EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
|
|
|
- Esther Joan Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission control system Catalytic converter Air/fuel (A/F) control system Ignition control system Evaporative emission control system On-board refueling vapor recovery (ORVR) system EC(H4DOTC)-2
3 SYSTEM OVERVIEW Item Main components Function Crankcase emission control system Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve Draws blow-by gas into intake manifold from crankcase and burn it together with air-fuel mixture. Amount of blow-by gas to be drawn in is controlled by intake manifold pressure. Exhaust emission control system Catalytic converter Air/fuel (A/F) control system Pre Catalytic converter Oxidizes HC and CO contained in exhaust gases as Front well as reducing NOx. Rear Engine control module (ECM) Front oxygen (A/F) sensor Rear oxygen sensor Throttle position sensor Manifold absolute pressure sensor Mass air flow and intake air temperature sensor Receives input signals from various sensors, compares signals with stored data, and emits a signal for optimal control of air-fuel mixture ratio. Detects density of oxygen contained exhaust gases. Detects density of oxygen contained in exhaust gases. Detects throttle opening. Detects absolute pressure of intake manifold. Detects amount of intake air. Detects intake air temperature at air cleaner case. Ignition control system ECM Receives various signals, compares signals with basic data stored in memory, and emits a signal for optimal control of ignition timing. Crankshaft position sensor Detects engine speed (revolution). Camshaft position sensor Detects reference signal for combustion cylinder discrimination. Engine coolant temperature sensor Detects coolant temperature. Knock sensor Detects engine knocking. Evaporative emission control system Canister Purge control solenoid valve Pressure control solenoid valve Absorbs evaporative gas that accumulates in fuel tank when engine stops, and releases it to combustion chambers for a complete burn when the engine is started. This prevents HC from being discharged into atmosphere. Receives a signal from ECM and controls purge of evaporative gas absorbed by canister. Receives a signal from ECM and controls evaporative gas pressure in fuel tank. ORVR system Vent valve Closes the port to the canister when the fuel tank is full of fuel. Drain valve Closes the evaporation line by receiving a signal from ECM to check the evaporation gas leak. EC(H4DOTC)-3
4 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS 2. Schematic Diagrams (54) (61) (60) (64) (55) (59) (62) (63) (57) (56) (58) (48) (47) (49) (50) (51) (10) (6) (5) (15) (11) (14) (52) (12) (8) (7) (13) (9) (17) (16) (45) (44) (53) (43) (42) (37) (46) (38) (36) (35) (33) (40) (22) (34) (39) (19) (21) (23) (31) (32) (18) (28) (25) (26) (24) (27) (30) (29) (20) (66) (67) (68) (65) (3) (4) (41) EC EC(H4DOTC)-4
5 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS Engine control module (ECM) (35) Exhaust temperature sensor Atmospheric pressure sensor (36) Pre-catalytic converter (3) Battery (37) Turbocharger (4) Ignition relay (38) Wastegate valve (5) Fuel pump relay (39) Rear oxygen sensor (6) Fuel pump control unit (40) Rear catalytic converter (7) Fuel tank (41) Chamber (8) Fuel pump (42) Air cleaner element (9) Fuel filter (43) Mass air flow and intake air temperature sensor (10) Pressure control solenoid valve (44) Orifice (11) Fuel tank pressure sensor (45) Wastegate control solenoid valve (12) Canister (46) Wastegate actuator (13) Purge control solenoid valve (47) To water pump (14) Fuel tank sensor control valve (48) From radiator (15) Shut-off valve (49) Engine coolant filler tank (16) Fuel temperature sensor (50) To reservoir tank (17) Fuel level sensor (51) From turbocharger (18) Pressure regulator (52) Purge valve (19) Intercooler (53) PCV hose assembly (20) Air bypass valve (54) Radiator fan (21) Electronic control throttle (55) Fan control relay (22) Manifold absolute pressure sensor (56) A/C compressor (23) PCV valve (57) A/C relay (24) Fuel injector (58) A/C control module (25) Intake camshaft position sensor (59) Body integrated unit (26) Intake oil flow control solenoid valve (60) Engine warning light (27) Ignition coil and igniter assembly (61) Tachometer (28) Tumble generator valve position sensor (62) Neutral switch (MT models) (29) Tumble generator valve actuator (63) Transmission control module (AT models) (30) Knock sensor (64) Neutral switch (AT models) (31) Crankshaft position sensor (65) Accelerator pedal position sensor (32) Engine coolant temperature sensor (66) ABS/VDC control module (33) Front catalytic converter (67) Vehicle speed signal (34) Front oxygen (A/F) sensor (68) Data link connector EC(H4DOTC)-5
