Rear Axle. Table of Contents
|
|
|
- Peter Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rear Axle Table of Contents Sub-Headings Safety 2 Warnings 2 Cautions 2 s 2 Introduction 2 Standard Single Reduction Carriers Without Differential Lock 5 Disassembly 6 Remove Differential Carrier from Axle Housing 6 Brass Drift Method 7 Air Hammer Vibration Method 8 Carrier Removal from Axle 8 Remove the Differential/Ring Gear 10 Disassemble the Differential/Ring Gear Assembly 13 Remove Drive Pinion and Bearing Cage 14 Disassemble Drive Pinion/Bearing Cage 16 Preparing Parts for Assembly 19 Cleaning Ground and Polished Parts 19 Cleaning Rough Parts 20 Cleaning Axle Assemblies 20 Drying Parts After Cleaning 20 Preventing Corrosion on Cleaned Parts 20 Inspecting Parts 21 Repair or Replacement of Parts, General 23 Repair Axle by Welding 23 Bending or Straightening Drive Axle Housings 24 Removing Dri-Loc Fasteners 24 Installing Fasteners with Pre-Applied Adhesive, Meritor Liquid Adhesive 2297-C-7049, Loctite 680 Liquid Adhesive or Equivalent 25 Installing Original or Used Fasteners Using Meritor Liquid Adhesive 2297-C-7049 or Loctite 680 or Equivalent 25 Application of Meritor Adhesive 229-T Application of Three Bond 1216 or Equivalent Silicon Gasket Material 26 Installing Tight Fit Yokes/POSE Seal 27 Installing Any Type Yoke with UPS 28 Clean, Inspect and Install the Yoke 29 General Yoke and U-Joint Reassembly 30 Gear Set Information (Drive Pinion/Ring Gear Marks) 30 Assembly 31 Assemble Drive Pinion, Bearing Cage 31 Adjusting Preload of Pinion Bearings 36 Press Method 36 Yoke or Flange Method 37 Adjusting Shim Pack Thickness for Pinion 40 Installing Drive Pinion, Bearing Cage 42 Installing Tight Fit Yokes and POSE Seal 43 Installing Any Type Yoke with UPS 44 Clean, Inspect and Install Yoke 46 Assemble Main Differential/Ring Gear 47 Rotating Resistance Check Gears 50 Install the Differential/Ring Gear 49 Adjust Preload of Differential Bearings 50 Check Runout of Ring Gear 55 Ring Gear Backlash Adjustment 55 Checking Tooth Contact Patterns 57 Tooth Contact Patterns of Generoid Hypoid Gear Sets 57 Install and Adjust Thrust Screw 60 Install Differential Carrier into Axle Housing 61 Straight Holes, Nuts and Hardened Washers 62 Tapered Dowel, Hardened Washer/Nut 63 Lubrication 63 Lubricant Capacities 65 Torque Values for Fasteners 65 Fasteners Torque Information 66 Adjustments and Specifications 69 1
2 Rear Axle Safety The purpose of this safety summary is twofold. First, it is to ensure the safety and health of individuals performing service on, and operation of, the Blue Bird All American Series bus. Second, it is to help protect equipment. Before performing any service or operating procedure on the All American bus, individuals should read and adhere to the applicable warnings, cautions and notes located throughout this Blue Bird Service Manual. Warnings Warnings apply to a procedure or practice that, if not correctly adhered to, could result in injury or death. Particular attention should be paid to sections of this manual where warnings appear. Cautions Cautions apply to a procedure or practice that, if not correctly adhered to, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment. s s are used to explain, clarify or otherwise give additional insight for a given subject, product or procedure. Please note that on occasion, notes, too, may advise of potential safety issues. Introduction The purpose of this section is to provide instructions for service maintenance on the Blue Bird All American Series rear axle components. 2
3 Figure 1 3
4 Item A A 18B A A Description Nut Drive Pinion* Washer Drive Pinion* Input Yoke* or Flange* Deflector POSE Seal Triple Lip (Main) Seal Bearing Cone Outer Bearing Cup Inner Sensor Switch Lock Nut Sensor Switch Plug Adjusting Ring Right Hand Shift Fork Spring Shift Shaft Shift Shaft Pin Spring Retaining Washer* or Silastic* - Air Cylinder Tube Air Cylinder Screw-In Differential Lock Cylinder Cylinder Cover Capscrew Manual Actuation Plug Cylinder Cover Gasket Plug Cover Capscrews Cylinder Cover Washers Cylinder Cover Plug Cylinder Cover Gasket Cover Plug Copper Gasket Cylinder Cover O-Ring Piston Piston Shift Collar Pins Shift Fork Capscrews* Lock Plate* Washers* Lock Plate* Lock Plate Adjusting Plate Capscrews Differential Bearing Cap Washers Caps Differential Bearing Side Gears Differential Thrust Washers Differential Pinion Pinions Differential Differential Side Gears Thrust Washers Differential Side Gear Cone Differential Bearing Cup Differential Bearing Thru Bolt Bolts* Differential Case Washers Differential Case Case Assembly Main Differential Spider Differential Bolts* or Rivets* - Ring Gear and Case Half Ring Gear (Pinion Drive Gear) Case Half Flange Washers Case Half Nuts* - Case Half Bearing Cone Differential Left Hand Bearing Cup Differential Left Hand Washer for Thru Bolt Nut for Thru Bolt Capscrews Differential Bearing Cup Washers Caps Differential Bearing Carrier Adjusting Ring Cotter Pin Adjusting Ring Jam Nut* Thrust Screw* Thrust Screw* Snap Ring Spigot Bearing Drive Pinion Bearing Cone Pinion Inner Bearing Cup Pinion Inner Spacer Pinion Bearing Shims Bearing Cage Drive Pinion Capscrews Bearing Cage Washer Clip and Cable Holder Cover Bolt-On Washer Bolt Cover Screw-In *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts.
5 Standard Single Reduction Carriers Without Differential Lock Meritor single reduction standard carriers are used in most Meritor single axles, rear of tandem axles, and front drive steering axles. Figure 1a. The single reduction carrier models are front mounted into the axle housing. These carriers have a hypoid drive pinion and ring gear set and bevel gears in the differential assembly. A straight roller bearing (spigot) is mounted on the head of the drive pinion. All other bearings in the carrier are tapered roller bearings. When the carrier operates, there is normal differential action between the wheels all the time. Figure 1a 5
6 Disassembly Remove Differential Carrier from Axle Housing Warning To prevent serious eye injury, always wear safe eye protection when you perform vehicle maintenance or service. 1. Raise the end of vehicle where the axle is mounted. Use a jack or other lifting tool, and place safety stands under each side of the axle. Figure 2. Warning Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving. Support the vehicle with safety stands. Do not work under a vehicle supported only by jacks. Jacks can slip and fall over. Serious personal injury can result. 2. Place jack stands under each spring seat of the axle to hold vehicle in the raised position. 3. Remove the plug from bottom of axle housing and drain lubricant from the assembly. 4. Disconnect the driveline universal joint from the pinion input yoke or flange on the carrier. Figure 3. Figure 2 5. Remove the capscrews* and washers or stud nut* and washers from t he flanges of both axle shafts. 6. Loosen the tapered dowels* in the axle flanges of both axle shafts using one of the following methods. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 6
7 Figure 3 Brass Drift Method Warning Do not strike the round driving lugs on the flange of an axle shaft. Pieces can break off and cause serious personal injury. 1. Hold a 1-1/2 inch diameter brass drift against the center of the axle shaft, inside the round driving lugs. Figure 4. Figure 4 7
8 A 1-1/2 inch diameter brass hammer can be used as a drift. 2. Strike the end of the drift with a large hammer (five to six pounds) and the axle shaft and tapered dowels will loosen. 3. Mark to identify each axle shaft before it is removed from the axle assembly. 4. Remove the tapered dowels and separate the axle shafts from the main axle hub assembly. Figure Install a cover over the open end of each axle assembly hub where an axle shaft was removed. 1. Use a round hammer bit and an air hammer such as Chicago Pneumatic CP-4181-Puler, or equivalent, to loosen tapered dowels and axle shaft. 2. Place the round hammer bit against the axle shaft (flange) between the hub studs. Operate the air hammer at alternate locations between the studs to loosen the tapered dowels and axle shaft from the hub. Figure 6. Figure 6 3. Mark to identify each axle shaft before it is removed from the axle assembly. 4. Remove the tapered dowels and separate the axle shaft from the main axle hub assembly. Figure 5. Figure 5 Air Hammer Vibration Method Warning Wear safe eye protection when using an air hammer. When using power tools, axle components can loosen and break off causing serious personal injury. Caution Do not use a chisel or wedge to loosen the axle shaft and tapered dowels. Using a chisel or wedge can result in damage to the axle shaft, the gasket and seal, and/or the axle hub. 8 Caution Do not use a chisel or wedge to loosen the axle shaft and tapered dowels. Using a chisel or wedge can result in damage to the axle shaft, the gasket and seal, and/or the axle hub. Carrier Removal from Axle 1. Place a hydraulic roller jack under the differential carrier to support the assembly. Figure Remove all but the top two carrier to housing capscrews or stud nuts and washers. 3. Loosen the top two carrier-to-housing fasteners and leave attached to the assembly. The fasteners will hold the carrier in the housing.
9 4. Loosen the differential carrier in the axle housing. Use a leather mallet to hit the mounting flange of carrier at several points. 5. After the carrier is loosened, remove the top two fasteners. A carrier stand, part number J 3409-D is available from Kent-Moore, Heavy-Duty Division, Mound Road, Warren, MI Caution When using a pry bar, be careful not to damage the carrier or housing flange. Damage to these surfaces will cause oil leaks. 6. Carefully remove the carrier from the axle housing using the hydraulic roller jack. Use a pry bar that has a round end to help remove the carrier from the housing. 7. Lift the differential carrier by the input yoke or flange and place the assembly in a repair stand. Figure 8. Use a lifting tool for this procedure. Do not lift by hand. A carrier stand can be built by referring to Figure 9. Figure 7 Figure 8 9
10 Figure 9 Remove the Differential and Ring Gear from the Carrier Before working on the differential carrier, inspect the hypoid gear set for damage. If inspection shows no damage, the same gear set can be used 10 again. Measure the backlash of the gear set and make a record of the dimension. Figure 10. (Refer to "Ring Gear Backlash Adjustment", steps 1-5 and Figure 108) During differential reassembly, adjust the backlash to the original recorded dimension when the gear set is installed into the carrier.
11 Figure 12 Figure Rotate the differential carrier in the repair stand until the ring gear is at the top of the assembly. 4. Mark one carrier leg and bearing cap to correctly match the parts during carrier assembly. Mark the parts using a center punch and hammer. Figure 13. Figure Loosen the jam nut* on the thrust screw. 2. Remove the thrust screw* and jam nut* from the differential carrier. Figure 11 and Figure 12. Figure 13 *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 11
12 5. Remove the cotter keys*, pins*, or lock plates* that hold the bearing adjusting rings in position. Use a small drift and hammer to remove pins. Each lock plate is held in position by two capscrews. Figure Remove the capscrews and washers that hold the two bearing caps on the carrier. Each cap is held in position by two capscrews and washers. Figure Remove the bearing caps and bearing adjusting rings from the carrier. Figure Safely lift the main differential and ring gear assembly from the carrier. Place the assembly on a work bench. Figure 17. Figure 15 Figure 16 Figure 14 *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Figure 17 12
13 Disassemble the Differential and Ring Gear Assembly 5. If the ring gear needs to be replaced, remove the bolts*, nuts*, and washers* that hold the gear to the flange case half. 1. If the matching marks on the case halves of the differential assembly are not visible, mark each case half with a center punch and hammer. The purpose of the marks is to match the plain half and flange half correctly when you assemble the carrier. Figure 18. Figure 19 Warning Figure Remove the capscrews* and washers* or bolts*, nuts* and washers that hold the halves together. Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the pressure manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. Warning Use a brass or leather mallet for assembly and disassembly procedures. D not hit steel parts with a steel hammer. Pieces of a part can break off and cause serious personal injury. 3. Separate the case halves. If necessary, use a brass, plastic or leather mallet to loosen the parts. 4. Remove the differential spider (cross), four pinion gears, two side gears and six thrust washers from inside the case halves. Figure 19. * Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Caution Do not remove the rivets or rivet heads with a chisel and hammer. Using a flat edge tool can cause damage to the flange case. Refer to Figure If rivets* hold the ring gear to the flange case half, remove the rivets as follows: a. Carefully center punch each rivet head in the center, o the ring gear side of the assembly. 13
14 b. Drill each rivet head on the ring gear side of the assembly to a depth equal to the thickness of one rivet head. Use a drill bit that is 1/32 of an inch smaller than the body diameter of the rivets. Figure 20. Figure 20 Figure 21 c. Press the rivets through holes in the ring gear and flange case half. Press from the drilled rivet head. Warning Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the press manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. 7. Separate the case half and ring gear using a press. Support the assembly under the ring gear with metal or wood blocks and press the case half through the gear. Figure If the differential bearings need to be replaced, remove the bearing cones from the case halves. Use a bearing puller or press. Figure 21a. Figure 21a Remove the Drive Pinion and Bearing Cage from Carrier 1. Fasten a flange bar to the input yoke or flange. When the nut is removed, the bar will hold the drive pinion in position. Figure
15 Figure Remove the nut and washer* from the drive pinion. Figure Remove the yoke or flange bar. Figure 23 Caution Do not use a hammer or mallet to loosen and remove the yoke or flange. A hammer or mallet can damage the parts and cause driveline runout, or driveline imbalance problems after carrier to driveline assembly. 4. Remove the yoke or flange from the drive pinion. If the yoke or flange is tight on the pinion, use a puller for removal. Figure Remove the capscrews and washers that hold the bearing cage in the carrier. Figure 24. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Figure 24 Warning Use a brass or leather mallet for assembly and disassembly procedures. Do not hit steel parts with a steel hammer. Pieces of a part can break off and cause serious personal injury. Caution Do not use a pry bar to remove the bearing cage and shims from the carrier. A pry bar can damage the bearing, shims and carrier. 15
16 6. Remove the drive pinion, bearing cage and shims from the carrier. If the bearing cage is tight in the carrier, hit the bearing cage at several points around the flange area with a leather, plastic or rubber mallet. Figure 25. Figure Place the drive pinion and bearing cage in a press. The pinion shaft must be toward the top of the assembly. Figure 27. Figure If the shims are in good condition, keep the shims together for use later when the carrier is assembled. 8. If shims are to be discarded because of damage, first measure the total thickness of the pack. Make a note of the dimension. The dimension will be needed to calculate the depth of the drive pinion in the carrier when the gear set is installed. Disassemble the Drive Pinion and Bearing Cage Warning Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the press manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. Figure Support the bearing cage under the flange area with metal or wood blocks. Figure Press the drive pinion through the bearing cage. Figure 27. Warning Use a brass or leather mallet for assembly and disassembly procedures. Do not hit steel parts with a steel hammer. Pieces of a part can break off and cause serious personal injury. 16
17 The inner bearing cone and bearing spacer will remain on the pinion shaft. support the bearing cage under the flange area with metal or wood blocks. 4. If a press is not available, use a leather, plastic or rubber mallet to drive the pinion through the bearing cage. Caution Be careful when removing the seal. Do not damage the wall of bore. Damage to the bore wall can result in oil leaks. When the oil seal has been removed, always replace it with a new seal during component reassembly. 5. Use a press and a sleeve to remove the triplelip or unitized oil seal from the bearing cage. If a press is not available, place a tool with a flat blade under the flange to remove the oil seal from the cage. Figure 28. Figure If the pinion bearings need to be replaced, remove the inner bearing cone from the drive pinion with a press or bearing puller. The puller must fit under the inner race of the cone to remove the cone correctly without damage. Figure 30. Figure 28 Warning Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the press manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. 6. If the pinion bears need to be replaced, remove the inner and outer bearing cups from the inside of cage. Use a press and sleeve, bearing puller or a small drift hammer. The type of tool used depends on the design of the bearing cage. Figure 29. When a press is used, Figure If the spigot bearing needs to be replaced, place the drive pinion in a vise. Install a soft 17
