Phase. Trade of Motor Mechanic. Module 5. Unit 1. Fuel Supply System
|
|
|
- Egbert Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 5 Unit 1
2 Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision SOLAS 2013
3 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Unit Objective Health, Safety and Environmental Awareness Health and Safety Petrol fire Classification Fuel Tank Structure Fuel Tanks Tank Repairs Filler Pipe Testing Fuel Level Gauge Using a Potentiometer Fuel Gauge Return-Type Components Return-Type Fuel Lines Fuel Pump Motor The Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Filters Fuel Rail Fuel Pressure Regulator Inertia Switches The Electric Fuel Pump (Rotary Type) Fuel Pumps Removal and Refitting of Fuel Pumps Removing and Replacing Petrol Fuel Filters Changing the Fuel Filter Replacing a Fuel Filter Return-Type Components Fuel Injection Pressures Typical Fuel Pressures Fuel Distribution Rail and Inlet Manifold Pressures Fuel Pressure Versus Inlet Manifold Vacuum Constant Pressure Difference Explained Maintaining Constant Pressure Differential Electrical Circuit for the EFI Wiring Diagram Servicing Fuel Pump Relays Applicable NCT/DoT VTM Requirements NCT/Dot VTM Requirements Self Assessment Suggested Exercises Training Resources Task Sheets Replacing a Fuel Filter Obtaining & Interpreting Scan Tool Data Suggested Further Reading... 35
4
5 Introduction There are 3 Units in this Module. Unit 1 focuses on Fuel Supply Systems, Unit 2 on Electronic Fuel Injection and Unit 3 on Emissions. Module 5 Petrol Fuel Injection Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Fuel Supply Electronic Fuel Emmissions System Injection Module 5 of this course covers the Petrol Fuel Injection aspect of automotive technology. This is the first unit in module 5 and introduces the. The purpose of any fuel supply system is to deliver fuel to the engine in a form in which it can mix with air to form a combustible mixture. The components related to the fuel supply system will be covered in this unit. Health and safety issues related to this unit will also be covered. 1
6 Unit Objective By the end of this unit each apprentice will be able to: State and apply the health, safety and environmental awareness and precautionary procedures applicable to working on petrol fuel supply systems Identify the correct fire extinguishers required for various types of petrol fuel fires Describe the structure of a fuel tank and the appropriate cleaning/repair methods Test the operation of a fuel level gauge using a potentiometer On a fuel injected vehicle/training unit, locate and identify each component involved in the return-type fuel supply system State the function and describe the principles of operation of the return-type fuel supply system components Describe the structure and operating principle of the externally-mounted electric fuel pump (rotary type) Remove and refit external and/or submerged fuel pumps Remove and replace petrol fuel filters Specify the typical fuel system pressures applicable to singlepoint (throttle body) and multi-point fuel injection systems Explain why a constant pressure differential needs to be maintained between the fuel distribution rail and the inlet manifold Draw a typical electrical circuit for the fuel supply system Remove, test and refit fuel pump relays Outline the NCT/DoT VTM requirements applicable to the fuel tank, filter, fuel lines and air filter of a petrol engine 2
7 1.0 Health, Safety and Environmental Awareness Key Learning Points Health, safety and environmental awareness issues and procedures relating to personal and fire hazards from fuel spillage/leakage/ storage, sparks/ignition sources (including static electricity and mobile phones) and system pressure during component removal/ replacement; precautions necessary to avoid damage to catalytic converter due to unburned fuel etc. Identification of the correct fire extinguishers required for various types of petrol fuel fires 1.1 Health and Safety Improper storage, leaks and spillage of fuel could lead to fire due to sparks/ignition sources (including static electricity and mobile phones) Instruction is given on the correct and safe storage of fuel (use of correct container etc.) leaks repaired and mopped as soon as they occur and disposed in an environmental friendly manner. Pressurised fuel can be sprayed out when components are being removed or replaced, this could lead to injury to eyes, face etc. also fire. Instruction is given on the correct and safe method for removing and replacing components also the correct use and type of fire extinguisher. Safety precautions need also be applied to prevent damage to the catalytic converter as un-burnt fuel will damage the unit. 1.2 Petrol fire Classification "B" class fires involve flammable liquids such as petrol. Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers are most effective when used against B C and E class fires. The gas is heavier than air and provides an inert blanket that smothers the fire. A carbon dioxide fire extinguisher will spray small ice particles with the gas. This is normal. Dry Powder fire extinguishers contain a fine powder usually sodium bicarbonate held under pressure by an inert gas. The extinguisher smothers the fire with a fine powder. These extinguishers are good to fight any fuel or liquid fire. Foam fire extinguishers contain a chemical that forms a soft foam that floats over the target area and smothers the fire. 3
8 2.0 Fuel Tank Structure Key Learning Points Fuel tank structure and materials, methods of filling Fuel tank cleaning and repair methods 2.1 Fuel Tanks Where the tank is mounted depends on where the engine is and on space and styling. Safety demands that it is positioned well away from heated components and outside the passenger compartment. Most tanks are made of tinned sheet steel that has been pressed into shape. Some passenger car tanks are made of non-metallic materials. Aluminium or steel is used on commercial vehicles. Today s modern petrol car has a smaller filling hole than that of diesel this is to insure only unleaded fuel is put into the tank. The tank is usually in 2 parts, joined by a continuous weld around the flanges where the parts fit together. Baffles make the tank more rigid. They also stop surging of fuel and ensure fuel is available at the pickup-tube. Fuel expands and contracts as temperature rises and falls. So fuel tanks are vented to let them breathe. Modern emission controls prevent tanks being vented directly to the atmosphere. They must use evaporative control systems. Vapour from the fuel tank is trapped in a charcoal canister and stored there, until it is burned in the engine. A vapour or vent line with a check valve connects the space above the liquid fuel with the canister. This valve opens when pressure starts to rise and lets vapour through, but not liquid. Liquid fuel closes the check valve and blocks the line, stopping liquid fuel reaching the charcoal. Some systems have a small container, called a liquid-vapour separator, above the fuel tank. It also prevents liquid fuel reaching the charcoal filter. 4
9 The cap on the petrol tank also stops petrol vapour escaping and polluting the atmosphere. This is important for petrol which is very volatile and vaporizes easily, especially in warmer climates. Some petrol caps have a low pressure valve built-in. It keeps a balance between the pressure in the tank and the outside atmospheric pressure. As petrol in the tank is used, the air space above the fuel increases. This causes a fall in pressure, compared to outside atmospheric pressure. The valve then opens and lets more air into the tank. A fall in temperature can cause a fall in the pressure in the tank. The valve opens to admit more air until inside and outside pressures equalize again. The fuel gauge shows how much fuel is still in the tank. It has a gauge unit on the dash and a sender unit in the tank. This unit indicates the level of fuel in the tank and transmits this information to the gauge in the dash-panel. 2.2 Tank Repairs Most vehicle manufacturer s recommend no repairs are to be carried out on fuel tanks. Damaged or leaking tanks should be replaced with an original manufacturer s replacement tank. If the tank has to be cleaned it should be removed from the vehicle and correct safety and environmental precautions observed. Tanks that are empty of fuel are extremely dangerous as they contain highly explosive fuel vapours. Any sparks or external heat source may cause an explosion! Be very careful of fuel tanks; always consult vehicles manufactures data for precise information on the service or removal/fitting of automobile fuel tanks. 2.3 Filler Pipe On unleaded petrol vehicles with catalytic converters, the filler neck is designed to prevent leaded fuel being added. Its diameter is smaller than those on leaded vehicles and a trapdoor inside the filler can only be opened by the nozzle of the unleaded petrol spout. 5
10 3.0 Testing Fuel Level Gauge Using a Potentiometer Key Learning Points Use of a potentiometer to test the operation of a fuel level gauge 3.1 Fuel Gauge A fuel gauge is used to indicate the level of fuel contained in a tank. The sending unit usually uses a float connected to a variable resistor. When the tank is full, the resistor is set to its low resistance value. As the tank empties the float drops and slides a moving contact along the resistor, increasing its resistance, finally reaching its highest value when the tank is empty. Meanwhile, the indicator unit mounted on the instrument panel is measuring and displaying the amount of electrical current flowing through the sending unit. When the tank level is high and maximum current is flowing, the needle points to full indicating a full tank. When the tank is empty and the least current is flowing, the needle points to empty indicating an empty tank. The testing of a fuel gauge sender has to be carried out in strict accordance with manufactures instructions. 6
