Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems
|
|
|
- Stuart Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
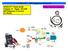
1 Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems Página 1 de 5 Search this site Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems Posted 11/5/1997 By Henry Guzman Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems were introduced in the early '70s to reduce an exhaust emission that was not being cleaned by the other smog controls. Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) are formed when temperatures in the combustion chamber get too hot. At 2500 degrees Fahrenheit or hotter, the nitrogen and oxygen in the combustion chamber can chemically combine to form nitrous oxides, which, when combined with hydrocarbons (HCs) and the presence of sunlight, produces an ugly haze in our skies known commonly as smog. How to reduce NOx NOx formation can be reduced by: Enriching the air fuel (A/F) mixture to reduce combustion temperatures. However, this increases HC and carbon monoxide (CO) emissions. Lowering the compression ratio and retarding ignition timing; but this leads to reduced performance and fuel economy. Recirculating some exhaust gases. How EGR systems work The EGR valve recirculates exhaust into the intake stream. Exhaust gases have already combusted, so they do not burn again when they are recirculated. These gases displace some of the normal intake charge. This chemically slows and cools the combustion process by several hundred degrees, thus reducing NOx formation. The design challenge The EGR system of today must precisely control the flow of recirculated exhaust. Too much flow will retard engine performance and cause a hesitation on acceleration. Too little flow will increase NOx and cause engine ping. A well-designed system will actually increase engine performance and economy. Why? As the combustion chamber temperature is reduced, engine detonation potential is also reduced. This factor enabled the software engineers to write a more aggressive timing advance curve into the spark timing program. If the EGR valve is not flowing, onboard diagnostics (OBD) systems will set a code and the power control module (PCM) will use a backup timing curve that has less advance to prevent engine ping. Less timing advance means less performance and economy. Do your customer a favor and fix those EGR codes that you may have previously deemed as unimportant. Evolution of the EGR systems The first EGR valves appeared in 1973 on GM cars. Bolted to the intake manifold next to the carburetor, it has ports to the intake and exhaust manifolds. It has a diaphragm that pulls open a valve stem, which allows exhaust to enter the intake manifold when ported vacuum is applied to it. Ported vacuum increases with throttle opening. A thermal vacuum switch prevents vacuum from reaching the EGR during cold engine starts. This system had many problems. It would often open too soon or too much, which caused a hesitation on
2 Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems Página 2 de 5 acceleration as massive amounts of recirculated exhaust hit the combustion chamber. Many people simply disconnected it when it began to cause problems because they did not understand its importance or design. By 1975, if you unplugged an EGR valve, you'd have a driveability complaint of engine ping. Manufacturers and technicians of that era experimented with vacuum orifice restrictors and vacuum delay valves to try to find a happy medium between clean air and performance. Closed loop systems By 1981, closed loop computer controls were in place. EGR flow was now more carefully controlled with dual diaphragm and back-pressure EGR valves. Modulating the vacuum to the EGR valve's pull, open diaphragm controlled the flow of recirculated ex- haust. Called by various names such as amplifiers, transducers and modulators, both remote and integral vacuum modulated devices were used. The flow of vacuum was further controlled by solenoids that blocked the vacuum ports until certain criteria were met such as engine temperature, rpm and manifold absolute pressure (MAP). As the manufacturers began to use these complex schemes with vacuum amplifiers, delay valves and solenoids, they added a lot of "spaghetti" to the engine compartment. Plastic vacuum connections would break and rot with age and were not very reliable. Vacuum diagrams were invented and became essential to the smog driveability technicians of the day. As these systems evolved, they had fewer parts and less vacuum tubing. This was achieved by the use of pulse width modulated EGR solenoids. The PCM controlled EGR flow through the use of these solenoids to modulate vacuum to the EGR valve instead of just turning it on or off periodically. What is pulse width modulation? Let's take a moment to discuss how computers think so we can better understand this common form of PCM control. Computers are binary. The machine language they operate in consists of only two variables: on or off, true or false, high or low. That's the only way a PCM can think. As a result, computer controlled outputs are always on or off, high (system voltage) or low (ground). Therefore, a computer output is always a square wave, or an on-off step when viewed on a lab scope. The high portion of the waveform will usually be battery voltage or PCM voltage of approximately 5 volts, with a few exceptions where the PCM operates at a different voltage. Once the PCM receives its inputs, such as rpm, throttle angle, coolant temperature and MAP, it then calculates a response based on the software program that is embedded into it. Next, it makes its decision and sends a command in the form of a pulse width modulated signal to turn the EGR solenoid on and off rapidly. The EGR solenoid has two vacuum nipples. One side gets either manifold or ported engine vacuum. The other nipple goes to the EGR valve. Its default position is to block vacuum to the EGR valve. A vent is incorporated to bleed off vacuum when the solenoid is being pulsed. Vacuum flows to the EGR in rapid on-off pulses as the solenoid is commanded by the PCM. OBD I systems With each succeeding year, the EGR designs became more refined. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) liked GM and Chrysler's onboard diagnostic systems. In 1988, CARB required that all cars sold in California be equipped with an onboard diagnostic system and a "check engine" light to notify the driver of emission system failure. By this time, all manufacturers had to have an EGR system that was capable of alerting the driver if it was not working. OBD I diagnostics and trouble codes were added in to flag opens, shorts and sticking solenoids. OBD II EGR systems OBD II requires that the EGR system be monitored for abnormally low or high flow rate malfunctions. The EGR is considered malfunctioning when an EGR component fails or a fault in the flow rate results in the vehicle exceeding the Federal Test Procedure (FTP) by 1.5 times. FTP is the government-mandated drive cycle smog test that all new cars must pass and
