Charging System. Maintenance
|
|
|
- Vernon Flynn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chassis Electrical Charging System The charging system provides electrical current for the lights, radio, heater blower and the engine s electrical systems. It also maintains the batteries in a charged state, recharging them as necessary to provide cranking power. The charging system has three main components, or component areas: the alternator, the voltage regulator, and the battery. The alternator is driven by a belt from the engine crankshaft and produces the electrical power to operate the systems on the bus. It also recharges the battery. The voltage regulator acts as a control valve for the alternator output. It senses the current load and maintains a constant voltage in the charging system, independent of the current load, up to its rated output. The eece Neville alternator on the lue ird Vision has a built in voltage regulator. It is excited (started) by the ignition system. The battery is the reservoir of chemical electrical power. Its primary purpose is to crank the engine. It also supplies power to the accessories for a short time when the demand is too high for the alternator alone (i.e., while the bus is at idle). nother key role of the battery is to act as a filter for the charging system. The lue ird Vision has a 12-volt electrical system. The alternator is a 175-ampere, 12-volt device. eece Neville model number C is standard. Maintenance Clean the alternator and all connection points. Dirt buildup restricting air flow through to the alternator will cause excessive heat and premature failure. Corrosion at any connecting point will produce resistance to current flow, heat and diminished power for the starter and accessories. Ensure that all the components in the charging system are mounted securely. Check the torque at all mounting bolts both the bolts that hold the alternator in the mounting bracket and the bolts that secure the mounting brackets to the engine. The torque value for mounting bolts at the engine and at the alternator should be ft lb ( Nm) lue ird Vision buses are equipped with an automatic belt tensioner. Ensure that all the grooves fit properly into the pulleys in the correct path. The drive belt should be inspected every 11,000 miles (17,700 km), 250 hours of service life, or every 3 months; whichever occurs first. 751 lso check: attery voltage lternator output Starter current draw
2 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Troubleshooting Timely preventive maintenance of the charging system should keep it running smoothly. However, when a problem occurs, effective troubleshooting procedures will help locate and correct the problem quickly and economically. [Warning] atteries emit an explosive gas. Never smoke while working on the charging system. atteries can explode from a spark. lways remove the negative battery cable at the battery post before removing any other wires in the charging system. e careful not to short the system while you are working on it. Do not wear jewelry. efore you begin to analyze the charging system, it is necessary that you ensure the battery is properly tested and charged to at least 75% of their rated capacity. Failure to confirm the condition of the battery will make the results of any diagnostic testing unreliable. Refer to the battery manufacturer s publications on battery maintenance and testing. Digital Volt/Ohm Meter lternator Performance Test 1. Connect a digital volt/ohmmeter (VOM) to the output terminals of the alternator. mmeter [Caution] Ensure that the test leads are connected properly. Observe the polarity and make secure connections Connect an ammeter to the positive terminal of the alternator. Observe that the clamp on the ammeter is located at least 6 inches (15 cm) from the alternator to lessen the possibility of faulty readings due to spurious emissions. 3. Verify that the voltage output from the alternator is between 13.6 and 14.2 volts with the engine at operating RPM (1700 RPM minimum) and not idle. 4. Ensure that all loads are in the off position. The reading on the ammeter should be less than 20 amps. If the amp reading is higher than 20 amps, ensure all accessories are turned off. Ensure the battery is charged to at least 75% of their rated capacity. 5. Record the voltage. If the voltage is not within the specified range or the amperage is not within the specified range, the alternator is defective.
3 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 6. If the alternator is determined to be defective, repair or replace it in accordance with the instructions below. See lternator Removal. 7. If the alternator is determined to be functioning properly, proceed as follows: 8. Continue to operate the engine at about 1700 RPM, and with the test equipment set up as illustrated. 9. Turn on vehicle loads (accessories) until the ammeter displays 132 amps, which is 75% of the rated capac-ity (175 amps). Record the voltage at this point. 10. Compare the voltage reading with the voltage reading observed in Step 3 above. 11. If the alternator voltage drops more than.5 (1/2) volt, the alternator is defective. n alternate method of checking the alternator under load is to use a carbon pile load. Connect the carbon pile across the battery and adjust it until the ammeter reads 75% of the alternator rated capacity. Record the voltage at this point, shut off the engine, and compare the readings. lternator Cable Tests To test the positive alternator cable: 1. Clamp the ammeter on the positive cable at least 6 inches (15 cm) from the alternator. See Figure Connect the negative lead of the VOM to the positive post of the alternator. Digital Volt/Ohm Meter Connect the positive lead of the VOM to the positive battery post. 4. Start the engine and let it run at about 1700 RPM. mmeter 5. Turn on accessories until the ammeter reads 132 amps, which is 75% of the rated alternator capacity (175 amps). Use a carbon pile if necessary to achieve the load. 6. Record the voltage reading on the VOM.
4 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l 7. If the VOM reads more than -.25 volts, there is a problem with the positive cable. Volt/Ohm Meter Check and clean all the connections and the condition of all the cables/wires in the circuit. Re-test the circuit. 8. If the reading is less than -.25 volts, the cable and connections are good. mmeter 9. Connect the lead negative of the VOM to the negative terminal of the battery. Solenoid 10. Connect the positive lead of the VOM to the negative terminal of the alternator. Starter 11. Repeat Steps 4 through 8 for the negative cable. 754
5 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l osch lternator Removal [Warning] lways disconnect the negative (-) cable from the battery terminal first to avoid arcing, which could ignite explosive battery gases. 1. Park the bus on a smooth, flat surface. 2. Chock the wheels in both directions. 3. Ensure the engine is not running, the ignition switch is in the OFF position and the key is removed. 4. Disconnect the negative (ground) cable from the battery post. 5. ift the automatic belt tensioner to remove the drive belt from the alternator. 6. Remove the drive belt. 7. Inspect the drive belt; discard it if any signs of wear are present. few minor cracks across the belt are acceptable. ongitudinal cracks are NOT acceptable. Replace the drive belt when any crack is observed to be running lengthwise or with the belt, or when the belt appears frayed. [Warning] lways disconnect the negative (-) battery cable at the battery before removing any wiring from the alternator. elt Wear 8. Remove the negative (-) cable from the alternator Remove the positive (+) cable from the alternator. 10. Remove the bottom mounting bolts. 11. Support the alternator and remove the top bolts. 12. Remove the alternator.
6 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l lternator Reinstallation Installation of the alternator is accomplished in the reverse order of the removal instructions above. 1. Position the alternator and install the top and bottom bolts. Torque bolts to ft. lbs. 2. Install the positive cable on the positive (+) post. Carefully tighten to avoid breaking or stripping the stud. 3. Install the negative cable on the negative ( -) post. Carefully tighten to avoid breaking or stripping the stud. 4. Using a square drive tool, position the automatic tensioner so that the drive belt can be installed. Inspect the drive belt carefully. Replace the belt if any signs of wear are present. 5. Install the drive belt. Ensure that the grooves in the belt fit into the proper places on all the pulleys. 6. Start the engine and test the alternator output. 756
7 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l utomatic elt Tensioner The automatic tensioner is spring loaded to provide the proper tension for the drive belt. The automatic tensioner should travel at least 71º, and the torque to move the tensioner 25º from the at rest position must be 9 11 ft lb ( Nm). Inspect the belt tensioner for any unusual noise, excessive looseness and shaking at the bearings. utomatic Tensioner Removal 1. Remove the drive belt in accordance with the instruc-tions above. 2. Remove the capscrew (1) from the automatic ten-sioner. See Figure 8. To install a new automatic tensioner, reverse the removal instructions. Torque the capscrew (1) to ft lb (38 56 Nm). 757
8 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Starter There are 5 main components or component areas in the starting system: the ignition switch, a neutral safety switch, the starter solenoid, the starter motor and the batteries. When the key is turned to the start position, electrical current flows to the starter solenoid from the batteries. The flow is interrupted if the transmission shift lever is not in the neutral position or if the neutral sensor switch is defective. The starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch mounted on the starter motor. When electric current energizes coils inside the solenoid, a magnetic field is induced which pulls a plunger. t one end of this plunger is a shift lever. The lever is connected to the drive pinion and clutch assembly of the starter motor. The plunger also connects the electrical power from the batteries to the starter motor as it engages the flywheel ring gear. The starter motor is a relatively small electric motor, but it can deliver large amounts of torque for a short time. When the operator releases the ignition switch it returns to the run position. The solenoid is disconnected from the batteries and the magnetic field collapses. This allows the spring in the solenoid to move the plunger in the opposite direction, disengaging the flywheel and removing electrical current from the starter motor. The lue ird Vision has a 12-volt electrical system. The starter motor is Model , Presto-lite/eece/Neville M100R series. The Starter motor is capable of 4kw cranking power for peak loads of no more than 30 seconds duration. Preventative Maintenance There are two preventative maintenance procedures that can greatly enhance the efficiency of the starting system. These two steps are also the first two steps taken when troubleshooting a malfunctioning starting system. 758 n engine that needs a tune up will be difficult to crank; over cranking will lead to starter motor failure. Poor connections due to road dirt, grease, corrosion, loose connectors, or broken insulation at any connecting point rob the starting system of electrical power and cause it to over-crank. Troubleshooting efore beginning to troubleshoot the starting system, ensure the batteries are properly maintained and charged to at least 75% of their rated capacity. drained battery will cause any further diagnostic tests to be inaccurate. Common causes of starting system malfunction include: 1. battery that is low, poorly charged, or defective places high demands on the starting system; voltage at the battery should be 12.4 volts or greater to crank the engine. If the batteries aren t adequately charging, a problem in the charging system. Refer to the lternator section of this Service Manual for information on the charging system.
9 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 2. starter motor can be damaged by heat that is generated by excessive cranking. The starter should never be engaged for more than 30 seconds. It must rest (cool off) a minimum of 2 minutes between starting attempts. 3. oose, dirty, or corroded connections in the starting system rob the system of the power needed to turn the engine. The case of the starter motor is the ground or return connection for the starter motor and solenoid. 4. loose starter motor will allow vibration that can damage the motor. In addition, the ring gear could be damaged. 5. Improper or excessive use of starting fluid will cause extra stress on the starting system. 6. defective solenoid will fail to engage the starter motor. failed pull-up coil will cause the plunger to fail to pull in. failed hold-in coil may cause the starter to fail to stay engaged, or may fail to switch the starter motor on. If the solinoid is suspect, test the wiring of the solenoid circuit before replacing the solenoid. The starting circuit is among those incorporated into the Vision s Multiplex System. Therefore, Multiplex diagnostics procedure can help to quickly isolate the root cause of most starting problems, and thereby minimize downtime. Refer to the Multiplex chapter for full details on performing Multiplex diagnostics. 1. Refer to the Multiplex Output Table to find out which Port/Pin (3-07) and which Output ED (3-O02) pertain to the Starter Signal Output. The chart also shows which adder ogic ine (#20) describes the logic of the circuit. 2. Use the Diagnostic Switch to cycle the MPX Module to the appropriate Diagnostic Mode (Showing 3 Outputs). Check the ED to see if the Starter Signal Output (3-O03) is ctive. If the Output ED is Inactive, refer to adder ogic line #20 to systematically verify that each requirement for an ctive Output is true Once the Output is ctive, if the starter is still not operating, verify a ground at Pin 3-07 on the MPX Module. If the ground output is present, the problem exists downstream of the Multiplex system, and the starter itself is suspect.
10 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Ignition/Run Test egin by determining whether the problem is with the ignition switch or the pilot relay, and their associated wiring; or if it is in the solenoid and/or starting motor. To begin with the ignition switch: Volt/Ohm Meter 1. Connect the positive lead of a VOM to the ignition switch terminal on the solenoid. 2. Connect the negative lead of the VOM to the chassis ground. Solenoid lternator 3. While attempting to crank the engine, record the voltage displayed on the VOM. Observe the following: Starter No voltage ow voltage Normal voltage with slow cranking Normal voltage with no cranking at all. 4. Connect a remote start switch to the positive battery post. 5. Connect the other end of the remote start switch to the ignition post of the solenoid ttempt to crank the engine with the remote switch. Record the voltage displayed on the VOM. If there is less than 1 volt difference from the previous reading, the ignition switch is okay. If there is more than 1 volt difference, the switch is defective. 7. With the VOM negative lead connected to the chassis ground, move through the switch system one connection at a time. If your first voltage test has revealed low voltage, the starter motor may be shorted. 8. If the first voltage test indicated normal voltage, but there is slow cranking or no cranking at all, a problem with the batteries, battery cables, or a damaged starter motor is indicated.