6 CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 3. Crankcase Emission Control System The positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system prevents air pollution that will be caused by blow-by gas being emitted from the crankcase. The system consists of a sealed oil filler cap, rocker covers with fresh air inlet, connecting hoses, a PCV valve and an air intake duct. In a part-throttle condition, the blow-by gas in the crankcase flows into the intake manifold through the connecting hose of crankcase and PCV valve by the strong vacuum created in the intake manifold. Under this condition, fresh air is introduced into the crankcase through the connecting hose of the rocker cover. In a wide-open-throttle condition, a part of blow-by gas flows into the air intake duct through the connecting hose and is drawn into the throttle chamber, because under this is condition, the intake manifold vacuum is not strong enough to introduce through the PCV valve all blow-by gases that increase in the amount with engine speed. The PCV hose is provided with a leak detection function. (5) (9) (3) (6) (7) (A) (8) (4) EC Intake duct (6) Valve (A) To intake manifold PCV valve (7) Spring (3) Intake manifold (8) PCV valve (4) Crankcase (9) PCV hose assembly (5) Case EC(H4DOTC)-6
7 4. Catalytic Converter CATALYTIC CONVERTER The basic materials of the three-way catalytic converter are platinum (Pt), rhodium (Rh) and palladium (Pd), and a thin coat of their mixture is applied onto a honeycomb or porous ceramic (carrier). To avoid damaging the catalytic converter, only unleaded gasoline should be used. The catalytic converter reduces HC, CO and NOx in exhaust gases through chemical reactions (oxidation and reduction). These harmful components are reduced most efficiently when their concentrations are in a certain balance. These concentrations vary with the air-fuel ratio. The ideal airfuel ratio for reduction of these components is the stoichiometric ratio. Therefore, the air-fuel ratio needs to be controlled to around the stoichiometric ratio to purify the exhaust gases most efficiently. EC(H4DOTC)-7
8 AIR/FUEL (A/F) CONTROL SYSTEM 5. Air/fuel (A/F) Control System The air/fuel (A/F) control system makes a correction to the basic fuel injection duration in accordance with the signals from the front oxygen (A/F) sensor and the rear oxygen sensor so that the stoichiometric ratio is maintained, thus ensuring most effective exhaust gas purification by the threeway catalytic converter.different basic fuel injection durations are preset for various engine speeds and loads, as well as the amount of intake air. This system also has a learning control function which stores the corrected data in relation to the basic fuel injection in the memory map.this allows an appropriate air-fuel ratio correction to be added automatically in quick response to any situation that requires such an effect. Thus, the air-fuel ratio is optimally maintained under various conditions while purifying exhaust gases most effectively, improving driving performance and compensating for changes in sensors performance over time. EC(H4DOTC)-8
9 6. Ignition Control System IGNITION CONTROL SYSTEM The ignition system is controlled by the ECM. The ECM monitors the operating condition of the engine using the signals from the sensors and switches shown below and determines the ignition timing most appropriate for each engine operating condition. Then it sends a signal to the igniter, commanding generation of a spark at that timing. The ECM uses a preprogrammed map for a closed-loop control which provides its ignition timing control with excellent transient characteristics, i.e., highly responsive ignition timing control. (5) (3) (8) (6) (6) (6) (6) (4) (7) (4) (9) EC Battery (6) Ignition coil and igniter assembly Ignition switch (7) Knock sensor (3) ECM (8) Mass air flow and intake air temperature sensor (4) Camshaft position sensor (9) Engine coolant temperature sensor (5) Crankshaft position sensor EC(H4DOTC)-9
10 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere.this system includes a canister, purge control solenoid valve, fuel cut valve, and the lines connecting them. Fuel vapors in the fuel tank is introduced into the canister through the evaporation line, and are absorbed by activated carbon in it.the fuel cut valve is also incorporated in the fuel tank line. The purge control solenoid valve is controlled optimally by the ECM according to the engine condition. The pressure control solenoid valve incorporated in the fuel tank evaporation line regulates the pressure/vacuum in the fuel tank under the control of the ECM which uses the signal from the fuel tank pressure sensor. (4) (3) (5) (17) (15) (14) (16) (7) (9) (8) (10) (13) (12) (11) (6) EC Fuel gauge (7) Pressure control solenoid valve (13) Fuel tank Intake manifold (8) Drain valve (14) Fuel cut valve (3) Throttle body (9) Drain filter (15) Fuel tank pressure sensor (4) Purge control solenoid valve (10) Shut-off valve (16) Vent valve (5) ECM (11) Fuel temperature sensor (17) Fuel tank sensor control valve (6) Canister (12) Fuel level sensor B: FUEL CUT VALVE The fuel cut valve is incorporated in the fuel tank. The rising level of the fuel in the fuel tank causes the float to move up and close the cap hole so that no fuel can enter the evaporation line. EC(H4DOTC)-10