18 metal cover over each vise jaw to protect the drive pinion. 9. Remove the snap ring* from the end of drive pinion with snap ring pliers that expand. Figure 31. Some spigot bearings are a two-piece assembly. Remove the inner race from the pinion with a bearing puller. Remove the outer race/roller assembly from carrier with a drift or a press. Figure 34. Some spigot bearings are fastened to the drive pinion with a special peening tool. Figure 32. Figure 33 Figure 31 Figure 32 Figure 34 *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 10. Remove the spigot bearing from the drive pinion with a bearing puller. Figure
19 Preparing Parts for Assembly Clean and Inspect Yokes Warnings To prevent serious eye injury, always wear safe eye protection when you perform vehicle maintenance or service. Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetraphcloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures: Wear safe eye protection. Wear clothing that protects your skin. Work in a well-ventilated area. Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. 1. Clean the ground and polished surface of the yoke journal using a clean shop towel and a safe cleaning solvent. Do not use abrasive cleaners, towels, or scrubbers to clean yoke or flange surface. DO NOT USE GASOLINE. 2. Inspect the original yoke seal surface for any grooves. a. The rubber inner sleeve of the unitized pinion seal (UPS) allows the reuse of yokes with grooves unless the groove depths are excessively deep. If grooves are present, measure the groove diameters with calipers. Refer to Figure 35 to determine if yoke is usable. b. If grooves are present on yoke hubs that are used with single or triple lip seals, then the yokes must be replaced. 3. If any of the yoke grooves measure less than the dimensions in Figure 35, replace the yoke. The rubber inner sleeve of the unitized pinion seal (UPS) is designed to seal on the yoke and rotate with the yoke. Figure 35 Caution Do not install a press on shaft excluder (or POSE seal) after installation of a unitized pinion seal. The use of a POSE seal will prevent correct seating of the unitized pinion seal on the yoke and will result in lubricant leakage at the seal. POSE seal installation is recommended only for triple lip and other previous design seals. Do not use thin metal wear sleeves to refresh the yoke surface. Wear sleeves pressed onto the yoke will prevent correct seating of the pinion seal and damage the pinion seal assembly. Wear sleeve usage will cause the seal to leak. Cleaning Ground and Polished Parts Warning To prevent serious eye injury, always wear safe eye protection when you perform vehicle maintenance or service. 1. Use a cleaning solvent to clean ground or polished parts or surfaces. Kerosene or diesel fuel oil can be used for this purpose. Do not use gasoline. Warning 19
20 Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetrachloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures: Wear safe eye protection. Wear clothing the protects your skin. Work in a well-ventilated area. Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. 2. Use a tool with a flat blade if required, to remove sealant material from parts. Be careful not to damage the polished or smooth surfaces. Caution Do not use hot solution tanks or water and alkaline solutions to clean ground or polished parts. Damage to parts will result. 3. Do not clean ground or polished parts with water or steam. Do not immerse ground or polished parts in a hot solution tank or use strong alkaline solutions for cleaning, or the smooth sealing surface may be damaged. Wear safe eye protection Wear clothing that protects your skin. Work in a well-ventilated area. Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. 4. Parts must be washed with water until all traces of the alkaline solution are removed. Cleaning Axle Assemblies 1. A complete axle assembly can be steam cleaned on the outside to remove dirt. 2. Before the axle is steam cleaned, close or place a cover over all openings in the axle assembly. Examples of openings are breathers or vents in air chambers. Drying Parts After Cleaning 1. Parts must be dried immediately after cleaning and washing. 2. Dr the parts using soft, clean paper or cloth rags. Caution Damage to bearings can result when they are rotated and dried with compressed air. Cleaning Rough Parts 1. Clean rough parts with the same method as cleaning ground and polished parts. 2. Rough parts can be cleaned in hot solution tanks with a weak or diluted alkaline solution. 3. Parts must remain in hot solution tanks until heated and completely cleaned. Warning Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetrachloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures: 3. Except for bearings, parts can be dried with compressed air. Preventing Corrosion on Cleaned Parts 1. Apply axle lubricant to cleaned and dried parts that are not damaged and are to be assembled. 2. To store parts, apply a special material that prevents corrosion to all surfaces. Wrap cleaned parts in a special paper that will protect the parts from moisture and prevent corrosion. 20
21 Inspecting Parts It is very important to inspect all parts carefully and completely before the axle or carrier is assembled. Check all parts for wear and replace damaged parts. Replacement of damaged or worn parts now, will prevent failure of the assembly later. 1. Inspecting Tapered Roller Bearings: Inspect the cup, cone, rollers and cage of all tapered roller bearings in the assembly. If any of the following conditions exist, the bearing must be replaced. a. The center of large-diameter end of rollers worn level with or below the outer surface. Figure 36. b. The radius at large-diameter end of rollers worn to a sharp edge. Figure 36. Figure 37 Figure 38 Figure 36 c. A visible roller groove in the cup or cone inner race surfaces. The groove can be seen at the small- or large-diameter end of both parts. Figure 37. d. Deep cracks or breaks in the cup, cone inner race or roller surfaces. Figure 37. e. Bright wear marks on the outer surface of the roller cage. Figure 38. f. Damage on rollers and on surfaces of the cup and cone inner race that touch the rollers. Figure 39. g. Damage on the cup and cone inner race surfaces that touch the rollers. Figure 40. Figure 39 21
22 Figure 40 Caution Hypoid drive pinions and ring gears are machined in matched sets. When a drive pinion or ring gear of a hypoid set needs to be replaced, both drive gear and pinion must be replaced at the same time. 2. Inspect hypoid pinions and gears for wear or damage. Gears that are worn or damaged must be replaced. Caution Always replace thrust washers, differential side gears and pinion gears in full matched sets. A higher stress on original parts and early failure of the entire assembly will result if a new part is used in combination with parts that are older or worn. 3. Inspect the Main Differential Assembly: Inspect the following parts for wear or stress. Parts that are damaged must be replaced. Figure 41. Figure 41 a. Inside surfaces of both case halves. b. Both surfaces of all thrust washers. c. The four trunnion ends of the spider (cross). d. Teeth and splines of both differential side gears. e. Teeth and bore of all differential pinions. 4. Inspect Axle Shafts: a. Inspect axle shafts for wear and cracks at the flange, shaft and splines. b. Replace axle shafts, if required. 22
23 Repair or Replacement of Parts, General 1. Meritor will permit repairing drive axle housing assemblies by welding only in the following areas: Replace worn or damaged parts of an axle assembly. The following are some examples in checking for part replacement or repair. a. Only RT axles housing to cover weld joints. Refer to TP b. Snorkel welds. c. Housing seam welds between t he suspension attaching brackets. d. Bracket welding to drive axle housing. Refer to TP e. Refer to Meritor Maintenance Manual 8 for approved axle welding procedures. 1. Replace any fastener if corners of the head are worn. 2. Replace washers if damaged. 3. Replace gaskets, oil seals or grease seals at the time of axle or carrier repair. 4. Clean parts and apply new silicone gasket material where required when axle or carrier is assembled. Figure 42. Warnings Using wrong welding procedures or welding at locations other than the three areas permitted by Meritor will make the heat-treated component weak. A weak component will cause poor or unsafe operation of the vehicle and early axle failure. The following procedure must be used. Figure Remove nicks, mars and burrs from parts with machined or ground surfaces. Use a fine file, india stone, emery cloth or crocus cloth for this purpose. Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetrachloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures: Caution Threads must be without damage and clean so that accurate adjustments and correct torque values can be applied to fasteners and parts. 6. Clean and repair threads of fasteners and holes. Use a die or tap of the correct size or a fine file for this purpose. Warning Repair of axle housings by bending or straightening will cause poor or unsafe vehicle operation and early failure at the axle. Wear safe eye protection Wear clothing that protects your skin. Work in a well-ventilated area. Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Caution Welding can be used when the crack or damaged area is within the old weld material. Replace the axle housing if the crack extends into the metal next to the old weld. A repaired housing must be used in correct applications. 2. Welding Procedure a. Drain the lubricant from the axle assembly. Repair Axle by Welding 23
24 b. Remove the axle shafts and differential carrier from the axle housing. c. Remove hub, drum, wheel bearing and brake air chambers. d. Clean the damaged area inside and outside the housing. Cleaning solvent can be used. e. Grind the damaged weld to the base metal. f. Warm the complete axle housing to a temperature of 70 F-80 F (21 C-27 C) or higher. g. Before you start welding, heat the damaged area to be repaired to approximately 300 F (149 C). h. Use a 70,000 psi tensile weld material and the correct voltage and amperage for the diameter weld rod used. Examples of weld rods that can be used are E-7018 or ER-70S-3. i. Fill in the weld gap as follows: Cautions If the E-7018 weld rod is used, the rod must be kept dry. Electrodes that are not stored in the correct sealed containers must be heated at 700 F (371 C) for one hour before welding. Wet electrodes must be dried at 180 F (82 C) for one to two hours and then heated at 700 F (371 C) for one hour before welding. Do not connect the ground cable at any point on the axle assembly that will place a bearing between the ground cable and weld area. If a bearing is between the ground cable and weld, the bearing will be damaged because of electricity arcing. A good location to connect the ground cable is the spring mounting pad of the housing. 1. The opening in cover welds must be filled level with the old weld. 2. The opening in seam welds must be ground out to 70% of the wall thickness. The wall thickness can be measured at the carrier opening of housing. 3. Clean the new weld area. Carefully remove all the rough weld material. 4. Install the differential carrier and axle shafts. 5. Fill the axle assembly with the correct amount of lubricant. Refer to Maintenance Manual 1, Lubrication, for information on lubricants. Before welding brackets or other components to the axle housing, contact Meritor for proper welding procedures. Bending or Straightening Drive Axle Housings Meritor is emphatically opposed to any attempt to correct or modify drive axle housings by bending or straightening. All damaged drive axle housings should be replaced. Warning Do not bend or straighten damaged drive axle housings. Any bending or straightening process may result in misalignment or weakening of the axle housing and result in component damage or serious personal injury. Removing Dri-Loc Fasteners If it is difficult to remove fasteners from components, the strength of Dri-Loc, Meritor adhesive or Loctite 277 can be decreased b heating. Use the following procedure: 1. Heat the fastener for three to five seconds only and try to loosen the fastener with a wrench. Do not use an impact wrench to loosen the fastener or hit the fastener with a hammer. Caution Do not exceed 350 F (177 C) maximum. Heating must be done slowly to prevent thermal stresses in the other components. 2. Repeat step 1 until the fastener can be removed. 24
25 General Information Installing Fasteners with Pre- Applied Adhesive, Meritor Liquid Adhesive 2297-C-7049, Loctite 680 Liquid Adhesive or Equivalent 2. Apply four or five drops of Meritor Liquid Adhesive, Loctite 680 or equivalent inside each threaded hole or bore ONLY. Make sure the adhesive is applied inside to the bore threads. Figure 43. Installing New Fasteners with Pre- Applied Adhesive Patches Warning To prevent serious eye injury, always wear safe eye protection when you perform vehicle maintenance or service. 1. Clean the oil and dirt from threaded holes. Use a wire brush. There is no other special cleaning required. Caution Do not apply adhesives or sealants on new fasteners with pre-applied adhesive patches or inside closed threaded holes. If other adhesives or sealants are used, the new adhesive will not function correctly. 2. Assemble parts using the new pre-applied adhesive fasteners. There is no drying time required for fasteners with pre-applied adhesive. Figure 43 Caution Do not apply adhesive directly to the fastener threads. Air pressure in a closed hole will push the adhesive out and away from mating surfaces as the fastener is installed. 3. Tighten the fasteners to the required torque value for that size fastener. There is no drying time required for Meritor Liquid Adhesive 2297-C-7049, Loctite 680 or equivalent. 3. Tighten the fasteners to the required torque value for that size fastener. Installing Original or Used Fasteners Using Meritor Liquid Adhesive 2297-C-7049 or Loctite 680 or Equivalent 1. Clean the oil, dirt and old adhesive from all threads and threaded holes. Use a wire brush. Application of Meritor Adhesive 229-T-4180 in Bearing Bores for the Differential Use adhesive 2297-T-4180 for all axles. 1. Clean the oil and dirt from outer diameters of bearing cups and bearing bores in the carrier and bearing caps. There is no special cleaning required. 25
26 2. Apply axle lubricant to the bearing cones and the inner diameters of the bearing cups of the main differential. Do not get oil on the outer diameter of the bearing cup and do not permit oil to drip on the bearing bores. 3. Apply a single continuous bead of the adhesive to the bearing bores in the carrier and bearing caps. Apply the adhesive 360 degrees around the smooth, ground surfaces only. Do not place adhesive on threaded areas. Figure 44. Application of Three Bond 1216 or Equivalent Silicone Gasket Material Warning When you apply some silicone gasket materials, small amounts of acid vapor are present. To prevent possible serious injury, the work area must be well ventilated. If the silicone gasket material gets into your eyes, flush them with water for 15 minutes. Have your eyes checked by a doctor as soon as possible. The following silicone gasket products or equivalent can be used for Meritor components: Figure 44 Meritor adhesive 2297-T-4180 will become hard (dry) in approximately two hours. The following two steps of the procedure must be done in two hours from the time the adhesive was applied. If two hours have passed since application, clean the adhesive from the parts again and apply new adhesive. 4. Install the main differential assembly, bearing cups and bearing caps into the carrier. Use the normal procedure, refer to "Install the Differential and Ring Gear Assembly" and Figure 96 through Figure Adjust preload of the differential bearings, backlash and tooth contact patterns of the gear set as required using the normal procedures. Refer to "Adjust Preload of Differential Bearings" through "Install Differential Carrier into Axle Housing". Three Bond Liquid Gasket No. TB 1216 (Grey) Loctite Ultra Grey Adhesive/Sealant #18581 From Meritor: Ten ounce tubes, Part No F Remove all old gasket material from both surfaces. Figure Clean the surfaces where silicone gasket material will be applied. Remove all oil, grease, dirt and moisture without damaging the mating surfaces. Figure Dry both surfaces. Figure 45 Caution The amount of silicone gasket material applied must not exceed inch (3 mm) diameter bead. 26