11 Practical Task Fuel Gauge Operation A potentiometer is a mechanically variable resistor which, in EFI applications, is normally a film-type. This type of unit is usually fitted in the fuel tank and is known as a fuel gauge or sender unit. It can be linear, or circular, in construction and has 3 electrical connecting points. Two are at the ends of the resistor and a third is attached to a centre sliding contact, arranged to move across the resistor. A reference voltage is applied to the resistor so that a steady current flows through it. As the centre sliding contact moves across the resistor, it measures the voltage at the point it is in contact with and provides a reference voltage for that position. Fuel gauge testing can only be done following manufactures recommended procedures.please refer to your instructor for additional information, which is available from the automotive technical manuals. 7
12 4.0 Return-Type Fuel Supply System Components Key Learning Points Function and principles of operation of each return-type fuel supply system component 4.1 Return-Type This is called the standard system; fuel is supplied to the engine mounted, fuel distribution rail with the injectors, the pressure regulator which is fitted to this rail controls the fuel pressure and excess fuel is carried back to the tank. 4.2 Fuel Lines Fuel lines are usually made of metal tubing or synthetic materials. A fuel supply line carries fuel from the tank to the engine. A return line may also be provided to allow excess fuel to return to the tank. This helps prevent the formation of vapour that can occur in the fuel supply during hot conditions. 8
13 4.3 Fuel Pump Motor An electric rotary pump can be located inside the tank, but may be fitted externally, particularly on older models. Petrol enters at one end and leaves at the other so it is always full. This lubricates the pump motor and keeps it cool. Lack of oxygen inside the pump eliminates the dangers of fire/ explosion and spark-suppression elements may be fitted in the end plate. 4.4 The Fuel Pump Relay This is the relay that responds to the voltage signal from the ECU to switch on the pump to develop fuel pressure. When the ignition is first turned on, the pump will run for some seconds to build this fuel pressure but the control unit will then switch off this relay until a signal from the crankshaft position sensor indicates to the ECU that the engine is rotating and starting and the relay will be energised once again. This relay can be located in the main fuse box. 9
14 4.5 Fuel Filters It is very important to supply clean fuel to the fuel rail in EFI systems. Small particles of dirt can block an injection nozzle and cause an irregular spray pattern. Any water in the fuel will corrode the inside of the injector - especially if the engine stands unused for long periods. The first filtering occurs with a strainer or fine gauze in the fuel tank. The next time filtering occurs at the in-line filter, on the highpressure side of the pump. This is a large-capacity filter encased, in a steel shell or aluminium housing. This housing must be rigid, to withstand the high pressures in the system. The filter is a pleated paper type with pore size of about 10 microns. A fluted support plate keeps the filter stable in the housing. The filter is directional and it must be fitted in the direction of fuel flow. Due to the pressure in the system it is important to depressurise the system before changing fuel filters. Removing and replacing fuel filters should be carried out according to manufactures specifications. Final filtering occurs with a small conical filter at the fuel entry to the injector. 10
15 4.6 Fuel Rail The fuel rail is a large diameter pipe used to carry the high pressure fuel to the individual injectors of multi-point injection systems. All injectors are attached to this rail and therefore all have equal fuel line pressure. A fuel pressure damper may be fitted to the rail to steady out the small pressure oscillations in the fuel due to the pump and injector actions. Single point systems have the fuel delivered from the filter directly to the single or central injector. 4.7 Fuel Pressure Regulator Typical Fuel pressures for a single point injection system is approx. 3 bar. For multi injection it is higher between 4 and 5bar. Please refer to manufactures data when checking each system. In multi-point injection systems, the fuel pressure regulator is located on the outlet from the fuel rail. Fuel circulates continuously, but the fuel pressure regulator controls the quantity of fuel returning to the tank. This in turn controls the pressure in the fuel rail. It consists of a metal housing with a spring-loaded diaphragm between the 2 halves of a steel pressed shell. A valve attached to the diaphragm controls the exposure of the opening to the return line. With the pump operating, fuel pressure builds up on the underside of the diaphragm and raises it against the force of the spring. The central valve is carried with it, which lets fuel return to the tank. Fuel in the rail is now kept under pressure that s determined by the force in the spring. Further control is needed as fuel pressure has to stay at a constant value above manifold pressure. Otherwise, the fuel quantity delivered won t be accurate. Examples of fuel system pressure for single and multi point injection can be obtained in the Autodata CD from your instructor. 11
16 The spring housing above the diaphragm is sealed and connected to the intake manifold. Low pressure in the manifold then acts on the diaphragm and helps its movement against the spring. As a result, fuel pressure is continually corrected in step with changes in manifold pressure. When manifold pressure is low, as at idle, fuel pressure will be lowered. When manifold pressure is high i.e. at full throttle the fuel pressure increases. As a result, the quantity of fuel injected into the engine is set solely by the duration of the electrical pulse from the control unit. 4.8 Inertia Switches A safety device is fitted to automatically switch off the electrical supply to the fuel pump in the event of the vehicle being involved in a collision or a severe bump. This is called an inertia or impact safety switch. This is to avoid the possibility of petrol that is under working pressure (up to 3.0 bar) being sprayed indiscriminately through a leaking pipe/fuel line or fractured component that may cause fire. The switch should not be reset until the fuel system has been fully checked for possible leaks. Access to this switch is in the interior of vehicle, usually in the driver or front passenger, footwell. Operation of the Inertia Fuel Cut Off Switch This switch uses a mechanical device consisting of a steel ball in a funnel. The ball is held in place by a magnet. When subjected to shock, the ball breaks away from the magnet and rolls up the side of the funnel, hitting an actuating arm of the switch mechanism. When this happens, the linkage in the switch opens the electrical circuit and cuts off current to the pump. The switch remains open until it is reset. 12
17 5.0 The Electric Fuel Pump (Rotary Type) Key Learning Points Structure and operating principle of the externally mounted electric fuel pump (rotary type) including purpose of pressure relief valve and non-return valve 5.1 Fuel Pumps In an electronic fuel-injected engine, the fuel for the injectors must be pressurized before the engine can be started, so an electric fuel pump is necessary. An electric rotary pump can be located in the tank, or externally, on the underside of the body and should be checked and replaced according to manufactures recommendations. Petrol enters at one end and leaves at the other, so it is always full. This lubricates the pump motor and keeps it cool. The pumping element is a rollercell device driven by an electric motor. A rotor disc is mounted eccentrically in the pump housing. It has recesses around its edge, containing metal rollers. As the disc rotates, centrifugal force pushes them outward. This forms a rotating seal and fuel is carried round in the cavities formed between the rollers. Because of the eccentric mounting of the disc, these cavities expand as they pass the inlet and contract passing the outlet. This pressurises the fuel and forces it into the fuel line. For a short time after an engine is switched off, engine temperature keeps rising and that can cause excess vapour in the fuel lines. 13
18 This pump stops this, with a non-return valve on its outlet, which maintains the pressure in the fuel line during that short time. If a fuel blockage occurs further along the fuel line, it can overload the pump motor and make it overheat. So a high-pressure relief valve inside the pump lets fuel keep circulating. When the pump is mounted externally, a low-pressure pump can be used to supply fuel to the main pump s inlet. This low-pressure pump is mounted in the fuel tank. It s an electrical centrifugal type and it operates in the same way as the other high-pressure pump. 14