11 C: FUEL TANK CAP EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM The fuel tank cap is of a quick lock type and can be opened or closed in 1/4 of a full turn. The fuel tank cap has a relief valve, which prevents development of vacuum in the fuel tank in the event of a problem with the fuel vapor line. When there is no problem with the fuel vapor line, the filler pipe is sealed at the portion (A) and by the seal pressed against the filler pipe end. If vacuum develops in the fuel tank, the atmospheric pressure forces the spring down to open the valve; consequently outside air flows into the fuel tank, thus controlling the inside pressure. (4) (A) (3) EC Seal Spring (3) Valve (4) Filter EC(H4DOTC)-11
12 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM D: CANISTER The canister incorporates a drain valve and a drain filter. The charcoal filled in the canister temporarily stores fuel vapors. When the purge control solenoid valve is opened by a signal from the ECM, the external fresh air entering the canister carries the fuel vapors into the collector chamber. The drain filter is installed at the air inlet port of the drain valve. It cleans the air taken in the canister through the drain valve. (A) (C) (B) EC Drain valve (A) Air Drain filter (B) To pressure control solenoid valve (C) From fuel tank EC(H4DOTC)-12
13 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM E: PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE (Until '05MY) The purge control solenoid valve is on the evaporation line between the canister and intake manifold. The valve is installed under the intake manifold and lets the evaporative gas absorbed by the canister be drawn into the intake manifold. (A) (B) EC (A) (B) To canister To intake manifold EC(H4DOTC)-13
14 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM F: PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE (FROM '06MY) The purge control solenoid valve is a part of the fuel evaporation gas emission control device, and is configured as follows. (3) (5) (4) (16) (6) (15) (17) (8) (11) (10) (9) (14) (13) (12) (7) EC Fuel gauge (7) Canister (13) Fuel level sensor Intake manifold (8) Pressure control solenoid valve (14) Fuel tank (3) Throttle body (9) Drain valve (15) Fuel cut valve (4) Purge control solenoid valve 1 (10) Drain filter (16) Fuel tank pressure sensor (5) Purge control solenoid valve 2 (11) Shut off valve (17) Vent valve (6) Engine control module (ECM) (12) Fuel temperature sensor EC(H4DOTC)-14
15 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM The purge control solenoid valve 1 and purge control solenoid valve 2 are optimally controlled by the ECM according to the engine status. (a) (b) (A) (b) (c) (B) EC (A) Purge control solenoid valve 2 (B) Purge control solenoid valve 1 (a) To intake duct (b) From fuel pipe (c) To intake manifold PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE OPERATION Intake manifold pressure During vacuum At pressure (pressurized) Purge control solenoid valve 1 Operating Not operating Purge control solenoid valve 2 Not operating Operating EC(H4DOTC)-15
16 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM G: PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE The fuel tank pressure control solenoid valve is located in the evaporation line between the canister and the fuel tank. It adjusts the fuel tank inside pressure under the control of the ECM. When the tank inside pressure becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure, the valve is opened allowing fuel vapors to be introduced into the canister. On the other hand, when the tank inside pressure becomes lower than the atmospheric pressure, external air is taken from the drain valve into the canister. (A) (3) (4) (B) (C) (5) EC Filter (A) Atmospheric pressure Coil (B) Shut-off valve (3) Connector terminal (C) To fuel tank (4) Diaphragm (5) Valve H: VENT VALVE The vent valve is located inside of the fuel tank. During filling the fuel tank, fuel vapors are introduced into the canister through the vent valve. When the fuel vapor pressure becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure and overcomes the spring force which is applied to the back side of the diaphragm, the port toward the canister is opened. The vent valve also has a float which rises and block the port toward the canister when the fuel is full. EC(H4DOTC)-16
17 I: SHUT-OFF VALVE EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM The shut-off valve is located at the top of the fuel filler pipe. When a filler gun is inserted into the filler pipe, the shut-off valve closes the evaporation line. (A) (B) (3) (5) (4) (6) EC Pin (A) To canister Valve (B) To fuel tank (3) Spring (4) Plate (5) Shaft (6) Pin EC(H4DOTC)-17
18 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM J: FUEL TANK SENSOR CONTROL VALVE The fuel tank sensor control valve is installed on the top of the fuel tank and its one end is connected to the fuel tank pressure sensor while its other end is open to the atmosphere. Normally the passage to the fuel tank pressure sensor is open to the atmosphere, however, the passage is closed when the ECM sends a signal to make a diagnosis of the evaporative emission control system. EC EC(H4DOTC)-18
