows two typical cabinet cooling solutions. The air inlet is at the bottom of the cabinet, while the outlet is at the top, either on the upper part of the door or on the roof. Air outlet Air inlet Arrange the cooling air flow through the modules so that the requirements given in chapter Technical data are met: cooling air flow Note: The values in Technical data apply to continuous nominal load. If the load is less than nominal, less cooling air is required. allowed ambient temperature. Make sure the air inlets and outlets are sufficient in size. Please note that in addition to the power loss of the drive module, the heat dissipated by cables and other additional equipment must also be ventilated. The internal cooling fans of the modules are usually sufficient to keep the component temperatures low enough in IP22 cabinets. In IP54 cabinets, thick filter mats are used to prevent water splashes from entering the cabinet. This entails the installation of additional cooling equipment, such as a hot air exhaust fan. The installation site must be sufficiently ventilated. Planning the cabinet assembly
30 30 Preventing the recirculation of hot air Typical vertical mounting Cabinet (side view) HOT AREA Main airflow out Air baffle plates COOL AREA Main airflow in Outside the cabinet Prevent hot air circulation outside the cabinet by leading the outcoming hot air away from the area where the inlet air to the cabinet is taken. Possible solutions are listed below: gratings that guide air flow at the air inlet and outlet air inlet and outlet at different sides of the cabinet cool air inlet in the lower part of the front door and an extra exhaust fan on the roof of the cabinet. Inside the cabinet Prevent hot air circulation inside the cabinet with leak-proof air baffle plates; make sure the air vents of the drive module remain clear. No gaskets are usually required. Planning the cabinet assembly
31 31 Cabinet heaters EMC requirements Use a cabinet heater if there is a risk of condensation in the cabinet. Although the primary function of the heater is to keep the air dry, it may also be required for heating at low temperatures. When placing the heater, follow the instructions provided by its manufacturer. Generally, the fewer and smaller the holes in the cabinet, the better the interference attenuation. The maximum recommended diameter of a hole in galvanic metal contact in the covering cabinet structure is 100 mm. Special attention must be paid to the cooling air inlet and outlet gratings. The best galvanic connection between the steel panels is achieved by welding them together as no holes are necessary. If welding is not possible, the seams between the panels are recommended to be left unpainted and equipped with special conductive EMC strips to provide adequate galvanic connection. Usually, reliable strips are made of flexible silicon mass covered with a metal mesh. The nontightened touch-contact of the metal surfaces is not sufficient, so a conductive gasket between the surfaces is required. The maximum recommended distance between assembly screws is 100 mm. Sufficient high-frequency grounding network must be constructed in the cabinet to avoid voltage differences and forming of high-impedance radiator structures. A good high-frequency grounding is made with short flat copper braids for low inductance. One-point high-frequency grounding cannot be used due to the long distances inside the cabinet. First environment EMC compliance (defined under Compliance with the European EMC Directive in chapter Technical data) of the drive requires 360 high frequency grounding of the motor cable shields at their entries. The grounding can be implemented by a knitted wire mesh shielding as shown below. Cable ties Bare cable shield Knitted wire mesh Lead-through plate Cable Cabinet bottom plate Planning the cabinet assembly
32 high frequency grounding of the control cable shields is recommended at their entries. The shields can be grounded by means of conductive shielding cushions pressed against the cable shield from both directions: Bare cable shield Shielding cushion (conductive) Cabinet bottom plate Cable grommet Cable Planning the cabinet assembly
33 33 Mechanical installation Contents of the package The drive is delivered in a box made of plywood and cardboard. The box contains: drive module, with factory-installed options one cable clamp plate for control cabling with screws screw-type terminal blocks to be attached to the headers on the JCU control unit control panel mounting kit if ordered with option code +J410 printed Quick guides (multilingual), manuals CD, printed manuals if ordered. Moving, unpacking and checking the delivery Move the transport package by pallet truck to the installation site. Check that all items shown in the package layout drawings below are present. Check that there are no signs of damage. Check the information on the type designation label of the drive to verify that the unit is of the correct type. The label is located on the left-hand side of the drive module. Type designation key + options (see page 24) Compliance markings Frame size Ratings Serial number The first digit of the serial number refers to the manufacturing plant. The 2nd and 3rd digit indicate the year of manufacture, while the 4th and 5th digits indicate the week. Digits 6 to 10 are a running integer starting every week at Mechanical installation
34 34 Before installation Check the installation site according to the requirements below. Refer to Dimension drawings for frame details. Requirements for the installation site See chapter Technical data for the allowed operation conditions of the drive. The drive is to be mounted in an upright position. The surface that the drive is to be mounted on must be as even as possible, of non-flammable material and strong enough to carry the weight of the drive. The floor/material below the drive must be non-flammable. Connection to an IT (ungrounded) or a corner-grounded power system The internal EMC filter must be disconnected if the drive is to be supplied from a corner-grounded power system or an IT power system [an ungrounded power system or a high resistance-grounded (over 30 ohms) power system]. As the procedure involves the removal of drive module covers, it is convenient to perform it before the drive is installed. See page 52 for directions. Installation procedure Direct surface mounting 1. Mark the locations for the four holes. The mounting points are shown in Dimension drawings. 2. Fix the screws or bolts to the marked locations. 3. Position the drive onto the screws on the surface. Note: Only lift the drive by its lifting holes. 4. Tighten the screws. Braking resistor installation See chapter Resistor braking on page 101. Mechanical installation
35 35 Planning the electrical installation What this chapter contains This chapter contains the instructions that you must follow when selecting the motor, cables, protections, cable routing and way of operation for the drive. If the recommendations given by ABB are not followed, the drive may experience problems that the warranty does not cover. Note: The installation must always be designed and made according to applicable local laws and regulations. ABB does not assume any liability whatsoever for any installation which breaches the local laws and/or other regulations. Protecting the motor insulation and bearings The drive employs modern IGBT inverter technology. Regardless of frequency, the drive output comprises pulses of approximately the drive DC bus voltage with a very short rise time. The pulse voltage can almost double at the motor terminals, depending on the attenuation and reflection properties of the motor cable and the terminals. This can cause additional stress on the motor and motor cable insulation. Modern variable speed drives with their fast rising voltage pulses and high switching frequencies can generate current pulses that flow through the motor bearings. This can gradually erode the bearing races and rolling elements. Optional du/dt filters protect motor insulation system and reduce bearing currents. Optional common mode filters mainly reduce bearing currents. Insulated N-end (non-drive end) bearings protect the motor bearings. Checking the compatibility of the motor and drive Use an asynchronous AC induction motor, a permanent magnet synchronous motor or an ABB synchronous reluctance motor (SynRM, option +N7502) with the drive. ABB SynRM motors ABB provides compatible packages of a SynRM motor and a drive, refer to ACS drives with SynRM motors (option +N7502) supplement (3AUA [English]). AC induction and permanent magnet synchronous motors Several induction motors can be connected to the drive at a time Only one permanent magnet synchronous motor can be connected to the inverter output. It is recommended to install a safety switch between the permanent magnet synchronous motor and the drive output in order to isolate the motor from the drive during maintenance work on the drive. Planning the electrical installation
36 36 Select the motor size and drive type from to the rating tables in chapter Technical data on basis of the AC line voltage and motor load. Use the DriveSize PC tool if you need to tune the selection more in detail. 1. Check that the motor ratings lie within the allowed ranges of the drive control program: motor nominal voltage is in the range of 1/2...2 U N motor nominal current is 1/ I Hd of the drive in DTC control and I Hd in scalar control. The control mode is selected by a control program parameter. 2. Check that the motor voltage rating meets the application requirements: When No resistor braking is in use Frequent or long term brake cycles will be used U N Input voltage of the drive the motor voltage rating should be U N 1.21 U N See chapter Resistor braking on page Consult the motor manufacturer before using a motor in a drive system where the motor nominal voltage differs from the AC power source voltage. 4. Ensure that the motor insulation system withstands the maximum peak voltage in the motor terminals. See the Requirements table below for the required motor insulation system and drive filtering. Example 1: When the supply voltage is 440 V and the drive is operating in the motor mode only, the maximum peak voltage in the motor terminals can be approximated as follows: 440 V = 1190 V. Check that the motor insulation system withstands this voltage. Planning the electrical installation
37 37 Requirements table The following table shows how to select the motor insulation system and when an optional drive du/dt and common mode filters and insulated N-end (non-drive end) motor bearings are required. ignoring the requirements or improper installation may shorten motor life or damage the motor bearings and voids the warranty. Motor type Nominal AC supply Requirement for voltage Motor insulation system ABB du/dt and common mode filters, insulated N-end motor bearings P N < 100 kw and frame size < IEC 315 P N < 134 hp and frame size < NEMA 500 ABB motors Random-wound M2_, M3_ and M4_ U N < 500 V Standard V < U N < 600 V Standard + du/dt or Reinforced V < U N < 690 V Reinforced + du/dt (cable length < 150 m) 600 V < U N < 690 V Reinforced - (cable length > 150 m) Form-wound HX_ and AM_ 380 V < U N < 690 V Standard n.a. Old* form-wound HX_ and modular 380 V < U N < 690 V Check with the motor manufacturer. Random-wound HX_ and AM_ ** 0 V < U N < 500 V Enamelled wire with fiber glass taping + du/dt with voltages over 500 V + N + CMF + N + CMF 500 V < U N < 690 V + du/dt + N + CMF HDP Consult the motor manufacturer. non-abb motors Random-wound and form-wound U N < 420 V Standard: Û LL = 1300 V V < U N < 500 V Standard: Û LL = 1300 V + du/dt or Reinforced: Û LL = 1600 V, microsecond rise time 500 V < U N < 600 V Reinforced: Û LL = 1600 V + du/dt or Reinforced: Û LL = 1800 V V < U N < 690 V Reinforced: Û LL = 1800 V + du/dt Reinforced: Û LL = 2000 V, 0.3 microsecond rise time *** - * manufactured before ** For motors manufactured before , check for additional instructions with the motor manufacturer. *** If the intermediate DC circuit voltage of the drive is increased from the nominal level by resistor braking, check with the motor manufacturer if additional output filters are needed in the applied drive operation range. Planning the electrical installation
38 38 The abbreviations used in the table are defined below. Abbr. U N Û LL P N du/dt CMF N n.a. Definition Nominal AC line voltage Peak line-to-line voltage at motor terminals which the motor insulation must withstand Motor nominal power du/dt filter at the output of the drive (option +E205) Common mode filter (option +E208) N-end bearing: insulated motor non-drive end bearing Motors of this power range are not available as standard units. Consult the motor manufacturer. Additional requirements for explosion-safe (EX) motors If you will use an explosion-safe (EX) motor, follow the rules in the requirements table above. In addition, consult the motor manufacturer for any further requirements. Additional requirements for ABB motors of types other than M2_, M3_, M4_, HX_ and AM_ Use the selection criteria given for non-abb motors. Additional requirements for the braking applications When the motor brakes the machinery, the intermediate circuit DC voltage of the drive increases, the effect being similar to increasing the motor supply voltage by up to 20 percent. Consider this voltage increase when specifying the motor insulation requirements if the motor will be braking a large part of its operation time. Example: Motor insulation requirement for a 400 V AC line voltage application must be selected as if the drive were supplied with 480 V. Additional requirements for ABB high-output and IP23 motors The rated output power of high output motors is higher than what is stated for the particular frame size in EN (2001). This table shows the requirements for ABB random-wound motor series (for example, M3AA, M3AP and M3BP). Nominal mains voltage (AC line voltage) Requirement for Motor insulation system ABB du/dt and common mode filters, insulated N-end motor bearings P N < 100 kw U N < 500 V Standard V < U N < 600 V Standard + du/dt or Reinforced V < U N < 690 V Reinforced + du/dt P N < 140 hp Planning the electrical installation