19 6.0 Removal and Refitting of Fuel Pumps Key Learning Points Removing/refitting external and/or submerged fuel pumps using manufacturer's recommended procedures Practical Task Please refer to your instructor for additional information, which is available from the automotive technical manuals. 7.0 Removing and Replacing Petrol Fuel Filters Key Learning Points Removing/replacing fuel filters using manufacturer's recommended procedures; importance of regular fuel filter replacement 7.1 Changing the Fuel Filter The fuel pump has a one-way valve on the fuel output side and this maintains a residual pressure on the fuel when the engine is not running and therefore it is important to depressurise the system before opening any fuel line. Removing and replacing fuel filters should be carried out according to manufactures recommended procedures. Always beware of the danger of imminent and future fire! Therefore, always examine the fully pressurised system carefully for possible leaks after fitting a replacement filter. 15
20 7.2 Replacing a Fuel Filter Objective Preparation and Safety Remove and replace a fuel filter. Personal Safety Safety Check Whenever you perform a task in the workshop you must use personal protective clothing and equipment that is appropriate for the task and which conforms to your local safety regulations and policies. Among other items, this may include: Work clothing - such as coveralls and steel-capped footwear Eye protection - such as safety glasses and face masks Ear protection - such as earmuffs and earplugs Hand protection such as rubber gloves and barrier cream Respiratory equipment such as face masks etc. If you are not certain what are appropriate or required, ask your instructor Petrol fuel, in particular petrol vapour, is explosive and highly flammable. Be careful not to spill any fuel onto a hot engine component where it could ignite and start a fire. Be careful not to cause any sparks while you are changing a fuel filter. Collect the petrol waste in a metal container and dispose of it in an environmentally prescribed way. Always make sure that you wear the appropriate personal protection equipment before starting the job. It is very easy to hurt yourself even when the most exhaustive protection measures are taken. 16
21 Points to Note Always make sure that your work area/environment is as safe as you can make it. Do not use damaged, broken or worn out workshop equipment. Always follow any manufacturer's personal safety instructions to prevent damage to the vehicle you are servicing. Make sure that you understand and observe all legislative and personal safety procedures when carrying out the following tasks. If you are unsure of what these are, ask your supervisor. There are a variety of fuel filters, so before you start always check the shop manual for the correct type of filter for the vehicle and the specific procedure for removing and replacing it. There are several ways to relieve the static pressure in the fuel system before removing the fuel lines. For example, some fuel injection systems have a valve specifically to bleed off pressure. Other methods include bypassing the fuel pump relay with a jumper wire, or removing the fuel pump fuse and running the engine until it uses up the remaining fuel in the system and stops. Refer to the shop manual for the recommended method for your vehicle. 17
22 If the fuel lines are flexible hoses rather than metal lines, check their condition to determine whether it is necessary to replace the hoses and clamps when you replace the filter. Some replacement filters come with these items and when they are supplied you should always use them. If these are not supplied, but you need to replace them anyway, obtain a sufficient length of new fuel line and suitable clamps. There are different types of clamps for flexible fuel lines -- spring type, worm type or rolled edge. You will need to obtain and use the appropriate tool when installing new clamps on the hoses. Step-by-Step Instruction 1. Locate fuel filter: Refer to the vehicle service manual to identify the location and type of fuel filter and the correct procedure for removing and replacing it. 2. Remove static pressure from fuel system: If the engine is fitted with an electric fuel pump, locate the fuel pump fuse using the service manual and remove it. Start the engine and wait for it to stop as it runs out of fuel. Switch the ignition off. 3. Obtain correct replacement: Obtain the correct replacement filter and components. If the vehicle has a carburetted fuel system, new intake and outlet hoses may have been supplied with the filter. If so, then attach them to the new filter before you disconnect the old one. 4. Using correct equipment, remove fuel filter: Loosen the clamps on the fuel line on the engine side of the filter at the outer end of the hose and disconnect it. If necessary drain any excess fuel into the fuel proof container. 18
23 5. Install carburetted system filter: Connect the new filter hose and tighten the clamp. Make sure that you have the filter facing in the right direction, with the flow indicator arrow pointing towards the engine. Then remove the old filter and reconnect the new one to the fuel intake. If you do this quickly, very little of the residual fuel in the line should leak from the system. 6. Remove old EFI system filter: In a fuel injected system, the fuel is under greater pressure, so the fuel lines are normally made of metal, which are not replaced at the same time as the filter. Using the correct tool, loosen the metal line connectors and remove the filter, catching any leaking fuel in a fuel-proof container. 7. Install EFI system filter: Connect the new filter and tighten the line connectors. Make sure that you have the filter facing in the right direction, with the flow indicator arrow pointing towards the engine. Finally, remember to replace the fuel pump fuse. 19
24 8.0 Return-Type Fuel Supply System Components Key Learning Points Location and identification of return-type fuel supply system components including fuel pump relay, fuel filter, fuel supply and return pipes, fuel distribution rail, fuel pressure regulator, inertia/impact/collision switch Practical Task Please refer to your instructor for additional information, which is available from the automotive technical manuals. 9.0 Fuel Injection Pressures Key Learning Points Fuel system pressures applicable to single-point (throttlebody) and multi-point injection systems Practical Task Please refer to your instructor for additional information, which is available from the automotive technical manuals. 9.1 Typical Fuel Pressures For a single point injection system is approx. 3 bar. For multi point injection it is higher between 4 and 5 bar. Please refer to manufactures data when checking each system. 20
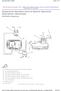
25 10.0 Fuel Distribution Rail and Inlet Manifold Pressures Key Learning Points Purpose of constant pressure differential between fuel distribution rail and inlet manifold 10.1 Fuel Pressure Versus Inlet Manifold Vacuum This is because a constant pressure differential must be maintained between the fuel distribution rail and the inlet manifold pressure. Constant means steady or the same. The difference in value between the fuel pressure in the distribution rail (approx. 3 bar) and the inlet manifold pressure (e.g bar) must be maintained at a constant or steady value at all times and under all operating conditions because, the quantity of fuel released by the injector for combustion is determined by the length of time that the ECU transmits the injector open signal and the most accurate matching of this fuel quantity is required so that the engine can meet its exhaust emission targets. Throttle valve open Throttle valve partly open When the throttle valve is When the throttle valve is fully open there is high air/ closed or partly open there gas pressure (low vacuum) is low air/gas pressure (high vacuum) Fuel distribution rail, pressure gauge 21
26 10.2 Constant Pressure Difference Explained The fuel pressure available at the injector is produced by the pump and controlled by the pressure regulator, but the level of vacuum in the inlet manifold is determined by the throttle valve position and engine speed but, the quantity of fuel being injected at any time is determined as you have seen, by the injector opening time, which is controlled by the *pre-set parameters in the map of the ECU. The injectors of multi-point injection systems inject their fuel below the throttle valve and therefore, the level of vacuum in that area of the inlet manifold is affected by the action of that valve. Therefore, in times of low levels of inlet manifold vacuum (air pressure close to normal atmospheric air pressure) e.g. open throttle valve, a relatively high level of air/fuel vapour pressure would be acting externally on the injector nozzle to resist the exit of fuel, but in periods of high inlet manifold vacuum e.g. light load, the low level of atmospheric air/vapour pressure acting externally against the fuel exit nozzle would support the exit of fuel, i.e. it would help draw an excess of fuel from the injector. (*Control units can carry out adaptation to outputs on certain circuits, under certain circumstances, see manufacturer s manuals for further information) 10.3 Maintaining Constant Pressure Differential A constant difference in these pressures is achieved by the fitting of a vacuum reference pipe from a point inside the throttle valve of the inlet manifold to the sealed spring housing of the regulator. The differing levels of low pressure in the manifold then act on the diaphragm and help its movement against the spring. As a result, fuel pressure is continually corrected in step with changes in manifold pressure, e.g. low air pressure (partial vacuum) will assist the fuel pressure to raise the regulator valve and this then reduces the fuel pressure relative to the inlet manifold pressure. 22