3 Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems Página 3 de 5 adhere to. The diagnostic executive, also called the diagnostic task manager by Chrysler, controls the EGR monitor. The executive is an OBD II software agent given the task of managing all the onboard monitors and the scan tool interface. The executive coordinates the sequencing and actuation of all the monitor's test routines. There are eight main monitors whose sole function is to directly monitor and test the components assigned to them to ensure they meet FTP standards for life. These monitors are: Catalyst monitor EGR monitor EVAP monitor Fuel system monitor Misfire monitor Oxygen monitor Oxygen heater monitor Secondary air injection monitor A closer look at the EGR monitor Monitor tests are both intrusive and nonintrusive. An example of an intrusive test is when the EGR monitor cycles the EGR valve during a condition when it normally would be closed. In some cases, the customer may feel an intrusive test as a slight miss. The method of testing used by the EGR monitor varies according to the manufacturer, but there are three main types. One method includes looking for a change in manifold pressure as the EGR valve is actuated on and off. A second method involves cycling the EGR valve and looking for a change in shortterm fuel trim. When the EGR valve is opened, it displaces some of the air fuel mixture. When the EGR valve is closed, more oxygen enters the combustion chamber, which then leans the mixture somewhat. The O2 sensor will respond with a lean signal to the PCM, which in turn increases pulse width. This is called short-term fuel trim compensation. The EGR monitor looks to see that all these things are occurring as they should. It repeats the tests and averages the results. Before the EGR monitor can begin its testing, it must first receive clearance from the diagnostic executive. The executive ensures that there are no conflicting conditions that would invalidate the EGR monitor's tests. For example, if the car had a lazy O2 sensor, fuel trim compensation to the EGR opening and closing would be inaccurate. Therefore, there are many safeguards built into OBD II to prevent this type of occurrence from happening. OBD II also has rationality checks. In other words, it uses deductive logic and constantly compares its inputs against each other to make sure all are in sync with one another. After the EGR monitor gets the OK to run its tests, it uses strict enabling criteria to ensure accurate testing such as: Engine temperature more than 170 F. Ambient air temperature more than 20 F. Engine run time more than three minutes since 170 F. Engine speed (auto. trans.), (manual trans.). Manifold absolute pressure from 5-20 hg. Short Term Adaptive Fuel Trim is adjusting pulse width by less than +7 percent and more than -8 percent. TP sensor from 0.6 to 1.8 volts. Vehicle speed sensor more than 40 mph. The above is used for illustrative purposes only. Refer to your manual or CD-ROM
4 Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems Página 4 de 5 information system for specifics to the car you are working on. The third type of EGR monitoring design includes monitoring an EGR position sensor and a back-pressure sensor. Some Fords use a differential pressure feedback sensor that reads exhaust back-pressure upstream and downstream of the EGR valve to determine its flow rate and operation. While OBD I systems would usually flag an inoperative EGR system, OBD II systems are given the task of determining the correct amount of EGR flow to keep the car running clean. Next month, we will get into diagnosis, testing and repair techniques for all the different types of EGR systems. I will also cover pattern failures of all types, including mechanical problems such as plugged EGR passages that can cause rpm specific misfire concerns. Henry Guzman is an ASE master tech with L1 certification. He has 20 years of experience working as a technician on foreign and domestic cars. MOST ACCESSED ARTICLES RATE THIS ARTICLE nmlkj nmlkj nmlkj nmlkj nmlkj What do you think of this article? Your input will help AutoInc. develop additional articles on this subject. Share your thoughts! Fuel Injection Service, Not Just Cleaning The Art of Extraction EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Proactive Target Marketing:_Rethinking Your Business Strategy Engine Performance: HO2S Diagnostics Your name MOST ED ARTICLES Your address Send Reset Developing Employee Potential How Critical Thinking Can Help Your Business How to Diagnose the Ford Glow Plug What to Look for When Shopping for the Right Shop Management Software Putting a Price Tag on Complaints AutoInc. Web Site ASA Web Site Implementing the New Clean Air Regulations Understanding Exhaust Gas Recirculation Systems Is the Chemistry Right for Sectioning Repairs? The Training Enigma - Part II A Look Back at CARS '97 How to Work with Media Shop Owners Critical to Success of Training Programs Hunting for Profit Guest Editorial Tech Tips Shop Profile Net Worth Chairman's Message Copyright Automotive Service Association. All rights reserved. Add RSS headlines.
5 EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Página 1 de 5 Search this site EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Posted 12/18/1997 By Henry Guzman Last month, we covered the reasons why exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems were created, which is primarily to control and reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) formation, and secondarily to improve engine performance with ping control. We covered the evolution of EGR systems and ended with a look at how onboard diagnostic (OBD-II) EGR systems operate. This month, we will detail the operation and testing of EGR systems. It's helpful to remember that if a hard trouble code has been set, the power control module (PCM) has determined that a gross emission failure has occurred. Gross failure is defined as excessive exhaust emissions more than 1 1/2 times what the car was designed to produce, according to the Federal Test Procedure (FTP). This can happen if too little or too much EGR is flowing. In the case of an EGR code, that would be 1 1/2 times the NOx that is allowable. Even if the car appears to run well, excess smog is being produced. An EGR failure will not only cause excess NOx, back up strategies will often entail enriching the mixture or retarding the timing. This in turn increases HC and CO emissions. Even if you don't see it on a 4-gas exhaust analysis test, the emissions are being created and the catalytic converter will not always cover them up. EGR valves and components To diagnose EGR systems properly, it's important to understand how they work and what kind of communication they have with PCMs. Knowing this will help you understand a flow chart and wiring diagram, and to come up with a test strategy that you are able to complete with your available tools and equipment. Let's start with that golden oldie, the single diaphragm EGR valve. It consists of a spring-loaded diaphragm that is connected to a pintle and seat by a slender steel shaft. Normally closed by spring tension, as it receives ported vacuum, the diaphragm rises, which pulls the pintle off its seat and enables exhaust to flow into the valve's chamber and then on to the intake manifold. To test this component, use a hand-held vacuum pump connected to the vacuum nipple to raise and hold the diaphragm. About eight inches of vacuum should do the trick. The valve should hold vacuum and raise the pintle in a linear fashion. When the engine is idling, pumping it up should stall the engine. This type of valve may or may not have vacuum modulation. Remember, vacuum modulation to the EGR is a vital ingredient of good driveability and precise NOx control. This type of EGR valve is used with a thermal vacuum switch and maybe an inline vacuum delay valve. The positive back pressure EGR valve can be identified by the letter "P" stamped next to the part number and date code. A back pressure valve is easy to spot because its pintle shaft is much thicker than the single diaphragm type. This is so because the shaft is hollow. The hollow design allows exhaust gases to flow into the shaft and push up on it. When positive back pressure in the exhaust system is