27 Too much gasket material can block lubrication passages and result in damage to the components. 4. Apply inch (3 mm) diameter continuous bead of the silicone gasket material around one surface. Also apply the gasket material around the edge of all fastener holes on that surface. Figure Assemble the components immediately to permit the silicone gasket material to compress evenly between the parts. Tighten fasteners to the required torque value for that size fastener. There is no special procedure or additional torque value required. Refer to Table J. 6. Wait 20 minutes before filling the assembly with lubricant. 1. Apply the same lubricant used in the axle housing to the hub of the yoke or flange. 2. Inspect and make sure the lips of the POSE seal and the outer retainer of the triple-lip seal (main seal) are clean and free from dirt and particles that may cause lubricant leakage between the seals. 3. Install the POSE seal on the hub of the yoke or flange by hand. The lips of the seal must face toward the end of the hub (opposite shoulder). Slide the POSE seal on the hub until the lips are from 0.25 inch to 0.50 inch (6.4 mm-12.7 mm) from the end of the hub. Do not install the POSE seal against the shoulder. Figure 48. The POSE seal will position itself correctly as the yoke or flange is pressed on the shaft. 4. Before you install the yoke or flange on the shaft, again apply the same lubricant used in the axle housing to the hub. Figure 46 Installing Tight Fit Yokes and POSE Seal Figure Before you install the yoke or flange on the shaft, again apply the same lubricant used in the axle housing to the hub. Figure 47 The yoke must be completely seated before tightening pinion nut to the input shaft. 27
28 Installing Any Type Yoke with a Unitized Pinion Seal (UPS) Cautions Once the yoke is partially or fully installed and the removed for any reason, the unitized pinion seal will be damaged and unusable. If the yoke and unitized pinion seal are removed after partial of full installation, remove and discard the original unitized pinion seal and replace it with another new unitized pinion seal. 2. Select the correct seal driver from Table A. Each seal driver is designed to correctly install a specific diameter seal. To determine the yoke seal diameter, measure the yoke journal. Refer to Table A Unitized Pinion Seals and Seal Drivers. 3. Position the seal on the driver. If the inner sleeve of the seal is removed, the seal is not usable. A new seal is required. This will occur is a yoke is installed into the seal and then removed. 1. Remove the replacement unitized seal from the package. Figure 49. Figure 49 Single Models RS RS RS RS RS /A RS /A RS /A RS RS-185 RS Tandem Models RT /P RT /P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT /P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT EH/P RT-46-16HEH/P RT /P RT * RT * Meritor Unitized Pinion Seal A-1205-R-2592 A-1205-P-2590 A-1205-N-2588 A-1205-Q-2591 Seal Installation Location Tandem Forward Input (145 models from 11/93 to present) Tandem Forward Output (Tandem Forward Input 145 models before 11/93 with seal A F-2424) Tandem and Single Rear Input (145 models) Tandem and Single Rear Input (160/164/185 models) Meritor Seal Driver R R R R To obtain Meritor seal driver KIT 4454, call * Forward and rear input only. Table A Unitized Pinion Seals and Seal Drivers Yoke Seal Diameter Inches
29 Caution Use a rubber mallet to install the seal. Do not use a steel, brass or plastic hammer to install the seal. Using a steel, brass or plastic hammer can damage the sea and driver tool. 4. Use a rubber mallet to drive the seal into or against the bearing cage. The seal must fully seat into or against the bearing cage. Figure 50. Clean, Inspect and Install the Yoke After Installing a Unitized Pinion Seal Warning Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetrachloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures: Figure Use a inch shim to check for clearance between the entire seal flange circumference and the bearing cage. If the inch shim slides between the seal flange and bearing cage: Correctly position the seal driver and drive the seal into the bore until the inch shim cannot slide between the seal flange and bearing cage at any point around the seal flange. Figure 51. Wear safe eye protection Wear clothing that protects your skin. Work in a well-ventilated area. Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully 1. Clean the ground and polished surface of the yoke journal using a clean shop towel and a safe cleaning solvent. Do not use gasoline, abrasive cleaners, towels, or scrubbers to clean the yoke. Do not attempt to polish the yoke. The unitized seal features a rubber inner sleeve that is designed to seal and rotate with the yoke. This feature allows you to reuse a yoke with minor grooves. 2. Inspect the yoke seal surface for grooves. If you find grooves on the yoke: Use calipers to measure the groove diameters. If any groove diameter measures less than the dimensions shown in Figure 52, replace the yoke. Figure 51 29
30 Gear Set Information (Drive Pinion and Ring Gear Marks) Read the following information before installing a new gear set in the carrier. Always check the gear set for correct marks to make sure the gears are a matched set. The location of the marks is shown in Figure 53. Figure 52 Cautions Do not install a POSE seal after you install a unitized pinion seal. The use of a POSE seal will prevent correct seating of the unitized pinion seal on the yoke and can result in lubricant leakage at the seal. POSE seal installation is recommended only for triple lip and other previous design seals. Do not use thin metal wear sleeves to refresh the yoke surface. Wear sleeves pressed onto the yoke can prevent correct seating of the pinion seal, damage the pinion seal assembly and can cause the seal to leak. Figure Before you install the yoke, lightly lubricate or coat the yoke seal journal with axle oil. 4. Align the yoke splines with the shaft splines. Slide the yoke over the shaft spline. General Yoke and U-Joint Reassembly Install the end yoke hub capscrews by hand after seating the U-joint. Tighten the capscrews according to manufacturer's torque specifications. 1. Part Number a. Examples of gear set part numbers: Conventional ring gear, Conventional drive pinion, Generoid ring gear, K or K2 Generoid drive pinion, K or K2 The last digit in part numbers for Generoid gears is a letter or letter and number. b. Location on Drive Pinion: End at threads. c. Location on Ring Gear: Front face or outer diameter. 30
31 2. Tooth Combination Number a. Example of a tooth combination number: A 5-37 Gear set has a 5-tooth drive pinion and a 37-tooth ring gear. b. Location on Drive Pinion: Ends at threads. c. Location on Ring Gear: Front face or outer diameter. 3. Gear Set Match Number Figure 54 Meritor drive pinions and ring gears are available only as matched sets. Both gears of a set have a match number. a. Example of a gear set match number: M29. A gear set match number has any combination of a number or letter and number. b. Location on Drive Pinion: End of gear head. c. Location on Ring Gear: Front face or outer diameter. 4. Pinion Cone Variation Number The pinion cone variation number is not used when checking for a matched gear set. The number is used when you adjust the depth of the pinion in the carrier. Refer to the procedure for adjusting the shim pack thickness under the pinion cage in "Adjusting Shim Pack Thickness for the Pinion Cage (Depth of Pinion)". a. Examples refer to Figure 54. Pinion cone variation numbers: PC mm PC mm b. Location on Gear Set: End of pinion gear head or outer diameter of ring gear. Assembly Assemble the Drive Pinion, Bearings and Bearing Cage Warnings To prevent serious eye injury, always wear safe eye protection when you perform vehicle maintenance or service. Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the press manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. 1. Place the bearing cage in a press. Figure 55. Figure 55 31
32 2. Support the bearing cage with metal or wood blocks. 3. Press the bearing cup into the bore of bearing cage until cup is flat against bottom of bore. Use a sleeve of the correct size to install bearing cup. Figure 55. Use the same procedure for both bearing cups. 6. Installing the One-Piece Spigot Bearing on the Drive pinion with Snap Ring a. Place the drive pinion in a press, gear head (teeth) toward the top. Figure 56a. b. Press the spigot bearing on the end of drive pinion until the bearing is flat against the gear head. Use a sleeve of the correct size against the bearing inner race. Figure 56a. 4. Place the drive pinion in a press, gear head (teeth) toward the bottom. Figure 56. Figure 56 Figure 56a 5. Press the inner bearing cone on the shaft of the drive pinion until the cone is flat against the gear head. Use a sleeve of the correct size against the bearing inner race. c. Install the snap ring* into groove in end of drive pinion with snap ring pliers. Figure 57. s Spigot bearings are usually fastened to the drive pinion with a snap ring. Some are fastened with a peening tool, and some are a two-piece bearing assembly with the inner race pressed on the hose of the pinion and the outer race pressed into its bore in the carrier. Use the following procedure to install the spigot bearing. The following procedure applies to all axles except: 32 Some 160 Series single axles may use snap rings. Some 160 and 180 Series rear tandem axles may use snap rings. Figure 57
33 The following procedure applies to some 180 Series rear tandem axles with existing snap ring components. 7. Staking the One-Piece Spigot Bearing on the Drive Pinion (Without Snap Ring) Specification Apply 6,614 lb (3,000 kg) force on a inch (10 mm) ball. Stake the end of drive pinion at a minimum of five points. Figure 57a. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Figure 57b a. Place the drive pinion and the tube of the staking tool in a press, spigot bearing toward the top. Figure 57c. b. Calculate the amount of force that will be required on the staking tool. Refer to specification and example calculation. c. Place the punch of the staking tool over the end of the pinion and spigot bearing. Apply the required amount of force on the punch. Figure 57c. Figure 57a When using a staking tool and press (Figure 57a), calculate the force required on the tool as follows. 6,614 lb (3,000 kg) x amount of balls in tool = pounds or kilograms Example Figure 57c 6,614 lb x 3 balls = 19,842 pounds For information about the staking tool, contact your local Meritor representative. Figure 57b. Caution Do not align new points with grooves in end of drive pinion or in old points. If the new staked points are placed in the wrong areas, the spigot bearing will not be held correctly on the pinion shaft. 33
34 d. Rotate the punch as many times as required for a minimum of five points. Repeat step C for each point. indicating liquid through the hole in the shield. Figure 59. If a three-ball stake tool is used, rotate the tool 180 degrees. 8. Installing and Staking the Two-Piece Spigot Bearing on the Drive Pinion s This procedure applies to some 160 Series single rear axles and rear tandem axles. These axles may also use a one-piece spigot bearing with a snap ring retainer. The inner race of two-piece spigot bearings must be staked in place on RS and RR-160 series rear axles. Before you stake the pinion, you must heat the pinion stem to soften it. Kent-Moore Kit J includes the staking tool, temperature indicating liquid, heating shield and plastigage needed for this job. a. Apply two stripes of temperature indicating liquid on the pinion stem from the top to the bottom. Figure 58. Apply a green stripe to indicate 400 degrees F (205 degrees C) and a blue stripe to indicate 500 degrees F (260 degrees C). Figure 59 Warning Always wear safe clothing, gloves and eye protection when working with a torch for heating parts to prevent serious personal injury during assembly. Caution Do not heat the pinion stem without the heat shield in place. Also, do not overheat the pinion stem or you will weaken the metal, which can cause early failure. Correct heating will take approximately seconds, depending on how hot the torch is. c. Light and adjust the torch until the white part of the flame is approximately ¼ inch long. Keep the white part of the flame approximately 1/8 inch from the top of the stem. Figure 60. Move the flame around the outer diameter of the top of the pinion stem. The green temperature indicating liquid will turn black before the blue liquid does. Heat the stem until the blue liquid turns black at a point in the middle of the window. Figure 58 b. Place the heating shield over the pinion stem so that you can see the temperature 34
35 f. Place the staking tool over the bearing race. Cut a one inch piece from the green plastigage strip and place in between the punch and the staking tool. Figure 61 View A. Figure 60 d. Remove the flame and the heat shield from the pinion. Let the pinion air cool for 10 minutes. Use a razor blade to remove the temperature indicating liquid. Warning Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the press manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. Caution Do not press or directly strike the new inner race in step e or damage to the bearing will result. e. Use a press, if available, or a brass hammer to install the new inner race. Use the old inner race as a sleeve. The face is completely seated when you cannot fir a inch feeler gauge between the race and the pinion shoulder. s To hold the races in place, use a staking tool, instead of the old race, to start the new race on the stem. The old race can be used to completely seat the new race. In Step f, you do not need to use the plastigage for every stake. Use the plastigage until you are sure you are hitting the punch with the correct amount of force. Figure 61 g. Strike the punch with a two-three pound brass hammer to upset the end of the pinion stem. Then, remove the strip and measure its thickness against the gauge on the wrapper that the strip came in. The strip must not be less than inch thick. This thickness indicates that you are using enough force when you hit the punch. If the strip is too thin, then you must hit the punch harder so the stake will hold the race in place. Rotate the tool and repeat this procedure until there are six evenly spaced stake marks around the stem. Figure 61 View B. h. With a press or a soft mallet and sleeve, install the outer race and roller assembly into its bore in the carrier. Use a sleeve that is the same size as the outer race and press the bearing until it is squarely against the shoulder in the bottom of its bore. 9. Apply axle lubricant to the bearing cups and t the bearing cones in the cage. 10. Install the drive pinion into the bearing cage. 35
36 11. Install the bearing spacer or spacers on pinion shaft against the inner bearing cone. Figure 62. Adjusting Preload of Pinion Bearings Specifications The spacer or spacers control the preload adjustment of the drive pinion bearings. 12. Install the outer bearing cone on pinion shaft against the spacer. Figure 62. Do not install pinion seal in bearing cage. Continue with adjusting preload of pinion bearings. New pinion bearings torque - 5 to 45 lb-in ( Nm) New pinion bearing in good condition torque - 10 to 30 lb-in ( Nm) Press Method s If a press is not available, or the press does not have a pressure gauge, use the yoke or flange method to adjust pinion bearing preload. Refer to "Yoke or Flange Method". Do not read starting torque. Read only the torque value after the cage starts to rotate. Starting torque will give a false reading. a. Place the drive pinion and cage assembly in a press, gear head (teeth) toward the bottom. b. Install a sleeve of the correct size against the inner race of the outer bearing. Figure 63. c. Apply and hold the correct amount pressure to the pinion bearings. Refer to Table B. As pressure is applied, rotate the bearing cage several times so that bearings make normal contact. Figure 62 Thread Size of Pinion Shaft 7/8"-20 1"-20 1 ¼"-12 1 ¼" ½"-12 1 ½"-18 1 ¾"-12 2"-12 Press Pressure Needed on Bearings for Correct Preload Pounds/tons (kg/metric tons) 22,000/1 9979/10 30,000/15 (13608/13.6) 54,000/27 (24494/24.5) 54,000/27 (24494/24.5) 54,000/27 (24494/24.5) 54,000/27 (24494/ ,000/25 (22680/22.7) 50,000/25 (22680/22.7) Torque Value Needed on Pinion Nut for Correct Bearing Preload Lb-ft (Nm) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (1627/2034) Table B 36
37 d. While pressure is held against the assembly, wind a cord around the bearing cage several times. e. Attach a spring scale to the end of the cord. f. Pull the cord with scale on a horizontal line. As the bearing cage rotates, read the value indicated on scale. Write down and record the reading. Figure 63. Pounds Pulled x Radius (inches) = lb-in Preload - Preload x 0.113=Nm Preload Kilograms Pulled x Radius (cm) = kg-cm lb-in Preload - Preload x = Nm Preload or Examples Reading from spring scale = 7.5 pounds (3.4 kg) Diameter of bearing cage = 6.62 inches (16.8 cm) Radius of bearing cage = 3.31 inches (8.4 cm) 7.5 lb x 3.31 in. = 24.8 in-lb Preload Preload x = 2.8 Nm Preload or 3.4 kg x 8.4 cm = 28.6 kg-cm Preload Preload x = 2.8 Nm Preload Figure 63 j. g. Measure the diameter of bearing cage where the cord was wound. Measure in inches or centimeters. Figure 64. h. Divide the dimension in half to get the radius. Write down and record the radius dimension. If the preload (torque) of pinion bearings is not within specifications, do the following procedure, then repeat steps a through i. To increase preload, install a thinner bearing spacer. To decrease preload, install a thicker bearing spacer. k. Check the bearing preload with the drive pinion and cage assembly installed in the carrier. Follow the procedures to adjust preload of pinion bearings, yoke or flange method. Yoke or Flange Method Warning Observe all warnings and cautions provided by the press manufacturer to avoid damage to components and serious personal injury. Figure 64 i. Use the following procedure to calculate the bearing preload (torque). 37