11 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l ow Voltage Test There are various reasons for low voltage but the troubleshooting methods are the same. If the solenoid clicks, it means that either current is flowing through the solenoid contacts but not through the main contacts; or that the current through the main contacts is insufficient due to low batteries. Solenoid Volt/Ohm Meter 1. Connect the positive lead of the VOM to the starter motor terminal of the solenoid. lternator 2. Connect the negative lead of the VOM to the chassis ground. Starter 3. While attempting to crank the engine, if there is no voltage displayed on the VOM, the main contacts are not functioning properly. 4. If there is voltage present at the solenoid terminal during Step 3, the problem is in the starter motor or its cabling. 5. If the first voltage check in Step 3 under Ignition/Run Test indicated normal voltage but slow or no cranking, the next step is to check the starter motor and its connections. 6. If the drive pinion jumps out of mesh with the flywheel ring gear, check for a broken or loose ground wire at the solenoid. 7. While attempting to crank the engine, place an ammeter on the positive battery cable. If the power drain is higher than the OEM specifications, the starter motor is defective. n exception would be if the engine was not properly tuned or is difficult to turn over; in which case, a new starter motor would be a temporary fix. Main Contacts 761 mmeter Solenoid lternator Starter
12 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Slow Cranking Sluggish cranking can be caused by a small amount of extra resistance in the cranking circuit. This extra resistance can come from loose or dirty (corroded) connections, or broken wires and/or cables. First check the positive cables and connections of the starter motor, then the negative circuit. Volt/Ohm Meter mmeter 1. Connect the positive lead of a VOM to the positive battery terminal. 2. Position an ammeter between the solenoid and the positive terminal of the solenoid. Solenoid lternator 3. Connect the negative lead of the VOM to the positive terminal of the solenoid. Starter 4. Connect the negative lead of the VOM to the negative battery post. This is the unloaded voltage. Record the reading; leave the VOM connected. Carbon Pile Tester 5. Connect one lead of a carbon pile tester to chassis ground. 6. Connect the other lead from the carbon pile tester to the positive terminal of the solenoid. 7. djust the carbon pile tester until the ammeter on the tester reads 500 amps Record the voltage display on the VOM; it should not be less than 0.4-volts less than the unloaded value. 9. Turn the carbon pile tester to the OFF position. 10. Connect the positive lead of the VOM to chassis ground. 11. Connect the negative lead of the VOM to the negative battery post. Record the reading; leave the VOM connected. 12. Position the ammeter in on the negative battery cable. 13. Turn on the carbon pile tester and adjust it to read 500 amps. 14. Record the voltage on the VOM; it should not drop more than 0.4-volts from the unloaded reading.
13 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 15. Turn the carbon pile tester to the OFF position. 16. If the voltage drop was more than 0.4-volts in step 8, the positive cabling is defective. ook for a broken cable or a loose or corroded connection. 17. If the voltage drop in step 14 is more than 0.4 volts, look for a problem in the negative cabling; look for broken or defective cables, and loose or corroded connections. Final check at solenoid terminals. 1. Disconnect the carbon pile tester. Volt/Ohm Meter 2. Disconnect the VOM. 3. Remove the ammeter. 4. Connect the positive lead of the VOM to the positive (battery) terminal of the solenoid. Solenoid 5. Set the VOM so that it can read the full battery volt-age; at least 14 volts. lternator 6. Connect the negative VOM lead to the starter motor terminal of the solenoid. Starter 7. Crank the engine and record the voltage while cranking. There should be no more than 0.2 volts drop between the solenoid contacts while cranking. 8. The voltage reading in these last three tests (the positive cable check, the negative cable check and the solenoid test), should not total more than 1.0 volts. If the voltage drop is more than allowable, repeat the cable tests using a jumper cable. If the tests then indicate an acceptable drop, the cable(s) is (are) defective. 763
14 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Starter Motor Removal 1. Disconnect the negative (ground) cable from the battery. Wrap it with tape or other suitable insulation to prevent shorts. 2. Disconnect positive cable from the battery. Wrap it with tape or other suitable insulation to prevent shorts. 3. Identify and tag each wire on the starter motor for reinstallation. 4. Remove all electrical connections from the starter motor. e sure to identify and tag all electrical connection locations. 5. Remove 3 capscrews. 6. Remove starter motor from flywheel housing. Starter Motor Installation The starter motor is installed in the reverse order of the removal instructions above. 1. Carefully place the starter motor into position on the flywheel housing. 2. Install 3 capscrews (1). Torque to 32 ft lb (43 Nm). See Figure eing careful to observe the identification of the electrical wires, connect the wires to the appropriate terminal on the starter motor. See Figure 7. [Warning] lways remove the negative (-) cable from the battery terminal first. lways connect the negative (-) cable to the battery terminal last to avoid arcing that could ignite explosive battery gases. 4. Install the positive cable on the battery post. 5. Install the negative cable on the battery post.
15 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l Chassis Harness Routing Diagrams The following pages illustrate the routings of the main chassis wiring harnesses applicable to most Vision chassis. 765
16 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l FRME RI GM FUSE OCK GROUP 31 TTERIES STRTER CURRENT SENSOR STUD POWER STUD With attery Disconnect Switch Option 766 TERNTOR CK OF PDU
17 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 8D TTERIES FRME RI GM FUSE OCK STRTER CURRENT SENSOR POWER STUD STUD With attery Disconnect Switch Option CK OF PDU 767 TERNTOR Power Cable Routing Sheet 1
18 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Chassis Harness Routing Sheet 2 Frame Rail Typical at Crossmembers Exhaust racket Typical at Exhaust rackets Exhaust racket Typical at Exhaust rackets Crossmember 768 Start of Hydraulic Harness To bs Connection on Front Hub To PDU Panel. See Sheet 3. ir Dryer Typical at Wiring Supports To bs Connection on Front Hub
19 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l eft Frame Rail eft Frame Rail Harness Routing To Front For Hydraulic TO FRONT OF US Fuel Filter Modulator ssy Hydraulic rakes DETI H (HYD RKE) Fuel Tank Hydraulic rakes Fuel Tank rea eft Frame Rail eft Frame Rail ir rakes 769 ir rakes Harness Routing To Front For S Filter ssy Valve ssy To S Modules Fuel Tank
20 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Chassis Harness Routing Sheet 3 Ground 24, 26, 27 Stud Mounting locks on Engine Compartment Side of Firewall Power 24, 26, 27 mmeter On units with mmeter, item 24, 26, or 27 attaches to mmeter Stud. On units without mmeter, item 24, 26, or 27 attaches to Power Stud. To Engine Compartment Interface To Engine 1 Interface To Engine 2 Interface To Transmission/S Interface To J1939 Datalink Components of Harness , 26, 27 Electronic Power Chassis Power From attery Electronic Ground Torque Studs to ft lb. Chassis Ground
21 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 771
22 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Frame Rails Cables Fuel ines : Electronic Power To Disconnect Switch : attery To Disconnect Switch C: Electronic Ground To PDU D: attery Ground E: Disconnect Switch (Electronic Power) To PDU F: Disconnect Switch (attery) To Rem Pwr To PDU Panel To atteries E F See Detail on Sheet 1 D C On back of Transmission ell housing C D To Electronic Power Stud (See Sheet 3) To Rem Power Stud (See Sheet 3) To Electronic Ground Stud (See Sheet 3) To Pdu Ground Stud (See Sheet 3) Torque bolt to 21 ft lb. Coat connection With Glyptal sealant. Route attery Cable Thru Tie Wrap Neg Pos Neg Pos Using 2 8D atteries (Feature ) 772 E F C D C D Neg Neg Neg Pos Pos Pos Using 3 Delco Group 31 atteries (Feature )
23 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 4/0 Positive Cable 4 Ga Positive Cable 4/0 Positive Cable 4 Ga Positive Cable With Heavy Duty ox Only attery Tray From Positive attery With attery Disconnect Switch (Feature ) SEE DETI C & E SEE DETI E Electronic Power to PDU Electronic Ground to PDU 773 Supplied with Switch (For Delphi) (For 8D att) (For Delphi) Torque 1/2" stud to 100 in lb. Torque10-32 stud to 14 in lb. Remove the two 10/32 nuts supplied with switch. Install lock washers supplied with switch on bottom and between cables. Chassis Harness Routing Sheet 4
24 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Frame Rail To PDU Panel Cables Fuel ines To atteries : Electronic Power To PDU : attery To Remote Power C: Electronic Ground To PDU D: attery Ground D C On back of Transmission ell housing C D To Electronic Power Stud (See Sheet 3) To Rem Power Stud (See Sheet 3) To Electronic Ground Stud (See Sheet 3) To Pdu Ground Stud (See Sheet 3) Torque bolt to 21 ft lb. Coat connection With Glyptal sealant. Route attery Cable Thru Tie Wrap See Detail Pos Neg Pos Neg Using 2 8D atteries (Feature ) 774 C D C D Neg Neg Neg Pos Pos Pos Using 3 Delco Group 31 atteries (Feature )
25 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 4/0 Positive Cable 4 Ga Positive Cable 4/0 Positive Cable 4 Ga Positive Cable With Heavy Duty ox Only attery Tray 775 Chassis Harness Routing Sheet 5
26 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Power Distribution Unit ayout The PDU houses the Main us Controller of the Multiplex system (MPX Module), chassis fuses, relays and interface connections to some of the main chassis harnesses. The diagram shown here is representative of standard equipment Visions with air or hydraulic brakes. lthough some differences occur in the cases of specific equipment options (such as circuit breakers in lieu of fuses, exhaust brake, or manual transmission), the general layout of the PDU components is the same