6 EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Página 2 de 5 sufficient, the shaft raises up and seals the built-in control valve. Once the control valve is closed, it allows applied vacuum to pull up on the diaphragm. Without back pressure to lift the hollow shaft and close the control valve opening, the EGR valve will not hold vacuum. It is bled off to the atmosphere. This design thus modulates EGR flow by modulating the applied vacuum. As engine load increases, so does engine back pressure, which causes the control valve inside the EGR to trap vacuum and open up. To test this valve, bring the engine up to 2,000 rpms to create back pressure, then apply vacuum. EGR should open and cause a 100 rpm drop or more. Exhaust leaks or a modified exhaust system can create havoc here. Adding dual exhaust or headers on a car designed for a single exhaust will reduce back pressure and set a Code 32 on GM cars. Positive back pressure EGR valves are used in simple vacuum controlled systems, as well as more complex pulse width modulated applications. EGR solenoids are used with all types of EGR valves, especially back pressure type valves. The EGR solenoid will have two or more vacuum lines and an electrical connector. The solenoid also has an air bleed and sometimes an air filter. Vacuum is bled off through the filter vent. The PCM uses the solenoid to regulate vacuum to the EGR valve. The vacuum can be manifold or ported vacuum. The solenoid is a vacuum switch with inlet and outlet vacuum ports. The PCM calculates intended EGR flow from various other inputs and then sends a pulsed "on/off" signal to the solenoid. No vacuum flows until commanded by the PCM. This signal turns the vacuum on and off in rapid succession. This is called "pulse width modulation." If the filter becomes clogged, the vacuum cannot bleed off and too strong a signal will be sent to the valve. If that happens, the EGR valve will open too much and cause a driveability problem. Remote vacuum transducers All manufacturers use them, but they are very popular with Toyotas and other Asian cars. Shaped like a flying saucer with three or more vacuum ports, they modulate vacuum by using manifold and ported vacuum against each other along with an exhaust back pressure input. The result is a carefully controlled vacuum signal to the EGR valve that is mechanically modulated by engine load. Your best bet with these is to study the vacuum diagram on the underhood emissions label. Make sure the vacuum hoses are in good condition and properly routed. Many of these units have air filters also. You can clean them out to prevent too much EGR flow. The negative back pressure EGR valve is identified by the letter "N" and looks similar to the positive back pressure EGR valve. The valve is opened by a combination of applied engine vacuum to the control valve and negative exhaust system pulses that happen as each exhaust valve closes. As soon as the pintle opens, back pressure is reduced slightly, which opens a control valve vacuum bleed and then the valve quickly closes. In this manner, EGR is modulated by negative exhaust system pulses. To test it, apply vacuum with a hand pump when the engine is off. The valve should open and hold vacuum. Integrated electronic/mechanical EGR valves This type of valve has different names with each manufacturer. It is easily identified because it has a single vacuum source inlet and a three-wire electrical connector. Mechanically, it operates like a single diaphragm EGR valve with a twist. It has a pintle position sensor riding atop the EGR diaphragm. This tells the PCM the amount of EGR valve opening as it is actuated. The PCM then commands a pulse width modulated solenoid to apply an appropriate amount of vacuum ontime. GM makes one of these units that has the integral pintle sensor and an integral solenoid with air filter. The only separately serviceable part is the air filter. Ford, Honda and Mazda all use a variation of this design with remotely mounted solenoids. The idea behind the pintle sensor is to give the PCM precise feedback as to exactly where the EGR valve is positioned. The PCM can then modulate the vacuum signal to it accordingly. The pintle position sensor is a potentiometer. Like a throttle position sensor, it is a variable resistor. The wiper arm within the sensor
7 EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Página 3 de 5 can wear and develop opens in the sensor return signal. A sweep test with a digital volt/ohm meter (DVOM) or scope can be used to test the sensor. The PCM has an internal "map" of where the pintle sensor should be at any given time. If the sensor's voltage reading is too high or low, a trouble code will be set. With Fords, it is the infamous Code 31. This code could be caused by several different factors. If the pintle position sensor (Ford calls it the EVP sensor) is shorted or open, you could have a code set. If the EGR valve becomes carboned up and does not seat fully, the EVP sensor gives a high reading and a code is set. If the diaphragm of the EGR valve is bad, then it, too, is flagged. The fix On Fords and Mazdas, the only sure fix is to replace the sensor and valve as an assembly. Sometimes you can get temporary relief by filing down the pintle sensor stem to lower the sensor return voltage to specs. Or you could add a thicker gasket between the valve and sensor. You can spend a lot of time trying to capture the intermittent failure in the act. This is not recommended. The codes are rarely false. Note that there are two interchangeable sensors; one is gray and the other is black. Key-on-engine-off (KOEO) voltage for the gray sensor is 0.40 volt and for the black sensor is about 0.83 volt. Don't mix them up, or Code 31 won't go away. On Hondas, the fix is sometimes achieved by cleaning out moisture and crud from the EGR vacuum lines with shop air pressure. Disassembly of the vacuum air box is required for access. Digital EGR valves are unique in several ways. Only GM uses them. They are completely electronic, controlled solely by the PCM. They come in two or three solenoid models, depending on the application. Part of the valve is open to exhaust flow at all times. When the solenoid pulls the pintle open, exhaust leaves the EGR valve chamber and directly enters the intake manifold. This method is different from all other EGR valves. All other EGR valves open to allow exhaust to enter their chamber first, then circulate through the valve on to the intake passage. The benefit of the digital EGR valve is speed and accuracy. It meters EGR flow 10 times faster than a vacuum modulated system. The valve is actuated by an individual quad driver from the PCM for each solenoid the valve has. Battery power is fed through terminal D when the key is turned on through a 15-amp ignition fuse. When the PCM grounds a solenoid, a magnetic field is created that causes the armature to lift open the pintle. The PCM uses this system to actuate each solenoid in increments. The increments are displayed on a scan tool as percentages of total flow. With a bi-directional scan tool, the digital EGR valve can be commanded open in a variety of increments. Don't despair if you do not have a bi-directional scan tool. You can still work with this! It's easy. Simply unplug the four-wire connector. Run a fused 12-volt wire to terminal D and alternately touch each of the other terminals to ground with a test probe. This will cause each solenoid to pull open. You can do this test with the engine idling and check for an rpm drop as you ground each solenoid. If you don't get a good rpm drop on this or any other EGR valve, you may have plugged or restricted EGR passages, which can cause a code to be set. The linear EGR valve is a high-tech system. It uses a closed loop method for the utmost in EGR control and driveability. All electronic, its built-in pintle-position sensor allows the PCM to continuously monitor "actual pintle position" and adjust it to the "desired pintle position" as a percentage. A generic scan tool will display these parameters just as it does "actual rpm" and "desired rpm." This feature is a boon to troubleshooting. For example, I had a '92 Chevy half-ton drive into our shop running terribly. The Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) was on steady. My aftermarket scan tool pulled up a Code 32. A quick look at the data stream showed that actual and desired pintle position did not match - at idle, "desired pintle position" was zero; "actual" was about 40 percent. This told me the PCM was