39 39 Additional requirements for non-abb high-output and IP23 motors The rated output power of high output motors is higher than what is stated for the particular frame size in EN (2001). The table below shows the requirements for random-wound and form-wound non-abb motors. Nominal AC line voltage Requirement for Motor insulation system ABB du/dt filter, insulated N-end bearing and ABB common mode filter P N < 100 kw or frame size < IEC 315 P N < 134 hp or frame size < NEMA 500 U N < 420 V Standard: Û LL = 1300 V + N or CMF 420 V < U N < 500 V Standard: Û LL = 1300 V + du/dt + (N or CMF) or Reinforced: Û LL = 1600 V, + N or CMF 0.2 microsecond rise time 500 V < U N < 600 V Reinforced: Û LL = 1600 V + du/dt + (N or CMF) or Reinforced: Û LL = 1800 V + N or CMF 600 V < U N < 690 V Reinforced: Û LL = 1800 V + du/dt + N Reinforced: Û LL = 2000 V, 0.3 microsecond rise time *** N + CMF *** If the intermediate DC circuit voltage of the drive is increased from the nominal level by resistor braking, check with the motor manufacturer if additional output filters are needed in the applied drive operation range. Additional data for calculating the rise time and the peak line-to-line voltage If you need to calculate the actual peak voltage and voltage rise time considering the actual cable length, proceed as follows: Peak line-to line voltage: Read the relative Û LL /U N value from the appropriate diagram below and multiply it by the nominal supply voltage (U N ). Planning the electrical installation
40 40 Voltage rise time: Read the relative values Û LL /U N and (du/dt)/u N from the appropriate diagram below. Multiply the values by the nominal supply voltage (U N ) and substitute into equation t = 0.8 Û LL /(du/dt) A 5.5 Û LL /U N B du/dt (1/ s) U N du/dt (1/ s) U N Û LL /U N l (m) l (m) A Drive with du/dt filter B Drive without du/dt filter I Motor cable length Û LL /U N Relative peak line-to-line voltage (du/dt)/u N Relative du/dt value Note: ÛLL and du/dt values are approximately 20% higher with resistor braking. Additional note for sine filters Sine filters protect the motor insulation system. Therefore, du/dt filter can be replaced with a sine filter. The peak phase-to-phase voltage with the sine filter is approximately 1.5 U N. Supply connection Use a fixed connection to the AC power line. WARNING! As the leakage current of the device typically exceeds 3.5 ma, a fixed installation is required according to IEC Planning the electrical installation
41 41 Supply disconnecting device Install a hand-operated input disconnecting device (disconnecting means) between the AC power source and the drive. The disconnecting device must be of a type that can be locked to the open position for installation and maintenance work. Europe If the drive is used in an application which must meet the European Union Machinery Directive according to standard EN Safety of Machinery, the disconnecting device must be one of the following types: a switch-disconnector of utilization category AC-23B (EN ) a disconnector that has an auxiliary contact that in all cases causes switching devices to break the load circuit before the opening of the main contacts of the disconnector (EN ) a circuit breaker suitable for isolation in accordance with EN Other regions The disconnecting means must conform to the applicable safety regulations. For more information, see page 94. Thermal overload and short circuit protection Thermal overload protection The drive protects itself and the input and motor cables against thermal overload when the cables are dimensioned according to the nominal current of the drive. No additional thermal protection devices are needed. WARNING! If the drive is connected to multiple motors, a separate thermal overload switch or a circuit breaker must be used for protecting each cable and motor. These devices may require a separate fuse to cut off the short-circuit current. Protection against short-circuit in motor cable The drive protects the motor cable and the motor in a short-circuit situation when the motor cable is dimensioned according to the nominal current of the drive. No additional protection devices are needed. Protection against short-circuit in the supply cable or the drive Protect the supply cable with fuses or circuit breakers. Fuse recommendations are given in chapter Technical data. When placed at the distribution board, standard IEC gg fuses or UL type T fuses will protect the input cable in short-circuit situations, restrict drive damage and prevent damage to adjoining equipment in case of a short circuit inside the drive. Planning the electrical installation
42 42 Operating time of the fuses and circuit breakers The operating time depends on the type, the supply network impedance, and the cross-sectional area, material and length of the supply cable. US fuses must be of the non-time delay type. Circuit breakers The protective characteristics of circuit breakers depend on the supply voltage as well as the type and construction of the breakers. There are also limitations pertaining to the short-circuit capacity of the supply network. Your local ABB representative can help you in selecting the breaker type when the supply network characteristics are known. Motor thermal protection According to regulations, the motor must be protected against thermal overload and the current must be switched off when overloading is detected. The drive includes a motor thermal protection function that protects the motor and switches off the current when necessary. Depending on a drive parameter value, the function either monitors a calculated temperature value (based on a motor thermal model) or an actual temperature indication given by motor temperature sensors. The user can tune the thermal model further by feeding in additional motor and load data. KTY84, PTC or Pt100 sensors can be connected to the ACS See page 71 in this manual, and the appropriate Firmware manual for the parameter settings concerning motor thermal protection. Ground fault protection The drive is equipped with an internal ground fault protective function to protect the unit against ground faults in the motor and the motor cable. This is not a personal safety or a fire protection feature. The ground fault protective function can be disabled with a parameter, refer to the appropriate Firmware manual. The internal mains filter includes capacitors connected between the main circuit and the frame. These capacitors and long motor cables increase the ground leakage current and may cause fault current circuit breakers to function. Emergency stop devices For safety reasons, install the emergency stop devices at each operator control station and at other operating stations where emergency stop may be needed. Note: Pressing the stop key on the control panel of the drive does not generate an emergency stop of the motor or separate the drive from dangerous potential. Planning the electrical installation
43 43 Safe torque off The drive supports the Safe torque off function (STO) according to standards EN :2007; EN ISO :2008, IEC 61508, IEC 61511:2004 and EN 62061:2005. The function also corresponds to prevention of unexpected start-up of EN The Safe torque off function disables the control voltage of the power semiconductors of the drive output stage, thus preventing the inverter from generating the voltage required to rotate the motor (see the diagram below). By using this function, short-time operations (like cleaning) and/or maintenance work on non-electrical parts of the machinery can be performed without switching off the power supply to the drive. Start up and validate the Safe torque off function according to Safe torque off function for ACS850 and ACQ810 drives application guide (3AFE [English]). The manual includes the safety data for the function. Drive +24 V XSTO:1 XSTO:2 Safe torque off connection on JCU Activation switch XSTO:3 XSTO:4 UDC+ Control circuit Output stage (1 phase shown) U2/V2/W2 UDC- Notes: The contacts of the activation switch must open/close within 200 ms of each other. The maximum cable length between the drive and the activation switch is 25 m (82 ft) WARNING! The Safe torque off function does not disconnect the voltage of the main and auxiliary circuits from the drive. Therefore maintenance work on electrical parts of the drive or the motor can only be carried out after isolating the drive system from the main supply. Planning the electrical installation
44 44 Note: It is not recommended to stop the drive by using the Safe torque off function. If a running drive is stopped by using the function, the drive will trip and stop by coasting. If this causes danger or is not acceptable, the drive and machinery must be stopped using the appropriate stopping mode before using the Safe torque off function. For further information on the function, refer to Safe torque off function for ACS850 and ACQ810 drives application guide (3AFE [English]). Note concerning permanent magnet motor drives in case of a multiple IGBT power semiconductor failure: In spite of the activation of the Safe torque off function, the drive system can produce an alignment torque which maximally rotates the motor shaft by 180/p degrees. p denotes the pole pair number. Selecting the power cables General rules Dimension the supply (input power) and motor cables according to local regulations. The cable must be able to carry the drive load current. See chapter Technical data for the rated currents. The cable must be rated for at least 70 C (US: 75 C [167 F]) maximum permissible temperature of conductor in continuous use. The inductance and impedance of the PE conductor/cable (grounding wire) must be rated according to permissible touch voltage appearing under fault conditions (so that the fault point voltage will not rise excessively when a ground fault occurs). 600 V AC cable is accepted for up to 500 V AC. Refer to chapter Technical data for EMC requirements. Symmetrical shielded motor cable must be used (see the figure below) to meet the EMC requirements of the CE and C-tick marks. A four-conductor system is allowed for input cabling, but shielded symmetrical cable is recommended. To operate as a protective conductor, the shield conductivity must be as follows when the protective conductor is made of the same metal as the phase conductors: Cross-sectional area of one phase conductor (S) S < 16 mm 2 Minimum cross-sectional area of protective conductor (S p ) S 16 mm 2 < S < 35 mm 2 16 mm 2 35 mm 2 < S S/2 Planning the electrical installation
45 45 Compared to a four-conductor system, the use of symmetrical shielded cable reduces electromagnetic emission of the whole drive system as well as motor bearing currents and wear. The motor cable and its PE pigtail (twisted shield) should be kept as short as possible in order to reduce electromagnetic emission, as well as stray currents outside the cable and capacitive current. Alternative power cable types Power cable types that can be used with the drive are represented below. Motor cable (also recommended for supply cabling) Symmetrical shielded cable: three phase conductors and a concentric or otherwise symmetrically constructed PE conductor, and a shield Note: A separate PE conductor is required if the conductivity of the cable shield is not sufficient for the purpose. PE conductor and shield Shield Shield PE PE Allowed for supply cabling Shield A four-conductor system: three phase conductors and a protective conductor. PE PE Motor cable shield To function as a protective conductor, the shield must have the same cross-sectional area as a phase conductor when they are made of the same metal. To effectively suppress radiated and conducted radio-frequency emissions, the shield conductivity must be at least 1/10 of the phase conductor conductivity. The requirements are easily met with a copper or aluminium shield. The minimum requirement of the motor cable shield of the drive is shown below. It consists of a concentric layer of copper wires with an open helix of copper tape. The better and tighter the shield, the lower the emission level and the bearing currents. Insulation jacket Copper wire screen Helix of copper tape Inner insulation Cable core Planning the electrical installation
46 46 Protecting the relay output contacts and attenuating disturbances in case of inductive loads Inductive loads (relays, contactors, motors) cause voltage transients when switched off. The relay output on the drive is protected with varistors (250 V) against overvoltage peaks. In addition, it is highly recommended to equip inductive loads with noise attenuating circuits (varistors, RC filters [AC] or diodes [DC]) in order to minimize the electromagnetic emissions at switch-off. If not suppressed, the disturbances may connect capacitively or inductively to other conductors in the control cable and form a risk of malfunction in other parts of the system. Install the protective component as close to the inductive load as possible, not at the relay output. Varistor Relay output 230 VAC RC filter Relay output 230 VAC Diode Relay output 24 VDC Planning the electrical installation
47 47 Selecting the control cables It is recommended that all control cables be shielded. Double-shielded twisted pair cable is recommended for analogue signals. For pulse encoder cabling, follow the instructions given by the encoder manufacturer. Use one individually-shielded pair for each signal. Do not use a common return for different analogue signals. Double-shielded cable is the best alternative for low-voltage digital signals but single-shielded twisted multipair cable (Figure b) is also usable. a Double-shielded twisted pair cable b Single-shielded twisted multipair cable Run analogue and digital signals in separate cables. Relay-controlled signals, providing their voltage does not exceed 48 V, can be run in the same cables as digital input signals. It is recommended that the relay-controlled signals be run as twisted pairs. Never mix 24 V DC and 115/230 V AC signals in the same cable. Relay cable The cable type with braided metallic screen (e.g. ÖLFLEX by Lapp Kabel, Germany) has been tested and approved by ABB. Control panel cable The cable connecting the control panel to the drive must not exceed 3 metres in length. The cable type tested and approved by ABB is used in control panel option kits. Connection of a motor temperature sensor to the drive I/O See page 71. Routing the cables Route the motor cable away from other cable routes. Motor cables of several drives can be run in parallel installed next to each other. It is recommended that the motor cable, input power cable and control cables be installed on separate trays. Avoid long parallel runs of motor cables with other cables in order to decrease electromagnetic interference caused by the rapid changes in the drive output voltage. Planning the electrical installation