38 Caution Do not install tight fit yokes or flanges on shafts using a hammer or mallet. A hammer or mallet will damage the yoke or flange. Use a press to install the yoke or flange. Figure 65. c. Install the bearing cage to carrier capscrews. Washers are not required at this time. Tighten the capscrews by hand until snug. d. Fasten a yoke or flange bar to the input yoke or flange. The bar will hold the drive pinion in position when the nut is tightened. Figure 67. a. Install the input yoke or flange, nut and washer* on the drive pinion. The yoke or flange must be seated against the outer bearing. b. Temporarily install the drive pinion and cage assembly in the carrier. Do not install shims under the bearing cage. Figure 66. Figure 67 e. Tighten the nut on drive pinion to the correct torque value. Figure 67. Refer to Table B. f. Remove the yoke or flange bar. g. Attach a torque wrench on the drive pinion nut. Rotate the drive pinion and read the value indicated on torque wrench. Figure 68. Figure 65 Figure 66 *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 38 Figure 68
39 h. If t he preload (torque) of pinion bearings is not within specifications, remove the pinion and cage assembly from carrier. Do the following procedures, then repeat steps a through g. To increase preload, install a thinner bearing spacer. To decrease preload, install a thicker bearing spacer. 13. After adjusting preload of pinion bearings, remove the drive pinion and bearing cage from carrier. Follow steps 1-5 in "Remove the Drive Pinion and Bearing Cage from Carrier". 14. Install a new triple-lip seal as follows. Caution Make sure that the seal lips are clean and free from dirt and particles that will cause a leak between the yoke and the seal. a. Apply the same lubricant used in the axle housing to the outer surface of the seal and the seal bore in the bearing cage. Figure 69. Figure 69 b. Place the drive pinion and cage assembly in a press, seal bore toward the top. If a press is not available, use a mallet and the sleeve or driver to install the seal. Figure 71. c. Press the seal into bearing cage until flange is flat against the top of bearing cage. Use a sleeve or seal driver of the correct size that fits against the metal flange of seal. The diameter of the sleeve or driver must be larger than the diameter of the flange. Figure
40 Check the gap with a feeler gauge at several points around the seal. The gap must be within to inch ( mm). The difference between the largest and smallest gap measurement must not exceed inch ( mm). Figure 72 Figure 70 Adjusting Shim Pack Thickness for the Pinion Cage (Depth of Pinion) Use this procedure if a new drive pinion and ring gear is installed, or if the depth of the drive pinion has to be adjusted. Figure 73. Figure 71 Warning Use a brass or leather mallet for assembly and disassembly procedures. Do not hit steel parts with a steel hammer. Pieces of a part can break off and cause serious personal injury. d. After the triple-lip seal is installed, a gap of approximately to inch ( mm) between the flange and bearing cage is normal. Figure
41 Figure 75 Figure Measure the thickness of the old shim pack that was removed from under the pinion cage with a micrometer. Record the measurement for use later. Figure 74. The pinion cone number can be either 100ths of a millimeter or 1,000ths of an inch. Refer to the following examples: PC +3, PC 3, +3, or 3= inch PC +.03, PC 0.03 mm, m or 0.03=0.03 mm To change millimeters to inches millimeters x Figure Look at the pinion cone (PC) variation number on the old drive pinion that is being replaced. Refer to Gear Set Information at the end of Section 4 for examples and location of the number. Record the number for later use. If (PC) variation number cannot be located, assembly gear set with shim pack thickness found in step 1. Figure If the old pinion cone number is a plus (+) number, subtract the number from the old shim pack thickness that was measured in step If the old pinion cone number is a minus (-1) number, add the number to the old shim pack thickness that was measured in step Look at the pinion cone (PC) variation number on the new drive pinion that will be installed. Record the number for later use. 6. If the new pinion cone number is a plus (+) number, add the number to the standard shim pack thickness that was calculated in step 3 or If the new pinion cone number is a minus (-) number, subtract the number from the standard shim pack thickness that was calculated in step 3 or Install the drive pinion bearing cage and new shim pack into the carrier. 41
42 The value calculated in step 3 or 4 is the thickness of the stand shim pack, without a variation. To change inches to millimeters inches x The value calculated in step 6 or 7 is the thickness of the new shim pack that will be installed. Refer to the following examples, Table C. 1. Old Shim Pack Thickness Old PC Number, PC +2 inches (0.05 mm) Standard Shim Pack Thickness New PC Number, PC +5 inches (0.13 mm) New Shim Pack Thickness Examples Inches Mm = = = = Old Shim Pack Thickness Old PC Number, PC 2 inches (-0.05 mm) Standard Shim Pack Thickness New PC Number, PC +5 inches (+0.13 mm) New Shim Pack Thickness 3. Old Shim Pack Thickness Old PC Number, PC +2 inches (0.05 mm) Standard Shim Pack Thickness New PC Number, PC 5 inches (-0.13 mm) New Shim Pack Thickness 4. Old Shim Pack Thickness Old PC Number, PC 2 inches (-0.05 mm) Standard Shim Pack Thickness New PC Number PC 5 inches (-0.13 mm) = = = = = = = = = = = New Shim Pack Thickness Table C Drive pinions and ring gears MUST be replaced as fully matched sets. Installing the Drive Pinion, Bearing Cage and Shim Pack into the Carrier If a new drive pinion and ring gear set is installed, or if the depth of the drive pinion has to be adjusted, calculate the thickness of the shim pack. Refer to the procedure "Adjusting Shim Pack Thickness for the Pinion Cage (Depth of Pinion)". 1. Select the correct shim pack between the bearing cage and carrier. Figure Apply Loctite 518 Gasket Eliminator to face of carrier. 3. Align the oil slots in the shims with oil slots in the bearing cage and carrier. The use of guide studs will help align the shims. Figure
43 6. Install the bearing cage to carrier capscrews and washers. Tighten capscrews to correct torque value. Refer to Table J. Figure 77. Figure 76 Figure 77 If the pack is made from different thickness shims, install the thinnest shims on both sides of the pack for maximum sealing. 4. Apply Loctite 518 Gasket Eliminator to top of shim pack. Warning Use a brass or leather mallet for assembly and disassembly procedures. Do not hit steel parts with a steel hammer. Pieces of a part can break off and cause serious personal injury. 5. Install the drive pinion and bearing cage into the carrier. If necessary, use a rubber, plastic or leather mallet to hit the assembly into position. Figure 76a. Installing Tight Fit Yokes and POSE Seal Cautions Make sure that the seal lips are clean and free from dirt and particles that will cause a leak between the yoke and the seal. Do not install tight fit yokes on shafts using a hammer or mallet. Using a hammer or mallet can damage the yoke. Make sure that the seal lips are clean and free from dirt and particles that can cause a leak between the yoke and the POSE seal. Do not install POSE seal all the way against the yoke shoulder. This seal is designed to position itself as yoke is installed. 1. Apply axle lubricant on the yoke seal. 2. Check all surfaces of the yoke hub for damage. If carrier uses a POSE seal element, install a new POSE seal as follows: a. Lightly lubricate yoke journal with same lubricant used in the axle housing. Figure 76a 43
44 b. Partially install the POSE seal onto the yoke to ¼ inch ½ inch as shown in Figure 78. Figure 79 Figure 78 c. Before installing the yoke onto the drive pinion, lubricate the yoke again with the same lubricant used in the axle housing. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 3. Slide the yoke over the input shaft pinion. Align the yoke splines with the shaft splines. Installing Any Type Yoke with a Unitized Pinion Seal (UPS) Caution Cautions Do not use a hammer or mallet to install the yoke to the input pinion shaft. Using a hammer or mallet can damage the yoke or flange. 4. Install the input yoke flange onto the drive pinion shaft. The yoke or flange must be fully seated against the outer differential bearing before the nut is torqued to specifications. 5. Install the drive pinion nut and washer* on the input pinion shaft and against the yoke collar. Tighten the nut against yoke collar to torque specifications. Figure 79. Refer to Table J. 44 Once the yoke is partially or fully installed and then removed for any reason, the unitized pinion seal will be damaged and unusable. If the yoke and unitized pinion seal are removed after partial or full installation, remove and discard the original unitized pinion seal and replace it with another new unitized pinion seal. If the inner sleeve of the seal is removed, the seal is not usable. A new seal is required. This will occur if a yoke is installed into the seal and then removed. 1. Remove the replacement unitized seal from the package. Figure Select the correct seal driver from Table D. Each seal driver is designed to correctly install a specific diameter seal. To determine the yoke seal diameter, measure the yoke journal. Refer to Table D. 3. Position the seal on the driver.
45 Single Models RS RS RS RS RS /A RS /A RS /A RS RS RS Figure 80 Tandem Models RT /P RT /P RT /A/P RT /P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT /A/P RT EH/P RT-46-16HEH/P RT /P RT * RT * Meritor Unitized Pinion Seal A-1205-R A-1205-P A-1205-N A-1205-Q Seal Installation Location Tandem Forward Input (145 Models from 11/93 to present) Tandem Forward Output (Tandem Forward Input 145 Models before 11/93 with seal A F-2424) Tandem and Single Rear Input (145 models) Tandem and Single Rear Input (160/164/185 models) Meritor Seal Driver Yoke Seal Diameter Inches R R R R To obtain Meritor seal driver KIT 4454, call * Forward and rear input only. Table D Unitized Pinion Seals and Seal Drivers Caution Use a rubber mallet to install the seal. Do not use a steel, brass or plastic hammer to install the seal. Using a steel, brass or plastic hammer can damage the seal and driver tool. 45
46 4. Use a rubber mallet to drive the seal into or against the bearing cage. The seal must be fully seated into or against the bearing cage. Figure 81. Clean, Inspect and Install the Yoke After Installing a Unitized Pinion Seal Warning Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetrachloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures: Figure Use a inch shim to check for clearance between the entire seal flange circumference and the bearing cage. If the inch shim slides between the seal flange and bearing cage: Correctly position the seal driver and drive the seal into the bore until the inch shim cannot slide between the seal flange and bearing cage at any point around the seal flange. Figure 82. Wear safe eye protection Wear clothing that protects your skin Work in a well-ventilated area Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. 1. Clean the ground and polished surface of the yoke journal using a clean shop towel and a safe cleaning solvent. Do not use gasoline, abrasive cleaners, towels, or scrubbers to clean the yoke. Do not attempt to polish the yoke. The unitized seal features a rubber inner sleeve that is designed to seal and rotate with the yoke. This feature allows you to reuse a yoke with minor grooves. 2. Inspect the yoke seal surface for grooves. If you find grooves on the yoke: Use calipers to measure the groove diameters. If any groove diameter measures less than the dimensions shown in Figure 83, replace the yoke. Figure 82 46
47 Figure 84 Figure 83 Cautions Do not install a POSE seal after you install a unitized pinion seal. The use of a POSE seal will prevent correct seating of the unitized pinion seal on the yoke and can result in lubricant leakage at the seal. POSE seal installation is recommended only for triple lip and other previous design seals. Do not use thin metal wear sleeves to refresh the yoke surface. Wear sleeves pressed onto the yoke can prevent correct seating of t he pinion seal, damage the pinion seal assembly and can cause the seal to leak. 3. Before you install the yoke, lightly lubricate or coat the yoke seal journal with axle oil. 4. Align the yoke splines with the shaft splines. Slide the yoke over the shaft spline. Assemble the Main Differential and Ring Gear Assembly Caution Do not press a cold ring gear on the flange case half. A cold ring gear will damage the case half because of the tight fit. Metal particles between the parts will cause gear runout that exceeds the Meritor specification of inch (0.2 mm). 1. Expand the ring gear by heating the gear in a tank of water to a temperature of 160 F to 180 F (71 C to 82 C) for 10 to 15 minutes. Warning Caution Do not use a hammer or mallet to install the yoke to the input pinion shaft. Using a hammer or mallet can damage the yoke or flange. 5. Install the input yoke flange onto the drive pinion shaft. The yoke or flange must be fully seated against the outer differential bearing before the nut is torqued to specifications. 6. Install the drive pinion nut (and washer if required) on the input pinion shaft and against the yoke collar. Tighten the nut against yoke collar to torque specifications. Figure 84. Refer to Table J. Wear safe clothing and gloves for protection from injury when working with the hot ring gear. 2. Safely lift the ring gear from the tank of water using a lifting tool. 3. Install the ring gear on the flange case half immediately after the gear is heated. If the ring gear does not fit easily on the case half, heat the gear again. Repeat step Align fastener holes of the ring gear and flange case half. Rotate the ring gear as needed. 5. If rivets* were used to hold the ring gear to the flange case half, replace them with bolts, nuts and washers. 47
48 6. Install the bolts*, nuts* and washers* that hold the ring gear to the flange case half. Install the bolts from the gear side of the assembly. The bolt heads must be against the ring gear. Figure 85. Figure Install the bearing cones on both of the case halves. Use a press and sleeve of the correct size. Figure 87. Figure Tighten the bolts* and nuts* to the correct torque value. Refer to Table J. a. After the bolts are installed, check for gaps between the back surface of the ring gear and the case flange. Use an 0.08 mm (0.003 inch) feeler gauge and check at four points around the assembly. Figure 86. b. Check the flange case half and ring gear for the problem that causes the gap. Repair or replace parts. c. After the parts are repaired or replaced, assemble the ring gear on the flange case half. Repeat the procedure in "Installing Tight Fit Yokes and POSE Seal", and steps a through c. Figure 87 *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 48
49 9. Apply axle lubricant on the inside surfaces of both case halves, spider (cross), thrust washers, side gears and differential pinions. 10. Place the flange case half on a bench, ring gear teeth toward top. 11. Install one thrust washer and side gear into the flange case half. Figure 88. Figure Place the plain half of the differential case over the flange half and gears. Rotate the plain half as needed to align the match marks. Figure 90 and Figure 91. Figure 88 Caution The side gears in some carrier models have hubs of different lengths. Install the correct length side gear into the flange case half. 12. Install the spider (cross), differential pinions and thrust washers into the flange case half. Figure Install the second side gear and thrust washer over spider and differential pinions. Figure 90. Figure Install Dri-Loc fasteners into the case halves. Refer to "General Information" and the following steps a and b. a. Install four capscrews and washers or bolts*, nuts* and washers* into the case halves. The distance between the fasteners must be equal. Tighten the fasteners to the correct torque value in a progressive criss-cross pattern opposite each other. Refer to Figure 92 and Table J. Figure 89 49
50 b. Install the other fasteners into the case halves. Tighten the fasteners to the correct torque value. Refer to Table J. c. Install the tool into the differential until the splines of the tool and one side gear are engaged. Figure 94. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. 16. Check the rotating resistance of the differential gears. Use the following procedures: Figure 93 Figure 92 Rotating Resistance Check of Differential Gears Specification 50 lb-ft (67.8 Nm) maximum torque applied to one side gear. Make a tool for checking the rotating resistance of the differential gears. The tool can be made from an axle shaft that matches the spline size of the differential side gear. Refer to Figure 93. Figure 94 d. Attach a torque wrench to the nut of the tool and rotate the differential gears. As the differential gears rotate, read the value indicated on the torque wrench. Figure 95. a. Install soft metal covers over vise jaws to protect the ring gear. Figure 94. b. Place the differential and ring gear assembly in the vise. 50