8 EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Página 4 de 5 trying to close the EGR valve but could not. Twenty minutes later, I had the EGR valve out of the vehicle and found a large chunk of carbon stuck between the pintle and its seat. Spring tension was holding it tightly and, of course, the PCM was squeezing it as it tried to close the valve. I pried the carbon out, reinstalled the valve, and all was well. Repeat failure Repeat failure is a common problem. You can recommend a top engine clean to the customer and attempt to clean loose carbon from the upper intake. GM has noted the problem and come up with a software update for the PCM. Essentially, what the update does is periodically command the EGR to 100 percent opening to prevent or flush out carbon chunks. The new prom numbers were in a "special policy" procedure bulletin and not a regular TSB. The special policy number is 96067(A). It refers to '92-'94 S/T, M/L and C trucks with the 4.3 V6 engine and linear EGR valve. The bulletin number is It refers to '95 C, S/T and M/L trucks with the 4.3 V6 engine and linear EGR valve. EGR/PCM strategy GM's Code 32 has been around a long time and can be caused by a variety of reasons. Every three to five years, the PCM strategy on this code changes. Make sure you review the proper flow chart any time you work on one on these. The strategy is slightly different depending on which engine, transmission, body type or year the car is. The most common strategy entails the PCM looking for fuel integrator counts to decrease momentarily when the EGR is commanded open. Why? There is no oxygen in the inert EGR gas, so the integrator subtracts fuel to compensate. For this to happen you must have a good working oxygen (O2) sensor. O2 sensor checks are usually not in the Code 32 flow chart, so be aware. Newer models and other makes look for a change in manifold absolute pressure (MAP) when EGR is flowing, which is a more reliable method. Mechanical failures In closing, I'll leave you with a pattern failure seen in '85-'92 Nissans, models 240 SX and Stanza, and some Hondas about the same vintage. They have individual EGR passages running to each cylinder. Eventually, some of these passages (one or two) will plug up with carbon while others stay open. The remaining passages receive 4-runner EGR volume, which is far too much and causes a misfire on the affected cylinders. It happens above idle and under load. Sometimes you can unscrew Allen head access plugs to clean out the passages, other times you must remove the upper intake plenum chamber to do the repair. Henry Guzman is an ASE master tech with L1 certification. He has 20 years of experience working as a technician on foreign and domestic cars. MOST ACCESSED ARTICLES RATE THIS ARTICLE nmlkj nmlkj nmlkj nmlkj nmlkj What do you think of this article? Your input will help AutoInc. develop additional articles on this subject. Share your thoughts! Fuel Injection Service, Not Just Cleaning The Art of Extraction EGR Systems: Operation and Diagnosis Proactive Target Marketing:_Rethinking Your Business Strategy Engine Performance: HO2S Diagnostics MOST ED ARTICLES
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
Emissions Theory and Diagnostics
 SECTION 1 Introduction 5-Gas Theory Emissions History OBD II SECTION 2 PCV System Function Failure Diagnosis Emissions Theory and Diagnostics SECTION 3 EGR EGR Theory Vacuum Systems Backpressure Systems
SECTION 1 Introduction 5-Gas Theory Emissions History OBD II SECTION 2 PCV System Function Failure Diagnosis Emissions Theory and Diagnostics SECTION 3 EGR EGR Theory Vacuum Systems Backpressure Systems
Module 12 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
 Module 12 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443
Module 12 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443
ATASA 5 th. Engine Performance Systems. Please Read The Summary. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages Engine Performance Systems 100 Points
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages 725 763 100 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Engine systems are those responsible for how an engine runs. Performance Emission Control Electronic 2. The correct
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages 725 763 100 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Engine systems are those responsible for how an engine runs. Performance Emission Control Electronic 2. The correct
Are you as confident and
 64 March 2007 BY BOB PATTENGALE Although Mode $06 is still a work in progress, it can be used to baseline a failure prior to repairs, then verify the accuracy of the diagnosis after repairs are completed.
64 March 2007 BY BOB PATTENGALE Although Mode $06 is still a work in progress, it can be used to baseline a failure prior to repairs, then verify the accuracy of the diagnosis after repairs are completed.
Catalytic Converter Testing
 Catalytic Converter Testing The first catalytic converter was created before the use of onboard computer systems its job was to oxidize HC and CO into CO2 and H2O. The term oxidizes means to add O2 to
Catalytic Converter Testing The first catalytic converter was created before the use of onboard computer systems its job was to oxidize HC and CO into CO2 and H2O. The term oxidizes means to add O2 to
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
OBD II Data Interpretation
 OBD II Data Interpretation What is OBDII? OBDII stands for on board diagnostics second generation superseding that of OBD1.OBDII is a system that was mandated by the Federal EPA and was developed by the
OBD II Data Interpretation What is OBDII? OBDII stands for on board diagnostics second generation superseding that of OBD1.OBDII is a system that was mandated by the Federal EPA and was developed by the
ATASA 5 th. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 31 Pages EFI Diagnosis & Service 47 Points. Please Read The Summary
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 31 Pages 922 948 47 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Troubleshooting EFI systems requires step by step test procedures mostly due to the many interrelated components and
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 31 Pages 922 948 47 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Troubleshooting EFI systems requires step by step test procedures mostly due to the many interrelated components and
Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors
 Light Vehicle Diesel Engines First Edition Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors LEARNING OBJECTIVES (1 of 2) 20.1 Prepare for the Light Vehicle Diesel Engine (A9) ASE certification fuel system diagnosis and
Light Vehicle Diesel Engines First Edition Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors LEARNING OBJECTIVES (1 of 2) 20.1 Prepare for the Light Vehicle Diesel Engine (A9) ASE certification fuel system diagnosis and
Module 11 Thermistor Inputs
 Module 11 Thermistor Inputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
Module 11 Thermistor Inputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
VAPOR TRAILS: FINDING & FIXING EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM FAULTS. by 1975 and established the U.S. Environmental
 VAPOR TRAILS: FINDING & FIXING EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM FAULTS BY BOB PATTENGALE Current OBD II systems can detect evap system leaks too small to see, or even smell. Finding and fixing these and other system
VAPOR TRAILS: FINDING & FIXING EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM FAULTS BY BOB PATTENGALE Current OBD II systems can detect evap system leaks too small to see, or even smell. Finding and fixing these and other system
2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD
 2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD DTC P0410 Description The control module activates the secondary air injection (AIR) system by grounding both the pump relay and the vacuum control solenoid control circuits.