48 48 Where control cables must cross power cables make sure they are arranged at an angle as near to 90 degrees as possible. Do not run extra cables through the drive. The cable trays must have good electrical bonding to each other and to the grounding electrodes. Aluminium tray systems can be used to improve local equalizing of potential. A diagram of the cable routing is below. Supply cable Motor cable min 300 mm (12 ) Drive Control cables Supply cable min 200 mm (20 ) 90 min 500 mm (20 ) Motor cable 90 Braking resistor cable 90 min 500 mm (20 ) Control cable ducts 24 V 230 V 24 V 230 V Not allowed unless the 24 V cable is insulated for 230 V or insulated with an insulation sleeving for 230 V. Lead 24 V and 230 V control cables in separate ducts inside the cabinet. Planning the electrical installation
49 49 Electrical installation What this chapter contains This chapter describes the electrical installation procedure of the drive. WARNING! The work described in this chapter may only be carried out by a qualified electrician. Follow the Safety instructions on the first pages of this manual. Ignoring the safety instructions can cause injury or death. Make sure that the drive is disconnected from the supply (input power) during installation. If the drive is already connected to the supply, wait for 5 minutes after disconnecting the input power. Removing the cover assembly The cover assembly needs to be removed before the installation of optional modules and the connection of control cabling. Follow this procedure to remove the cover assembly. The numbers refer to the illustrations below. Press the tab (1) slightly with a screwdriver. Slide the lower cover plate slightly downwards and pull it out (2). Disconnect the panel cable (3) if present. Remove the screw (4) at the top of the cover assembly. Carefully pull the lower part of the base outwards by the two tabs (5). Refit the cover in reverse order to the above procedure. Electrical installation
50 Electrical installation
51 51 Checking the insulation of the assembly Drive Do not make any voltage tolerance or insulation resistance tests on any part of the drive as testing can damage the drive. Every drive has been tested for insulation between the main circuit and the chassis at the factory. Also, there are voltagelimiting circuits inside the drive which cut down the testing voltage automatically. Supply cable Check the insulation of the supply (input) cable according to local regulations before connecting to the drive. Motor and motor cable Check the insulation of the motor and motor cable as follows: 1. Check that the motor cable is connected to the motor, and disconnected from the drive output terminals U2, V2 and W2. 2. Measure the insulation resistance between each phase conductor and the Protective Earth conductor using a measuring voltage of 500 V DC. The insulation resistance of an ABB motor must exceed 100 Mohm (reference value at 25 C or 77 F). For the insulation resistance of other motors, please consult the manufacturer s instructions. Note: Moisture inside the motor casing will reduce the insulation resistance. If moisture is suspected, dry the motor and repeat the measurement. ohm U1 M V1 3~ W1 PE Braking resistor assembly Check the insulation of the braking resistor assembly (if present) as follows: 1. Check that the resistor cable is connected to the resistor, and disconnected from the drive output terminals R+ and R-. 2. At the drive end, connect the R+ and R- conductors of the resistor cable together. Measure the insulation resistance between the combined conductors and the PE conductor by using a measuring voltage of 1 kv DC. The insulation resistance must be higher than 1 Mohm. R+ ohm R- PE Electrical installation
52 52 Connection to an IT (ungrounded) power system WARNING! Before connecting the drive to an IT power system [an ungrounded power system or a high resistance-grounded (over 30 ohms) power system] or a corner-grounded power system, the internal EMC filtering of the drive must be disconnected. If a drive with its internal EMC filtering connected is installed on an IT system or a corner-grounded system, the drive system will be connected to earth potential through the EMC filter capacitors of the drive. This may cause danger or damage the unit. 1st environment EMC filtering (option +E202) must be disconnected, 2nd environment EMC filtering (option +E210) can be connected. Frame size E0: Disconnection of internal EMC filtering (option +E202 included) 1. Place the drive module on its back on a level surface. 2. Press the tab slightly with a screwdriver. 3. Slide the lower cover plate slightly downwards and pull it out. Electrical installation
53 53 4. Remove the screw at the top of the cover assembly. 5. Disconnect the panel cable (if present). Electrical installation
54 54 6. Carefully pull the lower part of the base outwards by the two tabs. 7. Lift the cover assembly up. Electrical installation
55 55 8. Remove the option modules (if any) in options slots 1 and Release the two screws holding the JCU control unit. Electrical installation
56 Lift the left-hand edge of the JCU control unit until the connector beneath disengages, then move JCU to the left to remove it Disconnect the two cables coming to the mounting base of the JCU. Electrical installation
57 Remove the two screws holding the drive module cover. 13. First slide the cover a bit upwards, then lift off the cover. Electrical installation
58 Remove the two screws (marked X2 and X3) on top of the RRFC/RVAR circuit board. 15. Refit the module cover and fasten using the screws removed at step Reconnect the cables that were disconnected at step Refit the JCU control unit. Electrical installation
59 59 Frame size E: Disconnection of internal EMC filtering (option +E202 included) 1. Place the drive module on its back on a level surface. 2. Remove the cover assembly and JCU control unit and disconnect the two cables. Follow the same instructions as with frame size E0, steps 1 to Remove the screw in the middle of the air outlet grating. 4. Remove the three screws holding the drive module cover. Electrical installation
60 60 5. First slide the cover a bit upwards, then lift off the cover. 6. Undo the screw connecting the grounding wire to a standoff right next to the EMC filter. Cut off the lug. Discard the screw and the tubular insulator. EMC filter Standoff covered by insulator Electrical installation
61 61 7. Insulate the end of the grounding wire reliably with insulating tape, tube sleeving and a cable tie. Electrical installation
62 62 8. Near the top of the module, remove the grounding clip (held by two screws) that connects the varistor board to the module cover. Fasten the removed screws to mount the varistor board. 9. Refit the module cover (top edge first) and fasten using the screws removed at step 4. (The screw in the middle of the air outlet grating that was removed at step 3 is no longer needed.) 10. Reconnect the cables that were disconnected at step Refit the JCU control unit. Electrical installation
63 63 Power cable connection Power cable connection diagram ACS PE INPUT UDC+ UDC- OUTPUT U1 V1 W1 R+ U2 V2 W2 R- 1) 2) For alternatives, see Planning the electrical installation: Supply disconnecting device. (PE) PE (PE) L1 L2 L3 Optional braking resistor (360 grounding required) U1 V1 W1 3~ Motor PE 3) Notes: Do not use a non-shielded or asymmetrically-constructed motor cable. It is recommended to use a shielded cable also as an supply (input) cable. If shielded supply (input) cable is used (shielded cables are recommended), and the conductivity of the shield is less than 50% of the conductivity of a phase conductor, use a cable with a ground conductor (1) or a separate PE cable (2). For motor cabling, use a separate ground cable (3) if the conductivity of the cable shield is less than 50% of the conductivity of a phase conductor and the cable has no symmetrical ground conductors. If there is a symmetrically-constructed ground conductor in the motor cable in addition to the conductive shield, connect it to the ground connectors at both the drive and motor ends. Electrical installation
64 64 Procedure 1. Remove the plastic shroud covering the main terminals. Lift up with a screw driver from the corner. 2. Connect the twisted shields of the power cables and separate grounding conductors to the grounding terminals of the drive module. 3. Connect the phase conductors of the supply cable to the U1, V1 and W1 terminals, and the phase conductors of the motor cable to the U2, V2 and W2 terminals. The recommended stripping length is 16 mm (0.63 ) for frame size E0 and 28 mm (1.1 ) for frame size E. 4. Secure the cables mechanically outside the drive module. 5. Cut holes for the installed cables into the clear plastic shroud to accommodate the power cables. Press the shroud onto the terminals. 6. Connect the other ends of the power cables. To ensure safety, pay special attention to connection of the grounding conductors. Frame size E0: Screw terminal installation PE U1 V1 W1 R- UDC+ R+ UDC- U2 V2 W2 PE PE 15 N m (11 lbf ft) 15 N m (11 lbf ft) Input power cable Motor cable For more information on the terminal wire size capacity, see Supply cable fuses on page 87. Electrical installation
65 65 Frame size E: Cable lug installation (16 to 70 mm 2 [AWG6 to AWG2/0] cables) UDC+ U1 V1 W1 R- R+ UDC- U2 V2 W N m (22 32 lbf ft) Insulate the ends of the cable lugs with tape or shrink tube PE 8 N m (5.9 lbf ft) Input power cable Motor cable For more information on the terminal wire size capacity, see Supply cable fuses on page 87. Electrical installation
66 66 Frame size E: Screw terminal installation (95 to 240 mm 2 [AWG3/0 to 400MCM] cables) UDC+ U1 V1 W1 R- R+ UDC- U2 V2 W2 a b PE 8 N m (5.9 lbf ft) a. Connect the cable to the terminal. Tighten the Allen screw to N m (15 30 lbf ft). b. Connect the terminal to the drive. Tighten to N m (22 32 lbf ft). WARNING! If the wire size is less than 95 mm 2 (3/0 AWG), a crimp lug must be used. A cable of wire size less than 95 mm 2 (3/0 AWG) connected to this terminal will loosen and may damage the drive. Input power cable Motor cable Grounding the motor cable shield at the motor end For minimum radio frequency interference, ground the cable shield 360 degrees at the lead-through of the motor terminal box 360 degrees grounding Conductive gaskets or ground the cable by twisting the shield so that the flattened shield is wider than 1/5 of its length. b > 1/5 a a b Electrical installation
67 67 DC connection The UDC+ and UDC terminals are intended for common DC configurations of a number of ACS850 drives, allowing regenerative energy from one drive to be utilised by the other drives in motoring mode. One or more drives are connected to the AC supply depending on the power requirement. In case two or more drives are connected to the AC supply, each AC connection must be equipped with a mains choke (internal, not shown in the diagram below) to ensure even current distribution between the rectifiers. The diagram below shows two configuration examples. AC supply UDC+ ~ ~ UDC+ ~ ~ UDC+ ~ ~ UDC UDC UDC M 3~ M 3~ M 3~ AC supply UDC+ UDC ~ ~ UDC+ UDC ~ ~ UDC+ UDC ~ ~ M 3~ M 3~ M 3~ The ratings of the DC connection are given in Common DC configuration for ACS drives application guide (3AUA [English]). Electrical installation
68 68 Note: When supplying the drive through the DC connection, set parameter Cross connection to No to avoid nuisance fault trips. For more information, refer to Common DC configuration for ACS drives application guide (3AUA [English]) Installation of optional modules Optional modules such as fieldbus adapters, I/O extensions and encoder interfaces ordered using option codes (see page 24) are pre-installed at the factory. Instructions for installing additional modules into the slots on the JCU control unit (see page 22 for the available slots) are presented below. Mechanical installation Remove the cover assembly from on the JCU control unit (refer to page 49). Remove the protective cover (if present) from the connector of the slot. Insert the module carefully into its position on the drive. Fasten the screw. Note: Correct installation of the screw is essential for fulfilling the EMC requirements and for proper operation of the module. Electrical installation See section Grounding and routing the control cables on page 73. See the appropriate option manual for specific installation and wiring instructions. Electrical installation
69 69 Connecting the control cables Control connections to the JCU control unit Notes: [Default setting with ACS850 standard control program (Factory macro). See Firmware manual for other macros.] *Total maximum current: 200 ma The wiring shown is for demonstrative purposes only. Further information of the usage of the connectors and jumpers are given in the text; see also chapter Technical data. Wire sizes and tightening torques: XPOW, XRO1, XRO2, XRO3, XD24: mm 2 (24 12 AWG). Torque: 0.5 N m (5 lbf in) XDI, XDIO, XAI, XAO, XD2D, XSTO: mm 2 (28 14 AWG). Torque: 0.3 N m (3 lbf in) Order of terminal headers and jumpers XPOW (2-pole, 2.5 mm 2 ) XRO1 (3-pole, 2.5 mm 2 ) XRO2 (3-pole, 2.5 mm 2 ) XRO3 (3-pole, 2.5 mm 2 ) XD24 (4-pole, 2.5 mm 2 ) DI/DIO grounding selection XDI (7-pole, 1.5 mm 2 ) XDIO (2-pole, 1.5 mm 2 ) XAI (7-pole, 1.5 mm 2 ) AI1, AI2 XAO (4-pole, 1.5 mm 2 ) T XD2D (3-pole, 1.5 mm 2 ) XSTO (orange) (4-pole, 1.5 mm 2 ) External power input 24 V DC, 1.6 A Relay output RO1 [Ready] 250 V AC / 30 V DC 2 A Relay output RO2 [Modulating] 250 V AC / 30 V DC 2 A XPOW +24VI 1 GND 2 XRO1, XRO2, XRO3 NO 1 COM 2 NC 3 NO 4 COM 5 NC 6 Relay output RO3 [Fault(-1)] NO V AC / 30 V DC COM 8 2 A NC 9 XD V DC* +24VD 1 Digital input ground DIGND V DC* +24VD 3 Digital input/output ground DIOGND 4 Ground selection jumper AI1 XDI Digital input DI1 [Stop/Start] DI1 1 Digital input DI2 DI2 2 Digital input DI3 [Reset] DI3 3 Digital input DI4 DI4 4 Digital input DI5 DI5 5 Digital input DI6 or thermistor input DI6 6 Start interlock (0 = Stop) DIIL A XDIO Digital input/output DIO1 [Output: Ready] DIO1 1 Digital input/output DIO2 [Output: Running] DIO2 2 XAI Reference voltage (+) +VREF 1 Reference voltage ( ) -VREF 2 Ground AGND 3 Analog input AI1 (Current or voltage, selectable by jumper AI1) AI1+ 4 [Speed reference 1] AI1-5 Analog input AI2 (Current or voltage, selectable by jumper AI2) AI1 current/voltage selection jumper AI2 current/voltage selection jumper Analog output AO1 [Current %] Analog output AO2 [Speed %] Drive-to-drive link termination jumper Drive-to-drive link. Safe torque off. Both circuits must be closed for the drive to start. Control panel connection Memory unit connection AI2+ 6 AI2-7 AI1 AI2 XAO AO1+ 1 AO1-2 AO2+ 3 AO2-4 XD2D T B 1 A 2 BGND 3 XSTO OUT1 1 OUT2 2 IN1 3 IN2 4 Electrical installation
