DC Generator. - The direction of current flow in the conductor is given by Fleming s right hand rule. Figure 2: Change in current direction
|
|
|
- Godfrey Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DC Generator 1. THE DIRECTION OF CURRENT DUE TO INDUCED VOLTAGE: UNDERSTANDING FLEMING S RIGHT HAND RULE - The direction of current flow in the conductor is given by Fleming s right hand rule Figure 1: Fleming s right hand rule - The directions are: Thumb indicates: relative motion of conductor Pointing finger indicates: flux Middle finger indicates: current Figure 2: Change in current direction Key point : If the direction of relative motion of the conductor is reversed keeping the flux direction same or if the flux direction is reversed keeping the direction of relative motion of conductor same, the direction of induced emf and hence the direction of current is reversed. Stamford University Bangladesh Page 1
2 2. THE AMOUNT OF INDUCED EMF - The induced emf in conductor depends on the position of plane of flux direction and plane of conductor s rotation. - Mathematically it is found that if the plane of rotation is parallel to the plane of flux, there will no cut of flux; hence there will be no induced emf. - The flux cutting, and hence induced emf is maximum when the plane of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of flux. - In between these two extremes, for any angle between the plane of rotation and plane of flux, the induced emf depends on the perpendicular projection of rotation to the plane of flux. - The induced emf is given by E= BL(vsinα) Where, B = magnetic field L = active length of the conductor v = relative velocity of the conductor α = angle between the plane of rotation and plane of flux Plane of rotation α Plane of flux Figure 3: Flux induced in conductor Key point: For an induced emf in the conductor, not only the relative motion between conductor and flux is necessary but also the plane of rotation should not be parallel to the plane of flux. 3. OPERATION OF A SINGLE COIL DC GENERATOR - A single coil dc generator is composed of three elements: o Armature: The moving part of a magnetic device consisting of one or more coils that are electrically connected to create the rotatable section of a generator. Stamford University Bangladesh Page 2
3 o Slip Rings: A slip ring is a method of making an electrical connection through a rotating assembly, commonly found in electrical generators. o Brushes: conducts current between rotating and stationary parts of a generator. Figure 4: Single coil dc generator Figure 5: Operation of a single coil dc generator. Stamford University Bangladesh Page 3
4 - Initially the conductor is in the position A. In this position it has no induced emf in it, because the plane of motion is parallel to the plane of flux. - Next the rotor starts to rotate clockwise i.e. Leg 1 [darker portion of the conductor] is moving toward the south pole and Leg 2 [lighter portion of the conductor] is moving toward the north pole [see position B]. - As a result Leg 1 is moving downward and Leg 2 is moving upward. - Emf starts to induce in the conductor, hence it causes to current flow in the direction given by Fleming s right hand rule. - The induced emf and consequently the current is maximum when plane of motion is perpendicular to the plane of flux [see position C]. - In the next quarter, the emf starts to reduce [see position D] until the conductor reaches the position E and at this position the induced emf is zero again. - Moving toward the next quarter [see position F] results in such a way that Leg 1 is now moving upward and Leg 2 is in downward i.e. the exact opposite phenomenon is happening to the position B. - According to Fleming s right hand rule now, the current flow in the external circuit is opposite to that of in the first half cycle. - The current in opposite direction becomes maximum at the position G. In next quarter the current reduces [see position H] and become zero after finishing one cycle [see position A]. 4. MAKING THE CURRENT UNIDIRECTIONAL IN THE EXTERNAL CIRCUIT: - The current produced from a dc generator using slip sing is alternating in every cycle in the external circuit. - To make this current unidirectional in the external circuit, slip ring is replaced by split ring. The split ring has two parts. Each part is connected to the corresponding brushes. - The split ring is allowed to rotate at the same velocity of the rotation of conductor while the brush positions are remain unchanged - As a result, after every half cycle the one part of split ring goes in touch of other brush form the first one to whom it did touch in first half cycle. - Consequently, current becomes unidirectional in the external circuit. Stamford University Bangladesh Page 4
5 Figure 6 : Making current unidirectional References: 1. U. A. Bakshi, V. U. Bakshi, Electrical Technology, 4 th Edition 2009, Technical Publication Pune. 2. whs.wsd.wednet.edu Stamford University Bangladesh Page 5
Question 2: Around the bar magnet draw its magnetic fields. Answer:
 Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: What is the reason behind the compass needle is deflected when it is brought close to the bar magnet? Compass needles work as a small bar magnet;
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Answer: A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet,
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Answer: A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet,
INTRODUCTION Principle
 DC Generators INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using the principle of magnetic induction. Principle Whenever a conductor is moved within a
DC Generators INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using the principle of magnetic induction. Principle Whenever a conductor is moved within a
UNIT 2. INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES. General Objective
 DC GENERATOR (Part 1) E2063/ Unit 2/ 1 UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES General Objective : To apply the basic principle of DC generator, construction principle and types of DC generator.