2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD DTC P0410 Description The control module activates the secondary air injection (AIR) system by grounding both the pump relay and the vacuum control solenoid control circuits.
DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2
 2000 Chevrolet/Geo S10 Pickup - 4WD DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 Circuit Description In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the
2000 Chevrolet/Geo S10 Pickup - 4WD DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 Circuit Description In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the
#97-T-20A: MIL (Service Engine Soon Telltale Lamp) On and EGR DTCs P0401, P0404, P0405, P1404 and/or P1406 in PCM Memory - (Jan 6, 2003)
 #97-T-20A: MIL (Service Engine Soon Telltale Lamp) On and EGR DTCs P0401, P0404, P0405, P1404 and/or P1406 in PCM Memory - (Jan 6, 2003) Subject: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON Telltale
#97-T-20A: MIL (Service Engine Soon Telltale Lamp) On and EGR DTCs P0401, P0404, P0405, P1404 and/or P1406 in PCM Memory - (Jan 6, 2003) Subject: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (SERVICE ENGINE SOON Telltale
Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Cavalier (CNG) Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit Table 1: AF ECU Function Parameters The (AF ECU) controls alternative fuel engine operation. The control unit monitors various engine
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Cavalier (CNG) Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit Table 1: AF ECU Function Parameters The (AF ECU) controls alternative fuel engine operation. The control unit monitors various engine
Dealing with customer concerns related to electronic throttle bodies By: Bernie Thompson
 Dealing with customer concerns related to electronic throttle bodies By: Bernie Thompson In order to regulate the power produced from the gasoline internal combustion engine (ICE), a restriction is used
Dealing with customer concerns related to electronic throttle bodies By: Bernie Thompson In order to regulate the power produced from the gasoline internal combustion engine (ICE), a restriction is used
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review
 Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
WEBER CARBURETOR TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
 This guide is to help pinpoint problems by diagnosing engine symptoms associated with specific vehicle operating conditions. The chart will guide you step by step to help correct these problems. For successful
This guide is to help pinpoint problems by diagnosing engine symptoms associated with specific vehicle operating conditions. The chart will guide you step by step to help correct these problems. For successful
P0401-EGR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
 P0401-EGR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE P0401-EGR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE http://dh.identifix.com/searchfixes/index?roid=176514061&vid=2189101&vsm=2&locationid=2#kw=p0401&soption=1&vetid=8&stmode=1&p 1/6 For a complete
P0401-EGR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE P0401-EGR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE http://dh.identifix.com/searchfixes/index?roid=176514061&vid=2189101&vsm=2&locationid=2#kw=p0401&soption=1&vetid=8&stmode=1&p 1/6 For a complete
 Page 1 of 18 2004 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests Procedure revision date: 10/26/2007 H: Fuel Control H: Introduction H1 PERFORM THE KOER SELF-TEST Engine at normal operating temperature.
Page 1 of 18 2004 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests Procedure revision date: 10/26/2007 H: Fuel Control H: Introduction H1 PERFORM THE KOER SELF-TEST Engine at normal operating temperature.
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01
 Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
cylinder cars / trucks (except Saturn S-series cars) ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC PARAMETERS
 2001 4-cylinder cars / trucks (except Saturn S-series cars) ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC S SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure Too
2001 4-cylinder cars / trucks (except Saturn S-series cars) ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC S SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure Too
(P0135/P0155), (P0141/P0161), (P1131/P1151), (P1132/P1152). To further clarify this, see the more detailed scenario as follows:
 1. Always reset KAM after performing a repair: After performing a repair on a vehicle with the MIL on, and/or DTCs present, always clear KAM. When a malfunction is present, the PCM adapts (attempts to
1. Always reset KAM after performing a repair: After performing a repair on a vehicle with the MIL on, and/or DTCs present, always clear KAM. When a malfunction is present, the PCM adapts (attempts to
Happy Birthday OBD II Emission Control System becomes diagnostic tool
 FEATURE ARTICLE Happy Birthday OBD II Emission Control System becomes diagnostic tool 4 Bring out the birthday cake and light the candles, the second generation of onboard diagnostics, universally known
FEATURE ARTICLE Happy Birthday OBD II Emission Control System becomes diagnostic tool 4 Bring out the birthday cake and light the candles, the second generation of onboard diagnostics, universally known
DTC P0420. Circuit Description. Conditions for Running the DTC.
 Page 1 of 5 DTC P0420 2003 Buick LeSabre LeSabre (VIN H) Service Manual Document ID: 792202 Circuit Description In order to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen
Page 1 of 5 DTC P0420 2003 Buick LeSabre LeSabre (VIN H) Service Manual Document ID: 792202 Circuit Description In order to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2
 Table of Contents YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2 ABOUT THE CODE READER VEHICLES COVERED... 3 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 4 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 5 ONBOARD DIAGNOSTICS COMPUTER
Table of Contents YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2 ABOUT THE CODE READER VEHICLES COVERED... 3 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 4 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 5 ONBOARD DIAGNOSTICS COMPUTER
UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS
 UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS AND EMISSIONS Gas Diagnostic Steps This procedure will help in your efforts to figure out what the five-gas reading are telling you. In order for five gas analyses to be conclusive
UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS AND EMISSIONS Gas Diagnostic Steps This procedure will help in your efforts to figure out what the five-gas reading are telling you. In order for five gas analyses to be conclusive
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. Self-Diagnostics - RAV4. Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs).