70 70 Jumpers DI/DIO grounding selector (located between XD24 and XDI) Determines whether the DIGND (ground for digital inputs DI1 DI5) floats, or if it is connected to DIOGND (ground for DI6, DIO1 and DIO2). (See the JCU isolation and grounding diagram on page 90.) If DIGND floats, the common of digital inputs DI1 DI5 should be connected to XD24:2. The common can be either GND or V cc as DI1 DI5 are of the NPN/PNP type. DIGND floats DIGND tied to DIOGND XD XD AI1 Determines whether Analog input AI1 is used as a current or voltage input. Current Voltage 7 AI1 AI2 1 7 AI1 AI2 1 AI2 Determines whether Analog input AI2 is used as a current or voltage input. Current Voltage 7 AI1 AI2 1 7 AI1 AI2 1 T Drive-to-drive link termination. Must be set to the ON position when the drive is the last unit on the link. Termination ON T Termination OFF T External power supply for the JCU control unit (XPOW) External +24 V (minimum 1.6 A) power supply for the JCU control unit can be connected to terminal block XPOW. Using an external supply is recommended if the application requires fast start after connecting the drive to the main supply fieldbus communication is required when the input power supply is disconnected. Electrical installation
71 71 DI6 (XDI:6) as a thermistor input 1 3 PTC sensors can be connected to this input for motor temperature measurement. One sensor Three sensors Motor T 3.3 nf > 630 VAC XDI:6 XD24:1 T Motor T T 3.3 nf > 630 VAC XDI:6 XD24:1 Notes: Do not connect both ends of the cable shields directly to ground. If a capacitor cannot be used at one end, leave that end of the shield unconnected. The connection of temperature sensors involves parameter adjustment. See the Firmware manual of the drive. PTC (as well as KTY84) sensors can alternatively be connected to a FEN-xx encoder interface. See the User s manual of the interface for wiring information. Pt100 sensors are not to be connected to the thermistor input. Instead, an analog input and an analog current output (located either on the JCU or on an I/O extension module) are used as shown below. The analog input must be set to voltage. One Pt100 sensor Three Pt100 sensors Motor AI1+ (U) AI1- (U) Motor AI1+ (U) AI1- (U) T AOx (I) T T T AOx (I) AGND AGND 3.3 nf > 630 VAC 3.3 nf > 630 VAC Electrical installation
72 72 WARNING! As the inputs pictured above are not insulated according to IEC 60664, the connection of the motor temperature sensor requires double or reinforced insulation between motor live parts and the sensor. If the assembly does not fulfil the requirement, all I/O terminals must be protected against contact and must not be connected to other equipment or the temperature sensor must be isolated from the I/O terminals. Drive-to-drive link (XD2D) The drive-to-drive link is a daisy-chained RS-485 transmission line that allows basic master/follower communication with one master drive and multiple followers. Termination activation jumper T (see section Jumpers above) next to this terminal block must be set to the ON position on the drives at the ends of the drive-to-drive link. On intermediate drives, the jumper must be set to the OFF position. Shielded twisted-pair cable (~100 ohm, e.g. PROFIBUS-compatible cable) must be used for the wiring. For best immunity, high quality cable is recommended. The cable should be kept as short as possible; the maximum length of the link is 100 metres (328 ft). Unnecessary loops and running the cable near power cables (such as motor cables) must be avoided. The cable shields are to be grounded to the control cable clamp plate on the drive as shown on page 73. The following diagram shows the wiring of the drive-to-drive link. T B A BGND T B A BGND T B A BGND XD2D Termination ON XD2D Termination OFF... XD2D Termination ON JCU Drive 1 JCU Drive 2 JCU Drive n Note: The drive-to-drive link can be used only if the embedded fieldbus interface is disabled. For more information on the embedded fieldbus interface, see the Firmware manual. Electrical installation
73 73 Safe torque off (XSTO) For the drive to start, both connections (OUT1 to IN1, and OUT2 to IN2) must be closed. This is implemented by means of a safety switch and related wiring. See page 43. By default, the terminal block has jumpers to close the circuit. Remove the jumpers before connecting an external Safe Torque Off circuitry to the drive. See page 43. More information is available in Safe torque off function for ACS850 and ACQ810 drives application guide (3AFE [English]). For related parameter settings, see the appropriate Firmware manual. Grounding and routing the control cables The shields of all control cables connected to the JCU control unit must be grounded at the control cable clamp plate. Use four M4 screws to fasten the plate as shown below (two of the screws are also used to hold the cover mounting bracket). The plate can be fitted either at the top or bottom of the drive. Before connecting the wires, run the cables through the cover mounting bracket. The cables going to the terminal blocks on the control unit are to be run along the righthand side of the drive module. See the drawings below. The shields should be continuous as close to the terminals of the JCU as possible. Only remove the outer jacket of the cable at the cable clamp so that the clamp presses on the bare shield. At the terminal block, use shrink tubing or insulating tape to contain any stray strands. The shield (especially in case of multiple shields) can also be terminated with a lug and fastened with a screw at the clamp plate. Leave the other end of the shield unconnected or ground it indirectly via a few nanofarads high-frequency capacitor (e.g. 3.3 nf / 630 V). The shield can also be grounded directly at both ends if they are in the same ground line with no significant voltage drop between the end points. Keep any signal wire pairs twisted as close to the terminals as possible. Twisting the wire with its return wire reduces disturbances caused by inductive coupling. Before re-installing the cover assembly, remove the appropriate punch-outs on the right side of the cover base to create entries for the control cables going to the terminal blocks. Re-install the cover assembly according to the instructions on page 49. Electrical installation
74 74 Mounting the clamp plate 0.7 N m (6.2 lbf in) Electrical installation
75 75 Routing the control cables Run cables through the cover mounting bracket Use shrink tubing or tape to contain strands Remove outer jacket of the cable at clamp to expose cable shield. Tighten clamp to 1.5 N m (13 lbf in) Electrical installation
76 76 Electrical installation
77 77 Installation checklist What this chapter contains This chapter contains a list for checking the mechanical and electrical installation of the drive. Checklist Check the mechanical and electrical installation of the drive before start-up. Go through the checklist below together with another person. Read the Safety instructions on the first pages of this manual before you work on the unit. Check that... MECHANICAL INSTALLATION The ambient operating conditions are allowable. (See Mechanical installation, Technical data: Ratings, Ambient conditions.) The unit is fastened properly to the cabinet. (See Planning the cabinet assembly and Mechanical installation.) The cooling air will flow freely. The motor and the driven equipment are ready for start. (See Planning the electrical installation, Technical data: Motor connection.) ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION (See Planning the electrical installation, Electrical installation.) The internal C2 EMC filter (option + E202) is disconnected if the drive is connected to an IT (ungrounded) or corner-grounded supply network. The capacitors are reformed if stored over one year (ask local ABB representative for more information). The drive is grounded properly. 1) There is a proper PE connector, 2) PE connector is tightened properly, and 3) there is a proper galvanic connection between the drive frame and the cabinet (fastening points are unpainted). The supply (input power) voltage matches the drive nominal input voltage. The supply (input power) is connected to U1/V1/W1 (UDC+/UDC- in case of a DC supply) and the terminals are tightened to specified torque. Appropriate supply (input power) fuses and disconnector are installed. The motor is connected to U2/V2/W2, and the terminals are tightened to specified torque. The braking resistor (if present) is connected to R+/R-, and the terminals are tightened to specified torque. Installation checklist
78 78 Check that... The motor cable (and braking resistor cable, if present) is routed away from other cables. There are no power factor compensation capacitors in the motor cable. The external control connections to the JCU control unit are OK. There are no tools, foreign objects or dust from drilling inside the drive. The supply (input power) voltage cannot be applied to the output of the drive through a bypass connection. Motor connection box and other covers are in place. Installation checklist
79 79 Maintenance What this chapter contains Safety This chapter contains preventive maintenance instructions. WARNING! Read the Safety instructions on the first pages of this manual before performing any maintenance on the equipment. Ignoring the safety instructions can cause injury or death. Maintenance intervals The table below lists the routine maintenance intervals recommended by ABB. Consult a local ABB Service representative for more details. In the Internet, go to select Drive Services, and Maintenance and Field Services. Interval Maintenance Instruction Every year of storage Every 6 to 12 months depending on the dustiness of the environment Every year Every 3 years if the ambient temperature is higher than 40 C (104 F). Otherwise, every 6 years. Every 3 years Every 6 years if the ambient temperature is higher than 40 C (104 F) or if the drive is subjected to cyclic heavy load or continuous nominal load. Otherwise, every 9 years DC capacitor reforming Heatsink temperature check and cleaning Inspection of tightness of power connections Visual inspection of cooling fan Cooling fan replacement Change of additional cooling fan (only frame size E0) DC capacitor replacement See Capacitors. See Heatsink. See pages See Cooling fan. See Cooling fan. See Additional cooling fan replacement (frame E0). See Capacitors. Maintenance
80 80 Every 10 years Control panel battery replacement The battery is housed on the rear of the control panel. Replace with a new CR 2032 battery. Heatsink The heatsink fins pick up dust from the cooling air. The drive runs into overtemperature warnings and faults if the heatsink is not clean. In a normal environment, the heatsink should be checked annually, in a dusty environment more often. Clean the heatsink as follows (when necessary): 1. Remove the cooling fan (see section Cooling fan). 2. Blow clean compressed air (not humid) from bottom to top and simultaneously use a vacuum cleaner at the air outlet to trap the dust. Note: If there is a risk of the dust entering adjoining equipment, perform the cleaning in another room. 3. Refit the cooling fan. Maintenance
81 81 Cooling fan The actual lifespan of the cooling fan depends on the drive usage and ambient temperature. Fan failure can be predicted by the increasing noise from fan bearings and the gradual rise in the heatsink temperature in spite of heatsink cleaning. If the drive is operated in a critical part of a process, fan replacement is recommended once these symptoms start appearing. Replacement fans are available from ABB. Do not use other than ABB-specified spare parts. Fan replacement (frame E0) 1. Undo the fixing screw of the cooling fan holder. 2. Remove the cooling fan holder and disconnect the cable. 3. Undo the fastening screws of the fan. Install the new fan in reverse order. Frame size E0, bottom view 1 3 Maintenance
82 82 Fan replacement (frame E) 1. Undo the fixing screw of the cooling fan holder. 2. Slide out the cable connector and disconnect it. 3. Remove the cooling fan holder and replace the fan onto the holder s pins. Install the cooling fan holder in reverse order. Frame size E, bottom view 3 1 Maintenance
83 83 Additional cooling fan replacement (frame E0) The fan is located on top of the module. 1. Undo the fixing screw of the cooling fan holder (1 pc PZ2 screw). 2. Pull the fan holder out. 3. Disconnect the fan cable. 4. Undo the fastening screws of the fan (4 pcs PZ2 screws, circled in the picture below) and remove the fan. 5. Install the new fan and tighten the fastening screws to 0.5 N m. 6. Reconnect the fan cable, assemble the fan holder back and tighten the fixing screw to 1.2 N m Capacitors Reforming The capacitors must be reformed if the drive has been stored for a year or more. See page 33 for information on finding out the manufacturing date. For the reforming instructions, see Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link, capacitor reforming instructions (3BFE [English]). Changing The drive intermediate circuit employs several electrolytic capacitors. Their lifespan depends on drive loading and ambient temperature. Capacitor life can be prolonged by lowering the ambient temperature. It is not possible to predict a capacitor failure. Capacitor failure is usually followed by a mains fuse failure or a fault trip. Contact ABB if capacitor failure is suspected. Replacements are available from ABB. Do not use other than ABB specified spare parts. Maintenance
ACSM1. Hardware Manual ACSM1-04 Drive Modules (0.75 to 45 kw)