DC GENERATOR (Part 1) E2063/ Unit 2/ 1 UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES General Objective : To apply the basic principle of DC generator, construction principle and types of DC generator.
Page 1 of 19. Website: Mobile:
 Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with
Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with
Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
 Intext Exercise 1 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact
Intext Exercise 1 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact
(d) The magnetic field lines, produced around a straight current-carrying conductor, are concentric circles. Their centres lie on the wire.
 Page 240»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire? (a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire (b) The field
Page 240»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire? (a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire (b) The field
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
 1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? The needle of a compass is a small magnet. That s why when a compass needle is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? The needle of a compass is a small magnet. That s why when a compass needle is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO MOTORS AND GENERATORS
 CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO MOTORS AND GENERATORS Objective Describe the necessary conditions for motor and generator operation. Calculate the force on a conductor carrying current in the presence of the
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO MOTORS AND GENERATORS Objective Describe the necessary conditions for motor and generator operation. Calculate the force on a conductor carrying current in the presence of the
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current carrying conductor the needle of compass gets deflected because of flow of electricity. This shows that
FARADAY S LAW ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 FARADAY S LAW ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION magnetic flux density, magnetic field strength, -field, magnetic induction [tesla T] magnetic flux [weber Wb or T.m 2 ] A area [m 2 ] battery back t T f angle between
FARADAY S LAW ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION magnetic flux density, magnetic field strength, -field, magnetic induction [tesla T] magnetic flux [weber Wb or T.m 2 ] A area [m 2 ] battery back t T f angle between
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
 CHAPTER13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Multiple Choice Questions 1. Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field (a) The direction of magnetic field at a
CHAPTER13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Multiple Choice Questions 1. Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field (a) The direction of magnetic field at a
Electrical machines - generators and motors
 Electrical machines - generators and motors We have seen that when a conductor is moved in a magnetic field or when a magnet is moved near a conductor, a current flows in the conductor. The amount of current
Electrical machines - generators and motors We have seen that when a conductor is moved in a magnetic field or when a magnet is moved near a conductor, a current flows in the conductor. The amount of current
DC MOTOR. Prashant Ambadekar
 DC MOTOR Prashant Ambadekar Electric Motor: The input is electrical energy (from the supply source), and the output is mechanical energy (to the load). Electric Generator: The Input is mechanical energy
DC MOTOR Prashant Ambadekar Electric Motor: The input is electrical energy (from the supply source), and the output is mechanical energy (to the load). Electric Generator: The Input is mechanical energy
EE6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT I D.C. MACHINES PART A
 EE6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is prime mover? UNIT I D.C. MACHINES PART A The basic source of mechanical power which drives the armature of the generator is called prime mover.
EE6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is prime mover? UNIT I D.C. MACHINES PART A The basic source of mechanical power which drives the armature of the generator is called prime mover.
UNIT I D.C. MACHINES PART A. 3. What are factors on which hysteresis loss? It depends on magnetic flux density, frequency & volume of the material.
 EE6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT I D.C. MACHINES PART A 1. What is prime mover? The basic source of mechanical power which drives the armature of the generator is called prime mover.
EE6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT I D.C. MACHINES PART A 1. What is prime mover? The basic source of mechanical power which drives the armature of the generator is called prime mover.
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 6 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 06.01 Electromagnetic induction When the magnetic flux linked with a coil or conductor changes, an emf is developed in it. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
6 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 06.01 Electromagnetic induction When the magnetic flux linked with a coil or conductor changes, an emf is developed in it. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
EXPERIMENT 13 QUALITATIVE STUDY OF INDUCED EMF
 220 13-1 I. THEORY EXPERIMENT 13 QUALITATIVE STUDY OF INDUCED EMF Along the extended central axis of a bar magnet, the magnetic field vector B r, on the side nearer the North pole, points away from this
220 13-1 I. THEORY EXPERIMENT 13 QUALITATIVE STUDY OF INDUCED EMF Along the extended central axis of a bar magnet, the magnetic field vector B r, on the side nearer the North pole, points away from this
AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the north poles of
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the north poles of
MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO A CURRENT CARRYING CONDUCTOR
 Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor 1. A current carrying straight conductor behaves as a magnet. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the Right-Hand Thumb Rule. The
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor 1. A current carrying straight conductor behaves as a magnet. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the Right-Hand Thumb Rule. The
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name:
 Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
The Fleming s Left Hand Rule shows what happens when electrons in a current enter a magnetic field.