27 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l IGN PWR F1 HTD FUE PWR (20) F2 INTEROCK PWR (10) F3 IR DRYER PWR (10) F4 SPRE Units with ir rakes RKE WRN IGN (15) Units with Hydraulic rakes F5 HTD DRIN PWR (20) F6 ODY IGN (15) TT PWR F7 SPRE Units with ir rakes RK OOST (40) Units with Hydraulic rakes F8 STRT RE PWR (5) F9 REV SENS+ (10) F10 STOP IGHT PWR (15) F11 SPRE Units with ir rakes HYD INTK (30) Units with Hydraulic rakes F12 S TT (30) Units with ir rakes MOD PMP TT (30) Units with Hydraulic rakes F13 DPWR (3) F14 SPRE EEC PWR F15 TRNS TT (10) F16 EECM PWR (40) F17 MC PWR (10) F18 SPRE Units with ir rakes S TT (25) Units with Hydraulic rakes 777 ECM IGN F19 F20 F21 F22 EJ170 IGN (10) TRNS IGN (40) S IGN (10) DSH IGN (10)
28 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l 778
29 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l Chassis Wiring Schematics The following pages contain the main wiring schematics applicable to lue ird Vision Propane with 8.1 GM engine chassis. The schematics are provided for your convenience when you are limited to use of the print manual. dditional schematics specific to your bus may be viewed, printed, or downloaded in dobe PDF format by pointing your web browser to the Customer ccess website at: 779
30 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l Hydraulic rake ooster Harness This schematic describes the wiring of the endix HydroMax brake master cylinder/ booster harness on lue ird Visions equipped with hydraulic brakes. uffer Warning Signal (output to IP) Ground Ignition Warning Signal Input rake ight Signal rake ight Signal To ground stud on HydroMax body Ignition Warning Signal to IP Ground rake ight Signal 780
31 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l Electrical Diagrams for GM 8.1 Engine Description Sheet Drawing Number Index Starting nd Charging Starting nd Charging (with Florida circuit breakers) GM 8.1 PG Engine Powertrain Schematic Powertrain Schematic Dimmer / acklights S - endix (air) S Wabco (hydraulic) Multiplex Module Multiplex Module C Multiplex Module Mirror Heat / Exterior Speaker / Wiper Washer Hydraulic rake oost Frame Components Crossing rm Instrument Cluster Driver s Control Module, ir Driver s Control Module, Hydraulic MC Module ody Interface J1939 Datalink, Hyd J1939 Datalink, ir Wire Colors UE K CK N ROWN TN TN WH WHITE Y YEOW PK PINK OR ORNGE RD RED GN GREEN PU PURPE GY GRY Schematic egend PD PDU PNE C IR CENER RCKET IP INSTRUMENT PNE FW FIREW SP SHIFTER PNE DC DCM Electrical Component Index 781 Micro Relay Heavy Duty Relay Fuse Voltage Stud Shunt Switch Ngr Rocker (Non-typical) 3 Wire Twisting 2 Wire Twisting 2 Wire Twisting with Shield Mini Relay Horn Speaker ight Circuit reaker Multiplex Wire Indexing (Circuit Number Code) Example: (Zone, Connector, 12 Volts, Pin #11) Zone Connector Voltage (0 = Ground, 1 = 12 Volts) Connector Pin Number Sheet SCHEMTIC, WRG, GM 8.1, INDEX
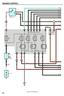
32 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l TTERY DISCONNECT SWITCH (ONY WITH OPTION ) 12V ECM IGNITION REY 30/40 C ECM IGN (PK) RY GND (WH) PD 12V S26 PDU STUD PD V EEC EEC PWR (K) DIG PWR (OR) EEC PWR (K) CURRENT SENSOR 12V PDU STUD DC 12V PD DIO PWR (RD) TT PWR (RD) S25 PD C1 60 PRK RKE OCK SOENOID OPTION MC GND (WH) MC GND (WH) MC PWR 2 (RD) MC PWR 1 (RD) (RD) (WH) C1 - + C D PD TT IGN PWR (RD) 782 FRME GND DC SEN IGN (RD) MMETER SIG (RD) SEN GND (WH) COPPER USR MIN ODY 12V FEED TO SOENOID IN ODY EEC PNE MIN ODY & STRTER FUSE 200 PD STRTER PWR (RD) GND GND PDU GND STUD C14 STRTER REY PD 85 FOR POWER CES & DISTRIUTION SEE DRWINGS # , , ND STRTER (RD) STRT RE GND (WH) C703 12
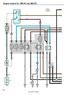
33 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 12V ECM IGNITION US PD IGN 1 (RD) 20 IGN 2 (RD) S IGN (OR) DSH IGN (PK) RKE WRN IGN (OR) GM ENGINE, SHT. 4 GM ENGINE, SHT. 4 S, SHT. 8/9 IP, SHT. 17 HYD RKE OOST, SHT (OR) MODUE, SHT 10 MC GND (WH) MC GND (WH) MC PWR 2 (RD) MC MODUE, SHT. 20 MC PWR 1 (RH) DIG PWR (OR) DIGNOSTIC, SHT 22/23 12V EEC PWR US PD FUE DOOR + (RD) MC PWR (RD) S TT (RD) FRME COMPONENTS, SHT. 15 MC MODUE, SHT. 20 S, SHT. 9 RKE OCK (RD) GND (WH) PDU STUD 12V TTERY US PD DPWR (K) STOP GT PWR (RD) PMP MTR TT (RD) RKE OOST TT (RD) HYD INTK PWR (RD) INTEROCK PWR (RD) REV SENS + (RD) D DIG PWR (K) RKE SW PWR (RD) -114 (RD) IP, SHT. 17 MODUE, SHT. 10 S, SHT. 9 HYD RKE OOST, SHT. 14 DRIVER'S CNTR MODUE, SHT. 18 DRIVERS CONTRO MOD, SHT. 19 SEE DIGRM,WRG FE 2226 DRIVER'S CNTR MODUE, SHT 18/19 DRIVER'S CNTR MODUE, SHT 18/19 MODUE, SHT S26 IGN RE GND (WH) PD IGN PWR (RD) -113 (PK) C13 IGNITION REY 70 12V IGNITION US PD (PK) HTD FUE PWR (PK) HTD DRIN PWR (N) IR DRYER PWR () MODUE, SHT 10 FRME COMPONENTS, SHT. 15 PDU STUD 15 ODY IGN (OR) ODY INTERFCE, SHT. 21 MMETER SIG (RD) SEN IGN (RD) STRTER (RD) INSTRUMENT CUSTER, SHT 17 MMETER, SHT 15 GM ENGINE, SHT 4 Sheet STRTING ND CHRGING
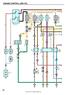
34 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l TTERY DISCONNECT SWITCH (ONY WITH OPTION ) 12V ECM IGNITION REY 30/40 C9 87 PD V ECM IGN (PK) RY GND (WH) S26 PDU STUD PD V EEC EEC PWR (K) DIG PWR (OR) EEC PWR (K) CURRENT SENSOR 12V PDU STUD DC 12V PD DIO PWR (RD) TT PWR (RD) S25 PD C1 60 PRK RKE OCK SOENOID OPTION MC GND (WH) MC GND (WH) MC PWR 2 (RD) MC PWR 1 (RD) (RD) (WH) C1 - + C D PD TT IGN PWR (RD) 784 FRME GND DC SEN IGN (RD) MMETER SIG (RD) SEN GND (WH) COPPER USR MIN ODY 12V FEED TO SOENOID IN ODY EEC PNE MIN ODY & STRTER FUSE 200 PD STRTER PWR (RD) GND GND PDU GND STUD C14 STRTER REY PD 85 FOR POWER CES & DISTRIUTION SEE DRWINGS # , , ND STRTER (RD) STRT RE GND (WH) C703 12
35 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l 12V ECM IGNITION US PD IGN 1 (RD) 20 IGN 2 (RD) S IGN (OR) DSH IGN (PK) RKE WRN IGN (OR) GM ENGINE, SHT. 4 GM ENGINE, SHT. 4 S, SHT. 8/9 IP, SHT. 17 HYD RKE OOST, SHT (OR) MODUE, SHT 10 MC GND (WH) MC GND (WH) MC PWR 2 (RD) MC MODUE, SHT. 20 MC PWR 1 (RH) DIG PWR (OR) DIGNOSTIC, SHT 22/23 12V EEC PWR US PD FUE DOOR + (RD) MC PWR (RD) S TT (RD) FRME COMPONENTS, SHT. 15 MC MODUE, SHT. 20 S, SHT. 9 RKE OCK (RD) GND (WH) PDU STUD 12V TTERY US PD DPWR (K) STOP GT PWR (RD) PMP MTR TT (RD) RKE OOST TT (RD) HYD INTK PWR (RD) INTEROCK PWR (RD) REV SENS + (RD) D DIG PWR (K) RKE SW PWR (RD) -114 (RD) IP, SHT. 17 MODUE, SHT. 10 S, SHT. 9 HYD RKE OOST, SHT. 14 DRIVER'S CNTR MODUE, SHT. 18 DRIVERS CONTRO MOD, SHT. 19 SEE DIGRM,WRG FE 2226 DRIVER'S CNTR MODUE, SHT 18/19 DRIVER'S CNTR MODUE, SHT 18/19 MODUE, SHT S26 IGN RE GND (WH) PD IGN PWR (RD) -113 (PK) C13 IGNITION REY 70 12V IGNITION US PD (PK) HTD FUE PWR (PK) HTD DRIN PWR (N) IR DRYER PWR () MODUE, SHT 10 FRME COMPONENTS, SHT. 15 PDU STUD 15 ODY IGN (OR) ODY INTERFCE, SHT. 21 MMETER SIG (RD) SEN IGN (RD) STRTER (RD) INSTRUMENT CUSTER, SHT 17 MMETER, SHT 15 GM ENGINE, SHT 4 Sheet STRTING ND CHRGING, W/FE (Florida circuit breakers)
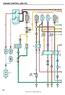
36 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l INSTRUMENT CUSTER, SHT 17 TO C MODUE, SHT 12 DRIVER'S CONTRO MODUE, SHT 18/19 TO MODUE, SHT 11 DRIVER'S CONTRO, SHT 17/18 INSTRUMENT CUSTER, SHT 17 DRIVER'S CONTRO MODJUE, SHT 18/19 DIGNOSTIC CONNECTOR, SHT 22/23 DRIVER'S CONTRO MODUE, SHT 18/19 DIGNOSTIC CONNECTOR, SHT 22/23 DIGNOSTIC CONNECTOR, SHT 22/23 DIGNOSTIC CONNECTOR, SHT 22/23 DIGNOSTIC CONNECTOR, SHT 22/ STRT/CHRGE, SHT 2/3
37 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l WIT STRT (GN) DR SIG () THROT PWR 1 () THROT RET 1 (PK) THROT SIG 1 (N) -003 (RD) -004 () -107 (RD) -001 (OR) THROT SIG 2 (GY) FUE TNK SIG (K) CC ON/OFF (GY) CSS 2 (GY) CC SET (N) CC RESUME (GN) THROT PWR 2 () CC CNCE (RD) THROT RET 2 (GN) GM N + (Y) GM N - () EJ (Y) EJ (GN) C WIT TO STRT MP SIGN DY TIME RUN IGHT SIGN FROM PSI SWITCH THROTTE SUPPY VOTGE #1 THROTTE RETURN #1 THROTTE SIGN #1 3 MPH SIGN FROM TRNSMISSION REVERSE SIGN FROM TRNSMISSION NEUTR SIGN HIGH IDE TO ENGINE THROTTE SIGN #2 FUE SENDER SIGN CRUISE CONTRO ON/OFF TO ENGINE GM CSS 2 SERI DT (J1850) CRUISE CONTRO SET SWITCH TO ENGINE CRUISE CONTRO RESUME SWITCH TO ENGINE THROTTE SUPPY VOTGE #2 CRUISE CONTRO CNCE/TCC/RKE SWITCH THROTTE RETURN #2 GM N + DT (NOT USED) GM N - DT (NOT USED) SE J DT SE J DT REFER TO SHEETS 5 & 6 FOR ENGINE WIRING ND TRNSMISSION. 787 STRTER (RD) EECM GND (WH) 20 IGN 1 (RD) 20 IGN 2 (RD) C704 R S T U V W X Y Z STRTER SIGN TO ENGINE 20 MPS OF IGNITION POWER 20 MPS OF IGNITION POWER PDU EECTRONIC STUD Sheet GM 8.1 ENGINE
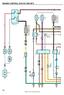
38 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l C033 THROTTE CTUTOR MODUE 2 THROTTE SUPPY VOTGE 2 THROTTE SIGN 2 THROTTE RETURN 2 THROTTE SIGN 1 THROTTE SUPPY VOTGE 1 THROTTE RETURN 1 C D F G J OI PSI SWITCH N.O. C C032 THROTE CTUTOR CONTRO MODUE C/C S/C SW C/C RESUME SW C/C ON SW IGNITION RKE SIGN URT SERI DT 2 URT SERI DT 3 5 VOT REFERENCE TP SENSOR 1 SIGN TP SENSOR 2 SIGN 5 VOT REFERENCE OW REFERENCE TC MOTOR CONTRO 2 OW REFERENCE TC MOTOR CONTRO C034 THROTTE ODY INTFC TC MOTOR CONTRO 1 OW REFERENCE TC MOTOR CONTRO 2 OW REFERENCE 5 VOT REFERENCE TP SENSOR 2 SIGN TP SENSOR 1 SIGN 5 VOT REFERENCE C D E F G H C112 FUE INJECTION FUE INJECTOR 1 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 8 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 4 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 3 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 6 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 5 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 7 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 2 CONTRO IGNITION IGNITION C D E F G H J K C030 MNIFOD SOUTE PSI SENSOR OW REFERENCE MP SENSOR SIGN 5 VOT REFERENCE C TO UE IRD INTERFCE, SHT 4 THROTTE SUPPY VOTGE 2 THROTTE SIGN 2 THROTTE RETURN 2 THROTTE SIGN 1 THROTTE SUPPY VOTGE 1 THROTTE RETURN 1 DY TIME RUN IGHT SIGN C/C S/C SW C/C RESUME SW C/C ON SW C/C CNCE HIGH IDE SWITCH SIGN J1850 DT/CSS 2 FUE EVE SENSOR SIGN 3 MPH SIGN REVERSE SIGN SHIFT INHIIT SIGN WT TO STRT MP NEUTR SIGN SE 1939(+) DT SE 1939(-) DT C () 1162 (GY) 1272 (GN) 1161 (N) 1164 (K) 1271 (PK) DR SIG () 84 (DK ) 87 (GY/K) 397 (GY) 420 (PU) 534 (DK GN) 1049 (GY) 1589C (DK GN/WH) 1480 (T ) 1524 (GY) 1147 (TN) 3 (Y) 8 (RD) 5001 (Y) 5002 (GN) 1162 (GY) 1272 (GN) 1161 (N) 1164 (K) 1271 (PK) DR SIG () DR PWR (RD) 84 (DK ) 87 (GY/K) 397 (GY) 439E (PK) 351 (WH/K) 1320 () 1061 (OR/K) 774 (DK /WH) 416 (GY) 485 (DK GN) 486 (PU) 1688 (T /K) 452 (K) 582 (N) 1704 (K/WH) 581 (Y) 582 (N) 452 (K) 1688 (T /K) 486 (PU) 485 (DK GN) 416 (GY) 1744 (K) 878 (DK /WH) 844 (T /K) 1746 (PK/K) 846 (Y/K) 845 (K/WH) 877 (RD/K) 1745 (T GN/K) 539 (PK) 339 (PK) 597 (GY) 432 (T GN) 469 (OR/K) TO NEUTR REY, SHT 6 TO CEN FUES CONTROER, SHT 6 TO FUSE OX, SHT 6 TO CEN FUES CONTROER, SHT 6 TO J1850 CONVERTER MODUE, SHT 6 8 (RD) 3 (Y) 439 (PK) 439C (PK) 1020D (PK) TO STRTER REY T GM FUSE OCK, SHT (-) DT, SHT (+) DT, SHT 6 TO UE IRD INTERFCE, SHT 4 STRTER SIGN TO ENGINE IGNITION IGNITION CEN C704 W Y Z X 1433C (RD) 5002C (GN) 5001C (Y) 1433C (RD) 1020F (PK) 439D (PK) 351M (WH) S17 S14 S11 S TRNSMISSION TCM CONNECTOR-C (-) DT (+) DT (+) DT SHIFT INHIIT SIGN 1 REVERSE SIGN 65 3 MPH SIGN 4 IGNITION 63 REQUESTED TORQUE SIGN J1850/CSS 2 DT +12 VDC TTERY +12 VDC TTERY SIGN HIGH-RER CRNK SHFT SENSOR SUPPY VOTGE DEUGGED TORQUE SIGN INPUT SPEED OW INPUT SPEED HIGH TURINE SPEED OW TURINE SPEED HIGH VEHICE SPEED OW VEHICE SPEED HIGH TRNS ID DIGIT SIGN DIGIT SIGN DIGIT SIGN DIGIT SIGN C SD MIN MOD SD PCS2 HSD2 SD PCS1 HSD1 PS4 SD TCC SIGN RETURN SUMP TEMP PS2 PS3 PS1 SD SS3 SD SS2 SD SS MIN TRNSMISSION-C175 SD SS1 SD SS2 SD SS3 PS1 P63 P52 SUMP TEMP SIGN RETURN SD TCC PS4 HSD1 SD PCS1 HSD2 SD PCS2 SD MIN MOD DIGIT SIGN C DIGIT SIGN DIGIT SIGN DIGIT SIGN P TRNS ID DIGT SIGN NS (GN) 5001 (Y) 5001D (Y) 351G (K/WH) 351H (K) 1147 (TN) 1524 (GY) 1480 (T ) 1020 (PK) 463 (OR/K) 2470 (Y) 440C (OR) 440D (OR) 2221 (T ) 2467 (WH) 464 (TN/K) 1231 (DK /WH) 1230 (RD/K) 1984 (T ) 1983 (DK ) 822 (/GN/K) 1681 (PU/WH) 2471 (PU) 776 (WH) 771 (K/WH) 772 (Y) 773 (GY) 1530 (DK ) 2469 (N/WH) 323 (N) 1229 (T /WH) 2528 (DK GN/WH) 2529 (T GN/K) 1994 (WH) 407 (K) 1227 (Y/K) 1225 (DK ) 1226 (RD) 1224 (PK) 2527 (OR/WH) 2879 (Y/K) 898 (PU) 898 (PU) 2879 (Y/K) 2527 (OR/WH) 1224 (PK) 1226 (RD) 1225 (DK ) 1227 (Y/K) 407 (K) 1994 (WH) 2529 (T GN/K) 2528 (DK GN/WH) 1229 (T /WH) 323 (N) 2469 (N/WH) 1530 (DK ) 773 (GY) 772 (Y) 771 (K/WH) 776 (WH) 2471 (PU) 1786 (OR/K) 1020E (PK) S (PU/WH) 822 (/GN/K) C005 VEHICE SPEED SENSOR 1983 (DK ) 1984 (T ) C006 TURINE SPEED SENSOR 1230 (RD/K) 1231 (DK /WH) C007 INPUT SPEED SENSOR S10 651C (WH) 1589 (PU) RESISTOR R1 150 OHMS TO SHT (OR/K)
39 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l C029 KNOCK SENSOR RIGHT NK C028 KNOCK SENSOR EFT NK C019 CM SENSOR C RIGHT NK C EFT NK C011 OI PSI SENSOR C009 OI EVE SWITCH C004 COONT TEMP SENSOR C003 CRNK POSITION SENSOR KS2 SIGN KS1 SIGN 12 VOT REFERENCE OW REFERENCE CM SENSOR SIGN OW REFERENCE HIGH SIGN IGNITION HETER OW CONTRO 02 OW SIGN 02 HI SIGN IGNITION HETER OW CONTRO OW REFERENCE 5 VOT REFERENCE OI PSI SENSOR SIGN OI V SW SIGN OW REFERENCE COONT TEMP SIGN 12 VOT REFERENCE OW REFERENCE CKP POSITION SIGN 1 1 C C D E C D E C C 1876 (T ) 496 (DK ) 631 (RD) 632 (PK/K) 633 (N/WH) 1667 (TN) 1666 (PU) 739 (PK) 3212 (T GN) 1664 (TN) 1665 (PU/WH) 739 (PK) 3113 (K/WH) 407 (K) 705 (GY) 332 (TN/WH) 1174 (N) 250 (T GN/WH) 720 (GY) 410 (Y) 1867 (T GN) 1868 (Y/K) 1869 (DK /WH) 639 (PK) 339 (PK) 539 (PK) 1320 () TO GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO TC MODUE RKE RIGHT, SHT 6 S20 420C (PU) 440E (OR) 1786 (OR/K) 447 (Y) TO TC MODUE RKE SIGN REY T GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO NEUTR REY T GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO STRTER REY T GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 S21 S1 251 (K/WH) 251 (K/WH) 447 (Y) 1786 (OR/K) 440 (OR) 440 (OR) 420 (PU) 1869 (DK /WH) 1868 (Y/K) 1867 (T GN) 410 (Y) 720 (GY) 1174 (N) 705 (GY) 407 (K) 1665 (PU/WH) 1664 (TN) 1666 (PU) 1667 (TN) 633 (N/WH) 632 (PK/K) 496 (DK ) 1876 (T ) 597 (GY) 469 (OR/K) 1745 (T GN/K) 877 (RD/K) 845 (K/WH) 846 (Y/K) 1746 (PK/K) 844 (T /K) 878 (DK /WH) 1744 (K) (DK /WH) (OR/K) (PK) (PK) (OR/K) (DK GN) (DK GN) (K/WH) (K/WH) 40 C001-POWERTRIN CONTRO MODUE-ENG COMPRTMENT ON DCM STRTER REY COI CONTRO 34 TRNS RNGE SW SIGN-PRIETY IT (ISON MD) 20 TTERY POSITIVE VOTGE 57 TTERY POSITIVE VOTGE 33 TCC RKE SWITCH/CRUISE CONTRO REESE SIGN 12 CKP SENSOR SIGN 21 OW REFERENCE 2 12 VOT REFERENCE 74 ECT SENSOR SIGN 80 OW REFERENCE 70 OW REFERENCE 7 5 VOT REFERENCE OW REFERENCE HO2S HIGH SIGN - NK 1 SENSOR 1 HO2S OW SIGN - NK 1 SENSOR 1 HO2S HIGH SIGN - NK 2 SENSOR 1 HO2S OW SIGN - NK 2 SENSOR 1 CMP SENSOR SIGN OW REFERENCE KS1 SIGN KS2 SIGN 5 VOT REFERENCE OW REFERENCE FUE INJECTOR 2 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 7 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 5 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 6 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 3 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 4 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 8 CONTRO FUE INJECTOR 1 CONTRO URT SERI DT (TERTIRY) URT SERI DT (SECONDRY) IGNITION 12 VOTGE OFF/RUN/CRNK VOTGE REQUESTED TORQUE SIGN ECM.PCM/VCM CSS 2 SERI DT HIGH IDE SWITCH SIGN 2470 (Y) 1589C (GN/WH) 332 (TN/WH) 3113 (K/WH) 3212 (T GN) 631 (RD) 432 (T GN) 1589 (PU) 2221 (T ) 2467 (WH) 464 (TN/K) 2127 (RD) 2125 (DK GN) 2129 (N) 2123 (T ) 2121 (PU) 2122 (RD/WH) 2124 (DK GN/WH) 2130 (N/WH) 2126 (T /WH) 2128 (PU/WH) 465 (DK GN/WH) 472 (TN) 492 (Y) 428 (DK GN/WH) 552 (K) 1433 (DK GN) 351C (K/WH) 351D (K/WH) TO J1850 CONVERTER MODUE, SHT 6 TO FUE EVE SENSOR SIGN, SHT 6 C002-POWERTRIN CONTRO MODUE-ENG COMPRTMENT ON DCM 58 OI PRESSURE SENSOR SIGN 72 HO2S HETER HIGH CONTRO - NK 2 SENSOR 1 74 HO2S HETER HIGH CONTRO - NK 2 SENSOR VOT REFERENCE 32 MP SENSOR SIGN 54 FUE EVE SENSOR SIGN - PRIMRY 21 SIGN HIGH - RER 2 CRNKSHFT SENSOR SUPPY VOTGE (ISON MD) 5 DEIVERED TORQUE SIGN (ISON MD) 27 IC7 CONTRO 68 IC 5 CONTRO 60 OW REFERENCE 69 IC 3 CONTRO 26 IC 1 CONTRO 67 IC 2 CONTRO 29 IC 4 CONTRO 61 OW REFERENCE 28 IC 6 CONTRO 66 IC 8 CONTRO FUE PUMP REY CONTRO - PRIMRY 1T SENSOR SIGN MF SENSOR SIGN EVP CMSTER PURGE SOENOID CONTRO OW REFERENCE PNP/CUTCH STRT SWITCH SIGN (RD) 2125 (DK GN) 2129 (N) 2123 (T ) 2121 (PU) 539 (PK) 250 (K) 2122 (RD/WH) 2124 (DK GN/WH) 2130 (N/WH) 2126 (T /WH) 2128 (PU/WH) 339 (PK) 250C (K) 1433 (DK GN) 552 (K) 428 (DK GN/WH) 492 (Y) 472 (TN) 465 (DK GN/WH) 539 (PK) 339 (PK) TO STRTER REY GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO IGNITION FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO EVP PURGE VVE, SHT 6 TO MSS IR SENSOR, SHT 6 TO MSS IR SENSOR, SHT 6 TO CEN FUES CONTROER, SHT 6 TO GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 TO GM FUSE OCK, SHT 6 C E F G H IC 7 CONTRO IC 5 CONTRO OW REFERENCE IC 3 CONTRO IC 1 CONTRO IGNITION C110 IGNITION COIS EFT C E F G H IC 2 CONTRO IC 4 CONTRO OW REFERENCE IC 6 CONTRO IC 8 CONTRO IGNITION C111 IGNITION COS RIGHT Sheet Powertrain Schematic 1, GM 8.1
40 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l NEUTR REY REY # C3 D1 D3 C (OR) 8 (RD) 9 (OR/K) 5005 (OR) FUE PUMP REY REY # (OR) 465 (GY) 251E (K) 465C (GN) IGNITION REY REY # (RD) 2000 (RD) 251F (K) 439 (PK) STRTER REY TC MODUE RKE SIGN REY REY # REY # D9 E7 E9 D7 243 (RD) 6 (PU) 447 (Y) 1433 (PU) 251H (K) 1320 () 251G (K) 251H (K) 420C (PU) S2 C016 GM FUSE OCK T ENGINE COMPRTMENT OCTED ON CROSSMEMER OVE ENGINE 790 TO SHT 5 TO TC 2 MODUE, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO STRTER SIGN-C704, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO IGNITION POWER, SHT 5 TO NEUTR SIGN,UE IRD INTF C701, SHT 5 TO TRNSMISSION, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 420C (PU) 1320 () 1433 (GN) 1433C (RD) 447 (Y) 439 (PK) 8 (RD) 1786 (OR/K) 1786 (OR/K) S22 6 (PU) 4 (DK ) 351J (K/WH) 552 (K) 472 (TN) 239 (PK) 492 (Y) 351R (K/WH) 239 (PK) 428 (DK GN/WH) 465 (GY) 2 (RD) 1589C (DK GN/WH) 1 (GN/K) 651 (K) 651 (N) 1 (GN/K) 4 DK (DK ) 465C (GN) 242 (RD) 439C (PK) 465 (DK GN/WH) 3 (Y) 351K (K/WH) S PURGE SOENOID PWR C010 GM STRTER 1 2 C020 CEN FUE PURGE VVE OW REFERENCE IT SENSOR SIGN IGNITION #1 VOTGE MF SENSOR SIGN MOUNTED ON PRESSURE REGUTOR D E C C031 MSS IR SENSOR PURGE VVE PWR OW SIGN 1 2 C025 EVPORTIVE PURGE E D C FUE PUMP REY +12 VDC TTERY FUE EVE SENSOR SIGN CEN FUE CONTRO C008 FUE PUMP CONTRO HRNESS INTFC PI FUE TNK INTERFCE See PI WIRING SCHEMTIC F PURGE SOENOID CEN FUE CONTROER FUE PUMP REY TTERY POSITIVE IGNITION FUE PUMP CNTR - PRIMRY WIT TO STRT MP SUPPY C021 CEN FUES CONTROER (MOUNTED ON DCM) FUE CONTRO UNIT (FCU)
41 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l +12 VDC TTERY T PDU STUD USS TERMIN STUD FUSE OCK RED 6 G CE 5010 (RD) 242 TT (RD) 243 (RD) 5003 (RD) 1042 (RD) 335 (OR) 7 (OR) 2 (RD) M3 50 N3 M4 50 N4 M7 20 N7 C016 GM FUSE OCK T ENGINE COMPRTMENT STRTER POWER/CEN FUES POWER MIN ENGINE ECM/FUE PUMP 242 (RD) 639 (PK) K J4 10 H3 242 TT (RD) 5004 (OR) 5005 (OR) 239 (PK) 239 (PK) 539 (PK) 539 (PK) G4 10 F3 G6 15 F K (RD) 440E (OR) G8 10 F (RD) 2000 (RD) 335 (OR) 8 10 K7 H5 15 J6 G2 10 F1 339 (PK) 339 (PK) 335 (OR) 339 (PK) 339 (PK) TO IGN COIS RIGHT, SHT 5 TO FUE INJECTION, SHT 5 C016 GM FUSE OCK T ENGINE COMPRTMENT 440E (OR) 539 (PK) 539 (PK) 639 (PK) 552 (K) 472 (TN) 492 (Y) 428 (DK GN/WH) 1589C (DK GN/WH) 439C (PK) 465 (DK GN/WH) 3 (Y) 1020D (PK) 2470 (Y) 5002C (GN) 5001C (Y) TO TTERY POWER, SHT 5 TO FUE INJECTION, SHT 5 TO IGN COIS EFT. SHT 5 TO O2 SENSORS, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO FUE SIGN, SHT 5 TO IGNITION, SHT 5 TO POWER TRIN CONTRO MODUE, SHT 5 TO WIT TO STRT, UE IRD INTFC, SHT 5 TO IGNITION, SHT 5 TO J1850/CSS 2 DT, SHT 5 TO SE 1939(-), SHT 5 TO SE 1939(+), SHT VDC TTERY IGNITION J1850 SE 1939(-) SE 1939(+) 335 (OR) 1020D (PK) 2470 (Y) 5002C (GN) 5001C (Y) 251C (K/WH) C015 J1850 TO J1939 CONNECTOR Sheet Powertrain Schematic 2, GM 8.1
42 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l TYPIC DSH SWITCH CKIGHTING/DIMMER CIRCUITS. DIMMER POWER ND S CONTINUE TO OOP FROM SWITCH TO SWITCH. 792
43 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l IUM J () TO OTHER IUM IUM () ODY INTERFCE, SHT 21 IUM H () INSTRUMENT CUSTER, SHT 17 S12 IUM C () C12 C D F -106D (N) -106C (N) MODUE, SHT 11 DIMMER SWITCH 793 Sheet DIMMER/CKIGHTS
44 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l S POWER/STRT/CHRGE, SHT. 2/3 S T (RD) S IGN (OR) EFT FRONT SENSOR RIGHT FRONT SENSOR EFT FRONT MOD VVE H S E RIGHT FRONT MOD VVE H S E S IGN (OR) S GND (WH) S T (RD) TC SS (RD) S IR (GN) C504 C D E F C C C C S GT (GN) S TT (RD) S GND (WH) S IGN (OR) TC SS (RD) F SENSOR IN (PU) F SENSOR RTN (K) RF SENSOR IN (PK) RF SENSOR RTN (K) S S 794 R SENSOR IN (PU) R SENSOR RTN (K) RR SENSOR IN (PK) RR SENSOR RTN (K) R MOD EXH (TN) R MOD COM (GY) R MOD HOD () RR MOD EXH (OR) RR MOD COM (GY) RR MOD HOD (GN) F MOD EXH (TN) F MOD COM (GY) F MOD HOD () RF MOD HOD (GN) RF MOD COM (GY) RF MOD EXH (OR) S GND (WH) EFT RER SENSOR RIGHT RER SENSOR EFT RER MOD VVE H E RIGHT RER MOD VVE H E S C C C C TRCTION CONTRO VVE C514 TCV RTN TCV IN