 ACSM1 Hardware Manual ACSM1-04 Drive Modules (0.75 to 45 kw) ACSM1-04 Drive Modules 0.75 to 45 kw Hardware Manual 3AFE68797543 REV C EN EFFECTIVE: 11.6.2007 2007 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 5 Safety
ACSM1 Hardware Manual ACSM1-04 Drive Modules (0.75 to 45 kw) ACSM1-04 Drive Modules 0.75 to 45 kw Hardware Manual 3AFE68797543 REV C EN EFFECTIVE: 11.6.2007 2007 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 5 Safety
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (0.55 to 110 kw) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 to 150 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-01 Drives (0.55 to 110 kw) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 to 150 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-01 Drives (0.55 to 110 kw) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 to 150 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS 800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (0.55 to 110 kw) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 to 150 HP)
 ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-01 Drives (0.55 to 110 kw) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 to 150 HP) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-01 Drives (0.55 to 110 kw) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 to 150 HP) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U31 Drives (7.5 to 125 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-31 Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U31 Drives (7.5 to 125 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-31 Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U31 Drives (7.5 to 125 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U7 Drives (50 to 600 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-07 Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U7 Drives (50 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-07 Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U7 Drives (50 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (55 to 2500 kw / 75 to 2800 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-17 Drives (55 to 2500 kw / 75 to 2800 HP) ACS800-17 Drives 55 to 2500 kw (75 to 2800 HP) Hardware Manual 3AFE68397260 REV B EN EFFECTIVE: 26.10.2005 2005 ABB Oy. All Rights
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-17 Drives (55 to 2500 kw / 75 to 2800 HP) ACS800-17 Drives 55 to 2500 kw (75 to 2800 HP) Hardware Manual 3AFE68397260 REV B EN EFFECTIVE: 26.10.2005 2005 ABB Oy. All Rights
ACS 800. Hardware Manual ACS Drive Modules (90 to 500 kw) ACS800-U4 Drive Modules (125 to 600 HP)
 ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-04 Drive Modules (90 to 500 kw) ACS800-U4 Drive Modules (125 to 600 HP) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1
ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-04 Drive Modules (90 to 500 kw) ACS800-U4 Drive Modules (125 to 600 HP) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (45 to 500 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (60 to 600 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-02 Drives (45 to 500 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (60 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-02 Drives (45 to 500 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (60 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U11 Drives (7.5 to 125 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-11 Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U11 Drives (7.5 to 125 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-11 Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U11 Drives (7.5 to 125 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (60 to 600 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-02 Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (60 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-02 Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (60 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U7 Drives (50 to 600 HP)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-07 Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U7 Drives (50 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-07 Drives (45 to 560 kw) ACS800-U7 Drives (50 to 600 HP) ACS800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware
ACS580, ACH580 and ACQ580 drive module frames R3 and R5 to R9 for cabinet installation (options +P940 and +P944) Supplement
 ABB GENERAL DRIVES, ABB DRIVES FOR HVAC, ABB DRIVES FOR WATER ACS580, ACH580 and ACQ580 drive module frames R3 and R5 to R9 for cabinet installation (options +P940 and +P944) Supplement Supplement ACS580,
ABB GENERAL DRIVES, ABB DRIVES FOR HVAC, ABB DRIVES FOR WATER ACS580, ACH580 and ACQ580 drive module frames R3 and R5 to R9 for cabinet installation (options +P940 and +P944) Supplement Supplement ACS580,
ACS 800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (90 to 500 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (125 to 600 HP)
 ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-02 Drives (90 to 500 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (125 to 600 HP) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS800-01/U1 Hardware Manual 1.1 to 110 kw (1.5 to 150 HP) 3AFE 64382101
ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-02 Drives (90 to 500 kw) ACS800-U2 Drives (125 to 600 HP) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS800-01/U1 Hardware Manual 1.1 to 110 kw (1.5 to 150 HP) 3AFE 64382101
ACS 800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (500 to 2800 kw)
 ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-07 Drives (500 to 2800 kw) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware Manual 0.55 to 110 kw (0.75
ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-07 Drives (500 to 2800 kw) ACS 800 Single Drive Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS (appropriate manual is included in the delivery) ACS800-01/U1 Hardware Manual 0.55 to 110 kw (0.75
ABB industrial drives. Supplement ACS N7502 drives for SynRM motors (0.8 to 200 kw)
 ABB industrial drives Supplement ACS880-01 +N7502 drives for SynRM motors (0.8 to 200 kw) List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides ACS880-01 hardware manual ACS880-01 +N7502 drives for
ABB industrial drives Supplement ACS880-01 +N7502 drives for SynRM motors (0.8 to 200 kw) List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides ACS880-01 hardware manual ACS880-01 +N7502 drives for
ABB SINGLE DRIVES ACS880-01/04 +C132 marine typeapproved. Supplement
 ABB SINGLE DRIVES ACS880-01/04 +C132 marine typeapproved drives Supplement Supplement ACS880-01/04 +C132 marine type-approved drives Table of contents 2018 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 3AXD50000010521
ABB SINGLE DRIVES ACS880-01/04 +C132 marine typeapproved drives Supplement Supplement ACS880-01/04 +C132 marine type-approved drives Table of contents 2018 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 3AXD50000010521
User s Manual. ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass Supplement for ACS550-01/U1 Drives User s Manual
 User s Manual ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass Supplement for ACS550-01/U1 Drives User s Manual ii ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass ACS550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS550-01/U1 Drives User's
User s Manual ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass Supplement for ACS550-01/U1 Drives User s Manual ii ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass ACS550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS550-01/U1 Drives User's
User s Manual. ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass Supplement for ACS550-01/U1 Drives User s Manual
 User s Manual ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass Supplement for ACS550-01/U1 Drives User s Manual ii ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass ACS550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS550-01/U1 Drives User's
User s Manual ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass Supplement for ACS550-01/U1 Drives User s Manual ii ACS550-CC Packaged Drive with Bypass ACS550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS550-01/U1 Drives User's
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U31 Drives (7.5 to 125 hp)
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-31 Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U31 Drives (7.5 to 125 hp) List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides ACS800-31/U31 Hardware Manual (5.5 to 110 kw, 7.5 to
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-31 Drives (5.5 to 110 kw) ACS800-U31 Drives (7.5 to 125 hp) List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides ACS800-31/U31 Hardware Manual (5.5 to 110 kw, 7.5 to
Hardware manual Sine filters
 Options for ABB drives Hardware manual Sine filters M 3~ Drive Sine filter List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals Drive firmware manuals You can find manuals and other product documents in PDF
Options for ABB drives Hardware manual Sine filters M 3~ Drive Sine filter List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals Drive firmware manuals You can find manuals and other product documents in PDF
ACS 800. Hardware Manual ACS Drives (75 to 1120 kw)
 ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-17 Drives (75 to 1120 kw) ACS800-17 Drives (75 to 1120 kw) Hardware Manual 3AFE 64681338 Rev A EN EFFECTIVE: 01.11.2002 2002 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 5 Safety instructions
ACS 800 Hardware Manual ACS800-17 Drives (75 to 1120 kw) ACS800-17 Drives (75 to 1120 kw) Hardware Manual 3AFE 64681338 Rev A EN EFFECTIVE: 01.11.2002 2002 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 5 Safety instructions
R5 ACS580-01, ACH580-01
 ABB LOW VOLTAGE DRIV Main switch and EMC C1 filter options (+F278, +F316, +E223), IP55 frames R1 to R5 ACS580-01, ACH580-01 and ACQ580-01 drives Installation supplement English......... 5 3AXD50000155132
ABB LOW VOLTAGE DRIV Main switch and EMC C1 filter options (+F278, +F316, +E223), IP55 frames R1 to R5 ACS580-01, ACH580-01 and ACQ580-01 drives Installation supplement English......... 5 3AXD50000155132
User s Manual. ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass Supplement for ACH550-UH HVAC User s Manual
 User s Manual ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass Supplement for ACH550-UH HVAC User s Manual ii ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass ACH550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACH550-UH
User s Manual ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass Supplement for ACH550-UH HVAC User s Manual ii ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass ACH550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACH550-UH
User s Manual. ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass Supplement for ACH550-UH HVAC User s Manual
 User s Manual ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass Supplement for ACH550-UH HVAC User s Manual ii ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass ACH550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACH550-UH
User s Manual ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass Supplement for ACH550-UH HVAC User s Manual ii ACH550-CC/CD Packaged Drive with Classic Bypass ACH550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACH550-UH
Update notice. General safety. Type code key. Update notice 1
 Update notice 1 Update notice The notice concerns the ACS880-01 hardware manuals listed below. Contents of the notice: New drive s 442A-3 and 441A-5, changed ar fuses, added minimum switching frequency
Update notice 1 Update notice The notice concerns the ACS880-01 hardware manuals listed below. Contents of the notice: New drive s 442A-3 and 441A-5, changed ar fuses, added minimum switching frequency
ABB machinery drives. Application guide Common DC system for ACS380 drives
 ABB machinery drives Application guide Common DC system for ACS380 drives List of related manuals Drive manuals and guides ACS380 hardware manual ACS380 firmware manual ACS380 quick installation and start-up
ABB machinery drives Application guide Common DC system for ACS380 drives List of related manuals Drive manuals and guides ACS380 hardware manual ACS380 firmware manual ACS380 quick installation and start-up
Cabinet-built single drives, ACS880-07
 Cabinet-built single drives, ACS880-07 Our cabinet-built single drives are built to order, meeting customer needs despite any technical challenges. Designed on ABB's common drives architecture, this compact
Cabinet-built single drives, ACS880-07 Our cabinet-built single drives are built to order, meeting customer needs despite any technical challenges. Designed on ABB's common drives architecture, this compact
High performance Vector Control. Ratings. System configuration
 System configuration High performance Vector Control Low harmonic or regenerative drive IP54 full range Compact design and robustness Built-in filter (according to C3 class) Built-in fuses (from 200 kw)
System configuration High performance Vector Control Low harmonic or regenerative drive IP54 full range Compact design and robustness Built-in filter (according to C3 class) Built-in fuses (from 200 kw)
ABB industrial drives. Application guide ACS drives and ACS drive modules Common DC systems
 ABB industrial drives Application guide ACS880-01 drives and ACS880-04 drive modules Common DC systems List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides ACS880-01 hardware manual ACS880-01 quick
ABB industrial drives Application guide ACS880-01 drives and ACS880-04 drive modules Common DC systems List of related manuals Drive hardware manuals and guides ACS880-01 hardware manual ACS880-01 quick
User s Manual. ACS550-PC/PD Packaged Drive with Disconnect Supplement to ACS550-01/U1 User s Manual
 User s Manual ACS550-PC/PD Packaged Drive with Disconnect Supplement to ACS550-01/U1 User s Manual ii ACS550-PC/PD Packaged Drive with Disconnect ACS550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS550-01/U1 User's
User s Manual ACS550-PC/PD Packaged Drive with Disconnect Supplement to ACS550-01/U1 User s Manual ii ACS550-PC/PD Packaged Drive with Disconnect ACS550 Drive Manuals GENERAL MANUALS ACS550-01/U1 User's
Welcome to ABB machinery drives training. This training module will introduce you to the ACS850-04, the ABB machinery drive module.