 M4: Electrical Actuators M4.1 Fleming s Left Hand Rule The Fleming s Left Hand Rule shows what happens when electrons in a current enter a magnetic field. According to this rule if the index finger is
M4: Electrical Actuators M4.1 Fleming s Left Hand Rule The Fleming s Left Hand Rule shows what happens when electrons in a current enter a magnetic field. According to this rule if the index finger is
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT
 Magnet A magnet is an object, which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel and cobalt. Naturally Occurring Magnet Lodestone is a naturally occurring magnet. It is actually a black coloured, oxide ore of
Magnet A magnet is an object, which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel and cobalt. Naturally Occurring Magnet Lodestone is a naturally occurring magnet. It is actually a black coloured, oxide ore of
CURRENT ELECTRICITY - II
 SALIENT FEATURES Faraday s laws of electrolysis Magnetic effects of electricity Electro magnetic induction CURRENT ELECTRICITY - II FARADAY S LAWS OF ELECTROYLYSIS ELECTROLYSIS The process of decomposition
SALIENT FEATURES Faraday s laws of electrolysis Magnetic effects of electricity Electro magnetic induction CURRENT ELECTRICITY - II FARADAY S LAWS OF ELECTROYLYSIS ELECTROLYSIS The process of decomposition
PHY 152 (ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM)
 PHY 152 (ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM) ELECTRIC MOTORS (AC & DC) ELECTRIC GENERATORS (AC & DC) AIMS Students should be able to Describe the principle of magnetic induction as it applies to DC and AC generators.
PHY 152 (ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM) ELECTRIC MOTORS (AC & DC) ELECTRIC GENERATORS (AC & DC) AIMS Students should be able to Describe the principle of magnetic induction as it applies to DC and AC generators.
CHAPTER -13 MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 CHAPTER -13 MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Madhu:8095226364 Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Answer 1: Magnetic compass needle and bar magnet both
CHAPTER -13 MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Madhu:8095226364 Question 1: Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Answer 1: Magnetic compass needle and bar magnet both
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM L (P.599-604) The large-scale production of electrical energy that we have today is possible because of electromagnetic induction. The electric generator,
CHAPTER THREE DC MOTOR OVERVIEW AND MATHEMATICAL MODEL
 CHAPTER THREE DC MOTOR OVERVIEW AND MATHEMATICAL MODEL 3.1 Introduction Almost every mechanical movement that we see around us is accomplished by an electric motor. Electric machines are a means of converting
CHAPTER THREE DC MOTOR OVERVIEW AND MATHEMATICAL MODEL 3.1 Introduction Almost every mechanical movement that we see around us is accomplished by an electric motor. Electric machines are a means of converting
Electromagnetic Induction Chapter Questions. 1. What is the Electromagnetic Force (EMF)? What are the units of EMF?
 Electromagnetic Induction Chapter Questions 1. What is the Electromagnetic Force (EMF)? What are the units of EMF? 2. The discovery of electric currents generating an magnetic field led physicists to look
Electromagnetic Induction Chapter Questions 1. What is the Electromagnetic Force (EMF)? What are the units of EMF? 2. The discovery of electric currents generating an magnetic field led physicists to look
MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA Class X MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 1. Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor (a) Nature of magnetic field: The magnetic field lines due
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA Class X MAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 1. Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor (a) Nature of magnetic field: The magnetic field lines due
Describe an experiment to demonstrate that there is a magnetic field around a current carrying conductor.