51 Figure 95 Figure 96 e. If the torque value exceeds the specification, disassemble the differential gears from the case halves. f. Check the case halves, spider, gears and thrust washers for the problem that causes the torque value to exceed the specification. Repair or replace parts. 4. Install the bearing cups over the bearing cones that are assembled on the case halves. Figure Safely lift the differential and ring gear assembly and install into the carrier. The bearing cups must be flat against the bores between the carrier legs. Figure 97. After the parts are repaired or replaced, assemble the parts and repeat steps a through f. Install the Differential and Ring Gear Assembly 1. Clean and dry the bearing cups and bores of the carrier legs and bearing caps. 2. Apply axle lubricant on the inner diameter of the bearing cups and on both bearing cones that are assembled on the case halves. 3. Apply Meritor Adhesive into the bearing bores of the carrier legs and bearing caps. Make certain not to allow adhesive to contact adjusting ring threads. Refer to "General Information". Figure 96. Figure Install both of the bearing adjusting rings into position between the carrier legs. Turn each adjusting ring hand-tight against the bearing cup. Figure
52 8. Seat each bearing cap with a light leather, plastic or rubber mallet. The caps must fit easily against the bearings, adjusting rings and carrier. Do not force the bearing caps into position. Caution If bearing caps are not installed in correct locations, the bores and threads in caps will not match the carrier. You will have problems assembling the caps on the carrier and damage to parts can occur. Do not force the bearing caps into position. Figure Install the bearing caps over the bearings and adjusting rings in the correct location as marked before removal. Figure If bearing caps do not correctly fit into position, check the alignment of match marks between caps and carrier. Remove the caps and repeat steps Install the capscrews and washers that hold bearing caps to the carrier. Tighten the capscrews by hand four to six turns, and then tighten the capscrews to the correct torque value. Refer to Table J. Do not install the cotter keys*, pins*, or lock plates* that hold the bearing adjusting rings in position. Continue by adjusting the preload of differential bearings, adjust backlash of the hypoid gear and check tooth contact patterns. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Figure 99 Warning Use a brass or leather mallet for assembly and disassembly procedures. Do not hit steel parts with a steel hammer. Pieces of a part can break off and cause serious personal injury. Adjust Preload of Differential Bearings Specifications Preload of differential bearings (all carrier models) - 15 to 35 lb-in ( Nm) torque 52
53 Expansion between bearing caps (leg spread) - RS-140, RS-145 and RS-160 carrier models: to inch ( mm) a. Use two pry bars that fit between the bearing adjusting rings and ends of the differential case. The pry bars must not touch the differential bearings. Figure RS 120 and all other carrier models: to inch ( mm) Method 1 1. Attach a dial indicator on the mounting flange of the carrier. 2. Adjust the dial indicator so that the plunger or pointer is against the back surface of the ring gear. Figure 100. Figure 101 Figure 100 Caution When you turn the adjusting rings, always use a tool that engages two or more opposite notches in the ring. A "T" bar wrench can be used for this purpose. If the tool does not correctly fit into the notches, damage to the lugs will occur. Figure Loosen the bearing adjusting ring that is opposite the ring gear so that a small amount of end play shows on the dial indicator. Figure 101. Move the differential and ring gear to the left and right with pry bars while you read the dial indicator. Use the following step a or b. Figure 102 b. Use two pry bars between the differential case or ring gear and the carrier at the locations other than described in step a. The pry bars must not touch the differential bearings. Figure
54 Figure 104 Figure Tighten the same bearing adjusting ring so that no end play shows on the dial indicator. Move the differential and ring gear to the left and right as needed. Repeat step a or b. 5. Tighten each bearing adjusting ring one notch from the zero end play measured in step Continue by checking runout of the ring gear. Method 2 A second method of checking preload is to measure the expansion between the bearing caps (leg spread) after the adjusting rings are tightened. Use the following procedure. 1. Turn both adjusting rings hand tight against the differential bearings. 2. Measure the distance X or Y between opposite surfaces of the bearing caps. Use a large micrometer of the correct size. Figure 104 and Figure 105. Record the measurement. Figure Tighten each bearing adjusting ring one notch. 4. Measure the distance X or Y again. Compare the dimension with the distance X or Y measured in step 2. The difference between the two dimensions is the amount the bearing caps have expanded. Example 54 Measurement of RS-145 carrier Distance X or Y - before tightening adjusting rings = inch ( mm)
55 Distance X or Y - after tightening adjusting rings = inch ( mm) inch inch = inch (0.23 mm) difference. If the dimension is within specifications, continue by checking runout of the ring gear. If the dimension is less than specifications, repeat steps 3 and 4 as needed. Check Runout of Ring Gear If the runout of the ring gear exceeds specifications, remove the differential and ring gear assembly from the carrier. Refer to "Remove the Differential and Ring Gear from the Carrier" and the following steps 5 and Check the differential parts including the carrier for the problem that causes the runout of gear to exceed specifications. Repair or replace parts. 6. After the parts are repaired or replaced, install the differential and ring gear into the carrier. Refer to "Install the Differential and Ring Gear Assembly". 7. Repeat preload adjustment of differential bearings. Runout Specification inch (0.20 mm) 1. Attach a dial indicator on the mounting flange of the carrier. Figure 106. Ring Gear Backlash Adjustment Runout Specifications Ring gears that have a pitch diameter of less than 17 inches (431.8 mm) - range of backlash setting: 0.08 to inch ( mm) - backlash setting for new gear sets: inch (0.30 mm) Ring gears that have a pitch diameter greater than 17 inches (431.8 mm) - range of backlash setting: to inch ( mm) Figure Adjust the dial indicator so that the plunger or pointer is against the back surface of the ring gear. 3. Set the dial indicator to zero (0). 4. Rotate the differential and ring gear and read the dial indicator. The runout of the ring gear must not exceed inch (0.20 mm). Figure backlash setting for new gear sets: inch (0.38 mm) Measure the outer diameter of ring gear for approximate pitch diameter. Figure
56 3. Adjust the indicator dial to zero (0). 4. Hold the drive pinion in position. 5. After reading the dial indicator, rotate the differential and ring gear a small amount in both directions, against the drive pinion teeth. If the backlash reading is within specification, continue checking tooth contact patterns. If the backlash reading is not within specifications, adjust backlash as needed. Continue following steps 6 and 7. Figure 107 If the old gear set is installed, adjust the backlash to the setting that was measured before the carrier was disassembled. If a new gear set is installed, adjust the backlash to the correct specification for new gear sets. After checking of the tooth contact patterns, the backlash can be adjusted within specification limits, if needed. To change t he location of the pattern, use the following procedures. 1. Attach a dial indicator on the mounting flange of the carrier. Figure 108. Figure 109 s Backlash is increased by moving the ring gear away from the drive pinion. Figure 109. Backlash is decreased by moving the ring gear toward the drive pinion. Figure Loosen one bearing adjusting ring one notch, then tighten the opposite ring the same amount. Refer to Figure 109 and Figure 110. When you adjust backlash, move the ring gear ONLY. Do not move the drive pinion. 7. Repeat steps 2-6 until the backlash is within specifications. Figure Adjust the dial indicator so that the plunger or pointer is against the tooth surface. Figure
57 In the following procedures, movement of contact pattern in the length of the tooth is indicated as toward the 'heel' or 'toe' of the ring gear. Figure 112. Always check tooth contact patterns on the drive side of the gear teeth. Figure 113. Figure 110 Checking Tooth Contact Patterns (Backlash) of the Gear Set Figure 112 General Information Meritor carriers can have a generoid hypoid gear set. The tooth contact patterns for each type of gear set are different. Look at the part numbers to see what type of gear set is in the carrier. Refer to Figure 111 for the location of part numbers. Figure 113 Figure 111 Examples Part Numbers for generoid gear sets K or K2 for the ring gear K or K2 for the drive pinion Tooth Contact Patterns of Generoid Hypoid Gear Sets 1. Adjust the backlash of a new gear set to either inch (0.305 mm) or inch (0.380 mm) depending on the size of the ring gear. Adjust the backlash of an old gear set to the setting that was measured before the carrier was disassembled. Refer to "Ring Gear Backlash Adjustment". 2. Apply a marking compound to approximately 12 gear teeth of the ring gear. Rotate the ring 57
58 gear so that the 12 gear teeth are next to the drive pinion. Figure 114. Figure Look at the contact patterns on the ring gear teeth. Compare the patterns to Figure 115, Figure 116, and Figure 117. Figure Rotate ring gear forward and backward so that the 12 gear teeth go past the drive pinion six times to get the contact patterns. Repeat if needed to get a clearer pattern. The Location of Good Hand-Rolled Contact Patterns New Conventional and Generoid Gear Sets - toward the toe of the gear tooth and in the center between the top and bottom of the tooth. Refer to Figure 115. When the carrier is operated, a good pattern will extend approximately the full length of the gear tooth. The top of the pattern will be near the top of the gear tooth. Refer to Figure 118. Figure 115 The location of a good hand-rolled contact pattern for an old gear set must match the wear pattern in the ring gear. The new contact pattern will be smaller in area than the old wear pattern. If the contact patterns require adjustment, continue by following step 5 to move the contact patterns between the top and bottom of the gear teeth. If the contact patterns are in the center of the gear teeth, continue by following step 6. Figure
59 Figure 118 Figure 119 A high contact pattern indicates that the drive pinion was not installed deep enough into the carrier. A low contact pattern indicates that the drive pinion was installed too deep in the carrier. 5. Change the thickness of the shim pack under bearing cage to move the contact patterns between the top and bottom of the gear teeth. Use the following procedures. a. Remove the drive pinion and bearing cage from the carrier. Refer to "Remove the Drive Pinion and Bearing Cage from Carrier". b. To correct a high contact pattern, Figure 116, decrease the thickness of the shim pack under the bearing cage. When decreasing the thickness of the shim pack, the drive pinion will move toward the ring gear. Figure 119. d. Repeat steps 2-5 until the contact patterns are in the center between the top and bottom of the gear teeth. To correct a low contact pattern, Figure 120, increase the thickness of shim pack under the bearing cage. When increasing the thickness of the shim pack, the drive pinion will move away from the ring gear. 6. Adjust backlash of the ring gear within specification range to move the contact patterns to the correct location in the length of the gear teeth. Refer to "Ring Gear Backlash Adjustment". c. Install the drive pinion, bearing cage and shims into the carrier. Refer to "Adjusting Shim Pack Thickness for the Pinion Cage (Depth of Pinion)". Figure 120 a. Decrease backlash to move the contact patterns toward the toe of the ring gear teeth. Figure 121. b. Increase backlash to move the contact patterns toward the heel of the ring gear teeth. Figure
60 b. Pins* Install pin through boss of the bearing cap until the pin is between lugs of the adjusting ring. Use a drift and hammer to install the pin. Figure 123. c. Lock Plates* Install lock plate on bearing cap so that the tab is between lugs of the adjusting ring. Install the two capscrews that hold the lock plate to the bearing cap. Tighten the capscrews to correct torque value. Refer to Table J. Figure 123. Figure 121 Figure 122 c. Repeat steps 2-4 and 6 until the contact patterns are at the correct location in the length of the gear teeth. Caution If the carrier has cotter keys, lock the adjusting rings only with cotter keys. If you carrier has roll pins, reuse the roll pins or lock the adjusting rings with cotter keys. Do not force a roll pin into a cotter key hole. 7. Install cotter keys*, pins*, or lock plates* that hold the two bearing adjusting rings in position. Use the following procedures. a. Cotter Keys* Install cotter keys between lugs of the adjusting ring and through the boss of the bearing cap. Bend the two ends of the cotter key around the boss. Figure Figure 123 *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Install and Adjust the Thrust Screw* Specification Clearance between thrust screw and ring gear to inch ( mm) Loosen the thrust screw ½ turn or 180 degrees.
61 1. Rotate the carrier in the repair stand until the back surface of ring gear is toward the top. 2. Install the jam nut* on the thrust screw*, one half the distance between both ends. Figure Loosen the thrust screw* ½ turn, 180 degrees. Figure 125. *Some Meritor carriers do not have these described parts. Figure 124 Figure 126 Install Differential Carrier into Axle Housing Warning Figure Tighten the jam nut* to the correct torque value against the carrier. Refer to Table J. Figure 126. To complete the assembly of axles equipped with driver-controlled main differential locks, refer to "Installation of the DCDL Assembly into Carrier" through "Traction Control Video Package". Start with "Installation of the DCDL Assembly into Carrier". Solvent cleaners can be flammable, poisonous and cause burns. Examples of solvent cleaners are carbon tetrachloride, emulsion-type cleaners and petroleum-based cleaners. To avoid serious personal injury when you use solvent cleaners, you must carefully follow the manufacturer's product instructions and these procedures. Wear safe eye protection. Wear clothing that protects your skin. Work in a well-ventilated area. Do not use gasoline, or solvents that contain gasoline. Gasoline can explode. You must use hot solution tanks or alkaline solutions correctly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. 1. Clean the inside of axle housing and the mounting surface where the carrier fastens. 61
62 Use a cleaning solvent and rags to remove dirt. Blow dry the cleaned areas with air. Also, refer to "Cleaning Axle Assemblies". Inspect the axle housing for damage. Repair or replace the axle housing. Refer to "Repair or Replacement of Parts, General", "Repair Axle by Welding", and "Bending or Straightening Drive Axle Housings". Check for loose studs* in the mounting surface of the housing where the carrier fastens. Remove and clean the studs* that are loose. Apply liquid adhesive to the threaded holes and install the studs* into axle housing. Refer to "Application of Meritor Adhesive 2297-T4180 in Bearing Bores for the Differential." Tighten studs* to correct torque value. Refer to Table J. Apply silicone gasket material to the mounting surface of the housing where the carrier fastens. Refer to the "Application of Three Bond 1216 or Equivalent Silicone Gasket Material". Figure Carefully push the carrier into position. Tighten the four fasteners two or three turns each in a pattern opposite each other. Refer to Figure 128. Figure Repeat step 8 until the four fasteners are tightened to the correct torque value. Refer to Table J. 10. Install the other fasteners and washers that hold the carrier in the axle housing. Tighten fasteners to the correct torque value Refer to Table J. 11. Connect the driveline universal joint to the pinion input yoke or flange on the carrier. 12. Install the gaskets and axle shafts into the axle housing and carrier. The gasket and flange of the axle shafts must fit flat against the wheel hub. Figure 129. Straight Holes, Nuts and Hardened Washers Figure Install the carrier into the axle housing. Use a hydraulic roller jack or a lifting tool. Caution Do not install the carriers using a hammer of mallet. A hammer or mallet will damage the mounting flange of carrier and cause oil leaks. 7. Install nuts* and washers or capscrews and washers in the four corner locations around the carrier and axle housing. Tighten the fasteners hand tight at this time. Figure Clean the mating surfaces of the axle shaft and the wheel hub. 2. If silicone gasket material is used, apply a 1/8 inch diameter bead of the gasket material around the mating surface of the hub and around the edge of each fastener hole in that surface. 3. Install the gasket and the axle shaft into the housing. The gasket and the flange of the axle shaft MUST fit flat against the wheel hub. Refer to Figure Install the Grade 8 nuts and hardened washers on the stud. (Lock washers are an acceptable alternative.) Tighten the stud nuts to the torque specified in Table E.