45 c h a s s i s e l e c t r i c a l J1587+ (Y) J1587- () C513 J1587+ (Y) J1587- () TC SS (RD) J1587+ (Y) J1587- () STOP IGHT SIGN MODUE, SHT. 10 I/P J1587, SHT. 17 S IR (GN) S/TC IGHTS IP, SHT. 17 J1939+ (Y) J1939- (GN) C507 J1939+ J1939- J1939 DTINK (IR), SHT S GND (WH) S IGN (OR) TCV RTN TCV IN J1939-(GN) J1939+(Y) TC SS (RD) RR SENSOR IN (PK) RR SENSOR RTN (K) S GT GND (WH) J1587- () J1587+ (Y) S TT (RD) S GT (GN) C505 C506 F MOD HOD () F MOD EXH (TN) F MOD COM (GY) RF MOD HOD (GN) F SENSOR IN (PU) RF MOD COM (GY) RF MOD EXH (OR) F SENSOR RTN (K) RR MOD COM (GY) RR MOD HOD (GN) RF SENSOR IN (PK) R MOD COMMON (GY) RR MOD EXH (OR) RF SENSOR RTN (K) R SENSOR IN (PU) R MOD HOD () R MOD EXH (TN) R SENSOR RTN (K) 1 S/TC 2 TRIER S W (NOT CONNCTED) 3 IGNITION (5 FUSED) 4 TCV RTN 5 TCV IN 6 TC MP/TC ORS (TC ONY) 7 J1939-O 8 J1939-HI 9 SS (TC ONY) 10 RIGHT RER SENSOR + 11 RIGHT RER SENSOR - 12 S W/ GND 13 J J W INTEROCK (NOT CONNCTED) 16 TTERY (30 FUSED) 17 RETRDER (NOT CONNECTED) 18 S W X2 X1 1 EFT FRONT MOD HOD 2 EFT FRONT MOD EXHUST 3 EFT FRONT MOD COMMON 4 RIGHT FRONT MOD HOD 5 EFT FRONT SENSOR (+) 6 RIGHT FRONT MOD COMMON 7 RIGHT FRONT MOD EXHUST 8 EFT FRONT SENSOR (-) 9 RIGHT MOD COMMON 10 RIGHT MOD HOD 11 RIGHT FRONT SENSOR (+) 12 EFT RER MOD COMMON 13 RIGHT RER MOD EXHUST 14 RIGHT FRONT SENSOR (-) 15 EFT RER SENSOR + 16 EFT RER MOD HOD 17 EFT RER MOD EXHUST 18 EFT RER SENSOR - X3 (NOT CONNECTED) S ECU ENDIX EC-60 C MOUNT 795 S HRNESS TC HRNESS SEE CHRT C515 TRCTION CONTRO VVE 1 S ORS 2 DIFF 3 DIFF_CMN 4 NOT USED 5 RESERVED 6 NOT USED 7 DDITION MOD EXHUST 8 RESERVED 9 DDITION MOD COMMON 10 DDITION MOD HOD 11 DDITION EFT SENSOR(+) 12 DDITION RIGHT SENSOR(+) 13 NOT USED 14 DDITION EFT SENSOR(-) 15 DDITION RIGHT SENSOR(-) Sheet S - ENDIX
46 Vision [propane] s e r v i c e m a n u a l S POWER STRT/CHRGE SHT 2/3 MOD PMP T (RD) S IGN (OR) J1587- () J1587+ (Y) S T (RD) S GND (WH) J1939- (GN) J1939+ (Y) S ECU 16 WY CONNECTOR C513 C D E F G H J K M N P R S PMP MTR T (RD) S IGN (OR) J1587- () J1587+ (Y) S T (RD) S REF GND (WH) J1939- (GN) J1939+ (Y) DT INK SHT 22/ F SENS IN (N) F SENS GND (K) R SENS IN (N) R SENS GND (K) RR SENS IN (N) RR SENS GND (K) RF SENS IN (N) RF SENS GND (K) C C C C EFT FRONT SPEED SENS EFT RER SPEED SENS RIGHT RER SPEED SENS RIGHT FRONT SPEED SENS
ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS 4 F WIRING DIAGRAMS
 EECTRIC SYSTEMS 4 F WIRING DIGRMS Table of Contents Page Wiring Colors for MerCruiser............... 4F- Engine.................................. 4F- MCM (Stern Drive)..................... 4F- MIE (Inboard)
EECTRIC SYSTEMS 4 F WIRING DIGRMS Table of Contents Page Wiring Colors for MerCruiser............... 4F- Engine.................................. 4F- MCM (Stern Drive)..................... 4F- MIE (Inboard)
ENGINE CONTROL MR2 (EWD498U) R W R W R W B 7 IC1 I10 IGNITION SW R W W R W R 40A MAIN ST 5 AM2 C/OPN RELAY 7. 5A RELAY B Y B Y B L B R G R B Y
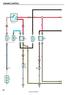 ENGINE CONTRO 5 M IG 6 R IC R 7 R 0 R R IC I0 IGNITION S ST 4 R 7 IC R R 5 5 5 M 40 MIN ST REY 7. 5 ST C/OPN REY 3 3 R F FUE PUMP R 4 5 Y (*) Y (*) 0 I3 Y (*) F MIN. 0 C 9 CUTCH STRT S M TTERY (*) I K
ENGINE CONTRO 5 M IG 6 R IC R 7 R 0 R R IC I0 IGNITION S ST 4 R 7 IC R R 5 5 5 M 40 MIN ST REY 7. 5 ST C/OPN REY 3 3 R F FUE PUMP R 4 5 Y (*) Y (*) 0 I3 Y (*) F MIN. 0 C 9 CUTCH STRT S M TTERY (*) I K
ENGINE CONTROL RUNNER (EWD425U) B- R II4 G- B GR- B B- R B- R FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 48) 4 1I W- L G- B 10A IGN 10A STOP 20A EFI BZ1
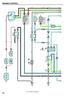 ENINE CONTRO R- I 7 J FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PE 8) 7 M I 6 ST 8 - R I INITION S STRTER REY 0 F - 0 IN EFI REY R- - R 0 EFI - R F 0 STOP 7 I S STOP IHT S - Y - R Z N IE - - R - R - - I I D D D 0 M
ENINE CONTRO R- I 7 J FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PE 8) 7 M I 6 ST 8 - R I INITION S STRTER REY 0 F - 0 IN EFI REY R- - R 0 EFI - R F 0 STOP 7 I S STOP IHT S - Y - R Z N IE - - R - R - - I I D D D 0 M
ENGINE CONTROL (3VZ E)
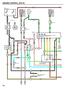 ENGINE CONTRO (3VZ E) I5 IGNITION S R C R M M 7. 5 IGN 5 EFI 5 STOP ST IG 7 7 7 C C 5 Y G G G R STRTER REY [R/ NO. ] 5 3 80 T 3 FUSE OX [R/ NO. ] Y G 5 EFI MIN REY 0 G C G 5 C S8 STOP IGHT S R (/T) 3 3
ENGINE CONTRO (3VZ E) I5 IGNITION S R C R M M 7. 5 IGN 5 EFI 5 STOP ST IG 7 7 7 C C 5 Y G G G R STRTER REY [R/ NO. ] 5 3 80 T 3 FUSE OX [R/ NO. ] Y G 5 EFI MIN REY 0 G C G 5 C S8 STOP IGHT S R (/T) 3 3
ENGINE CONTROL AND ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM
 ENINE CONTRO ND ENINE IMMOIISER SSTEM FROM POER SOURCE SSTEM (SEE PE 0) 7 M I 6 ST 8 O /F HTR O R C 6 C I INITION S C 6 7. IN 6 R IH /F HETER RE CIRCUIT OPENIN RE 8 I 0 M E I M R O F6 FUE PUMP F 9 FUSIE
ENINE CONTRO ND ENINE IMMOIISER SSTEM FROM POER SOURCE SSTEM (SEE PE 0) 7 M I 6 ST 8 O /F HTR O R C 6 C I INITION S C 6 7. IN 6 R IH /F HETER RE CIRCUIT OPENIN RE 8 I 0 M E I M R O F6 FUE PUMP F 9 FUSIE
STARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 1 STARTING SYSTEMS CONTENTS
 TJ STARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 1 STARTING SYSTEMS CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION STARTER MOTOR... 2 STARTER RELAY... 3 STARTING SYSTEM... 1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING STARTER MOTOR... 8 STARTER MOTOR NOISE
TJ STARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 1 STARTING SYSTEMS CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION STARTER MOTOR... 2 STARTER RELAY... 3 STARTING SYSTEM... 1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING STARTER MOTOR... 8 STARTER MOTOR NOISE
Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views
 Page 1 of 11 Document ID# 1568678 2006 Chevrolet TrailBlazer - 2WD Feedback Print Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views Connector 1: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) C1 Connector
Page 1 of 11 Document ID# 1568678 2006 Chevrolet TrailBlazer - 2WD Feedback Print Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views Connector 1: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) C1 Connector
Engine Control Module Connector End Views
 Engine Control Module Connector End Views Connector 1: Engine Control Module (ECM) C1 Connector 2: Engine Control Module (ECM) C2 Connector 3: Engine Control Module (ECM) C3 Engine Control Module (ECM)
Engine Control Module Connector End Views Connector 1: Engine Control Module (ECM) C1 Connector 2: Engine Control Module (ECM) C2 Connector 3: Engine Control Module (ECM) C3 Engine Control Module (ECM)
Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views
 Page 1 of 6 2005 GMC Truck Canyon Pickup - 4WD Canyon, Colorado (VIN S/T) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 3.5L (L52) Diagnostic Information and Procedures Powertrain Control Module Connector End
Page 1 of 6 2005 GMC Truck Canyon Pickup - 4WD Canyon, Colorado (VIN S/T) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 3.5L (L52) Diagnostic Information and Procedures Powertrain Control Module Connector End
Starter, Delco Remy 15.01
 Starter, Delco Remy.0 General Information General Information The Delco Remy starter mounts at the forward face of the flywheel bell housing on the right side of the engine. The starter assembly consists
Starter, Delco Remy.0 General Information General Information The Delco Remy starter mounts at the forward face of the flywheel bell housing on the right side of the engine. The starter assembly consists
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
ELECTRICAL / GENERAL INFORMATION
 ELECTRICAL / GENERAL INFORMATION General Information Reading Electrical Schematics The schematic is made up of individual circuits laid out in a sequence of related functions. It is formatted with all
ELECTRICAL / GENERAL INFORMATION General Information Reading Electrical Schematics The schematic is made up of individual circuits laid out in a sequence of related functions. It is formatted with all
Troubleshooting Guide
 Troubleshooting Guide P/N 0153180 July 1999 P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317 Fax: 816-360-9379 www.snorkelusa.com GENERAL INFORMATION This manual contains procedures for locating
Troubleshooting Guide P/N 0153180 July 1999 P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317 Fax: 816-360-9379 www.snorkelusa.com GENERAL INFORMATION This manual contains procedures for locating
COMPONENT LOCATIONS GROUP CONTENTS FUSIBLE LINK, FUSE AND IOD OR STORAGE CONNECTOR OTHER DEVICES SENSOR...
 70-1 GROUP 70 COMPONENT LOCTIONS CONTENTS FUSILE LINK, FUSE ND IOD OR STORGE...... 70-2 GROUNDING CLE............ 70-3 GROUNDING................... 70-4 INSPECTION TERMINL......... 70-6 OTHER DEVICES................
70-1 GROUP 70 COMPONENT LOCTIONS CONTENTS FUSILE LINK, FUSE ND IOD OR STORGE...... 70-2 GROUNDING CLE............ 70-3 GROUNDING................... 70-4 INSPECTION TERMINL......... 70-6 OTHER DEVICES................
Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views
 Page 1 of 13 2007 Chevrolet Colorado Pickup - 2WD Canyon, Colorado, I-290, I-370 VIN S/T Service Manual Power and Signal Distribution Wiring Systems and Power Management Component Locator Powertrain Control
Page 1 of 13 2007 Chevrolet Colorado Pickup - 2WD Canyon, Colorado, I-290, I-370 VIN S/T Service Manual Power and Signal Distribution Wiring Systems and Power Management Component Locator Powertrain Control
ELECTRICAL TABLE OF CONTENTS
 ELECTRICAL TABLE OF CONTENTS Electrical Table of Contents General Information...205 Reading Electrical Schematics...205 Theory Of Operation Information...206 Diagnostic Information...206 Wire Color Abbreviation
ELECTRICAL TABLE OF CONTENTS Electrical Table of Contents General Information...205 Reading Electrical Schematics...205 Theory Of Operation Information...206 Diagnostic Information...206 Wire Color Abbreviation
This manual provides information on the electrical circuits installed on vehicles by dividing them into a circuit for each system.