 EXERCISE 10 (A) Question 1: Describe an experiment to demonstrate that there is a magnetic field around a current carrying conductor. Solution 1: Experiment: In Fig, AB is a wire lying in the north- south
EXERCISE 10 (A) Question 1: Describe an experiment to demonstrate that there is a magnetic field around a current carrying conductor. Solution 1: Experiment: In Fig, AB is a wire lying in the north- south
BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS
 CHAPTER 13 BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle is based on the
CHAPTER 13 BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle is based on the
Operation Construction Classification Applications. DC Motors
 Operation Construction Classification Applications DC Motors A DC Motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Special applications where dc motors are used include: in steel mills, mines
Operation Construction Classification Applications DC Motors A DC Motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Special applications where dc motors are used include: in steel mills, mines
Ch 20 Inductance and Faraday s Law 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 17, 21, 25, 30, 31, 39, 41, 49
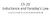 Ch 20 Inductance and Faraday s Law 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 17, 21, 25, 30, 31, 39, 41, 49 The coil with the switch is connected to a battery. (Primary coil) When current goes through a coil, it produces
Ch 20 Inductance and Faraday s Law 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 17, 21, 25, 30, 31, 39, 41, 49 The coil with the switch is connected to a battery. (Primary coil) When current goes through a coil, it produces
SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 28-B/7, Jia Sarai, Near IIT, Hauz Khas, New Delhi-110016. Ph. 011-26514888. www.engineersinstitute.com 2 CONTENT 1. : DC MACHINE,
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 28-B/7, Jia Sarai, Near IIT, Hauz Khas, New Delhi-110016. Ph. 011-26514888. www.engineersinstitute.com 2 CONTENT 1. : DC MACHINE,
CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Compass needle:- It is a small bar magnet, whose north end is pointing towards north pole and south end is pointing towards south pole of earth..hans Oersted
CHAPTER 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT Compass needle:- It is a small bar magnet, whose north end is pointing towards north pole and south end is pointing towards south pole of earth..hans Oersted
Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday s Experiment
 Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday s Experiment A current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. First shown in an experiment by Michael Faraday A primary coil is connected to a battery. A secondary
Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday s Experiment A current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. First shown in an experiment by Michael Faraday A primary coil is connected to a battery. A secondary
 DC MOTORS DC Motors DC Motor is a Machine which converts Electrical energy into Mechanical energy. Dc motors are used in steel plants, paper mills, textile mills, cranes, printing presses, Electrical locomotives
DC MOTORS DC Motors DC Motor is a Machine which converts Electrical energy into Mechanical energy. Dc motors are used in steel plants, paper mills, textile mills, cranes, printing presses, Electrical locomotives
ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II
 ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II 2.1.General Arrangement of DC Machine Objecties To instill an understanding of the underlying electromagnetic effects permitting electric machine operation and introduce
ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II 2.1.General Arrangement of DC Machine Objecties To instill an understanding of the underlying electromagnetic effects permitting electric machine operation and introduce
ELECTROMAGNETISM. 1. the number of turns. 2. An increase in current. Unlike an ordinary magnet, electromagnets can be switched on and off.
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Unlike an ordinary magnet, electromagnets can be switched on and off. A simple electromagnet consists of: - a core (usually iron) - several turns of insulated copper wire When current
ELECTROMAGNETISM Unlike an ordinary magnet, electromagnets can be switched on and off. A simple electromagnet consists of: - a core (usually iron) - several turns of insulated copper wire When current
SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism. If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0.
 SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism GALVAOMETERS If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0. otice how the current runs in the opposite directions on opposite
SPH3U1 Lesson 10 Magnetism GALVAOMETERS If the wire through a magnetic field is bent into a loop, the loop can be made to turn up to 90 0. otice how the current runs in the opposite directions on opposite
1. What type of material can be induced to become a temporary magnet? A) diamagnetic B) ferromagnetic C) monomagnetic D) paramagnetic
 Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Assignment 1 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Name: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Show appropriate workings. 1. What type of
Single Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX
 Single Phase Induction Motor Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX Application :- The single-phase induction machine is the most frequently used motor for refrigerators, washing machines, clocks, drills,
Single Phase Induction Motor Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX Application :- The single-phase induction machine is the most frequently used motor for refrigerators, washing machines, clocks, drills,
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM
 CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1: MAGNETIC EFFECT OF A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR Electromagnets 1. Conductor is a material that can flow.. current 2. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between.and
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1: MAGNETIC EFFECT OF A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR Electromagnets 1. Conductor is a material that can flow.. current 2. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between.and