 Welcome to ABB machinery drives training. This training module will introduce you to the ACS850-04, the ABB machinery drive module. 1 Upon the completion of this module, you will be able to describe the
Welcome to ABB machinery drives training. This training module will introduce you to the ACS850-04, the ABB machinery drive module. 1 Upon the completion of this module, you will be able to describe the
LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES. ABB machinery drives ACS380, 0.25 to 22 kw/0.37 to 30 hp
 LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES ABB machinery drives ACS380, 0.25 to 22 kw/0.37 to 30 hp 2 ABB MACHINERY DRIVES, ACS380, CATALOG Persistent and adaptable performance. ACS380 machinery drives. 3 Table of contents
LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES ABB machinery drives ACS380, 0.25 to 22 kw/0.37 to 30 hp 2 ABB MACHINERY DRIVES, ACS380, CATALOG Persistent and adaptable performance. ACS380 machinery drives. 3 Table of contents
ABB industrial drives ACS800, drive modules 0.55 to 2900 kw Catalog
 Low voltage AC drives ABB industrial drives ACS800, drive modules 0.55 to 2900 kw Catalog Selecting and ordering your drive Build up your own ordering code using the type designation key below or contact
Low voltage AC drives ABB industrial drives ACS800, drive modules 0.55 to 2900 kw Catalog Selecting and ordering your drive Build up your own ordering code using the type designation key below or contact
Welcome to the ABB Industrial Drives, ACS800 planning the installation training module. If you need help navigating this module, click the Help
 Welcome to the ABB Industrial Drives, ACS800 planning the installation training module. If you need help navigating this module, click the Help button in the top right corner. To view the presenter notes
Welcome to the ABB Industrial Drives, ACS800 planning the installation training module. If you need help navigating this module, click the Help button in the top right corner. To view the presenter notes
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 5600 kw
 ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 5600 kw Technical catalogue PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents 1 2 Type code Product series Single drives
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 5600 kw Technical catalogue PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents 1 2 Type code Product series Single drives
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 2800 kw
 ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 2800 kw Technical catalogue PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents 1 2 3 Type code Product series Single drives
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 2800 kw Technical catalogue PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents 1 2 3 Type code Product series Single drives
Catalog. ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 5600 kw
 Catalog ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 5600 kw Contents 1 2 Type code Product series Single drives Types and constructions Ratings Voltages Dimensions ACS800-01 - XXXX - X + XXXX
Catalog ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.55 to 5600 kw Contents 1 2 Type code Product series Single drives Types and constructions Ratings Voltages Dimensions ACS800-01 - XXXX - X + XXXX
Unidrive M600 High performance drive for induction and sensorless permanent magnet motors
 Unidrive M600 High performance drive for induction and sensorless permanent magnet motors 0.75 kw - 2.8 MW Heavy Duty (1.0 hp - 4,200 hp) 200 V 400 V 575 V 690 V Unidrive M600 features Easy click-in keypad
Unidrive M600 High performance drive for induction and sensorless permanent magnet motors 0.75 kw - 2.8 MW Heavy Duty (1.0 hp - 4,200 hp) 200 V 400 V 575 V 690 V Unidrive M600 features Easy click-in keypad
ABB industrial drives ACS800, drive modules. 2 to Vac 5 to Vac
 ABB industrial drives ACS800, drive modules Technical catalog 0.75 to 250 HP @ 240 Vac 2 to 2800 HP @ 480 Vac 5 to 2400 HP @ 600 Vac Contents ABB industrial drives 1 2 3 4 Product series Drive Modules
ABB industrial drives ACS800, drive modules Technical catalog 0.75 to 250 HP @ 240 Vac 2 to 2800 HP @ 480 Vac 5 to 2400 HP @ 600 Vac Contents ABB industrial drives 1 2 3 4 Product series Drive Modules
ACS800. Hardware Manual ACS Wind Turbine Converters for Asynchronous Slip Ring Generators
 ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-67 Wind Turbine Converters for Asynchronous Slip Ring Generators ACS800-67 Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS ACS800-67 Wind Turbine Converters for Asynchronous Slip Ring Generators
ACS800 Hardware Manual ACS800-67 Wind Turbine Converters for Asynchronous Slip Ring Generators ACS800-67 Manuals HARDWARE MANUALS ACS800-67 Wind Turbine Converters for Asynchronous Slip Ring Generators
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives ACS800, regenerative AC drives ACS800, ultra low harmonic drives
 ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives ACS800, regenerative AC drives ACS800, ultra low harmonic drives Technical catalog 0.75 to 75 HP @ 240 Vac 2 to 2250 HP @ 480 Vac 5 to 3000 HP @ 600 Vac BUSINESS
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives ACS800, regenerative AC drives ACS800, ultra low harmonic drives Technical catalog 0.75 to 75 HP @ 240 Vac 2 to 2250 HP @ 480 Vac 5 to 3000 HP @ 600 Vac BUSINESS
Low voltage AC drives
 General machinery drives Main features and dimensions Unique features Fast and extensive I/O PID control Application macros Many installation possibilities 200 to 480 V, 1-phase or 3-phase More value for
General machinery drives Main features and dimensions Unique features Fast and extensive I/O PID control Application macros Many installation possibilities 200 to 480 V, 1-phase or 3-phase More value for
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives ACS800, regenerative AC drives ACS800, ultra low harmonic drives
 ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives ACS800, regenerative AC drives ACS800, ultra low harmonic drives Technical catalog 0.75 to 75 HP @ 240 Vac 2 to 2250 HP @ 480 Vac 5 to 3000 HP @ 600 Vac BUSINESS
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives ACS800, regenerative AC drives ACS800, ultra low harmonic drives Technical catalog 0.75 to 75 HP @ 240 Vac 2 to 2250 HP @ 480 Vac 5 to 3000 HP @ 600 Vac BUSINESS
Low voltage AC drives. ABB micro drives ACS to 3 hp/0.18 to 2.2 kw Catalog
 Low voltage AC drives ABB micro drives ACS55 0.25 to 3 hp/0.18 to 2.2 kw Catalog ACS55 IP20 Overview ACS55 micro drives are designed for use in a wide variety of simple machinery applications where only
Low voltage AC drives ABB micro drives ACS55 0.25 to 3 hp/0.18 to 2.2 kw Catalog ACS55 IP20 Overview ACS55 micro drives are designed for use in a wide variety of simple machinery applications where only
ABB LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES, WIND TURBINE CONVERTERS AND SOLAR INVERTERS Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link Capacitor
 ABB LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES, WIND TURBINE CONVERTERS AND SOLAR INVERTERS Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link Capacitor reforming instructions 3 Table of contents 1. Introduction
ABB LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES, WIND TURBINE CONVERTERS AND SOLAR INVERTERS Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link Capacitor reforming instructions 3 Table of contents 1. Introduction
SUPPLEMENT MANUAL IM250R03. AQUAVAR CPC SUPPLEMENT A - Variable Speed Drive SUPPLEMENT TO THE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL (IM167)
 SUPPLEMENT MANUAL IM250R03 AQUAVAR CPC SUPPLEMENT A - Variable Speed Drive SUPPLEMENT TO THE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL (IM167) TABLE OF CONTENTS SAFETY Use of Warnings and Notes...3 INSTALLATION
SUPPLEMENT MANUAL IM250R03 AQUAVAR CPC SUPPLEMENT A - Variable Speed Drive SUPPLEMENT TO THE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL (IM167) TABLE OF CONTENTS SAFETY Use of Warnings and Notes...3 INSTALLATION
CATALOG. ABB micro drives ACS55, 0.18 to 2.2 kw
 CATALOG ABB micro drives ACS55, 0.18 to 2.2 kw 2 ABB MICRO DRIVES, ACS55, 0.18 TO 2.2 KW/0.25 TO 3 HP Ease of integration. ACS55 drives. 3 Table of contents 004 ABB micro drives, ACS55 005 Easily integrated
CATALOG ABB micro drives ACS55, 0.18 to 2.2 kw 2 ABB MICRO DRIVES, ACS55, 0.18 TO 2.2 KW/0.25 TO 3 HP Ease of integration. ACS55 drives. 3 Table of contents 004 ABB micro drives, ACS55 005 Easily integrated
Frame size R2, IP20 / NEMA 1
 Dimension drawings 395 Frame size R2, IP20 / NEMA 1 1) 1) Extension modules add 26 mm (1.02 in) to the depth measure. 3AUA0000067783-A Frame size R2, IP20 / NEMA 1 396 Dimension drawings Frame size R3,
Dimension drawings 395 Frame size R2, IP20 / NEMA 1 1) 1) Extension modules add 26 mm (1.02 in) to the depth measure. 3AUA0000067783-A Frame size R2, IP20 / NEMA 1 396 Dimension drawings Frame size R3,
Unidrive M700 Class leading performance with onboard real-time Ethernet
 Unidrive M Class leading performance with onboard real-time Ethernet. kw -.8 MW Heavy Duty (. hp -, hp) V V V 9 V Unidrive M features Easy click-in keypad connection Range of multi-language LCD keypads
Unidrive M Class leading performance with onboard real-time Ethernet. kw -.8 MW Heavy Duty (. hp -, hp) V V V 9 V Unidrive M features Easy click-in keypad connection Range of multi-language LCD keypads
ABB wind turbine converters. Supplement to hardware manual ACS upgrade kits
 ABB wind turbine converters Supplement to hardware manual ACS800-67 upgrade kits List of related manuals ACS800-67 manuals ACS800-67 wind turbine converters for asynchronous slip ring generators hardware
ABB wind turbine converters Supplement to hardware manual ACS800-67 upgrade kits List of related manuals ACS800-67 manuals ACS800-67 wind turbine converters for asynchronous slip ring generators hardware
ABB Component Drives ACS150, 0.5 to 5 Hp
 ABB Component Drives ACS150, 0.5 to 5 Hp Technical Catalog BUSINESS PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents Choice 1: Simply contact your local ABB drives sales office
ABB Component Drives ACS150, 0.5 to 5 Hp Technical Catalog BUSINESS PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents Choice 1: Simply contact your local ABB drives sales office
LOW VOLTAGE WIND CONVERTERS. ABB wind turbine converters ACS880, 800 kw to 8 MW
 LOW VOLTAGE WIND CONVERTERS ABB wind turbine converters ACS880, 800 kw to 8 MW 2 ABB WIND CONVERTERS, ACS880 WIND TURBINE CONVERTERS ACS880 wind turbine converter Flexible solution The ACS880 converter
LOW VOLTAGE WIND CONVERTERS ABB wind turbine converters ACS880, 800 kw to 8 MW 2 ABB WIND CONVERTERS, ACS880 WIND TURBINE CONVERTERS ACS880 wind turbine converter Flexible solution The ACS880 converter
ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.75 to 6000 hp
 Catalog ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.75 to 6000 hp Contents ABB industrial drives 1 2 Product series Single Drives 3 4 Hardware options Control connections and communications 5 6 7 8
Catalog ABB industrial drives ACS800, single drives, 0.75 to 6000 hp Contents ABB industrial drives 1 2 Product series Single Drives 3 4 Hardware options Control connections and communications 5 6 7 8
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER. SERIES B Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR REL MTE Corporation