 2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE CODE READER VEHICLES COVERED... 4 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 5 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS...
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE CODE READER VEHICLES COVERED... 4 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 5 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS...
4.0L CEC SYSTEM Jeep Cherokee DESCRIPTION OPERATION FUEL CONTROL DATA SENSORS & SWITCHES
 4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2
 Table of Contents YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2 ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 3 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 4 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 5 DISPLAY AND SETTINGS... 6 ONBOARD
Table of Contents YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2 ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 3 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 4 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 5 DISPLAY AND SETTINGS... 6 ONBOARD
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich
 Page 1 of 6 1997 Chevrolet Cavalier Cavalier, Sunfire (VIN J) Service Manual Document ID: 47788 DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich System Description A Closed Loop air/fuel metering system is used to provide
Page 1 of 6 1997 Chevrolet Cavalier Cavalier, Sunfire (VIN J) Service Manual Document ID: 47788 DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich System Description A Closed Loop air/fuel metering system is used to provide
ABOUT THE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 DIAGNOSTIC TOOL CONTROLS
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 DIAGNOSTIC TOOL CONTROLS
For. Code Reader. User Manual
 For OBD2 Code Reader User Manual http://www.motodok.com Table of Contents 1. Description... 2 2. Features... 2 3. Getting Started... 3 1. Connect Code Reader to Vehicle's Test Connector... 3 2. Read Diagnostic
For OBD2 Code Reader User Manual http://www.motodok.com Table of Contents 1. Description... 2 2. Features... 2 3. Getting Started... 3 1. Connect Code Reader to Vehicle's Test Connector... 3 2. Read Diagnostic
Computers and Control Systems: Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures C Charts. Part 1 of 6. Chart C-1 (1 Of 6)
 1993 Cadillac DeVille V8-300 4.9L Page 1 Computers and Control Systems: Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures C Charts Part 1 of 6 Chart C-1 (1 Of 6) 1993 Cadillac DeVille V8-300 4.9L Page 2 Wiring Diagram.
1993 Cadillac DeVille V8-300 4.9L Page 1 Computers and Control Systems: Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures C Charts Part 1 of 6 Chart C-1 (1 Of 6) 1993 Cadillac DeVille V8-300 4.9L Page 2 Wiring Diagram.
YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2
 Table of Contents YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2 ABOUT THE VEHICLES COVERED... 3 ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS... 4 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 6 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 7 ONBOARD DIAGNOSTICS
Table of Contents YOU CAN DO IT!... 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 2 ABOUT THE VEHICLES COVERED... 3 ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS... 4 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 6 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 7 ONBOARD DIAGNOSTICS
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
Monitoring The Problem
 Monitoring The Problem by Kerry Jonsson Every so often we run into the problem of not having a problem to solve. What do we do when we have a vehicle that is not setting codes, but it is also not running
Monitoring The Problem by Kerry Jonsson Every so often we run into the problem of not having a problem to solve. What do we do when we have a vehicle that is not setting codes, but it is also not running
On Board Diagnostics (OBD) Monitors
 2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 1: Description and Operation Procedure revision date: 03/29/2006 On Board Diagnostics (OBD) Monitors OBD-I, OBD-II and Engine Manufacturer Diagnostics (EMD) Overview
2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 1: Description and Operation Procedure revision date: 03/29/2006 On Board Diagnostics (OBD) Monitors OBD-I, OBD-II and Engine Manufacturer Diagnostics (EMD) Overview
INDEX. 1.Safety Precautions and Warnings...3
 INDEX 1.Safety Precautions and Warnings...3 2. General Information...5 2.1 On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) II... 5 2.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)... 6 2.3 Location of the Data Link Connector (DLC)...7
INDEX 1.Safety Precautions and Warnings...3 2. General Information...5 2.1 On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) II... 5 2.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)... 6 2.3 Location of the Data Link Connector (DLC)...7
1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L
 INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
E - THEORY/OPERATION ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L
 E - THEORY/OPERATION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and
E - THEORY/OPERATION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and
DTC P1415 Secondary Air Injection (AIR) System Bank 1
 Page 1 of 5 2000 GMC Truck GMC K Sierra - 4WD Sierra, Silverado, Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Document ID: 546887 DTC P1415 Secondary Air Injection (AIR) System Bank 1 Circuit Description
Page 1 of 5 2000 GMC Truck GMC K Sierra - 4WD Sierra, Silverado, Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Document ID: 546887 DTC P1415 Secondary Air Injection (AIR) System Bank 1 Circuit Description
SECONDARY PARAMETERS AND ENABLE CONDITIONS
 SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure Sensor Rationality Manifold Pressure Too Low Manifold Pressure Too High Intake Air Temperature Sensor Shorted Intake Air Temperature Sensor Open Coolant Temperature Sensor
SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure Sensor Rationality Manifold Pressure Too Low Manifold Pressure Too High Intake Air Temperature Sensor Shorted Intake Air Temperature Sensor Open Coolant Temperature Sensor
GROUP 13Ab. 13Ab-2 CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS...