1. This question is about electrical energy and associated phenomena.
 1. This question is about electrical energy and associated phenomena. Electromagnetism The current in the circuit is switched on. electromagnet State Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction and use
1. This question is about electrical energy and associated phenomena. Electromagnetism The current in the circuit is switched on. electromagnet State Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction and use
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 One mark for each of: when the pressure switch (A) is pushed, a current flows the electromagnet (B) is activated/switched on the armature (C) is attracted to the electromagnet the clapper
QUESTIONSHEET 1 One mark for each of: when the pressure switch (A) is pushed, a current flows the electromagnet (B) is activated/switched on the armature (C) is attracted to the electromagnet the clapper
DC motor theory. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 DC motor theory This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
DC motor theory This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Motional EMF. F = qvb
 Motional EMF When a conducting rod moves through a constant magnetic field, a voltage is induced in the rod. This special case of electromagnetic induction arises as a result of the magnetic force that
Motional EMF When a conducting rod moves through a constant magnetic field, a voltage is induced in the rod. This special case of electromagnetic induction arises as a result of the magnetic force that
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction
 Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
Chapter 22: Electric motors and electromagnetic induction The motor effect movement from electricity When a current is passed through a wire placed in a magnetic field a force is produced which acts on
Phys102 Lecture 20/21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law
 Phys102 Lecture 20/21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law Key Points Induced EMF Faraday s Law of Induction; Lenz s Law References SFU Ed: 29-1,2,3,4,5,6. 6 th Ed: 21-1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Induced EMF
Phys102 Lecture 20/21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law Key Points Induced EMF Faraday s Law of Induction; Lenz s Law References SFU Ed: 29-1,2,3,4,5,6. 6 th Ed: 21-1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Induced EMF
Motional emf. as long as the velocity, field, and length are mutually perpendicular.
 Motional emf Motional emf is the voltage induced across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. If a metal rod of length L moves at velocity v through a magnetic field B, the motional emf is: ε =
Motional emf Motional emf is the voltage induced across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. If a metal rod of length L moves at velocity v through a magnetic field B, the motional emf is: ε =
ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II
 ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II 2.2 Main Structural Elements of DC Machine Construction of DC Machines A DC machine consists of two main parts 1. Stationary Part (Stator):-It is designed mainly for producing
ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II 2.2 Main Structural Elements of DC Machine Construction of DC Machines A DC machine consists of two main parts 1. Stationary Part (Stator):-It is designed mainly for producing
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM
 CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1 Effect of a Magnet on a Current-carrying Conductor 8.1.1 Straight Wire Magnetic fields are circular Field is strongest close to the wire Increasing the current increases
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM 8.1 Effect of a Magnet on a Current-carrying Conductor 8.1.1 Straight Wire Magnetic fields are circular Field is strongest close to the wire Increasing the current increases
21.2 Electromagnetism
 In 1820 Hans Oersted discovered how magnetism and electricity are connected. A unit of measure of magnetic field strength, the oersted, is named after him. Electricity and Magnetism How can an electric
In 1820 Hans Oersted discovered how magnetism and electricity are connected. A unit of measure of magnetic field strength, the oersted, is named after him. Electricity and Magnetism How can an electric
ELEN 236 DC Motors 1 DC Motors
 ELEN 236 DC Motors 1 DC Motors Pictures source: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/mothow.html#c1 1 2 3 Some DC Motor Terms: 1. rotor: The movable part of the DC motor 2. armature: The
ELEN 236 DC Motors 1 DC Motors Pictures source: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/mothow.html#c1 1 2 3 Some DC Motor Terms: 1. rotor: The movable part of the DC motor 2. armature: The
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Generators Transformers Cell Phones Recall Oersted's principle: when a current passes through a straight conductor there will be a circular magnetic field
Almost 200 years ago, Faraday looked for evidence that a magnetic field would induce an electric current with this apparatus:
 Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law Chapter 21 Induced EMF Faraday s Law of Induction; Lenz s Law EMF Induced in a Moving Conductor Changing Magnetic Flux Produces an E Field Inductance
Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law Chapter 21 Induced EMF Faraday s Law of Induction; Lenz s Law EMF Induced in a Moving Conductor Changing Magnetic Flux Produces an E Field Inductance
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 1. Name the type of current: (a) used in household supply. (b) given by a cell. (a) Alternating current. (b) Direct current.
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 1. Name the type of current: (a) used in household supply. (b) given by a cell. (a) Alternating current. (b) Direct current.
Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism
 Name: Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism 1. An electron, travelling with a constant velocity, enters a region of uniform magnetic field. Which of the following is not a possible pathway? 2. A bar magnet
Name: Physics12 Unit 8/9 Electromagnetism 1. An electron, travelling with a constant velocity, enters a region of uniform magnetic field. Which of the following is not a possible pathway? 2. A bar magnet
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy
 Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
Science 30 Unit C Electromagnetic Energy Outcome 1: Students will explain field theory and analyze its applications in technologies used to produce, transmit and transform electrical energy. Specific Outcome
KS3 Revision. 8J Magnets and Electromagnets
 KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
KS3 Revision 8J Magnets and Electromagnets 1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Contents 8J Magnets and Electromagnets Magnetic materials Magnetic fields Electromagnets Summary activities 2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd
Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law
 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law Solenoid Magnetic Field of a Current Loop Solenoids produce a strong magnetic field by combining several loops. A solenoid is a long, helically wound coil of
Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law Solenoid Magnetic Field of a Current Loop Solenoids produce a strong magnetic field by combining several loops. A solenoid is a long, helically wound coil of
Lecture Outline Chapter 23. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 23 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction Units of Chapter 23 Induced Electromotive Force Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction
Lecture Outline Chapter 23 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction Units of Chapter 23 Induced Electromotive Force Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT Q1. What is a magnet? What are its types? Ans. A magnet is a substance that attracts pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel, etc and aligns itself in the north- south direction when
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT Q1. What is a magnet? What are its types? Ans. A magnet is a substance that attracts pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel, etc and aligns itself in the north- south direction when
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
 CHAPTER 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current In the previous Chapter on Electricity we learnt about the heating effects of electric current. What could be the other effects of electric current? We know
CHAPTER 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current In the previous Chapter on Electricity we learnt about the heating effects of electric current. What could be the other effects of electric current? We know
AC Motors vs DC Motors. DC Motors. DC Motor Classification ... Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq
 AC Motors vs DC Motors DC Motors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology ME 6401: Advanced Mechatronics
AC Motors vs DC Motors DC Motors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology ME 6401: Advanced Mechatronics
Introduction: Electromagnetism:
 This model of both an AC and DC electric motor is easy to assemble and disassemble. The model can also be used to demonstrate both permanent and electromagnetic motors. Everything comes packed in its own
This model of both an AC and DC electric motor is easy to assemble and disassemble. The model can also be used to demonstrate both permanent and electromagnetic motors. Everything comes packed in its own
Pre-lab Questions: Please review chapters 19 and 20 of your textbook
 Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
2006 MINI Cooper S GENINFO Starting - Overview - MINI
 MINI STARTING SYSTEM * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * 2002-07 GENINFO Starting - Overview - MINI For information on starter removal and installation, see the following articles. For Cooper, see STARTER WITH
MINI STARTING SYSTEM * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * 2002-07 GENINFO Starting - Overview - MINI For information on starter removal and installation, see the following articles. For Cooper, see STARTER WITH
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current P-1
 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current P-1 Magnetic Field: The space or region around a magnet (or a current Carrying wire) with in which its influence can be felt or magnetic force can be felt by another
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current P-1 Magnetic Field: The space or region around a magnet (or a current Carrying wire) with in which its influence can be felt or magnetic force can be felt by another
2 Principles of d.c. machines
 2 Principles of d.c. machines D.C. machines are the electro mechanical energy converters which work from a d.c. source and generate mechanical power or convert mechanical power into a d.c. power. These
2 Principles of d.c. machines D.C. machines are the electro mechanical energy converters which work from a d.c. source and generate mechanical power or convert mechanical power into a d.c. power. These
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT. To understand Magnetic effects of Electric current, first we should know what is the Magnet?
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT To understand Magnetic effects of Electric current, first we should know what is the Magnet? Magnet A Magnet is an object which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT To understand Magnetic effects of Electric current, first we should know what is the Magnet? Magnet A Magnet is an object which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel
Chapter 4 DC Machines
 Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics Chapter 4 DC Machines Third Edition P. C. Sen Chapter 4 DC machine Electric machine Type: rotating machine Applications: generator (electric source)
Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics Chapter 4 DC Machines Third Edition P. C. Sen Chapter 4 DC machine Electric machine Type: rotating machine Applications: generator (electric source)
Faraday s Law. HPP Activity 75v1. Exploration. Obtain. 50 or 100 turn wire coil bar magnet galvanometer
 HPP Activity 75v1 Faraday s Law Exploration Obtain 50 or 100 turn wire coil bar magnet galvanometer Connect the coil to the galvanometer so that a clockwise current will produce a leftward deflection of
HPP Activity 75v1 Faraday s Law Exploration Obtain 50 or 100 turn wire coil bar magnet galvanometer Connect the coil to the galvanometer so that a clockwise current will produce a leftward deflection of
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT EDULABZ. the mere presence of magnet, is called...
 Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
Magnetism and Electricity ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below. List : magnetic field, magnetic keepers, electric bell, stop, magnetic induction,
Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator
 Exercise 2 Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator EXERCIE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the construction of permanent magnet dc motors as well as
Exercise 2 Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator EXERCIE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the construction of permanent magnet dc motors as well as
Historical Development
 TOPIC 3 DC MACHINES DC Machines 2 Historical Development Direct current (DC) motor is one of the first machines devised to convert electrical power into mechanical power. Its origin can be traced to the
TOPIC 3 DC MACHINES DC Machines 2 Historical Development Direct current (DC) motor is one of the first machines devised to convert electrical power into mechanical power. Its origin can be traced to the
Magnetism - General Properties
 Magnetism - General Properties A magnet, when suspended from a string, will align itself along the north - south direction. Two like poles of a magnet will repel each other, while opposite poles will attract.
Magnetism - General Properties A magnet, when suspended from a string, will align itself along the north - south direction. Two like poles of a magnet will repel each other, while opposite poles will attract.
Principles of Electrical Engineering
 D.C GENERATORS Principle of operation of D.C machines, types of D.C Generators, e.m.f equation of D.C Generator, O.C.C of a D.C Shunt Generator, Load characteristics of D.C.Generators GENERATOR PRINCIPLE:
D.C GENERATORS Principle of operation of D.C machines, types of D.C Generators, e.m.f equation of D.C Generator, O.C.C of a D.C Shunt Generator, Load characteristics of D.C.Generators GENERATOR PRINCIPLE:
Note 8. Electric Actuators
 Note 8 Electric Actuators Department of Mechanical Engineering, University Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drive, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada 1 1. Introduction In a typical closed-loop, or feedback, control
Note 8 Electric Actuators Department of Mechanical Engineering, University Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drive, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada 1 1. Introduction In a typical closed-loop, or feedback, control
Comprehensive Technical Training
 Comprehensive Technical Training For Sugar Mills Staff on Operation & Maintenance of Baggase Based HP Cogeneration System Schedule: 10 th July to 13 th July, 2017 A.C. GENERATOR Topics Covered. Introduction.
Comprehensive Technical Training For Sugar Mills Staff on Operation & Maintenance of Baggase Based HP Cogeneration System Schedule: 10 th July to 13 th July, 2017 A.C. GENERATOR Topics Covered. Introduction.
AC MOTOR TYPES. DESCRIBE how torque is produced in a single-phase AC motor. EXPLAIN why an AC synchronous motor does not have starting torque.
 Various types of AC motors are used for specific applications. By matching the type of motor to the appropriate application, increased equipment performance can be obtained. EO 1.5 EO 1.6 EO 1.7 EO 1.8
Various types of AC motors are used for specific applications. By matching the type of motor to the appropriate application, increased equipment performance can be obtained. EO 1.5 EO 1.6 EO 1.7 EO 1.8
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law 29.1 Induced EMF Units of Chapter 29 : 1-8 29.3 EMF Induced in a Moving Conductor: 9, 10 29.4 Electric Generators: 11 29.5 Counter EMF and Torque;
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law 29.1 Induced EMF Units of Chapter 29 : 1-8 29.3 EMF Induced in a Moving Conductor: 9, 10 29.4 Electric Generators: 11 29.5 Counter EMF and Torque;
Lecture 19 Chapter 30 Faraday s Law Course website:
 Lecture 19 Chapter 30 Faraday s Law Who cares that Faraday s Law is used here? Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 30: Section
Lecture 19 Chapter 30 Faraday s Law Who cares that Faraday s Law is used here? Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 30: Section
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT MAGNET:
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT MAGNET: A magnet is a substance that attracts pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel, etc and aligns itself in the north- south direction when suspended freely. The Greeks knew the
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT MAGNET: A magnet is a substance that attracts pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel, etc and aligns itself in the north- south direction when suspended freely. The Greeks knew the
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS
 ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
ELECTRICITY: ELECTROMAGNETISM QUESTIONS The flying fox (2017;3) Sam has a flying fox (zip line) that he wants to use in the dark. Sam connects a 12.0 V battery to a spotlight, using two 1.60-metre-long
Chapter 31. Faraday s Law
 Chapter 31 Faraday s Law Michael Faraday 1791 1867 British physicist and chemist Great experimental scientist Contributions to early electricity include: Invention of motor, generator, and transformer
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law Michael Faraday 1791 1867 British physicist and chemist Great experimental scientist Contributions to early electricity include: Invention of motor, generator, and transformer
Electrical Machines II. Week 5-6: Induction Motor Construction, theory of operation, rotating magnetic field and equivalent circuit
 Electrical Machines II Week 5-6: Induction Motor Construction, theory of operation, rotating magnetic field and equivalent circuit Asynchronous (Induction) Motor: industrial construction Two types of induction
Electrical Machines II Week 5-6: Induction Motor Construction, theory of operation, rotating magnetic field and equivalent circuit Asynchronous (Induction) Motor: industrial construction Two types of induction
Pre-lab Questions: Please review chapters 19 and 20 of your textbook
 Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
Introduction Magnetism and electricity are closely related. Moving charges make magnetic fields. Wires carrying electrical current in a part of space where there is a magnetic field experience a force.