27 11.0 Electrical Circuit for the Fuel Supply System Key Learning Points Draw a Electrical circuit for fuel supply system (to include pump, pump relay, ECU and inertia/impact/collision switch) Please refer to your instructor for additional information, which is available from the automotive technical manuals EFI Wiring Diagram The battery is grounded to the vehicle frame at the negative terminal. Its positive terminal is connected to a tachometric relay and to the ignition switch. A connecting wire runs from the tachometric relay, to the positive terminal on the fuel pump. A fuse in the connecting wire protects the circuit. The fuel pump circuit is completed by grounding the fuel pump negative terminal to the frame of the vehicle. When the fuel pump operates current flows from the battery to the petrol pump. It flows through the pump to rotate the armature and completes the circuit by flowing from the negative terminal, through the vehicle frame, to the battery negative terminal. Testing of this circuit is done according to manufactures recommendations. 23
28 Positive connections are made to a number of components from the tachometric relay. The relay only operates when the engine is cranking, or running, so no current flows in any connecting wires at other times. More wiring diagrams are available from automotive technical manuals. Basic Electric Fuel Pump Wiring Circuit 24
29 12.0 Servicing Fuel Pump Relays Key Learning Points Testing fuel pump relays using manufacturer's recommended procedures Practical Task Please refer to your instructor for additional information, which is available from the automotive technical manuals Applicable NCT/DoT VTM Requirements Key Learning Points NCT/DoT VTM requirements applicable to the fuel tank, fuel filter systems, fuel lines and air filter assembly of petrol powered engines Use of data manuals/manufacturer's manuals/nct/dot VTM Manual 13.1 NCT/Dot VTM Requirements Please refer to the item number 50 of the (2004) NCT manual for the relevant specifications. 25
30 Self Assessment Q1: Baffles in the fuel tank are fitted in order to: (Tick ONE box only) 1. Increase tank volume 2. Strengthen the fuel tank 3. Reduce fuel surge 4. Provide vapour space Q2: How is a submersible electric fuel pump lubricated? (Tick ONE box only) 1. Cool air surrounding the pump 2. By the fuel 3. Oil sealed within the pump 4. No lubrication is required Q3: Technician A says that when changing a fuel filter on an EFI system it must be depressurized first; Technician B says that because the engine in switched off the system is already depressurized to the point that the filter can be changed. Who is correct? (Tick ONE box only) 1. Technician A 2. Technician B 3. Both Technician A and Technician B 4. Neither Technician A nor Technician B Q4 The purpose of the Inertia Switch is to? (Tick ONE box only) 1. Trigger the air bag system 2. Open the vehicle doors 3. Switch off the power supply to the fuel pump 4. Operate the cooling fan Q5: All fuel tanks can be repaired (Tick ONE box only) 1. True 2. False 26
31 Q6: In multi-point EFI systems, fuel is transferred from the tank to the fuel rail by the: (Tick one box only) 1. Fuel filter 2. Fuel pump 3. Fuel regulator 4. Fuel accumulator 27
32 Suggested Exercises 1. Use an electronic data facility to procure manufacturer s appropriate data for use with practical exercises 2. Test the operation of a fuel level gauge using a potentiometer 3. Locate and identify each component in the return-type fuel supply system on a fuel injected vehicle/training unit 4. Remove and refit external and/or submerged fuel pumps using manufacturer's recommended procedures 5. Remove and replace petrol fuel filters using manufacturer's recommended procedures 6. Remove and test fuel pump relay with ohmmeter across winding circuit (86/85) 7. Energise relay and test contact circuit (30/87) with ohmmeter Training Resources Fuel injected vehicles/training units, Multimeters, data manuals, manufacturer's manuals, NCT/DoT VTM manual, video/multimedia resources Potentiometers Selection of fuel supply system components including fuel level sender units, fuel level gauges, electric fuel pumps, fuel pump relays, sectioned fuel filters, fuel supply and return pipes, fuel distribution rails, fuel pressure regulators, inertia/impact/ collision switches Appropriate petrol storage containers and fire extinguishers 28
33 Task Sheets Replacing a Fuel Filter Objective Preparation and Safety Remove and replace a fuel filter. Personal Safety Safety Check Whenever you perform a task in the workshop you must use personal protective clothing and equipment that is appropriate for the task and which conforms to your local safety regulations and policies. Among other items, this may include: Work clothing - such as coveralls and steel-capped footwear Eye protection - such as safety glasses and face masks Ear protection - such as earmuffs and earplugs Hand protection such as rubber gloves and barrier cream Respiratory equipment such as face masks etc. If you are not certain what are appropriate or required, ask your instructor Petrol, in particular petrol vapour, is explosive and highly flammable. Be careful not to spill any fuel onto a hot engine component where it could ignite and start a fire. Be careful not to cause any sparks while you are changing a fuel filter. Collect the petrol waste in a metal container and dispose of it in an environmentally prescribed way. 29
34 Points to Note Always make sure that you wear the appropriate personal protection equipment before starting the job. It is very easy to hurt yourself even when the most exhaustive protection measures are taken. Always make sure that your work area/environment is as safe as you can make it. Do not use damaged, broken or worn out workshop equipment. Always follow any manufacturer's personal safety instructions to prevent damage to the vehicle you are servicing. Make sure that you understand and observe all legislative and personal safety procedures when carrying out the following tasks. If you are unsure of what these are, ask your supervisor. There are a variety of fuel filters, so before you start always check the shop manual for the correct type of filter for the vehicle and the specific procedure for removing and replacing it. There are several ways to relieve the static pressure in the fuel system before removing the fuel lines. For instance, some fuel injection systems have a valve specifically to bleed off pressure. Other methods include bypassing the fuel pump relay with a jumper wire, or removing the fuel pump fuse and running the engine until it uses up the remaining fuel in the system and stops. Refer to the shop manual for the recommended method for your vehicle. 30
35 If the fuel lines are flexible hoses rather than metal lines, check their condition to determine whether it is necessary to replace the hoses and clamps when you replace the filter. Some replacement filters come with these items and when they are supplied you should always use them. If these are not supplied, but you need to replace them anyway, obtain a sufficient length of new fuel line and suitable clamps. There are different types of clamps for flexible fuel lines -- spring type, worm type or rolled edge. You will need to obtain and use the appropriate tool when installing new clamps on the hoses. 31
36 Step-by-Step Instruction 1. Locate fuel filter: Refer to the vehicle service manual to identify the location and type of fuel filter and the correct procedure for removing and replacing it. 2. Remove static pressure from fuel system: If the engine is fitted with an electric fuel pump, locate the fuel pump fuse using the service manual and remove it. Start the engine and wait for it to stop as it runs out of fuel. Switch the ignition off. 3. Obtain correct replacement: Obtain the correct replacement filter and components. If the vehicle has a carburetted fuel system, new intake and outlet hoses may have been supplied with the filter. If so, then attach them to the new filter before you disconnect the old one. 4. Using correct equipment, remove fuel filter: Loosen the clamps on the fuel line on the engine side of the filter at the outer end of the hose and disconnect it. If necessary drain any excess fuel into the fuel proof container. 5. Install carburetted system filter: Connect the new filter hose and tighten the clamp. Make sure that you have the filter facing in the right direction, with the flow indicator arrow pointing towards the engine. Then remove the old filter and reconnect the new one to the fuel intake. If you do this quickly, very little of the residual fuel in the line should leak from the system. 6. Remove old EFI system filter: In a fuel injected system, the fuel is under greater pressure, so the fuel lines are normally made of metal, which are not replaced at the same time as the filter. Using the correct tool, loosen the metal line connectors and remove the filter, catching any leaking fuel in a fuel-proof container. 7. Install EFI system filter: Connect the new filter and tighten the line connectors. Make sure that you have the filter facing in the right direction, with the flow indicator arrow pointing towards the engine. Finally, remember to replace the fuel pump fuse. 32