19 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM K: FUEL TANK PRESSURE SENSOR The fuel tank pressure sensor is installed on the top of the fuel tank and measures the pressure in the fuel tank. The measured pressure is converted into an electrical signal and sent to the ECM for diagnosis of the evaporative emission control system. (A) (D) (C) (B) EC Connector (A) Output voltage Terminal (B) Input pressure (C) To fuel tank (D) To fuel tank sensor control valve EC(H4DOTC)-19
20 ON-BOARD REFUELING VAPOR RECOVERY (ORVR) SYSTEM 8. On-board Refueling Vapor Recovery (ORVR) System A: GENERAL The on-board refueling vapor recovery system allows the fuel vapors in the fuel tank to be introduced directly into the canister through the vent valve when the fuel tank inside pressure increases as a result of refueling. The diagnosis of the system is performed by monitoring the fuel tank inside pressure data from the fuel tank pressure sensor while forcibly closing the drain valve. B: OPERATION While driving Since the back side of the diaphragm in the pressure control solenoid valve is open to the atmosphere, the diaphragm is held pressed by the atmospheric pressure in the position where only the external air is introduced into the canister. When the fuel vapor pressure acting on the other side of the diaphragm increases and overcomes the atmospheric pressure, it pushes the diaphragm and opens the port through which the fuel vapors make their way to the canister. (4) (3) (5) EC Canister (4) Intake manifold Pressure control solenoid valve (5) Shut-off valve: open (3) Purge control solenoid valve EC(H4DOTC)-20
21 ON-BOARD REFUELING VAPOR RECOVERY (ORVR) SYSTEM While refueling As the fuel enters the fuel tank, the tank inside pressure increases. When the inside pressure becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure, the port of the vent valve opens, allowing the fuel vapors to be introduced into the canister through the vent line. The fuel vapors are absorbed by charcoal in the canister, so the air discharged from the drain valve contains no fuel. When a filler gun is inserted, the shut-off valve closes the evaporation line. (3) (4) (5) EC Canister (4) Shut-off valve: closed Pressure control solenoid valve (5) Filler gun (3) Vent valve EC(H4DOTC)-21
22 VACUUM CONNECTIONS 9. Vacuum Connections The hose and pipe connections of the intake manifold, throttle body and other related parts are as shown in the illustration. (3) (C) (A) (E) (4) (B) (D) EC Pressure regulator (A) Delivery pipe Purge control solenoid valve (B) Return pipe (3) Intake manifold (C) Evaporation pipe (4) Purge valve (D) Front of vehicle (E) To intake duct EC(H4DOTC)-22
23 SECONDARY AIR SYSTEM (FROM '06MY) 10.Secondary Air System (From '06MY) A: GENERAL The secondary air system reduces harmful emissions by initiating the actuation of the catalyzer early by supplying air to the exhaust port of the cylinder head when the engine is cold started to reburn unburned gas. B: COMPONENT The secondary air system consists of the two secondary air combination valves (depending on the specification, there are vehicles with only one air combination valve.), pipes and air passages running through the cylinder head. The secondary air pump and the secondary air combination valves are controlled by the ECM which judges the startup conditions of the engine. (3) (4) (7) (5) (6) (6) EC ECM (4) Secondary air pump (6) Pipe Secondary air combination valve relay (3) Secondary air pump relay (5) Secondary air combination valve (with built-in pressure sensor) (7) Secondary air combination valve EC(H4DOTC)-23
24 SECONDARY AIR SYSTEM (FROM '06MY) C: OPERATION 1. SECONDARY AIR PUMP The secondary air pump compresses the air drawn in by the DC motor, and supplies this compressed air to the secondary air combination valve. There is a filter at the inlet of the secondary air pump to prevent drawing in dust and foreign objects. EC Secondary air pump EC(H4DOTC)-24
25 SECONDARY AIR SYSTEM (FROM '06MY) 2. SECONDARY AIR COMBINATION VALVE The secondary air combination valve consists of an air valve, a reed valve that prevents the reverse flow of exhaust gas, and a solenoid for opening/closing the air valve. Compressed air whose flow is controlled by the secondary air combination valve is supplied to the cylinder head through a pipe. One of the secondary air combination valves is equipped with a pressure sensor for malfunction diagnosis. (B) (A) EC (A) Secondary air pump (B) To cylinder head Secondary air combination valve Pressure sensor EC(H4DOTC)-25
26 SECONDARY AIR SYSTEM (FROM '06MY) 3. CYLINDER HEAD Inside the cylinder head are air passages as shown in the diagram. The compressed air supplied from the secondary air combination valve travels through these air passages to be sprayed on the back face of the exhaust valve. EC Air passage Exhaust valve EC(H4DOTC)-26
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
7. Evaporative Emission Control System
 W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
SVX +++ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM AND VACUUM FITTING 2-1 SUBARU
 EMSSON CONTROL SYSTEM AND VACUUM FTTNG 2-1 SUBARU SVX 1992 Page 1. System Application......................................................... 2 2. Schematic Drawing..........................................................