 M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER SERIES B 380-415 Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 015 REL. 060628 2006 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation Matrix Filter
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER SERIES B 380-415 Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 015 REL. 060628 2006 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation Matrix Filter
Installation and Start-up Guide. ACS-BRK Brake Units
 Installation and Start-up Guide ACS-BRK Brake Units ACS-BRK Brake Units Installation and Start-up Guide 3AFY 61514309 REV C EN Effective: 16.09.2002 2002 ABB Oy. Safety Warning! All electrical installation
Installation and Start-up Guide ACS-BRK Brake Units ACS-BRK Brake Units Installation and Start-up Guide 3AFY 61514309 REV C EN Effective: 16.09.2002 2002 ABB Oy. Safety Warning! All electrical installation
SINAMICS SM150. 4/2 Overview. 4/2 Benefits. 4/2 Design. 4/6 Function. 4/8 Selection and ordering data. 4/8 Options
 /2 Overview /2 Benefits /2 Design /6 Function /8 Selection and ordering data /8 Options Technical data /1 General technical data /15 Control properties /15 Ambient conditions /16 Installation conditions
/2 Overview /2 Benefits /2 Design /6 Function /8 Selection and ordering data /8 Options Technical data /1 General technical data /15 Control properties /15 Ambient conditions /16 Installation conditions
RVS-AX Instruction Manual
 RVS-AX Analog Soft Starter 8-170A, 220-600V Instruction Manual Ver. 10/11/2009 2 Table of Content RVS-AX Instruction Manual 1. TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Table of Content...2 2. Safety & Warnings...3 2.1 Safety...3
RVS-AX Analog Soft Starter 8-170A, 220-600V Instruction Manual Ver. 10/11/2009 2 Table of Content RVS-AX Instruction Manual 1. TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Table of Content...2 2. Safety & Warnings...3 2.1 Safety...3
MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE. Quick Setup VLT FCM 300 Series. Phone: Fax: Web: -
 MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Quick Setup VLT FCM 300 Series Factory setting Motors type B14 & B34 mounting Reset (pushbutton) Start Jog Speed reference Fig. 1 - Reset to be closed short time for resetting
MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Quick Setup VLT FCM 300 Series Factory setting Motors type B14 & B34 mounting Reset (pushbutton) Start Jog Speed reference Fig. 1 - Reset to be closed short time for resetting
Unidrive M400 Fast set-up and diagnostics with real-text display, integrated PLC and safety inputs
 Unidrive M400 Fast set-up and diagnostics with real-text display, integrated PLC and safety inputs 0.25 kw - 110 kw (0.33 hp - 150 hp) 100 V 200 V 400 V 575 V 690 V Unidrive M400 features Optional AI-485
Unidrive M400 Fast set-up and diagnostics with real-text display, integrated PLC and safety inputs 0.25 kw - 110 kw (0.33 hp - 150 hp) 100 V 200 V 400 V 575 V 690 V Unidrive M400 features Optional AI-485
Low voltage AC drives. ABB component drives ACS to 2.2 kw / 0.25 to 3 hp Catalog
 Low voltage AC drives ABB component drives ACS55 0.18 to 2.2 kw / 0.25 to 3 hp Catalog ABB component drives ABB component drives ABB component drives are designed to be incorporated into a wide variety
Low voltage AC drives ABB component drives ACS55 0.18 to 2.2 kw / 0.25 to 3 hp Catalog ABB component drives ABB component drives ABB component drives are designed to be incorporated into a wide variety
Matrix APAX. 380V-415V 50Hz TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL
 Matrix APAX 380V-415V 50Hz TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL WARNING High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation of this filter. Quick Reference ❶ Performance Data Pages
Matrix APAX 380V-415V 50Hz TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL WARNING High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation of this filter. Quick Reference ❶ Performance Data Pages
Appendix: Safety and application notes for... 15
 Contents Safety... 2 Warnings... 2 Symbols used in this manual... 2 Operator s safety... 2 Avoid filter module damage... 2 DC-link resonance... 2 Description... 3 Description... 3 Ordering numbers, 380-415
Contents Safety... 2 Warnings... 2 Symbols used in this manual... 2 Operator s safety... 2 Avoid filter module damage... 2 DC-link resonance... 2 Description... 3 Description... 3 Ordering numbers, 380-415
Capacitor reforming instructions Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link
 ABB low voltage AC drives, wind converters and solar inverters Capacitor reforming instructions Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link 2009 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 3BFE64059629
ABB low voltage AC drives, wind converters and solar inverters Capacitor reforming instructions Converter modules with electrolytic DC capacitors in the DC link 2009 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 3BFE64059629
dv Sentry TM 208V 600V INSTALLATION GUIDE Quick Reference ❶ How to Install Pages 6 14 ❷ Startup/Troubleshooting Pages WARNING
 dv Sentry TM 208V 600V INSTALLATION GUIDE FORM: DVS-IG-E REL. January 2018 REV. 003 2018 MTE Corporation High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation of this filter.
dv Sentry TM 208V 600V INSTALLATION GUIDE FORM: DVS-IG-E REL. January 2018 REV. 003 2018 MTE Corporation High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation of this filter.
Instruction Manual. Harmonic Filter AHF 005/010. Drives Solutions
 Harmonic Filter AHF 005/010 Instruction Manual Drives Solutions Contents Safety... 2 Warnings... 2 Symbols used in this manual... 2 Operator s safety... 2 Avoid filter module damage... 2 DC-link resonance...
Harmonic Filter AHF 005/010 Instruction Manual Drives Solutions Contents Safety... 2 Warnings... 2 Symbols used in this manual... 2 Operator s safety... 2 Avoid filter module damage... 2 DC-link resonance...
Quick guide. Plug-in fans GPPM with FC101_106 August 2014
 Quick guide Plug-in fans GPPM with FC101_106 August 2014 Fläkt Woods permanent magnet motors and speed controllers for plug fans GPPM 1. General Fläkt Woods offers a wide range of permanent magnet motors
Quick guide Plug-in fans GPPM with FC101_106 August 2014 Fläkt Woods permanent magnet motors and speed controllers for plug fans GPPM 1. General Fläkt Woods offers a wide range of permanent magnet motors
DCT880. Quick guide DCT880 Thyristor power controller (20 A bis 4160 A)
 DCT880 Quick guide DCT880 Thyristor power controller (20 A bis 4160 A) 3 Safety Instructions Chapter overview This chapter contains the safety instructions you must follow when installing, operating and
DCT880 Quick guide DCT880 Thyristor power controller (20 A bis 4160 A) 3 Safety Instructions Chapter overview This chapter contains the safety instructions you must follow when installing, operating and
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER. SERIES B Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR REL MTE Corporation
 M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER SERIES B 380-415 Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 015 REL. 040709 2003 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation Matrix Filter
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER SERIES B 380-415 Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 015 REL. 040709 2003 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation Matrix Filter
Burden Fuse Rating Resistor SAF / SAK6 1NM 10mm M8 12NM SAF / SAK10 2NM 16mm M8 12NM
 Contents Section Page 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 Specification 1-4 3.0 Installation 5-8 4.0 Programming 9-10 5.0 Menus 10-12 6.0 Fault Finding/Diagnostics 12-13 7.0 Communication 13 8.0 Setting Up 13-16 1.0
Contents Section Page 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 Specification 1-4 3.0 Installation 5-8 4.0 Programming 9-10 5.0 Menus 10-12 6.0 Fault Finding/Diagnostics 12-13 7.0 Communication 13 8.0 Setting Up 13-16 1.0
SINAMICS GM150 IGCT version
 /2 Overview /2 Benefits /2 Design /6 Function /8 Selection and ordering data /8 Options Technical data /14 General technical data /15 Control properties /15 Ambient conditions /16 Installation conditions
/2 Overview /2 Benefits /2 Design /6 Function /8 Selection and ordering data /8 Options Technical data /14 General technical data /15 Control properties /15 Ambient conditions /16 Installation conditions
Technical Data Sheet. Uninterruptible Power Supply. Critical Power. imagination at work
 Technical Data Sheet Uninterruptible Power Supply SGSE_010-040_S1_UPS_GE_01 GE Consumer & Industrial SA General Electric Company CH 6595 Riazzino (Locarno) Switzerland T +41 (0)91 / 850 51 51 F +41 (0)91
Technical Data Sheet Uninterruptible Power Supply SGSE_010-040_S1_UPS_GE_01 GE Consumer & Industrial SA General Electric Company CH 6595 Riazzino (Locarno) Switzerland T +41 (0)91 / 850 51 51 F +41 (0)91
LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES. ABB industrial drives ACS880, single drives 0.55 to 3200 kw
 LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES ABB industrial drives ACS880, single drives 0.55 to 3200 kw 2 ABB INDUSTRIAL DRIVES, ACS880, SINGLE DRIVES, CATALOG Reliability, performance and safety. ACS880 series. 3 Table of
LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES ABB industrial drives ACS880, single drives 0.55 to 3200 kw 2 ABB INDUSTRIAL DRIVES, ACS880, SINGLE DRIVES, CATALOG Reliability, performance and safety. ACS880 series. 3 Table of
Presentation Soft starters 0 Altistart 48 soft start - soft stop units
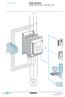 Presentation Soft starters 5 6 7 65_Ver.-EN.fm/ Presentation (continued) Soft starters Applications The Altistart 8 soft start - soft stop unit is a controller with 6 thyristors which is used for the torque-controlled
Presentation Soft starters 5 6 7 65_Ver.-EN.fm/ Presentation (continued) Soft starters Applications The Altistart 8 soft start - soft stop unit is a controller with 6 thyristors which is used for the torque-controlled
 Standard Features 200-600V, 50/60Hz input power supply Built-in run rated (AC1) By-pass contactor up to 820 A * Rated 450% current Conformal coated circuit board Voltage ramp or current limit start modes
Standard Features 200-600V, 50/60Hz input power supply Built-in run rated (AC1) By-pass contactor up to 820 A * Rated 450% current Conformal coated circuit board Voltage ramp or current limit start modes
FLÄKTGROUP PM-MOTOR WITH INTEGRATED FC 106 FREQUENCY CONVERTER
 FLÄKTGROUP PM-MOTOR WITH INTEGRATED FC 106 FREQUENCY CONVERTER INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS Risk of electric shock: Motor terminals may still be live if the impeller is rotating, even when
FLÄKTGROUP PM-MOTOR WITH INTEGRATED FC 106 FREQUENCY CONVERTER INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS Risk of electric shock: Motor terminals may still be live if the impeller is rotating, even when
ABB component drives ACS150, 0.5 to 5 Hp
 ABB component drives ACS150, 0.5 to 5 Hp Technical Catalog BUSINESS PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents Choice 1: Simply contact your local ABB drives sales office
ABB component drives ACS150, 0.5 to 5 Hp Technical Catalog BUSINESS PROFILE INDUSTRIES PRODUCTS APPLICATIONS EXPERTISE PARTNERS SERVICES Contents Choice 1: Simply contact your local ABB drives sales office
DENVER PUBLIC SCHOOLS DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS This Standard is for guidance only. SECTION MOTORS, STARTERS & DRIVES