Physics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 11 Faraday s Law of Induction
 Physics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 11 Faraday s Law of Induction Contents: 121P11-1P, 3P,4P, 5P, 7P, 17P, 19P, 24P, 27P, 28P, 31P Overview Magnetic Flux Motional EMF Two Magnetic Induction Experiments
Physics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 11 Faraday s Law of Induction Contents: 121P11-1P, 3P,4P, 5P, 7P, 17P, 19P, 24P, 27P, 28P, 31P Overview Magnetic Flux Motional EMF Two Magnetic Induction Experiments
DC Motor and Generator Theory By
 DC Principles Study Unit DC Motor and Generator Theory By Robert Cecci iii Preview DC motors and generators are widely used in industrial applications. Both motors and generators are devices that produce
DC Principles Study Unit DC Motor and Generator Theory By Robert Cecci iii Preview DC motors and generators are widely used in industrial applications. Both motors and generators are devices that produce
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS
 ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
ELECTRIC POWER AND HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT Heating effect of electricity is one of the widely-used effects in the world. When electric current is passed through a conductor, it generates
1. Which device creates a current based on the principle of electromagnetic induction?
 Assignment 2 Electromagnetism Name: 1. Which device creates a current based on the principle of electromagnetic induction? A) galvanometer B) generator C) motor D) solenoid 2. The bar magnet below enters
Assignment 2 Electromagnetism Name: 1. Which device creates a current based on the principle of electromagnetic induction? A) galvanometer B) generator C) motor D) solenoid 2. The bar magnet below enters
AGN Single Phase Loading for Re- Connectable 3-Phase Windings
 Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Alternator Technologies AGN 154 - Single Phase Loading for Re- Connectable 3-Phase Windings TECHNICAL OVERVIEW It must be accepted; when reconnecting
Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Alternator Technologies AGN 154 - Single Phase Loading for Re- Connectable 3-Phase Windings TECHNICAL OVERVIEW It must be accepted; when reconnecting
Induced Emf and Magnetic Flux *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42390 1 Induced Emf and Magnetic Flux * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract Calculate the ux of
OpenStax-CNX module: m42390 1 Induced Emf and Magnetic Flux * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract Calculate the ux of
1 A strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. core. current. coil. pins. What happens when the current in the coil is halved?
 1 strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. current core pins coil What happens when the current in the coil is halved? No pins are attracted. Some pins are attracted, but not as many. The same number
1 strong electromagnet is used to attract pins. current core pins coil What happens when the current in the coil is halved? No pins are attracted. Some pins are attracted, but not as many. The same number
Single Phase Induction Motors
 Single Phase Induction Motors Prof. T. H. Panchal Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Technology Nirma University, Ahmedabad Introduction As the name suggests, these motors
Single Phase Induction Motors Prof. T. H. Panchal Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Technology Nirma University, Ahmedabad Introduction As the name suggests, these motors
If the magnetic field is created by an electromagnet, what happens if we keep it stationary but vary its strength by changing the current through it?
 If a moving electron in a magnetic field experiences a force pushing on it at right angles to its motion, what happens when we take a copper wire (with lots of easily dislodged electrons in it) and move
If a moving electron in a magnetic field experiences a force pushing on it at right angles to its motion, what happens when we take a copper wire (with lots of easily dislodged electrons in it) and move
ALTERNATING CURRENT - PART 1
 Reading 9 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com ALTERNATING CURRENT - PART 1 This is a very important topic. You may be thinking that when I speak of alternating current (AC), I am talking
Reading 9 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com ALTERNATING CURRENT - PART 1 This is a very important topic. You may be thinking that when I speak of alternating current (AC), I am talking
Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary
 Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary Term Definition Coil Solenoid Electric Motor Parts of an electric motor: Rotor commutator armature brushes Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law of Induction Generator
Electromagnets & Induction Vocabulary Term Definition Coil Solenoid Electric Motor Parts of an electric motor: Rotor commutator armature brushes Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law of Induction Generator