EMSSON CONTROL SYSTEM AND VACUUM FTTNG 2-1 SUBARU SVX 1992 Page 1. System Application......................................................... 2 2. Schematic Drawing..........................................................
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 -1 ENGINE CONTROL.......... GENERAL INFORMATION...... SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE......... ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT.................... ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL......................
-1 ENGINE CONTROL.......... GENERAL INFORMATION...... SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE......... ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT.................... ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL......................
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
Federal and California Emissions Warranties Parts List
 Emissions warranties are state specific. Refer to the years/miles 1 columns below as follows: A Minimum coverage for all vehicles in all states. B Vehicles registered and normally operated in California,
Emissions warranties are state specific. Refer to the years/miles 1 columns below as follows: A Minimum coverage for all vehicles in all states. B Vehicles registered and normally operated in California,
ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL
 17 ENGINE & EMISSION CONTROL 1996 Engine Control System ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Post-installation Operation (Refer to Adjusting the Accelerator Cable.)
17 ENGINE & EMISSION CONTROL 1996 Engine Control System ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Post-installation Operation (Refer to Adjusting the Accelerator Cable.)
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION...... 17-3 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS.................. 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION...... 17-3 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS.................. 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
2. Air Line AIR LINE FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL B: MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR FU(H4DOTC)-3
 W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
Module 5: Emission Control for SI Engines Lecture20:ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS
 ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS The Lecture Contains: Crankcase Emission Control (PCV System) Evaporative Emission Control Exhaust Gas Recirculation Water Injection file:///c /...%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture20/20_1.htm[6/15/2012
ADD-ON SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL OF ENGINE-OUT EMISSIONS The Lecture Contains: Crankcase Emission Control (PCV System) Evaporative Emission Control Exhaust Gas Recirculation Water Injection file:///c /...%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture20/20_1.htm[6/15/2012
A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF) B B B
 5. Specified Data A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen heater Engine coolant temperature Signal
5. Specified Data A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen heater Engine coolant temperature Signal
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION...... 17-3 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS.................. 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION...... 17-3 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS.................. 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
TROUBLESHOOTING
 174501 053 1. TROUBLESHOOTING 054 2. LAYOUT 1. Exhaust Manifold Assy 2. Exhaust Manifold Gasket 3. Hex Flange Nut 4. Heat Protector Assy 5. Hex Bolt (M6 X 1 X 25) 6. Heat Protector Assy 7. Hex Bolt (M8
174501 053 1. TROUBLESHOOTING 054 2. LAYOUT 1. Exhaust Manifold Assy 2. Exhaust Manifold Gasket 3. Hex Flange Nut 4. Heat Protector Assy 5. Hex Bolt (M6 X 1 X 25) 6. Heat Protector Assy 7. Hex Bolt (M8
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal S008526
 5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal S008526 A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION S008526A08 1. MT VEHICLES S008526A0801 B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal S008526 A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION S008526A08 1. MT VEHICLES S008526A0801 B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS EC1 EC2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) System Purpose System SYSTEM PURPOSE Abbreviation Purpose Positive crankcase ventilation Fuel evaporative
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS EC1 EC2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) System Purpose System SYSTEM PURPOSE Abbreviation Purpose Positive crankcase ventilation Fuel evaporative
13. Evaporative Emission Control System
 85 13. Evaporative Emission Control System General The evaporative emission control system prevents the fuel vapors that are created in the fuel tank from being released directly into the atmosphere. The