 13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
DTC P0420 or P0430. Circuit Description. DTC Descriptors. Conditions for Running the DTC
 Page 1 of 5 2005 Cadillac STS STS (VIN D) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.6L (LH2) Diagnostic Information and Procedures DTC P0420 or P0430 Circuit Description A three-way catalytic converter
Page 1 of 5 2005 Cadillac STS STS (VIN D) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.6L (LH2) Diagnostic Information and Procedures DTC P0420 or P0430 Circuit Description A three-way catalytic converter
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis
 Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
OBDII INSPECTION GUIDE
 OBDII INSPECTION GUIDE Texas Department of Public Safety September 2002 Prepared by: dkc de la Torre Klausmeier Consulting, Inc. ª2002 dkc Table of Contents GLOSSARY OF OBD TERMS...2 INTRODUCTION...12
OBDII INSPECTION GUIDE Texas Department of Public Safety September 2002 Prepared by: dkc de la Torre Klausmeier Consulting, Inc. ª2002 dkc Table of Contents GLOSSARY OF OBD TERMS...2 INTRODUCTION...12
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
Table of Contents. CarScan+OBD1
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 SCAN TOOL CONTROLS CONTROLS
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 SCAN TOOL CONTROLS CONTROLS
Honda Accord/Prelude
 Honda Accord/Prelude 1984-1995 In Tank Fuel Pumps TEST 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. On the Accord, remove the screws securing the underdash fuse box to its mount. Remove the fuel cut off relay from the
Honda Accord/Prelude 1984-1995 In Tank Fuel Pumps TEST 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. On the Accord, remove the screws securing the underdash fuse box to its mount. Remove the fuel cut off relay from the
Table of Contents. 3120f
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 DIAGNOSTIC TOOL CONTROLS
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 DIAGNOSTIC TOOL CONTROLS
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
Powertrain DTC Summaries OBD II
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
ATASA 5 th. Detailed Diagnosis & Sensors. Please Read The Summary
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 26 Pages 764 809 51 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Many different sensors are involved in the overall driveability of a vehicle. Input Processing Output Electronic Engine
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 26 Pages 764 809 51 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Many different sensors are involved in the overall driveability of a vehicle. Input Processing Output Electronic Engine
Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION GENERAL INFORMATION-ABOUT OBDII/EOBD PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS OPERATIONS...11
 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. GENERAL INFORMATION-ABOUT OBDII/EOBD...1 2.1 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD) II...1 2.2 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)...2 2.3 LOCATION OF THE DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)...3
Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. GENERAL INFORMATION-ABOUT OBDII/EOBD...1 2.1 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD) II...1 2.2 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)...2 2.3 LOCATION OF THE DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC)...3
Catalytic Failures. Engine running too hot.
 Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
Scan Tool Test Procedures Steve Zack Technical Instructor Bosch AA-AS
 Scan Tool Test Procedures Steve Zack Technical Instructor Bosch AA-AS Steve Zack 8.10.15 1 This class will develop the technician skills to use their scan tool to resolve difficult technical issues efficiently.
Scan Tool Test Procedures Steve Zack Technical Instructor Bosch AA-AS Steve Zack 8.10.15 1 This class will develop the technician skills to use their scan tool to resolve difficult technical issues efficiently.
L (LL8) Engine Diagnostic Parameters
 Cam Shaft Position Actuator Control VCP System Performance VCP = variable cam phaser VCP Crank/Cam Correlation Error P0013 P0014 P0016 DESCRIPTION Detects an open or shorted control circuit by monitoring
Cam Shaft Position Actuator Control VCP System Performance VCP = variable cam phaser VCP Crank/Cam Correlation Error P0013 P0014 P0016 DESCRIPTION Detects an open or shorted control circuit by monitoring
Chapter. On-Board Diagnostics and Scan Tools
 Chapter 24 On-Board Diagnostics and Scan Tools Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Discuss the purpose and operation of onboard diagnostic systems. Explain the use of scan tools
Chapter 24 On-Board Diagnostics and Scan Tools Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Discuss the purpose and operation of onboard diagnostic systems. Explain the use of scan tools
INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL SAFETY FIRST!... 3 VEHICLES COVERED... 4 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 5 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 6 INITIAL ADJUSTMENTS...
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL SAFETY FIRST!... 3 VEHICLES COVERED... 4 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS... 5 DISPLAY FUNCTIONS... 6 INITIAL ADJUSTMENTS...
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
 Solarity with InfoTech Software Solarity, powered by Genisys technology, is a powerful 4-channel scope with the functionality required to analyze the most sophisticated vehicles. InfoTech Software provides
Solarity with InfoTech Software Solarity, powered by Genisys technology, is a powerful 4-channel scope with the functionality required to analyze the most sophisticated vehicles. InfoTech Software provides
Module 22 Ignition Systems - Outputs
 Module 22 Ignition Systems - Outputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
Module 22 Ignition Systems - Outputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
Oregon Fuel Injection
 2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
P0441-EVAP PURGE SYSTEM PERFO... P0441-EVAP PURGE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
 P0441-EVAP PURGE SYSTEM PERFO... P0441-EVAP PURGE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE For a complete wiring diagram, refer to the Wiring Information. Theory of Operation EVAP SYSTEM COMPONENTS CALLOUT DESCRIPTION 1 Filter
P0441-EVAP PURGE SYSTEM PERFO... P0441-EVAP PURGE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE For a complete wiring diagram, refer to the Wiring Information. Theory of Operation EVAP SYSTEM COMPONENTS CALLOUT DESCRIPTION 1 Filter
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
Selected excerpts from the book: Lab Scopes: Introductory & Advanced. Steven McAfee
 Selected excerpts from the book: Lab Scopes: Introductory & Advanced Steven McAfee 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Excerpt from Chapter 1 Lab Scopes How do they work? (page 6) Excerpt from Chapter 3 Pattern Recognition
Selected excerpts from the book: Lab Scopes: Introductory & Advanced Steven McAfee 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Excerpt from Chapter 1 Lab Scopes How do they work? (page 6) Excerpt from Chapter 3 Pattern Recognition
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Technical Service Bulletin
 Number 02-36-030 Subject OBD-II READINESS TEST DRIVE CYCLE FOR 1996-1998 SONATA Date Model DECEMBER, 2002 1996-1998 SONATA DESCRIPTION: This TSB describes Drive Cycles which may assist the vehicle s OBD-II
Number 02-36-030 Subject OBD-II READINESS TEST DRIVE CYCLE FOR 1996-1998 SONATA Date Model DECEMBER, 2002 1996-1998 SONATA DESCRIPTION: This TSB describes Drive Cycles which may assist the vehicle s OBD-II
DESCRIPTION Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20. Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI
 Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
Powertrain Control Software
 2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 1: Description and Operation Procedure revision date: 03/29/2006 Powertrain Control Software Computer Controlled Shutdown The powertrain control module (PCM) controls
2007 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 1: Description and Operation Procedure revision date: 03/29/2006 Powertrain Control Software Computer Controlled Shutdown The powertrain control module (PCM) controls
1GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM
 134 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage
134 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage
Module 9 Closed Loop Strategies - Theory
 Module 9 Closed Loop Strategies - Theory Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443
Module 9 Closed Loop Strategies - Theory Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control
 The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
Code 32. Diagnostic Trouble Code 32
 Code 32 Diagnostic Trouble Code 32 EGR Solenoid Circuit CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The ECM operates a solenoid to control the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve. This solenoid is normally close EGR valve.