 PART 0 DESIGN STANDARDS 0.01 GENERAL DESIGN GUIDELINES A. Coordinate starter needs for mechanical equipment prior to 50% CD and confirm again for 100% CD submittal. B. Coordinate temperature controls requirements
PART 0 DESIGN STANDARDS 0.01 GENERAL DESIGN GUIDELINES A. Coordinate starter needs for mechanical equipment prior to 50% CD and confirm again for 100% CD submittal. B. Coordinate temperature controls requirements
Technical Data Sheets
 GE Digital Energy Power Quality Technical Data Sheets Digital Energy Uninterruptible Power Supply SG-CE Series 60 80 100 120 kva PurePulse 400 Vac CE Series 1 SG-CE Series 100-120 kva PurePulse SG-CE Series
GE Digital Energy Power Quality Technical Data Sheets Digital Energy Uninterruptible Power Supply SG-CE Series 60 80 100 120 kva PurePulse 400 Vac CE Series 1 SG-CE Series 100-120 kva PurePulse SG-CE Series
ABB industrial drive ACS800 multidrive, 1.5 kw kw ACS800 multidrive modules, 1.5 kw kw Technical catalogue
 ABB industrial drive ACS800 multidrive,.5 kw - 5600 kw ACS800 multidrive modules,.5 kw - 000 kw Technical catalogue Drive IT Low Voltage AC Drive PRODUCTS Type code structure Type code ACS800 - X07-0003
ABB industrial drive ACS800 multidrive,.5 kw - 5600 kw ACS800 multidrive modules,.5 kw - 000 kw Technical catalogue Drive IT Low Voltage AC Drive PRODUCTS Type code structure Type code ACS800 - X07-0003
ABB drives for water and wastewater ACQ to 500 kw
 Low voltage AC drives ABB drives for water and wastewater ACQ810 0.37 to 500 kw The intelligent drive choice for water and wastewater applications The ACQ810 drive for water and wastewater applications
Low voltage AC drives ABB drives for water and wastewater ACQ810 0.37 to 500 kw The intelligent drive choice for water and wastewater applications The ACQ810 drive for water and wastewater applications
Technical Data Sheet. Uninterruptible Power Supply. Critical Power. imagination at work
 Technical Data Sheet Uninterruptible Power Supply TLES_040-120_S1_UPS_GE_Floor_01 GE Consumer & Industrial SA General Electric Company CH 6595 Riazzino (Locarno) Switzerland T +41 (0)91 / 850 51 51 F +41
Technical Data Sheet Uninterruptible Power Supply TLES_040-120_S1_UPS_GE_Floor_01 GE Consumer & Industrial SA General Electric Company CH 6595 Riazzino (Locarno) Switzerland T +41 (0)91 / 850 51 51 F +41
EDB6032_G/GB Antriebstechnik. Operating Instructions. Brake chopper 6032/6033/6034
 EDB6032_G/GB 00376698 Antriebstechnik Operating Instructions Brake chopper 6032/6033/6034 These operating instructions are valid for the devices with the nameplate data: 6032_G.2E 6033_G.2E 6034_G.1A Type
EDB6032_G/GB 00376698 Antriebstechnik Operating Instructions Brake chopper 6032/6033/6034 These operating instructions are valid for the devices with the nameplate data: 6032_G.2E 6033_G.2E 6034_G.1A Type
High Frequency SineWave Guardian TM
 High Frequency SineWave Guardian TM 380V 480V INSTALLATION GUIDE FORM: SHF-IG-E REL. January 2018 REV. 002 2018 MTE Corporation High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation
High Frequency SineWave Guardian TM 380V 480V INSTALLATION GUIDE FORM: SHF-IG-E REL. January 2018 REV. 002 2018 MTE Corporation High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation
VFD Best Practices: Getting the Most from Your VFD Investment
 TECH TOPICS VFD Best Practices: Getting the Most from Your VFD Investment The purpose of this document is to outline best practices for successful application and installation of VFDs. Following these
TECH TOPICS VFD Best Practices: Getting the Most from Your VFD Investment The purpose of this document is to outline best practices for successful application and installation of VFDs. Following these
UNIDRIVE M600. Manufacturing Automation drive. High performance drive for induction and sensorless permanent magnet motors
 UNIDRIVE M600 Manufacturing Automation drive High performance drive for induction and sensorless permanent magnet motors Unidrive M100 Unidrive M200 Unidrive M300 Unidrive M400 Unidrive M600 Unidrive M700
UNIDRIVE M600 Manufacturing Automation drive High performance drive for induction and sensorless permanent magnet motors Unidrive M100 Unidrive M200 Unidrive M300 Unidrive M400 Unidrive M600 Unidrive M700
SOLSTART Instruction Manual
 Solstart Analog Soft Starter 8-58A, 220-600V Instruction Manual Ver. 23/03/2009 2 Table of Content SOLSTART Instruction Manual 1. TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Table of Content...2 2. Safety & Warnings...3 2.1 Safety...3
Solstart Analog Soft Starter 8-58A, 220-600V Instruction Manual Ver. 23/03/2009 2 Table of Content SOLSTART Instruction Manual 1. TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Table of Content...2 2. Safety & Warnings...3 2.1 Safety...3
Safety Working with LV Drives
 US1008e_LV Drive Safety_C, April 2009 Safety Working with LV Drives Intended Audience Only qualified electricians and engineers are allowed to install and maintain a LV Drive Students of this training
US1008e_LV Drive Safety_C, April 2009 Safety Working with LV Drives Intended Audience Only qualified electricians and engineers are allowed to install and maintain a LV Drive Students of this training
Cat. No. I526-E1-1 USER S MANUAL 3G3IV-PLKEB2 /4. Braking Resistor Units 3G3IV-PCDBR2 B/4 B. Braking Units
 Cat. No. I526-E1-1 USER S MANUAL 3G3IV-PLKEB2 /4 Braking Resistor Units 3G3IV-PCDBR2 B/4 B Braking Units Thank you for choosing an OMRON Braking Resistor Unit and Braking Unit. Proper use and handling
Cat. No. I526-E1-1 USER S MANUAL 3G3IV-PLKEB2 /4 Braking Resistor Units 3G3IV-PCDBR2 B/4 B Braking Units Thank you for choosing an OMRON Braking Resistor Unit and Braking Unit. Proper use and handling
SINAMICS S120 drive system
 s in booksize format Siemens AG 2007 Design (continued) Jumper for connecting the 24 V DC busbar to the adjacent Motor Module 24 V terminal adapter Connector X21 for digital inputs/outputs Connector X22
s in booksize format Siemens AG 2007 Design (continued) Jumper for connecting the 24 V DC busbar to the adjacent Motor Module 24 V terminal adapter Connector X21 for digital inputs/outputs Connector X22
SINUS PENTA 2T/4T SINUS PENTA 2T/4T
 SINUS PENTA 2T/4T SINUS PENTA 2T/4T Technical Highlights One product, 5 integrated functions - IFD (Inverter Frequency Drive): vector modulation function for general-purpose applications (V/F pattern).
SINUS PENTA 2T/4T SINUS PENTA 2T/4T Technical Highlights One product, 5 integrated functions - IFD (Inverter Frequency Drive): vector modulation function for general-purpose applications (V/F pattern).
Appendix: Safety and application notes for 19
 Contents Safety 2 Warnings 2 Symbols used in this manual 2 Operator's safety 2 Avoid filter module damage 2 DC-link resonance 2 Description 3 Description 3 Ordering numbers, 380-415 V, 50 Hz 4 Ordering
Contents Safety 2 Warnings 2 Symbols used in this manual 2 Operator's safety 2 Avoid filter module damage 2 DC-link resonance 2 Description 3 Description 3 Ordering numbers, 380-415 V, 50 Hz 4 Ordering
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n. dv/dt Filter. Series A VAC USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR REL MTE Corporation
 M T E C o r p o r a t i o n dv/dt Filter Series A 440-600 VAC USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 019 REL. 041119 2004 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation dv/dt Filter is designed
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n dv/dt Filter Series A 440-600 VAC USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 019 REL. 041119 2004 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation dv/dt Filter is designed
SD700FR. Regenerative Active Front End VARIABLE SPEED DRIVES POWER ELECTRONICS / SD700 SERIES 4 QUADRANT. icool
 FR VARIABLE SPEED DRIVES Regenerative Active Front End icool 4 QUADRANT POWER ELECTRONICS / SD700 SERIES FR SD700FR SERIES goes one step ahead keeping the family unique characteristics. Based on the latest
FR VARIABLE SPEED DRIVES Regenerative Active Front End icool 4 QUADRANT POWER ELECTRONICS / SD700 SERIES FR SD700FR SERIES goes one step ahead keeping the family unique characteristics. Based on the latest
IRT 4000 AT-S/M/L. Technical Manual. quality IN MOTION. quality IN MOTION
 IRT quality IN MOTION www.irtsa.com 4000 AT-S/M/L Technical Manual IRT quality IN MOTION E2 0 8 4 1 5 September 2013-Rev. 5 UL Requirements Drives Series 2000 / 4000 AT 1. Field wiring terminal to use
IRT quality IN MOTION www.irtsa.com 4000 AT-S/M/L Technical Manual IRT quality IN MOTION E2 0 8 4 1 5 September 2013-Rev. 5 UL Requirements Drives Series 2000 / 4000 AT 1. Field wiring terminal to use
LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES. ABB industrial drives ACS880, drive modules 0.55 to 3200 kw
 LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES ABB industrial drives ACS880, drive modules 0.55 to 3200 kw 2 ABB INDUSTRIAL DRIVES, ACS880 DRIVE MODULES, CATALOG Reliability, performance and safety. ACS880 series. 3 Table of contents
LOW VOLTAGE AC DRIVES ABB industrial drives ACS880, drive modules 0.55 to 3200 kw 2 ABB INDUSTRIAL DRIVES, ACS880 DRIVE MODULES, CATALOG Reliability, performance and safety. ACS880 series. 3 Table of contents
REFERENCE MANUAL FORM: MX-TRM-E REL REV MTE
 Matrix APAX 380V-415V 50Hz TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL FORM: MX-TRM-E REL. September 2014 REV. 002 2014 MTE Corporation WARNING High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation
Matrix APAX 380V-415V 50Hz TECHNICAL REFERENCE MANUAL FORM: MX-TRM-E REL. September 2014 REV. 002 2014 MTE Corporation WARNING High Voltage! Only a qualified electrician can carry out the electrical installation
Operating Manual (Edition 04/2004) sinamics. Braking Module / Braking Resistor SINAMICS G130
 Operating Manual (Edition 04/2004) sinamics Braking Module / Braking Resistor SINAMICS G130 04/04 Contents Contents 1 Safety Information 1-1 2 General 2-1 3 Mechanical Installation 3-1 4 Connection 4-1
Operating Manual (Edition 04/2004) sinamics Braking Module / Braking Resistor SINAMICS G130 04/04 Contents Contents 1 Safety Information 1-1 2 General 2-1 3 Mechanical Installation 3-1 4 Connection 4-1
WARREN COUNTY, N.Y. M/E REFERENCE A. Submit manufacturer's product data on all motors and adjustable speed drives.
 SECTION 230513 - MOTORS AND ADJUSTABLE SPEED DRIVES PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. Provide labor, materials, equipment and services as required for the complete installation designed in Contract Documents.
SECTION 230513 - MOTORS AND ADJUSTABLE SPEED DRIVES PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. Provide labor, materials, equipment and services as required for the complete installation designed in Contract Documents.
Powerdrive FX Ultra compact regenerative drive solution
 Powerdrive FX Ultra compact regenerative drive solution 22 kw - 90 kw (30 hp - 125 hp) 400 V 480 V Powerdrive FX Drives with dynamic braking Based on innovative C-Light 4 Quadrant technology, the variable
Powerdrive FX Ultra compact regenerative drive solution 22 kw - 90 kw (30 hp - 125 hp) 400 V 480 V Powerdrive FX Drives with dynamic braking Based on innovative C-Light 4 Quadrant technology, the variable
LV Capacitor CLMD03 Power Module Instruction manual
 LV Capacitor CLMD03 Power Module Instruction manual Table of Contents 1 Safety... 3 2 Upon reception... 3 2.1 Inspection on reception... 3 2.2 Storage- transportation handling... 3 3 Hardware Description...
LV Capacitor CLMD03 Power Module Instruction manual Table of Contents 1 Safety... 3 2 Upon reception... 3 2.1 Inspection on reception... 3 2.2 Storage- transportation handling... 3 3 Hardware Description...