 HO TO USE THIS MNUL This manual provides information on the electrical circuits installed on vehicles by dividing them into a circuit for each system. The actual wiring of each system circuit is shown
HO TO USE THIS MNUL This manual provides information on the electrical circuits installed on vehicles by dividing them into a circuit for each system. The actual wiring of each system circuit is shown
Fuller Heavy Duty Transmissions TRTS0020 EN-US October 2007
 Troubleshooting Guide Fuller Heavy Duty Transmissions TRTS0020 EN-US October 2007 RT-11109-T RT-11109-TR RT-11109-TS RT-12109-T RT-14109-TS RTO-11109-T RTO-11109-TS RTO-11109-T RTO-11109-TE RTO-11109-TR
Troubleshooting Guide Fuller Heavy Duty Transmissions TRTS0020 EN-US October 2007 RT-11109-T RT-11109-TR RT-11109-TS RT-12109-T RT-14109-TS RTO-11109-T RTO-11109-TS RTO-11109-T RTO-11109-TE RTO-11109-TR
4.0L CEC SYSTEM Jeep Cherokee DESCRIPTION OPERATION FUEL CONTROL DATA SENSORS & SWITCHES
 4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
Powertrain DTC Summaries OBD II
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Miata - Workshop Manual - Engine
 Page 1 of 8 2003 - Miata - Workshop Manual - Engine NO.6 CRANKS NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT START 6 Cranks normally but will not start Starter cranks engine at normal speed but engine will not run. DESCRIPTION
Page 1 of 8 2003 - Miata - Workshop Manual - Engine NO.6 CRANKS NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT START 6 Cranks normally but will not start Starter cranks engine at normal speed but engine will not run. DESCRIPTION
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
 http://www.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=tr... Page of //0 00 Chevrolet Silverado.L Eng 00 Service Manual: WIRING DIAGRAMS - 00 Print Date: //0 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Tip:
http://www.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=tr... Page of //0 00 Chevrolet Silverado.L Eng 00 Service Manual: WIRING DIAGRAMS - 00 Print Date: //0 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Tip:
S E R V I C E M A N U A L C C 3 0. Cooling System Major Components
 C C 3 0 C O O I N G Overview The cooling system on the Blue Bird Vision is designed to maintain the temperature of the engine within the optimum operating range, throughout the conditions for which the
C C 3 0 C O O I N G Overview The cooling system on the Blue Bird Vision is designed to maintain the temperature of the engine within the optimum operating range, throughout the conditions for which the
Troubleshooting Guide
 Troubleshooting Guide diesel - gasoline - LPG P/N 0172021 June 1999 P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317 Fax: 816-360-9379 www.snorkelusa.com GENERAL INFORMATION This manual contains
Troubleshooting Guide diesel - gasoline - LPG P/N 0172021 June 1999 P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317 Fax: 816-360-9379 www.snorkelusa.com GENERAL INFORMATION This manual contains
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Models Affected: 2009 through 2012 Model Year GM 8.1 Propane Vision Models CORRECTIVE ACTION ---- PROCEDURE
 Models Affected: 2009 through 2012 Model Year GM 8.1 Propane Vision Models ISSUE Bus will start if fuel door is either open or closed if the circuit is broken by a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker.
Models Affected: 2009 through 2012 Model Year GM 8.1 Propane Vision Models ISSUE Bus will start if fuel door is either open or closed if the circuit is broken by a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker.
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
2007 Dodge Nitro R/T ENGINE Starting - Service Information - Nitro. Starting - Service Information - Nitro
 STARTING INFORMATION DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION 2007 ENGINE Starting - Service Information - Nitro The Remote Starting System allows the vehicle to be started up to 300 feet (91 meters) away from the vehicle
STARTING INFORMATION DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION 2007 ENGINE Starting - Service Information - Nitro The Remote Starting System allows the vehicle to be started up to 300 feet (91 meters) away from the vehicle
CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS
 ZG CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION OVERVIEW... 1 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR... 2 CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION... 1 ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR...
ZG CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION OVERVIEW... 1 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR... 2 CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION... 1 ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR...
ENGINE CONTROL 2001 AVALON (EWD431U) L- O B- W B- W B- W B- W I15 IGNITION SW W- R B- W B- W B- O B- O I 7 B- O IF1 B- W W- R B- O B- O B- R L- O
 ENINE ONTRO - O 7 M I 6 ST 8 - R I5 INITION S IF I 7 - R - O 7 9 6 F J 7 0 M 5 EFI NO. 7. 5 EFI NO. 5 /F 5 I 5 5 5 EFI REY /F REY I REY 0 F F 6, F 7 FUSIE INK OK 8 II IF - F MIN. 0 TTERY ED 8 00 VON (EDU)
ENINE ONTRO - O 7 M I 6 ST 8 - R I5 INITION S IF I 7 - R - O 7 9 6 F J 7 0 M 5 EFI NO. 7. 5 EFI NO. 5 /F 5 I 5 5 5 EFI REY /F REY I REY 0 F F 6, F 7 FUSIE INK OK 8 II IF - F MIN. 0 TTERY ED 8 00 VON (EDU)
Headlight Switch Connector. Brake Switch. Lead Wires. Main Power Feed from Starter. Fuse Box Connections (viewed from underside)
 0 Heller Pl #17 W ellmawr, NJ 0031 6-933-001 TH KT DOE NOT UPPORT TOCK (ORGNL) GENERTOR. THE DEGN OF THE KT DEGNED TO UPPLY MORE POWER THN THE GENERTOR LE TO UPPLY. 16 6 4D 4C 4D 0 0 0 4C 4 4 43 7 39 3
0 Heller Pl #17 W ellmawr, NJ 0031 6-933-001 TH KT DOE NOT UPPORT TOCK (ORGNL) GENERTOR. THE DEGN OF THE KT DEGNED TO UPPLY MORE POWER THN THE GENERTOR LE TO UPPLY. 16 6 4D 4C 4D 0 0 0 4C 4 4 43 7 39 3
Headlight Switch Connector. Brake Switch. Lead Wires. Main Power Feed from Starter
 40 3C 40, 2E 2C 2 2F Dimmer witch 12 11 & 11 2C 2 Horn Relay Dome Courtesy feed 40 16 Main Power Feed from tarter 2 12 V attery rake witch rake witch 40 17 17 rake witch Third rake Light Headlight witch
40 3C 40, 2E 2C 2 2F Dimmer witch 12 11 & 11 2C 2 Horn Relay Dome Courtesy feed 40 16 Main Power Feed from tarter 2 12 V attery rake witch rake witch 40 17 17 rake witch Third rake Light Headlight witch
ELECTRICAL BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
 Z ELECTRICAL 8A - 1 ELECTRICAL GROUP INDEX page AUDIO SYSTEMS... 8F BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE... 8B BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS... 8A CHIME WARNING/REMINDER SYSTEM... 8U HORNS...
Z ELECTRICAL 8A - 1 ELECTRICAL GROUP INDEX page AUDIO SYSTEMS... 8F BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE... 8B BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS... 8A CHIME WARNING/REMINDER SYSTEM... 8U HORNS...
ELECTRICAL. Contents - Wiring Diagrams
 Contents - Wiring Diagrams T-Bar (Floating Deck - Hydro)............................................ 8-16 T-Bar (Fixed Deck - Gear)............................................... 8-17 T-Bar (Fixed Deck
Contents - Wiring Diagrams T-Bar (Floating Deck - Hydro)............................................ 8-16 T-Bar (Fixed Deck - Gear)............................................... 8-17 T-Bar (Fixed Deck
ENGINE CONTROL (3RZ FE)
 ENINE CONTRO (3RZ FE) 7 IF Y R 7 AM I 6 3 I FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAE 4) AM ACC I 7. A STA 7. A IN 0A EFI 7. A OD 0A STOP ST 30A AM ATTERY P PARK/NEUTRA POSITION S 40A AM 0A AT I4 INITION S P N
ENINE CONTRO (3RZ FE) 7 IF Y R 7 AM I 6 3 I FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAE 4) AM ACC I 7. A STA 7. A IN 0A EFI 7. A OD 0A STOP ST 30A AM ATTERY P PARK/NEUTRA POSITION S 40A AM 0A AT I4 INITION S P N
ENGINE CONTROL (2RZ FE)
 ENINE CONTRO (RZ FE) 7 IF Y R(A/T) 7 AM I 6 I FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAE ) AM ACC I 7. A STA 7. A IN 0A EFI 7. A OD 0A STOP ST I INITION S 6 0 Y R E E Y R(A/T) O O I Y Y Y O Y Y 0A AM P PARK/NEUTRA
ENINE CONTRO (RZ FE) 7 IF Y R(A/T) 7 AM I 6 I FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAE ) AM ACC I 7. A STA 7. A IN 0A EFI 7. A OD 0A STOP ST I INITION S 6 0 Y R E E Y R(A/T) O O I Y Y Y O Y Y 0A AM P PARK/NEUTRA
DASH/MAIN HARNESS. NOTE: wires 400 & 401, must be twisted together.
 Electric Speedo Ground 151 Turn Flasher 16A 4 150 8A, Cluster Connections 31 33 30 35 151 (electric speedo) 402 401 NOTE: wires 400 & 401, must be twisted together. 156D, E Panel Dimmer 8A 9, C 2D Headlight
Electric Speedo Ground 151 Turn Flasher 16A 4 150 8A, Cluster Connections 31 33 30 35 151 (electric speedo) 402 401 NOTE: wires 400 & 401, must be twisted together. 156D, E Panel Dimmer 8A 9, C 2D Headlight
2000 F-150 Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 14 SECTION 303-06: Starting System 2000 F-150 Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/17/1999 Starting System Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 20, Starting System for schematic
Page 1 of 14 SECTION 303-06: Starting System 2000 F-150 Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/17/1999 Starting System Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 20, Starting System for schematic
TELORVEK II RJ-32 Big Block RamJet Fuel Injection System
 Page #1 TELORVEK II RJ-32 Big Block RamJet Fuel Injection System This wiring system is compatible with the GM Performance part big block Ramjet 502 engine. The harness is designed to dress up the appearance
Page #1 TELORVEK II RJ-32 Big Block RamJet Fuel Injection System This wiring system is compatible with the GM Performance part big block Ramjet 502 engine. The harness is designed to dress up the appearance
SECOND GENERATION Use this guide with unit serial number prefix beginning with BWF using Terra Power separator.
 Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide for SECOND GENERATION Use this guide with unit serial number prefix beginning with BWF using Terra Power separator. This guide will assist you in becoming more
Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide for SECOND GENERATION Use this guide with unit serial number prefix beginning with BWF using Terra Power separator. This guide will assist you in becoming more
ENGINE CONTROL (5VZ-FE 2WD M/T)
 ENINE CONTRO (Z-FE WD M/T) 7 IF 7 AM I 6 FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAE 4) AM ACC I 0A EFI 7. A OD 7. A IN ST W 30A AM W ATTERY 40A AM 0A AT I4 INITION SW - Y- R Y 0 C 9 CUTCH START SW 3 6 8 I F 7.
ENINE CONTRO (Z-FE WD M/T) 7 IF 7 AM I 6 FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAE 4) AM ACC I 0A EFI 7. A OD 7. A IN ST W 30A AM W ATTERY 40A AM 0A AT I4 INITION SW - Y- R Y 0 C 9 CUTCH START SW 3 6 8 I F 7.
BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
 BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2001 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Basic Diagnostic Procedures - Cars Except Metro & Prizm MODEL IDENTIFICATION MODEL IDENTIFICATION Body Code (1) Model C... Park
BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2001 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Basic Diagnostic Procedures - Cars Except Metro & Prizm MODEL IDENTIFICATION MODEL IDENTIFICATION Body Code (1) Model C... Park
ENGINE CONTROL (2RZ-FE) SYSTEM OUTLINE
 ENGINE CONTRO (RZ-FE) SYSTEM OUTINE THE ENGINE CONTRO SYSTEM UTIIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERA CONTRO OF THE ENGINE, TRANSMISSION, ETC. AN OUTINE OF ENGINE CONTRO IS GIVEN HERE.. INPUT SIGNA
ENGINE CONTRO (RZ-FE) SYSTEM OUTINE THE ENGINE CONTRO SYSTEM UTIIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERA CONTRO OF THE ENGINE, TRANSMISSION, ETC. AN OUTINE OF ENGINE CONTRO IS GIVEN HERE.. INPUT SIGNA
Engine Control for 3MZ-FE
 Engine Control for MZ-FE - Y M CC IG ST - Y - R(*) 7 M IG 6 R- (*) ST I - R I Ignition S 8 IG8 - Y 7. M IG - - - R - Y - - R- E 9 C 8 C - G 0 IG - - 0 T 0 M /F 0 EFI EFI Relay C/ON Relay /F HTR Relay C
Engine Control for MZ-FE - Y M CC IG ST - Y - R(*) 7 M IG 6 R- (*) ST I - R I Ignition S 8 IG8 - Y 7. M IG - - - R - Y - - R- E 9 C 8 C - G 0 IG - - 0 T 0 M /F 0 EFI EFI Relay C/ON Relay /F HTR Relay C
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/21/2000
 2001 F-350 Applies to: Gasoline Report a problem with this article Subarticles Inspection and Verification Symptom Chart Pinpoint Tests Component Tests SECTION 303-06A: Starting System Gasoline Engines
2001 F-350 Applies to: Gasoline Report a problem with this article Subarticles Inspection and Verification Symptom Chart Pinpoint Tests Component Tests SECTION 303-06A: Starting System Gasoline Engines
2001 Cougar Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 7 SECTION 303-06: Starting System 2001 Cougar Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 09/14/2001 Starting System Refer to Wiring Diagrams Section 303-06 for schematic and
Page 1 of 7 SECTION 303-06: Starting System 2001 Cougar Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 09/14/2001 Starting System Refer to Wiring Diagrams Section 303-06 for schematic and
Alternator, Leece-Neville 15.00
 Alternator, Leece-Neville 5.00 General Information General Description The Leece-Neville JB series alternator is a 4-volt self-load-limiting alternator equipped with a threestep adjustable voltage regulator.