85 13. Evaporative Emission Control System General The evaporative emission control system prevents the fuel vapors that are created in the fuel tank from being released directly into the atmosphere. The
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
For Troubleshooting of DTC related components, see chart on page INTAKE AIR BYPASS (IAB) HIGH CONTROL SOLENOID
 Index For Troubleshooting of DTC related components, see chart on page 11-53. '96-99 models: EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) and LIFT MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) INTAKE AIR BYPASS (IAB) HIGH page
Index For Troubleshooting of DTC related components, see chart on page 11-53. '96-99 models: EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) and LIFT MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) INTAKE AIR BYPASS (IAB) HIGH page
Evaporative Emissions
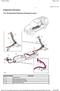 Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
3. Fuel System FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-7
 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
 Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
Page 1 of 6 SECTION 303-08: Engine Emission Control 2011 F-250, 350, 450, 550 Super Duty Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 03/12/2010 Engine Emission Control 6.7L Diesel
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
2. Turbocharger System
 INTAKE (INDUCTION) 2. Turbocharger System A: GENERAL The turbocharger system consists of a water-cooled turbocharger, air-cooled intercooler, wastegate control solenoid valve, etc. The turbine rotated
INTAKE (INDUCTION) 2. Turbocharger System A: GENERAL The turbocharger system consists of a water-cooled turbocharger, air-cooled intercooler, wastegate control solenoid valve, etc. The turbine rotated
Technicians Reference Booklet
 Technicians Reference Booklet Basic Emission and Fuel Systems Module 405 MSA5P0160C Copyright 2001 Subaru of America, Inc. All rights reserved. This book may not be reproduced in whole or in part without
Technicians Reference Booklet Basic Emission and Fuel Systems Module 405 MSA5P0160C Copyright 2001 Subaru of America, Inc. All rights reserved. This book may not be reproduced in whole or in part without
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ): P Code Charts General Information
 P0133 O2-Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 / Sensor 1) - The linear O2 sensor is mounted on the front side of the Catalytic Converter (warm-up catalytic converter) or in the front exhaust pipe. It detects
P0133 O2-Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 / Sensor 1) - The linear O2 sensor is mounted on the front side of the Catalytic Converter (warm-up catalytic converter) or in the front exhaust pipe. It detects
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Turbo>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview. Study Guide. Course Code: 8777
 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide Course Code: 8777 1 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide 2015 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive, Lisle, IL 60532. All rights reserved. No part of
2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide Course Code: 8777 1 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide 2015 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive, Lisle, IL 60532. All rights reserved. No part of
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Non-Turbo>
 13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13A-2 FUEL INJECTI CTROL...... 13A-6 IDLE SPEED CTROL (ISC)..... 13A-7 IGNITI TIMING AND DISTRIBUTI CTROL........
13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13A-2 FUEL INJECTI CTROL...... 13A-6 IDLE SPEED CTROL (ISC)..... 13A-7 IGNITI TIMING AND DISTRIBUTI CTROL........
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Fuel System Description
 Page 1 of 9 2005 Pontiac GTO GTO (VIN V) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 6.0L Description and Operation Document ID: 1550920 Fuel System Description System Overview The fuel tank stores the fuel
Page 1 of 9 2005 Pontiac GTO GTO (VIN V) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 6.0L Description and Operation Document ID: 1550920 Fuel System Description System Overview The fuel tank stores the fuel
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited
 Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table
 Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
NewtonNet. Emissions Control System (G4GC - GSL2.0/G6BA - GSL2.7)
 Emissions Control System (G4GC - GSL2.0/G6BA - GSL2.7) GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS... EC-2 TIGHTENING TO R Q U E... EC-2 TROUBLESHOOTING...EC-2 COM PONENTS...EC-2 COMPONENTS LOCATION...EC-3 SCHEMATIC DRAW ING...
Emissions Control System (G4GC - GSL2.0/G6BA - GSL2.7) GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS... EC-2 TIGHTENING TO R Q U E... EC-2 TROUBLESHOOTING...EC-2 COM PONENTS...EC-2 COMPONENTS LOCATION...EC-3 SCHEMATIC DRAW ING...
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
INTAKE AND EXHAUST GROUP CONTENTS CHARGE AIR COOLER <2.0L ENGINE> GENERAL DESCRIPTION SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS...