63 Fastener Stud Nut (Axle Shaft) Studs Thread Size All Torque Value Grade 8 Nuts lb-ft (Nm) Plain Nut Lock Nut ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Install the course thread end of stud into hub and tighten to last thread. Table E Shaft-to-Hub Torque Fastener Chart Non-Tapered Dowel Applications Tapered Dowel, Hardened Washer and Hardened Nut 1. Clean the mating surfaces of the axle shaft and the wheel hub. 2. If silicone gasket material is used, apply a 1/8 inch diameter bead of the gasket material around the mating surface of the hub and around the edge of each fastener hole in that surface. 3. Install the gasket and the axle shaft into the housing. The gasket and the flange of the axle shaft MUST fit flat against the wheel hub. Refer to Figure Install solid tapered dowels over each stud and into the flange of the axle shaft. Use a punch or a drift and hammer, if necessary. 5. Install the Grade 8 nuts and hardened washers on the stud. (Lock washers are an acceptable alternative.) Tighten the stud nuts to the torque specified in Table F. Fastener Thread Size Stud Nut (Axle Shaft) Studs All Figure 129 Torque Value-Grade 8 Nuts lb-ft (Nm) Plain Nut Lock Nut (67-88) (81-102) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Install the course thread end of stud into hub and tighten to last thread. Table F-Shaft-to-Hub Torque Fastener Chart-Tapered Dowel Applications Lubrication Refer to Table G, Table H and Table I for standard information on lubricants, schedules and capacities. For complete information on lubricating drive axles and carriers, refer to Maintenance Manual 1, Lubrication. 63
Single Reduction Differential Carriers
 Revised 10-00 $2.50 Single Reduction Differential Carriers Maintenance Manual 5 Standard Carriers Including: Single Axles, Rear of Tandem Axles, Front Drive Steering Axles Excluding RS and RT Series (Rear
Revised 10-00 $2.50 Single Reduction Differential Carriers Maintenance Manual 5 Standard Carriers Including: Single Axles, Rear of Tandem Axles, Front Drive Steering Axles Excluding RS and RT Series (Rear
Single-Reduction Differential Carriers
 Revised 10-06 Single-Reduction Differential Carriers Maintenance Manual 5 Standard Carriers Including: Single Axles, Rear of Tandem Axles, Front Drive Steering Axles Excluding RS and RT Series (Rear Only),
Revised 10-06 Single-Reduction Differential Carriers Maintenance Manual 5 Standard Carriers Including: Single Axles, Rear of Tandem Axles, Front Drive Steering Axles Excluding RS and RT Series (Rear Only),
Single-Reduction Differential Carriers
 Revised 0-0 Single-Reduction Differential Carriers Single Rear Drive Axles, Rear-Rear Tandem Drive Axles and Front Drive Steer Axles Maintenance Manual 5A RS and RT Series Single-Reduction Axles (Single,
Revised 0-0 Single-Reduction Differential Carriers Single Rear Drive Axles, Rear-Rear Tandem Drive Axles and Front Drive Steer Axles Maintenance Manual 5A RS and RT Series Single-Reduction Axles (Single,
Single Rear Drive Axles, Rear-Rear Tandem Drive Axles and Front Drive Steer Axles Revised 02-18
 Maintenance Manual 5A Single-Reduction Differential Carriers Single Rear Drive Axles, Rear-Rear Tandem Drive Axles and Front Drive Steer Axles Revised 02-18 Service Notes About This Manual This manual
Maintenance Manual 5A Single-Reduction Differential Carriers Single Rear Drive Axles, Rear-Rear Tandem Drive Axles and Front Drive Steer Axles Revised 02-18 Service Notes About This Manual This manual
Rear Axle Single-Reduction Carrier
 Revised 08-0 Rear Axle Single-Reduction Carrier Model MS-3 Maintenance Manual MM-030 Service Notes Service Notes Notes About This Manual This manual provides instructions for Meritor s model MS-3 single-reduction
Revised 08-0 Rear Axle Single-Reduction Carrier Model MS-3 Maintenance Manual MM-030 Service Notes Service Notes Notes About This Manual This manual provides instructions for Meritor s model MS-3 single-reduction
Amboid Rear Differential Carrier
 Maintenance Manual MM-0250 Amboid Rear Differential Carrier Rear/Rear Carrier on MT-40-143MA-N Tandem Drive Axles Revised 09-05 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides instructions for the
Maintenance Manual MM-0250 Amboid Rear Differential Carrier Rear/Rear Carrier on MT-40-143MA-N Tandem Drive Axles Revised 09-05 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides instructions for the
Single-Reduction Forward Differential Carriers on Tandem and Tridem Axles
 Maintenance Manual 5L Single-Reduction Forward Differential Carriers on Tandem and Tridem Axles Revised 08-15 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service information for
Maintenance Manual 5L Single-Reduction Forward Differential Carriers on Tandem and Tridem Axles Revised 08-15 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service information for
Single-Reduction Forward Differential Carriers on Tandem and Tridem Axles
 Maintenance Manual 5L Single-Reduction Forward Differential Carriers on Tandem and Tridem Axles Revised 12-10 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service information for
Maintenance Manual 5L Single-Reduction Forward Differential Carriers on Tandem and Tridem Axles Revised 12-10 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service information for
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Yoke Removal and Installation Procedure for Meritor Drive Axles. Remove the Yoke and Pinion Seal WARNING CAUTION CAUTION.
 Issued 11-99 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Yoke Removal and Installation Procedure for Meritor Drive Axles Remove the Yoke and Pinion Seal Figure 1 WARNING Park the vehicle on a level surface. Block the wheels to
Issued 11-99 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Yoke Removal and Installation Procedure for Meritor Drive Axles Remove the Yoke and Pinion Seal Figure 1 WARNING Park the vehicle on a level surface. Block the wheels to
MAINTENANCE MANUAL. Differential Axle MS Edition october/11
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL Differential Axle MS - 113 Edition october/11 Index 1 - Notes to Technical Assistance... 03 2 - Exploded View MS-113... 04 3 - Exploded View MS-113 Plus... 05 4 - Introduction... 06
MAINTENANCE MANUAL Differential Axle MS - 113 Edition october/11 Index 1 - Notes to Technical Assistance... 03 2 - Exploded View MS-113... 04 3 - Exploded View MS-113 Plus... 05 4 - Introduction... 06
Off-Highway Axle Planetary Wheel Ends
 Maintenance Manual MM-1189 Off-Highway Axle Planetary Wheel Ends Revised 06-16 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides service and repair procedures for planetary wheel ends on off-highway
Maintenance Manual MM-1189 Off-Highway Axle Planetary Wheel Ends Revised 06-16 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides service and repair procedures for planetary wheel ends on off-highway
Maintenance Manual MM-0220 Single Reduction Differential Forward Carrier MD15. Issue November 2017
 Maintenance Manual MM-0220 Single Reduction Differential Forward Carrier MD15 Issue November 2017 Service Notes Before You Begin This publication provides installation and maintenance procedures for the
Maintenance Manual MM-0220 Single Reduction Differential Forward Carrier MD15 Issue November 2017 Service Notes Before You Begin This publication provides installation and maintenance procedures for the
Input Adjusting Ring Leak Repair Procedure for Meritor MT-14X Series Forward Differential Carriers
 Revised 01-16 Technical Bulletin Input Adjusting Ring Leak Repair Procedure for Meritor MT-14X Series Forward Differential Carriers Revised 1 Technical 01- Bulletin 16 Hazard Alert Messages Read and observe
Revised 01-16 Technical Bulletin Input Adjusting Ring Leak Repair Procedure for Meritor MT-14X Series Forward Differential Carriers Revised 1 Technical 01- Bulletin 16 Hazard Alert Messages Read and observe
Amboid Rear Differential Carrier
 Maintenance Manual MM-0990 Amboid Rear Differential Carrier Rear/Rear Carrier on MT-40-14X Series Tandem Drive Axles Revised 09-15 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides instructions for
Maintenance Manual MM-0990 Amboid Rear Differential Carrier Rear/Rear Carrier on MT-40-14X Series Tandem Drive Axles Revised 09-15 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides instructions for
TL (TIL03029) REPAIR MANUAL. Telma model FN72-40 replacement on Arvin Meritor forward tandem carrier. Page 1 of JUL-11.
 REPAIR MANUAL Telma model FN72-40 replacement on Arvin Meritor forward tandem carrier Page 1 of 10 29-JUL-11 Exploded view P/N: FE962100 Stator Carrier Kit Includes: Qty Description Telma P/N 1 Stator
REPAIR MANUAL Telma model FN72-40 replacement on Arvin Meritor forward tandem carrier Page 1 of 10 29-JUL-11 Exploded view P/N: FE962100 Stator Carrier Kit Includes: Qty Description Telma P/N 1 Stator
2012 Expedition, Navigator Workshop Manual
 Item Part Number Description 1 W720586 Differential housing cover bolt (12 required) 2 4033 Differential housing cover 3 Differential bearing cap bolts (part of 4010) (4 required) 4 Differential bearing
Item Part Number Description 1 W720586 Differential housing cover bolt (12 required) 2 4033 Differential housing cover 3 Differential bearing cap bolts (part of 4010) (4 required) 4 Differential bearing
DRIVE AXLE Nissan 240SX DESCRIPTION & OPERATION AXLE RATIO & IDENTIFICATION AXLE SHAFT & BEARING R & I DRIVE SHAFT R & I
 DRIVE AXLE 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 DRIVE AXLES Rear Axle - R200 240SX, 300ZX DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The axle assembly is a hypoid type gear with integral carrier housing. The pinion bearing preload adjustment
DRIVE AXLE 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 DRIVE AXLES Rear Axle - R200 240SX, 300ZX DESCRIPTION & OPERATION The axle assembly is a hypoid type gear with integral carrier housing. The pinion bearing preload adjustment
Transmission Overhaul Procedures-Bench Service
 How to Assemble the Lower Reverse Idler Gear Assembly Special Instructions In 1996 Eaton changed the reverse idler system design. In the nut design, the reverse idler bearing was lubricated through a hole
How to Assemble the Lower Reverse Idler Gear Assembly Special Instructions In 1996 Eaton changed the reverse idler system design. In the nut design, the reverse idler bearing was lubricated through a hole
Maintenance Instructions
 General Note These instructions contain information common to more than one model of Bevel Gear Drive. To simplify reading, similar models have been grouped as follows: GROUP 1 Models 11, 0, 1,, (illustrated),,
General Note These instructions contain information common to more than one model of Bevel Gear Drive. To simplify reading, similar models have been grouped as follows: GROUP 1 Models 11, 0, 1,, (illustrated),,
TO INDEX DIFFERENTIAL FRONT DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER OIL SEAL (4WD) FRONT DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY (4WD) REAR DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER OIL SEAL
 TO INDEX DRIVE LINE / AXLE DIFFERENTIAL DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS.............................................. OPERATION CHECK......................................... PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE.................................
TO INDEX DRIVE LINE / AXLE DIFFERENTIAL DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS.............................................. OPERATION CHECK......................................... PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE.................................
T-276 Two-Speed Carrier Mounted Input Transmission Transmission montée en entrée de nez de pont à deux vitesses
 TM T-276 Two-Speed Carrier Mounted Input Transmission Transmission montée en entrée de nez de pont à deux vitesses Maintenance Manual MM5.2 Manuel de maintenance MM5.2 Issued 10-03 Edité Octobre 03 Models
TM T-276 Two-Speed Carrier Mounted Input Transmission Transmission montée en entrée de nez de pont à deux vitesses Maintenance Manual MM5.2 Manuel de maintenance MM5.2 Issued 10-03 Edité Octobre 03 Models
MANUAL TRANSAXLE Return to Main Table of Contents
 MANUAL TRANSAXLE Return to Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTROL... 12 SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY... 14 MANUAL TRANSAXLE... 15 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY... 17 FIFTH SPEED SYNCHRONIZER
MANUAL TRANSAXLE Return to Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTROL... 12 SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY... 14 MANUAL TRANSAXLE... 15 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY... 17 FIFTH SPEED SYNCHRONIZER
TC Series Rear Axle. Table of Contents. TC Series Rear Axle
 TC Series Rear Axle Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Safety...2 Warnings and Cautions...2 Introduction...2 Description of Operation...2 Service Parts and Axle Identification...3 Special Tools...3
TC Series Rear Axle Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Safety...2 Warnings and Cautions...2 Introduction...2 Description of Operation...2 Service Parts and Axle Identification...3 Special Tools...3
1984 Dodge W250 PICKUP
 1984 Dodge W250 PICKUP Submodel: Engine Type: V8 Liters: 5.2 Fuel Delivery: CARB Fuel: GAS Dana 44 MODELS THROUGH 1984 2. Raise and safely support the vehicle, then remove the wheel hub and bearings as
1984 Dodge W250 PICKUP Submodel: Engine Type: V8 Liters: 5.2 Fuel Delivery: CARB Fuel: GAS Dana 44 MODELS THROUGH 1984 2. Raise and safely support the vehicle, then remove the wheel hub and bearings as
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION AXLE SHAFTS & BEARINGS Removal CAUTION: Failure to turn off air suspension power before raising vehicle may result in unexpected inflation or deflation of air springs. DO NOT reconnect
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION AXLE SHAFTS & BEARINGS Removal CAUTION: Failure to turn off air suspension power before raising vehicle may result in unexpected inflation or deflation of air springs. DO NOT reconnect
Input Cage Leak Repair
 Revised 10-12 Input Cage Leak Repair Technical Bulletin Meritor Forward Tandem Drive Axles RP 140 and 160 Series (With a Pump) MD and RD 140 and 160 Series (Without a Pump) Revised 1 Technical 10-12 Bulletin
Revised 10-12 Input Cage Leak Repair Technical Bulletin Meritor Forward Tandem Drive Axles RP 140 and 160 Series (With a Pump) MD and RD 140 and 160 Series (Without a Pump) Revised 1 Technical 10-12 Bulletin
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
 205-03-1 Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 205-03-1 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s) 2-Jaw Puller 205-D072 (D97L-4221-A) Special Tool(s) Carrier Bearing Replacer
205-03-1 Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 205-03-1 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s) 2-Jaw Puller 205-D072 (D97L-4221-A) Special Tool(s) Carrier Bearing Replacer
TROUBLESHOOTING SPECIAL TOOL ASSEMBLY AND ADJUSTMENT
 1 INDEX Models FD, FE, FF and SG REAR AXLE 10-1 10-108E-07 CHAPTER 10 REAR AXLE Models FD, FE, FF and SG TROUBLESHOOTING...10-2 10 SPECIAL TOOL...10-3 WHEEL HUB AND RELATED PARTS DISASSEMBLY...10-7 INSPECTION...10-9
1 INDEX Models FD, FE, FF and SG REAR AXLE 10-1 10-108E-07 CHAPTER 10 REAR AXLE Models FD, FE, FF and SG TROUBLESHOOTING...10-2 10 SPECIAL TOOL...10-3 WHEEL HUB AND RELATED PARTS DISASSEMBLY...10-7 INSPECTION...10-9
PROPELLER SHAFT & DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER SECTIONPD CONTENTS
 PROPELLER SHAFT & DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER SECTIONPD CONTENTS PREPARATION...2 PROPELLER SHAFT...5 On-Vehicle Service...6 Removal and Installation...7 Inspection...7 Disassembly...7 Assembly...8 ON-VEHICLE
PROPELLER SHAFT & DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER SECTIONPD CONTENTS PREPARATION...2 PROPELLER SHAFT...5 On-Vehicle Service...6 Removal and Installation...7 Inspection...7 Disassembly...7 Assembly...8 ON-VEHICLE
Slack Adjuster. Table of Contents
 Slack Adjuster Table of Contents Sub-Headings Automatic Slack Adjuster Service 2 PayMaster Automatic Slack Adjuster 2 How the Automatic Slack Adjuster Works 2 Pressed-In, Sealed Actuator Boot 3 Handed
Slack Adjuster Table of Contents Sub-Headings Automatic Slack Adjuster Service 2 PayMaster Automatic Slack Adjuster 2 How the Automatic Slack Adjuster Works 2 Pressed-In, Sealed Actuator Boot 3 Handed
1999 F-150/250 Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 30 SECTION 205-03: Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 1999 F-150/250 Workshop Manual DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Procedure revision date: 01/08/2003 Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s)
Page 1 of 30 SECTION 205-03: Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 1999 F-150/250 Workshop Manual DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Procedure revision date: 01/08/2003 Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s)
Differential Ring And Pinion
 SECTION 205-02B: Rear Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual IN-VEHICLE REPAIR Procedure revision date: 01/06/2010 Differential Ring And Pinion Special Tool(s) 2 Jaw
SECTION 205-02B: Rear Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual IN-VEHICLE REPAIR Procedure revision date: 01/06/2010 Differential Ring And Pinion Special Tool(s) 2 Jaw
Steer Axles. Spicer. Service Manual. AXSM-0070 November Front Drive Steer Axle Model 60
 Spicer Steer Axles Service Manual AXSM-0070 November 2017 Front Drive Steer Axle Model 60 General Information The description and specifications contained in this service publication are current at the
Spicer Steer Axles Service Manual AXSM-0070 November 2017 Front Drive Steer Axle Model 60 General Information The description and specifications contained in this service publication are current at the
SECTION Front Drive Axle/Differential
 205-03-i Front Drive Axle/Differential 205-03-i SECTION 205-03 Front Drive Axle/Differential CONTENTS PAGE Axle... 205-03-2 205-03-2 Front Drive Axle/Differential 205-03-2 Axle Special Tool(s) C-Frame
205-03-i Front Drive Axle/Differential 205-03-i SECTION 205-03 Front Drive Axle/Differential CONTENTS PAGE Axle... 205-03-2 205-03-2 Front Drive Axle/Differential 205-03-2 Axle Special Tool(s) C-Frame
DRIVE AXLE Volvo 960 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION AXLE IDENTIFICATION DRIVE AXLES Volvo Differentials & Axle Shafts
 DRIVE AXLE 1994 Volvo 960 1994 DRIVE AXLES Volvo Differentials & Axle Shafts 960 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION All 960 station wagon models use type 1041 rear axle assembly. All 960 4-door models use type 1045
DRIVE AXLE 1994 Volvo 960 1994 DRIVE AXLES Volvo Differentials & Axle Shafts 960 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION All 960 station wagon models use type 1041 rear axle assembly. All 960 4-door models use type 1045
2005 Toyota RAV AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS U240E & U241E Overhaul
 2001-05 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS U240E & U241E Overhaul APPLICATION CAUTION: Flush oil cooler and oil cooler lines prior to transaxle installation. Oil cooling system contamination may cause premature transaxle
2001-05 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS U240E & U241E Overhaul APPLICATION CAUTION: Flush oil cooler and oil cooler lines prior to transaxle installation. Oil cooling system contamination may cause premature transaxle
DRIVE AXLE - INTEGRAL HOUSING
 DRIVE AXLE - INTEGRAL HOUSING 1993 Toyota Celica 1993 DRIVE AXLES Toyota Differentials & Axle Shafts - Integral Housing Toyota; Celica All-Trac DESCRIPTION Drive axle assembly is a hypoid type with integral
DRIVE AXLE - INTEGRAL HOUSING 1993 Toyota Celica 1993 DRIVE AXLES Toyota Differentials & Axle Shafts - Integral Housing Toyota; Celica All-Trac DESCRIPTION Drive axle assembly is a hypoid type with integral
TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
 DR TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21-1 TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE TABLE OF CONTENTS page MANUAL TRANSMISSION- G56- SERVICE INFORMATION...1 MANUAL TRANSMISSION- GETRAG 238- SERVICEINFORMATION...69 MANUAL
DR TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21-1 TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE TABLE OF CONTENTS page MANUAL TRANSMISSION- G56- SERVICE INFORMATION...1 MANUAL TRANSMISSION- GETRAG 238- SERVICEINFORMATION...69 MANUAL
Maintenance Information
 16573370 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder 99V Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16573370 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder 99V Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. TP Issued Servicing Rockwell s TB Series Trailer Axles with Unitized Hub Assemblies
 TECHNICAL BULLETIN TP-96175 Issued 12-96 Servicing Rockwell s TB Series Trailer Axles with Unitized Hub Assemblies TB Series Trailer Axles Introduction Rockwell s TB series trailer axle features a permanently
TECHNICAL BULLETIN TP-96175 Issued 12-96 Servicing Rockwell s TB Series Trailer Axles with Unitized Hub Assemblies TB Series Trailer Axles Introduction Rockwell s TB series trailer axle features a permanently
Maintenance Information
 16575128 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Sander or Polisher 77A Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid
16575128 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Sander or Polisher 77A Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid
LIFT TRUCK SERIES: G35S-2 G40S-2 G45S-2 G40SC-2 G45SC-2 G50SC-2. November 15, 2000 CODE 3150 LT3150-L0 SUBJECT: NEW DRIVE AXLE
 LIFT TRUCK SERIES: G35S-2 G40S-2 G45S-2 G40SC-2 G45SC-2 G50SC-2 November 15, 2000 CODE 3150 LT3150-L0 SUBJECT: NEW DRIVE AXLE A new drive axle has been introduced in the above model lift trucks. The purpose
LIFT TRUCK SERIES: G35S-2 G40S-2 G45S-2 G40SC-2 G45SC-2 G50SC-2 November 15, 2000 CODE 3150 LT3150-L0 SUBJECT: NEW DRIVE AXLE A new drive axle has been introduced in the above model lift trucks. The purpose
DF 15. DIFFERENTIAL 1GR-FE FRONT DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY (for 4WD) REMOVAL
 DIFFERENTIAL 1GR-FE FRONT DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY (for 4WD) 15 REMOVAL 1. REMOVE FRONT WHEELS 2. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER ASSEMBLY (a) Remove the 6 bolts and engine under cover assembly. 3.