Alternator, Leece-Neville 5.00 General Information General Description The Leece-Neville JB series alternator is a 4-volt self-load-limiting alternator equipped with a threestep adjustable voltage regulator.
ALTERNATOR REQUESTED INFORMATION. Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty
![ALTERNATOR REQUESTED INFORMATION. Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty ALTERNATOR REQUESTED INFORMATION. Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty](/thumbs/72/66590437.jpg) ALTERNATOR 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty REQUESTED INFORMATION Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] Fig 1: Rotating Drive Belt Tensioner Clockwise 1. Remove the accessory drive
ALTERNATOR 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty REQUESTED INFORMATION Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] Fig 1: Rotating Drive Belt Tensioner Clockwise 1. Remove the accessory drive
Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views
 Page 1 of 11 Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views Connector 1: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) C1 (NU3) Connector 2: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) C1 (w/o NU3) Connector 3: Powertrain Control
Page 1 of 11 Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views Connector 1: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) C1 (NU3) Connector 2: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) C1 (w/o NU3) Connector 3: Powertrain Control
 http://www.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=t... Page of // 0 Chevrolet Traverse.L Eng LT Service Manual: WIRING DIAGRAMS Print Date: // ENGINE PERFORMANCE >.L VIN D Fig
http://www.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=t... Page of // 0 Chevrolet Traverse.L Eng LT Service Manual: WIRING DIAGRAMS Print Date: // ENGINE PERFORMANCE >.L VIN D Fig
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. Self-Diagnostics - RAV4. Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs).
 2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
1999 Toyota RAV ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4
 1999 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4 DESCRIPTION WARNING: Deactivate air bag system before performing any service operation. See AIR BAG RESTRAINT SYSTEMS article. DO NOT apply electrical
1999 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4 DESCRIPTION WARNING: Deactivate air bag system before performing any service operation. See AIR BAG RESTRAINT SYSTEMS article. DO NOT apply electrical
Engine Control for 1MZ-FE and 3MZ-FE
 Engine Control for MZ-FE and MZ-FE CC * : MZ- FE * : TMC Made * : TMMK Made * : Shielded M I ST - Y - Y 7 M I - ST I Ignition S 8 - IF - M - Y - E IF 8 C - - Y - 0 I E 9 C - 0 M /F 0 EFI EFI elay C/OPN
Engine Control for MZ-FE and MZ-FE CC * : MZ- FE * : TMC Made * : TMMK Made * : Shielded M I ST - Y - Y 7 M I - ST I Ignition S 8 - IF - M - Y - E IF 8 C - - Y - 0 I E 9 C - 0 M /F 0 EFI EFI elay C/OPN
Troubleshooting Guide
 Troubleshooting Guide diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG P/N 0191681 May, 1999 An ISO 9001 Registered Company P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317
Troubleshooting Guide diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG diesel - gasoline - LPG P/N 0191681 May, 1999 An ISO 9001 Registered Company P.O. Box 1160 St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 1-800-255-0317
1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L
 INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
TELORVEK EFI 5.0 Coyote Sequential Fuel Injection System Part # CY-11
 Page #1 TELORVEK EFI 5.0 Coyote Sequential Fuel Injection System Part # CY-11 WIRING INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for purchasing the absolute finest of wiring kits for the Ford Motor Co. Coyote modular engine.
Page #1 TELORVEK EFI 5.0 Coyote Sequential Fuel Injection System Part # CY-11 WIRING INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for purchasing the absolute finest of wiring kits for the Ford Motor Co. Coyote modular engine.
C.E. Niehoff & Co. N1601, N1602, N1603, and N1604 Alternator Troubleshooting Guide NOTICE. Hazard Definitions. Battery Charge Volt and Amp Values
 C.E. Niehoff & Co. N1601, N1602, N1603, and N1604 Alternator Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazard(s) of various risk levels or to important
C.E. Niehoff & Co. N1601, N1602, N1603, and N1604 Alternator Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazard(s) of various risk levels or to important
MSD 7AL-3, Ignition Control PN 7230
 MSD 7AL-3, Ignition Control PN 7230 Important: Read the instructions before attempting the installation. Parts Included: 1-7AL-3, PN 7230 1 - Parts bag (wires and connectors) 4 - RPM Modules 3000, 7000,
MSD 7AL-3, Ignition Control PN 7230 Important: Read the instructions before attempting the installation. Parts Included: 1-7AL-3, PN 7230 1 - Parts bag (wires and connectors) 4 - RPM Modules 3000, 7000,
SRS (SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM)
 SRS (SUPPEMENT RESTRINT SYSTEM) NOTICE: When inspecting or repairing the SRS (supplemental restraint system), perform the operation in accordance with the following precautionary instructions and the procedure
SRS (SUPPEMENT RESTRINT SYSTEM) NOTICE: When inspecting or repairing the SRS (supplemental restraint system), perform the operation in accordance with the following precautionary instructions and the procedure
2003 Explorer/Mountaineer Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 11 SECTION 414-00: Battery and Charging System 2003 Explorer/Mountaineer Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/18/2002 Charging System Printable View (257 KB) Refer
Page 1 of 11 SECTION 414-00: Battery and Charging System 2003 Explorer/Mountaineer Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/18/2002 Charging System Printable View (257 KB) Refer
Third Generation NITE Phoenix
 Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide for Third Generation NITE Phoenix Use this guide with unit serial number prefix beginning with BYC, CAI built after 2-10-2012 and CCA, CDJ, CIA units after 6/25/2012
Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide for Third Generation NITE Phoenix Use this guide with unit serial number prefix beginning with BYC, CAI built after 2-10-2012 and CCA, CDJ, CIA units after 6/25/2012
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 414-00-1 Charging System General Information 414-00-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Charging System The charging system voltage is controlled by the PCM. The generator charges the battery, and at the Special Tool(s)
414-00-1 Charging System General Information 414-00-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Charging System The charging system voltage is controlled by the PCM. The generator charges the battery, and at the Special Tool(s)
w w w. h d o n l i n e s h o p. d e HEATED HAND GRIP KITS GENERAL REMOVAL -J02983 REV Kit Number Models Kit numbers Service Parts
 -J098 REV. 007-0-0 GENERAL Kit Number 56047-0B, 5607-0B, 5674-0B, 5696-0B, 565-0B, 5669-0A, 56694-04A, 56750-04A, 5688-0A, 569-05, 5696-05, 56997-07 Models For model fitment information, please see the
-J098 REV. 007-0-0 GENERAL Kit Number 56047-0B, 5607-0B, 5674-0B, 5696-0B, 565-0B, 5669-0A, 56694-04A, 56750-04A, 5688-0A, 569-05, 5696-05, 56997-07 Models For model fitment information, please see the
C.E. Niehoff & Co. C653/C653A and C625 Alternators Troubleshooting Guide NOTICE. Hazard Definitions. Battery Charge Volt and Amp Values
 C.E. Niehoff & Co. C653/C653A and C625 Alternators Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information
C.E. Niehoff & Co. C653/C653A and C625 Alternators Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information
Starting Systems & Traction Motor Systems. ATASA 5 th. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 18 Pages Starting & Traction Motor Systems 62 Points
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 18 Pages 537 570 Starting & Traction Motor Systems 62 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Electric are used to start the engine & in hybrids are used to move the vehicle. Motors
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 18 Pages 537 570 Starting & Traction Motor Systems 62 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Electric are used to start the engine & in hybrids are used to move the vehicle. Motors
ENGINE CONTROL (1MZ-FE)
 NGIN CONTRO (MZ-F) (*) - - R - R - R - G - R K C 7 M IG 6 I6 IGNITION S 0 M C F F 6 F MIN. 0 FUSI INK OCK ST 8 I 8 INJCTOR NO., - (*) S FROM POR SOURC SSTM (S PG ) 7 IK - R K IGN 7 - R STRTR R - R R J
NGIN CONTRO (MZ-F) (*) - - R - R - R - G - R K C 7 M IG 6 I6 IGNITION S 0 M C F F 6 F MIN. 0 FUSI INK OCK ST 8 I 8 INJCTOR NO., - (*) S FROM POR SOURC SSTM (S PG ) 7 IK - R K IGN 7 - R STRTR R - R R J
DRIVEABILITY - GAS. All symptoms listed above are diagnosed using the same tests. The title for the tests will be P0300-MULTIPLE CYLINDER MIS-FIRE.
 Symptom List: P0300-MULTIPLE CYLINDER MIS-FIRE P0301-CYLINDER #1 MISFIRE P0302-CYLINDER #2 MISFIRE P0303-CYLINDER #3 MISFIRE P0304-CYLINDER #4 MISFIRE P0305-CYLINDER #5 MISFIRE P0306-CYLINDER #6 MISFIRE
Symptom List: P0300-MULTIPLE CYLINDER MIS-FIRE P0301-CYLINDER #1 MISFIRE P0302-CYLINDER #2 MISFIRE P0303-CYLINDER #3 MISFIRE P0304-CYLINDER #4 MISFIRE P0305-CYLINDER #5 MISFIRE P0306-CYLINDER #6 MISFIRE
Classic Update Series
 Classic Update Series 1964-1966 Ford Mustang START HERE! PLEASE READ THIS EFORE STARTING INSTALLATION! This wiring kit is designed for ease of installation. Please read the guidelines below, EFORE STARTING
Classic Update Series 1964-1966 Ford Mustang START HERE! PLEASE READ THIS EFORE STARTING INSTALLATION! This wiring kit is designed for ease of installation. Please read the guidelines below, EFORE STARTING
Engine Control (1MZ-FE)
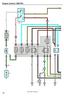 Engine Control (MZ-FE) - M CC IG ST - 7 M IG 6 ST - I5 Ignition S IF - - 5 M 3 IF6 C E - G - - - 0 IG - - E 4 9 3 4 C 0 T 30 M 5 /F 0 EFI 5 3 EFI elay C/OPN elay 5 3 /F HT elay 5 3 5 C 6 K 4 D 6 C 7 C
Engine Control (MZ-FE) - M CC IG ST - 7 M IG 6 ST - I5 Ignition S IF - - 5 M 3 IF6 C E - G - - - 0 IG - - E 4 9 3 4 C 0 T 30 M 5 /F 0 EFI 5 3 EFI elay C/OPN elay 5 3 /F HT elay 5 3 5 C 6 K 4 D 6 C 7 C
DTC Summaries. NipponDenso V12 Engine Management
 DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
Section 6. Electrical System
 Section 6 Electrical System Introduction. This machine incorporates a 12-volt DC electrical system. Optional equipment selected by the customer will determine the electrical equipment to be installed in
Section 6 Electrical System Introduction. This machine incorporates a 12-volt DC electrical system. Optional equipment selected by the customer will determine the electrical equipment to be installed in
HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
 26 HOW TO TROULESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED S DLC3 CN VIM Intelligent Tester GENERL FORMTION large number of ECU controlled systems are used in the TOYOT TCOM. In general, ECU controlled systems are considered
26 HOW TO TROULESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED S DLC3 CN VIM Intelligent Tester GENERL FORMTION large number of ECU controlled systems are used in the TOYOT TCOM. In general, ECU controlled systems are considered
Classic Update Series
 Classic Update Series 62-65 Ford Fairlane and 62-63 Mercury Meteor end view of terminal START HERE! PLEASE READ THIS EFORE STARTING INSTALLATION! This wiring kit is designed for ease of installation. Please
Classic Update Series 62-65 Ford Fairlane and 62-63 Mercury Meteor end view of terminal START HERE! PLEASE READ THIS EFORE STARTING INSTALLATION! This wiring kit is designed for ease of installation. Please
ENGINE COOLING FAN Toyota Celica ELECTRIC COOLING FAN RADIATOR COOLING FAN SYSTEM TEST ENGINE COOLING Toyota Engine Cooling Fans
 ENGINE COOLING FAN 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE COOLING Toyota Engine Cooling Fans Celica 1.8L 4-Cyl ELECTRIC COOLING FAN NOTE: Electric cooling fan may be used for radiator or condenser. To verify electric
ENGINE COOLING FAN 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE COOLING Toyota Engine Cooling Fans Celica 1.8L 4-Cyl ELECTRIC COOLING FAN NOTE: Electric cooling fan may be used for radiator or condenser. To verify electric
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT
 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
N1387 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N Alternators
 N1387 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1387-1 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
N1387 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1387-1 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
Headlight Switch Connector. Brake Switch. Lead Wires. Main Power Feed from Starter. Fuse Box Connections (viewed from underside)
 www.americanautowire.com 86-933-0801 TH KT DOE NOT UPPORT TOCK (ORGNAL) GENERATOR. THE DEGN OF THE KT DEGNED TO UPPLY MORE POWER THAN THE GENERATOR ALE TO UPPLY. 16 68A 4D 4C 4D 0 0 0 4C 4 43 7 39 3 Dimmer
www.americanautowire.com 86-933-0801 TH KT DOE NOT UPPORT TOCK (ORGNAL) GENERATOR. THE DEGN OF THE KT DEGNED TO UPPLY MORE POWER THAN THE GENERATOR ALE TO UPPLY. 16 68A 4D 4C 4D 0 0 0 4C 4 43 7 39 3 Dimmer
Electrical Systems. Introduction
 Electrical Systems Figure 1. Major Components of the Car s Electrical System Introduction Electricity is used in nearly all systems of the automobile (Figure 1). It is much easier to understand what electricity
Electrical Systems Figure 1. Major Components of the Car s Electrical System Introduction Electricity is used in nearly all systems of the automobile (Figure 1). It is much easier to understand what electricity
./#0#. 1"&." 1994 ELECTRICAL Suzuki of America Corp. - Starters. Swift
 !"" #$%!& '()!)((*(+,*)- 1994 ELECTRICAL Suzuki of America Corp. - Starters Swift Two types of starter motors are used, conventional and reduction gear. Both types of starters consist of yoke assembly,
!"" #$%!& '()!)((*(+,*)- 1994 ELECTRICAL Suzuki of America Corp. - Starters Swift Two types of starter motors are used, conventional and reduction gear. Both types of starters consist of yoke assembly,
UNIVERSAL WIRING HARNESS Installation Manual
 UNIVERSAL WIRING HARNESS Installation Manual Terminals are provided for most connections on your wiring kit. Following the gauge manufacturer s instructions, use the terminals supplied with your gauge
UNIVERSAL WIRING HARNESS Installation Manual Terminals are provided for most connections on your wiring kit. Following the gauge manufacturer s instructions, use the terminals supplied with your gauge
ENGINE CONTROL (1ZZ-FE)
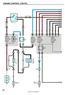 ENGINE ONTO (ZZ-FE) - - - 5 M IG 6 - O 4 IK 6 I - O - - 9 IK I I0 IGNITION S ST 4 IE - - - 6 F 4 H 0 F 4 F 4 3 4 5 6 8 F 9 F 5 7. 5 M 40 MIN ST EY 7. 5 ST 0 EFI NO. 0 EFI NO. 3 3 H 5 /ON EY 3-3 I IE4 4
ENGINE ONTO (ZZ-FE) - - - 5 M IG 6 - O 4 IK 6 I - O - - 9 IK I I0 IGNITION S ST 4 IE - - - 6 F 4 H 0 F 4 F 4 3 4 5 6 8 F 9 F 5 7. 5 M 40 MIN ST EY 7. 5 ST 0 EFI NO. 0 EFI NO. 3 3 H 5 /ON EY 3-3 I IE4 4
3/14/2018 Engine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA
 //0 Engine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA 00 Chrysler Truck PT Cruiser L-.L VIN X Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Diagrams > Electrical - Interactive Color (Non OE) Engine Controls - Page
//0 Engine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA 00 Chrysler Truck PT Cruiser L-.L VIN X Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Diagrams > Electrical - Interactive Color (Non OE) Engine Controls - Page
This chapter contains information on DC Generation, External Power, and Electrical Load Distribution.