37 Obtaining & Interpreting Scan Tool Data Objective Preparation and Safety Retrieve, record and clear stored OBD I & II diagnostic trouble codes using a scan tool. Personal Safety Safety Check Whenever you perform a task in the workshop you must use personal protective clothing and equipment that is appropriate for the task and which conforms to your local safety regulations and policies. Among other items, this may include: Work clothing - such as coveralls and steel-capped footwear Eye protection - such as safety glasses and face masks Ear protection - such as earmuffs and earplugs Hand protection such as rubber gloves and barrier cream Respiratory equipment such as face masks etc. If you are not certain what are appropriate or required, ask your instructor. If the vehicle is to be run inside the workshop use exhaust extraction hoses. Output solenoids can be energized from the scan tool, activating components without warning. It is imperative that the operator should follow the service manual procedures. Make sure that you understand and observe all legislative and personal safety procedures when carrying out the following tasks. If you are unsure of what these are, ask your supervisor. 33
38 Points to Note Make sure that you follow service manual procedures for the vehicle you are working on. The standard procedure for retrieving codes for an OBD I vehicle, is to access the codes, write them down, clear the codes, start the vehicle and recheck for any codes that reset. The standard procedure for diagnosing an OBD II vehicle is different as it requires that the codes should NOT be cleared until the vehicle is repaired. Clearing the codes also clears all of the freeze frame data in the system that is useful for the diagnosis process. It may take several 'trips' for the code to reset, so with OBDII you must complete the diagnosis process first before clearing the codes. Always check for any applicable service bulletins when diagnosing computer related problems, as they can provide valuable information about new faults that emerge on vehicles as their operational characteristics change as the vehicles get older. Step-by-Step Instruction 1. Connect the scan tool: Locate the scan tool access point and connect the scan tool using the appropriate connector for the vehicle. Turn on the vehicle ignition. Turn on the scan tool. Run the scan tool diagnostic program and navigate through each of the different systems in turn to access the diagnostic trouble codes from the vehicles electronic control module. Note your findings for each vehicle system. 2. Check your findings: Look up what each code means and present the information to your supervisor. Any fault indicated by the diagnostic trouble codes will need to be corrected before you clear the codes. 3. Clear fault codes: To clear the fault codes from the vehicle; select the delete codes option on the scan tool. Check that the codes have cleared and turn off the vehicle ignition. 4. Recheck for fault codes: Turn on the vehicle ignition. Run the scan tool diagnostic program and navigate through each system again to check the codes do not reactivate. If the fault codes reactivate, take your findings to your instructor. Turn off the vehicle ignition. Turn off the scan tool and disconnect from the access point. 34
39 Suggested Further Reading Advanced Automotive Diagnosis. Tom Denton. ISBN Automobile Electrical and Electronic Systems (3rd Edition). Tom Denton. ISBN Automotive Mechanics (10th Edition). William H. Crouse and Donald L. Anglin. ISBN Bosch Automotive Electrics Automotive Electronics: Systems and Components (4th Edition). Robert Bosch. ISBN Bosch Automotive Handbook (6th Edition). Robert Bosch. ISBN Bosch Automotive Technology Technical Instruction booklet series (numerous titles) Hillier s Fundamentals of Motor Vehicle Technology: Book One (5th Edition). V.A.W. Hillier and Peter Coombes. ISBN Hillier s Fundamentals of Motor Vehicle Technology: Book Two (5th Edition). V.A.W. Hillier and Peter Coombes. ISBN Modern Automotive Technology. James E. Duffy. ISBN Motor Vehicle Craft Studies - Principles. F.K. Sully. ISBN X National Car Test (NCT) Manual (Department of Transport, Vehicle Testers Manual - DoT VTM). Department of Transport Transmission, Chassis and Related Systems (Vehicle Maintenance and Repair Series: Level 3) (3rd Edition) John Whipp and Roy Brooks. ISBN X Vehicle and Engine Technology (2nd Edition). Heinz Heisler. ISBN Automotive Encyclopedia and Text Book Resource (CD version of e-textbook), Available from your instructor. 35
40 Notes
41
42 27-33 Upper Baggot Street Dublin 4
Phase. Trade of Motor Mechanic. Module 2. Unit 5. Starter Motor/Circuit
 Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 2 Unit 5 Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision 2.2 16-01-07 SOLAS 2013 Table of Contents Introduction...
Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 2 Unit 5 Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision 2.2 16-01-07 SOLAS 2013 Table of Contents Introduction...
Trade of Motor Mechanic
 Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 2 Unit 4 Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision 2.2 16-01-07 SOLAS 2013 Table of Contents Introduction...
Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 2 Unit 4 Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision 2.2 16-01-07 SOLAS 2013 Table of Contents Introduction...
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine. And how it works
 Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
3. Fuel System FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-7
 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator
 Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator Introduction Some of the notes here are repetitious in order to review the components
Rover SD1 Efi System Fuel Supply Components - Explanation and Testing of the Fuel Pump, Filter and Fuel Pressure Regulator Introduction Some of the notes here are repetitious in order to review the components
51. absolute pressure sensor
 51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: 3.5-4.5 V output voltage at 2000m: 2.5-3.5
NZQA Expiring unit standard 3400 version 4 Page 1 of 6. Check a four stroke petrol engine for condition using hand held test equipment
 Page 1 of 6 Title Check a four stroke petrol engine for condition using hand held test equipment Level 3 Credits 4 Purpose This unit standard is for people in the automotive repair industry. People credited
Page 1 of 6 Title Check a four stroke petrol engine for condition using hand held test equipment Level 3 Credits 4 Purpose This unit standard is for people in the automotive repair industry. People credited
Fuel System Diagnosis
 1996 Chevrolet Impala Caprice, Impala, Roadmaster (VIN B) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.3L (Caprice Only) and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 37723 Fuel System Diagnosis
1996 Chevrolet Impala Caprice, Impala, Roadmaster (VIN B) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.3L (Caprice Only) and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 37723 Fuel System Diagnosis
Fuel Tank and Lines Fuel Delivery System Component Location Item Part Number Description
 Page 1 of 10 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Fuel Tank and Lines Fuel Delivery System Component Location 1 - Filler cap and lanyard 2 - Breather line 'Y' piece to charcoal canister 3 - Charcoal canister purge
Page 1 of 10 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Fuel Tank and Lines Fuel Delivery System Component Location 1 - Filler cap and lanyard 2 - Breather line 'Y' piece to charcoal canister 3 - Charcoal canister purge
DESCRIPTION Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20. Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI
 Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Phase. Trade of Motor Mechanic. Module 7. Unit 3. Steering, Alignment & Geometry
 Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 7 Unit 3 Steering, Alignment & Geometry Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision 2.2 16-01-07 SOLAS
Phase 2 Trade of Motor Mechanic Module 7 Unit 3 Steering, Alignment & Geometry Produced by In cooperation with: Subject Matter Experts Martin McMahon & CDX Global Curriculum Revision 2.2 16-01-07 SOLAS
(3) (4) (6) (5) (10) (9) (8) (7)
 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
Handout Activity: HA511
 Using a tire pressure gauge Engines: Motive Power Types: Handout Activity: HA511 HA511-2 Student/Intern information: Name Date Class Using a tire pressure gauge Summary There are two main types of tire
Using a tire pressure gauge Engines: Motive Power Types: Handout Activity: HA511 HA511-2 Student/Intern information: Name Date Class Using a tire pressure gauge Summary There are two main types of tire
Fuel System Description
 Page 1 of 9 2005 Pontiac GTO GTO (VIN V) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 6.0L Description and Operation Document ID: 1550920 Fuel System Description System Overview The fuel tank stores the fuel
Page 1 of 9 2005 Pontiac GTO GTO (VIN V) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 6.0L Description and Operation Document ID: 1550920 Fuel System Description System Overview The fuel tank stores the fuel
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Catalytic Failures. Engine running too hot.
 Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel System (Central SFI)
 Page 1 of 6 1997 GMC Truck GMC K Pickup - 4WD Chevy Pickup, GMC Pickup, Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L, 5.7L, and 7.4L Description and Operation Document
Page 1 of 6 1997 GMC Truck GMC K Pickup - 4WD Chevy Pickup, GMC Pickup, Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L, 5.7L, and 7.4L Description and Operation Document
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES)
 REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
Motronic September 1998
 The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT
 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
Fuel System Service & Diagnostic Equipment OPERATOR S MANUAL MCS 245
 Fuel System Service & Diagnostic Equipment OPERATOR S MANUAL MCS 245 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Overview...4 System Features and Functions...5 System Features and Functions... Hose and Battery
Fuel System Service & Diagnostic Equipment OPERATOR S MANUAL MCS 245 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Overview...4 System Features and Functions...5 System Features and Functions... Hose and Battery
Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors
 Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors 8183 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 6 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in
Demonstrate knowledge of the operation, service checks, fault diagnosis, and repair of carburettors 8183 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 6 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in
Today, we re going to talk about battery safety. We ll discuss all the key issues associated with using batteries safely, including battery hazards,
 Today, we re going to talk about battery safety. We ll discuss all the key issues associated with using batteries safely, including battery hazards, battery charging, and battery maintenance. Although
Today, we re going to talk about battery safety. We ll discuss all the key issues associated with using batteries safely, including battery hazards, battery charging, and battery maintenance. Although
Fuel Supply Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Supply Component Description FIGURE Central SFI Fuel System with Fuel Pressure Gauge(c) (1) Fuel Inlet (2) Bleed Hose (3) J 34730-1A Fuel Pressure Gage Assembly (4)
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Supply Component Description FIGURE Central SFI Fuel System with Fuel Pressure Gauge(c) (1) Fuel Inlet (2) Bleed Hose (3) J 34730-1A Fuel Pressure Gage Assembly (4)
Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description (Enhanced)
 Page 1 of 7 1999 Chevrolet Chevy Suburban - 2WD Escalade, Pickup (Classic), Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Document ID: 222842 Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description
Page 1 of 7 1999 Chevrolet Chevy Suburban - 2WD Escalade, Pickup (Classic), Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Document ID: 222842 Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description
7. Evaporative Emission Control System
 W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
Chapter 4 Part B: Fuel system - single-point fuel injection engines
 4B 1 Chapter 4 Part B: Fuel system - single-point fuel injection engines Contents Air cleaner assembly - removal and refitting................... 2 Air cleaner element renewal......................see
4B 1 Chapter 4 Part B: Fuel system - single-point fuel injection engines Contents Air cleaner assembly - removal and refitting................... 2 Air cleaner element renewal......................see
LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE AUTO MECHANICS 233 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL & FUEL SYSTEMS SPRING 2005
 LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE AUTO MECHANICS 233 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL & FUEL SYSTEMS SPRING 2005 SUBJECT MATTER AREA Automotive Technology COURSE NUMBER AMECH 233 SECTION NUMBER 31377 ROOM # MM128A/MM130 COURSE
LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE AUTO MECHANICS 233 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL & FUEL SYSTEMS SPRING 2005 SUBJECT MATTER AREA Automotive Technology COURSE NUMBER AMECH 233 SECTION NUMBER 31377 ROOM # MM128A/MM130 COURSE
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
NZQA Expiring unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 5. Perform minor servicing tasks on a petrol fuel system
 Page 1 of 5 Title Perform minor servicing tasks on a petrol fuel system Level 2 Credits 2 Purpose This unit standard is for people who wish to enter or are employed in the automotive repair industry. People
Page 1 of 5 Title Perform minor servicing tasks on a petrol fuel system Level 2 Credits 2 Purpose This unit standard is for people who wish to enter or are employed in the automotive repair industry. People
Troubleshooting A Vintage Distributor Ignition System
 Troubleshooting A Vintage Distributor Ignition System -Henry P. Olsen When the owners of vintage carburetor- and distributor-equipped vehicles see that a shop has a big-box engine analyzer, they believe
Troubleshooting A Vintage Distributor Ignition System -Henry P. Olsen When the owners of vintage carburetor- and distributor-equipped vehicles see that a shop has a big-box engine analyzer, they believe
1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L
 INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
VS403 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION & CONTENTS. fig.1
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER
 AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis
 Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
Wayne County Community College District
 AUT 151 Light Duty Diesel Engines CREDIT HOURS: 4.00 CONTACT HOURS: 60.00 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course covers the operation of light duty diesel engines. Students will diagnosis and repair mechanical
AUT 151 Light Duty Diesel Engines CREDIT HOURS: 4.00 CONTACT HOURS: 60.00 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course covers the operation of light duty diesel engines. Students will diagnosis and repair mechanical
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
EVAP system, servicing
 Page 1 of 65 20-130 EVAP system, servicing EVAP system components 1 - Cap nut 10 Nm 2 - Cover 3 - Stud For EVAP canister 15 Nm 4 - Sealing piece 5 - Bleed line To EVAP canister purge regulator valve -
Page 1 of 65 20-130 EVAP system, servicing EVAP system components 1 - Cap nut 10 Nm 2 - Cover 3 - Stud For EVAP canister 15 Nm 4 - Sealing piece 5 - Bleed line To EVAP canister purge regulator valve -
Lab #5 4-Cylinder Single Overhead Cam Engine Dissection
 Engr 3 Mission College Faculty: Kate Disney TA: Andrew Dina Lab #5 4-Cylinder Single Overhead Cam Engine Dissection Equipment: 4-Cylinder Mazda 16 Valve SOHC 92 (Manual Transmission) Ratchet with 2 and
Engr 3 Mission College Faculty: Kate Disney TA: Andrew Dina Lab #5 4-Cylinder Single Overhead Cam Engine Dissection Equipment: 4-Cylinder Mazda 16 Valve SOHC 92 (Manual Transmission) Ratchet with 2 and
Fuel System Diagnosis
 Page 1 of 9 1999 Chevrolet Express Express, Savana (VIN G) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 412957 Fuel System Diagnosis Circuit
Page 1 of 9 1999 Chevrolet Express Express, Savana (VIN G) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 412957 Fuel System Diagnosis Circuit
Related Electrical Systems 1
 Related Electrical Systems Student/intern information: Name Class Vehicle used for this activity: Year Make Model Odometer VIN Learning Objective/Task (Related Electrical Systems) 2007 NATEF Reference
Related Electrical Systems Student/intern information: Name Class Vehicle used for this activity: Year Make Model Odometer VIN Learning Objective/Task (Related Electrical Systems) 2007 NATEF Reference
SECTION 4 - FUEL SYSTEMS AND CARBURETION
 SECTION - FUEL SYSTEMS AND CARBURETION FUEL SYSTEMS - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -62 FUEL PUMP - - - - - - -
SECTION - FUEL SYSTEMS AND CARBURETION FUEL SYSTEMS - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -62 FUEL PUMP - - - - - - -
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) AUTOMOTIVE REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) AUTOMOTIVE REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009 (6021034) 12 November (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 This question paper consists of 8 pages. (6021034) -2- NC260(E)(N12)V
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) AUTOMOTIVE REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009 (6021034) 12 November (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 This question paper consists of 8 pages. (6021034) -2- NC260(E)(N12)V
F - BASIC TESTING Volvo 850 INTRODUCTION PRELIMINARY INSPECTION & ADJUSTMENTS VISUAL INSPECTION MECHANICAL INSPECTION
 F - BASIC TESTING 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Basic Diagnostic Procedures 850 INTRODUCTION NOTE: In this article, Engine Control Module (ECM) may also be referred to as Engine Control
F - BASIC TESTING 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Basic Diagnostic Procedures 850 INTRODUCTION NOTE: In this article, Engine Control Module (ECM) may also be referred to as Engine Control
FUEL KITS P/N & 526-2
 FUEL KITS P/N 526-1 & 526-2 NOTE: These instructions must be read and fully understood before beginning installation. If this manual is not fully understood, installation should not be attempted. Failure
FUEL KITS P/N 526-1 & 526-2 NOTE: These instructions must be read and fully understood before beginning installation. If this manual is not fully understood, installation should not be attempted. Failure
Chapter 4 Part D: Exhaust and emission control systems
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Exhaust and emission control systems Contents Air inlet heating system components - removal and refitting...... 4 Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Exhaust and emission control systems Contents Air inlet heating system components - removal and refitting...... 4 Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........