DIFFERENTIAL 1GR-FE FRONT DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY (for 4WD) 15 REMOVAL 1. REMOVE FRONT WHEELS 2. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER ASSEMBLY (a) Remove the 6 bolts and engine under cover assembly. 3.
SISU DP-330 DRIVE GEAR. Maintenance Manual
 SISU DP-330 DRIVE GEAR Maintenance Manual Sisu Axles, Inc. Autotehtaantie 1 PO Box 189 Fin-13101 Hameenlinna Finland Phone +358 204 55 2999 Fax +358 204 55 2900 DP330DG.PDF (3/2007) TABLE OF CONTENTS
SISU DP-330 DRIVE GEAR Maintenance Manual Sisu Axles, Inc. Autotehtaantie 1 PO Box 189 Fin-13101 Hameenlinna Finland Phone +358 204 55 2999 Fax +358 204 55 2900 DP330DG.PDF (3/2007) TABLE OF CONTENTS
4.2 WATER PUMP (GEAR CASE MOUNTED AND LATER) (GCM)
 SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL 4.2 WATER PUMP (GEAR CASE MOUNTED - 1991 AND LATER) (GCM) The centrifugal-type water pump circulates the engine coolant through the cooling system. The pump is mounted on the rear
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL 4.2 WATER PUMP (GEAR CASE MOUNTED - 1991 AND LATER) (GCM) The centrifugal-type water pump circulates the engine coolant through the cooling system. The pump is mounted on the rear
Amarillo PUMP DRIVES (250 HP THROUGH 350 HP) INSTRUCTIONS FOR REPAIRING MODELS 250, 300, and 350
 Amarillo PUMP DRIVES (250 HP THROUGH 350 HP) INSTRUCTIONS FOR REPAIRING MODELS 250, 300, and 350 Amarillo Right Angle Pump Drives, if properly installed and maintained, should provide years of service
Amarillo PUMP DRIVES (250 HP THROUGH 350 HP) INSTRUCTIONS FOR REPAIRING MODELS 250, 300, and 350 Amarillo Right Angle Pump Drives, if properly installed and maintained, should provide years of service
Installation Instructions
 Preparing your vehicle to install your brake system upgrade 1. Rack the vehicle. 2. If you don t have a rack, then you must take extra safety precautions. 3. Choose a firmly packed and level ground to
Preparing your vehicle to install your brake system upgrade 1. Rack the vehicle. 2. If you don t have a rack, then you must take extra safety precautions. 3. Choose a firmly packed and level ground to
Gear Products Inc N. 161st E. Ave. Tulsa, OK Phone (918) Fax (918)
 SERVICE MANUAL Disassembly & Assembly Procedures Worm Gear Swing Drive 003 Series Gear Products Inc. 1111 N. 161st E. Ave. Tulsa, OK 74116 Phone (918) 234-3044 Fax (918) 234-3455 Worm Gear Swing Drive
SERVICE MANUAL Disassembly & Assembly Procedures Worm Gear Swing Drive 003 Series Gear Products Inc. 1111 N. 161st E. Ave. Tulsa, OK 74116 Phone (918) 234-3044 Fax (918) 234-3455 Worm Gear Swing Drive
Injector. General Information CAUTION. Use only the specified injector for the engine.
 Page 1 of 32 006-026 Injector General Information CAUTION Use only the specified injector for the engine. All engines use closed nozzle, hole-type injectors. However, the injectors can have different part
Page 1 of 32 006-026 Injector General Information CAUTION Use only the specified injector for the engine. All engines use closed nozzle, hole-type injectors. However, the injectors can have different part
Medium-Duty Front Drive Steer Axles
 Maintenance Manual MM-0170 Medium-Duty Front Drive Steer Axles MX-120 and MX-120-EVO Series Applies to 120 Standard and 120-HR High-Retardation Carriers Revised 02-17 Service Notes About This Manual This
Maintenance Manual MM-0170 Medium-Duty Front Drive Steer Axles MX-120 and MX-120-EVO Series Applies to 120 Standard and 120-HR High-Retardation Carriers Revised 02-17 Service Notes About This Manual This
Installation Instructions
 Instructions Created by an: 86-95 Suzuki Samurai Samurai Front Axle Knuckle Rebuild Kits (SKU# SAX-KRK) Installation Instructions Revised 6-6-14 Suggested Tools: CAUTION: Safety glasses should be worn
Instructions Created by an: 86-95 Suzuki Samurai Samurai Front Axle Knuckle Rebuild Kits (SKU# SAX-KRK) Installation Instructions Revised 6-6-14 Suggested Tools: CAUTION: Safety glasses should be worn
REAR AXLE Click on the applicable bookmark to selected the required model year
 REAR AXLE 27-2 REAR AXLE General Information GENERAL INFORMATION 27100010118 The rear axle is a banjo-type semi-floating type. The axle shaft bearings are: *Single taper bearings for vehicles without
REAR AXLE 27-2 REAR AXLE General Information GENERAL INFORMATION 27100010118 The rear axle is a banjo-type semi-floating type. The axle shaft bearings are: *Single taper bearings for vehicles without
DF 43 DIFFERENTIAL REAR DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY REMOVAL
 DIFFERENTIAL REAR DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY 43 REMOVAL 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE BATTERY TERMINAL 2. REMOVE REAR WHEEL 3. DRAIN BRAKE FLUID 4. REMOVE REAR BRAKE DRUM SUB-ASSEMBLY (See page
DIFFERENTIAL REAR DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY 43 REMOVAL 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE BATTERY TERMINAL 2. REMOVE REAR WHEEL 3. DRAIN BRAKE FLUID 4. REMOVE REAR BRAKE DRUM SUB-ASSEMBLY (See page
PROPELLER SHAFT & DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER SECTIONPD CONTENTS IDX. PROPELLER SHAFT...3 Preparation...3 C200. REAR FINAL DRIVE...40 Preparation...
 PROPELLER SHAFT & DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER SECTIONPD GI MA EM LC EC CONTENTS FE PROPELLER SHAFT...3 Preparation...3 SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS...3 Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH) Troubleshooting...4 NVH TROUBLESHOOTING
PROPELLER SHAFT & DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER SECTIONPD GI MA EM LC EC CONTENTS FE PROPELLER SHAFT...3 Preparation...3 SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS...3 Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH) Troubleshooting...4 NVH TROUBLESHOOTING
Steering Gearbox Disassembly
 Steering Gearbox Disassembly Steering Rack Disassembly 5. Unbend the lock washer. Before disassembling the gearbox, wash it off with solvent and a brush. Do not dip seals and O-rings in solvent. 1. Remove
Steering Gearbox Disassembly Steering Rack Disassembly 5. Unbend the lock washer. Before disassembling the gearbox, wash it off with solvent and a brush. Do not dip seals and O-rings in solvent. 1. Remove
1988 Chevrolet Pickup V SUSPENSION - FRONT (4WD)' 'Front Suspension - "V" Series 1988 SUSPENSION - FRONT (4WD) Front Suspension - "V" Series
 1988 SUSPENSION - FRONT (4WD) Front Suspension - "V" Series DESCRIPTION NOTE: Vehicle serial numbers used in this article has been abbreviated for common reference to Chevrolet and GMC models. Chevrolet
1988 SUSPENSION - FRONT (4WD) Front Suspension - "V" Series DESCRIPTION NOTE: Vehicle serial numbers used in this article has been abbreviated for common reference to Chevrolet and GMC models. Chevrolet
DIFFERENTIALS & AXLE SHAFTS
 DIFFERENTIALS & AXLE SHAFTS 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2000-01 DRIVE AXLES General Motors Differentials & Axle Shafts Chevrolet; Camaro Pontiac; Firebird DESCRIPTION & OPERATION Drive axle is a semi-floating,
DIFFERENTIALS & AXLE SHAFTS 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2000-01 DRIVE AXLES General Motors Differentials & Axle Shafts Chevrolet; Camaro Pontiac; Firebird DESCRIPTION & OPERATION Drive axle is a semi-floating,
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION CENTER BEARING SUPPORT ASSEMBLY Removal 1. With transmission in neutral and parking brake off, raise vehicle. Scribe alignment marks on all flange/yokes and slip joints to be disassembled
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION CENTER BEARING SUPPORT ASSEMBLY Removal 1. With transmission in neutral and parking brake off, raise vehicle. Scribe alignment marks on all flange/yokes and slip joints to be disassembled
INSPECTION DF 80. Install the rear differential side gear and rear differential spider onto the differential case RH.
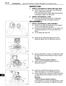 80 INSPECTION 1. INSPECT DIFFERENTIAL PINION AND SIDE GEAR (a) Check that there is no damage to the differential pinion or differential side gear. If the differential pinion and/or differential side gear
80 INSPECTION 1. INSPECT DIFFERENTIAL PINION AND SIDE GEAR (a) Check that there is no damage to the differential pinion or differential side gear. If the differential pinion and/or differential side gear
SPECIAL TOOLS Dodge Pickup 5.9L Eng R3500. Fig 1: Identifying Remover C-3985-B (Special Tool) 9/6/13 Printer Friendly View
 Procedures 2003 Dodge Pickup 5.9L Eng R3500 manual transmission SPECIAL TOOLS Fig 1: Identifying Remover C-3985-B (Special Tool) www2.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=true&ymms=false&classname=
Procedures 2003 Dodge Pickup 5.9L Eng R3500 manual transmission SPECIAL TOOLS Fig 1: Identifying Remover C-3985-B (Special Tool) www2.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=true&ymms=false&classname=
DF 78. HINT: Face the rough side of the thrust washer marked by # to the differential case. INSPECTION
 78 DIFFERENTIAL REAR DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY (w/ Differential Lock) Face the rough side of the thrust washer marked by # to the differential case. INSPECTION 1. DIFFERENTIAL SIDE GEAR (w/ LSD Differential)
78 DIFFERENTIAL REAR DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER ASSEMBLY (w/ Differential Lock) Face the rough side of the thrust washer marked by # to the differential case. INSPECTION 1. DIFFERENTIAL SIDE GEAR (w/ LSD Differential)
 DRUM BRAKE RIMS Periodic inspection of drum brake rims is necessary to determine indications of uneven or excessive wear. In general, brake rim failures other that regular wear are caused by brake linings
DRUM BRAKE RIMS Periodic inspection of drum brake rims is necessary to determine indications of uneven or excessive wear. In general, brake rim failures other that regular wear are caused by brake linings
-7 I Remove the brake shoe return springs.
 REAR AXLE 9-A.REAR AXLE SHAFT... 9: 1 9.A.1. Removing Rear Axle Shaft... 9 : 1 9.A.2 Disassembling Rear Axle Shaft... 9 : 2 9.A.3. Inspecting Rear Axle Shaft and Bearing... 9 : 3 9.A-4 Assembling Rear
REAR AXLE 9-A.REAR AXLE SHAFT... 9: 1 9.A.1. Removing Rear Axle Shaft... 9 : 1 9.A.2 Disassembling Rear Axle Shaft... 9 : 2 9.A.3. Inspecting Rear Axle Shaft and Bearing... 9 : 3 9.A-4 Assembling Rear
Single reduction Differential Carrier Series 7 - MS15 - MS16 - MS17 - MR15 Revised April 2003
 an ArvinMeritor brand Maintenance manual no. MM-0140 Single reduction Differential Carrier Series 7 - MS15 - MS16 - MS17 - MR15 Revised April 2003 Table of contents pg. 05 Section 1: Introduction 06 Description
an ArvinMeritor brand Maintenance manual no. MM-0140 Single reduction Differential Carrier Series 7 - MS15 - MS16 - MS17 - MR15 Revised April 2003 Table of contents pg. 05 Section 1: Introduction 06 Description
SERVICE MANUAL L130B / L4130 Series Logstacker Drive Axle With Bolt-On Stub End Retainer
 SERVICE MANUAL L130B / L4130 Series Logstacker Drive Axle With Bolt-On Stub End Retainer Page 1 Allied Form #80-930 Rev 07/2009 SERVICE MANUAL LOG STACKER DA202 DRIVE AXLE TABLE OF CONTENTS PROCEDURE FOR
SERVICE MANUAL L130B / L4130 Series Logstacker Drive Axle With Bolt-On Stub End Retainer Page 1 Allied Form #80-930 Rev 07/2009 SERVICE MANUAL LOG STACKER DA202 DRIVE AXLE TABLE OF CONTENTS PROCEDURE FOR
 Page 1 of 15 Transmission, Model S5-42 ZF Model S5-42 ZF Disassembly NOTE: For 4x4 and F-Super Duty vehicles, skip to Step 5. 1. Attach the transmission to the Bench Mounted Holding Fixture T57L-500-B
Page 1 of 15 Transmission, Model S5-42 ZF Model S5-42 ZF Disassembly NOTE: For 4x4 and F-Super Duty vehicles, skip to Step 5. 1. Attach the transmission to the Bench Mounted Holding Fixture T57L-500-B
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Servicing Meritor TM EASY STEER PLUS TM Series Unitized Truck Hub Unit Assembly
 TP-9819 Revised 12-97 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Servicing Meritor TM EASY STEER PLUS TM Series Unitized Truck Hub Unit Assembly Attention Freightliner dealers and direct warranty customers. Please discard this
TP-9819 Revised 12-97 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Servicing Meritor TM EASY STEER PLUS TM Series Unitized Truck Hub Unit Assembly Attention Freightliner dealers and direct warranty customers. Please discard this
MAINTENANCE MANUAL. Drivelines MM Edition october/11
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL Drivelines MM-96147 Edition october/11 Index 1 - Drivelines... 03 2 - Introduction... 05 3 - Inspection... 06 4 - RPL Series PermalubeTM... 12 5 - Full-Round... 23 6 - Wing-Style PermalubeTM...