 15-1 GROUP 15 INTAKE AND EXHAUST CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 15-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 15-2 DIAGNOSIS 15-2 INTRODUCTION 15-2 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 15-2 SYMPTOM CHART 15-2 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES 15-3
15-1 GROUP 15 INTAKE AND EXHAUST CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 15-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 15-2 DIAGNOSIS 15-2 INTRODUCTION 15-2 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 15-2 SYMPTOM CHART 15-2 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES 15-3
(3) (4) (6) (5) (10) (9) (8) (7)
 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
4. Sensors and Switches
 W1860BE.book Page 17 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions
W1860BE.book Page 17 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Lower Intake Manifold Replacement
 Lower Intake Manifold Replacement Removal Procedure 1. Turn OFF all the lamps and the accessories. 2. Ensure the ignition switch is in the OFF position. 3. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
Lower Intake Manifold Replacement Removal Procedure 1. Turn OFF all the lamps and the accessories. 2. Ensure the ignition switch is in the OFF position. 3. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
4. Sensors and Switches
 FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) SENSORS AND SWITCHES 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions exposed
FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) SENSORS AND SWITCHES 4. Sensors and Switches A: FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions exposed
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
). The equipment that is used to limit these pollutants is commonly called emission control equipment.
 Стр. 1 из 51 EMISSION CONTROLS Introduction There are three sources of automotive pollutants: crankcase fumes, exhaust gases and gasoline evaporation. The pollutants formed from these substances can be
Стр. 1 из 51 EMISSION CONTROLS Introduction There are three sources of automotive pollutants: crankcase fumes, exhaust gases and gasoline evaporation. The pollutants formed from these substances can be
Component Locations. Index. D16Y5 engine: Note: For troubleshooting of DTC related components see chart on page THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR
 Index Note: For troubleshooting of DTC related components see chart on page 11-97. D16Y5 engine: THROTTLE POSITION (TP) MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) VALVE and EXHAUST
Index Note: For troubleshooting of DTC related components see chart on page 11-97. D16Y5 engine: THROTTLE POSITION (TP) MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) VALVE and EXHAUST
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S
 ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT:
 DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
Swirl Flaps. A = Non swirl not active. B = Swirl active
 Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM... 2 GENERAL... 2 Outline of Changes... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATION... 2 VACUUM HOSE... 3 Vacuum Hose Piping Diagram...
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM... 2 GENERAL... 2 Outline of Changes... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATION... 2 VACUUM HOSE... 3 Vacuum Hose Piping Diagram...
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11-1 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES... 4 page TORQUE SPECIFICATION... 13 EXHAUST SYSTEMS The exhaust systems
Intake Manifold Replacement
 Page 1 of 14 2004 Chevrolet TrailBlazer - 4WD Bravada, Envoy, Rainier, TrailBlazer (VIN S/T) Service Manual Engine Engine Mechanical - 4.8L, 5.3L, and 6.0L Repair Instructions - On Vehicle Document ID:
Page 1 of 14 2004 Chevrolet TrailBlazer - 4WD Bravada, Envoy, Rainier, TrailBlazer (VIN S/T) Service Manual Engine Engine Mechanical - 4.8L, 5.3L, and 6.0L Repair Instructions - On Vehicle Document ID:
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components
 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
9. Subaru Select Monitor
 9. A: OPERATION 1. HOW TO USE SUBARU SELECT MONI- TOR 1) Prepare the kit. CAUTION: Do not connect the scan tools except for Subaru Select
9. A: OPERATION 1. HOW TO USE SUBARU SELECT MONI- TOR 1) Prepare the kit. CAUTION: Do not connect the scan tools except for Subaru Select
Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65).
 DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
DME control unit: N62TU meeknet.co.uk/e64 Installation location The DME control unit is located in the electronics box on the bulkhead (illustration shows E65). Item Description Item Description 1 Electronics
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
E - THEORY/OPERATION ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L
 E - THEORY/OPERATION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and
E - THEORY/OPERATION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Theory & Operation - 5.7L INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review
 Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
2004 IMPREZA SERVICE MANUAL QUICK REFERENCE INDEX
 2004 IMPREZA SERVICE MANUAL QUICK REFERENCE INDEX ENGINE SECTION 1 FU(H4SO) EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) INTAKE (INDUCTION) EC(H4SO) IN(H4SO) This service manual has been prepared to
2004 IMPREZA SERVICE MANUAL QUICK REFERENCE INDEX ENGINE SECTION 1 FU(H4SO) EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) INTAKE (INDUCTION) EC(H4SO) IN(H4SO) This service manual has been prepared to
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
DESCRIPTION Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20. Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI
 Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description (Enhanced)
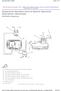 Page 1 of 7 1999 Chevrolet Chevy Suburban - 2WD Escalade, Pickup (Classic), Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Document ID: 222842 Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description