2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview. Study Guide. Course Code: 8777
 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide Course Code: 8777 1 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide 2015 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive, Lisle, IL 60532. All rights reserved. No part of
2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide Course Code: 8777 1 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide 2015 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive, Lisle, IL 60532. All rights reserved. No part of
INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM TESTER AND BRAKE BLEEDING KIT. MODEL No. VS4021.V2 1. SAFETY 2. INTRODUCTION 3. CONTENTS
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM TESTER AND BRAKE BLEEDING KIT MODEL No. VS4021.V2 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard, this product will, if used according to these instructions,
INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM TESTER AND BRAKE BLEEDING KIT MODEL No. VS4021.V2 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard, this product will, if used according to these instructions,
EVENING PROGRAM DESCRIPTIONS. California State Smog Repair Technician
 EVENING PROGRAM DESCRIPTIONS California State Smog Repair Technician School Name: Smog Tech Institute Course Name: Smog Repair Technician Course Number: TBA Program Title: Californian State Smog Repair
EVENING PROGRAM DESCRIPTIONS California State Smog Repair Technician School Name: Smog Tech Institute Course Name: Smog Repair Technician Course Number: TBA Program Title: Californian State Smog Repair
WEBER CARBURETOR TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
 This guide is to help pinpoint problems by diagnosing engine symptoms associated with specific vehicle operating conditions. The chart will guide you step by step to help correct these problems. For successful
This guide is to help pinpoint problems by diagnosing engine symptoms associated with specific vehicle operating conditions. The chart will guide you step by step to help correct these problems. For successful
Motronic injection system,
 Page 1 of 78 24-1 Motronic injection system, servicing Safety precautions If special testing equipment is required during road test, note the following: WARNING! Scan tools and testing devices must always
Page 1 of 78 24-1 Motronic injection system, servicing Safety precautions If special testing equipment is required during road test, note the following: WARNING! Scan tools and testing devices must always
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
Malfunction Criteria and Threshold Value Adaptive value. Secondary Parameters with Enable Conditions. >50.8 S Engine load 9-45% Delta fuel adaptation
 DTC Error Message P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) Diagnostic Procedure Check fuel pump delivery and quantity. Refer to page 126. Check Fuel pressure regulator and residual pressure. Refer to Fuel Injection
DTC Error Message P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) Diagnostic Procedure Check fuel pump delivery and quantity. Refer to page 126. Check Fuel pressure regulator and residual pressure. Refer to Fuel Injection
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
insider info. before it can be inspected for proper emissions. Misfire, Fuel System and Component
 insider info. Rough Idle On MPFI Vehicles If you encounter a rough idle complaint on any sequential injection MPFI vehicle, basic checks should be made to ensure that the correct injector wire connector
insider info. Rough Idle On MPFI Vehicles If you encounter a rough idle complaint on any sequential injection MPFI vehicle, basic checks should be made to ensure that the correct injector wire connector
Fuel System Delivery Overview Guide To Successful Fuel System Repairs
 Fuel System Delivery Overview Guide To Successful Fuel System Repairs 10 1 2 3 9 8 7 6 5 4 1 2 3 4 5 Fuel Filler Cap Tight seal is critical to proper OBD system operation. A loose cap can lead to a DTC
Fuel System Delivery Overview Guide To Successful Fuel System Repairs 10 1 2 3 9 8 7 6 5 4 1 2 3 4 5 Fuel Filler Cap Tight seal is critical to proper OBD system operation. A loose cap can lead to a DTC
ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION (EFI)
 Стр. 1 из 31 ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION (EFI) General Description The Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system was used on 1991 2.5L, 1986-92 3.0L (except SHO) and 1988-92 3.8L engines. The EFI fuel system
Стр. 1 из 31 ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION (EFI) General Description The Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system was used on 1991 2.5L, 1986-92 3.0L (except SHO) and 1988-92 3.8L engines. The EFI fuel system
Diagnosis of fuel tank systems with fuel tank leak diagnosis module (DMTL)
 Page 1 of 10 SIT-SIT-SI2002-160102890 Diagnosis of fuel tank systems with fuel tank leak diagnosis module (DMTL) All US models VIN: XXXXXXX Vehicle: 6'/E64/CONVERTIBLE/650i/N62/AUTO/USA/LL/2007/05 System
Page 1 of 10 SIT-SIT-SI2002-160102890 Diagnosis of fuel tank systems with fuel tank leak diagnosis module (DMTL) All US models VIN: XXXXXXX Vehicle: 6'/E64/CONVERTIBLE/650i/N62/AUTO/USA/LL/2007/05 System
F - BASIC TESTING Toyota Celica INTRODUCTION PRELIMINARY INSPECTION & ADJUSTMENTS VISUAL INSPECTION MECHANICAL INSPECTION
 F - BASIC TESTING 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 4-Cylinder Basic Diagnostic Procedures Celica INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
F - BASIC TESTING 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 4-Cylinder Basic Diagnostic Procedures Celica INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
SECTION 3.00 WARNING WARNING ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION
 SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
SECTION 3.00 ENGINE STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRESTART INSPECTION Be sure that the clutch, circuit breaker, or other main power transmission device is disconnected. Generators develop voltage as soon as the
Fuel System Diagnosis
 Page 1 of 6 2001 Chevrolet Express Express, Savana (VIN G) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 720867 Fuel System Diagnosis Circuit
Page 1 of 6 2001 Chevrolet Express Express, Savana (VIN G) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 720867 Fuel System Diagnosis Circuit
Chapter 4 Part C: Emissions control systems
 Chapter 4 Part C: Emissions control systems Contents Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........ 9 Crankcase emissions control system - testing and renewal....... 2 Exhaust emissions
Chapter 4 Part C: Emissions control systems Contents Catalytic converter - general information and precautions........ 9 Crankcase emissions control system - testing and renewal....... 2 Exhaust emissions
HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE
 16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace
 Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
RediCoat by Nordson. Hopper and VBF Dolly Systems. Customer Product Manual Part A Issued 10/07
 RediCoat by Nordson Hopper and VBF Dolly Systems Customer Product Manual Part 1082648A Issued 10/07 This document is subject to change without notice. Nordson Corporation Amherst, Ohio USA 2 Table of Contents
RediCoat by Nordson Hopper and VBF Dolly Systems Customer Product Manual Part 1082648A Issued 10/07 This document is subject to change without notice. Nordson Corporation Amherst, Ohio USA 2 Table of Contents
18 KG MOBILE SODA BLASTING UNIT
 OWNER S MANUAL PRODUCT CODE: 3043 18 KG MOBILE SODA BLASTING UNIT Working Air Hose Tank Volume Overall Dimensions Pressure Consumption Length 18KG 35 90psi 6-12CFM 2400mm 460 x 305 x 660 Made in China
OWNER S MANUAL PRODUCT CODE: 3043 18 KG MOBILE SODA BLASTING UNIT Working Air Hose Tank Volume Overall Dimensions Pressure Consumption Length 18KG 35 90psi 6-12CFM 2400mm 460 x 305 x 660 Made in China
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ADVANCED TRAINING INSTITUTE, HYDERABAD PR04/F01
 Revision: 01 LEARNING CONTENT Page 1 of 9 III COURSE CODE HE-01 COURSE TITLE BASIC AND MAINTAINENCE OF PETROL AND DIESEL ENGINE OBJECTES On completion of the course, the learner will be able to identify
Revision: 01 LEARNING CONTENT Page 1 of 9 III COURSE CODE HE-01 COURSE TITLE BASIC AND MAINTAINENCE OF PETROL AND DIESEL ENGINE OBJECTES On completion of the course, the learner will be able to identify
Module 7: Cooling System Components
 Â ÂÂ Â Basic Cooling System Components Radiators Common Types of Radiators Coolant Hoses Water Pumps Centrifugal Force Types of Drives for Water Pumps Types of Drive Belts Basic Cooling System Components
 Â  Basic Cooling System Components Radiators Common Types of Radiators Coolant Hoses Water Pumps Centrifugal Force Types of Drives for Water Pumps Types of Drive Belts Basic Cooling System Components
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
Module 4: Climate Control
 ÂÂ ÂÂ Air-Conditioning Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Â Controlling Cabin Air Temperature Servo Motors Electric Servo Motors ÂÂ Air-Conditioning Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Automatic Climate Control Sensors
ÂÂ ÂÂ Air-Conditioning Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Â Controlling Cabin Air Temperature Servo Motors Electric Servo Motors ÂÂ Air-Conditioning Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Automatic Climate Control Sensors
Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7
 Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Service. Self-Study Programme 253 Direct Petrol Injection System with Bosch Motronic MED 7 Design and Function The primary objective of engine development is to minimise fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.