MAINTENANCE MANUAL Drivelines MM-96147 Edition october/11 Index 1 - Drivelines... 03 2 - Introduction... 05 3 - Inspection... 06 4 - RPL Series PermalubeTM... 12 5 - Full-Round... 23 6 - Wing-Style PermalubeTM...
REAR AXLE Click on the applicable bookmark to selected the required model year
 REAR AXLE 27-1 REAR AXLE CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS................. 3 LUBRICANTS.............................. 3 SEALANTS AND ADHESIVES.............. 4 SPECIAL
REAR AXLE 27-1 REAR AXLE CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS................. 3 LUBRICANTS.............................. 3 SEALANTS AND ADHESIVES.............. 4 SPECIAL
STERNDRIVE UNIT 3 B GEAR HOUSINGS MR/ALPHA ONE/ALPHA ONE SS
 STERNDRIVE UNIT 3 B 23146 GEAR HOUSINGS MR/ALPHA ONE/ALPHA ONE SS Table of Contents Page Identification........................... 3B-1 Specifications.......................... 3B-1 Torque Specifications................
STERNDRIVE UNIT 3 B 23146 GEAR HOUSINGS MR/ALPHA ONE/ALPHA ONE SS Table of Contents Page Identification........................... 3B-1 Specifications.......................... 3B-1 Torque Specifications................
MC27610 Planetary Drive Axle
 Maintenance Manual MM-0727 MC27610 Planetary Drive Axle Revised 09-07 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service procedures for Meritor s MC27610 planetary drive axle.
Maintenance Manual MM-0727 MC27610 Planetary Drive Axle Revised 09-07 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service procedures for Meritor s MC27610 planetary drive axle.
SISU MP-330 DRIVE GEAR. Maintenance Manual
 SISU MP-330 DRIVE GEAR Maintenance Manual Sisu Axles, Inc. Autotehtaantie 1 PO Box 189 Fin-13101 Hameenlinna Finland Phone +358 204 55 2999 Fax +358 204 55 2900 MP330DG.PDF (4/2007) TABLE OF CONTENTS
SISU MP-330 DRIVE GEAR Maintenance Manual Sisu Axles, Inc. Autotehtaantie 1 PO Box 189 Fin-13101 Hameenlinna Finland Phone +358 204 55 2999 Fax +358 204 55 2900 MP330DG.PDF (4/2007) TABLE OF CONTENTS
Service Manual. Spicer Single Drive Axles. Single Reduction & Single Reduction with Differential Lock AXSM-0048 October 2015
 Spicer Single Drive Axles Service Manual Single Reduction & Single Reduction with Differential Lock AXSM-0048 October 05 5040S 9050S 9055S/D 065S/D 090S/D 065S/D 3070S/D 3080S/D 3085S/D 3090S/D 305S/D
Spicer Single Drive Axles Service Manual Single Reduction & Single Reduction with Differential Lock AXSM-0048 October 05 5040S 9050S 9055S/D 065S/D 090S/D 065S/D 3070S/D 3080S/D 3085S/D 3090S/D 305S/D
1. General Description
 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATION 1. MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND FRONT DIFFERENTIAL Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear Front differential Center differential Final
1. General Description A: SPECIFICATION 1. MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND FRONT DIFFERENTIAL Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear Front differential Center differential Final
Maintenance Information
 16573321 Edition 3 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 61H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16573321 Edition 3 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 61H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
Overhaul Special Tools Required
 1 of 31 Overhaul - Special Tools Required - Cylinder end seal remover attachment, 07NAD-SR3020A - Pilot collar, 07GAF-PH70100 - Valve seal ring sizing tool, 07NAG-SR3090A - Ball joint boot clip guide,
1 of 31 Overhaul - Special Tools Required - Cylinder end seal remover attachment, 07NAD-SR3020A - Pilot collar, 07GAF-PH70100 - Valve seal ring sizing tool, 07NAG-SR3090A - Ball joint boot clip guide,
Maintenance Information
 16573347 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 88H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16573347 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 88H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
HIGH PERFORMANCE TRANSMISSION PARTS Instructions. Line Pressure Booster Kit. TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit. Line Pressure Modulator Plunger Valve Kit
 Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
PROPELLER SHAFT / / PROPELLER SHAFT GENERAL OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. SPECIFICATION...
 3310-01/3310-00/3310-06 GENERAL 1. SPECIFICATION... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. OVERVIEW... 2. COMPONENT LOCATOR... 3310-01 FRONT... 3310-06 REAR... 3310-00 DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY PROPELLER
3310-01/3310-00/3310-06 GENERAL 1. SPECIFICATION... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. OVERVIEW... 2. COMPONENT LOCATOR... 3310-01 FRONT... 3310-06 REAR... 3310-00 DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY PROPELLER
Front Suspension 2015 E-Series REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 08/11/2014. Axle
 204-01 Front Suspension 2015 E-Series REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 08/11/2014 Axle 1 N620604 Axle pivot nut 2 N806859 Axle pivot bolt 3 3007 LH/ 3006 RH LH/ 3006 RH Axle Removal NOTICE:
204-01 Front Suspension 2015 E-Series REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Procedure revision date: 08/11/2014 Axle 1 N620604 Axle pivot nut 2 N806859 Axle pivot bolt 3 3007 LH/ 3006 RH LH/ 3006 RH Axle Removal NOTICE:
DRIVE AXLE - 4WD MODELS WITH INTEGRAL HOUSING
 DRIVE AXLE - 4WD MODELS WITH INTEGRAL HOUSING 1988 Toyota Celica DRIVE AXLES Toyota Integral Housing Celica (Rear) DESCRIPTION housing. Drive axle assembly is hypoid type with integral carrier AXLE RATIO
DRIVE AXLE - 4WD MODELS WITH INTEGRAL HOUSING 1988 Toyota Celica DRIVE AXLES Toyota Integral Housing Celica (Rear) DESCRIPTION housing. Drive axle assembly is hypoid type with integral carrier AXLE RATIO
TC20 Chain Driven Power Take-Off Overhaul Instructions
 TC20 Chain Driven Power Take-Off Overhaul Instructions Table of Contents Section Page Introduction 4 Ordering Repair Parts 4 General Information 5 Special Tools 6 Disassembly See Page 2 Reassembly See
TC20 Chain Driven Power Take-Off Overhaul Instructions Table of Contents Section Page Introduction 4 Ordering Repair Parts 4 General Information 5 Special Tools 6 Disassembly See Page 2 Reassembly See
Brake System H TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair
![Brake System H TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair Brake System H TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair](/thumbs/86/93834005.jpg) HMM180001 Brake System H1.5-1.8TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H2.5-3.5TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly fastened,
HMM180001 Brake System H1.5-1.8TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H2.5-3.5TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly fastened,
HIGH PERFORMANCE TRANSMISSION PARTS Instructions. Line Pressure Booster Kit. TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit. Line Pressure Modulator Plunger Valve Kit
 Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
Wheel end bearing and seal installation guide. Automotive edition Featuring front and rear wheel drive models
 Wheel end bearing and seal installation guide Automotive edition Featuring front and rear wheel drive models Introduction Contents The SKF Seal and Bearing lnstallation Guide (SKF #457809) covers the removal
Wheel end bearing and seal installation guide Automotive edition Featuring front and rear wheel drive models Introduction Contents The SKF Seal and Bearing lnstallation Guide (SKF #457809) covers the removal
4. Rear Differential REAR DIFFERENTIAL
 DIFFERENTIALS 4. Rear Differential A: REMOVAL 1) Set the vehicle on a lift. 2) Disconnect the ground cable from battery. 3) Move the select lever or gear shift lever to N. 4) Release the parking brake.
DIFFERENTIALS 4. Rear Differential A: REMOVAL 1) Set the vehicle on a lift. 2) Disconnect the ground cable from battery. 3) Move the select lever or gear shift lever to N. 4) Release the parking brake.
LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL INSTALLATION
 Installation of the limited slip gear can be done with axle out of car or with car lifted to gain access from underneath. Refer to repair manual for proper lifting instructions if car is to be lifted.
Installation of the limited slip gear can be done with axle out of car or with car lifted to gain access from underneath. Refer to repair manual for proper lifting instructions if car is to be lifted.
REAR AXLE AND SUSPENSION RA 1
 REAR AXLE AND SUSPENSION RA1 RA2 REAR AXLE AND SUSPENSION Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Wanders/pulls Tires worn or improperly inflated Replace tires or inflate to
REAR AXLE AND SUSPENSION RA1 RA2 REAR AXLE AND SUSPENSION Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Wanders/pulls Tires worn or improperly inflated Replace tires or inflate to
Dana Spicer Tandem Drive Axles
 Dana Spicer Tandem Drive Axles S400-S Service Manual AXSM-1951 September 1997 For the most current information, visit the Roadranger web site at www.roadranger.com TABLE OF CONTENTS Axle Identification...
Dana Spicer Tandem Drive Axles S400-S Service Manual AXSM-1951 September 1997 For the most current information, visit the Roadranger web site at www.roadranger.com TABLE OF CONTENTS Axle Identification...
This file is available for free download at
 This file is available for free download at http://www.iluvmyrx7.com This file is fully text-searchable select Edit and Find and type in what you re looking for. This file is intended more for online viewing
This file is available for free download at http://www.iluvmyrx7.com This file is fully text-searchable select Edit and Find and type in what you re looking for. This file is intended more for online viewing
Maintenance Information
 45528270 Edition 1 June 2007 Barring Motor T480 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this Barring Motor.
45528270 Edition 1 June 2007 Barring Motor T480 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this Barring Motor.
SERVICE MANUAL TC 180 TRANSFER CASE SERVICE MANUAL
 TC 180 TRANSFER CASE SERVICE MANUAL Table of Contents MODEL TC-180, Transfer Case........1.0 Introduction.......1.1 Assembly Views.......... 1.2 LUBRICATION...... 2.0 Recommended Lubricants....2.1 Inspection.........
TC 180 TRANSFER CASE SERVICE MANUAL Table of Contents MODEL TC-180, Transfer Case........1.0 Introduction.......1.1 Assembly Views.......... 1.2 LUBRICATION...... 2.0 Recommended Lubricants....2.1 Inspection.........
1. General Description
 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATIONS 1. Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear 2. TRANSMISSION GEAR OIL Recommended oil Final Transfer 5-forward speeds with synchromesh
1. General Description A: SPECIFICATIONS 1. Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear 2. TRANSMISSION GEAR OIL Recommended oil Final Transfer 5-forward speeds with synchromesh
CLUTCH CONTENTS SERVICE DIAGNOSIS. (a) Worn or damaged disc assembly. (b) Grease or oil on disc facings. (c) Improperly adjusted cover assembly.
 CLUTCH CONTENTS -GROUP 6 Page CLUTCH HOUSING ALIGNMENT... 6 CLUTCH PEDAL FREE PLAY 1 CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING 5 CLUTCH RELEASE FORK... 5 CLUTCH SERVICING 2 PILOT BUSHING CRANKSHAFT TO TRANSMISSION DRIVE
CLUTCH CONTENTS -GROUP 6 Page CLUTCH HOUSING ALIGNMENT... 6 CLUTCH PEDAL FREE PLAY 1 CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING 5 CLUTCH RELEASE FORK... 5 CLUTCH SERVICING 2 PILOT BUSHING CRANKSHAFT TO TRANSMISSION DRIVE
REAR FINAL DRIVE SECTION RFD CONTENTS D DRIVELINE/AXLE RFD-1 RFD
 REAR FINAL DRIVE D DRIVELINE/AXLE SECTION RFD A REAR FINAL DRIVE B C RFD CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions... 2 PREPARATION... 3 Special Service Tools... 3 Commercial Service Tools... 5 NOISE, VIBRATION
REAR FINAL DRIVE D DRIVELINE/AXLE SECTION RFD A REAR FINAL DRIVE B C RFD CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions... 2 PREPARATION... 3 Special Service Tools... 3 Commercial Service Tools... 5 NOISE, VIBRATION
M Ring and Pinion Installation
 !!! PLEASE READ ALL OF THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PRIOR TO INSTALLATION. Axle Shaft Removal (1994-2012 Mustang typical) STEP 1: STEP 2: Remove the 10 differential housing cover bolts and drain
!!! PLEASE READ ALL OF THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PRIOR TO INSTALLATION. Axle Shaft Removal (1994-2012 Mustang typical) STEP 1: STEP 2: Remove the 10 differential housing cover bolts and drain
This file is available for free download at
 This file is available for free download at http://www.iluvmyrx7.com This file is fully text-searchable select Edit and Find and type in what you re looking for. This file is intended more for online viewing
This file is available for free download at http://www.iluvmyrx7.com This file is fully text-searchable select Edit and Find and type in what you re looking for. This file is intended more for online viewing
BRAKE SYSTEM Nissan 240SX DESCRIPTION BRAKE BLEEDING * PLEASE READ FIRST * BLEEDING PROCEDURES ADJUSTMENTS BRAKE PEDAL HEIGHT SPECS TABLE
 BRAKE SYSTEM 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 BRAKE SYSTEMS Nissan Disc & Drum Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar NX, Sentra, Stanza, 240SX, 300ZX DESCRIPTION All brake systems are hydraulically operated
BRAKE SYSTEM 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 BRAKE SYSTEMS Nissan Disc & Drum Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar NX, Sentra, Stanza, 240SX, 300ZX DESCRIPTION All brake systems are hydraulically operated
SA 82 Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ ADD) Disassembly and Assembly of Differential (with A.D.D.)
 SA82 SUSPENSION AND AXLE Disassembly and Assembly of Differential (with A.D.D.) DISASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL 1. REMOVE ACTUATOR (a) Remove the four bolts. (b) Using a hammer, remove the actuator. SA83 2.
SA82 SUSPENSION AND AXLE Disassembly and Assembly of Differential (with A.D.D.) DISASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL 1. REMOVE ACTUATOR (a) Remove the four bolts. (b) Using a hammer, remove the actuator. SA83 2.
Spicer Single Drive Axles. Service Manual. AXSM0056 September S170 Series S190 Series S590 Series
 Spicer Single Drive Axles Service Manual AXSM0056 September 03 S70 Series S90 Series S590 Series General Information General Information The description and specifications contained in this service publication
Spicer Single Drive Axles Service Manual AXSM0056 September 03 S70 Series S90 Series S590 Series General Information General Information The description and specifications contained in this service publication