Code 32 Diagnostic Trouble Code 32 EGR Solenoid Circuit CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The ECM operates a solenoid to control the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve. This solenoid is normally close EGR valve.
4L80E Updates. Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: Chevrolet L80E. Updates ACTUATOR FEED LIMIT FLUID SPOOL VALVE SPRING
 Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: Technical Bulletin #266 4L80E Updates Chevrolet 1995 4L80E Updates Many electrical changes have occurred in the 4L80E transmission for the 1994 model year,
Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: Technical Bulletin #266 4L80E Updates Chevrolet 1995 4L80E Updates Many electrical changes have occurred in the 4L80E transmission for the 1994 model year,
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
GROUP 13Ab. 13Ab-2 CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-28 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS...
 13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-28 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE/BACKUP FUNCTION TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-28 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE/BACKUP FUNCTION TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION
 SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION A -- Ground G -- Fuel Pump B -- Diagnostic Terminal H -- Brake Sense Speed Input F -- TCC M -- Serial Data (special tool needed - Do Not Use) For ECM Trouble Codes,
SYTY Trouble Code: ALDL INFORMATION A -- Ground G -- Fuel Pump B -- Diagnostic Terminal H -- Brake Sense Speed Input F -- TCC M -- Serial Data (special tool needed - Do Not Use) For ECM Trouble Codes,
The Mark V Air/Fuel Controller - Technical Manual -
 Neutronics Enterprises Inc. The Mark V Air/Fuel Controller - Technical Manual - For Technical Information contact: Neutronics Enterprises Inc. 11421 West Bernardo Court. San Diego, CA. 92127 (858) 674-2250
Neutronics Enterprises Inc. The Mark V Air/Fuel Controller - Technical Manual - For Technical Information contact: Neutronics Enterprises Inc. 11421 West Bernardo Court. San Diego, CA. 92127 (858) 674-2250
VS403 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION & CONTENTS. fig.1
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
Fixed Right First Time. Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers
 Tech-Net Notes Fixed Right First Time Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers NO: 25-19 DATE: 6-30-2004 MODEL: 960-S/V90/850/S70/V70/C70 M. YEAR: 1996-1998 SUBJECT: Establishing Readiness for OBD
Tech-Net Notes Fixed Right First Time Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers NO: 25-19 DATE: 6-30-2004 MODEL: 960-S/V90/850/S70/V70/C70 M. YEAR: 1996-1998 SUBJECT: Establishing Readiness for OBD
INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE CODE READER VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 ADJUSTMENTS/SETTINGS AND
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION WHAT IS OBD?... 1 YOU CAN DO IT!... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS SAFETY FIRST!... 3 ABOUT THE CODE READER VEHICLES COVERED... 5 BATTERY REPLACEMENT... 6 ADJUSTMENTS/SETTINGS AND
ARTICLE BEGINNING INTRODUCTION SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM RETRIEVING DTCS ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline Cabrio, Golf III, GTI, Jetta III, Passat INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing preliminary
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline Cabrio, Golf III, GTI, Jetta III, Passat INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing preliminary
CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE PROCEEDING
 Daytona Sensors LLC Engine Controls and Instrumentation Systems Installation Instructions for Wide-Band Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor Interface CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE PROCEEDING OVERVIEW
Daytona Sensors LLC Engine Controls and Instrumentation Systems Installation Instructions for Wide-Band Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor Interface CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE PROCEEDING OVERVIEW
EVERY ALTERNATIVE ISLG Combustion Air and Emission Devices. Why Cooled EGR? 4/23/2013. Why Exhaust Gas Recirculation.
 EVERY ALTERNATIVE. 2007 ISLG Combustion Air and Emission Devices Why Exhaust Gas Recirculation Basic Science NOx (Oxides of Nitrogen) pollution occurs due to high cylinder temperatures during the combustion
EVERY ALTERNATIVE. 2007 ISLG Combustion Air and Emission Devices Why Exhaust Gas Recirculation Basic Science NOx (Oxides of Nitrogen) pollution occurs due to high cylinder temperatures during the combustion
Part 1. Reduced fuel flow due to a restricted inlet screen. Sluggish plunger movement due to contamination.
 http://www.datec.us/instructor/ More about the author http://www.datec.us /instructor SCREEN Part 1 There is not a good way to check the fuel distribution per cylinder. The intention of this session is
http://www.datec.us/instructor/ More about the author http://www.datec.us /instructor SCREEN Part 1 There is not a good way to check the fuel distribution per cylinder. The intention of this session is
INTRODUCTION. FOR ios DEVICES
 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION ABOUT QUICKLINK... 1 Vehicles Covered... 1 The QUICKLINK Device... 2 The QUICKLINK App... 2 COMPUTER ENGINE CONTROLS... 2 The Introduction of Electronic Engine Controls...
Table of Contents INTRODUCTION ABOUT QUICKLINK... 1 Vehicles Covered... 1 The QUICKLINK Device... 2 The QUICKLINK App... 2 COMPUTER ENGINE CONTROLS... 2 The Introduction of Electronic Engine Controls...
EDITOR'S NOTE: This article replaces "Use PGM FI Data List to Help Troubleshoot Inoperative A/C," issued in June 2012.
 2001 Honda Civic 1.7L Eng LX TROUBLESHOOTING AN INOPERATIVE A/C TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN Reference Number(s): 13 080J, Date of Issue: August, 2013 HONDA: '00 and later models with A/C APPLIES TO: '00
2001 Honda Civic 1.7L Eng LX TROUBLESHOOTING AN INOPERATIVE A/C TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN Reference Number(s): 13 080J, Date of Issue: August, 2013 HONDA: '00 and later models with A/C APPLIES TO: '00
Fuel System (Central SFI)
 Page 1 of 6 1997 GMC Truck GMC K Pickup - 4WD Chevy Pickup, GMC Pickup, Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L, 5.7L, and 7.4L Description and Operation Document
Page 1 of 6 1997 GMC Truck GMC K Pickup - 4WD Chevy Pickup, GMC Pickup, Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L, 5.7L, and 7.4L Description and Operation Document
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
A. Perform a vacuum gauge test to determine engine condition and performance.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