Page 1 of 7 1999 Chevrolet Chevy Suburban - 2WD Escalade, Pickup (Classic), Suburban, Tahoe, Yukon (VIN C/K) Service Manual Document ID: 222842 Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions Lecture 3: Introduction to Pollutant Formation POLLUTANT FORMATION
 Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
Module 2:Genesis and Mechanism of Formation of Engine Emissions POLLUTANT FORMATION The Lecture Contains: Engine Emissions Typical Exhaust Emission Concentrations Emission Formation in SI Engines Emission
ENGINE INTAKE SYSTEM GENERAL 1. ENGINE INTAKE SPECIFICATIONS. 1) Specifications
 04-3 GENERAL 1. ENGINE INTAKE SPECIFICATIONS 1) Specifications Element Type Service Interval Dry-Element Type - Initial cleaning: 5,000 km, Clean or change every 10,000 km as required. However, change
04-3 GENERAL 1. ENGINE INTAKE SPECIFICATIONS 1) Specifications Element Type Service Interval Dry-Element Type - Initial cleaning: 5,000 km, Clean or change every 10,000 km as required. However, change
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP(SEBP ) - Document Structure. Media Number -RENR Publication Date -01/02/2008 Date Updated -07/02/2008
 Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
AD07.61-P-4000AC ME-SFI fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory Possible cause Note Fault code description
 Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Page 1 of 11 AD07.61-P-4000AC fuel injection and ignition system (ME), DTC memory 14.6.00 ENGINE 112.942 as of 1.6.00 ENGINE 112.970 All tests of the electrical system of the fuel injection system on engine
Service Bulletin. DTC Detection Item Associated Monitor
 Service Bulletin 03-010 Applies To: All OBD II equipped models except SLX March 29, 2003 OBD II DTCs and Their Associated Monitors This is a list of all DTCs for all OBD II models. No one model has all
Service Bulletin 03-010 Applies To: All OBD II equipped models except SLX March 29, 2003 OBD II DTCs and Their Associated Monitors This is a list of all DTCs for all OBD II models. No one model has all
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
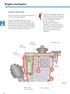 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM TURBOCHARGER TC 1
 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM TURBOCHARGER TC1 TC2 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM Description DESCRIPTION Systems which increase the amount of air sent to the engine are either turbocharger type (using exhaust gas to turn
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM TURBOCHARGER TC1 TC2 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM Description DESCRIPTION Systems which increase the amount of air sent to the engine are either turbocharger type (using exhaust gas to turn
Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB)
 Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB) 04-01-01 1 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials,
Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB) 04-01-01 1 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials,
DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175
 Page 1 of 6 2009 Pontiac G8 G8 Service Manual Document ID: 2076050 DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic
Page 1 of 6 2009 Pontiac G8 G8 Service Manual Document ID: 2076050 DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic
ProECU Subaru DIT. DTC List 2012-onward Model Year. v1.0
 ProECU Subaru DIT DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000B B CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000C A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE
ProECU Subaru DIT DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000B B CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000C A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE
ENGINE 1-1 CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 BASE ENGINE... 3 LUBRICATION SYSTEM... 4 COOLING SYSTEM... 5 INTAKE AND EXHAUST... 6
 1-1 ENGINE CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 Major Specifications... 2 BASE ENGINE... 3 Piston... 3 Piston Ring... 3 LUBRICATION SYSTEM... 4 Engine Oil Cooler... 4 COOLING SYSTEM... 5 Specifications...
1-1 ENGINE CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 Major Specifications... 2 BASE ENGINE... 3 Piston... 3 Piston Ring... 3 LUBRICATION SYSTEM... 4 Engine Oil Cooler... 4 COOLING SYSTEM... 5 Specifications...
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
INTAKE AND EXHAUST GROUP CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION SERVICE SPECIFICATION AIR CLEANER
 15-1 GROUP 15 INTAKE AND EXHAUST CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 15-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATION 15-2 DIAGNOSIS 15-2 INTRODUCTION 15-2 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 15-2 SYMPTOM CHART 15-2 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES 15-3 SPECIAL
15-1 GROUP 15 INTAKE AND EXHAUST CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 15-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATION 15-2 DIAGNOSIS 15-2 INTRODUCTION 15-2 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 15-2 SYMPTOM CHART 15-2 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES 15-3 SPECIAL
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number
 www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
www.golfmkv.com The 2.0L FSI Turbocharged Engine Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 821503 www.golfmkv.com Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 08/2005
Internal Combustion Engines
 Emissions & Air Pollution Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss emission control strategies: Fuel modifications Engine technology Exhaust gas aftertreatment We will become particularly familiar
Emissions & Air Pollution Lecture 3 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss emission control strategies: Fuel modifications Engine technology Exhaust gas aftertreatment We will become particularly familiar