 CIRRUS AIRPLANE MAINTENANCE MANUAL Electrical Power CHAPTER 24-00: ELECTRICAL POWER GENERAL 24-00: ELECTRICAL POWER 1. General This chapter contains information on DC Generation, External Power, and Electrical
CIRRUS AIRPLANE MAINTENANCE MANUAL Electrical Power CHAPTER 24-00: ELECTRICAL POWER GENERAL 24-00: ELECTRICAL POWER 1. General This chapter contains information on DC Generation, External Power, and Electrical
GROUP CONTENTS GROUND CABLE FUSIBLE LINK, FUSE AND STORAGE CONNECTOR CONTROL UNIT INSPECTION TERMINAL...
 70-1 GROUP 70 CONTENTS FUSILE LINK, FUSE N STORGE CONNECTOR................... 70-2 INSPECTION TERMINL......... 70-3 GROUNING................... 70-4 RELY........................ 70-6.......................
70-1 GROUP 70 CONTENTS FUSILE LINK, FUSE N STORGE CONNECTOR................... 70-2 INSPECTION TERMINL......... 70-3 GROUNING................... 70-4 RELY........................ 70-6.......................
ALTERNATOR PRECAUTIONS. Some precautions should be taken when working on this, or any other, AC charging system.
 The alternator charging system is a negative (-) ground system which consists of an alternator, a regulator, a charge indicator, a storage battery and wiring connecting the components, and fuse link wire.
The alternator charging system is a negative (-) ground system which consists of an alternator, a regulator, a charge indicator, a storage battery and wiring connecting the components, and fuse link wire.
 Page of 0 Chevrolet Aveo.L Eng LS Service Manual: WIRING DIAGRAMS Print Date: HEADLIGHTS Fig : Headlights Circuit LOW HIGH FRT FOG EF FRT FOG HOT W/ IGN ALL ENERGIZED TIMES DASH, IN DOOR OPENING) LO LH
Page of 0 Chevrolet Aveo.L Eng LS Service Manual: WIRING DIAGRAMS Print Date: HEADLIGHTS Fig : Headlights Circuit LOW HIGH FRT FOG EF FRT FOG HOT W/ IGN ALL ENERGIZED TIMES DASH, IN DOOR OPENING) LO LH
ENGINE CONTROL (2RZ FE)
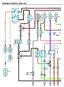 ENGINE CONTROL (RZ FE) IF (A/T) AM IG 6 FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 44) AM ACC IG ST IF. A STA F FUSE O. A IGN A EFI 0A OD A STOP I4 IGNITION S (A/T) (A/T) F 0 (M/T) Y Y V (A/T) IK3 (A/T) (M/T) 3
ENGINE CONTROL (RZ FE) IF (A/T) AM IG 6 FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 44) AM ACC IG ST IF. A STA F FUSE O. A IGN A EFI 0A OD A STOP I4 IGNITION S (A/T) (A/T) F 0 (M/T) Y Y V (A/T) IK3 (A/T) (M/T) 3
ENGINE CONTROL (22R E)
 ENGINE CONTRO (R E) I5 IGNITION S STARTER REAY [R/ NO. ] P N AM ST 5 IG 7 7 C 5 E 4 Y C (FOOR SHIFT) 80A AT P PARK/NEUTRA POSITION S AM (COUMN SHIFT) (NEUTRA START S) I4 C FUSE OX [R/ NO. ] 5 7 I C Y Y
ENGINE CONTRO (R E) I5 IGNITION S STARTER REAY [R/ NO. ] P N AM ST 5 IG 7 7 C 5 E 4 Y C (FOOR SHIFT) 80A AT P PARK/NEUTRA POSITION S AM (COUMN SHIFT) (NEUTRA START S) I4 C FUSE OX [R/ NO. ] 5 7 I C Y Y
ENGINE CONTROL (22R E)
 ENGINE CONTRO (R E) SYSTEM OUTINE THE ENGINE CONTRO SYSTEM UTIIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERA CONTRO OF THE ENGINE, TRANSMISSION, ETC.. AN OUTINE OF ENGINE CONTRO IS GIVEN HERE.. INPUT SIGNA ()
ENGINE CONTRO (R E) SYSTEM OUTINE THE ENGINE CONTRO SYSTEM UTIIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERA CONTRO OF THE ENGINE, TRANSMISSION, ETC.. AN OUTINE OF ENGINE CONTRO IS GIVEN HERE.. INPUT SIGNA ()
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRIC SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 ELECTRIC SYSTEM 1. ELECTRIC SYSTEM ELECTRIC SYSTEM 1.1 WIRING DIAGRAM CK20-USA 196WA00A S196-WOO Jul. 2003 10-3 CK20(M) CHAPTER 10 CK20-EU 196WA51A 10-4 S196-WOO Jul. 2003 ELECTRIC SYSTEM 1.2
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRIC SYSTEM 1. ELECTRIC SYSTEM ELECTRIC SYSTEM 1.1 WIRING DIAGRAM CK20-USA 196WA00A S196-WOO Jul. 2003 10-3 CK20(M) CHAPTER 10 CK20-EU 196WA51A 10-4 S196-WOO Jul. 2003 ELECTRIC SYSTEM 1.2
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM. 5. Specified Data. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF)
 1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
19. ELECTRIC STARTER 19-0 ELECTRIC STARTER XCITING 500/250
 19 ELECTRIC STARTER STARTING SYSTEM LAYOUT ----------------------------------------- 19-1 SERVICE INFORMATION------------------------------------------------ 19-2 TROUBLESHOOTING-----------------------------------------------------
19 ELECTRIC STARTER STARTING SYSTEM LAYOUT ----------------------------------------- 19-1 SERVICE INFORMATION------------------------------------------------ 19-2 TROUBLESHOOTING-----------------------------------------------------
CAUTION Fuel Lift Pump. Initial Check. Resistance Check. https://qsol2.cummins.com/qs2/pubsys2/xml/en/procedures/10/
 Page 1 of 16 View Related Topic 005-045 Fuel Lift Pump Initial Check Inspect the engine harness, the lift pump power connector, the lift pump relay power connector and the lift pump relay pins for the
Page 1 of 16 View Related Topic 005-045 Fuel Lift Pump Initial Check Inspect the engine harness, the lift pump power connector, the lift pump relay power connector and the lift pump relay pins for the
Wiring diagrams on page 29 are for reference only. For detailed vehicle wiring refer to Navistar documents.
 1 10/2014 REV 7 !!Attention!! Before performing diagnostics: Wiring diagrams on page 29 are for reference only. For detailed vehicle wiring refer to Navistar documents. Check for Fault Codes using the
1 10/2014 REV 7 !!Attention!! Before performing diagnostics: Wiring diagrams on page 29 are for reference only. For detailed vehicle wiring refer to Navistar documents. Check for Fault Codes using the
IDENTIFICATION IDENTIFICATION > ENGINE COMPARTMENT FUSE/RELAY CENTER Chevrolet Colorado 3.5L Eng. Vehicle Reference: FUSES & CIRCUIT BREAKERS
 1 of 6 2/1/2015 5:42 PM Vehicle Reference: FUSES & CIRCUIT BREAKERS IDENTIFICATION 2005 Chevrolet Colorado 3.5L Eng CAUTION: When battery is disconnected, vehicle computer and memory systems may lose memory
1 of 6 2/1/2015 5:42 PM Vehicle Reference: FUSES & CIRCUIT BREAKERS IDENTIFICATION 2005 Chevrolet Colorado 3.5L Eng CAUTION: When battery is disconnected, vehicle computer and memory systems may lose memory
https://qsol2.cummins.com/qs2/pubsys2/xml/en/outlines/ html
 (4022250) ISX15 CM2250 Service Manual https://qsol2.cummins.com/qs2/pubsys2/xml/en/outlines/4022250.html Page 1 of 1 (4022250) ISX15 CM2250 Service Manual Search Manual Search Help With Printing Front
(4022250) ISX15 CM2250 Service Manual https://qsol2.cummins.com/qs2/pubsys2/xml/en/outlines/4022250.html Page 1 of 1 (4022250) ISX15 CM2250 Service Manual Search Manual Search Help With Printing Front
Identify and understand the key components to the starting and charging system. Rotating Electrical Troubleshooting Guide. Battery.
 Rotating Electrical Troubleshooting Guide Battery Alternator Identify and understand the key components to the starting and charging system. Starter Motor TRUE SPECIALISTS CHOOSE EFEL 1 Efel_Trouble_Shooting_Guide_ENG_2016.indd
Rotating Electrical Troubleshooting Guide Battery Alternator Identify and understand the key components to the starting and charging system. Starter Motor TRUE SPECIALISTS CHOOSE EFEL 1 Efel_Trouble_Shooting_Guide_ENG_2016.indd
Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide RestStar Use this guide with 5700XE RestStar Unit. Western Star 5700XE.
 Western Star 5700XE RestStar 4 10-2017 1 Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide RestStar Use this guide with 5700XE RestStar Unit 2390 Blackhawk Road P.O. Box 6007 Rockford, IL 61125 nitesystem.com
Western Star 5700XE RestStar 4 10-2017 1 Technical Information and Diagnostic Guide RestStar Use this guide with 5700XE RestStar Unit 2390 Blackhawk Road P.O. Box 6007 Rockford, IL 61125 nitesystem.com
G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING [5VZ FE] TOYOTA TACOMA (EWD517U) Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
![G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING [5VZ FE] TOYOTA TACOMA (EWD517U) Position of Parts in Engine Compartment G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING [5VZ FE] TOYOTA TACOMA (EWD517U) Position of Parts in Engine Compartment](/thumbs/82/86578697.jpg) G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING [5VZ FE] Position of Parts in Engine Compartment A 5 A/C Magnetic Clutch A 7 A/T Oil Temp. Sensor A22 ABS Actuator with ECU A23 Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1) A24 ADD
G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING [5VZ FE] Position of Parts in Engine Compartment A 5 A/C Magnetic Clutch A 7 A/T Oil Temp. Sensor A22 ABS Actuator with ECU A23 Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1) A24 ADD