Forecourt safety Competent persons
 Forecourt safety Competent persons > Name: >> Section 001 Forecourt safety >> Section 002 Competent persons > Midland CO-OP >> Fourcourt Safety >> Section 001..Page 001 > Forecourt safety >> Petrol gives
Forecourt safety Competent persons > Name: >> Section 001 Forecourt safety >> Section 002 Competent persons > Midland CO-OP >> Fourcourt Safety >> Section 001..Page 001 > Forecourt safety >> Petrol gives
Chapter 4 Part B: Fuel system - fuel injection engines
 1 Chapter 4 Part B: Fuel system - fuel injection engines Contents Accelerator cable - removal, refitting and adjustment........... 4 Accelerator pedal - removal and refitting..................... 5 Air
1 Chapter 4 Part B: Fuel system - fuel injection engines Contents Accelerator cable - removal, refitting and adjustment........... 4 Accelerator pedal - removal and refitting..................... 5 Air
2001 Audi TT Quattro ENGINE PERFORMANCE' 'System & Component Testing
 FUEL SYSTEM WARNING: ALWAYS release fuel pressure before disconnecting fuel injection-related component. DO NOT allow fuel to contact engine or electrical components. FUEL INJECTOR TEST Fuel Injector Electrical
FUEL SYSTEM WARNING: ALWAYS release fuel pressure before disconnecting fuel injection-related component. DO NOT allow fuel to contact engine or electrical components. FUEL INJECTOR TEST Fuel Injector Electrical
For. Code Reader. User Manual
 For OBD2 Code Reader User Manual http://www.motodok.com Table of Contents 1. Description... 2 2. Features... 2 3. Getting Started... 3 1. Connect Code Reader to Vehicle's Test Connector... 3 2. Read Diagnostic
For OBD2 Code Reader User Manual http://www.motodok.com Table of Contents 1. Description... 2 2. Features... 2 3. Getting Started... 3 1. Connect Code Reader to Vehicle's Test Connector... 3 2. Read Diagnostic
FUEL SYSTEM PRECAUTION FU 1
 2GR-FE EL EL SYSTEM EL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. EXPRESSIONS OF IGNITION SWITCH (a) The type of the ignition switch used on this model differs according to the specifications of the vehicle. The expressions
2GR-FE EL EL SYSTEM EL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. EXPRESSIONS OF IGNITION SWITCH (a) The type of the ignition switch used on this model differs according to the specifications of the vehicle. The expressions
FUEL KITS P/N & 526-4
 FUEL KITS P/N 526-3 & 526-4 NOTE: These instructions must be read and fully understood before beginning installation. If this manual is not fully understood, installation should not be attempted. Failure
FUEL KITS P/N 526-3 & 526-4 NOTE: These instructions must be read and fully understood before beginning installation. If this manual is not fully understood, installation should not be attempted. Failure
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
F - BASIC TESTING Infiniti G20 INTRODUCTION PRELIMINARY INSPECTION & ADJUSTMENTS VISUAL INSPECTION MECHANICAL INSPECTION
 F - BASIC TESTING 1992 Infiniti G20 1992 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Infiniti Basic Diagnostic Procedures G20, M30, Q45 INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
F - BASIC TESTING 1992 Infiniti G20 1992 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Infiniti Basic Diagnostic Procedures G20, M30, Q45 INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
Mazda North American Operations Irvine, CA
 Service Bulletin Mazda North American Operations Irvine, CA 92618-2922 Subject: ENGINE CRANKS NO START Bulletin No: 01-015/08 2004-2008 RX-8 - ENGINE CRANKS NO START BULLETIN NOTE This bulletin supersedes
Service Bulletin Mazda North American Operations Irvine, CA 92618-2922 Subject: ENGINE CRANKS NO START Bulletin No: 01-015/08 2004-2008 RX-8 - ENGINE CRANKS NO START BULLETIN NOTE This bulletin supersedes
1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Basic Diagnostic Procedures. Cabriolet, Corrado SLC, EuroVan, Fox, Golf, GTI, Jetta, Passat GL, Passat GLX
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Basic Diagnostic Procedures Cabriolet, Corrado SLC, EuroVan, Fox, Golf, GTI, Jetta, Passat GL, Passat GLX INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Basic Diagnostic Procedures Cabriolet, Corrado SLC, EuroVan, Fox, Golf, GTI, Jetta, Passat GL, Passat GLX INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic
Heater capacity 250W 13.5V Injector System pressure 1800 bar High pressure fuel pump. Normal operating temperature. Operating temperature
 221001 033 1. SPECIFICATIONS Description Fuel Specification Diesel Fuel filter Type Fuel heater + priming pump + water separator integrated type Filter type Changeable filter element type Change interval
221001 033 1. SPECIFICATIONS Description Fuel Specification Diesel Fuel filter Type Fuel heater + priming pump + water separator integrated type Filter type Changeable filter element type Change interval
AUTO MECHANICS. PAPER 1: will consist of forty multiple-choice objective questions all of which are to be answered in 1 hour for 40 marks.
 SCHEME OF EXAMINATION AUTO MECHANICS There will be three papers, Papers1, 2 and 3 all of which must be taken. Papers 1 and 2 shall be a composite paper to be taken at one sitting. PAPER 1: will consist
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION AUTO MECHANICS There will be three papers, Papers1, 2 and 3 all of which must be taken. Papers 1 and 2 shall be a composite paper to be taken at one sitting. PAPER 1: will consist
Engine oil. Introduction. Warning and indicator lights WARNING
 Engine oil Introduction In this section you ll find information about: Warning and indicator lights Engine oil specifications Engine oil capacities Checking the engine oil level and adding oil Engine oil
Engine oil Introduction In this section you ll find information about: Warning and indicator lights Engine oil specifications Engine oil capacities Checking the engine oil level and adding oil Engine oil
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Operating and Installation Instructions
 Model Number 40401-c (-sp) Electronic Fuel Pump Operating and Installation Instructions This Product is Patent Pending. Application available upon request CAUTION! This product is to be installed only
Model Number 40401-c (-sp) Electronic Fuel Pump Operating and Installation Instructions This Product is Patent Pending. Application available upon request CAUTION! This product is to be installed only
NUMBER: S.M. REF.: Refer to 2.5 ENGINE: 60 DATE: January 2007
 NUMBER: 1 60 07 S.M. REF.: Refer to 2.5 ENGINE: 60 DATE: January 2007 SUBJECT: N3 ELECTRONIC INJECTOR PUBLICATION: 6SE483 The Series 60 Service Manual has been revised. Engine models built from December
NUMBER: 1 60 07 S.M. REF.: Refer to 2.5 ENGINE: 60 DATE: January 2007 SUBJECT: N3 ELECTRONIC INJECTOR PUBLICATION: 6SE483 The Series 60 Service Manual has been revised. Engine models built from December
